Abstract
Location-sensitive policies are tailored to the specific characteristics and needs of a place, supporting both local priorities and wider national objectives within a particular time frame. They are developed to deliver key strategic outcomes such as energy security, food security or the implementation of national policies at a local scale. Place reflects the perceptions and physical realities of a space and the sense of what it is to be a person living there. The purpose of this conceptual paper is to determine what policy interventions are of influence in accelerating agri-technology adoption in an evolving ‘place’. The example of accelerating agri-technology adoption in Lincolnshire, United Kingdom (UK) is used as an explanatory case. Spatial consciousness, the ordering and management of space, can conflict with spatial connectedness, the socially constructed relationships that shape place, especially at the interface where national development priorities meet local plans. Distinctions between location-sensitive and place-based policies lie in their strategic intent, the intervention processes used, and the meanings then attributed to outcomes by affected communities. Agri-technology adoption can deliver economic and social impact, but place-specific policy interventions are required to deliver just, inclusive and win–win outcomes.
1. Introduction
Place represents a loci where public and private forces (drivers) at different scales (from parochial to global) come together (coalesce or become), sometimes blur, disaggregate and recombine, i.e., actors can come together within, between and across places [1]. A place can have more than one meaning for individuals, e.g., the Brazilian rainforest as a ‘place’ has different meanings to different stakeholders, from the indigenous peoples that live there, to the individuals seeking to transition the place for economic gain to the often remote organizations seeking to quantify and trade the natural capital that resides there. The meaning ascribed to land, land use and land use change is shaped not only by the land’s location and what it visually and culturally represents to local, national and international populations, but also by the identities of those who interact with it, especially generational custodians whose heritage and traditions are tied to the land. Place also holds economic value for those who wish to gain access to, and then ‘occupy’, sometimes displacing those who have historically described this location as home [2]. This means ‘a place’ reflects the cultural aspects of the ways of living and of ‘being’ in a given location [3], and perceptions of what the place could transition to become. Becoming as an evolutionary state, in this context, is different to the notion of spatial development. However, a place, the people associated with a place, certain technologies and practices, and the outputs and products derived, can suffer from stigma or be stigmatized, causing damage to community and individual self-esteem [4]. The stigmatization of farmers has been widely examined in the literature, including in relation to the promotion of new, opposing, or potentially antagonistic farming practices [5,6]; characterizations of being the ‘good’ farmer [7,8,9]; the use of good technology [2,10,11]; aspects of rural poverty [12]; and territorial stigmatization of place due to perceived deficit in environmental or biodiversity value [13], especially when linked to agricultural activity. In summary, stigma “does not necessarily mean that greater risks are perceived or even present, but rather [stigma] generate[s] negative associations to [a] certain place, product or technology” [4], (p. 111).
Place attachment has been linked in previous research to concerns over land use change [4,14], and also to place-identity [4,15,16]. Proshansky [17] (p. 155) describes place-identity as
“those dimensions of self that define the individual’s personal identity in relation to the physical environment by means of a complex pattern of conscious and unconscious ideas, feelings, values, goals, preferences, skills, and behavioral tendencies relevant to a specific environment”.
The literature on place-identity encompasses both people’s place identity (the cultural, social, geo-political, and governance aspects that differentiate one place from another, a regional consciousness) and intrinsic place-identity (place attachment, place dependence, and the sense of place) [15,16]. Regional consciousness drives narratives of regional development and the promotion of place in terms of economic development and tourism, whereas place-identity encompasses the meanings and symbolism of place, i.e., the former (regional consciousness) is a spatial consciousness as opposed to place-identity, which is a more visceral and multi-layered socially constructed sense of identity [15,16], i.e., a spatial connectedness. Whilst there is little reflection on regional consciousness and land use in the academic literature, within the concept of spatial consciousness, the positivist viewpoint (managing place and creating order and definition through spatial organization) and the interpretivist viewpoint (socially constructed assemblages that are territorialized and reterritorialized according to spatial connectivity and potentially open to political challenge) are at odds with each other [18,19,20]. Indeed, western European cultures, such as the United Kingdom (UK), have been
“characterized by ideologies of state interventionism, liberal democracy, redistribution, and equal development, [so] reforms at the level of planning legislation and administration, as well as structural reforms of local and regional government, [have] led to the founding of national spatial planning systems. Influenced by positivist spatial planning perspectives… territorial reconfigurations based on sharp administrative divisions (counties and municipalities), a hierarchical positioning of cities and towns, and a continuity of access to public and private services throughout national territories [have taken place] which would have otherwise remained concentrated in just a few urban areas”.([20] p. 3)
Spatial consciousness is especially salient in the UK considering the introduction of the Land Use Framework consultation [21]. The positivist tone in terms of spatial consciousness of the press release for the consultation is clear:
“The Government is today (Friday 31 January 2025) launching a consultation on a new strategic approach to managing land use in England to give decision makers the data they need to protect our most productive agricultural land, boosting Britain’s food security in a time of global uncertainty and a changing climate. This will support the Government’s missions under the Plan for Change, including delivering new housebuilding, energy infrastructure and new towns (https://www.gov.uk/government/news/government-launches-national-conversation-on-land-use accessed on 2 March 2025).”
With regard to food production, the statement [21] goes on to outline:
“This Government has a cast-iron commitment to maintain long-term food production. The primary purpose of farming will always be to produce food that feeds the nation. This framework will give decision makers the toolkit they need to protect our highest quality agricultural land. This vision for land is one in which we guarantee our long-term food security and future-proof our farm businesses, support new housebuilding and energy infrastructure, and reduce conflicts that hold up development by creating land with multiple benefits—supporting economic growth on the limited land we have available. The Framework will help farm businesses to maximize the potential of multiple uses of land, supporting long-term food production capacity and unlocking opportunities for businesses to drive private finance into the sector. It will support the need to incentivize multi-functional land use that includes food production…”
The language is positivist, neodevelopmentalist (see [22]) and economically focused with a narrative of spatial consciousness, spatial planning and governance structures and limited reflection on other aspects of place, the social connectedness, otherwise described as the ‘aspatial’. In this context, Galland & Grønning ([20] p. 3) state that words matter in the discourse around spatial plans and the governance structures associated with it:
“From a planning perspective, we may thus distinguish between implicit and explicit spatial consciousness, as well as strongly or weakly articulated spatial consciousness… Based on forms of individual or collective awareness of one’s own spatial presence, as individual or community, and of real-world spatial phenomena and processes, explicit spatial consciousness may provide the intellectual means to bridge the gap between spatial and aspatial dimensions of social processes, governance, and participation”.
These terms, spatial consciousness and spatial connectedness, will be considered and reflected upon in this conceptual paper. Lincolnshire, a county in the UK and the case study for this research, has been recognized formally as a place from at least the Domesday Book of 1086 (see https://opendomesday.org/county/lincolnshire/ accessed on 2 March 2025), and the intrinsic place-based identity of people who live in Lincolnshire would be self-identifying as a ‘yellowbelly’. This term for a person belonging to Lincolnshire may come from a range of cultural origins [23]. However, a duality exists that relates to the narratives of self-identification for those who reside in Lincolnshire from ‘I live in Lincolnshire” as an example of spatial consciousness or the self-identity, spatial connectedness, aspects of “I am a yellow-belly”. Peng et al. [15] differentiate this duality, further (Table 1) reflecting people and place, external appearance and internal thoughts, and their work has been adapted here through the lens of self-identification and land use in particular.

Table 1.
Dimensions of the meanings of place identity through the lens of land use (adapted from [15]).
The interaction between place dependence and land use change has been considered in previous research, but not in the UK land use context. Place dependence describes “the functional bonds that people have with places. It develops when places provide the conditions and features required to meet people’s needs” ([24], p. 146). Thus, individuals may be concerned about policy intervention or societal change when it will prevent a place from meeting their needs, or there is a threat to the place potentially meeting their needs now or in the future, e.g., a change in employment opportunities, accessibility of provisions and services, income, land ownership, and environmental quality [25].
Place identity, as previously described, is more symbolic and reflects place-related meaning, what Trąbka [26] describes as ‘my heart is here’. Place inherited is a further aspect that affects an individual’s and a communities’ reactions to change. Place inherited is characterized as
“a strong and taken for granted bond, prevalent among people who have spent their whole life in one place, who have strong family connections in it and who cannot imagine leaving”.([26] p. 71)
The influence of place inherited in the rural context has had minimal empirical study and is worthy of wider exploration, especially its impact on the adoption of agri-technology. Research in the urban context suggests factors such as place-related artefacts, inherited infrastructure, and inherited resources which all influence place attachment [27]. Others argue that, in the rural context, and the rural/industrial interface of agri-food production, the inherited asset base (physical, financial, natural, human and social resources) can create inertia and lock-in due to their individual and collective influence on creating path dependence [2]. Place attachment includes both immediate forms, such as place dependence and place discovered (which reflects engagement with a place, especially compared to where an individual may have lived previously), and deep rooted forms of place attachment, namely place identity and place inherited [26,28].
