Abstract
During the extraction and utilization of coal resources, a large amount of CO2 and coal-based solid wastes (CBSW), such as coal gangue, are generated. To reduce the carbon and waste emissions, an effective approach is to mineralize the CO2 with the CBSW and then backfill the mineralized materials into the goaf area. However, efficient CO2 mineralization is challenging due to the low reactivity of coal gangue. To this end, mechanical activation was used for the modification of coal gangue, and the mechanical activation mechanism of coal gangue was revealed from a microcosmic perspective by dry powder laser particle size testing (DPLPST), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) analysis, Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that compared with the unground coal gangue, the average particle size of coal gangue after 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h milling decreases by 94.3%, 95%, and 95.3%, respectively; additionally, the amorphous structures of the coal gangue after milling increase, and their edges and corners gradually diminish. After the pressure mineralization of coal gangues with different activation times, thermogravimetric (TG) analysis was performed, and the CO2 mineralization effect of the mechanically activated coal gangue was explored. It is found that the carbon fixation capacity of the coal gangue after 0.5 h, 1.0 h, and 1.5 h mechanical activation is increased by 1.18%, 3.20%, and 7.57%, respectively. Through the XRD and SEM, the mechanism of CO2 mineralization in coal gangue was revealed from a microcosmic perspective as follows: during the mineralization process, alkali metal ions of calcium and magnesium in anorthite and muscovite are leached and participate in the mineralization reaction, resulting in the formation of stable carbonates such as calcium carbonate.
1. Introduction
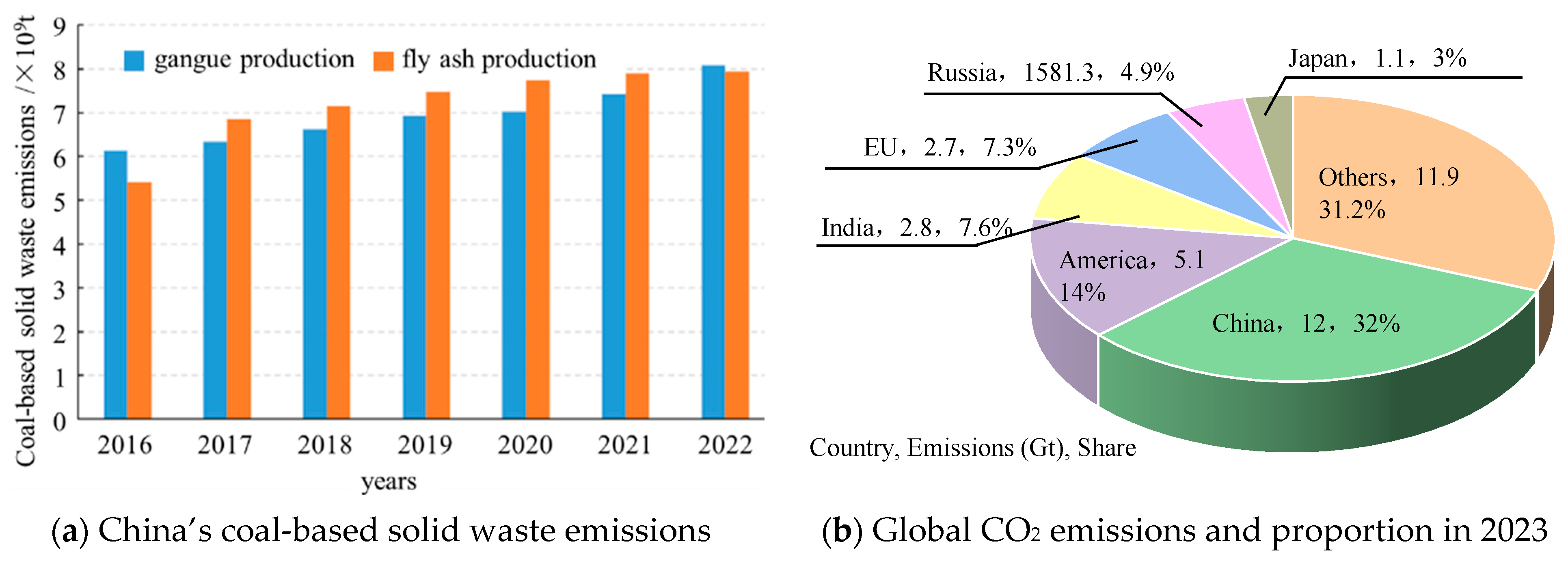
The resource endowment of China is characterized by abundant coal reserves, limited oil resources, and a scarcity of natural gas. Notably, coal occupies an unequivocal dominance in China’s primary energy structure. In 2022, China’s coal production reached 4.50 billion tons, with an increase of 9.0% over the previous year, and this positive trend is expected to persist in the next few years. Solid wastes and waste gas are produced during the production and utilization of coal resources. In recent years, the environmental pollution and land occupation caused by the massive accumulation of coal-based solid waste such as coal gangue and fly ash have become increasingly prominent [1,2]. In 2021, China’s comprehensive utilization rate of coal gangue and fly ash reached 73% [3], while the emissions of coal-based solid waste still exceeded 1 billion tons. It is estimated that there will still be 300 to 500 million tons of coal gangue in 2050. Meanwhile, coal-fired power plants also produce large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), and it was recorded that in 2006, China overtook the United States as the leading emitter of CO2 globally, becoming the largest contributor to CO2 emissions worldwide. In 2023, the amount of global CO2 emissions reached 36.8 Gt, of which China’s CO2 emission was about 12 Gt, accounting for 32% of the world’s emissions(Figure 1). There is an increasing challenge in the disposal of coal-based solid waste as well as CO2 storage and utilization. Therefore, how to manage bulk solid wastes and CO2 simultaneously is of great importance in the sustainable development of the coal mining industry.
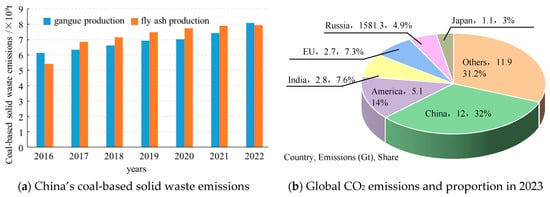
Figure 1.
Statistics on China’s coal-based solid waste emissions and global CO2 emissions.
Carbon capture and storage are considered the most effective means of reducing carbon emissions [4,5,6]. Among them, mineral carbonation of CO2 has the advantages of high CO2 adsorption capacity, high recovery rate, and low environmental risk. The basic principle is to permanently sequester CO2 in the form of stable carbonate minerals through the mineralization of alkaline minerals [7,8]. For example, given the high content of calcium and alkaline substances in magnesium, many studies have been carried out on CO2 mineralization capture using magnesium slag as raw material [9,10]. Coal-based solid waste materials, such as gangue, are difficult to react with other substances due to their tight structure, high lattice energy, and stable physical and chemical properties. Most of the gangue is directly used as inert backfilling aggregate, which limits the further improvement of the utilization rate of the gangue. To effectively improve the mineralization efficiency of gangue, physical and chemical modification is required to increase the content of active SiO2 and Al2O3 in the gangue to improve its activity.
Currently, the common activation methods include mechanical activation, thermal activation, chemical activation, and composite activation. Mechanical activation refers to the introduction and accumulation of mechanical energy through different mechanical forces, such as milling, compression, impact, friction, and shearing. Subsequently, the physical and chemical properties and structure of substances can be changed. Correspondingly, the reaction activity is improved. Thermal activation is usually used to change the material components in the substances through high-temperature calcination. For example, dolomite in the copper tailings can be decomposed to generate alumina and silicon oxide with a certain activity, thus improving the activity of copper tailings. In contrast, the modification of the crystal structure and surface properties by introducing chemical agents (e.g., activators, additives) is known as chemical activation. Obviously, the combination of two or more aforementioned activation approaches is composite activation. The pros and cons of the four activation methods are compared in Table 1 [11,12,13]. Considering the simplicity of the activation processes, mechanical activation is adopted in this study to increase the reactivity of the coal gangue. Yang et al. [14] studied the mechanical activation mechanism of sulfide ores. Li et al. [15] probed into the effects of mechanical activation on the physicochemical properties of leach residue in zinc calcine and the dissolution kinetics in sulfuric acid solution. Zhao et al. [16] investigated the effects of mechanical activation on particle size parameters, microstructure, and leaching performance of chalcopyrite and explored the occurrence and transformation of agglomeration and aggregation during the activation process. Although there are many studies on the activation of solid waste, the mechanism of the mechanical activation of gangue needs further investigation.

Table 1.
Advantages and disadvantages of different activation methods.
Currently, the main applications of activated gangue are the extraction of aluminum and iron [17] and the preparation of cementitious supplementary materials [18] and coal gangue-based geopolymers [19]. However, there are fewer studies on the mineralization of activated gangue. Zhang et al. [20] investigated the carbon sequestration performance of unactivated gangue under different mineralization conditions and found that the maximum amount of CO2 adsorbed was only 9.57 g/kg. Huo et al. [21,22] investigated the CO2 capture capacity of acid and alkali-modified gangue and found that the gangue captured 0.30 mmol/g CO2 when the addition of acetic acid was 2 wt%. In addition, Ma et al. [23] studied the performance of coal-based solid waste after CO2 mineralization by adding alkali activators. It was also found that the CO2 absorption amount decreases with the increase in fly ash content. Guo [24] et al. explored the mineralization properties of coal gangue-based solid waste with different mixing ratios. The results show that the water–cement ratio is the main factor in determining the amount of captured CO2. Chen et al. [25] studied the curing conditions of cemented-paste backfill (CPB) with different cement concentrations at a CO2 concentration of 1.5%. It is concluded that when the cement concentration is 15%, each ton of CPB can ideally absorb about 78.4 kg CO2. Through the BET theory, Johannesson et al. [26] measured the adsorption of water vapor by non-carbonized and well-carbonized cement mortars and evaluated the difference in specific surface area of the two samples. The results suggest that the specific surface area of the non-carbonized sample is 8% higher than that of the well-carbonized sample, and the small pore volume of well-carbonized cement mortar is approximately twice that of uncarbonized cement mortar.
Given the limited understanding of the mechanism of the mechanical activation of gangue and the corresponding mineralization ability of the mechanical-activated coal gangue (MACG), this research first investigates the effect of grinding time on the activation effect of coal gangue. Thereafter, the mineralization ability of the MACG with different grinding times is compared. The findings are of great importance in guiding the implementation of backfilling of the CO2-mineralized MACG in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
The washed gangue taken from a certain coal mine was used in this test. The gangue sample was crushed and sieved to obtain the fine powder with a particle size of less than 1 mm for mechanical activation. To analyze the mineralization effect of the gangue under different activation conditions, pressure mineralization of gangue after mechanical activation was carried out.
