Abstract
Coastal ecosystems form interconnected networks that are essential for the maintenance of marine biodiversity. This study investigates the dietary patterns of Apostichopus japonicus (sea cucumber) within a marine ranching ecosystem and reveals the influence of Zostera marina (seagrass) leaves from a distant bed on nutrient availability and trophic connectivity. Samples collected between September 2020 and March 2021 from Xiangyun Bay included A. japonicus, macroalgae, phytoplankton, and seagrass leaves. Stable isotope analysis (δ13C and δ15N), in conjunction with Bayesian mixing models, elucidated the contributions of different food sources to A. japonicus’ diet. Macroalgae constituted more than 50% of A. japonicus’ diet, while seagrass contributions ranged between 5.7% and 11.3%. The isotopic analysis confirmed the presence of seagrass debris in the marine ranching environment, indicating significant nutrient transport from a remote seagrass bed. This study underscores the crucial role played by macroalgae as the primary source of nutrients for A. japonicus within a marine ranching setting. Furthermore, detecting seagrass debris from a distant habitat highlights previously unrecognized ecological connectivity between seagrass ecosystems and artificial reef environments along coastal areas. This understanding of long-range nutrient transfers is vital for effective management and conservation strategies in coastal marine systems, emphasizing intricate yet significant ecological interdependencies across coastal environments.
1. Introduction
Seagrasses, highly productive submerged marine angiosperms found in shallow coastal and estuarine waters, form seagrass beds, which are vital underwater ecosystems providing diverse ecosystem services [1,2,3]. These beds serve as habitats, nurseries, and feeding grounds for marine organisms such as dugongs, green turtles, and waterfowl, thereby sustaining their populations [4]. Moreover, they contribute to sedimentation by settling suspended particles and preventing sediment resuspension, thus enhancing water transparency. Additionally, the robust rhizome and root systems of seagrasses effectively stabilize sediments against wave and tidal erosion along beaches and coasts. Lastly, they act as significant carbon sinks in marine environments with implications for climate regulation [5]. Despite these benefits, seagrass meadows have been experiencing a decline since 1990 at an average annual rate of 7%, resulting in the loss of approximately one-third of the total seagrass area due to natural and anthropogenic disturbances [6]. These declines raise heightened concerns regarding the conservation and restoration of seagrass meadows. Seagrass meadows sustain a diverse array of marine life by providing nourishment to numerous organisms, and among these, dugongs, manatees, green turtles, waterfowl, sea urchins, fish, and certain decapods predominantly rely on seagrass [7]. However, it is important to note that these creatures exhibit distinct feeding habits and seasonal preferences across different regions within seagrass ecosystems [8]. Dugongs, manatees, green turtles, waterfowl, sea urchins, and fish graze directly on living seagrass leaves [9]. Shrimp and crabs primarily feed on fresh seagrass leaf tissues along with leaf epiphytes, roots, and rhizomes [8]. Additionally, decomposed detritus derived from seagrass provides sustenance to organisms such as sea cucumbers, worms, crabs, anemones, and ascidians. This detritus also serves as a food source for organisms in distant locations including shores and the deep sea when transported from seagrass beds through various means [9].
Meadows of the eelgrass Zostera marina L. constitute crucial coastal ecosystems, providing habitats for diverse marine organisms, including Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka 1867) [10]. Within this ecosystem, seagrass detritus, a byproduct of decomposition, serves as sustenance for numerous deposit feeders. In temperate northern China, the leaves of the eelgrass Zostera marina L. detach during senescence, resulting in substantial eelgrass wrack during late summer or early autumn. Winds and currents facilitate the transport of this eelgrass wrack [11], potentially acting as an essential food source for adjacent ecosystems like the artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem in marine ranching. Z. marina, being the predominant seagrass species, thrives along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of the temperate northern hemisphere. In China, eelgrass distribution spans temperate waters encompassing coastal regions of Shandong, Hebei, and Liaoning Provinces. Over recent decades, escalating human activities have exerted significant stresses and disturbances on eelgrass beds, leading to substantial contraction or disappearance of numerous seagrass beds.
Artificial reefs in marine ranching serve as attachment structures to restore live oyster reef communities, while simultaneously establishing a natural seaweed meadow alongside, thus creating an artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem [12]. Oysters and macroalgae play crucial roles as foundational species within this ecosystem, combining the ecological functions of oyster reefs and seaweed meadows. This integrated ecosystem serves as spawning grounds and habitats for economically significant marine organisms, while also improving water quality through oyster filtration and algal nutrient absorption. In this marine ranching system, primary producers include macroalgae, benthic microalgae, and phytoplankton. The sea cucumber A. japonicus plays a crucial role as the primary consumer at the second trophic level in this ecosystem, making it one of the key species with significant ecological importance. This species also holds substantial commercial value, particularly within marine ranching ecosystems. The epibenthic species A. japonicus is primarily distributed in the temperate coastal waters of the North Pacific Ocean. It sustains itself as a deposit feeder by consuming organic matter detritus, including benthic microalgae, deceased aquatic fauna, and plant debris present in sediments [13]. Previous laboratory research has demonstrated that eelgrass wrack can be a viable food source for A. japonicus [10]. Additionally, considerable seagrass detritus was found in the digestive tracts of A. japonicus inhabiting seagrass habitats, indicating its significance as a primary food source within this ecosystem [14]. However, there is currently no documentation on whether seagrass detritus from seagrass ecosystems can serve as a nutritional source for A. japonicus in artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystems within marine ranching.
Coastal ecological connectivity includes hydrological, biological, geological, and geochemical processes through which nutrient transport across habitats signifies this connectivity [15]. Nutrients traverse between habitats via water movements, the carbon and nitrogen cycles, biological migrations, and within the food chain. This transportation of nutrients enhances the potential for organisms to access diverse nutrients, thereby bolstering population growth, reproduction, and adaptability to the environment [15]. Moreover, these transported nutrients significantly influence organisms at all trophic levels within food chains and webs, contributing substantially to increased ecosystem stability [15]. Therefore, the connectivity among ecosystems exerts a significant influence on species’ genetic diversity, population size, maintenance of population structure, restoration of endangered ecosystems, and overall biodiversity. However, exploration of ecological connectivity in coastal marine ecosystems commenced relatively late with a primary focus on estuarine wetlands, mangroves, seagrass beds, and coral reef ecosystems [15]. This delay stemmed from the dynamic nature and spatial diversity of coastal marine environments that posed challenges in differentiating between various ecosystem patches [15,16,17]. Currently, the research on ecological connectivity between seagrass beds and artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystems in marine ranching remains unexplored.