Conflicting narratives and views often arise around land use decisions, whether related to changes in existing land use, the adoption of new technologies (for food security, energy security or other reasons), or the resulting impacts on places, the people who reside there, and those connected to them. This conflict is characterized by the level of congruence, or alternatively disconnect, in the range of meanings and beliefs held by different stakeholders relating to that place [29]. The adoption of new forms of land use and agri-technology can prompt individuals to question not only where and how food is produced, but also the wider impacts of change on place. Such changes may also affect the self-identity, self-efficacy, and the perceived agency of those involved in food production. However, adopting new farming practices has been a part of food production for millennia, from changes such as transitioning from horse power to machine power, and from hand threshing to mechanized combine harvesters [30]. Thus, the socio-economic restructuring of agricultural sectors and adoption of alternative agricultural practices, as with technological transition in wider society, is nothing new.
To visualize these developmental stages, it has been positioned that a series of industrial phases have occurred since humans first began to undertake agricultural activity. Whilst there is a lack of consensus in the literature as to the time frames of Agriculture 1.0 through to 3.0, Agriculture 4.0 is articulated as the transitioning of agri-food production via automation and autonomy, digitalization and enabling the ability to communicate and inform decisions in ‘real-time’ [31,32]. The emerging aspects of Agriculture 5.0 have been described as “the design of human-centered smart environments that prioritize human well-being while maintaining production performance” ([33], p. 392). Additional societal benefits may also be derived, e.g., biodiversity recovery or reducing the impact of environmental footprints, that are not currently considered in reflections on efficiency, performance, and outputs which are the centered focus of Agriculture 4.0. Technological and digital transformation can increase efficiency through bottom–up and place-based innovation [34,35]. Thus, the digitalization aspects of Industry (Agriculture) 4.0, especially in industries that to date have focused on manual labor and low levels of technology adoption can offer great economic opportunities for growth and development, especially where they build upon existing regional strengths and capabilities [34]. A range of key performance indicators (KPIs) can be used to assess the success of a particular area of agricultural development while also accounting for both the focus of 4.0 and 5.0, as can be seen in Table 2.

Table 2.
Stages of agri-technology development (Agriculture 4.0 and 5.0) and the associated KPIs.
Unlike the more performance-centered emphasis of Agriculture 4.0., place-based policy approaches resonate with the principles of Agriculture 5.0. To effectively operationalize Agriculture 5.0, there is a need for explicit policy instruments that foreground social outcomes, including worker well-being (e.g., policies mandating ergonomic standards for agri-technology equipment, embedding appropriate technologies that reduce long work hours during harvesting that are a disincentive to working in the sector, and using technology to undertake mundane tasks) and utilizing technology to provide community agency. Examples of community agency could be the better monitoring of air, water and land to identify sources of pollution so action can be taken, e.g., the continuous monitoring of river systems to identify point source sewage emissions to minimize the fecal–oral route of pathogenic disease transmission. Embedding Agriculture 5.0 can be realized through inclusive policy interventions such as publicly funded workforce training programs aimed at transitioning manual agricultural labor into supervisory and collaborative roles alongside automated technologies, such as autonomous machines or self-steering tractors. Furthermore, the integration of participatory governance structures, including community advisory groups or stakeholder-engaged technology trials, ensures that the adoption of agri-technology aligns with localized values, needs and aspirations. Digital continuous monitoring of the quality of river systems that are used for ready-to-eat crop irrigation provides not only social benefit, but also environmental and economic benefit too. Therefore, achieving Agriculture 5.0 requires a reorientation of policy towards inclusive socially embedded innovation pathways. So, this leads to the question of what interventions can influence place-making to support the place-based adoption of agri-technology and the transition of agri-food businesses towards Agriculture 5.0?
The purpose of this conceptual paper is to determine what policy interventions can be of influence in accelerating agri-technology adoption in an evolving ‘place’. The study uses the example of accelerating agri-technology adoption in Lincolnshire, UK, as an explanatory case. The rationale for this is that the Greater Lincolnshire economy employes 75,000 people across agriculture, food processing and food distribution, including fish processing, horticulture (fresh produce and ornamentals), food logistics and marketing, poultry production and broadacre crops, representing 14% of the local workforce, compared to this sector representing 4% national employment [36]. This makes Lincolnshire both agriculturally significant and policy-relevant, offering a valuable context in which to examine the dynamics of agri-technology adoption. Its industrial composition and visibility within national and rural development agendas also position it as a useful exemplar for studying broader regional transitions. A wider exploration of Lincolnshire as a place for agri-technological transition is provided in Section 4 of this paper.
As previously articulated, spatial consciousness, i.e., the managing of a location and creating order and definition through spatial organization such as national and regional spatial development planning can be at odds with spatial connectedness (place-making) which reflects the socially constructed assemblage of place. To provide an example of this difference, developing spatial consciousness would be supported by activities such as the development and use of proxy indicators for the level of community connection to services (shops, schools, medical facilities); level of connectivity (mobile phone connection and connection to the internet, number and location of no-spots etc.); and mapping of existing infrastructure (roads, public transport provision, distance to nearest railway station) and then using these findings to inform spatial development strategies. Conversely, spatial connectedness can be operationalized in resource-depleted communities through capturing storytelling and narratives about community and place, mapping the social ties where people are anchored to the place, i.e., places where people gather socially (places of worship, where sport is played or hold social events), and identifying how social practices and traditions are tied to place. This evidence can then inform place-making activities.
There is a clear difference between location-sensitive policies and place-based policies in terms of their strategic intent, the processes for intervention and the meanings associated with outcomes within the communities that they impact. ‘Place’, with its associated meanings, can be reduced to ‘space’, a location solely designated for specific socio-economic needs without the consideration of place-identity or wider aspects of place attachment. Focusing on space and spatial development aligns with social consciousness resulting in spatial development strategies led by professional “space-makers” that focus on shaping a location to promote local economic growth as strategic priority, but these plans can fail to consider social connectedness, place-making and where aspects such as place identity and place inheritance reside. Space connectedness is achieved by mobilizing individuals and communities toward particular outcomes. Place-based policy can serve as a conduit for particular contexts and specific policy action. The large-scale adoption of agri-technology can deliver spatially conscious, place-based economic impact in line with Agriculture 4.0, but specific and focused policy interventions are required to deliver Agriculture 5.0, i.e., just, inclusive, spatially connected win–win outcomes in often fast-evolving places and policy agendas.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 1 provides an introduction to the paper. Section 2 describes the conceptual approach used in this structured review. Section 3 considers place-making and the role of policy in effective place-making given the spectrum in meanings of place attachment and the range of stakeholders involved. Section 4 uses an explanatory case to consider these aspects and provides a conceptual framework for inclusive agri-technology adoption. Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Conceptual Approach
This paper uses a grounded foundational narrative literature review and then an iterative exploration of secondary data to inductively derive meaning from the evidence itself [2]. The alternative would have been to use the deductive forcing of pre-existing theories which has limited value in an emergent, exploratory cross-disciplinary study. The search terms that emerged from the exploration of gray literature and scientific databases, namely Science Direct, Google Scholar and Google (using search terms such as place, place-identity, place-attachment, place dependence, place inherited, place-based policy, place-making, place-masking) were then used in multiple iterative combinations in subsequent searches until evidence saturation was reached [37], ensuring credibility and quality in this research approach whilst recognizing that the breadth and depth of the data available limited the degree to which conclusions could be drawn and the generalizability of fundings over a wider geographic location or conceptual positioning [38]. Evidence saturation was determined using Rahimi & Khatooni’s rational [38] of theoretical saturation in grounded theory, i.e., the point in iterative research at which no additional information is found that allows for the further development of the properties of the case and the associated concept in that context and thematic saturation where no new themes or relationships emerged from the information available.
The evidence highlighted in each search were then screened and considered for its relevancy, explanatory power, and applicability to the research area and the located case study. The explanatory case study then emerged from the evidence. The narrative and exploratory discourse in this paper was shaped by the triangulation of secondary evidence from a range of sources and academic disciplines. Any inferences derived from these sources have been framed within this methodological caveat. A total of 89 sources were used to support this paper. This flexible and reflexive approach to evidence synthesis, especially with emergent themes such as agri-technology adoption, policy, and with legislation being developed during over timescale of the research, gave rise to a more holistic reflection than would have been derived from other more structured and bounded methodological approaches [39].
The place of agri-food production in Lincolnshire has been used as an explanatory case in this research to reflect on the causal and contributory relationships within a real-world situation. There are three elements to this conceptual approach:
- Detailed exploration of a real-world context—using qualitative and quantitative data and studies to explore a given case in order to examine real situations rather than theoretical conjecture (the “what, where, when and who”);
- Causal and contributory factors and framings—considering causal and contributory factors and framings that inform certain outcomes (the “how and why”);
- Conceptual development—using existing concepts and theories to generate new insights (the “what, and what ifs”).
The explanatory case study method is an accepted approach [40,41] that can be used to explain complex contributory and causal links in real-life contexts and situations (contextual conditions) and any resulting outcomes [42]. The timespan of the data used in the case study was not pre-determined but was iteratively bounded by the data sources that were available. The next section considers place-making and place-masking, the influence of local and national policy and what makes place-based policy challenging to implement, especially in the context of Agriculture 4.0 and 5.0.