After the gangue was ground to less than 200 mesh, the chemical composition of the gangue was analyzed by an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF, Panalytical Axios, Alkmaar, The Netherlands). The analytical element range was 4Be–92U, and the quantitative element range was ppm–100%. The chemical composition and content of the coal gangue measured are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical composition and content of gangue.
2.2. Experimental Methods and Plans
2.2.1. Mechanical Activation and Schemes
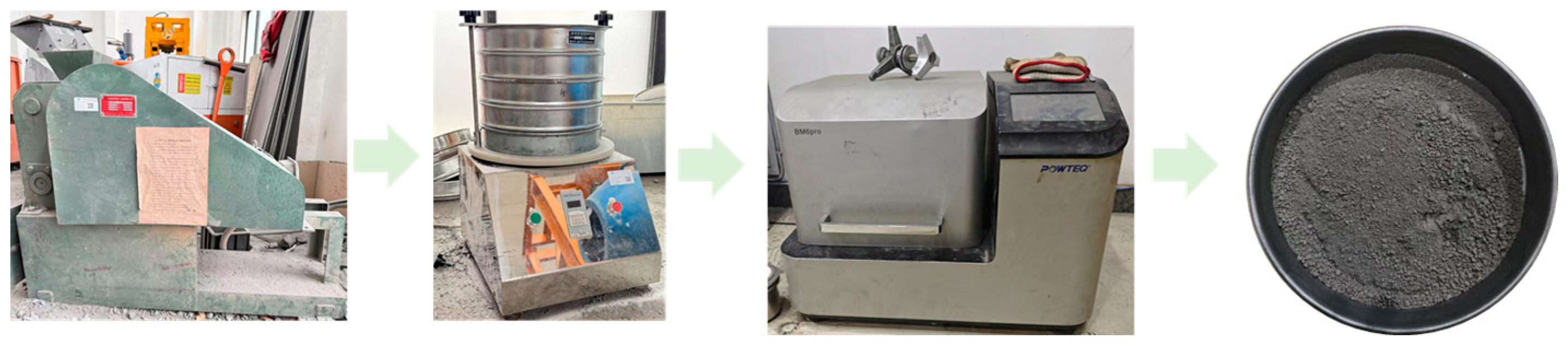
During the mechanical activation, a ball mill was used to study the impact of ball milling time on gangue particle size distribution, mineral components, chemical groups, and microstructure, thereby revealing the impact mechanism of different ball milling times on gangue activation. Before ball milling, the gangue was crushed and pre-treated. Specifically, large pieces of gangue were crushed through a jaw crusher, and the broken gangue was screened using a vibrating screen; then, gangue below 1 mm was ground by a ball mill. Figure 2 shows the specific process of mechanical activation.

Figure 2.
Mechanical activation process.
To analyze the impact of ball milling time on the mechanical activation effect, experimental settings were as follows: the milling time was 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h; the rotation speed of the ball mill was 400 r/min; zirconia was selected as the ball milling medium; the ball-to-material ratio was 3:1; and the milling speed was 400 r/min. The mass of the milling ball was 300 g, and for the ratio of milling balls with a large diameter (4 mm), a medium diameter (2 mm), and a small diameter (1 mm), the gradation was 3:3:4. During the experiment, the machine was stopped for cooling for 20 min every 0.5 h of milling to prevent the heat generated by milling from increasing the temperature in the milling jar. The ground samples were packaged for subsequent testing and characterization.
2.2.2. CO2 Mineralization Process and Plan for Mechanically Activated Gangue
During the mineralization of mechanically activated gangue, the coal gangue with different activation times was put into the reaction kettle of the CO2 mineralization testing platform for coal-based solid wastes. Through microscopic experiments, the mineralization mechanism of activated gangue was explored, the CO2 mineralization effect of gangue with different activation degrees was characterized, and the activation effect of gangue with different activation times was verified.
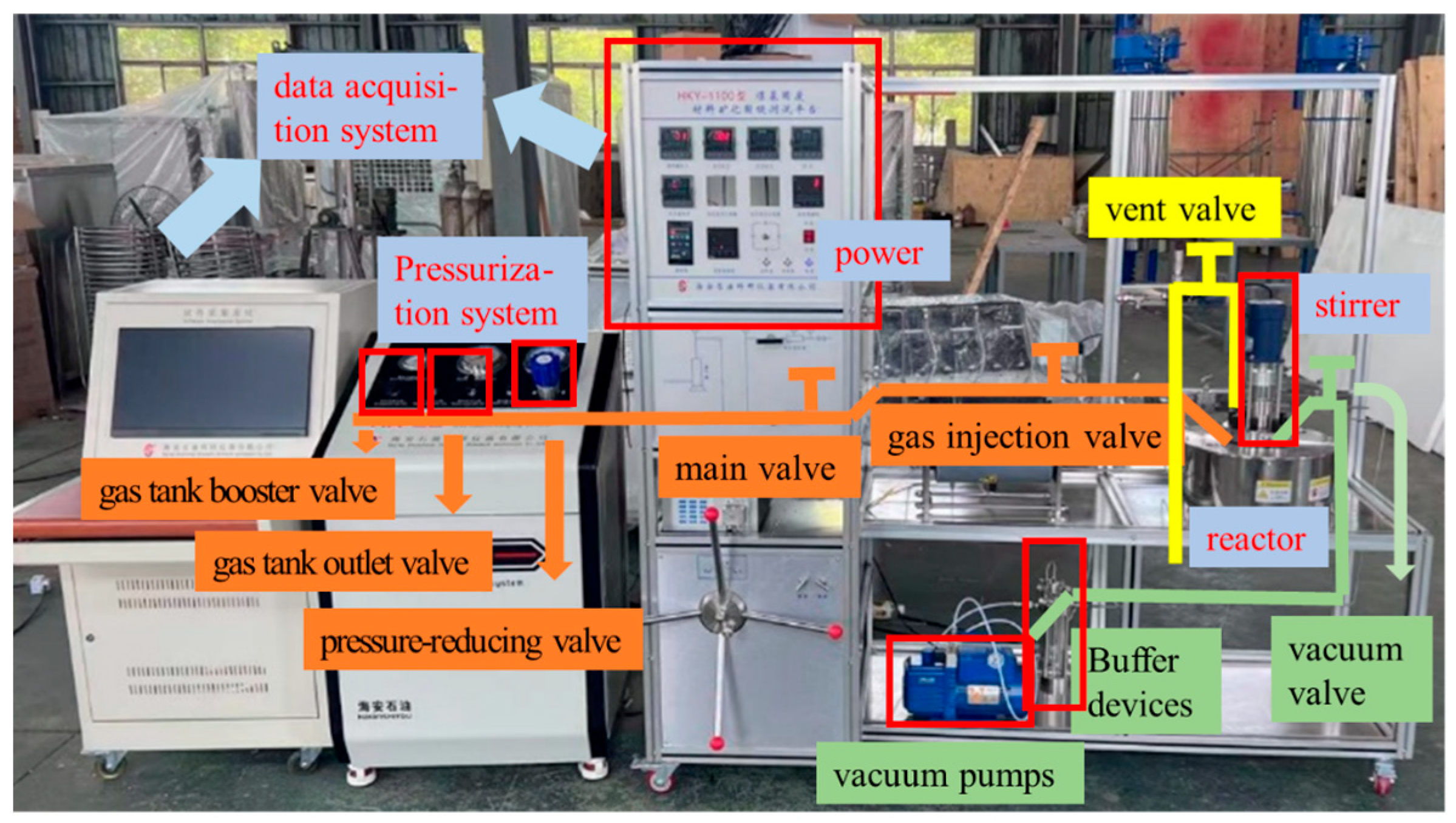
Figure 3 shows the CO2 mineralization testing platform for coal-based solid wastes, which is composed of a data acquisition system; a pressurization system; a reactor; a stirrer; and injection, vacuum, and venting pipelines. The data acquisition system can generate a CO2 injection curve in real time. The pressurization system can increase the tank pressure to more than 50 MPa. The internal volume of the reactor was 1.1 L. By manipulating valves, CO2 mineralization simulation was realized within a temperature range of 20 °C to +500 °C and within 50 MPa.
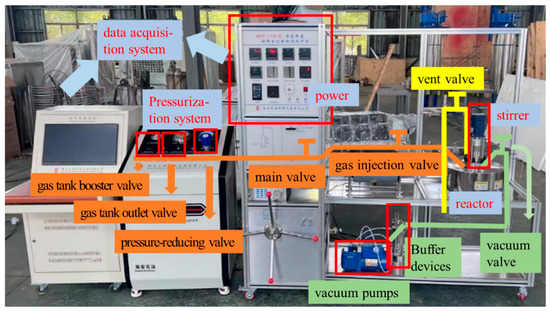
Figure 3.
CO2 mineralization testing platform for coal-based solid wastes.
Before the mineralization, the power of the data acquisition system was initiated, and the gas tank booster valve and the gas tank outlet valve were adjusted to increase the tank pressure to 20 MPa for backup. Subsequently, 268 g of water and 400 g of activated gangue powder were weighed by an electronic scale and poured into the reaction kettle; the hexagonal screws on the reaction kettle diagonally were tightened; and the injection, vacuum, and vent pipes were connected to the reaction kettle. After that, the main valve and the gas injection valve were opened, the pressure-reducing valve was adjusted to increase the pressure of the reaction kettle to 6 MPa, the mixer speed was set as 600 r/min, and the mineralization of 30 min was carried out. After mineralization was completed, the pressure-reducing valve, main valve, and air injection valve were closed in sequence, the vent valve was opened, and the pressure in the kettle was reduced to 0.1 MPa. All pipes were disconnected, the reactor was opened, and the mineralized slurry was dug out for use.
The mineralized gangue slurry was placed in a blast drying box, the temperature was set to 60 °C, and the mineralized gangue powder that had evaporated moisture was put into a sealed bag for later use.
2.3. Microscopic Analysis
The gangue activation mechanism and effect were characterized by analyzing the particle size, mineral composition, chemical groups, and microstructure of gangue powder at different activation times. The mineral composition, microstructure, and thermogravimetric (TG) analysis of mineralized gangue powder with different activation effects were carried out to explore the effect of activation on mineralization.
(1) DPLPST. After mechanical activation, the gangue particle size decreased significantly. The gangue powder was dried in a drying oven for 6 h, and then the gangue particle size was tested using the DPLPST (Jinan Micro-Nano Particle Instrument Co., Ltd., Winner 3009, Jinan, China). The particle size distribution of the mechanically activated gangue is evaluated with two indexes, namely uneven coefficient Cu and curvature coefficient Cc:
where D10 is the size of 10% of the sieved weight, known as the effective size; D30 is the size of 30% of the sieved weight; and D60 is the size of 60% of the sieved weight, known as the limiting or restricted size.