Stomach content analysis is a conventional method for meticulously examining diet composition and feeding ecology; however, its scope is limited as it solely portrays the short-term feeding status of organisms [18,19]. Fortunately, stable isotope analysis overcomes these limitations by offering a simplified sampling method and revealing the long-term feeding patterns of organisms through C and N isotope fractionation between predators and prey. This approach facilitates the identification of consumer nutritional sources, investigation of biotrophic interactions, and inference of biotrophic ecological niches [20,21]. Stable isotope analysis involving C and N has been extensively applied in various aquatic ecosystem studies [22,23,24,25], effectively exploring trophic connections among estuarine and marine habitats [26,27]. Previous studies suggest that detritivore consumers closer to the bottom of the food web, such as the sea cucumber A. japonicus, are more likely to assimilate plant debris rather than carnivorous fish [28,29]. For example, stable isotope analysis revealed that suspension-feeding bivalves (Dosinia spp.) in Whangapoua Estuary (New Zealand) assimilated seagrass and fringing vegetation detritus [27]. Building upon this precedent, our study employed stable isotope analysis fittingly to uncover trophic connections between seagrass beds and mariculture activities.
The present study provides evidence supporting the coastal ecological connectivity between a seagrass bed and an artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem, located 30 km away from the seagrass bed. This is demonstrated by establishing the trophic relationship between A. japonicus in a marine ranching environment and Z. marina leaves originating from a seagrass bed in Bohai Bay, China. The methodology involved the collection of biological samples from A. japonicus, seagrass leaves, phytoplankton, Ulva lactuca, and other macroalgae. Stable isotope analysis was conducted to determine consumer nutritional sources using the Bayesian mixing model MixSIAR. Our hypothesis suggests that significant eelgrass wrack drifting towards the marine ranching area could potentially serve as a food source for A. japonicus within the artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem, indicating nutrient exchange between the seagrass bed and the artificial reef ecosystem.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
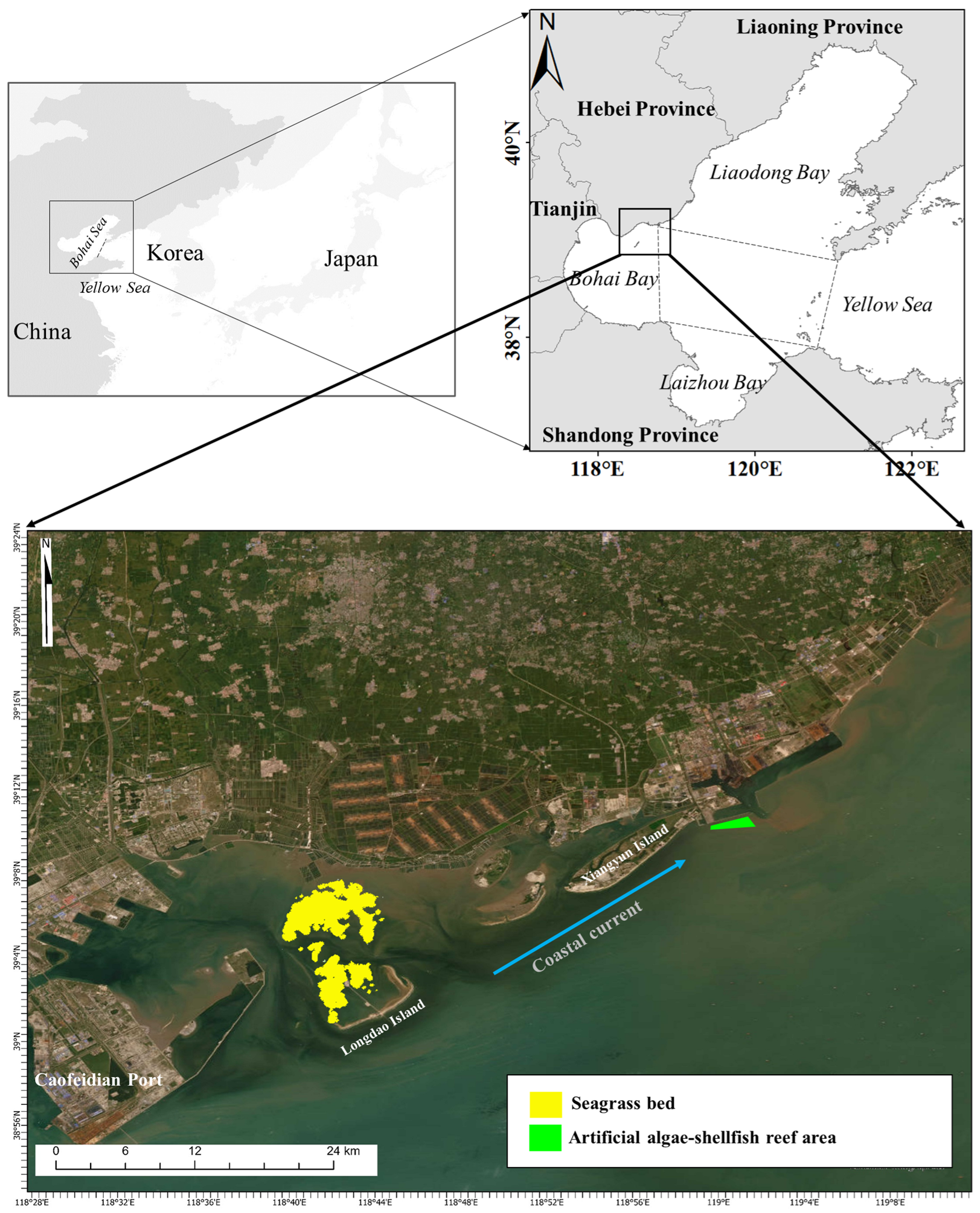
The Caofeidian shoal, formerly a part of the Luanhe River Delta, has undergone transformation into a barrier island–lagoon system as a result of wave and tidal erosion [30,31]. This lagoon experiences irregular semidiurnal mixed tides, with an average water depth ranging from 0 to 5 m and a tidal flat width spanning 15 to 25 km [32,33]. Within this system lies China’s largest eelgrass bed covering an area of 3217.32 ha. The foundation species Zostera marina exhibits a perennial life cycle (Figure 1) [34]. During late summer or early autumn, a substantial quantity of eelgrass leaves detach as part of the plant’s renewal process. These leaves are transported by winds and currents over approximately 30 km to reach the marine ranching area in Xiangyun Bay. The verified presence of floating seagrass northeast of the bed strongly supports the notion that seagrass is being transported towards the marine ranching area [35]. Consequently, some of these leaves settle within the ranching zone.
