Abstract
The purpose of this study is to explore the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects using corporate reputation and customer satisfaction as mediating variables. This study collected 141 valid data using the questionnaire method and used partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) to analyze the data. The PLS-SEM results showed that, in international construction projects, social responsibility has no direct impact on risk but has a positive impact on corporate reputation and customer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction mediated the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects, but corporate reputation did not mediate this relationship. This study also found that corporate reputation and customer satisfaction have a serial mediating role in this relationship. In addition, the fsQCA results further confirmed that improving customer satisfaction is a necessary condition for mitigating risks in international construction projects. In terms of the different dimensions of social responsibility, the protection of shareholders’ rights is a core condition for mitigating risks in international construction projects. This study provides useful insights for international construction project managers to develop risk mitigation plans from the perspective of social responsibility.
1. Introduction
International construction projects often face high risks in host countries due to a volatile international environment, cultural differences, and uncertainty [1,2]. If these risks are not properly handled, they can bring huge economic losses to international construction enterprises, as well as damage corporate image and international relations [3]. Therefore, it is important to effectively mitigate the risks of international construction projects to ensure the smooth implementation of the project in the host country. The existing studies on risk management have shown that construction enterprises, through risk prediction [4], risk identification [5], risk assessment [6], risk monitoring [7], and development of risk management plans [8], can effectively avoid and manage risks when implementing projects. However, risk cannot be completely avoided, and it is essential for international construction enterprises to learn how to improve project competitiveness in order to cope with risk shocks.
The existing research indicates that construction enterprises can improve construction efficiency and quality and enhance the comprehensive competitiveness of projects by strengthening technological innovation, thus mitigating the impact caused by risks [9]. In addition, some scholars have found that firms carrying out the following social responsibility actions can also improve firms’ competitiveness and help them better cope with external shocks; these actions include strengthening compliance management [10], complying with environmental rules [11], making charitable donations [12], and protecting stakeholders’ rights [13]. These studies provide new ideas for mitigating international construction project risks. Social responsibility serves as an effective tool and competitive strategy for companies to improve profitability, customer satisfaction, project performance, and corporate image [14,15,16]. Whether the implementation of social responsibility will mitigate the risks of international construction projects is still a question that deserves to be examined.
To better explain the mechanism of influence between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects, this study introduces the following mediating variables: customer satisfaction and corporate reputation. In international construction enterprises, customers act as important stakeholders and provide financial support for the projects [6]. Based on signaling theory, social responsibility functions as a signal sent by firms to customers and other stakeholders and affects customers’ perception of the firm and, thus, customer satisfaction [14,17]. Customers with high satisfaction are more willing to pay for corporate social responsibility (CSR) [18]. However, it is unclear whether risk shocks faced by international construction projects are mitigated by increasing customer satisfaction. Additionally, an increasing number of studies show that the active implementation of social responsibility by firms enhances corporate reputation, and a good corporate reputation can mitigate the impact of external shocks on firms [19]. However, when international construction enterprises build projects in host countries, project construction is a one-time process, and the enterprises usually leave once the project is completed. Therefore, whether the established corporate reputation can mitigate the risks faced in international construction projects remains a question to be analyzed.
In addition, there are multiple stakeholders in international construction projects. Considering the differing needs of different stakeholders, this study first identifies the stakeholders of international construction projects and develops a social responsibility questionnaire of international construction projects to measure social responsibility. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) were employed to analyze the data collected from 141 valid questionnaires. The objectives of this study are as follows: (1) to analyze the risk mitigation effects of social responsibility in international construction projects; (2) to examine the mediating roles of corporate reputation and customer satisfaction; and (3) to explore the configuration paths and core conditions for reducing risks in international construction projects. The remaining sections of the paper are arranged as follows: Section 2 examines the theoretical foundation and develops the research hypotheses. Section 3 presents the research methodology. Section 4 describes the results of the data analysis. Section 5 discusses the study findings and points out the limitations of this study. Section 6 reports the conclusion.