(2) XRD analysis. The gangue powder below 200 mesh was taken, and the degree of lattice amorphousness in the gangue material at different activation times was tested by XRD (Rigaku Company, Tokyo, Japan) to characterize the gangue activation degree and mineralization effect.
(3) FTIR analysis. FTIR (Bruker Company, Saarbrücken, Germany) was used to detect and analyze the vibration changes of the characteristic groups of mechanically activated gangue, and the activity of each substance in the gangue was determined by the vibration intensity of the characteristic groups.
(4) SEM analysis. To qualitatively analyze the degree of activation and mineralization effect, the grain size, morphology, and dispersion state of the gangue particle images before and after activation and before and after mineralization were compared by SEM (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA).
(5) TG analysis. TG (Netzsch Company, Selb, Germany) was used to analyze the carbonate loss on ignition in mineralized gangue under different activation times. Additionally, the carbonate loss on ignition in the gangue before and after mineralization was compared to explore the influence of activation time on the mineralization effect.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Activation Mechanism and Effect
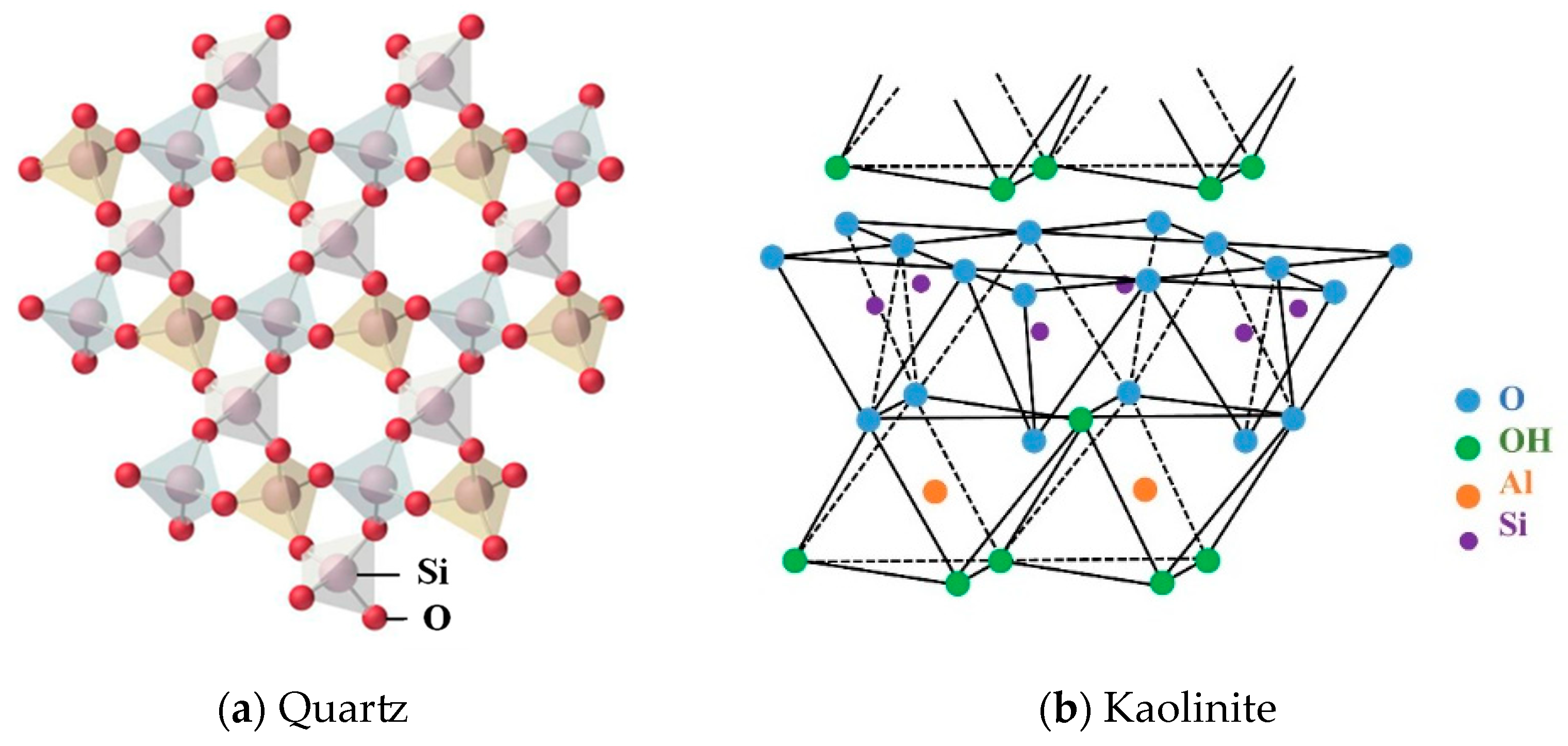
The main minerals of the gangue used in this study are quartz and kaolinite. Figure 4 shows their crystal structures. It can be seen that the composition of quartz is SiO2. The Si-O tetrahedrons in the crystal structure are connected by covalent bonds, resulting in a stable structure, a hard texture, and high wear resistance. Kaolinite is a typical 1:1 type lamellar aluminosilicate clay mineral with a theoretical structure of Al4[Si4O10](OH)8 and a crystal structure consisting of a cyclic arrangement of Si-O tetrahedron and a “hydroxauxite” octahedron (A1-O octahedron). The monocrystalline layer has a two-sided structure: one side is an -OH layer, and the other is an O-layer; the two layers are connected by hydrogen bonds with a weak stability. Research shows that kaolinite is prone to crystal layer slippage, curling, and failure under the condition of mechanical milling.
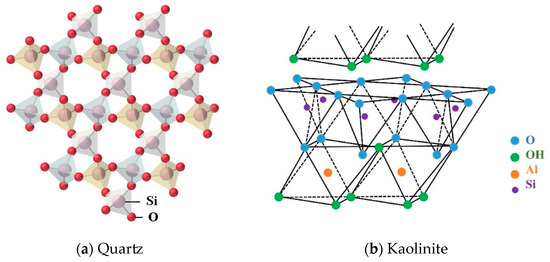
Figure 4.
Schematic of the crystal structure of quartz and kaolinite.
3.1.1. Particle Size of Mechanically Activated Gangue
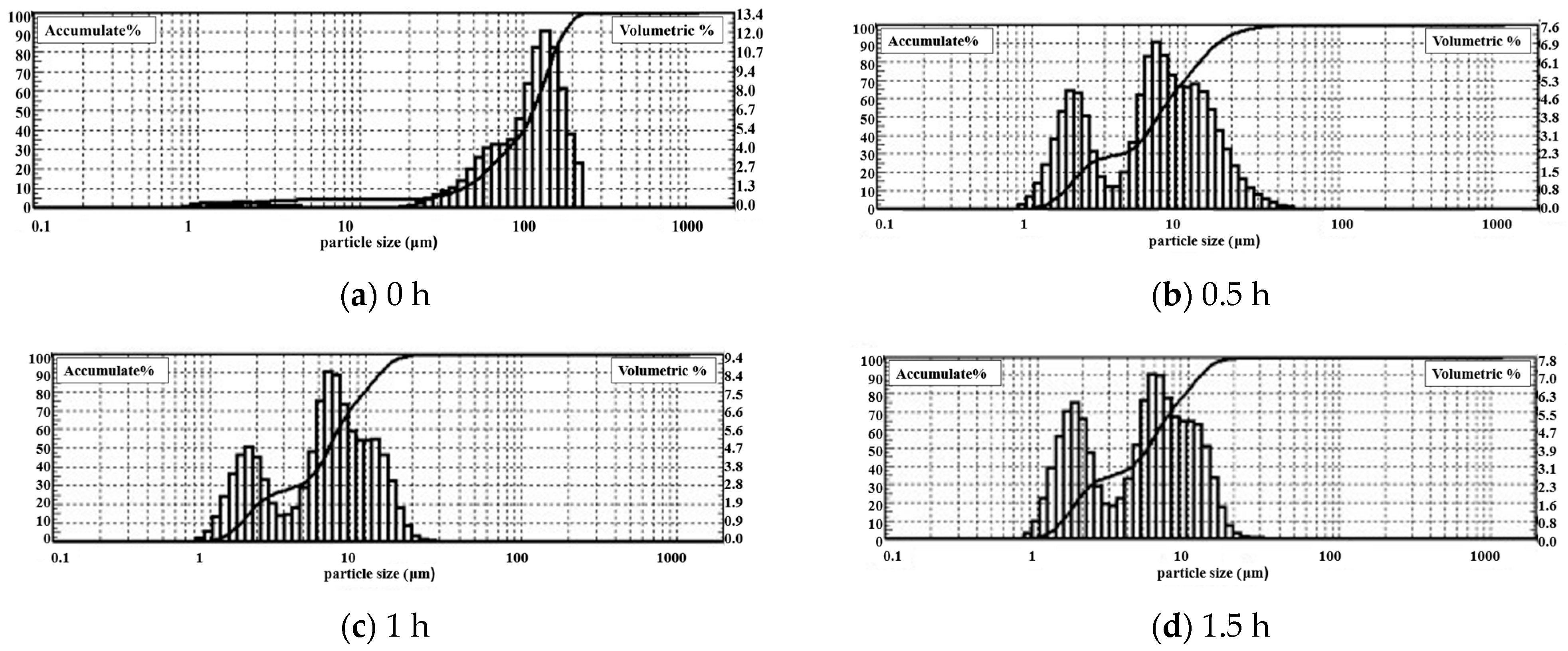
The DPLPST was performed on the gangue that was mechanically activated for 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h. Figure 5 shows the cumulative particle size curve obtained by software analysis. Table 3 shows the specific particle size distribution and gradation analysis.
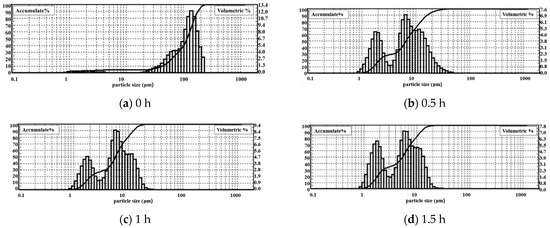
Figure 5.
Cumulative curve of coal gangue particle size at different milling times.

Table 3.
Particle size distribution and gradation of mechanically activated coal gangue.
As shown in Table 3, the average particle size and D90 of the gangue decrease rapidly under the action of mechanical force. After 0.5 h milling, the average particle size of the gangue drops from 115.6 μm to 6.6 μm, and 90% of the gangue particle size is less than 16.3 μm. When the milling time is extended to 1 h and 1.5 h, the average particle size decreases to 5.8 μm and 5.4 μm, and 90% of the gangue particle sizes reduce to about 12 μm. Compared with unground gangue, the average particle size of coal gangue after milling for 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h decreases by 94.3%, 95%, and 95.3%, respectively, and D90 decreases by 90.9%, 93%, and 93.2%, respectively. This indicates that the mechanical milling effect is significant. After 0.5 h milling, the gangue particle size is reduced by at least 90%. It can be found that as the milling time increases, the particle size continues to decrease, but the decreasing magnitude gradually declines.