3. Theoretical Framing of Place, Space, and Place-Related Policy
Place-making involves a series a dynamic and interrelated spatial and relational features framed by social construction, power relationships, progressive (re)assembling, and fluidity where place may or may not be an entity or a way of experiencing. Place will also have its “own materialist histories, [which are associated with] the labor and knowledges required to produce it” ([1], p. 486). Place-making as a term has “broad utility, but its theoretical heritage is imprecise and vague” ([43] p. 519). Place matters, especially in the agricultural context, in terms of the assets available in the place (e.g., infrastructure, people, and environmental resources such as soil), the services provided in the place (e.g., digital connectivity and access to wider health, education and other services), the local and national governance of place (both private and public actors) and, as already outlined in this paper, the identities formed by individuals and communities in place and also the convergence, or alternatively conflicting, nature of these multiple drivers [44]. More specifically,
- Assets in place include natural assets and resources, heritage and natural vistas, knowledge and climatic environment;
- Services encompass health, education, employment opportunities, justice, welfare and government support of communities, in terms of not only provision but also accessibility especially in rural areas;
- Governance embraces the processes and activities that support the communities to thrive or conversely fail to thrive;
- Identities reflect who we think we are and what we believe the place to be [44].
Policy can be place neutral or place-based, i.e., a given policy or policy agenda can impact positively, negatively or both, the socio-economic situation of a particular location or community [45]. Place-based policy in itself is not a new term and has been discussed in the literature for several decades [44,46]. Place-based policies can be implemented from a spatial perspective often with government intervention seeking to improve a location or area in terms of economic growth, job opportunities and higher wages, one example being the development of located enterprise zones [47]. Place-based policy approaches consider “the complex interplay between the social and physical environment”, and how this affects the final outcomes for communities [48]. There are multiple factors that can make place-based policy difficult to implement (Table 3), and each have different ethical aspects and outcomes to consider. However, for policy, to be place-based rather than space conscious, policy makers must become place-makers not space-makers and recognize how places and the people in them perceive their sense of self, their view of the world around them and beyond, and their capacity and sense of their agency to be able to shape it and act within it [44]. Spatial development initiatives driven by governments (national or regional) can occur in isolation but this policy approach runs the risk of being challenged by local communities if the policy or its perceived outcomes do not align with local notions of appropriate place-making. In short, strategic spatial development planning focuses on the macro aspects of development (policy development, economic growth, housing distributions, transport networks, zoning regulations, addressing national commitments to deliver environmental or social targets), whereas place-making focuses on the micro aspects of development in terms of human experience, and the co-created design of places where humans live, work and socialize. Embedding aspects of place-making can improve the implementation of strategic spatial development, and effective macro level strategic planning can support place-making, but it is important to distinguish between them here when considering the challenges to agri-technology adoption.
When considering the factors that make place-based policy difficult to implement (Table 3), the first factor is centralized and remote policy making that fails to consider localized impact in the widest sense. The positivist versus interpretivist framing of place has already been explored in this paper and the aspects of national and regional spatial consciousness inform location-based policy rather than place-based policy making. Definitional obscurity can lead to different actors ascribing different meanings to location-sensitive policy as well as having differing expectations of what a good outcome would be in terms of regional organization and regional connectedness. Policy can also be in explicit conflict when the rights of the individual and commitment to private property ownership are at odds with the collective benefits of delivering policy agendas such as The Methane Pledge, biodiversity (30 by 30), or national net zero emissions targets. Institutional separation in the government of economic concerns (treasury) and a wider range of social concerns (employment, welfare, health, education, justice) make it difficult to recognize and act where competing governmental interests either converge or are in conflict in the development of place-based policy. Indeed, one viewpoint is that place-making, given the power dynamics that exist, is “a contest over whose vision dominates, who has the resources to influence and who speaks, finances, designs and implements” ([43], p. 521).
To illustrate these tensions more explicitly, Table 4 provides specific empirical examples of land-use conflicts in Lincolnshire, highlighting the interplay between national policy objectives, corporate interests, and local community values. These examples illustrate the complex tensions that can arise in the implementation of spatial development strategies, particularly where national policy priorities and corporate interests intersect with local place-based values and practices. In Lincolnshire, land-use transitions associated with renewable energy projects and intensive agricultural developments, whilst providing national and regional energy and food security benefits, have prompted concerns regarding heritage preservation, environmental integrity, agricultural land loss, and the socio-cultural meaning of place. Such conflicts reflect the broader conceptual distinction explored in this paper between spatial consciousness, which prioritizes strategic development objectives, and spatial connectedness, which is rooted in community identity, local knowledge, and a sense of place. These cases underscore the importance of designing inclusive and participatory policy processes that acknowledge these diverse perspectives and seek to balance national imperatives with the lived realities of affected communities.
Economic restructuring intended to deliver growth can be implicitly aligned with aspects of renewal, regeneration, and gentrification, whereby place is actively changed and improved, but this ‘masks’ the potential displacement of people who were previously connected with the place, i.e., such policy can lead to place-masking [43]. Spatial development strategies can intentionally or unintentionally drive gentrification [2], by reshaping economic growth-related policies and future land use, changes in infrastructure (roads, public transport service investment, and by attracting investment) and generally increase the cost of living in those areas. Indeed, Fincher et al. ([43], p. 529) argue that
“place-making becomes a mask for the displacement of those incumbent low-income people seen as transgressive and undesirable, and for their replacement with a better-resourced and presumably better-behaved population in an envisioned, desired future”.
Manning [2] argues that this form of exclusionary displacement, or ‘hollowing out’, can lead to greater disparity between local housing costs and the salaries associated with long-standing local jobs [49,50,51], and often impact conflicted narratives surrounding current and future land use, exercised through local planning policy [49]. In summary, agri-technology adoption that causes exclusionary displacement will not deliver win–win outcomes for all stakeholders. When examining agricultural transitions, factors such as the technology itself, especially the use of artificial intelligence, the associated loss of employment [52], the distributional impact on winners and losers [53], and the influence of climate change [54] all highlight that the processes and the policies around agri-technology adoption, land use transition and food security are inherently value-laden and not ethics-free [55].

Table 3.
Factors that make place-based policy challenging to implement (adapted from [44]).
Table 3.
Factors that make place-based policy challenging to implement (adapted from [44]).
| Factor | Description | Ethical Perspectives |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized and remote policy making | Bureaucratic nature of government focuses on delivering broad, desirable objectives with less regard for localized desirable and undesirable outcomes. This can be described as national spatial development strategies such as in the draft UK Planning and Infrastructure Bill. | A utilitarian perspective arises from the adoption of spatial development strategies as the policy is designed to enable the greater good for the country or the region rather than win–win outcomes which recognize place. |
| Confusion between policies being location-sensitive and place-based | Whilst place-based policies reflect the heritage of values, aspirations, and identities of a place, location-sensitive policies reflect the needs of a location at a specific point in time. | A relativism perspective arises here. Place-based policies reflect cultural norms rather than applying general rules to all contexts. Location-sensitive policies reflect specific rules that can be applied to deliver specific objectives and meet specific needs. What is right and appropriate is relative to each type of policy. |
| Definitional obscurity | Where plans and specifications are obscure with different potential interpretations, or hidden meanings, this will impact on the effectiveness of their implementation and the level of ambiguity within associated narratives on what is intended in terms of objectives and outcomes. | Definitional obscurity will drive a different perspective in addressing a given issue promoting a relativist perspective. Different actors will have different perceptions of what is a good or bad intention or outcome based on their cultural norms and standards and viewpoints especially those who have a positivist viewpoint and those who have an interpretivist viewpoint. |
| Economic restructuring | Economic restructuring driven by technology adoption often results in labor displacement and shifts toward services or amenities that may not align with existing perceptions and identities of place. This can promote place-making based on future potential or place-masking, which overlooks existing place identities. | A utilitarian perspective arises where policy enables the greater good rather than win–win outcomes. The driver for economic restructuring, national and/or regional spatial development plans, and market level drivers for economic restructuring may limit the integration of place-making or even promote place-masking. |
| Policy where the individual and the greater good are explicitly in conflict | Policy can be in explicit conflict when the rights of the individual, commitment to private property ownership because they are pitched against collective benefits such as delivering policy agendas such the development and deployment of spatial development plans addressing The Methane Pledge, biodiversity (30 by 30) in the UK or national net zero emissions targets. | A utilitarian perspective arises where policy enables the greater good rather than win–win outcomes. Power dynamics and imbalances will influence who wins and who loses in these scenarios. |
| Sectoral organization of government | Institutional separation in the government of economic concerns (treasury) and a wider range of social concerns (employment, welfare, health, education, justice), make it difficult to recognize and act where competing governmental interests either converge or are in conflict. | Ethical egoism holds that moral norms serve the function of promoting the self-interest of a particular individual or agent. Self-interest can converge between agents or be in conflict. |
| Stakeholder communication and trust deficits | Lack of effective communication between local stakeholders (e.g., farmers, communities, policymakers) can lead to tensions, especially when individual decisions—such as adopting financially incentivized land uses like solar panels—conflict with community perceptions, expectations, or long-term visions for place. | A relational ethics perspective applies, emphasizing the need for dialogue, trust, and mutual understanding to balance individual choices with collective well-being. |

Table 4.
Empirical examples of land-use policy conflicts in Lincolnshire.
Table 4.