2. Theoretical Foundation and Hypotheses
2.1. Social Responsibility and Risk in International Construction Projects
Social responsibility refers to the obligation of businesspeople to make policies and decisions and to carry out actions that are in line with the objectives and values of society [20]. CSR implies that companies should voluntarily assume their social responsibility to be ethical in all their activities and consider the impact of their actions on their stakeholders, while contributing to global sustainability [21]. To help companies better fulfill social responsibilities, Zhang et al. [22] categorized the social responsibility of construction firms into eight key dimensions, which cover aspects such as shareholders’ rights, government commitment, and environmental protection. Alqershy and Shi [23] incorporated economic, environmental, legal, political, and philanthropic factors into the scope of social responsibility for the “Belt and Road” mega infrastructure projects. Ye et al. [24] suggested that the strategy of glocalisation is key for international construction companies to achieve CSR objectives in a globalized market. By combining globalization and localization approaches, companies can better adapt and respond to the social and environmental needs of different host countries while maintaining global consistency. Zhao et al. [25] proposed that the stakeholders of construction enterprises are employees, shareholders, customers, suppliers and partners, government, resource and environmental agencies, local communities, competitors, and public interest organizations. Drawing on the above existing research findings and through expert interviews, this study categorizes social responsibility in international construction projects into the following seven dimensions: shareholders rights, employee rights and career development, customer rights, supply chain management, environmental protection, fair competition, and community involvement and development.
International construction projects are defined as projects undertaken by construction companies outside their home country [19]. Risk is defined as uncertain events or conditions that may positively or negatively affect the project objectives [26]. In host countries, uncertainty of political events [27], economic fluctuations, and differences in national legal systems [28] result in international construction projects being exposed to political, economic, and legal risks. In addition, international construction projects are characterized by a long construction period, a large amount of capital, numerous participants, and increased technical requirements [29,30]. Because these projects are constrained by local laws, practices, the labor force, material conditions, and other factors [31], managing international construction projects is not an easy task. Research has found that the lack of contractor management ability is an important factor affecting the project schedule [32]. Hence, this study argues that international construction enterprises also face project management risks in host countries. These risks usually have a negative impact on project objectives and may lead to project termination. Therefore, this study focuses on measuring the impact of political, economic, legal, and project management risks on international construction projects.
Research on the relationship between social responsibility and risk currently holds two views: fulfilling social responsibility mitigates risk or exacerbates risk. The risk mitigation perspective suggests that firms engage in social responsibility activities to build ethical capital and thus mitigate the adverse effects of negative events [33]. From the point of view of increasing risk, social responsibility can lead to an increase in various costs and burdens, a reduction in business performance, and to some extent, a weakening of the competitiveness of companies [34]. However, some scholars have also found that although carrying out social responsibility activities can increase the cost of the firm in the short term, it can increase the revenue and value of the firm in the long term [35]. For example, Kim et al. [36] found that firms can increase their value and thus reduce future risks by accepting social responsibility. This study argues that international construction enterprises can improve project competitiveness and send a signal to stakeholders that the project is reliable by engaging in social responsibility activities when constructing projects in the host country. This signal can mitigate risk shocks faced by international construction projects when risks occur. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypothesis:
H1:
social responsibility has a negative impact on risk in international construction projects.
2.2. Social Responsibility, Corporate Reputation, and Risk in International Construction Projects
Corporate reputation is defined as the overall impression that reflects the perceptions of a collective group of stakeholders [37]. A company’s reputation is arguably its most valuable asset [38]. Peloza [38] argued that participation in social responsibility activities is similar to purchasing insurance for a company’s reputation. In today’s globalized business environment, companies seek advantages in the intense market competition. Social responsibility activities can be a strategic tool for firms to manage their relationships with multiple stakeholders, as these activities help firms to send the right signals to different stakeholders and shape their reputation perceptions [39]. Moreover, social responsibility initiatives can foster positive relationships between firms and stakeholder groups, as well as enhance corporate reputation [15,40]. On the basis of the above analysis, this study argues that international construction enterprises can also improve their corporate reputation by performing socially responsible actions when carrying out projects in host countries.