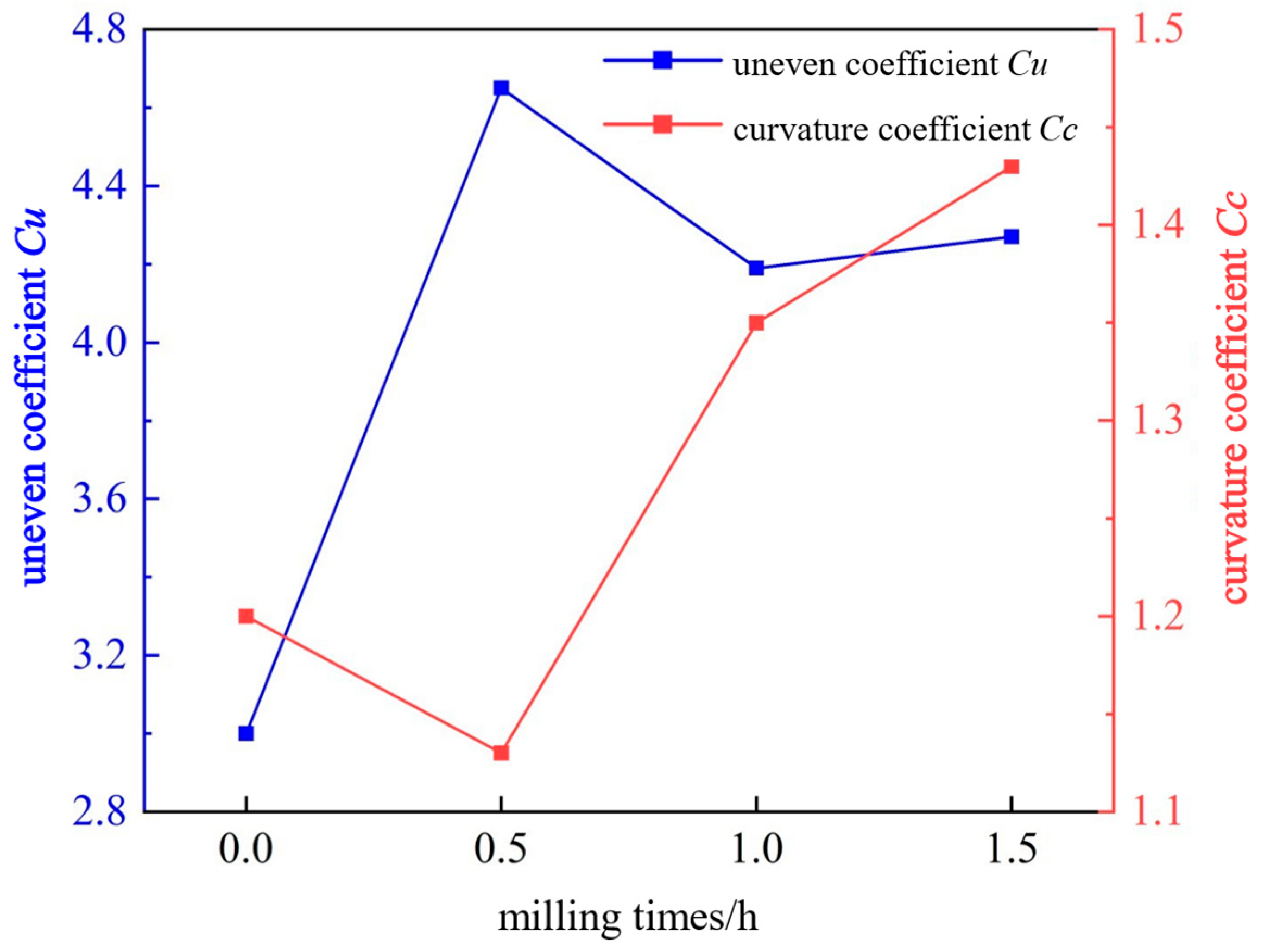
The uneven coefficient Cu and curvature coefficient Cc of the particles were further calculated through the particle size distribution, the particle gradation of the gangue was analyzed, and the change trend diagram of the uneven coefficient Cu and the curvature coefficient Cc under different milling times was drawn, as shown in Figure 6.
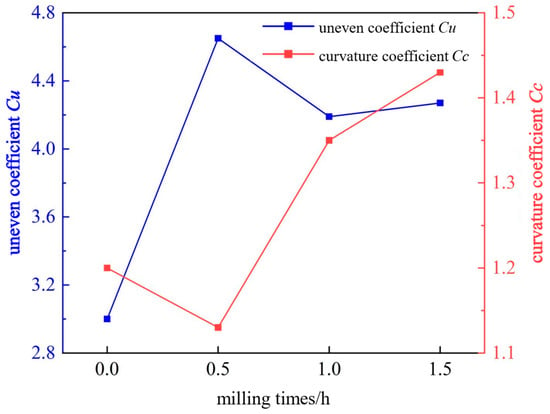
Figure 6.
Change curve of gangue particle gradation at different milling times.
As shown in Figure 6, after milling gangue for 0 to 1.5 h, the uneven coefficient Cu first increases and then decreases, with a value of 3–4.65. This indicates that the ground particles are extremely even, and the particle size distribution is relatively uniform. The curvature coefficient Cc first decreases and then increases, with values ranging from 1.2 to 1.43. This indicates that the gangue particles are relatively complete and continuous within their particle size distribution range. Referring to the analysis indicators, the coal gangue is of poor gradation after milling for 0–1.5 h.
The turning points of the curves all appear at 0.5 h. This is because coal gangue is an easy-to-grind material. When the milling time is short, the particles are first broken into irregular fine particles, resulting in a larger particle size difference and the dispersed particle size distribution. As a result, the uneven coefficient Cu increases, and the curvature coefficient Cc decreases. After milling for 1–1.5 h, the edges and corners of the particles are gradually smoothed and further refined, resulting in smaller particle size differences and more uniform particle size distribution. Consequently, the uneven coefficient Cu decreases, and the curvature coefficient Cc increases.
3.1.2. Mineral Composition of Mechanically Activated Gangue
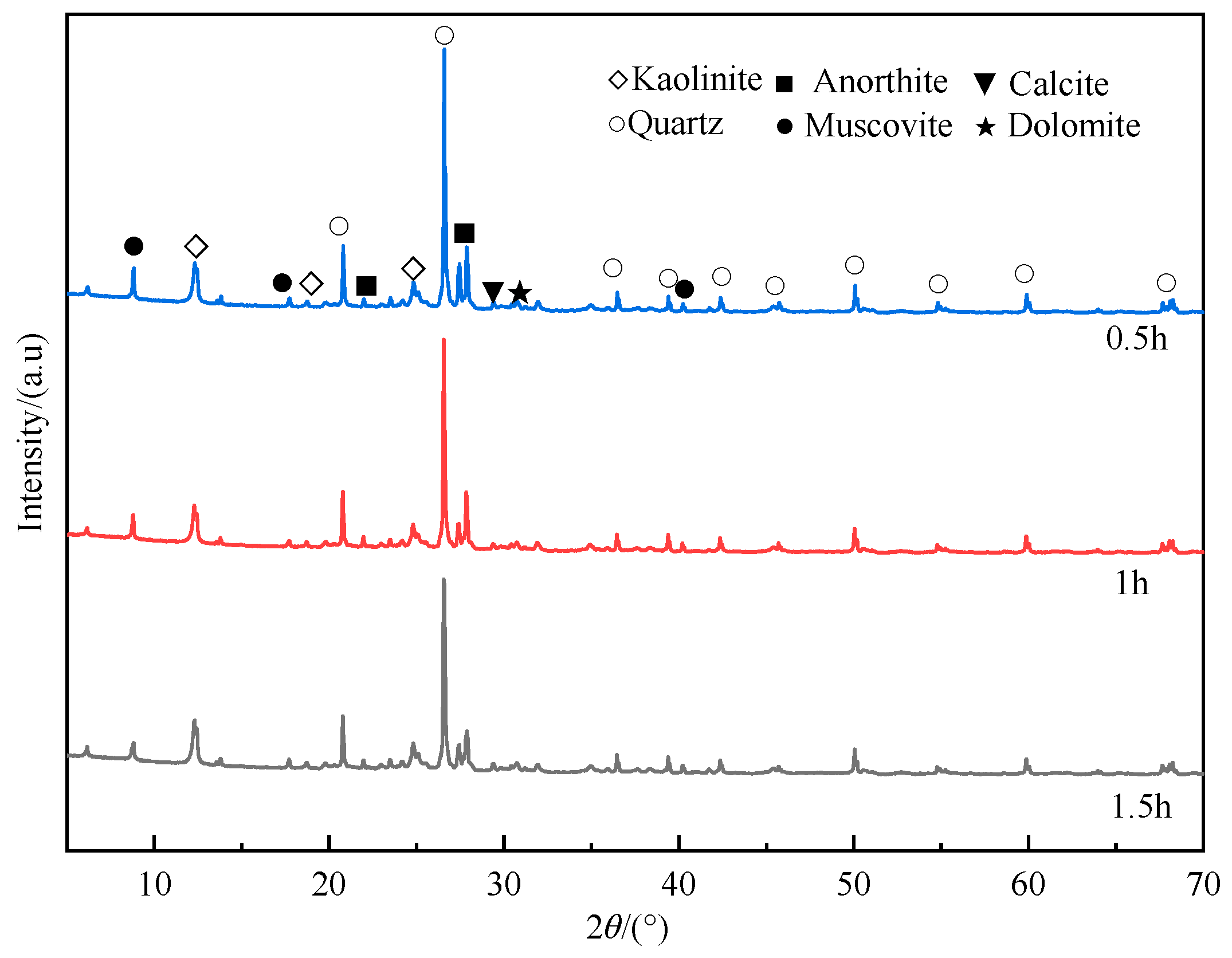
During the mechanical activation process, the mineral components of gangue undergo transformations in the mineral structure and crystal form under the action of mechanical force. XRD was used to detect the mineral composition of coal gangue after mechanical milling for 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h. Figure 7 shows the diffraction patterns of mechanically activated gangue.
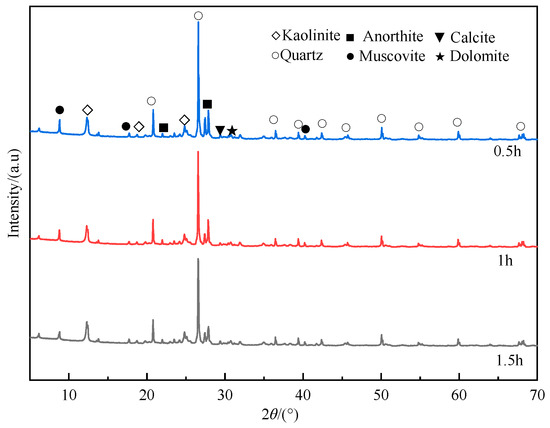
Figure 7.