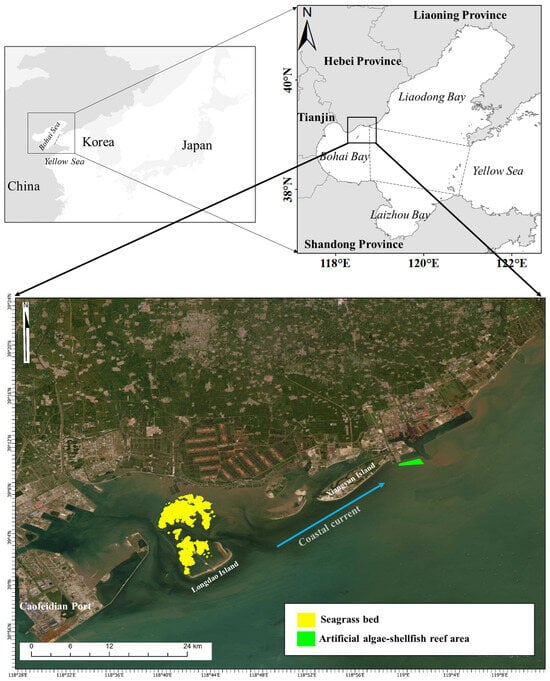
Figure 1.
Study area in the Bohai Sea, northern China.
To mitigate the decline in the coastal ecosystem, an artificial oyster reef ecosystem was established in Xiangyun Bay’s marine ranching area from 2011 onwards (Figure 1). By the end of 2018, approximately 930,000 m3 of diverse artificial reefs, primarily composed of natural limestone and concrete materials, had been deployed within this ecosystem, leading to its gradual stabilization. The development encompassed two consecutive zones for artificial oyster reefs spanning 200 ha and 57 ha, respectively, with the former constituting an artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem. Operating at an average depth of 6.5 m, this ecosystem experiences semidiurnal mixed tides with an average flow velocity ranging from 0.28 to 0.37 m/s. Yang [36] conducted a comparative analysis of resource characteristics both inside and outside the reef area using ground cages from 2016 to 2017, revealing a notable increase in fish species diversity within the reef area. The catch per unit effort, serving as an indirect measure of target species abundance, exhibited a significant rise, thereby indicating the positive ecological impact resulting from oyster reef construction. This study emphasizes the creation of more intricate communities and enhanced productivity as outcomes derived from oyster reef development.
2.2. Sample Collection
The biological samples, including A. japonicus, U. lactuca, other macroalgae, and phytoplankton, were collected from the artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem in Xiangyun Bay marine ranching between September 2020 and March 2021. Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus (SCUBA) diving was employed for the systematic hand collection of A. japonicus, U. lactuca, and other macroalgae specimens. Each sample of A. japonicus consisted of three individuals, while individual samples of U. lactuca and other macroalgae weighed at least 1 kg when wet biomass was considered. Phytoplankton samples were obtained by filtering through a nylon net with a pore size of 77 µm and stored in plastic buckets with a capacity of 2.5 L each during the sampling process.
In August 2020, a collection of floating seagrass leaves was conducted from the artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem due to significant detachment of eelgrass leaves. The collection comprised three samples, each containing a minimum of 1 kg of wet biomass.
All biological samples were transported to the laboratory and processed and stabilized within a 6 h timeframe.
The isotopic values of benthic microalgae were found to be comparable at artificial reef sites in the Yellow and Bohai Seas. Therefore, this study utilized data from the artificial reef areas of Yangma Island in the Yellow Sea, revealing δ13C values of −17.48‰ ± 0.26‰ and δ15N values of 3.55‰ ± 0.32‰ [37].
2.3. Sample Analysis
Muscles from three individuals of A. japonicus were meticulously removed and amalgamated to form one sample. The stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) measurements were conducted on a total of three samples.
The phytoplankton samples were filtered using pre-combusted (450 °C, 6 h) Whatman GF/F glass fiber filters with a pore size of 0.7 μm. Following filtration, the residue on the filter papers was rinsed with deionized water to remove salt content.
The eelgrass and macroalgae samples were thoroughly rinsed with freshwater to eliminate any salt and sediment, ensuring the removal of epiphytes, and other materials adhering to the eelgrass leaves was meticulously performed using a scalpel.
The samples were dried at 45 °C until a constant weight was achieved, followed by grinding and filtration through 100-mesh screens for stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) measurements. The C and N isotope ratios of all samples were determined using an isotope ratio mass spectrometer (Delta V Advantage, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), with the results expressed in delta (δ) notation:
δ (‰) = [(Rsample/Rstandard) − 1] × 1000
The values were reported relative to the international standards of Vienna Pee Dee belemnite for C and N2 for N. Throughout the measurements, the standards were measured once for every 10 samples. The reported δ values held an analytical precision of 0.1‰.
2.4. Data Analysis
The mean ± standard deviation was used to report the values. The Bayesian mixing model MixSIAR [38] was employed to determine the dietary contribution rates of primary food sources to A. japonicus in the Xiangyun Bay marine ranching. In this model, trophic discrimination factors were set at 0.75‰ ± 0.1‰ for Δδ13C and 2.75‰ ± 0.11‰ for Δδ15N [39], with an iteration number of 300,000. Markov chain convergence within the model results facilitated the determination of contribution proportions from various food sources to A. japonicus’ diet. Data analyses were performed using R 4.1.2 [40] and Excel 2019.