In addition, corporate reputation plays an essential role in reducing the uncertainty encountered by stakeholders in evaluating a company [41]. A good corporate reputation can act as a signal to convey internal corporate information to stakeholders, reduce information search costs, enhance trust, and mitigate the effects of market volatility. The existing literature argues that when firms are faced with negative events, the corporate reputation developed through the fulfillment of social responsibility can serve as a safeguard and mitigate the impact of these events on the social legitimacy of the firm [42]. Liu and Lu [43] found a negative relationship between corporate reputation and firm risk based on a study of data from Fortune magazine’s Most Admired Companies list. This study argues that when international construction enterprises have a good reputation, stakeholders such as owners, governments, and partners consider the enterprise more trustworthy, which reduces their perception of risk in construction projects. In view of the above analysis, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H2a:
social responsibility has a positive impact on corporate reputation in international construction projects.
H2b:
corporate reputation has a negative impact on risk in international construction projects.
H2c:
corporate reputation mediates the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects.
2.3. Social Responsibility, Customer Satisfaction and Risk in International Construction Projects
Customer satisfaction is defined as the positive response of customer fulfillment [44]. CSR affects the behavior of customers or other stakeholders towards a company, including whether they show loyalty, support, or satisfaction [45]. Most customers expect a company to engage in social responsibility activities related to employees, community involvement, the environment, and ethics [46]. Lee et al. [47] found that economic, ethical, and philanthropic CSR are important contributors to improving brand attitudes and service quality, contributing to higher customer retention rates. The social responsibility activities of a company can also leave a positive impression on customers, thus improving their attitudes and evaluations of the company [48]. Customers tend to support and identify with companies that engage in social responsibility because these companies care about the public and provide services to the public [49]. Therefore, this study hypothesizes that international construction enterprises engaging in social responsibility activities while carrying out projects in host countries can also attract potential customers and enhance customer satisfaction.
Moreover, CSR is a signal that companies are customer-focused and strive to maintain stakeholder relationships by incorporating social responsibility practices into company processes, thereby reducing customer risk [17]. Customer satisfaction is also an evaluation that is based on a comparison between the actual experience and the perceived experience [50]. When customer satisfaction is high, it means that customers are satisfied with the product or service, and this positive evaluation can be used as a signal to stakeholders or other potential customers, which can reduce the risk of international construction projects. In addition, research has found that in order to enhance customer satisfaction, more construction companies are adopting green materials and advanced technologies in the project construction process to reduce costs and improve project quality [16,51]. Based on the above analysis, this study argues that the fulfillment of social responsibility in international construction projects can also improve customer satisfaction and thus reduce risk. Therefore, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H3a:
social responsibility has a positive impact on customer satisfaction in international construction projects.
H3b:
customer satisfaction has a negative impact on risk in international construction projects.
H3c:
customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects.
2.4. Social Responsibility, Corporate Reputation, Customer Satisfaction, and Risk in International Construction Projects
Reputation is a motivation for construction enterprises to adopt social responsibility and an effective way for them to maintain brand differentiation in a sustainable way [16]. The competitive advantage of differentiation makes a firm’s products and services more attractive to customers, thus increasing customer satisfaction. Research has shown that customer needs and satisfaction are key factors for the success of construction enterprises [52]. Moreover, the extant literature shows that a firm’s reputation serves as a signal to customers, reducing their uncertainty [53]. In situations where information is incomplete, customers often rely on a company’s reputation to judge the quality of its products or services or to anticipate its future actions [54]. Therefore, this study infers that in the international market, if a company has a good reputation, this indicates that the company’s products and services are more trustworthy, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Previous studies have also revealed that corporate reputation has a positive impact on customer satisfaction [53,55,56]. Combined with the above analysis, we speculate that corporate reputation and customer satisfaction have a serial mediating role between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects. Thus, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H4a:
corporate reputation has a positive impact on customer satisfaction in international construction projects.
H4b:
corporate reputation and customer satisfaction serially mediate the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects.
