Influence of Phosphogypsum Waste on Rainwater Chemistry in a Highly Polluted Area with High Mortality Rates in Huelva Metropolitan Area, Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
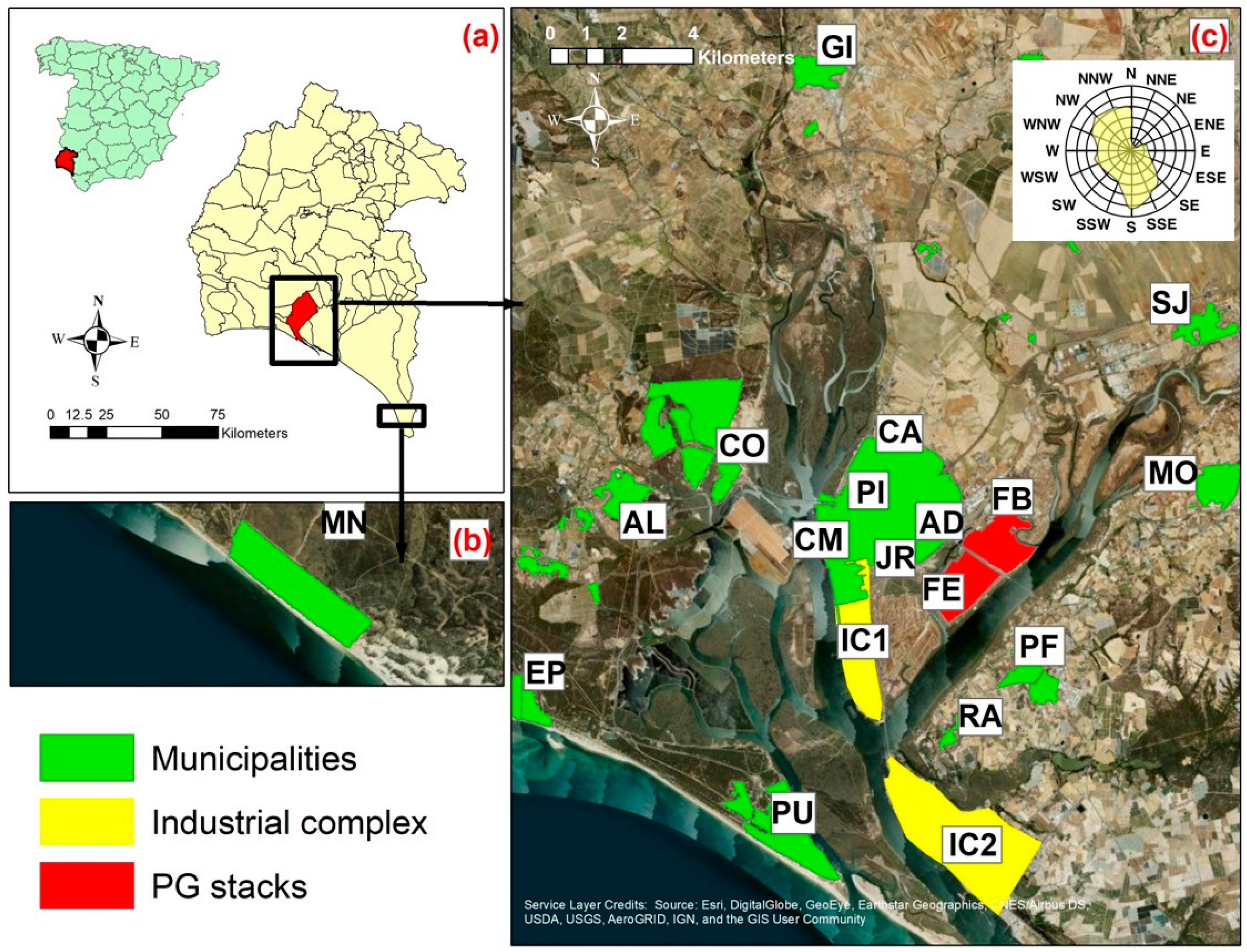
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Methodology
2.2.1. Rainwater Sampling and Hellman Rain Gauge Characteristics
2.2.2. pH and Conductivity
2.2.3. Major Anions and Cations
2.2.4. Trace Elements
2.2.5. Data Analyses and Spatial Variation
3. Results
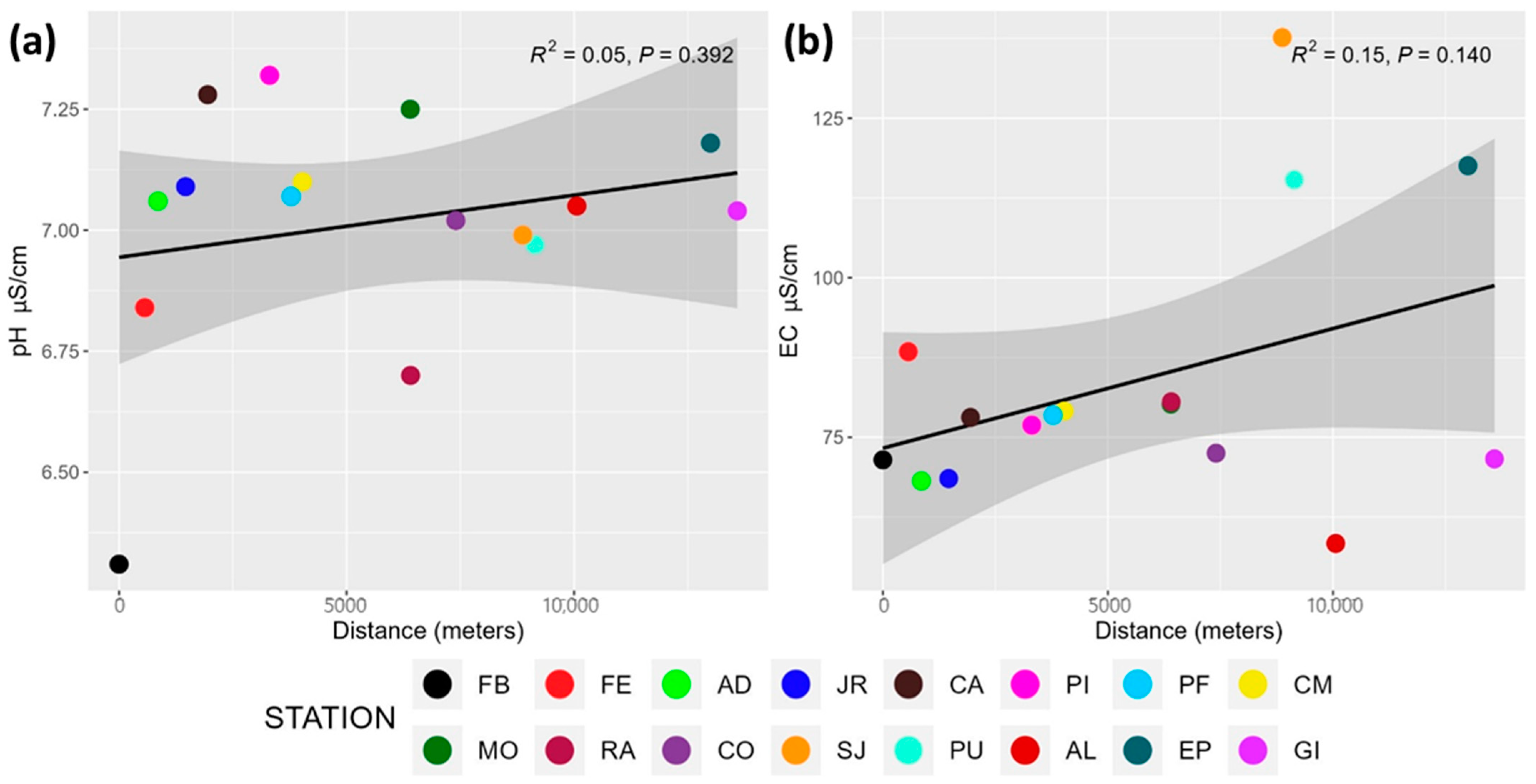
3.1. pH and Conductivity
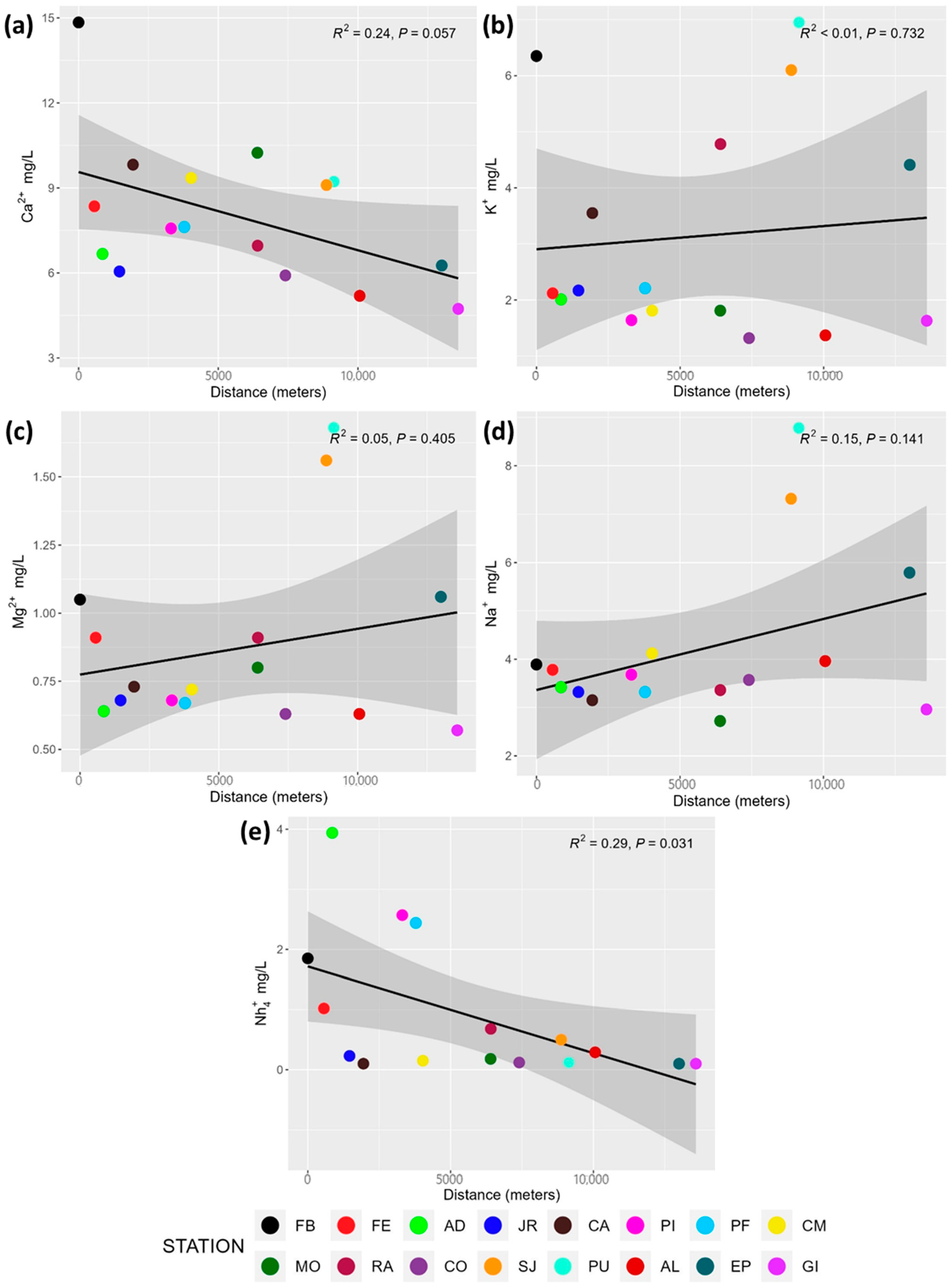
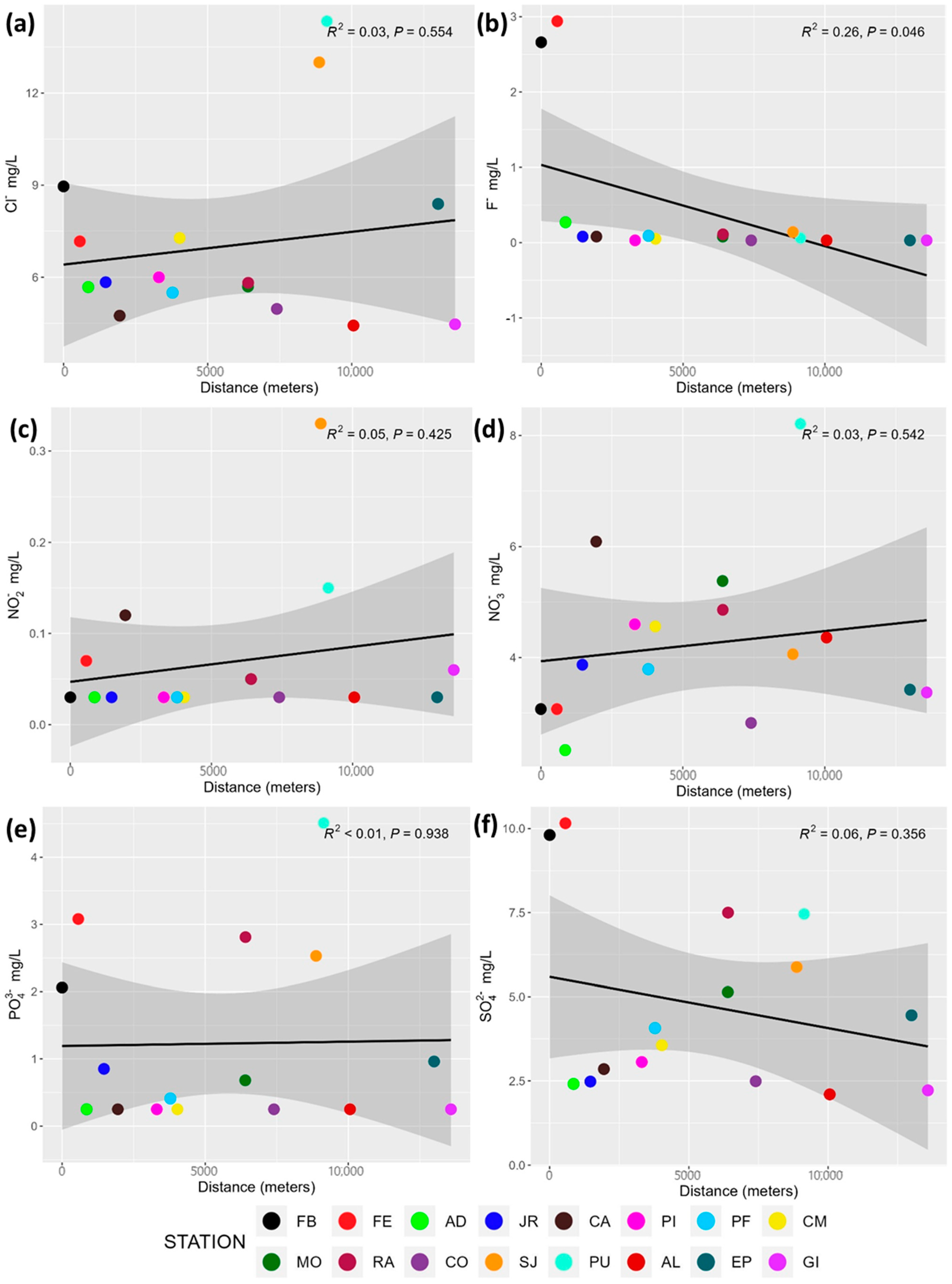
3.2. Major Anions and Cations
3.3. Trace Elements
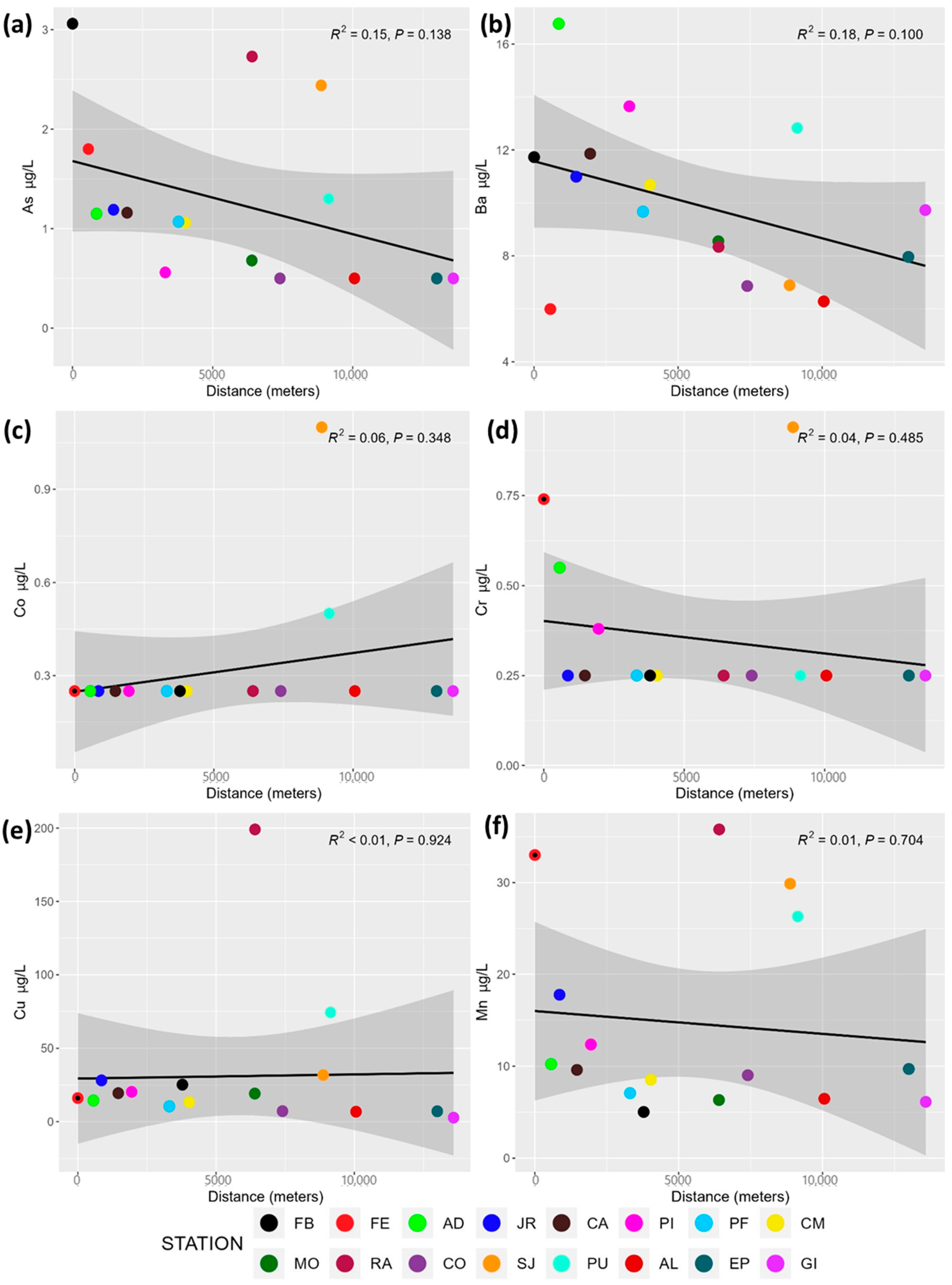
3.4. Spatial Variation
4. Discussion
4.1. pH and Conductivity
4.2. Major Anions and Cations
4.3. Trace Elements
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.S.; Olías, M.; Canovas, C.R.; Riba, I.; Kalman, J.; Delvalls, T.A. Acid mine drainage pollution in the Tinto and Odiel rivers (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain) and bioavailability of the transported metals to the Huelva Estuary. Environ. Int. 2020, 33, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, B.M.; Borrero-Santiago, A.R.; Fabbri, E.; Guerra, R. Trace metal levels and toxicity in the Huelva Estuary (Spain): A case study with comparisons to historical levels from the past decades. Environ. Chem. Ecotox. 2019, 1, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, J.; Ballester, F.; Donado-Campos, J.; Pollán, M.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Dictamen Realizado Por Encargo Del Defensor Del Pueblo Andaluz Sobre El Exceso de Mortalidad y Morbilidad Detectado en Varias Investigaciones en La Ría de Huelva; Grupo de Trabajo de la Sociedad Española de Epidemiología: Seville, Spain, 2014; Available online: https://www.defensordelpuebloandaluz.es/informe-epidemiologico-ria-de-huelva (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Benach, J.; Yasui, Y.; Borrell, C.; Rosa, E.; Pasarín, M.I.; Benach, N.; Español, E.; Martínez, J.M.; Daponte, A. Examining geographic patterns of mortality: The Atlas of mortality in small areas in Spain (1987–1995). Eur. J. Public Health 2003, 13, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Abente, G.; Aragones, N.; Ramis, R.; Hernandez-Barrera, V.; Perez-Gomez, B.; Escolar-Pujolar, A.; Pollan, M. Municipal distribution of bladder cancer mortality in Spain: Possible role of mining and industry. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Beneito, M.A.; Botella-Rocamora, P.; Corpas-Burgos, F.; Vergara- Hernández, C.; Pérez-Panadés, J.; Perpiñán-Fabuel, H. Atlas Nacional de Mortalidad en España (ANDEES); Fundación FISABIO y Dirección General de Salud Pública de la Generalitat Valenciana: Valencia, Spain, 2024; Available online: http://andees.fisabio.san.gva.es/ (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Aguilera, I.; Daponte, A.; Gil, F.; Hernández, A.F.; Godoy, P.; Pla, A.; Ramos, J.L. Urinary levels of arsenic and heavy metals in children and adolescents living in the industrialised area of Ria of Huelva (SW Spain). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Lacasaña, M.; Gil, F.; Lorca, A.; Alguacil, J.; Rohlman, D.S.; González-Alzaga, B.; Molina-Villalba, I.; Mendoza, R.; Aguilar-Garduño, C. Cadmium exposure and neuropsychological development in school children in southwestern Spain. Environ. Res. 2014, 134, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelo, R.; Rohlman, D.S.; Jara, R.; García, T.; Viñas, J.; Lorca, J.A.; Contreras-Llanes, M.; Alguacil, J. Residence in an Area with Environmental Exposure to Heavy Metals and Neurobehavioral Performance in Children 9–11 Years Old: An Explorative Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Caicedo, R.F.; Contreras-Llanes, M.; Capelo, R.; Zumel-Marne, A.; García-Sevillano, M.Á.; Santos-Sánchez, V.; Alguacil, J. Impact of Fish, Mollusk and Seafood Consumption before Sample Donation on Urinary and Toenail Metal Levels in Workers Exposed to Heavy Metals. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Llanes, M.; Santos-Sánchez, V.; Alguacil, J.; Castillo, J.M. Delineating distinct sediment pollution signatures from diverse sources in a heavily contaminated estuary near an area of high cancer and cardiovascular mortality. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Llanes, M.; Alguacil, J.; Capelo, R.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L.; García-Pérez, J.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Martin-Olmedo, P.; Santos-Sánchez, V. Internal cumulated dose of toxic metal(loid)s in a population residing near a Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material waste stacks and an industrial heavily polluted area with high mortality rates in Spain. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IAEA. Application of the Concepts of Exclusion Exemption and Clearance; Safety Standards Series; Safety Guide No. RS-G 17, STI/PUB/1202; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-Llanes, M.; Pérez-López, R.; Gázquez, M.J.; Morales, V.; Santos, A.; Esquivias, L.M.; Bolívar, J.P. Fractionation and fluxes of metals and radionuclides during the recycling process of phosphogypsum wastes applied to mineral CO2 sequestration. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M. Valorisation of Inorganic Waste for Obtaining Construction Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Huelva, Huelva, Spain, 19 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Committee of National Experts Coordinated from Huelva University About the RESTORE 2030 Plan. Technical Report on the Suitability of the RESTORE 20/30 Project as a Solution to the Problem of the Phosphogypsum Ponds and for the Recovery of the Marshes of the Tinto River Estuary. 2024. Available online: http://mesadelaria.es/documentos/Informe_280722_C_Expertos-Agosto2022.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Chopin, E.I.B.; Black, S.; Hodson, M.E.; Coleman, M.L.; Alloway, B.J. A preliminary investigation into mining and smelting impacts on trace element concentrations in the soils and vegetation around Tharsis, SW Spain. Mineral. Mag. 2003, 67, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, E.I.B.; Alloway, B.J. Trace element partitioning and soil particle characterisation around mining and smelting areas at Tharsis, Riotinto and Huelva, SW Spain. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 373, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; González, I.; Romero, A. Trace elements contamination of agricultural soils affected by sulphide exploitation (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SWSpain). Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, R.N.; Izquierdo, M.; Córdoba, P.; Moreno Palmerola, N.; Querol, X.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Font, O.; Cohen, H.; Knop, Y.; Torres-Sánchez, R.; et al. The evolution of brines from phosphogypsum deposits in Huelva (SW Spain) and its environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, R.; Nieto, J.M.; López-Coto, I.; Aguado, J.L.; Bolívar, J.P.; Santisteban, M. Dynamics of contaminants in phosphogypsum of the fertilizer industry of Huelva (SW Spain): From phosphate rock ore to the environment. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentería-Villalobos, M.; Vioque, I.; Mantero, J.; Manjón, G. Radiological, chemical and morphological characterizations of phosphate rock and phosphogypsum from phosphoric acid factories in SW Spain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumlee, G.S.; Morman, S.A. Mine wastes and human health. Elements 2011, 7, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotons, J.M.; Diaz, A.R.; Sarria, F.A.; Serrato, F.B. Wind erosion on mining waste in southeast Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csavina, J.; Field, J.; Taylor, M.P.; Gao, S.; Landázuri, A.; Betterton, E.A.; Sáez, A.E. A review on the importance of metals and metalloids in atmospheric dust and aerosol from mining operations. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.P.; Mackay, A.K.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Holz, E. Soil Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn contaminants around Mount Isa city, Queensland, Australia: Potential sources and risks to human health. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zota, A.; Willis, R.; Jim, R.; Norris, G.A.; Shine, J.P.; Duvall, R.M.; Schaider, L.A.; Spengler, J.D. Impact of mine waste on airborne respirable particulates in northeastern Oklahoma, United States. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khashman, O.A. Study of chemical composition in wet atmospheric precipitation in Eshidiya area, Jordan. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6175–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, A.; Fernández-López, C.; Vázquez, M.; Caparrós, A.; Ibarra, I.; García, C.; Zarroca, M.; Rodríguez, R. An assessment of the influence of sulfidic mine wastes on rainwater quality in a semiarid climate (SE Spain). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Jonard, M.; Ponette, Q. Influence of meteorological factors and polluting environment on rain chemistry and wet deposition in a rural area near Chimay, Belgium. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.; Alarcón, M. Relationship between precipitation chemistry and meteorological situations at a rural site in NE Spain. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicho, A.F.; Martins, L.D.; Nomi, S.N.; Solci, M.C. Integrated and sequential bulk and wet-only samplings of atmospheric precipitation in Londrina, South Brazil (1998–2002). Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6827–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, S.; Hara, H. Precipitation chemistry in western Japan: Its relationship to meteorological parameters. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Wu, Q.; Qu, R.; Ma, Q.; Chen, J.; Mao, S.; Ge, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z. Significant influence of urban human activities and marine input on rainwater chemistry in a coastal large city, China. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E. Composition of atmospheric precipitation. I: Nitrogen compounds. Tellus 1952, 4, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; de la Rosa, J.D.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C.; Gonzalez, I.; Romero, A. Contribution of mine wastes to atmospheric metal deposition in the surrounding area of an abandoned heavily polluted mining district (Rio Tinto mines, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, S.; de la Rosa, J.D.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Fernández-Camacho, R. Heavy metal deposition fluxes affecting an Atlantic coastal area in the southwest of Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Plana, F.; Viana, M.; Ruiz, C.R.; Sanchez de la Campa, A.; de la Rosa, J.; Mantilla, E.; García dos Santos, S. Identification and chemical characterization of industrial particulate matter sources in southwest Spain. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Stein, A.F.; Castell, N.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; de la Rosa, J.D. Modeling and evalua-tion of urban pollution events of atmospheric heavy metals from a large Cu-smelter. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Castanedo, Y.; Moreno, T.; Fernández-Camacho, R.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; de la Rosa, J. Size distribution and chemical composition of particulate matter stack emissions in and around a copper smelter. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Alastue, A.; de la Rosa, J.; Sánchez-de-la-Campa, A.; Plana, F.; Ruiz, C.R. Source apportionment analysis of atmos-pheric particulates in an industrialised urban site in southwestern Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; de la Rosa, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Mantilla, E. Geochemistry and origin of PM10 in the Huelva region, southwestern Spain. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; González Castanedo, Y.; de la Rosa, J.D. Geochemical anomalies of toxic elements and arsenic speciation in airborne particles from Cu mining and smelting activities: Influence on air quality. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 291, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; Alsioufi, L.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; de la Rosa, J.D. Air quality trends in an industrialised area of SW Spain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achterberg, E.P.; Herzl, V.M.C.; Braungardt, C.B.; Millward, G.E. Metal behaviour in an estuary polluted by acid mine drainage: The role of particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.F.O.