Empirical examples of land-use policy conflicts in Lincolnshire.
| Project/Site | Description | Nature of Conflict | Stakeholders Involved | Outcome/Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicathorpe Oil Drilling [56] | Oil drilling plans in the Lincolnshire Wolds, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) | Legal challenges due to environmental impacts and protected landscape status. | Local councils, environmental groups (SOS Biscathorpe), Planning Inspectorate. | High Court legal proceedings ongoing. |
| Gate Burton Energy Park [57] | Proposed large-scale solar farm in Lincolnshire. | Delays due to archaeological assessments, tensions between renewable energy goals and heritage preservation. | Developers, local authorities, archaeologists, local communities. | Project delayed by over six months, incurring an additional £1 million in costs. |
| Nocton Dairies ‘Super Dairy’ [58] | Proposal for intensive dairy operation housing up to 8100 cows. | Public opposition due to environmental concerns, animal welfare, and local community impact. | Nocton Dairies, Environment Agency, local residents, North Kesteven District Council. | Application withdrawn after extensive opposition and regulatory concerns. |
| Winterton Solar Farm [59] | 10 MW solar farm planned on agricultural land. | Conflict over landscape, biodiversity, renewable energy versus agricultural land preservation. | North Lincolnshire Council, developers, local residents. | Planning permission granted on appeal with mitigation conditions. |
Klerkx et al. [60], when considering Agriculture 4.0, stated there were several themes that emerged which we position herein need to be considered in place-based policy for agri-technology adoption. We would argue that many of these aspects are actually sitting within the emerging definition of Agriculture 5.0, namely
- Self-identity aspects (attitude, feelings and behavior) such as the effects of digitalization on farmer identity, farmer skills, and farm work;
- Institutional shape (see Table 1) namely power, ownership, privacy and ethics in digitalizing agricultural production systems and value chains and also economics and management of digitalized agricultural production systems and value chains and digitalization and agricultural knowledge and innovation systems (AKIS);
- Physical shape, i.e., the contextual geography of adoption, uses and adaptation of digital technologies on farm.
However, explicit aspects of symbolic shape of place and collective perceptions of place (see Table 1) are not contained explicitly within this characterization in the literature. As previously outlined, aspects of place attachment are nuanced and context dependent. However, place-making can be envisaged, usually by professional place-makers (planners, policy makers, designers, engineers), as a primarily a ‘physical and morals-free strategy’ to improve the image of a space, as a conduit for a particular political action for example, to promote local economic growth, and where the transitional agenda can mobilize individuals and communities can achieve a particular set of outcomes [43]. This, they could argue, means that there can be a focus on the events that are situated in a space, rather than the opportunities that are created within an existing place, the influence of the inherited place or the inclusionary/exclusionary nature of place-making, and by inference place-masking.
A just transition in this context involves developing place-based policy that considers ‘who wins, who loses, how and why’ ([61], p. 133). Therefore, just forms of spatial consciousness should consider not only what is physically intended for the space, but also the potential social outcomes [20]. This reflects a focus on embedding the human centric aspects of Agriculture 5.0, in contrast to the performance driven focus of Agriculture 4.0. Wester-Herber [4] states that these social outcomes, especially where processes of place stigmatization occur, such as framing agricultural work as low-skilled, low-paid, and poorly valued, can influence self-identity, and by extension, place-identity. Aspects for consideration, they argue, are:
- The influence of transition on self-esteem and well-being when self-identity is reframed to a new status that the individual (and wider community) does not identify with, and the place no longer provides a positive reinforcement of identity or values.
- The interaction between self-efficacy and place attachment, especially place dependence, and the ability of the individual (and wider community) to cope when the landscape and the practices within that landscape are stigmatized to drive policy change or are culturally stigmatized in the name of economic development [13], or to address nature recovery or the mitigation of pollution risk from agriculture [62]. The stigma can also extend to the derived products such as meat or milk when agricultural practices and the associated products, which are described as damaging in terms of greenhouse gas emissions versus plant-based alternatives.
- The continuity of self in relation to place-identity where changes to landscape are associated with grief or loss, i.e., land that has been in the possession of families for generations can be lost and also carry a stigma of something that is no longer pure or natural… where this bond between a person and land increases with age, it will become more difficult for new meanings to be given to communities if “the population is older and more rooted [in the place] as compared to an area with high mobility and a lower average age” [4] (p. 113).
- The loss of distinctiveness. Locations can have a heritage of particular breeds of livestock or crops (in the case of Lincolnshire, Lincoln Red cattle or Lincoln Longwool sheep), and a transition to types of agriculture where this distinctiveness is lost impact on perceptions of this new place.
In summary, a key distinction lies between viewing a place as bounded, definable and measurable, from a positivist viewpoint of spatial development, and perceiving place from a relational focus, where meaning is shaped by how various aspects connect, rather than by traditional development-related performance indicators (see [19]), herein described as place-making. This distinction between space-making and place-making underpins the context in which trade-offs between the benefits and challenges of agri-technology transition are evaluated. Whether the focus is space or place also influences whether adoption is perceived as a linear process, following a predetermined development path, or as an iterative process, offering opportunities for place-making throughout project development, deployment and evaluation. Roddis et al. [63] identified 28 factors that influenced a community’s acceptance of a large-scale solar (photo-voltaic) farm. These factors have been categorized in Table 5 as either space-making or place-making where the categories are grounded in the literature.

Table 5.
Aspects that influence community’ acceptance of in-field agri-technology adoption. (adapted from [63]).
There are clear differences between the economic environmental, process and life-cycle aspects of space-making and the more aesthetic, social, temporal, and impact aspects of place-making. These themes are now explored through the Lincolnshire case study.
4. Lincolnshire: Findings from an Explanatory Case Study
The detailed exploration of a real-world context requires using qualitative and quantitative data to examine real situations rather than theoretical conjecture (the what, where, when, and who). This approach has been used here. In 2019, Greater Lincolnshire had a total agricultural output of over GBP 2 billion (12% of England’s total production) [64]. Furthermore, the food chain provided 24% of jobs throughout Greater Lincolnshire (as compared with 13% nationally) and 21% of its economic output (7% nationally) [64]. The Greater Lincolnshire Local Enterprise Partnership Agri-Food Sector Plan (2017) [65] focused on three key areas: having a supply chain focus, production efficiency, and focusing on meeting customer needs which would be enabled by labor productivity and skills, integrated skills and innovation support, market focus and trade, investment in physical infrastructure, developing clusters of food businesses within enterprise zones, and seeking partnerships to ensure continued investment in transport infrastructure. Within the ‘UK Food Valley’, several key food clusters have emerged. Fish processing in the region accounts for 60% of the UK’s total fish processing capacity. The fresh produce sector supplies 26% of vegetables and salads, 13% of potatoes to national multiple food retailers and 19% of ornamentals to garden centers [36]. Poultry production is also significant, constituting 20% of the UK’s duck production, 18% of chicken and turkey production and 7% of egg production. Additionally, the area contributes 12% of England’s arable crop output and 11% of cereal production. Other important sectors include plants and alternative proteins (accounting for 11% of national dried pea and bean production), agri-technology and food technology development, as well as food logistics and marketing [36]. The report states [66] that 59% of agricultural output is with crop production and 41% livestock-based and
“The UK Food Valley food chain had average annual output over the period 2019–2021 estimated at: £10.7 billion of turnover in agriculture and food processing and distribution, generating a contribution to the economy of £4 billion; £3.9 billion of turnover in food retail and catering, generating £1.1 billion for the economy; to give a total food chain with sales of £14.6 billion and contributing £5.1 billion to the economy”.[66]
This output is summarized for 2021 in Figure 1 by crop type. Government data state that the value of agricultural outputs in Lincolnshire in 2023 was GBP 2.4 billion with 65% derived from crop outputs, 23% from livestock outputs and the rest from other agricultural activities, diversification and subsidies [67]. There are around 3500 farm holdings in Lincolnshire, with over one third (36%) being over 100 hectares in size, the number of horticultural holdings reduced to 209 in 2021, nearly 100 lower than in 2010 and the number of dairy holdings dropping to 14 in 2021 with cattle numbers (including beef) having fallen by 20% in that time [61]. In 2021, there were around 3500 dairy cows representing 0.3% of the total number in England. The beef herd in Lincolnshire represented 2.5% of the total for England, whilst the sheep in Lincolnshire represent 1% of England’s total. Pig numbers have increased by 16% (to 4.1% of England’s total) and poultry numbers by 20% (11.4% of England’s total), demonstrating a switch to more intensive livestock production [68].
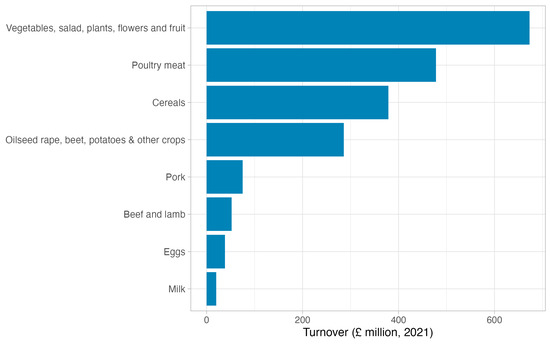
Figure 1.
Agricultural output data for Greater Lincolnshire 2021 (adapted from [36,68]).