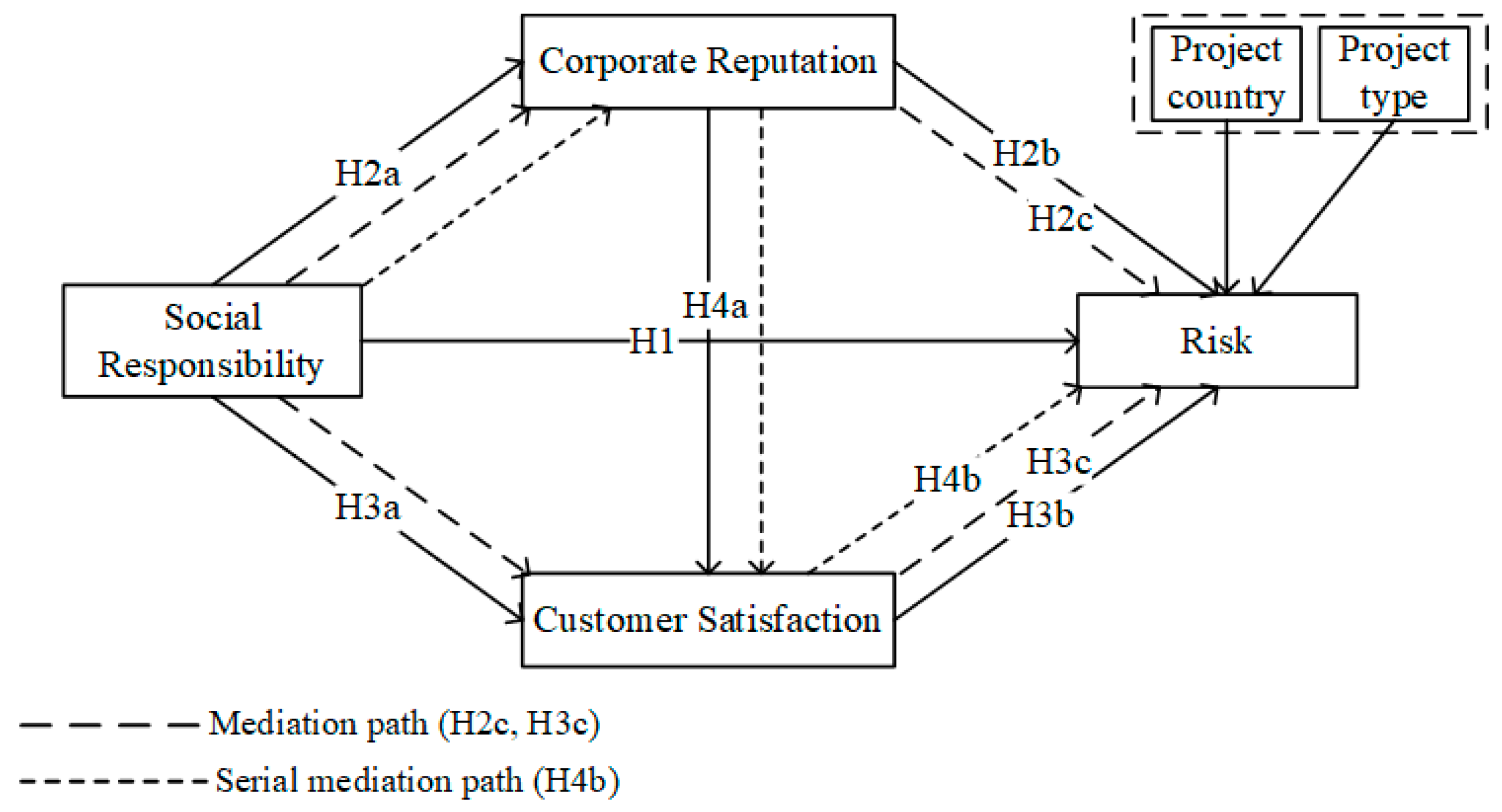
As shown in Figure 1, this study proposed a conceptual model to examine the impact of social responsibility on risk in international construction projects and to determine whether corporate reputation and customer satisfaction serve as mediators in these relationships. Due to the varying risks that different types of international construction projects face in different countries [57], this study chooses the project country and project type as control variables to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the research results.