3. Results
3.1. Isotopic Distribution
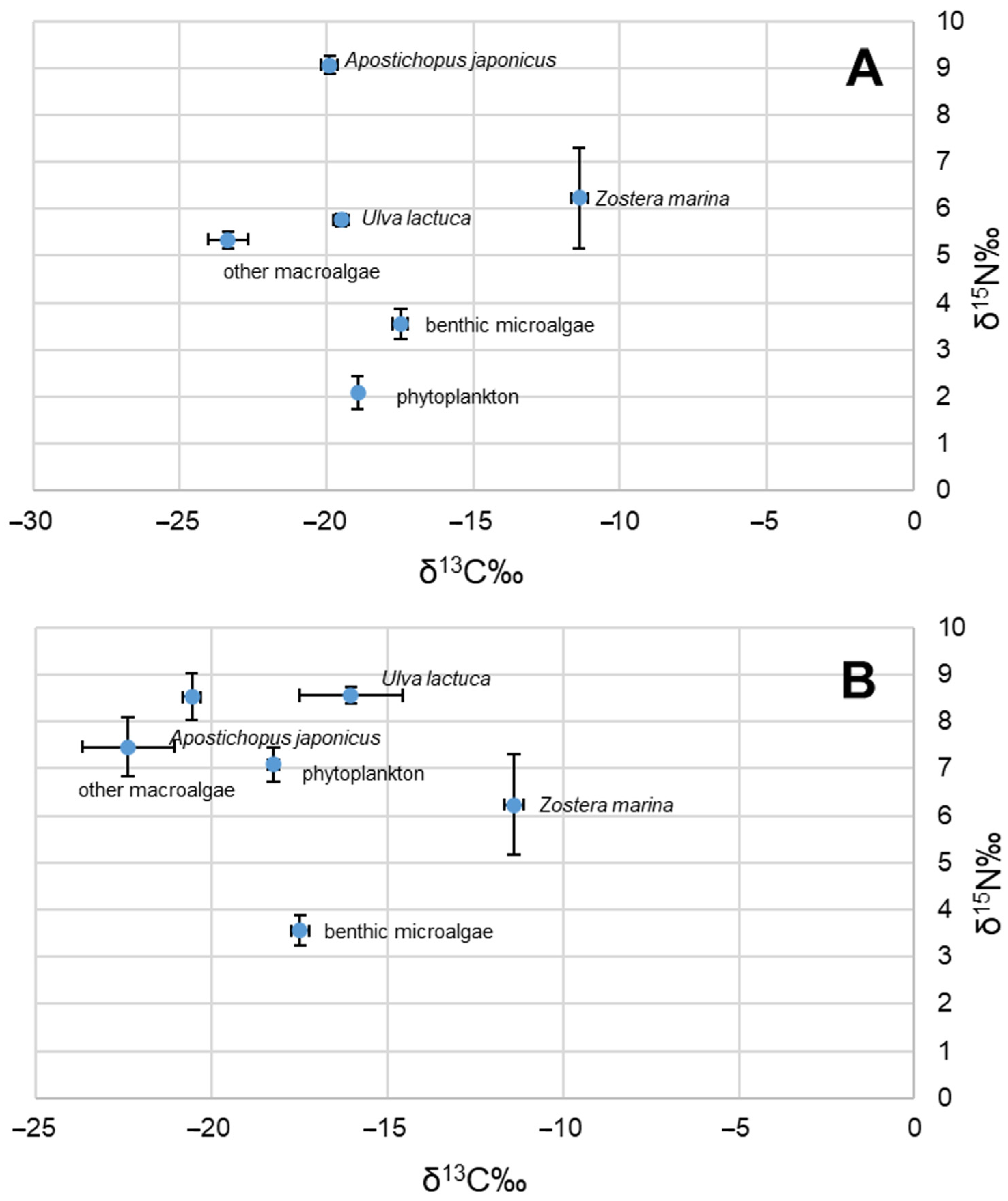
The δ13C and δ15N values exhibited significant variation among the four primary producers (δ13C: df = 11, F = 503.277, p < 0.01; and δ15N: df = 11, F = 32.495, p < 0.01, respectively). Within the marine ranching system, the δ13C values of primary producers ranged from −23.37‰ ± 0.67‰ (other macroalgae in September 2020) to −11.39‰ ± 0.28‰ (Zostera marina in August 2020), while the δ15N values ranged from 2.09‰ ± 0.35‰ (phytoplankton in September 2020) to 8.56‰ ± 0.17‰ (Ulva lactuca in March 2021).
In September, the carbon isotope composition of A. japonicus was measured to be −19.9‰ ± 0.28‰, while it decreased to −20.56‰ ± 0.25‰ by March of the following year (Table 1; Figure 2). Similarly, nitrogen isotope analysis revealed that its isotopic signature changed from a value of 9.06‰ ± 0.19‰ in September to 8.52‰ ± 0.49‰ by March (Table 1; Figure 2).

Table 1.
Values (‰) of δ13C and δ15N for Apostichopus japonicus and its main food sources.
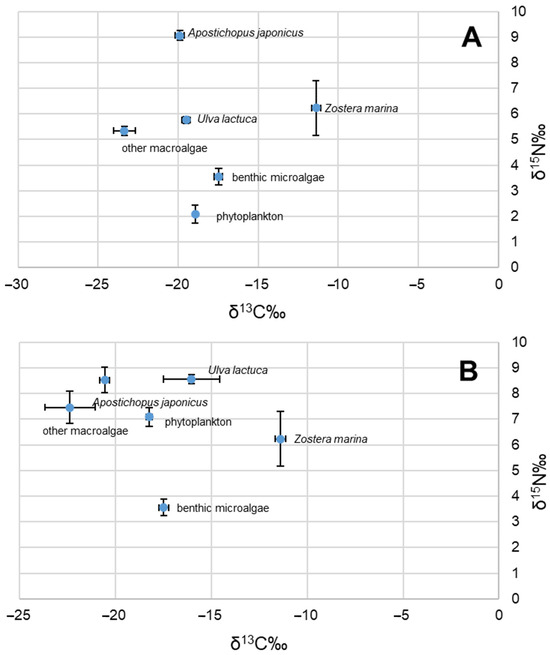
Figure 2.
Biplot of C and N stable isotope distribution in September 2020 (A) and March 2021 (B).
