Effect of High-Strength Wastewater on Formation Process and Characteristics of Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Determination of Wastewater Concentration
2.3. Weight of Periphytic Biofilm
2.4. Chlorophyll a (Chla.) of Periphytic Biofilm
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Scanning
2.7. Random Forest Prediction
2.8. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Changes
3.2. Formation Process and Structural Changes in Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms
3.3. Relationship Between Environmental Factors and Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms
3.4. Forecast of Formation Process of Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms
4. Discussions
4.1. Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilm Formation and Structure
4.2. Relation Between Biofilm Formation and Water Environmental Factors
4.3. Techno-Economic Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.A.; Cheng, H.F.; Tao, S. Environmental and human health challenges of industrial livestock and poultry farming in China and their mitigation. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.H.; Dzakpasu, M.; Zheng, Y.C.; Tian, Y.; Jin, P.K.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, X.C. Towards the formulation of rural sewage discharge standards in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Zhang, C.X.; Chen, P.Z.; Li, Q.; Tan, L. Systematically assess the advancing and limiting factors of using the multi-soil-layering system for treating rural sewage in China: From the economic, social, and environmental perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandros, S.I.; Akratos, C.S. Removal of pathogenic bacteria in constructed wetlands: Mechanisms and efficiency. Phytoremediat. Manag. Environ. Contam. 2016, 4, 327–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Gersberg, R.M.; Keat, T.S. Constructed wetlands in China. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. The phytoremediation of water with high concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus contamination by three selected wetland plants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.A.O.; Mier, M.V.; Estrada, J.A.E.; Domíguez, C.D. Nitrogen and potassium variation on contaminant removal for a vertical subsurface flow lab scale constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7745–7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.-K.; Sun, X.-C.; Mu, X.-H.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.-J.; Yuan, L.-X.; Mi, G.-H. Interaction effect of nitrogen form and planting density on plant growth and nutrient uptake in maize seedlings. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; Shan, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-H.; Du, Y.; Feng, K. Physiological Responses of Two Wheat Cultivars to Nitrogen Starvation. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.R.; Liu, F.; Luo, P.; Zhang, S.N.; Li, H.F.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.S. Pilot-scale constructed wetlands for swine wastewater treatment: Microbial community analysis in bacterioplankton and epiphyton and options for resource recovery. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Wu, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Rinklebe, J.; Xia, Y.F.; Lu, D.B.; Zhu, L.F.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Bioaccumulation of potentially toxic elements by submerged plants and biofilms: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Gong, L.X.; Mu, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, S.H. Characterization and co-occurrence of microbial community in epiphytic biofilms and surface sediments of wetlands with submersed macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Qin, Z.R.; Xia, L.L.; Zhang, D.; Mela, S.M.; Li, Y. The responding and ecological contribution of biofilm-leaves of submerged macrophytes on phenanthrene dissipation in sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Pang, S.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; Guo, C.; Addo, F.G.; Li, Y. Responses of bacterial community structure and denitrifying bacteria in biofilm to submerged macrophytes and nitrate. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Han, B.; Hua, Z.L.; Fu, D.W.; Li, P. Impacts of water flow on epiphytic microbes and nutrients removal in constructed wetlands dominated by Vallisneria natans with decreasing temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Zhang, S.H.; Lv, X.; Guo, S.Z.; Ma, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X.R. Interactions between suspended sediments and submerged macrophytes-epiphytic biofilms under water flow in shallow lakes. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Xia, Y.F.; Lu, D.B.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Ren, L.X.; Xu, C.D.; Hua, E.T.; Sun, G.J.; et al. The bacterial community structure in epiphytic biofilm on submerged macrophyte Potamogetom crispus L. and its contribution to heavy metal accumulation in an urban industrial area in Hangzhou. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Lv, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Han, B. Water flow and temperature drove epiphytic microbial community shift: Insight into nutrient removal in constructed wetlands from microbial assemblage and co-occurrence patterns. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermino, F.S.; de Campos Bicudo, D.; Bicudo, C. Seasonal influence of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on the floristic composition of the algal periphytic community in a shallow tropical, mesotrophic reservoir (São Paulo, Brazil). Oecol. Aust. 2011, 15, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shao, H.; Yang, L. Responses of periphyton morphology, structure, and function to extreme nutrient loading. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, H.; Vinocur, A.; Tell, G. Periphyton on artificial substrata from three lakes of different trophic status at Hope Bay (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2002, 25, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Chen, K.-E.; Tsay, Y.-F. Nitrate Transport, Signaling, and Use Efficiency. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 85–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Sheng, Y.S.; Xu, X.P.; Ma, J.C.; Ding, W.C.; He, P.; Ma, J.W. Quantifying synergistic effects of artificial and environmental variables on potato nutrient use efficiency in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 432, 139739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Jia, W.; Xie, H.; Gu, R.R.; Li, C.; Gao, B. Impact of COD/N ratio on nitrous oxide emission from microcosm wetlands and their performance in removing nitrogen from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2910–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zuo, R.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Riverbank filtration in China: A review and perspective. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapp, A.; David, L.C.; Chardin, C.; Girin, T.; Marmagne, A.; Leprince, A.-S.; Chaillou, S.; Ferrario-Méry, S.; Meyer, C.; Daniel-Vedele, F. Nitrate transport and signalling in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Feng, H.; Dong, W. A review of research progress of heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification microorganisms (HNADMs). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.C.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, W.B.; Yan, L.L.; Mu, X.Y.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, S.H. Vallisnerian natans tolerance and response of microbial community in wetlands to excess nutrients loading. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Shan, Y.; Zheng, Z. Comparison of four aquatic plant treatment systems for nutrient removal from eutrophied water. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gu, P.; Ji, X.Y.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, J.B.; Zheng, Z. Response of submerged macrophytes and periphyton biofilm to water flow in eutrophic environment: Plant structural, physicochemical and microbial properties. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, M.H.; Liu, L.