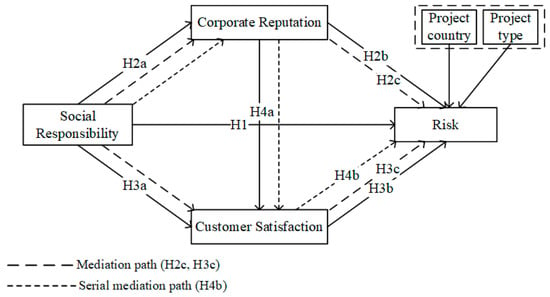
Figure 1.
Conceptual model.
3. Methodology
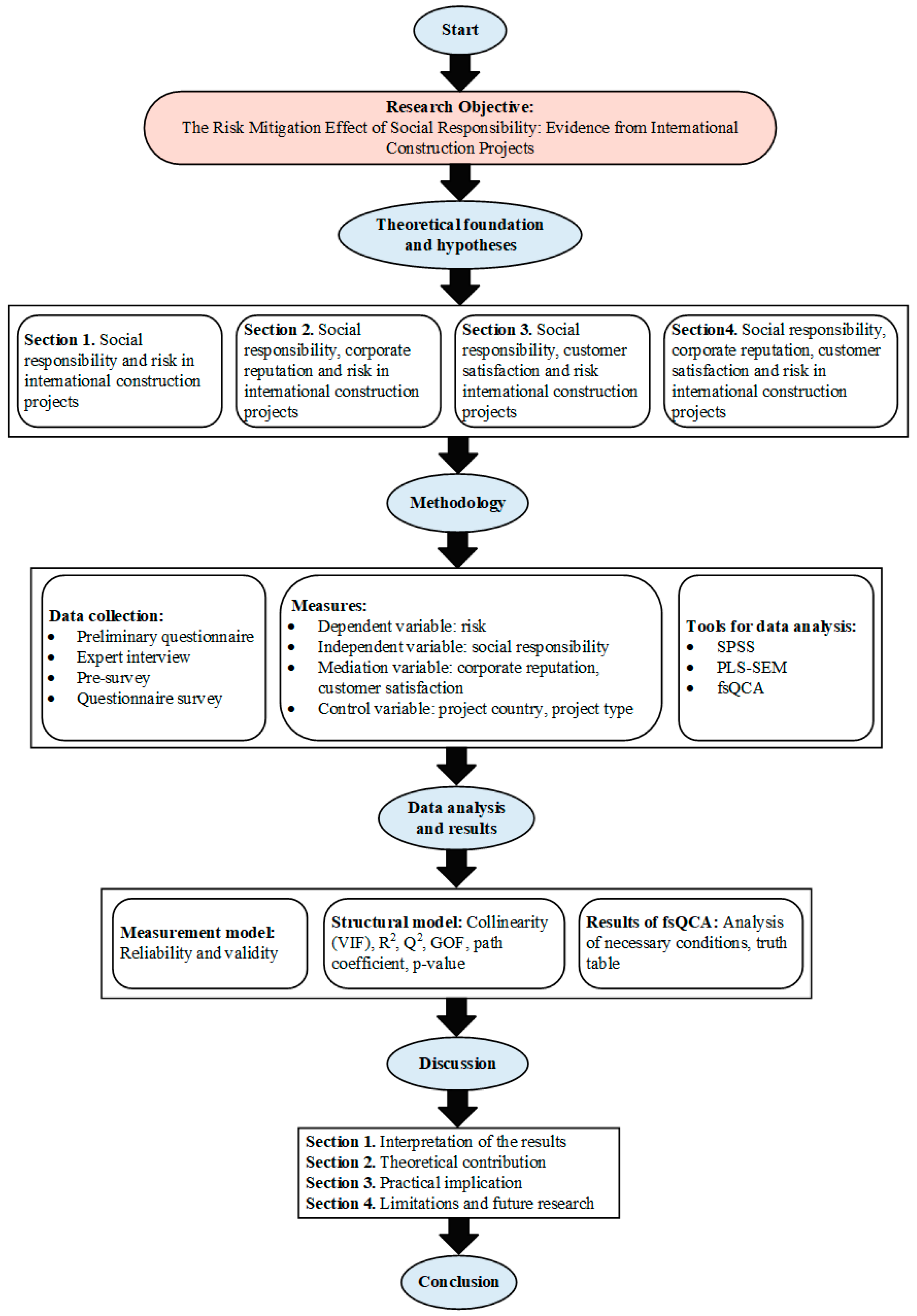
This study provided a research roadmap (Figure 2) that includes all the steps to explore how social responsibility affects risk in international construction projects.