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Crissien, T.J.; Santosh, M.; Bolivar, J.P.; Shao, L.; Dotto, G.L.; Gasparotto, J.; Schindler, M. A review on the environmental impact of phosphogypsum and potential health impacts through the release of nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Coto, I.; Mas, J.L.; Vargas, A.; Bolívar, J.P. Studying radon exhalation rates variability from phosphogypsum piles in the SW of Spain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sánchez, R.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Kandler, K.; Schneiders, K.; de la Rosa, J.D. Geochemistry and source contribution of fugitive phosphogypsum particles in Huelva, (SW Spain). Atmos. Res. 2019, 230, 104650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sánchez, R.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; de la Rosa, J.D. Hydrogen fluoride concentrations in ambient air of an urban area based on the emissions of a major phosphogypsum deposit (SW, Europe). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistel, J.M.; Marcoux, E.; Thieblemont, D.; Quesada, C.; Sanchez, A.; Almodovar, G.R.; Pascual, E.; Saez, R. The volcanic-hosted massive sulphide deposits of the Iberian Pyrite Belt. Miner. Depos. 1998, 33, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, R.; Millán-Becerro, R.; Basallote, M.D.; Carrero, S.; Parviainen, A.; Freydier, R.; Macías, F.; Cánovas, C.R. Effects of estuarine water mixing on the mobility of trace elements in acid mine drainage leachates. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, J.; Sáenz, V.; Gómez-Parra, A. Heavy metal fluxes at the sediment–water interface of three coastal ecosystems from south-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, J. Ion chromatography—A review of recent developments. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1987, 327, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Appendix B to Part 136. Definition and Procedure for the Determination of the Method Detection Limit; Revision 1.11. Fed. Regist. 49 (209), 43430. Also Referred to as “40 CFR Part 136”; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Jenner, G.A.; Longerich, H.P.; Jackson, S.E.; Fryer, B.J. ICP-MS—A powerful tool for high-precision trace-element analysis in Earth sciences: Evidence from analysis of se-lected U.S.G.S. reference samples. Chem. Geol. 1990, 83, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9001; Quality Management