Thus, with some caveats, as the comparison of data between sources demonstrates inconsistencies, business specialization in Lincolnshire can be demonstrated with milk (14 holdings from 3500), pork (53 holdings), poultry meat, and eggs (180 holdings) and beef and lamb (567 holdings), being a small proportion of the total. More granular data such as the degree of consolidation of agricultural holdings in a given business operation or the proportion of holdings that are contract farmed by larger agri-businesses or subject to rental agreements is challenging to find as this data is not commonly published. A key priority for Lincolnshire’s UK Food Valley is the focus on productivity by adopting digital and automation technology, developing low-carbon food chains, and promoting naturally healthy food and protein transition [66]. Since 2016, there has been over GBP 2.25 bn of investment in the food chain in Lincolnshire, creating over 7000 jobs. This includes new inward investments, upgrading and expansion of existing facilities and mergers and acquisition (over 70 international companies; 30 investments of GBP 10 m+ and 10 investments of GBP 50 m+) with over 40% of FDI investment in Greater Lincolnshire within the agri-food sector.
4.1. Causal and Contributory Factors and Framings—Considering Causal and Contributory Factors and Framings That Inform Certain Outcomes (The How and Why)
Lincolnshire, as a place for agri-food production, has already experienced a process of agricultural specialization, driving economies of scale and technological lock-in [2,69], although de Roest et al. [69] has argued that this has weakened the economic resilience of agricultural businesses and their ability to withstand market and geo-political shocks. De Roest et al. ([69] p. 233) assert that
“Specialized farmers delegate product marketing and the purchase of inputs to centralized agencies and concentrate their efforts solely on production activities… regions can only remain competitive if marketing and logistics are highly centralized, as this is the only way that production can meet the requirements of the centralized purchase platforms of large scale retailers”.
From an Agriculture 4.0 perspective, specialization in terms of operations such as horticulture, pork, and poultry production, cereals and dairy has led to productivity gains and geographic concentration enabling comparative cost advantage [69]. However, the high specialization of agriculture in Lincolnshire has led to some nature and biodiversity loss. Further specialization of agricultural production and land use in England through the Land Use Framework will drive a complex pluri-activity associated with land-use. The Planning and Infrastructure Bill [70] is currently going through the UK Parliament to be reviewed, revised and then to receive royal assent to become law. It currently states
“The Planning and Infrastructure Bill is central to the government’s plan to get Britain building again and deliver economic growth. The Bill will speed up and streamline the delivery of new homes and critical infrastructure, supporting delivery of the government’s Plan for Change milestones of building 1.5 million safe and decent homes in England and fast-tracking 150 planning decisions on major economic infrastructure projects by the end of this Parliament. It will also support delivery of the government’s Clean Power 2030 target by ensuring that key clean energy projects are built as quickly as possible”.[70]
The Bill [70] has five key objectives:
- Delivering a faster and more certain consenting process for critical infrastructure by “upgrading the country’s major economic infrastructure—including our electricity networks and clean energy sources, roads, public transport links and water supplies—is essential to delivering basic services and growing the economy”;
- Introducing a more strategic approach to nature recovery with introducing a new Nature Restoration Fund that “will unlock and accelerate development while going beyond simply offsetting harm to unlock the positive impact development can have in driving nature recovery”;
- Improving certainty and decision making in the planning system, where local communities shape decisions but that planning committees can still operate as effectively as possible so “the Bill will ensure that they play their proper role in scrutinizing development without obstructing it, whilst maximizing the use of experienced professional planners”.
- Unlocking land and securing public value for large-scale investment “to unlock more sites for development, the Bill will ensure that compensation paid to landowners through the compulsory purchase order process is fair but not excessive, and that development corporations can operate effectively”.
- Introducing effective new mechanisms for cross-boundary strategic planning “to develop strategic planning with effective cross-boundary working to address development and infrastructure needs”.
Under the proposals in the Bill, Lincolnshire will be required to have a spatial development strategy modeled on the system that has been previously used for development in London [71]. The proposal is that the national government can also develop strategic planning boards to prepare spatial development plans on behalf of specified groupings of county authorities. The Q&A document from the UK Government notes “Strategic planning will also be important in the delivery of Local Growth Plans and Local Nature Recovery Strategies”. Local government can still develop more localized strategic plans but this will be in alignment with the overall spatial development plans, not as a bottom–up plan. The Bill [72] also outlines the process for establishing development corporations, and as previously described, establishes a nature restoration fund (NRF) as a means for developers to meet environmental obligations relating to protected sites and species.
“It allows Natural England (or another designated delivery body) to bring forward Environmental Delivery Plans (EDPs), that will set out the strategic action to be taken to address the impact that development has on a protected site or species and, crucially, how these actions go further than the current approach and support nature recovery. Where an EDP is in place [developed by experts in Natural England] and a developer utilizes it, the developer would no longer be required to undertake their own assessments, or deliver project-specific interventions, for issues addressed by the EDP…. The budget allocated £14 million for the Nature Restoration Fund in the next financial year, but its steady state operation will be on a full cost recovery basis”.[72]
The draft Bill [73] states under Section 72:
“Natural England may acquire land compulsorily if the Secretary of State authorizes it to do so. The power … may be exercised in relation to land only if Natural England requires the land for purposes connected with the taking of a conservation measure”.
With the forthcoming English Devolution Bill, the UK Government intends to give strategic development management powers to strategic planning authorities that have elected mayors [71], which will be the case in Lincolnshire. The process will be top–down and local plans will need to align with the spatial development plans to ensure the effective delivery. So, how will these spatial development plans inform agri-technology adoption in Lincolnshire where the ‘place’ continuous to evolve?
4.2. Conceptual Development—Using Existing Concepts and Theories to Generate New Insights (The What, and What Ifs)
Open and inclusive policy making needs to be evidence-based, co-created, accessible, explainable and transparent for all citizens [74]. Creating pathways for inclusive transition requires the following:
- Sustained political will from political system to public support;
- Interagency co-ordination between national agencies and all levels of government;
- Capacity of national systems—strong institutional capacity (technical, human and financial);
- International and regional cooperation—collaboration with and support for international and regional partners and networks;
- Sustained financing—adequate, sustained and planned financing from a range of sources [75].
But, how do we develop pathways for inclusive innovation and inclusive policy in a time of transition through spatial development? Across the world, persistent problems, geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, economic crises and rising inequality, coincide with growing recognition that current socio-technical systems are neither resilient nor sustainable in meeting our fundamental societal needs [76]. Thus consideration of socio-technical systems and their distinct levels, especially in relation to how interventions, decisions, and innovations diffuse across these levels is essential. When inclusive policy goals are developed and communicated for a specific socio-technical system, policy makers should consider economic, environmental and social aspects and potential outcomes across all socio-technical levels (Table 6) and bridge across what is possible, desirable and achievable given the available resources, capabilities and knowledge base in a given situation [76]. A socio-technical regime is described as
“the deep structure that accounts for the stability of an existing socio-technical system. It refers to the semi-coherent set of rules that orient and coordinate the activities of the social groups that reproduce the various elements of socio-technical systems”.[77,78]
Understanding the interactions between these levels is key to identifying leverage points for fostering inclusive, just and sustainable transitions, particularly in agri-technology adoption and with a focus on Agriculture 5.0 (Table 6).

Table 6.
Socio-technical levels that underpin and drive agri-technology adoption (adapted from [79,80]).
Table 6.
Socio-technical levels that underpin and drive agri-technology adoption (adapted from [79,80]).
| System Level | Description | Drivers | Outputs | Agri-Technology Related Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Supranational bodies and associations | International geopolitical, environmental, and economic systems, influencing national policies and market conditions | Geo-political climate International non-governmental bodies Transnational corporations | Intergovernmental agreements International standards and codes of practice Pledges/commitments Policies | The Methane Pledge Sustainable Development Goals International Biodiversity Agreements |
| 2—Government (policy and budgeting) | National and regional governments setting laws, policies, and financial priorities | Political climate Public awareness Public finances Public opinion | Government spending plans Laws/legislation policy | 30 by 30 (biodiversity strategy) Planning and Infrastructure Bill |
| 3—Regulatory bodies and associations | Institutions translating legislation into enforceable regulations, standards, and rules | Legislation and intergovernmental agreements and commitments need to be converted into market-based rules and/or regulations | Judgments Laws Standards | Environmentally permitting for agri-technology Permitting and regulation for use of agri-technology in public spaces (e.g., autonomous machinery on public footpaths) Animal welfare standards GHG emissions regulations |
| 4—Local government (policy and budgeting) | Local authorities responsible for implementing national policies and addressing place-based needs | Local governance priorities Community engagement Budget constraints | Local planning decisions Infrastructure support Community initiatives | Local zoning for agri-technology facilities Support for local food hubs Funding for agri-technology training and educational programs at local educational institutions |
| 5—Organizations (companies and households) | Businesses, farms, cooperatives, and households making operational and investment decisions in response to market and regulatory conditions | Changing market conditions Changing regulatory conditions External company/household pressures Internal company/household pressures | Technology adoption Investment decisions Supply chain adjustments | Adoption of precision agriculture technology Adoption of solar panels on farmland Big data leveraged to inform decision making |
| 6—Technical and operational management | Day-to-day decision making and practices in farms, agribusinesses, and related operations | Technical feasibility Resource availability Skill levels | Implementation of technology Operational efficiency Environmental management | Use of AI-based crop monitoring Integrated pest management Data-driven irrigation systems |
| 7—Equipment and internal environment | The design, maintenance, and condition of the physical equipment and local operational environments. | Equipment availability Technological innovation Maintenance capacity | Equipment performance Workplace safety Production efficiency | Availability of automated machinery Use of renewable energy sources on farms Implementation of robotics in food processing |
| 8—People | The values, skills, attitudes, and wellbeing of individuals involved in the system—farm owners/managers, farm workers, consumers, policy makers | Education Training Social norms Health and wellbeing | Behavioral changes Workforce capability Community resilience | Farmer training in digital tools Stakeholder engagement in policy design Public trust in agri-technology |
Table 6 outlines these levels and connects them to relevant agri-technology examples, highlighting where policies and stakeholders can intervene to enable more inclusive and adaptive systems of agri-food production through agri-technology adoption. These socio-technical levels demonstrate how innovations and policies diffuse and interact across multiple layers of society, governance, and economy. Recognizing where interventions can be applied across the levels is crucial for fostering inclusive innovation agri-technology adoption pathways. It is at these varied levels that structural barriers, power asymmetries, and stakeholder dynamics either constrain or enable just and sustainable transitions via agri-technology adoption. To further illustrate how inclusion can be embedded throughout these systems, Table 7 maps levels of inclusion specifically within the context of agri-technology innovation, adapted from Mungai et al.’s. inclusive innovation framework [81]. This conceptual framework can support the consideration of agri-technology adoption in place, where place-based barriers can prevent adoption [2].