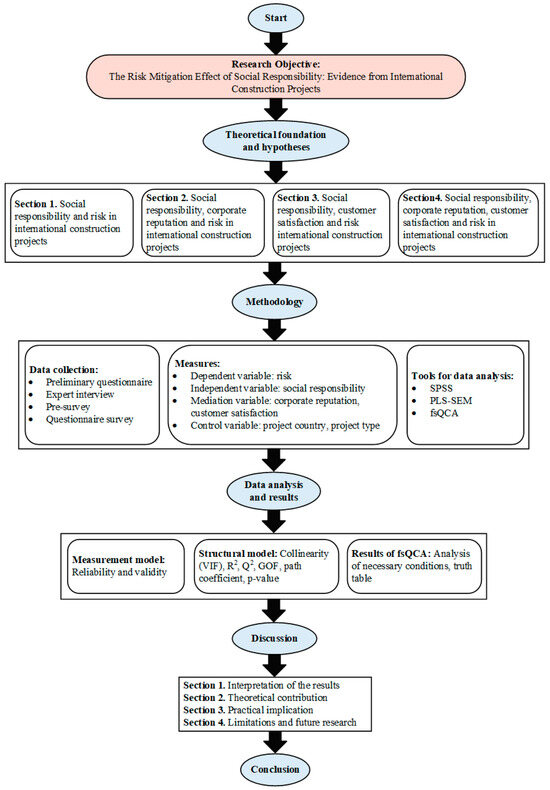
Figure 2.
Research roadmap.
3.1. Data Collection
In this study, the questionnaire method was used to collect data. First, this study conducted an extensive literature review; then, the study compiled a preliminary questionnaire based on mature scales from related studies, referring to existing research results and combining these with the actual situation of international construction projects. Second, this study invited experts with extensive experience in international construction project management to conduct interviews. According to their comments, this study revised the question scenarios in the questionnaire for construction field scenarios. In addition, the study corrected vague concepts and improper wording in the questionnaire items to make the questionnaire easier to understand and answer. Third, to ensure the reliability of the questionnaire, a pre-survey was conducted in this study. The pre-survey mainly invited interview experts and experienced international engineering project managers to fill in the questionnaires, and a total of 61 valid questionnaires were collected. This study conducted a reliability test on the data, and the results showed that the overall Cronbach’s alpha value was 0.946, and the Cronbach’s alpha values of all latent variables were higher than 0.6, which indicated that the questionnaire had good reliability and internal consistency. Fourth, this study used snowball sampling to conduct the questionnaire survey and distributed the questionnaires through email and online links to managers who have experience in international construction projects and understand the daily workflow of the projects; these managers subsequently forwarded the questionnaires to their acquaintances who meet these conditions.