3.2. Food Source Analysis
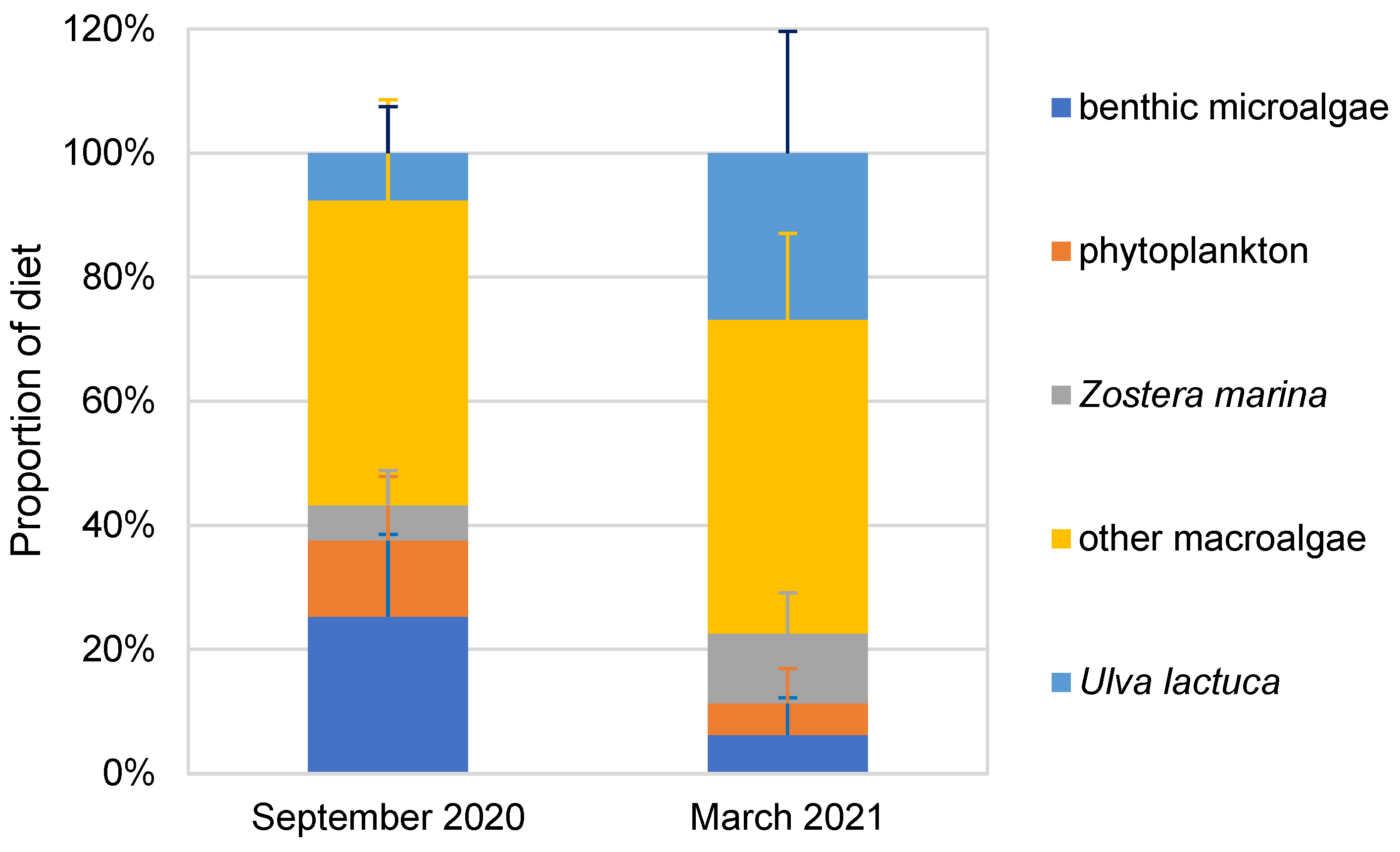
In September 2020, the primary dietary contribution to A. japonicus was predominantly derived from other macroalgae (49.2% ± 16.2%), followed by benthic microalgae (25.3% ± 13.3%) and phytoplankton (12.3% ± 10.3%). Minor contributions were observed from U. lactuca (7.6% ± 7.5%) and Z. marina (5.7% ± 5.6%) (Figure 3).
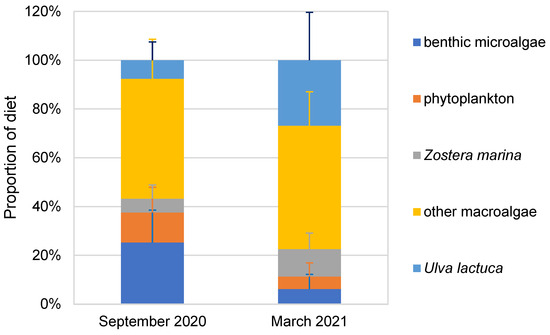
Figure 3.
Apostichopus japonicus dietary contributions in September 2020 and March 2021.
In March 2021, A. japonicus predominantly relied on macroalgae as a significant dietary component, accounting for 50.6% ± 13.9%, with U. lactuca (26.8% ± 19.6%) and Z. marina (11.3% ± 6.5%) following suit in importance. Conversely, benthic microalgae (6.2% ± 6%) and phytoplankton (5.1% ± 5.6%) made relatively smaller contributions.
In the marine ranching environment, macroalgae emerged as the predominant nutrient source for A. japonicus, while seagrass exhibited a comparatively lower dietary contribution ranging between 5.7% and 11.3%.
4. Discussion
Despite the emphasis on assessing fisheries associated with coral reefs due to their extensive species diversity and utilization, small-scale fisheries are frequently practiced within seagrass meadows near shorelines [41]. The pivotal role of seagrasses in supporting these productive activities is often underestimated. Orth et al. [42] argue that the relatively lower recognition of seagrass ecosystems, compared to the charisma associated with coral reefs, creates an imbalance in scientific research and management approaches. This bias towards coral reefs is particularly evident in the Indo-Pacific region [43]. Despite their widespread global distribution [44] and substantial provision of ecosystem goods and services, seagrasses have historically received less attention. While their local socio-ecological importance has been acknowledged [45], it is only recently that they have been identified as crucial social-ecological systems on a global scale [46]. Seagrasses play a vital role in coastal areas by providing essential ecosystem services [47], serving as critical habitats for various marine life stages including nursing, refuge, and spawning [5,48,49]. These beds support surrounding ecosystems, particularly coral reefs by sustaining predatory fish populations [50]. Research suggests that seagrass beds serve as nurseries for juvenile coral reef fish before they migrate to coral habitats [47]. They significantly enhance food production by promoting epifaunal growth on leaves or through detritus generation [51]. Importantly, our study revealed the passive transportation of seagrass debris over approximately 30 km from beds to marine ranching sites, offering a valuable food source for sea cucumbers.
Seagrass meadows play a crucial role as essential habitats and food sources for sea cucumbers [14]. Increasing research evidence supports the potential of seagrass debris in aquaculture, demonstrating that decaying Z. marina debris in muddy sediments can enhance A. japonicus growth. For example, the addition of 40% dry-weight proportion of Z. marina debris with 19.6% organic content resulted in high specific growth rates (1.54%·d−1) and fecal production rates (1.31 g·ind.−1 d−1) [10]. Similarly, Domínguez-Godino et al. [52] observed that Holothuria arguinensis benefited from Z. noltii debris, leading to increased growth rates (specific growth rate = 0.09 ± 0.06%/day) and a weight gain of 5.86 ± 3.57% over 57 days when fed a diet comprising 40 percent Z. noltii. This highlights the potential significance of seagrass restoration in sea cucumber fisheries.