XRD spectra of coal gangue at different milling times.
As shown in Figure 7, as the milling time increases, the diffraction peak at 26.56° decreases significantly. It suggests that the prolonged milling leads to a gradual decrease in the crystallization level of quartz, eventually resulting in its transformation into an amorphous state. The diffraction peak intensity of kaolinite at 12.30° and 24.80° slightly decreases as the milling time increases. The crystal structure and crystal layered structure of kaolinite are destroyed, the crystal lattice is defective and distorted, and kaolinite is gradually decomposed, causing the reduced diffraction peak of kaolinite. Additionally, the broadening of the diffraction peak occurs, indicating that the crystal integrity and symmetry are destroyed. The above phenomenon shows that under the action of mechanical force, the ordered structure of kaolinite in gangue is continuously disintegrated, and the structure gradually becomes disordered and transforms into an amorphous form. Muscovite, anorthite, calcite, and dolomite are calcium-containing minerals in the gangue. The intensity of their diffraction peaks at 8.78°, 27.84°, and 29.38° gradually weakens, indicating that the crystal structures of muscovite, anorthite, and calcite have been destroyed, and large crystals have disintegrated into small crystals. The destruction of these structures causes more calcium-containing crystal faces to be exposed, allowing them to bind CO2 more easily.
It can be found that during the high-speed ball milling process of gangue, the mineral composition and structure of the gangue are changed under mechanical action. As the milling time prolongs, some mineral phases are destroyed under the action of mechanical force and gradually disappear, such as kaolinite, muscovite, calcite, and other minerals. Additionally, there are also some minerals with stable structures. Under the action of mechanical force, some minerals with stable structures (such as quartz and other minerals) gradually have defects and distortions in crystal structure under the action of mechanical forces, showing an amorphous shape. It should be noted that the transformation of the amorphous state of quartz and kaolinite can effectively improve the activity of coal gangue.
3.1.3. Chemical Groups of Mechanically Activated Gangue
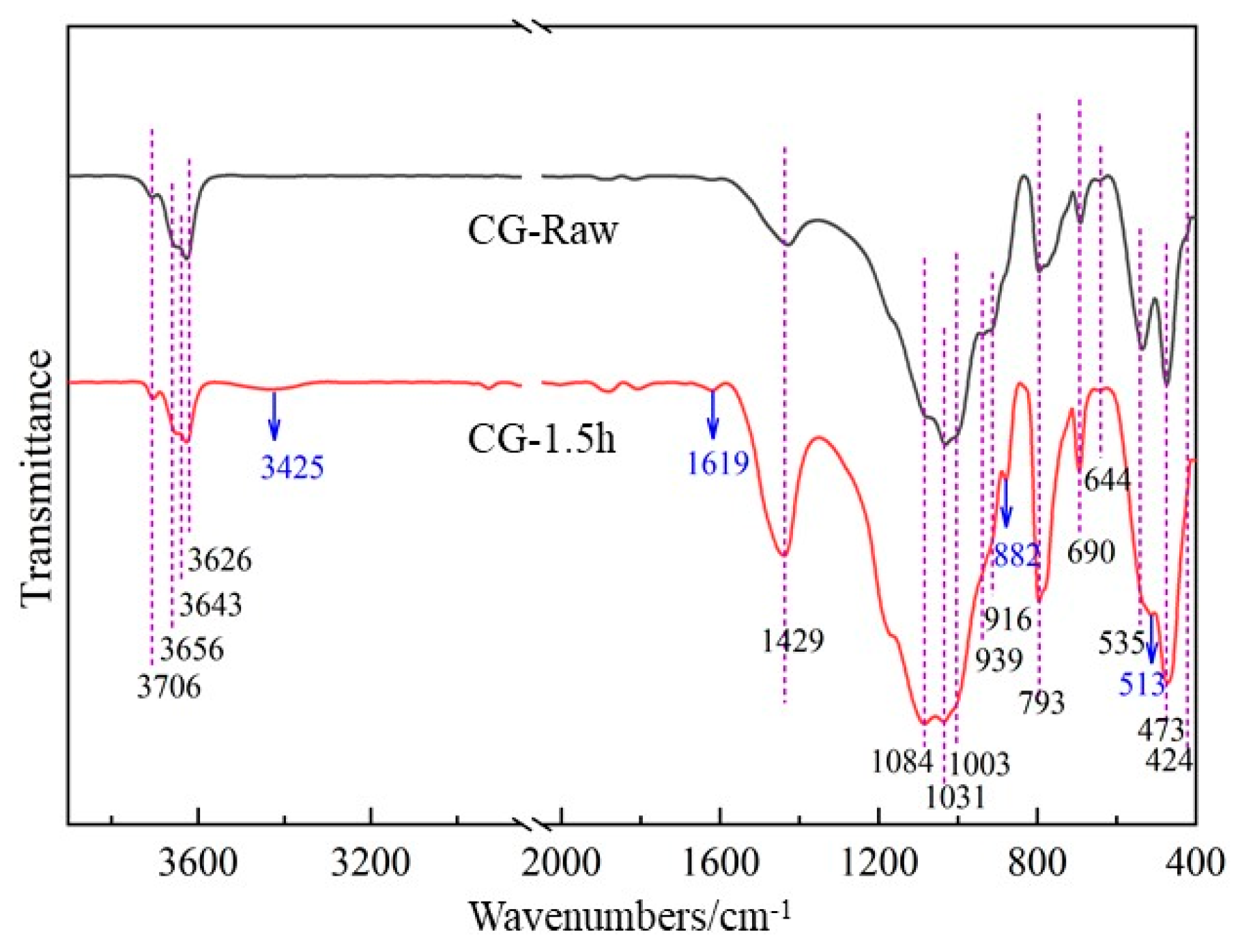
FTIR was used to detect and analyze the vibration changes of the characteristic groups of mechanically activated gangue. The particles and group vibration forms of the compounds correspond to the absorption bands in the infrared spectrum. For crystalline solid materials, the absorption band changes with the integrity of the crystallization. If the degree of crystallization is good, a sharp and strong absorption band can be observed; otherwise, a wider and weaker absorption band can be observed. Since short-time milling does not significantly change the infrared absorption spectrum of coal gangue, characteristic groups of the gangue with larger milling time intervals of 0 h and 1.5 h were compared. Figure 8 shows the FTIR spectra of coal gangue before and after mechanical activation.
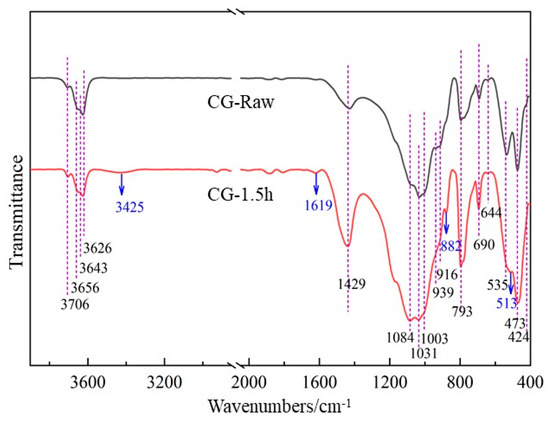
Figure 8.
FTIR spectra of coal gangue before and after mechanical activation.
As shown in Figure 8, the transmittance of 3200–3800 cm−1 and 1600–400 cm−1 wave numbers with obvious absorption bands in the infrared spectrum diagram was selected for analysis. The peaks of 3706 cm−1, 3656 cm−1, 3643 cm−1, 3626 cm−1, 939 cm−1, and 916 cm−1 in the range of 3600–3800 cm−1 are absorption bands generated by hydroxyl stretching vibration in gangue. Among them, 3706 cm−1, 3656 cm−1, and 3643 cm−1 are caused by the stretching vibration of the Al hydroxyl group on the inner surface, 3626 cm−1 is the stretching vibration of the inner hydroxyl group of Al-O octahedron, and 939 cm−1 and 916 cm−1 are the deformation vibration of the inner hydroxyl group and the inner hydroxyl group. After milling for 1.5 h, the intensity of the stretching vibration peak of hydroxyl groups shows a weakening trend, indicating that the hydroxyl structure in the gangue is gradually destroyed under the action of mechanical force. Relevant studies have also shown that as the milling time increases, the vibration peaks related to hydroxyl groups in coal gangue gradually weaken and disappear, while the removal of inner surface hydroxyl groups is easier than that of internal hydroxyl groups. The broad peaks in the range of 3200–3600 cm−1 are related to the hydrogen bonding of water molecules in coal gangue. Under the action of mechanical force, the broad peak at 3425 cm−1 begins to increase, which is due to the formation of adsorbed water after the removal of hydroxyl groups in kaolinite. At the same time, the broad peak at 1619 cm−1 shows an increasing trend, which further illustrates the formation of adsorbed water. In the mechanical milling process, part of the water generated by the removal of hydroxyl in the coal gangue (water produced by condensation between Al-OH) is attached to the active surface of the coal gangue in the form of coordination and adsorption to form hydrogen bonds, and the particles are agglomerated during the ball milling process. However, the coordination water involved in the coordination of part of Al is difficult to remove through drying. This leads to the gradual formation of an absorption band of water molecules in the mechanically ground sample. In the range of 1200–1000 cm−1, the symmetric or antisymmetric stretching vibration peaks of Si-O are mainly at wave numbers 1084 cm−1, 1031 cm−1, and 1003 cm−1. Among them, the signal is enhanced at 1084 cm−1, and the signals are weakened at 1031 cm−1 and 1003 cm−1, indicating that the change of Al-O bond further leads to the reduction of SiIV-O tetrahedron and the increase in amorphous Si-O structure. Vibration peaks at 535 cm−1, 513 cm−1, and 424 cm−1 are generated by Si-O-Si deformation vibration and Si-O-AlIV bending vibration. The signals at 535 cm−1 and 424 cm−1 are weakened, while the signals at 513 cm−1 are increased, indicating the reduction of the Si-O-AlIV structure and the formation of the Si-O-Al structure. Furthermore, a more hydrophilic AlIV-O tetrahedral structure is generated at 882 cm−1, which enhances the activity of coal gangue. In the wave number range of 650–800 cm−1, a vibration band associated with the deformation of the Si-O chain can be observed. The band at 473 cm−1 produced by O-Si-O vibration has no obvious change, indicating that the quartz structure remains unchanged. The vibration band at wave number 1429 cm−1 has a significant increase in intensity after mechanical milling for 1.5 h. This is due to the stretching vibration of O-C-O in carbonate ions, indicating that the gangue may contain carbonate. Related research has shown that this is caused by carbonization in the gangue during the milling process.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that during the mechanical activation process, the hydroxyl groups in the coal gangue are gradually removed, the kaolinite crystal structure is destroyed, the intangible Si-O structure and the tetrahedral structure of AlIV-O increases, which improves the activity of coal gangue to a certain extent.