The questionnaire consists of two parts: in the first part of the questionnaire, respondents are required to provide basic background information, including their position, work experience, country of the project, the type of project, etc. The questionnaire was initially screened based on the background information provided by the respondents. The second part consisted of specific questions, and respondents were asked to score each question. The study screens the final compliant questionnaires based on the completeness and quality check of the questionnaire responses. To ensure the accuracy of respondents’ responses, two measures were implemented in this study. First, since the questionnaire was collected online, to increase respondents’ motivation and to answer the questionnaire questions carefully, we offered each respondent a reward of RMB 50 (about USD 7). We stated in the invitation to the questionnaire that the reward would only be provided if the respondent filled out the questionnaire completely and carefully and passed the quality check. Second, attention checking was used in this study, where we designed the answers to a question to be reversed, and the questionnaire was invalidated if the respondents answered inconsistently. Finally, in this study, 357 questionnaires were distributed, and 141 valid questionnaire data were obtained, with an effective response rate of 39.50%. In construction enterprises, most questionnaires have a response rate of 15–30% [22,58,59]; thus, the questionnaire response rate in this study is appropriate. All participants in this study voluntarily participated and were informed in advance that the survey data would only be used for academic research. The study also assured the participants that no project or personal information would be disclosed. Additionally, all participants participated anonymously. All items except demographic information and sample characteristics were measured on a five-point Likert-type scale. Table 1 presents the demographic information and sample characteristics.

Table 1.
Demographic information and sample characteristics.
3.2. Measures
The measurement items were adapted from previously verified studies. The independent variable in this study is social responsibility, the mediating variables are corporate reputation and customer satisfaction, and the dependent variable is risk. Table 2 presents the items and sources. Social responsibility was adapted from the scale developed by Zhang et al. [22], Zhao et al. [25], Ye et al. [24], and Li et al. [60] and is organized into seven dimensions consisting of 26 items. The four items measuring corporate reputation were adapted from the variable scale developed by Fombrun et al. [61]. The four items measuring customer satisfaction were adapted from the scale developed by Galbreath and Shum [62] and by Zeithaml et al. [63]. The four items measuring risk were adapted from the scale developed by Ling and Hoang [28], Jung and Han [64], and Dandage et al. [26].

Table 2.
Measurement items.
3.3. Tools for Data Analysis
Before constructing the structural equation model, this study used item parceling to transform the seven dimensions of social responsibility into seven indicators. Item parceling involves packaging two or more items from the same scale into a new indicator and using the synthetic scores (total or mean) as the scores of the new indicator for analysis [65,66]. This study uses the mean as the score for the new indicator. Each dimension of the item parceling adopted in this study contained three or more question items. Item parceling will result in indicators with greater reliability and in more stable parameter estimates [67]. In addition, with the item parceling, the ratio between free parameters and the sample size used in this study was greater than the minimum requirement of 1:5 [68]. Therefore, it is appropriate to use the item parceling in this study.
Then, this study used PLS-SEM to test the hypotheses. PLS-SEM is suitable for small sample size studies [69]. Hair et al. [70] stated that the sample size for PLS-SEM should be at least 10 times the maximum number of paths of the latent variables. The sample size of this study is greater than 10 times the maximum number of paths of latent variables in the internal model. Therefore, the sample data of 141 were sufficient in this study. Moreover, the structural model in this study is complex and contains many structures, indicators, and model relationships, while PLS-SEM is suitable for constructing complex models containing multiple metrics or structures [69]. Furthermore, this study included mediating variables, and the PLS-SEM built-in bootstrap method technique outperformed the causal stepwise method and the Sobel test when analyzing mediating effects [71]. Therefore, it is appropriate to use PLS-SEM in this study.
Finally, this study used fsQCA to explore the core conditions and configuration paths that lead to low risk in international construction projects. In contrast to traditional regression-based techniques, fsQCA is an asymmetric approach that examines the relationship between antecedent conditions and outcomes, which implies that different combinations of causal conditions may produce the same results. fsQCA can reveal how multiple factors interact to affect the outcome variable and identify multiple configuration paths that lead to low risk in international construction projects [72]. In addition, the fsQCA data in this study were obtained from 141 valid questionnaire data. The data were calibrated in this study to ensure that the quality of the data met the requirements of fsQCA. Fiss [73] pointed out that fsQCA is not only applicable to large samples but also particularly suitable for small samples because it can identify complex causal relationships and the possibility of multiple explanations. When analyzing data using fsQCA, it is important to pay attention to the choice of threshold. With a properly set threshold, fsQCA can be applied even to small samples [74,75]. Therefore, fsQCA is applicable to this study.