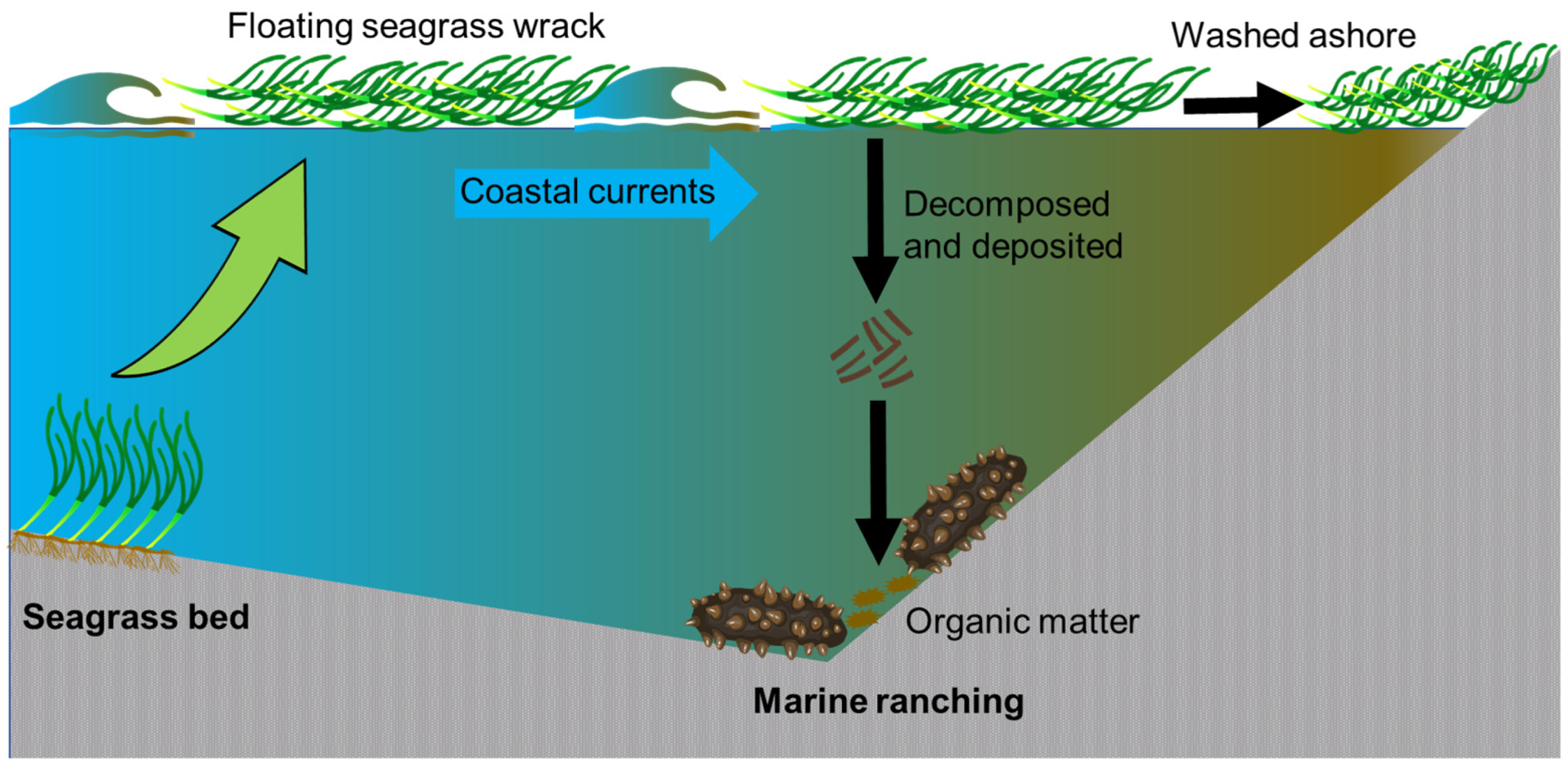
The national seagrass resource surveys conducted from 2015 to 2020 have revealed the presence of only one eelgrass bed in Tangshan’s coastal waters, which happens to be the largest in China. Strong evidence suggests that the floating seagrass consumed by A. japonicus in the marine ranching originates exclusively from this particular bed [34,35]. Due to its high primary productivity [53], seagrass meadows continuously shed leaves that eventually float to the sea surface [54] and are subsequently transported away by winds and currents [11,55]. These floating seagrass wracks travel across various habitats until they reach beaches or settle on the seafloor. The coastal currents play a crucial role in connecting the eelgrass bed with Xiangyun Bay’s marine ranching activities, facilitating significant transport of seagrass wrack. Eelgrass wrack production reaches its peak during late summer or early autumn in temperate northern China, allowing for a rough estimation of annual wrack production through comparison of aboveground biomass differences between seasons. With an area spanning 3217.32 ha, it is estimated that approximately 3975 dry-weight tons of wrack are generated annually by this seagrass bed based on aboveground biomass measurements of 240.67 ± 90.53 g m−2 dw in July and 117.12 ± 65.27 g m−2 dw in September [34]. A portion of this wrack decomposes and enriches sediment organic matter, which is crucial for A. japonicus’ diet requirements. The sediment within Xiangyun Bay’s marine ranching area contains a substantial amount of eelgrass debris (personal observation). Additionally, significant amounts of washed-ashore seagrass wrack have been reported along shorelines northeastward from the bed according to previous studies (Figure 4).
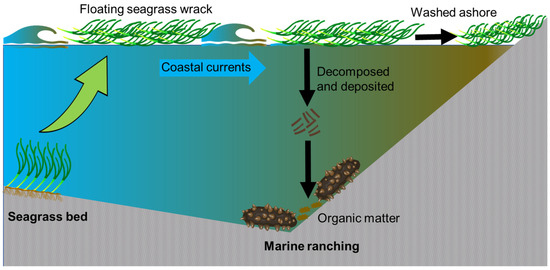
Figure 4.
Schematic depictions of floating seagrass wracks being transported from the seagrass bed to the marine ranching site.