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, J.S. Response of bacterial and micro-eukaryotic communities to spatio-temporal fluctuations of wastewater in full scale constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 136235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Tao, W.; Wang, Z.; Shayya, W. Effects of pH and seasonal temperature variation on simultaneous partial nitrification and anammox in free-water surface wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, E.; Giménez, J.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J.; Serralta, J. Effect of pH, substrate and free nitrous acid concentrations on ammonium oxidation rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 124, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, A.J.; Hamilton, S.K. Have we overemphasized the role of denitrification in aquatic ecosystems? A review of nitrate removal pathways. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A. Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 2009, 459, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, P.S.; Starnawski, P.; Poulsen, B.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Schramm, A.; Riis, T. Microbial community diversity and composition varies with habitat characteristics and biofilm function in macrophyte-rich streams. Oikos 2017, 126, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, A.; Tuckfield, R.; McArthur, J. Differences in the effect of coal pile runoff (low pH, high metal concentrations) versus natural Carolina bay water (low pH, low metal concentrations) on plant condition and associated bacterial epiphytes of Salvinia minima. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, K.; Plenkovic-Moraj, A.; Gligora, M.; Primc-Habdija, B.; Sipos, L. Structure of periphytic community on artificial substrata: Influence of depth, slide orientation and colonization time in karstic Lake Visovacko, Croatia. Hydrobiologia 2006, 560, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.M.; Taffs, K.H.; Corfield, J.L. A comparison of diatom community structure on natural and artificial substrata. Hydrobiologia 2003, 493, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahto, K.U.; Vandana; Priyadarshanee, M.; Samantaray, D.P.; Das, S. Bacterial biofilm and extracellular polymeric substances in the treatment of environmental pollutants: Beyond the protective role in survivability. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.T.; Chen, H.F.; Ge, S.F.; Yoshikawa, K. Effect of the hydrothermal pretreatment for the reduction of NO emission from sewage sludge combustion. Appl. Energy 2013, 111, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimova, M.; Quevedo, W.; Szyc, Ł.; Iannuzzi, M.; Wernet, P.; Odelius, M.; Nibbering, E.T. Aqueous solvation of ammonia and ammonium: Probing hydrogen bond motifs with FT-IR and soft X-ray spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12773–12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Zee, F.R.; Cervantes, F.J. Impact and application of electron shuttles on the redox (bio)transformation of contaminants: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.R.; Jung, M.