3.1.4. Microstructure of Mechanically Activated Gangue
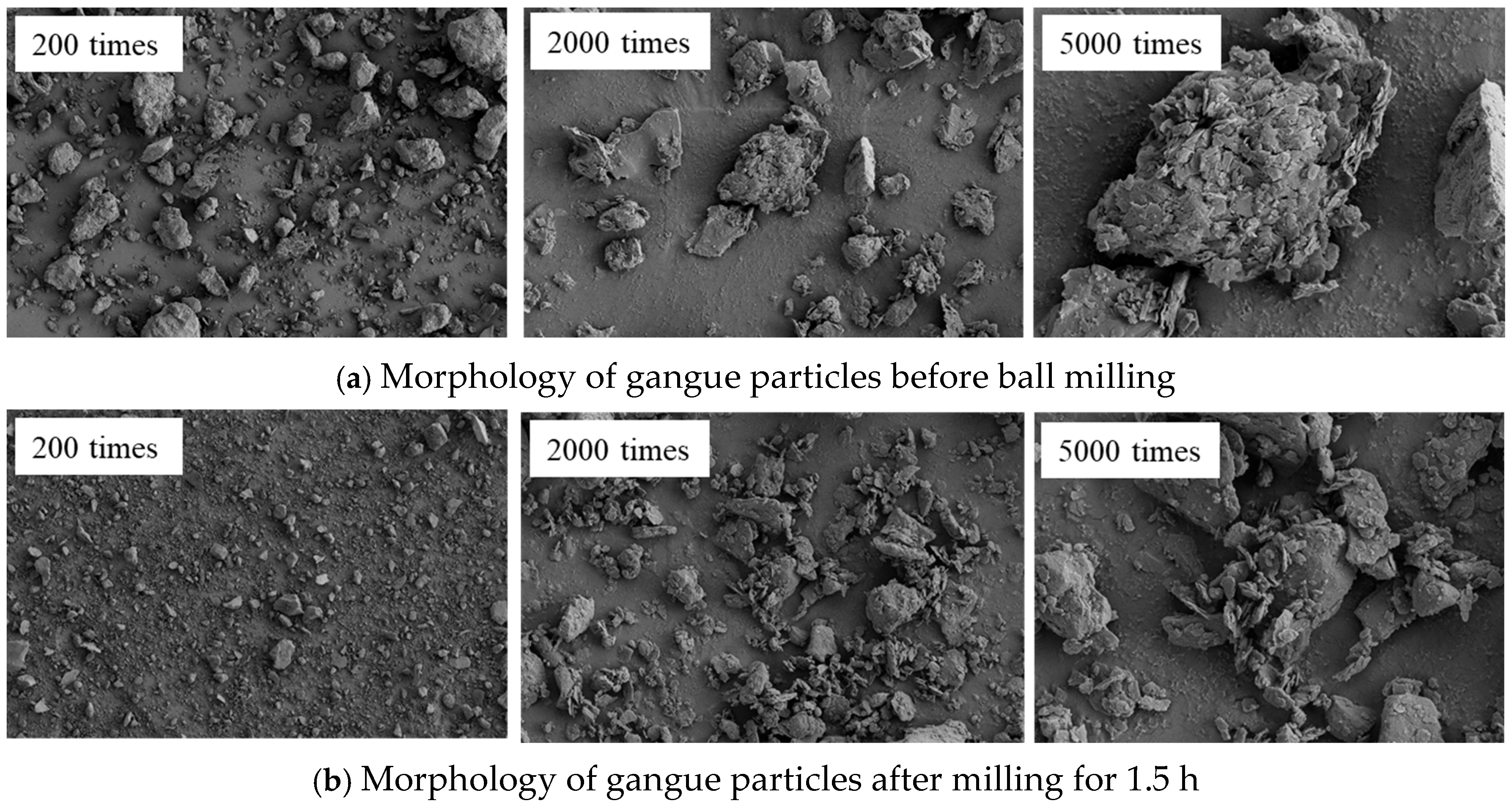
The grain size, morphology, and dispersion state of the gangue particles before and after ball milling for 1.5 h were compared by SEM. Figure 9 shows the comparison results.

Figure 9.
SEM images of coal gangue at different milling times.
As shown in Figure 9, the unground gangue particles exhibit distinct edges, irregular shapes, and a wide range of particle sizes. Additionally, there are large polygonal particles present. Under a magnification of 2000 times, it can be found that the surface of the particles mainly exhibits two morphological characteristics: smooth surface and rough surface (characterized by uneven and scaly features). The rough surface is primarily attributed to the intermingling of various minerals present in the coal gangue. After 1.5 h of high-energy mechanical milling, the particles are rapidly refined, and the particle size is reduced to less than 10 μm. This finding is consistent with the analysis results of the gangue particle size. Under a magnification of 5000 times, after the friction, collision, and extrusion of the milling medium on the particle surface, the particle size distribution is more uniform, and the edges of the particles are gradually worn off, resulting in blurred boundaries and a smoother surface. Consequently, smaller particles with indistinct edges are observed. It is also found that fine particles are adsorbed on the surface of larger particles, and the size of the particles during the mechanical milling process is closely related to the energy density. Under high-energy ball milling, the surface of the fine particles accumulates high surface energy, which promotes secondary agglomeration between particles and increases the particle size.
3.2. CO2 Mineralization Effect of Mechanically Activated Gangue
The CO2 adsorption and mineralization mechanism of mechanically activated gangue is mainly reflected in two aspects: (1) the alkaline oxides and alkaline cations in the gangue react with CO2 to form stable carbonate minerals, which is a safe and effective method for permanent storage of CO2, and (2) the activated gangue has a good interlayer structure and specific surface area and can be used as an adsorption material to adsorb CO2. At present, research on the modified adsorption function of coal gangue has been widely conducted, while research on its chemical mineralization has rarely been performed. In this study, the chemical mineralization effect of mechanically activated gangue was mainly studied.
3.2.1. Mineral Composition of Gangue After CO2 Mineralization
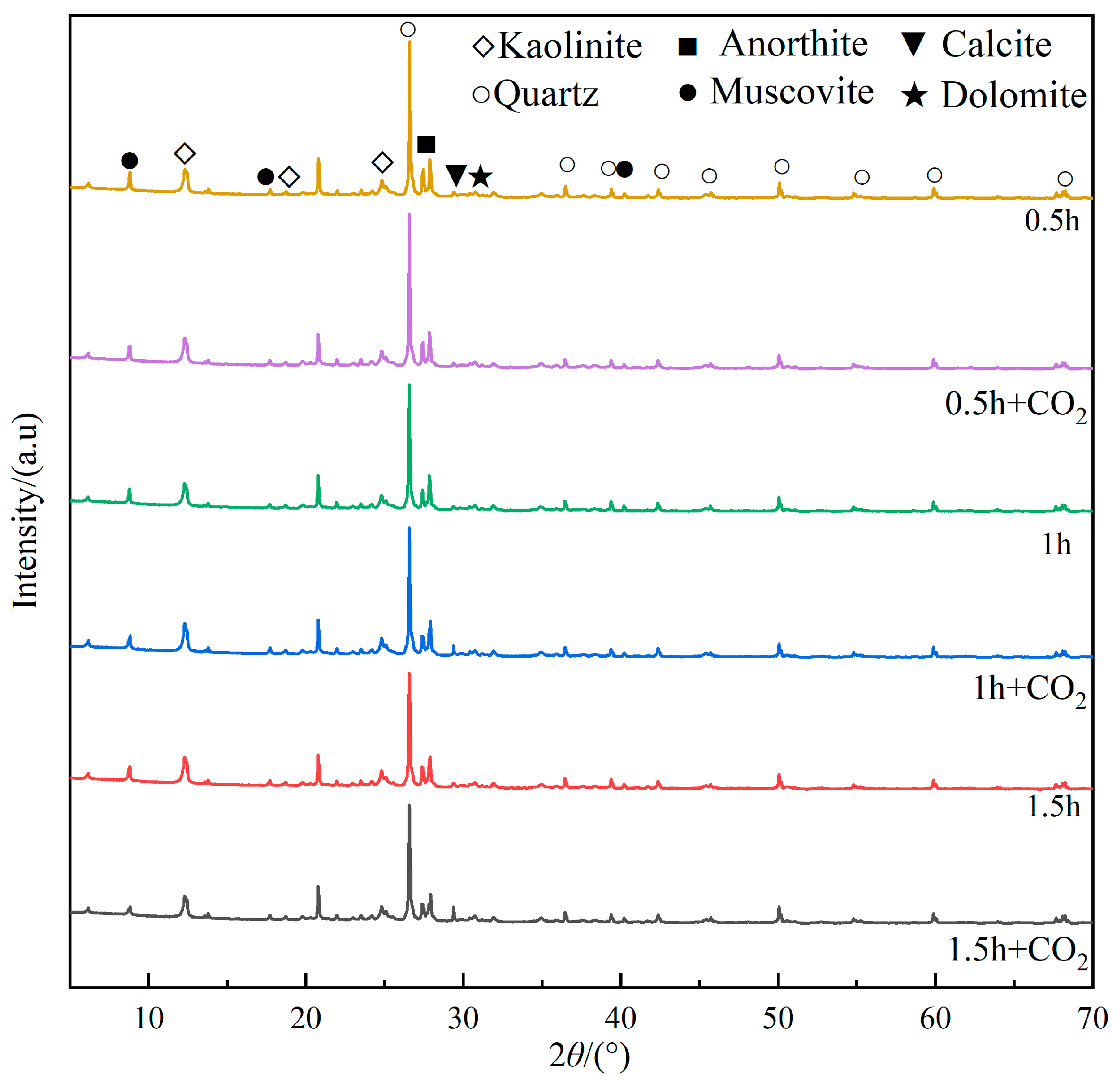
The mineral composition of coal gangue under different ball milling times before and after CO2 mineralization was detected by XRD. The diffraction pattern is shown in Figure 10.
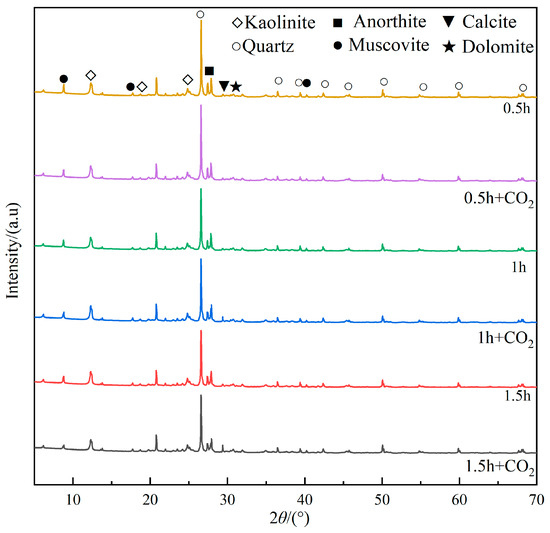
Figure 10.