Systems—Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 14001; Environmental Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 3rd ed.; Recommendations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 1, Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/204411/9789241547611_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Morales-Baquero, R.; Pulido-Villena, E.; Reche, I. Chemical signature of Saharan dust on dry and wet atmospheric deposition in the south-western Mediterranean region. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2013, 65, 18720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Rodhe, H. Factors controlling the acidity of natural rainwater. Nature 1982, 295, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Momani, I.F.; Tuncel, S.; Eler, Ü.; Örtel, E.; Sirin, G.; Tuncel, G. Major ion composition of wet and dry deposition in the eastern Mediterranean basin. Sci. Total. Environ. 1995, 164, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikaiakos, J.G.; Tsitouris, C.G.; Siskos, P.A.; Melissos, D.A.; Nastos, P. Rainwater composition in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 1990, 241, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, B.; Bayer, B.; Yesilyurt, C.; Tuncel, G. Ionic composition of precipitation at the central Anatolia, Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 5989–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noli, F.; Sidirelli, M.; Tsamos, P. The impact of phosphate fertilizer factory on the chemical and radiological pollution of the surrounding marine area (seawater and sediments) in northwestern Greece. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 73, 103458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayibi, H.; Choura, M.; López, F.A.; Alguacil, F.J.; López-Delgado, A. Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Arenas, V.M.; Rodríguez, R.; García, C.; Manteca, J.I.; Candela, L. Sulphide-mining impacts in the physical environment: Sierra de Cartagena-La Unión (SE Spain) case study. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranel, M.A.; Kimmel, R.O. Impacts of Lead Ammunition on Wildlife, the Environment, and Human Healthda—A Literature Review and Implications for Minnesota. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife and Humans; Watson, R.T., Fuller, M., Pokras, M., Hunt, W.G., Eds.; The Peregrine Fund: Boise, ID, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, S.; Funk, C.W.; Müller, K.; Raithel, D.J. The chemical composition and sources of road dust, and of tire and road wear particles–A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, E.; Llamas, M.R. Hidrología Subterranea; Omega: Barcelona, Spain, 1996; Volume I and II. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K.; Mays, L.W. Groundwater Hydrology, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wakida, F.T.; Lerner, D.N. Non-agricultural sources of groundwater nitrate: A review and case study. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, G.S.; Hayes, J.V. Acidity and conductivity of precipitation on central Long Island, New York, in relation to meteorological variables. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1981, 15, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granat, L. On the relation between pH and the chemical composition in atmospheric precipitation. Tellus 1972, 24, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Duan, L.; Qu, B. Atmospheric wet deposition of dissolved trace elements to Jiaozhou Bay, North China: Fluxes, sources and potential effects on aquatic environments. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Adhikari, N.P.; Gao, J.; Ahmed, N.; Bhuiyan, A.Q.; Ahsan, A.; Khan, H.R. Atmospheric wet deposition of trace elements in Bangladesh: A new insight into spatiotemporal variability and source apportionment. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contreras-Llanes, M.; Santos-Sánchez, V.; Alguacil, J.; Rodríguez-Pacheco, R. Influence of Phosphogypsum Waste on Rainwater Chemistry in a Highly Polluted Area with High Mortality Rates in Huelva Metropolitan Area, Spain. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073102
Contreras-Llanes M, Santos-Sánchez V, Alguacil J, Rodríguez-Pacheco R. Influence of Phosphogypsum Waste on Rainwater Chemistry in a Highly Polluted Area with High Mortality Rates in Huelva Metropolitan Area, Spain. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073102
Chicago/Turabian StyleContreras-Llanes, Manuel, Vanessa Santos-Sánchez, Juan Alguacil, and Roberto Rodríguez-Pacheco. 2025. "Influence of Phosphogypsum Waste on Rainwater Chemistry in a Highly Polluted Area with High Mortality Rates in Huelva Metropolitan Area, Spain" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073102
APA StyleContreras-Llanes, M., Santos-Sánchez, V., Alguacil, J., & Rodríguez-Pacheco, R. (2025). Influence of Phosphogypsum Waste on Rainwater Chemistry in a Highly Polluted Area with High Mortality Rates in Huelva Metropolitan Area, Spain. Sustainability, 17(7), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073102