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Wagner, M.; Daims, H.; Wanek, W. Nitrogen Kinetic Isotope Effects of Nitrification by the Complete Ammonia Oxidizer Nitrospira inopinata. mSphere 2021, 6, e00634-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.S.; Welch, K.T.; Prebyl, B.S.; Baker, D.C.; Meyers, A.J.; Sayler, G.S. Analysis and glycosyl composition of the exopolysaccharide isolated from the floc-forming wastewater bacterium Thauera sp. MZ1T. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, X.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yin, D.Q.; Yu, B.; Zhu, H.K. Effect of epiphytic algae on photosynthetic function of Potamogeton crispus. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2007, 22, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeder, U.; Ruzicka, J.; Goos, C. Characterization of the light attenuation by periphyton in lakes of different trophic state. Limnologica 2010, 40, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Little, B.J.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances in the environment, technology and medicine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L. Nitrogen loading affects microbes, nitrifiers and denitrifiers attached to submerged macrophyte in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Wang, J.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Lei, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C. Nitrogen enrichment stimulates rhizosphere multi-element cycling genes via mediating plant biomass and root exudates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 190, 109306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Feng, G.; Song, J. Osmotic regulation beyond nitrate nutrients in plant resistance to stress: A review. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 103, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Stewart, B. Responses of crop plants to ammonium and nitrate N. Adv. Agron. 2013, 118, 205–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor, D.W.; Boyle, F.A.; Keys, A.J.; Kendall, A.C.; Young, A.T. Nitrate nutrition and temperature effects on wheat—A synthesis of plant-growth and nitrogen uptake in relation to metabolic and physiological processes. J. Exp. Bot. 1988, 39, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.W.; Kontturi, M.; Young, A.T. Photosynthesis by Flag Leaves of Wheat in Relation to Protein, Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity and Nitrogen Supply. J. Exp. Bot. 1989, 40, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Different in root exudates and rhizosphere microorganisms effect on nitrogen removal between three emergent aquatic plants in surface flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, F.