Inclusive innovation is an important “driver of positive outcomes such as economic growth and societal well-being” [11], (p. 34). There are three particular constraints that influence inclusive innovation which are the path dependency of the drivers, the constraints associated with scale and the challenges of appropriation [82]. Indeed, existing power structures, regulatory and market regimes and infrastructural elements will constrain the degree of inclusivity of innovation [83]. Unlocking strategies can reduce the path dependency and inactivity at all socio-technical levels and are essential to drive an economically, environmentally and socially inclusive transition [2]. A key unlocking strategy to develop place-based rather than spatial development interventions is to ensure there is appropriate levels of stakeholder engagement at all stages of inclusive innovation from initial intentions through to deep ongoing involvement in governance structures. A failure to do so can result in local conflict arising, as has been shown in this Lincolnshire case study (see Table 4). Considering the context of Lincolnshire as a case, with a view to developing an inclusive agri-technology adoption framework, agri-technology innovation, including digital innovation reshapes the value landscape providing opportunities to realign resources and assets in a given ‘place’ to generate and capture new forms of value [84]. In this context, value can be considered in terms of ‘value in exchange’, ‘value in use’ and ‘value in purpose’ [84]. Digital social innovation in particular considers the use of digital technologies (products, processes, services and policy models) to address societal challenges and deliver social value [85]. In other words, digital social innovation addresses “societal challenges (e.g., poor education, poor health, gender inequality, climate change) with more effective, efficient, sustainable, or just solutions,” especially for economically disadvantaged groups ([85] p. 3). This approach to place-based policy embeds Agriculture 5.0 rather than Agriculture 4.0 with its solely productivity and efficiency centric focus. Agriculture 5.0 recognizes the socio-technical system in which technology is adopted and the barriers and enablers and the alternative non-financial value that can be derived from its adoption [33].

Table 7.
Levels of inclusion in agri-technology adoption framework to ensure place-based impact in Agriculture 5.0 (Adapted from [81]).
Table 7.
Levels of inclusion in agri-technology adoption framework to ensure place-based impact in Agriculture 5.0 (Adapted from [81]).
| Inclusion Level | Inclusion Activity | Government (Policy and Budgeting) | Regulatory Bodies and Associations | Local Government (Policy and Budgeting) | Organizations, Management, Environment | People |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1: Inclusion of Intention | Explicit commitments or stated goals to ensure relevant stakeholders are embedded in project planning documents and policy frameworks from the outset. These stakeholders will be from both national and regional settings. | Develop national strategies that require inclusive planning and stakeholder input. | Set expectations for stakeholder representation in funding frameworks and standards. | Embed stakeholder representation in local development and technology strategies, e.g., in Lincolnshire the Lincolnshire Food Valley initiative. | Consult with producer groups, environmental NGOs, and agri-technology networks. | Express interests, concerns, and priorities at the earliest stages. |
| Level 2: Inclusion of Consumption | End-users (e.g., farmers, cooperatives) are actively engaged in pilot projects or trials, providing real-time feedback on the usability and effectiveness of agri-technologies. This stage of engagement ensures place-based impact. | Fund real-life demonstration programs that promote stakeholder participation. | Support collaborative, multi-stakeholder workgroups Monitor performance and user inclusion in pilot initiatives and regulatory sandboxes. | Identify suitable pilot adoption sites and lead local engagement with farmer innovation networks. | Implement governance infrastructures, place-based impact accelerators such as LINCAM Ceres [86] and coordinate feedback mechanisms to deliver place-based impact. | Develop farmer and community networks to support participation in trials and testing and provide experiential feedback. |
| Level 3: Inclusion of Impact | Regular impact assessments are conducted, surveying both direct participants (e.g., technology adopters) and affected non-participating stakeholders to gauge broader socio-economic effects. This stage will consider socio-economic and environmental factors such as displacement of labor, impact on diffuse pollution from agricultural land, improvements in animal welfare etc. | Support regional impact evaluations and incorporate findings into policy. | Use impact data to inform regulatory review processes, e.g., the UK Industrial Strategy. Inform strategic funding of research and development in core impactful industrial sectors including agri-tech. | Facilitate local feedback collection and knowledge exchange forums. Provide opportunities for knowledge exchange which can feed into local policy innovation and through to national policy. | Conduct assessments and collect operational data. Provide opportunities for knowledge exchange which can feed into local policy innovation and through to national policy. | Contribute lived experience and reflections on the impact of technology. Provide opportunities for knowledge exchange which can feed into local policy innovation and through to national policy. Consider the impact on migrant harvest workers specifically who are engaging with place to ensure inclusion and appropriate impact assessment. |
| Level 4: Inclusion of Process | Participatory workshops or collaborative design sessions actively integrate stakeholder perspectives into technology design, adaptation, and implementation strategies. The development of inclusive processes of innovation will ensure both responsible research and innovation and inclusive innovation and that the processes themselves are fair, just and non-exclusionary. | Promote participatory approaches in innovation funding schemes. | Encourage inclusive design in technical and advisory guidance. | Co-lead collaborative design sessions with stakeholders. | Facilitate multi-actor workshops and inclusive design processes. Consider how participation can be encouraged from silent sectors of communities who have preciously not engaged in micro- and small business advocacy activities to promote inclusive and just transition. | Co-design solutions and influence implementation approaches. Consider how participation can be encouraged from silent communities who have preciously not engaged in community advocacy to promote inclusive and just transition. |
| Level 5: Inclusion of Structure | Stakeholder feedback is formalized within institutional processes and consistently informs strategic decisions and policies regarding agri-technology development and use. This stage will ensure that there is a focus not only on spatial consciousness but also the spatial connectedness and an integration of economic growth interventions and aspects of place-making. | Require multi-stakeholder governance structures in funded projects. | Include community representation in formal advisory groups. | Create permanent local governance mechanisms for oversight. Develop adaption and mitigation strategies for communities that are affected by spatial development, e.g., addressing loss of services and community spaces. | Integrate feedback processes into operational structures and develop adaption and mitigation strategies at the organizational level, e.g., retraining programs, redeployment programs for staff that are affected. | Contribute structured input through formal consultation processes; participate in scheduled reviews or standing committees. |
| Level 6: Post-structural inclusion | Stakeholders (e.g., farmers, local communities) have ongoing roles in governance, decision-making boards, or advisory committees shaping technology deployment and land use planning. This stage ensures that aspects of spatial connectedness continue to be central to spatial development strategies. | Enable legal or institutional pathways for community co-governance. | Adapt policy mechanisms to reflect shared governance and oversight. | Support and fund local advisory boards with long-term responsibilities. | Institutionalize bottom–up accountability and review structures. | Develop skills and capacity so individuals have confidence to participate in governance structures (e.g., community boards, land-use planning panels), with co-decision-making responsibilities. Consider the involvement of all place-based communities including migrant workers. |
Agriculture 5.0 needs to address and mitigate these factors in ways that have not generally been considered under the promotion of previous agricultural ‘revolutions’. Wider aspects in the UK context such as the socio-economic and geopolitical outcomes of Brexit and COVID-19, and the challenges with accessing manual agricultural labor [22,52,87] have impacted place-based policy and place-making and the nature of agricultural transition(s) that have occurred and continue to emerge. Given the complexity of the demands on land now, and going forward, and the complex nature of food systems, some argue that more reflexive processes are required at the governance landscape level to address issues such as extant culture, power dynamics, and the emerging socio-cultural framing (equity, fairness, moral hazard and so on) that influence the adoption of agri-technology. Such reflexivity is seen as key to delivering more just transitions and outcomes [54], and a new focal point as conceptualization of Agriculture 5.0 takes shape. Consideration of regional development and the contested challenges of political, social and cultural aspects and impacts of development is nothing new and the conflict between spatial consciousness and spatial connectedness can lead to processes that are contested, contingent, and the outcomes can be unpredictable [88]. Thus, the question of how regions such as Lincolnshire through focused place-based policies can become “competitive economic zones within a global economy, [and address] strategic political territories in a complex system of multi-level governance” ([89], p. 1177) is one worthy of further study in this place and other locations.