XRD spectra of mineralized coal gangue at different milling times.
As shown in Figure 10, compared with non-mineralized gangue, as the milling time increases, the diffraction peaks of mineralized gangue at 12.30°, 24.80°, 26.56°, and 30.70° still decrease significantly, and the peak intensity is close to that of non-mineralized gangue. This shows that mineralization has not caused significant changes in the crystallization degree of quartz (SiO2), kaolinite (Al4[Si4O10](OH)8), and dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), indicating that these minerals are hardly involved in the mineralization reaction.
The diffraction peak intensity of muscovite (KAl3Si3O10(OH)2, in which K exists in the form of KOH and some MgO impurities) and anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8) at 8.78° and 27.84° decreases after mineralization, suggesting that these substances have participated in the mineralization reaction. The specific reactions are as follows [27,28,29]:
The diffraction peak of the calcite (CaCO3) at 29.38° is enhanced after mineralization, indicating that calcite is generated at this stage. The specific reaction is as follows:
The absence of detectable magnesium carbonate formation can be attributed to a relatively low concentration of magnesium ions. Considering the precipitation of magnesium ions, it can be speculated that the following reaction also occurred during the mineralization process:
Due to the excess acid state in the reaction kettle, cations such as K+ and Na+ in the gangue also react with each other in the reaction kettle to form bicarbonate . However, neither potassium bicarbonate nor sodium bicarbonate will precipitate out. During the drying process, the grout is gradually pyrolyzed to potassium carbonate and sodium carbonate, and calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate to calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate.
After mineralization, the content of calcium carbonate in the gangue increases with the increase in milling time, indicating that the crystal structure of calcite (CaCO3) is generated after mineralization. Due to the effect of mechanical activation, the specific surface area of the gangue increases, leading to enhanced exposure of alkaline oxides and alkaline cations on its outer surface. Consequently, these components readily react with CO2 to generate carbonate compounds.
3.2.2. Microstructure of Gangue After CO2 Mineralization
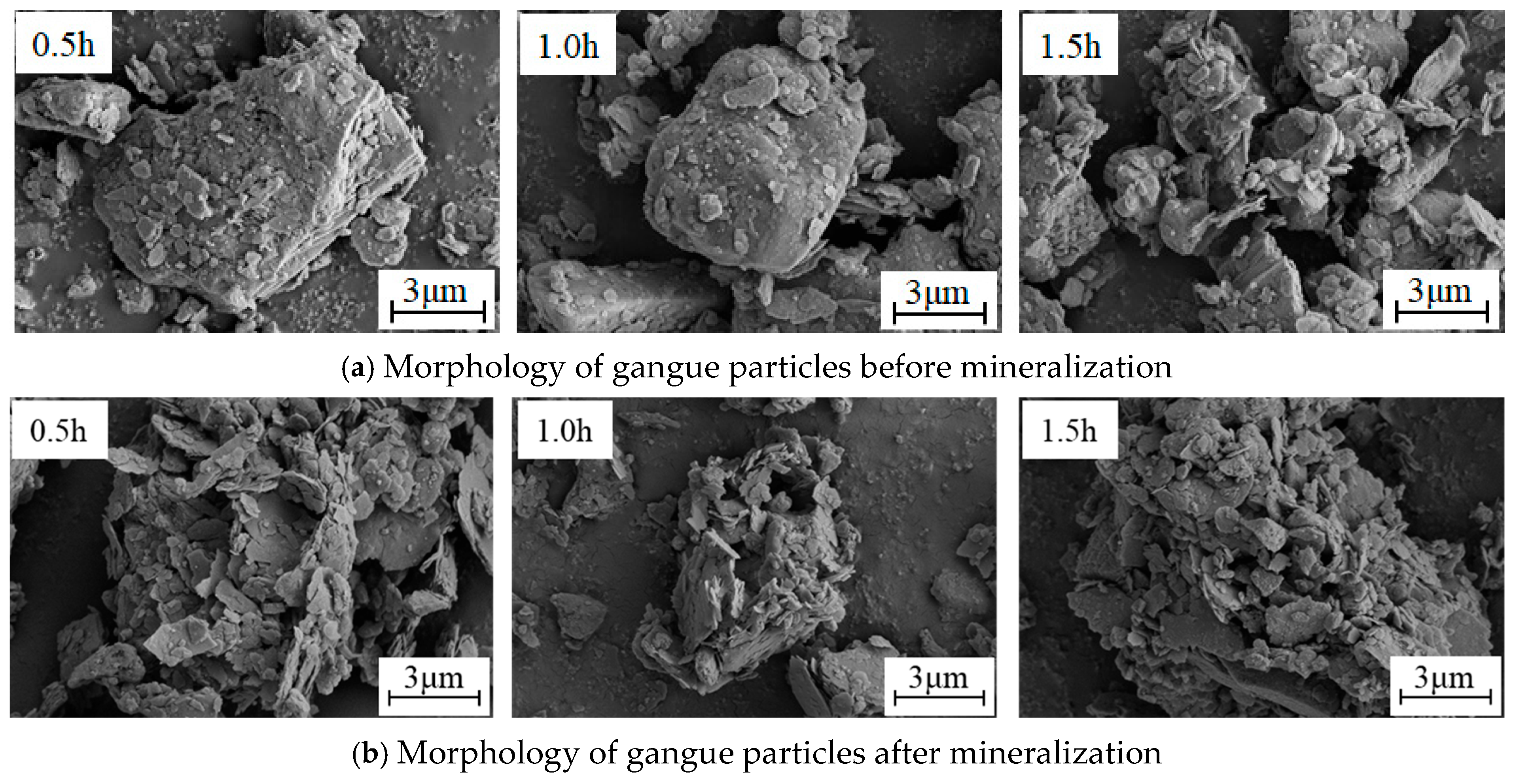
The morphology and dispersion state of the gangue particles before and after mineralization under different ball milling times were detected and analyzed by SEM. The results are shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11.
SEM images of coal gangue before and after mineralization at different milling times (8000 times).
As illustrated in Figure 11, the surface of unmineralized gangue is relatively smooth, and there are fewer fine particles adsorbed on the surface of large particles, while the surface of mineralized large-grained gangue is uneven and surrounded by scale-like fine particles. There are two reasons for the pits on the surface of the gangue particles after mineralization. First, due to the acid dissolution of the gangue during the mineralization process, the alkaline cations and alkaline oxides present in muscovite and anorthite react with CO2 to form bicarbonate, leading to their separation from the original mineral. Second, calcite is partially transformed into calcium bicarbonate due to an acidification reaction during the mineralization process under high pressure and excess carbonic acid conditions. The detachment of these components causes the uneven surface of the gangue. This phenomenon verifies the leaching effect of alkaline cations in the gangue, as shown in Formulas (2) and (3) under high pressure and excess carbonic acid.
The reason why the mineralized gangue is surrounded by fine scale-like particles is that after the leaching of alkaline cations, carbonate, and bicarbonate are dissolved in the reaction kettle according to Formulas (4)–(7). Then, the small carbonate particles generated by pyrolysis during the evaporation process are re-adsorbed on the large particles under the agglomeration effect.
3.2.3. CO2 Mineralization Effect on Coal Gangue
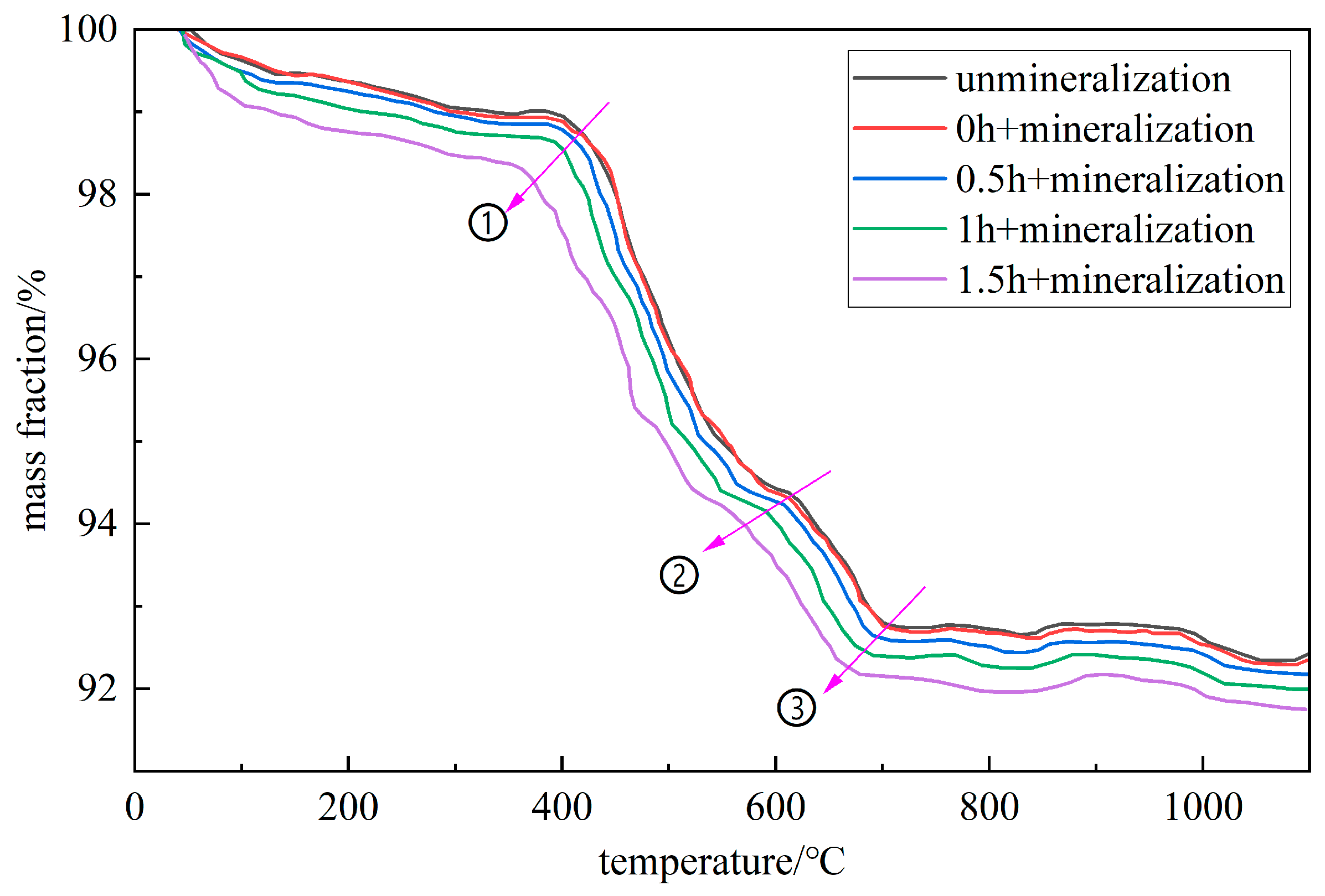
The pyrolysis effect of the gangue under different ball milling times before and after mineralization was detected and analyzed by TG. Figure 12 shows the TG results.