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, G.; Deng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhuang, X. Myriophyllum aquaticum constructed wetland effectively removes nitrogen in swine wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Lv, D.Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance and bacterial communities in a multi-stage surface flow constructed wetland treating rural domestic sewage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.M.; Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Xiao, R.L.; Wu, J.S. Seasonality distribution of the abundance and activity of nitrification and denitrification microorganisms in sediments of surface flow constructed wetlands planted with Myriophyllum elatinoides during swine wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



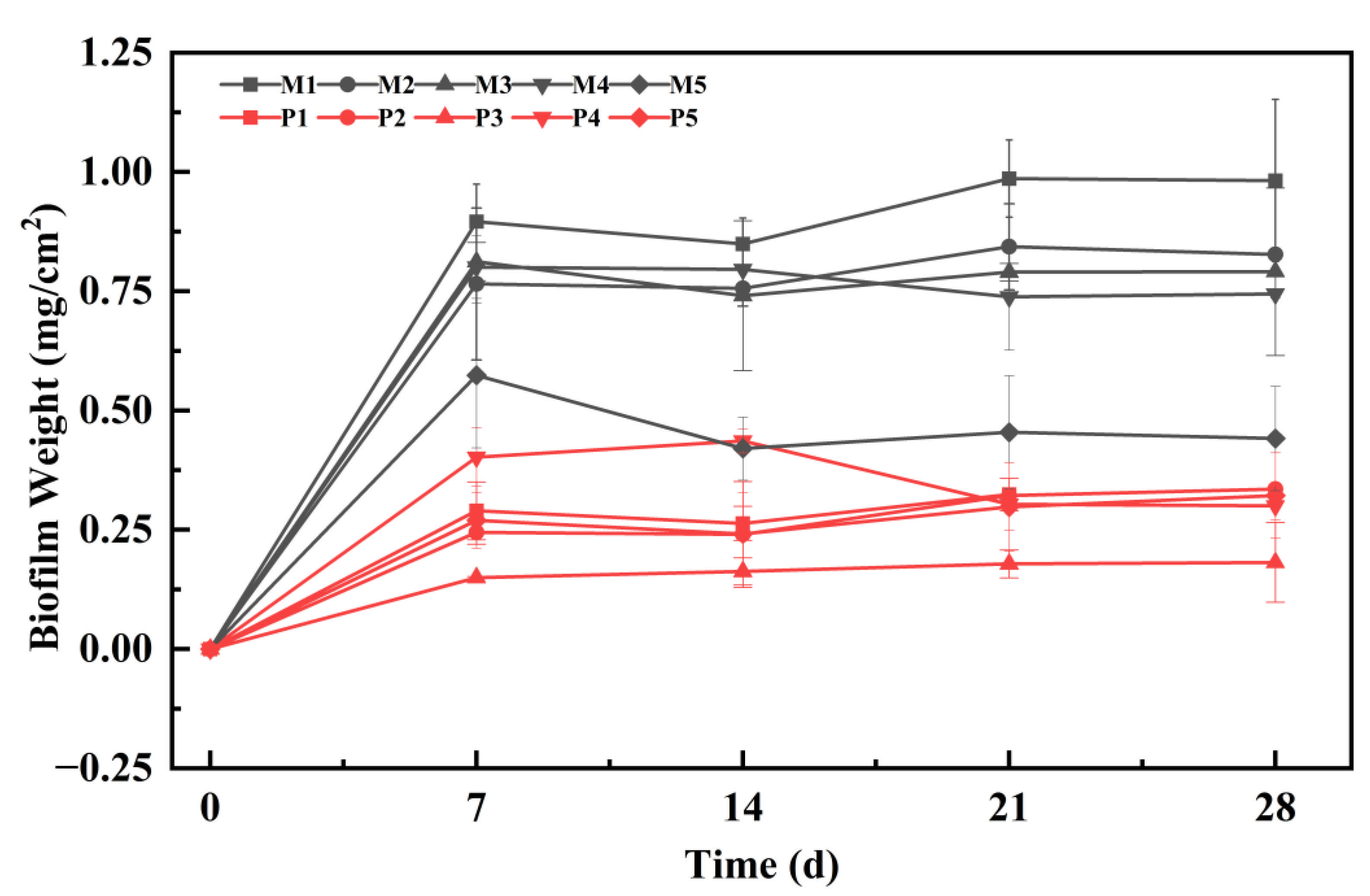


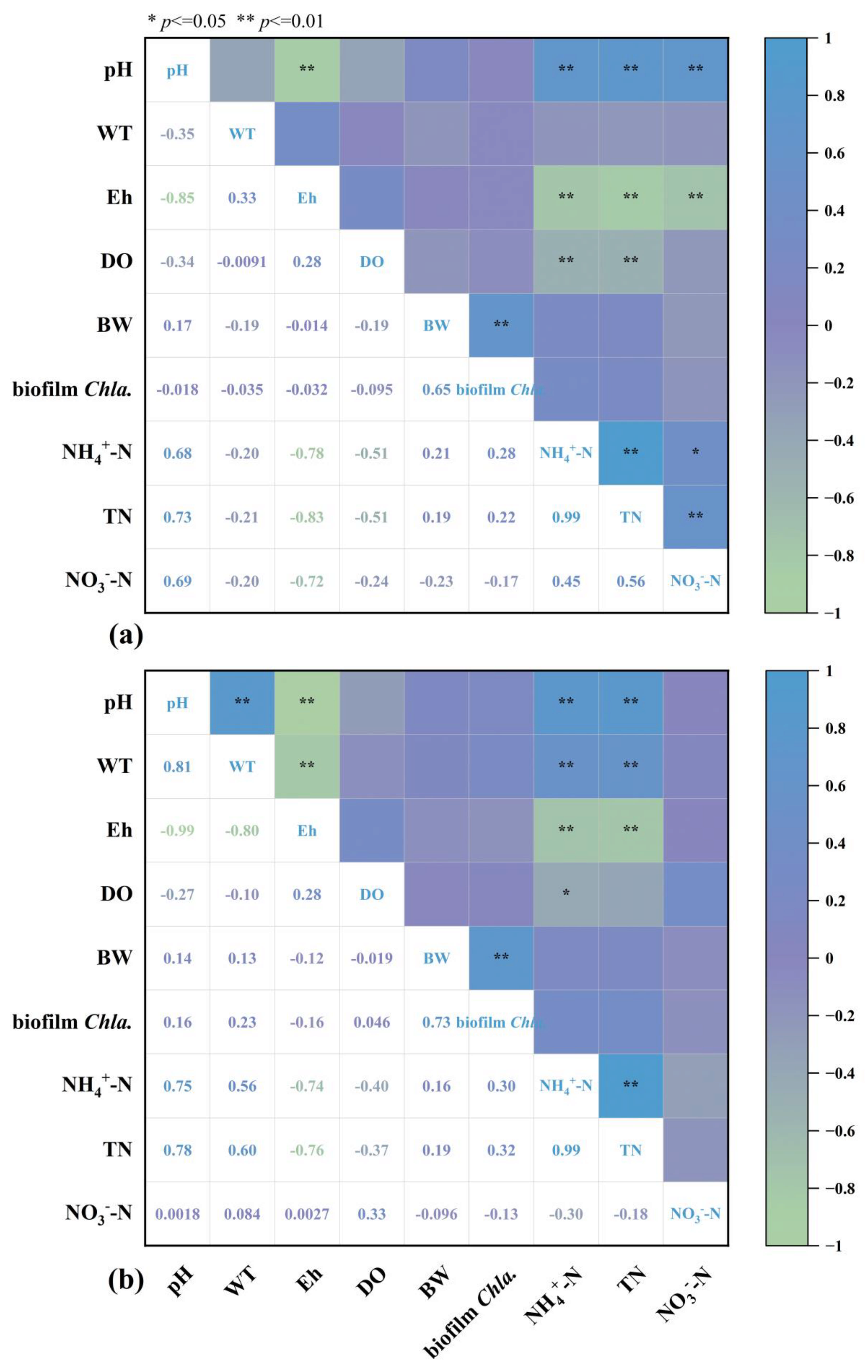
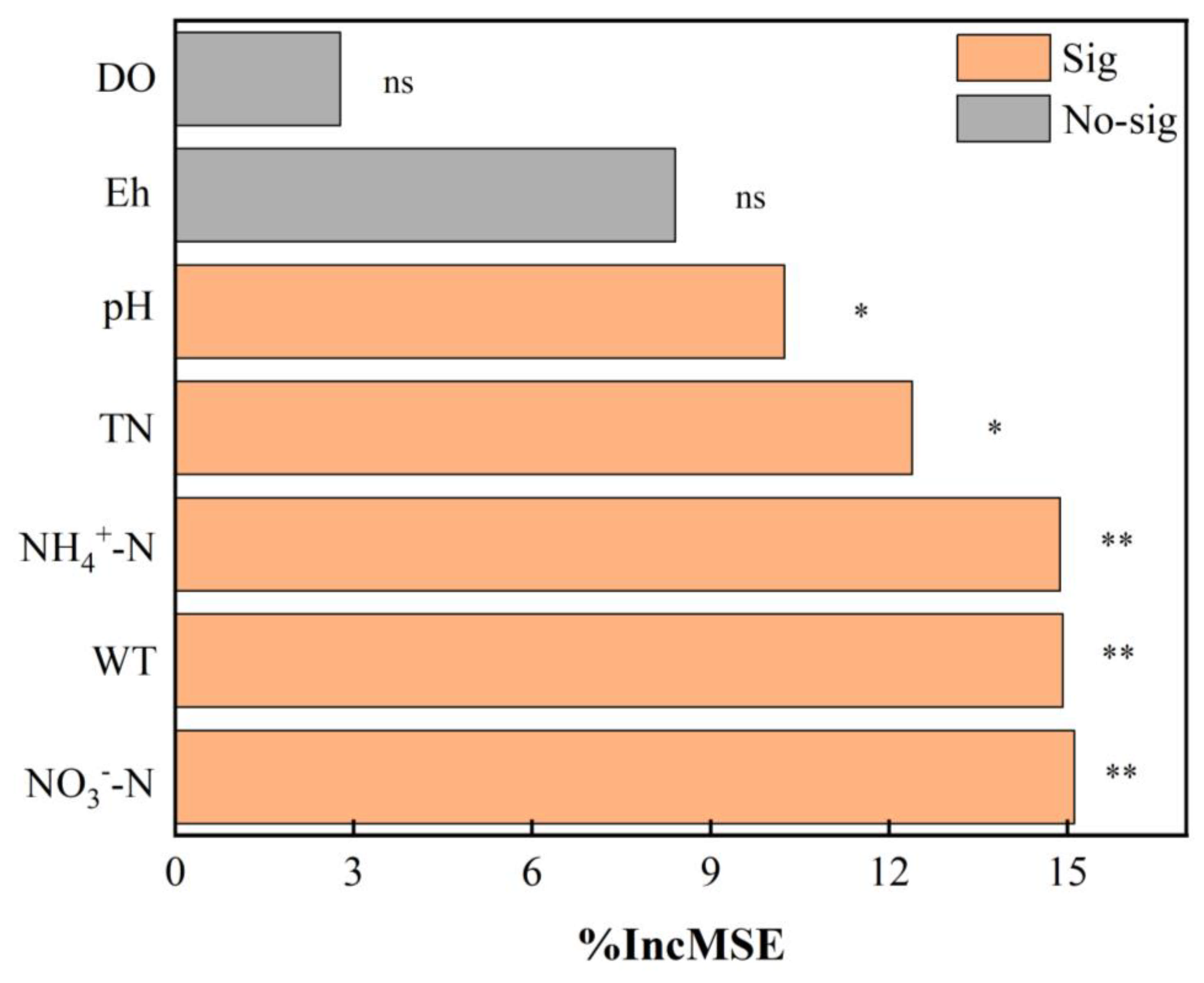
| Treatment | Ratio of Original Wastewater and Tap Water | TN Average Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | only original water | 201.7 |
| P1 | only original water | 201.7 |
| M2 | 1:1 | 104.0 |
| P2 | 1:1 | 104.0 |
| M3 | 1:2 | 70.9 |
| P3 | 1:2 | 70.9 |
| M4 | 1:3 | 56.9 |
| P4 | 1:3 | 56.9 |
| M5 | 1:4 | 46.1 |
| P5 | 1:4 | 46.1 |
| Treatment | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (d) | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 28 |
| Chla. content (μg/L) | 398.0 ± 2.3 | 96.7 ± 5.4 | 174.8 ± 2.6 | 213.9 ± 6.2 | 93.0 ± 4.1 | 152.5 ± 6.9 | 48.4 ± 1.0 | 39.1 ± 4.6 | 83.7 ± 7.7 | 130.2 ± 6.8 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 26.0 ± 3.3 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Effect of High-Strength Wastewater on Formation Process and Characteristics of Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062654
Chen L, Zhao M, Li X, Li Y, Wu J. Effect of High-Strength Wastewater on Formation Process and Characteristics of Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062654
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Luomeijie, Miao Zhao, Xi Li, Yuyuan Li, and Jinshui Wu. 2025. "Effect of High-Strength Wastewater on Formation Process and Characteristics of Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062654
APA StyleChen, L., Zhao, M., Li, X., Li, Y., & Wu, J. (2025). Effect of High-Strength Wastewater on Formation Process and Characteristics of Hydrophyte Periphytic Biofilms. Sustainability, 17(6), 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062654