5. Concluding Thoughts
Operationalizing Agriculture 5.0 requires that policy interventions at all stages of design and actualization address not only structural and technological conditions, but also the lived experiences of all stakeholders. This includes embedding ergonomic and wellbeing considerations in the design of technologies, ensuring access to education and training for those who may be replaced or displaced by technology, and developing governance structures that give voice to local actors throughout the policy development and implementation cycle. This will mean generally, and specifically with the embedding of food security and energy security related technology in a geographic location, that trade-offs between different interests are inevitably going to occur. National economic growth and spatial development strategies, the implementation of policies to devolve political power to regions and spatial development planning for large scale infrastructural projects and those specifically focused on national security (energy and food) will mean that national politico-economic objectives, aspects of local autonomy with inclusive policy pathways for place-making and the potential for regional inequalities will all need to be considered and addressed.
In examining how spatial development planning and in particular the adoption of place-based policies can accelerate agri-technology adoption, this paper highlights the critical tensions and synergies between spatial consciousness and spatial connectedness. Using Lincolnshire as an explanatory example, our research emphasizes that the successful integration of agri-technology in evolving rural places requires policy interventions that carefully balance economic objectives such as economic growth with socio-cultural values and place identities. Inclusive policy-making processes, which firstly recognize the difference between space-making and place-making, and secondly, recognize and reconcile different stakeholder meanings of place, are key to achieving sustainable and equitable outcomes of rural development that resonate and align with communities and specifically their sense of identity.
This paper contributes a conceptual framework (Table 7) that connects inclusive policy design to place-based agri-technology transitions which can vary from self-steer machinery and autonomous harvesting, replacing harvesting workers, through to landscape-based energy generation. By integrating levels of inclusion into a phased, actor-specific engagement model, the study provides a pathway for aligning technological innovation with ethical and locally grounded governance. The framework developed here is intended not as a static model, but as a flexible tool for guiding future research and policy design in diverse rural contexts.
Further empirical research with stakeholders should be undertaken to explore the interrelationship between space-making and place-making, the role of power dynamics, and to test the generalizability of our framework, in specific geographic locations where there are both converging and contested aspects to place to develop more depth to this work. The study has been limited to one location to date, which is a limitation and a wider application of the framework would both sense test and also refine it for wider application. The use of the socio-technical framework as an underpinning construct means that the framework can be applied at local, regional, national and international levels to identify the causal and contributory factors that impact on place-making.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M. and J.H.G.; investigation, L.M. and J.H.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M.; writing—review and editing, L.M. and J.H.G.; funding acquisition, L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
J.H. G.’s contribution to this work was funded by the Innovate UK-funded project Agri-OpenCore [grant number 10041179]. L.M.’s contribution to this work was funded by EPSRC, grant number 0007327—PBIAA—LINCAM.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No data was created in addition to this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Defra | Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs |
| EDP | Environmental Delivery Plan |
| NGO | Non Governmental Organisation |
| NRF | Nature Recovery Fund |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| UK | United Kingdom |
References
- Sonnino, R.; Marsden, T.; Moragues-Faus, A. Relationalities and convergences in food security narratives: Towards a place-based approach. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2016, 41, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L. Innovating in an Uncertain World: Understanding the Social, Technical and Systemic Barriers to Farmers Adopting New Technologies. Challenges 2024, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, W.; Bremer, S. The role of place-based narratives of change in climate risk governance. Clim. Risk Manag. 2020, 28, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester-Herber, M. Underlying concerns in land-use conflicts—The role of place-identity in risk perception. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.S.; Fynbo, L. Social Stigmatization of Pig Farmers: Medical Perspectives on Modern Pig Farming. In Risking Antimicrobial Resistance: A Collection of One-Health Studies of Antibiotics and Its Social and Health Consequences; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähdesmäki, M.; Siltaoja, M.; Luomala, H.; Puska, P.; Kurki, S. Empowered by stigma? Pioneer organic farmers’ stigma management strategies. J. Rural. Stud. 2019, 65, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.; Hamilton-Webb, A.; Little, R.; Maye, D. The ‘good farmer’: Farmer identities and the control of exotic livestock disease in England. Sociol. Rural. 2018, 58, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, J.; Pleijte, M.; Schrijver, R.; van Dam, R.; de Krom, M.; de Boer, T. Can a ‘good farmer’ be nature-inclusive? Shifting cultural norms in farming in The Netherlands. J. Rural. Stud. 2021, 88, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigors, B.; Wemelsfelder, F.; Lawrence, A.B. What symbolises a “good farmer” when it comes to farm animal welfare? J. Rural. Stud. 2023, 98, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L.; Dooley, J.J.; Dunsford, I.; Goodman, M.K.; MacMillan, T.C.; Morgans, L.C.; Rose, D.C.; Sexton, A.E. Threat or opportunity? An analysis of perceptions of cultured meat in the UK farming sector. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1277511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillo, R.S.; Robinson, R.M. Inclusive innovation in developed countries: The who, what, why, and how. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meij, E.; Haartsen, T.; Meijering, L. Enduring rural poverty: Stigma, class practices and social networks in a town in the Groninger Veenkoloniën. J. Rural. Stud. 2020, 79, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddau, F.; D’Oria, E.; Brondi, S. Coping with territorial stigma and devalued identities: How do social representations of an environmentally degraded place affect identity and agency? Sustainability 2023, 15, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selfa, T.; Marini, V.; Abrams, J. Place attachment and perceptions of land-use change: Cultural ecosystem services impacts of eucalyptus plantation expansion in Ubajay, Entre Ríos, Argentina. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Strijker, D.; Wu, Q. Place identity: How far have we come in exploring its meanings? Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yan, S.; Strijker, D.; Wu, Q.; Chen, W.; Ma, Z. The influence of place identity on perceptions of landscape change: Exploring evidence from rural land consolidation projects in Eastern China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshansky, H.M. The city and self-identity. Environ. Behav. 1978, 10, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, S.; Strange, I. (Eds.) Conceptions of Space and Place in Strategic Spatial Planning; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; pp. 7–42. [Google Scholar]
- Davoudi, S. The legacy of positivism and the emergence of interpretive tradition in spatial planning. Region. Stud. 2012, 46, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, D.; Grønning, M. Spatial consciousness. In The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopaedia of Urban and Regional Studies; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defra. (Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs) Land Use Framework for England. 2025. Available online: https://consult.defra.gov.uk/land-use-framework/land-use-consultation/supporting_documents/Land%20Use%20Consultation.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Lingham, S.; Kowalska, A.; Kowalski, J.; Maye, D.; Manning, L. The potential impact of Brexit on UK food standards and food security: Perspectives of repositioning neoliberalist policy. Foods 2025, 14, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBC (British Broadcasting Company). What on Earth Is a Yellowbelly? 2014. Available online: https://www.bbc.co.uk/lincolnshire/asop/people/what_is_a_yellowbelly.shtml (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Anton, C.E.; Lawrence, C. The relationship between place attachment, the theory of planned behaviour and residents’ response to place change. J. Environ. Psychol. 2016, 47, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayitno, G.; Rukmi, W.I.; Ashari, M.I. Assessing the social factors of place dependence and changes in land use in sustainable agriculture: Case of Pandaan District, Pasuruan Regency, Indonesia. J. Socioecon. Dev. 2021, 4, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trąbka, A. From functional bonds to place identity: Place attachment of Polish migrants living in London and Oslo. J. Environ. Psychol. 2019, 62, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R. The inherited city as a resource. In The Built Environment: Creative Enquiry into Design and Planning; Crisp: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 253–263. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/37051017/The_Built_Environment_A_Collaborative_Inquiry_Into_Design_and_Planning_2nd_Edi_3 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Williams, D.R.; Vaske, J.J. The measurement of place attachment: Validity and generalizability of a psychometric approach. For. Sci. 2003, 49, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, T.; Garkovich, L. Landscapes: The social construction of nature and the environment. Rural. Sociol. 1994, 59, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, A. “My father wasn’t really interested in machinery”: New perspectives on the modernisation of agriculture in 20th century Lincolnshire. Int. J. Reg. Local Hist. 2016, 11, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Foropon, C.; Godinho Filho, M. When titans meet–Can industry 4.0 revolutionise the environmentally-sustainable manufacturing wave? The role of critical success factors. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 132, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morella, P.; Lambán, M.P.; Royo, J.; Sánchez, J.C. Study and analysis of the implementation of 4.0 technologies in the agri-food supply chain: A state of the art. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Kiyokawa, T.; Ricardez, G.A.G.; Ramirez-Alpizar, I.G.; Venture, G.; Yamanobe, N. Evaluating quality in human-robot interaction: A systematic search and classification of performance and human-centered factors, measures and metrics towards an industry 5.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 63, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas-Oliver, J.L.; Estelles-Miguel, S.; Mallol-Gasch, G.; Boix-Palomero, J. A place-based policy for promoting Industry 4.0: The case of the Castellon ceramic tile district. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2019, 27, 1838–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panori, A.; Kakderi, C.; Komninos, N.; Fellnhofer, K.; Reid, A.; Mora, L. Smart systems of innovation for smart places: Challenges in deploying digital platforms for co-creation and data-intelligence. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RPG (Rural Policy Group). The Sustainable Food Report 2022. Available online: https://ruralpolicygroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/RPG-Sustainable-Food-Report-2023.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Kowalska, A.; Manning, L. Using the rapid alert system for food and feed: Potential benefits and problems on data interpretation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Khatooni, M. Saturation in qualitative research: An evolutionary concept analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. Adv. 2024, 6, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusar Poli, E.; Fontefrancesco, M.F. Trends in the implementation of biopesticides in the Euro-Mediterranean region: A narrative literary review. Sustain. Earth Rev. 2024, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Applications of Case Study Research; SAGE Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cash-Gibson, L.; Martinez-Herrera, E.; Escrig-Pinol, A.; Benach, J. Why and how Barcelona has become a health inequalities research hub? A realist explanatory case study. J. Crit. Realism 2023, 22, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincher, R.; Pardy, M.; Shaw, K. Place-making or place-masking? The everyday political economy of “making place”. Plan. Theory Pract. 2016, 17, 516–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, B.; Markey, S. Place-Based Policy: A Rural Perspective. Community Research Connexions. Funded by Human Resources and Social Development Canada. 2008. Available online: https://billreimer.net/research/files/ReimerMarkeyRuralPlaceBasedPolicySummaryPaper20081107.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Barca, F.; McCann, P.; Rodríguez-Pose, A. The case for regional development intervention: Place-based versus place-neutral approaches. J. Reg. Sci. 2012, 52, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Gregory, J.; Kline, P. Assessing the incidence and efficiency of a prominent place based policy. Am. Econ. Rev. 2013, 103, 897–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumark, D.; Simpson, H. Place-based policies. In Handbook of Regional and Urban Economics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 1197–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepac, B.; Mowle, A.; Riley, T.; Craike, M. Government, governance, and place-based approaches: Lessons from and for public policy. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2023, 21, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.B.; Oberg, A.; Nelson, L. Rural gentrification and linked migration in the United States. J. Rural. Stud. 2010, 26, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M. Rural gentrification and the processes of class colonization. J. Rural. Stud. 1993, 9, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Smith, D.; Brooking, H.; Duer, M. Re-placing displacement in gentrification studies: Temporality and multidimensionality in rural gentrification displacement. Geoforum 2021, 118, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korir, L.; Drake, A.; Collison, M.; Camacho Villa, C.; Sklar, E.; Pearson, S.; Manning, L. Investing in technology to address labour shortages in UK fresh produce and horticulture: How does this redefine standards of good agricultural practice? Local Econ. 2024, 29, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.C.; Wheeler, R.; Winter, M.; Lobley, M.; Chivers, C.A. Agriculture 4.0: Making it work for people, production, and the planet. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dono, G.; Cortignani, R.; Dell’Unto, D.; Deligios, P.; Doro, L.; Lacetera, N.; Mula, L.; Pasqui, M.; Quaresima, S.; Vitali, A.; et al. Winners and losers from climate change in agriculture: Insights from a case study in the Mediterranean basin. Agric. Syst. 2016, 147, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L.; Brewer, S.; Craigon, P.J.; Frey, J.; Gutierrez, A.; Jacobs, N.; Kanza, S.; Munday, S.; Sacks, J.; Pearson, S. Reflexive governance architectures: Considering the ethical implications of autonomous technology adoption in food supply chains. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Guardian. Campaigners Get Go-Ahead to Challenge Plans for Oilfield in Lincolnshire Wolds. 4 March 2024. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/mar/04/campaigners-get-go-ahead-to-challenge-plans-for-oilfiield-in-lincolnshire-wolds (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- The Times. Solar Power Developers Held Up by Search for Buried Relics. 12 February 2025. Available online: https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/solar-power-developers-held-up-by-search-for-buried-relics-sxzfnt9lj (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Smithers, R. Lincolnshire’s US-Style ‘Mega’ Dairy Farm on Hold as Plans Are Withdrawn. The Guardian, 16 February 2011. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2011/feb/16/lincolnshire-mega-dairy-farm-plans-withdrawn (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Planning Inspectorate. Appeal Decision: Winterton Solar Farm. January 2023. Available online: https://www.shropshire.gov.uk/media/27497/cd-722-winterton-solar-decision.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Klerkx, L.; Jakku, E.; Labarthe, P. A review of social science on digital agriculture, smart farming and agriculture 4.0: New contributions and a future research agenda. NJAS-Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2019, 90, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, P.; Mulvaney, D. The political economy of the ‘just transition’. Geogr. J. 2013, 179, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Chang, W.Y. Place Attachment, Self-Efficacy, and Farmers’ Farmland Quality Protection Behavior: Evidence from China. Land 2023, 12, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddis, P.; Roelich, K.; Tran, K.; Carver, S.; Dallimer, M.; Ziv, G. What shapes community acceptance of large-scale solar farms? A case study of the UK’s first ‘nationally significant’ solar farm. Sol. Energy 2020, 209, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greater Lincolnshire Local Enterprise. Agri-Food Sector. 2025. Available online: https://www.greaterlincolnshirelep.co.uk/priorities-and-plans/sectors/agri-food-sector/ (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Greater Lincolnshire Local Enterprise Partnership. Agri-Food Sector Plan. 2017. Available online: https://www.greaterlincolnshirelep.co.uk/assets/documents/8012_GL_LEP_2017_Agri_Food_Plan_2017_WEB.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- UK Food Valley. 2025. Available online: https://www.greaterlincolnshirelep.co.uk/funding-and-projects/uk-food-valley/ (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Official Statistics—Total Income from Farming in the East Midlands. Updated 30 October 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/total-income-from-farming-for-the-regions-of-england/total-income-from-farming-in-the-east-midlands (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Agriculture Across Lincolnshire. 2022. Available online: https://lincolnshire.moderngov.co.uk/documents/s57979/Appendix%20B%20-%20Agriculture%20Across%20Lincolnshire-%20Evidence%20Considered.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- De Roest, K.; Ferrari, P.; Knickel, K. Specialisation and economies of scale or diversification and economies of scope? Assessing different agricultural development pathways. J. Rural. Stud. 2018, 59, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- His Majesty’s Government. Guide to the Planning and Infrastructure Bill. 2025. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-planning-and-infrastructure-bill/guide-to-the-planning-and-infrastructure-bill (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- His Majesty’s Government. Factsheet: Strategic Planning. 2025. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-planning-and-infrastructure-bill/factsheet-strategic-planning (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Planning and Infrastructure Bill. Available online: https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/bills/cbill/59-01/0250/240250.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- His Majesty’s Government. Factsheet: Nature Restoration Fund. 2025. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-planning-and-infrastructure-bill/factsheet-nature-restoration-fund (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- OECD. Policy Guidance: Enabling Inclusive Governance; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Partnership for Education. Paving Pathways for Inclusion: 3 Levers Countries Can Use to Include Refugees in Education Systems. 2024. Available online: https://www.globalpartnership.org/blog/paving-pathways-inclusion-3-levers-countries-can-use-include-refugees-education-systems (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Schot, J.; Steinmueller, W.E. Three frames for innovation policy: R&D, systems of innovation and transformative change. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W. The multi-level perspective on sustainability transitions: Responses to seven criticisms. Environ. Innov. Soc. Trans. 2011, 1, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W. From sectoral systems of innovation to socio-technical systems: Insights about dynamics and change from sociology and institutional theory. Res. Policy 2004, 33, 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Waterson, P. ‘When Food Kills’: A socio-technical systems analysis of the UK Pennington 1996 and 2005 E. coli O157 Outbreak reports. Saf. Sci. 2016, 86, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedung, I.; Rasmussen, J. Graphic representation of accident scenarios: Mapping system structure and the causation of accidents. Saf. Sci. 2002, 40, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungai, P.; Jimenez, A.; Kleine, D.; Van Belle, J.P. The role of the marginalized and unusual suspects in the production of digital innovations: Models of innovation in an African context. In International Development Informatics Association Conference; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar]
- Chataway, J.; Hanlin, R.; Kaplinsky, R. Inclusive innovation: An architecture for policy development. Innov. Dev. 2014, 4, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W.; Sovacool, B.K.; Schwanen, T.; Sorrell, S. Sociotechnical transitions for deep decarbonization. Science 2017, 357, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henfridsson, O.; Nandhakumar, J.; Scarbrough, H.; Panourgias, N. Recombination in the open-ended value landscape of digital innovation. Inf. Organ. 2018, 28, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.; Krombacher, A.; Röglinger, M.; Körner-Wyrtki, K. Doing good by going digital: A taxonomy of digital social innovation in the context of incumbents. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2023, 32, 101806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exciting New Phase for Ceres Agri-Tech. Available online: https://www.ceresagritech.org/about/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Powell, J.M.; Shibeika, A. Brexit and beyond: Addressing skills shortage in the UK construction industry. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Manag. Procure. Law 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, G.; Jones, M. Renewing the Geography of Regions. Environ. Plan. D Soc. Space 2001, 9, 669–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, G.; Jones, M. Territorial, scalar, networked, connected: In what sense a ‘regional world’? Reg. Stud. 2007, 41, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).