In recent decades, the escalating demand for dried sea cucumbers in the Asiatic market has resulted in the overexploitation of traditional sea cucumber fishing grounds in the Pacific and Indian Oceans [56]. To address this issue, aquaculture has emerged as a significant industry, catering to a substantial portion of the market’s requirements [56]. A. japonicus, which plays a vital role in northern China’s waters, primarily feeds on surface sediment and shows preference for algae debris. Several studies have emphasized the significance of seagrass detritus as a major food source for sea cucumbers within seagrass ecosystems [57,58,59]. For instance, research conducted off the northeastern Spanish coast highlighted that Posidonia oceanica leaves and epiphytes contribute up to 63% to the diets of Holothuria polii and Holothuria tubulosa-mamatta complex [59]. Different studies present contrasting findings with regard to higher assimilation rates of seagrass detritus by specific sea cucumber species [57,60]. In our study, macroalgae accounted for over 50% of A. japonicus’ diet, while seagrass contributed 5.7% (autumn) and 11.3% (spring), both decomposing into essential sediment organic matter nutrients. The lower assimilation rate of seagrass observed in marine ranching possibly reflects its reduced abundance compared to natural seagrass ecosystems within artificial algae–shellfish reef sediments. Dietary contributions to sea cucumbers can vary based on location, seasonality, species diversity, and availability of different types of seagrasses.
Studies indicate that sea cucumbers can feed on suspended organic matter through their mouths [61]. Furthermore, the majority of organic matter in their intestines originates from water bodies rather than sediments [62]. Therefore, dissolved suspended organic matter derived from macroalgae could potentially serve as the primary food source for A. japonicus. In the artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem, macroalgae are likely to function as the main nutritional resource for primary consumers, contrasting with other marine and coastal ecosystems, where phytoplankton is typically considered the predominant nutrient source due to distinct structural characteristics.
During early autumn, the artificial algae–shellfish reef ecosystem experiences a significant increase in macroalgae biomass, leading to an elevation in organic detritus resulting from macroalgae decomposition and subsequently increasing the content of particle organic matter. Simultaneously, there is an increase in terrestrial organic matter input, which promotes phytoplankton production. In Caofeidian’s coastal areas near the current marine ranching site, phytoplankton abundance reaches its peak during autumn and declines during spring [63,64]. This temporal variation may explain why A. japonicus exhibits a higher dietary contribution from phytoplankton in autumn (September 2020) compared to spring (March 2021). Furthermore, A. japonicus shows a greater dietary contribution from Z. marina in spring than autumn due to the relatively low decomposition rate of Z. marina wrack despite its production occurring late summer or early autumn within the seagrass bed [65].
The present study investigates the trophic relationship between A. japonicus and Z. marina leaves in a marine ranching area, where seagrass from a distant bed is transported to the site. Our findings reveal that macroalgae play a predominant role as the primary nutrient source for A. japonicus during spring and autumn, contributing more than 50% to their diet in Xiangyun Bay’s marine ranching system. Despite seagrass accounting for a smaller proportion (5.7–11.3%) compared to macroalgae, its significance as a food source for A. japonicus at a marine ranching site located 30 km away from the seagrass bed is underscored by these results. By establishing coastal ecological connectivity, this study provides valuable insights for future research on marine ecological linkages; however, further investigation at an ecosystem level is crucial to comprehensively understand these interconnections.
Author Contributions
S.X. and X.W.: investigation, data curation, writing the original draft, software, and visualization; S.Y. and X.Z.: investigation and writing review and editing; Y.Z. (Yunling Zhang): investigation; C.L. and Y.Z. (Yi Zhou): funding acquisition, review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFB3901300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42206142, 42176106, 42030408, 32270405), the Shandong Postdoctoral Innovation Project (SDCX-ZG-202201018), and the Taishan Scholars Program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Yunling Zhang was employed by the company Tangshan Marine Ranching Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- do Amaral Camara Lima, M.; Bergamo, T.F.; Ward, R.D.; Joyce, C.B. A review of seagrass ecosystem services: Providing nature-based solutions for a changing world. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2655–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potouroglou, M.; Bull, J.C.; Krauss, K.W.; Kennedy, H.A.; Fusi, M.; Daffonchio, D.; Mangora, M.M.; Githaiga, M.N.; Diele, K.; Huxham, M. Measuring the role of seagrasses in regulating sediment surface elevation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.d.A.C.; Ward, R.D.; Joyce, C.B.; Kauer, K.; Sepp, K. Carbon stocks in southern England’s intertidal seagrass meadows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 275, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Santos, C.B.; Scott, A.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Jones, B.; Kennedy, H.; Mazarrasa, I.; McKenzie, L.; Nordlund, L.M.; de la Torre-Castro, M.d.l.T.; Unsworth, R.K. Seagrass ecosystem services: Assessment and scale of benefits. In Out of the Blue: The Value of Seagrasses to the Environment and to People; United Nations Environment: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Nordlund, L.M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Seagrass meadows support global fisheries production. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. Feeding Ecology of Two Megagrazers in Two Typical Bays. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, P.L.; Duffy, E.; Knowlton, N. Seagrass and seagrass beds. Ocean Portal 2018, 16, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Ru, S. Eelgrass detritus as a food source for the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Selenka (Echinidermata: Holothuroidea) in coastal waters of North China: An experimental study in flow-through systems. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, M.A.; Beltran, R.; Traveset, A.; Calleja, M.L.; Delgado-Huertas, A.; Marbà, N. Aeolian transport of seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) beach-cast to terrestrial systems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Strategic approach for mariculture to practice “Ocean Negative Carbon Emission”. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, C. Survival, growth, food availability and assimilation efficiency of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus bottom-cultured under a fish farm in southern China. Aquaculture 2014, 426, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floren, A.S.; Hayashizaki, K.-I.; Putchakarn, S.; Tuntiprapas, P.; Prathep, A. A review of factors influencing the seagrass-sea cucumber association in tropical seagrass meadows. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 696134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ye, G.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, B.; Hu, W.; Zheng, X. Progress and prospects of coastal ecological connectivity studies. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6923–6933. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, S.J.; Caldow, C.; Hile, S.D.; Monaco, M.E. Using seascape types to explain the spatial patterns of fish in the mangroves of SW Puerto Rico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 348, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, S.; McAlpine, C. Movements of marine fish and decapod crustaceans: Process, theory and application. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2003, 44, 205–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahlbeck, I.; Hansson, S.; Hjerne, O. Evaluating fish diet analysis methods by individual-based modelling. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1184–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, S.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Tanner, S.; Máguas, C.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H.N. Assessing food web dynamics and relative importance of organic matter sources for fish species in two Portuguese estuaries: A stable isotope approach. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 72, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER–Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.L.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L.; Moore, J.W.; Parnell, A.C.; Semmens, B.X.; Ward, E.J. Best practices for use of stable isotope mixing models in food-web studies. Can. J. Zool. 2014, 92, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, B.N.; Montagna, P.A. Meta-analysis of Ecopath models reveals secondary productivity patterns across the Gulf of Mexico. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 100, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresson, P.; Ruitton, S.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Artificial reefs do increase secondary biomass production: Mechanisms evidenced by stable isotopes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 509, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.Y.; Lee, B.-G.; Park, H.J.; Yun, S.-G.; Kang, C.-K. Trophic structures of artificial reef communities off the southern coast of the Korean peninsula as determined using stable isotope analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, A.; Robert, M.; Cresson, P.; Le Bris, H.; Kopp, D. Food web structure in relation to environmental drivers across a continental shelf ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granek, E.F.; Compton, J.E.; Phillips, D.L. Mangrove-exported nutrient incorporation by sessile coral reef invertebrates. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.; Thrush, S.F.; Lohrer, A.M.; Hewitt, J.E. Ecosystem services transcend boundaries: Estuaries provide resource subsidies and influence functional diversity in coastal benthic communities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.L.; Vieira, J.P. Feeding strategy of Menticirrhus americanus and Menticirrhus littoralis (Perciformes: Sciaenidae) juveniles in a sandy beach surf zone of southern Brazil. Zoologia 2010, 27, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, T.M.S.; Pessanha, A.L.M.; Araújo, F.G. Dieta de juvenis de Trachinotus carolinus (Actinopterygii, Carangidae) em praias arenosas na costa do Rio de Janeiro. Iheringia. Série Zool. 2010, 100, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shanming, G.; Yuanfang, L.; Fengtueng, A.; Fengxin, L. The formation of sand bars on the Luanhe River Delta and the change of the coast line. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1980, 2, 102–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, W.; Guanghe, F.; Yongzhan, Z. River-sea interactive sedimentation and plain morphological evolution. Quat. Sci. 2007, 27, 674–689. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zuo, L.; Ji, R.; Zhang, J. Effect of development of Caofeidian harbor area in Bohai Bay on hydrodynamic sediment environment. Adv. Water Sci. 2007, 18, 793–800. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.H. Thoughts on large area reclamation of Caofeidian shoal in Tangshan, Hebei Province. Mar. Geol. Lett. 2007, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, S.; Zhang, X.; Gu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Do adult eelgrass shoots rule seedling fate in a large seagrass meadow in a eutrophic bay in northern China? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. The distribution of large floating seagrass (Zostera marina) aggregations in northern temperate zones of Bohai Bay in the Bohai Sea, China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0201574. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. The Community Characteristics and Ecological Functions of Artificial Oyster Reef at Xiangyun Bay Marine Ranching. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. The Comparative Study of the Food Web Structure and Function between the Artificial and Natural Reefs in the Nearshore. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yantai, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, B.C.; Semmens, B.X. MixSIAR GUI User Manual. Version 3.1. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/brianstock/MixSIAR (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Caut, S.; Angulo, E.; Courchamp, F. Variation in discrimination factors (Δ15N and Δ13C): The effect of diet isotopic values and applications for diet reconstruction. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan, T.R. The near future of coral reefs. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 460–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. BioScience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; Cullen, L.C. Recognising the necessity for Indo-Pacific seagrass conservation. Conserv. Lett. 2010, 3, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.P.; Short, F.T. World Atlas of Seagrasses; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre-Castro, M.; Rönnbäck, P. Links between humans and seagrasses—An example from tropical East Africa. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2004, 47, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Nordlund, L.M.; Paddock, J.; Baker, S.; McKenzie, L.J.; Unsworth, R.K. Seagrass meadows globally as a coupled social–ecological system: Implications for human wellbeing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagelkerken, I.; van der Velde, G.; Gorissen, M.W.; Meijer, G.J.; Van’t Hof, T.; den Hartog, C. Importance of mangroves, seagrass beds and the shallow coral reef as a nursery for important coral reef fishes, using a visual census technique. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Fry, B.; Becker, A.; Moltschaniwskyj, N. Recruitment and connectivity influence the role of seagrass as a penaeid nursery habitat in a wave dominated estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, R.K.; De León, P.S.; Garrard, S.L.; Jompa, J.; Smith, D.J.; Bell, J.J. High connectivity of Indo-Pacific seagrass fish assemblages with mangrove and coral reef habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 353, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.; May, H.; Wheatley, M.; Holloway, M. Comparison of fish assemblages associated with seagrass and adjacent unvegetated habitats of Port Phillip Bay and Corner Inlet, Victoria, Australia, with emphasis on commercial species. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Godino, J.A.; Santos, T.F.; Pereira, H.; Custódio, L.; González-Wangüemert, M. Seagrass debris as potential food source to enhance Holothuria arguinensis’ growth in aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieman, J.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Iverson, R.L. Distribution, abundance and productivity of seagrasses and macroalgae in Florida Bay. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 292–311. [Google Scholar]
- Vandendriessche, S.; Messiaen, M.; O’Flynn, S.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Hiding and feeding in floating seaweed: Floating seaweed clumps as possible refuges or feeding grounds for fishes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A. Beach-cast Cymodocea nodosa along the shore of a semienclosed bay: Sampling and elements to assess its ecological implications. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.W.; Mercier, A.; Conand, C.; Hamel, J.F.; Toral-Granda, M.V.; Lovatelli, A.; Uthicke, S. Sea cucumber fisheries: Global analysis of stocks, management measures and drivers of overfishing. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 34–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floren, A.; Hayashizaki, K.; Tuntiprapas, P.; Prathep, A. Contributions of seagrasses and other sources to sea cucumber diets in a tropical seagrass ecosystem. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2021, 48, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, V.; Mazzola, A.; Vizzini, S. Holothuria tubulosa Gmelin 1791 (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata) enhances organic matter recycling in Posidonia oceanica meadows. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 461, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.M.; Dalmau, A.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J. Effects of landscape configuration on the exchange of materials in seagrass ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 532, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncagni, P.; Rakaj, A.; Fianchini, A.; Vizzini, S. Preferential assimilation of seagrass detritus by two coexisting Mediterranean sea cucumbers: Holothuria polii and Holothuria tubulosa. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 231, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.W. Particle captures and the method of suspension feeding by echinoderm larvae. Biol. Bull. 1991, 180, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H. Sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) eukaryotic food source composition determined by 18s rDNA barcoding. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Phytoplankton community and changes after reclamation in Caofeidian coastal waters. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, L.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, B. Net-phytoplankton community structure characteristics and its correlation with environmental factors in coastal waters of Caofeidian. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2019, 38, 252–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M. Carbon Cycling and Climate Resilience in Coastal Habitats of California; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).