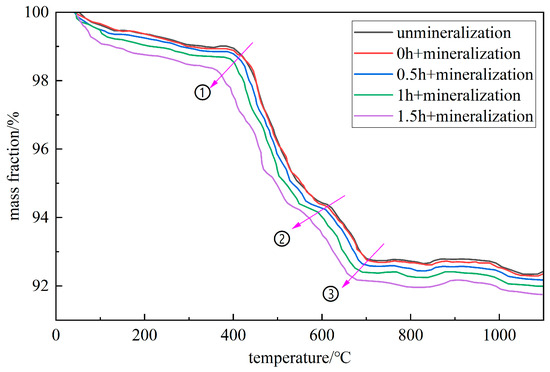
Figure 12.
TG curve of mineralized gangue with different activation times.
The pyrolysis curves in the figure are mainly divided into three stages: S1, S2, and S3. For unmineralized gangue, the mass change from room temperature to 140 °C is mainly caused by the evaporation of free water and the precipitation of structural water in the S1 stage; the change from 140 °C to 600 °C is mainly caused by the volatilization of organic matter and the dehydroxylation reaction of kaolinite in the S2 stage; and the mass change from 600 °C to 830 °C is mainly caused by the decomposition of calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate in the S3 stage. According to Figure 12, as the ball milling time increases, the inflection points of the pyrolysis curve occur earlier at points ①, ②, and ③ in the figure. This is due to the refining of gangue caused by ball milling, the increase in specific surface area, and the acceptance of more heat at the microscopic level [30,31,32]. The S3 stages of activated gangue for 0 h, 0.5 h, 1.0 h, and 1.5 h are 600–830 °C, 600–830 °C, 590–830 °C, and 560–820 °C, respectively. Based on this information, the combined amount of CO2 in the activated gangue can be calculated under different conditions.
In Figure 12, the loss on ignition M1 of unmineralized gangue in the S3 stage is 1.72%, and the loss on ignition M2, M3, M4, and M5 of the mineralized gangue in the S3 stage after activation for 0 h, 0.5 h, 1.0 h, and 1.5 h are 1.73%, 1.79%, 1.91%, and 2.17%, respectively. By subtracting M1 from M2, M3, M4, and M5, the CO2 carbon fixation capacity of gangue powder under each milling time is 0.01%, 0.07%, 0.19%, and 0.45% of its weight.
The XRF results show that the CaO, K2O, and MgO contents in this kind of gangue are 3.71%, 2.96%, and 1.49%, respectively. Based on Equation (8), the theoretical maximum carbon fixation capacity of this gangue is 5.94% of its own mass and the carbon fixation capacity of gangue after activation for 0.5 h, 1.0 h, and 1.5 h is increased by 1.18%, 3.20%, and 7.57%, respectively.
where is the theoretical maximum carbon fixation capacity of the gangue, is the type of oxide in the gangue, is the theoretical maximum carbon fixation capacity of a certain alkaline oxide in the gangue, is the mass fraction of a certain alkaline oxide in the gangue, is the molar mass of some basic oxide, and is the molar mass of CO2.
4. Perspective for Future Research
Despite the understanding of the mechanism of the mechanical activation on gangue and the corresponding mineralization ability of the MACG, there is much work yet to be performed to design a safe and cost-effective backfilling structure made with CO2-mineralized gangue. To shed light on this issue, more work is required to achieve the following:
(i) After Compare the mechanisms of other activation methods on coal gangue and determine which approach is more cost-effective and efficient;
(ii) Investigate the mechanical properties of the CO2-mineralized backfilling body, especially the uniaxial compressive strength, which is the key to assessing the stability of the overlying strata in mines.
5. Conclusions
In this study, DPLPST, XRD, FTIR, and SEM tests on mechanically activated gangue at 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h were conducted, and XRD, SEM, and TG analyses on mechanically activated gangue after mineralization treatment were performed. The conclusions are drawn as follows:
(1) After mechanical activation for 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h, the average particle size of the gangue drops from 115.6 μm to 6.6 μm, 5.8 μm, and 5.4 μm, respectively. The specific surface area of the gangue increases and the particle size distribution became more uniform. The calcium-containing crystal structures of muscovite, anorthite, and calcite are destroyed, the hydroxyl groups in the gangue are gradually removed, and the kaolinite crystal structure is damaged, leading to the increase in the intangible Si-O structure and the tetrahedron structure of AlIV-O. The edges and corners of the gangue particles are gradually worn away, while their activity is significantly enhanced.
(2) The XRD analysis results of the mineralized gangue show that anorthite and muscovite participate in the mineralization reaction to form a calcite crystal structure. Based on the TG analysis, it is calculated that after milling the gangue for 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, and 1.5 h, the carbon fixation capacity is increased to 0.01%, 0.07%, 0.19%, and 0.45% of its weight, respectively.
After milling the gangue for 1.5 h, the carbon fixation capacity is increased by 7.57%, and there is still a substantial potential for further development. In addition, the influence of long-term mechanical activation, thermal activation, and acid-base activation on the mineralization effect of coal gangue still needs to be explored. More importantly, the long-term stability of the product and the extension of the engineering scale also need to be investigated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.F.; Methodology, G.D. and Y.Z.; Investigation, C.L., G.D., Z.L. and L.J.; Data curation, G.D.; Writing—original draft, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52304159) and the Jiangsu Province ‘Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor 2023’ program (140923071). The APC was funded by the Science and Technology Project of China Coal Energy Research Institute. The project number is 2024210129.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All of the data in this paper are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Lei Zhu, Chengyong Liu and Zhicheng Liu were employed by China Coal Research Institute Co., Ltd. Ling Jin was employed by Changsha Digital Mine Info Tech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CBSW | coal-based solid wastes |
| DPLPST | dry powder laser particle size testing |
| XRD | X-ray diffractometer |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| TG | thermogravimetric |
| NCFM | negative carbon-filling material |
| CPB | cemented-paste backfill |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence spectrometer |
References
- Yang, F. Current situation analysis and prospect discussion on comprehensive utilization of coal resources for power generation. China Coal 2020, 46, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, F. Industrial development and prospect about comprehensive utilization of coal gangue. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X. Research on Identification and Impact of Key Elements in Energy Security Based on the Dual Perspectives of Low-Carbon Consumption Behavior and Supply-Demand. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, J.; Ma, X. Development Trend Analysis of Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Technology in China. Proc. CSEE 2019, 39, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochedi, F.O.; Liu, Y.; Adewuyi, Y.G. State-of-the-art review on capture of CO2 using adsorbents prepared from waste materials. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 139, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, B.; Cui, S. Underground CO2 storage and technical problems in coal miningarea under the “dual carbon” target. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Q.; Chen, W. The Summary of Carbon Capture and Storage Technology and Its Impact on China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2006, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L. Carbon Dioxide Sequestration by Mineralisation Ofcoal Fly Ash. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Hu, J.; Han, S.; Min, H.; Li, Y. Research progress on CO2 mineralization filling technology in coal mines. J. North China Inst. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, B.; Hou, D.; Zhen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Mei, W. CO2 storage-cavern construction and storage method based on functional backfill. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L. Experimental Study on Performance Optimization of Mechanically Activated Coal Gangue-Based Grouting Materials. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T. Preparation of Thermally Activated Copper Tailings-Gangue and Alkali-Excited Cementitious Materials. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Adebowale, K.O.; Olu-Owolabi, B.I.; Yang, L.Z.; Kong, L.X. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions onto sodium tetraborate-modified Kaolinite clay: Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Q.; Wu, C. Mechanism of mechanical activation for spontaneous combustion of sulfide minerals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Pan, L.P.; Wei, Y.S. Effect of mechanical activation on dissolution kinetics of neutral leach residue of zinc calcine in sulphuric acid. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Wang, G.R.; Yang, H.Y.; Chen, G.B.; Qiu, X.M. Agglomeration-aggregation and leaching properties of mechanically activated chalcopyrite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Che, M.; Liu, Y.; Che, Z.; Fu, Y. Experimental study on the extraction of aluminum and iron from coal gangue by thermal activation and acid leaching method. Energy Environ. Prot. 2024, 38, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Nehdi, M.L.; Zhang, Y. Exploring microwave activation as a novel method for activating coal gangue: Focus on microwave activation mechanisms and hydration characteristics of cementitious supplementary materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, C.; Huang, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, M.; Chai, J. Experimental Study on the Characteristics of Activated Coal Gangue and Coal Gangue-Based Geopolymer. Energies 2020, 13, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, N.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, H. Carbon negative backfill mining in coal mines for carbon neutralization: Chemical carbon fixation performances with mineralized gangue. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2025, 186, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, N.; Qiu, X.; Fang, K.; Wang, X. Effect of CO2 Mineralization on the Composition of Alkali-Activated Backfill Material with Different Coal-Based Solid Wastes. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Xing, S. Using recycled gangue to capture CO2 and prepare alkali-activated backfill paste: Adsorption and microevolution mechanisms. Fuel 2024, 358, 130194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhai, J.; Ichhuy, N. Experimental study on the preparation of water retention mining negative carbon filling material from CO2 mineralised coal-based solid waste. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 4228–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Long, K.; Ma, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, B. Experimental study on CO2 sequestration capacity and mechanical characteristics evolution of solid wastes based carbon-negative backfill materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Qi, C. The carbon uptake and mechanical property of cemented paste backfill carbonation curing for low concentration of CO2. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesson, B.; Utgenannt, P. Microstructural changes caused by carbonation of cement mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Yan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, C. A Theoretical Study on Mineral Carbonation for CO2 Sequestration. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2008, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Experimental Study of CO2 Sequestration from Flue Gasby Direct Aqueous Mineral Carbonation under Low-Medium Pressure Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Su, R.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, R.; Zhao, J. Water-Rock Interaction of Granite from Borehole BS34 at Different Temperatures. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2022, 44, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, J.; Niu, B.; Zhang, L.; Pu, G.; Tang, Q. Thermogravimetric study on pyrolysis performance and mechanism of coal residue J. China Coal Soc. 2006, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Li, R. Study of mixed pyrolysis of lignite and gangue. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2015, 36, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Research on the Combustion Characteristics and Influence Mechanism of Coal Gangue. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).