4. Data Analysis and Results
4.1. Measurement Model
As shown in Table 3, the values of the outer loadings for all observed variables are between 0.684 and 0.871, which is above the 0.50 threshold [76]. This proves that the values of outer loadings are acceptable and very reliable. To assess the reliability of internal consistency, Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability were calculated. In Table 3, the Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability values for all constructs are above the recommended value of 0.7 [69], indicating good internal consistency reliability. The appropriate average variance extracted (AVE) is 0.50 or higher, suggesting that the construct explains a minimum of 50% of the variance of its items [69]. The convergent validity of this study was as expected, as the AVE values for all constructs exceeded the critical value of 0.50, which was between 0.553 and 0.696. The Fornell–Larcker criterion and heterotrait–monotrait ratio of correlations (HTMT) criterion were used to assess the discriminant validity. The Fornell–Larcker criterion requires that the AVE square root of each construct should be higher than the link between constructs [77] and that the HTMT value between two constructs should be less than 0.85 [69]. As shown in Table 4, all data meet these requirements. In general, these data results meet the reliability and validity criteria of the measurement model in this study.

Table 3.
Measurement model results.

Table 4.
Discriminant validity.
4.2. Structural Model
To ensure that collinearity does not skew the regression results, it must be investigated prior to evaluating the structural correlations. VIF values of 5 or above indicate critical collinearity issues [69]. The data analysis results revealed that the VIF values of internal models were from 1.000 to 1.664 and that the VIF values of external models were from 1.371 to 3.568. The VIF values for every construct are less than 5, proving that there is no collinearity problem. To make sure that the model fit meets the requirements, R2, Q2, and goodness of fit (GoF) were calculated in this study. R2 is referred to as the coefficient of determination and is used to measure the predictive accuracy of a structural model. Chin [78] suggests that when the value of R2 is greater than 0.67, 0.33, and 0.19, the model is considered substantial, moderate, and weak, respectively. When the value of R2 is less than 0.19, it indicates that the model is unacceptable [78]. As shown in Figure 3, the R2 of all endogenous latent variables in this study is greater than 0.19, which indicates that the explanatory power of the model is good. In addition, the Q2 values of all endogenous latent variables in this study are above zero, indicating that the model has good predictive power [69]. GoF was used in this study to test the model fit; when GoF is less than 0.1, the model fit is not good; when GoF is greater than 0.36, the model fit is good. The GoF for this study was calculated to be 0.46, indicating that the model fit was good [79].
where is the average of all AVE and is the average of all R2.
In order to guarantee the robustness of the results, this study calculated the path coefficients and p-values by carrying out 5000 resamples using the bootstrap method [69]. The results in Table 5 show that social responsibility has a significant positive effect on corporate reputation (H2a: β = 0.633, p < 0.001) and customer satisfaction (H3a: β = 0.410, p < 0.001); thus, H2a and H3a are supported. Corporate reputation has a significant positive effect on customer satisfaction (H4a: β = 0.339, p < 0.01), supporting H4a. Customer satisfaction has a significant negative effect on risk in international construction projects (H3b: β = −0.534, p < 0.001), which supports H3b. Additionally, social responsibility and corporate reputation have no direct impact on risk in international construction projects: H1 and H2b are not supported.

Table 5.
Structural model result and hypothesis decision.
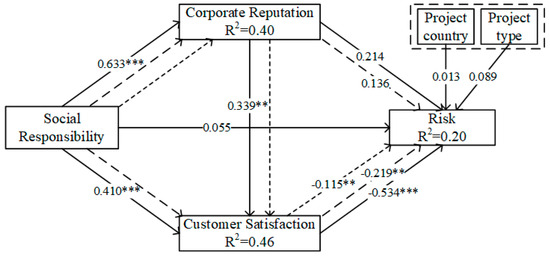
Figure 3.
Results for structural model (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
Figure 3.
Results for structural model (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
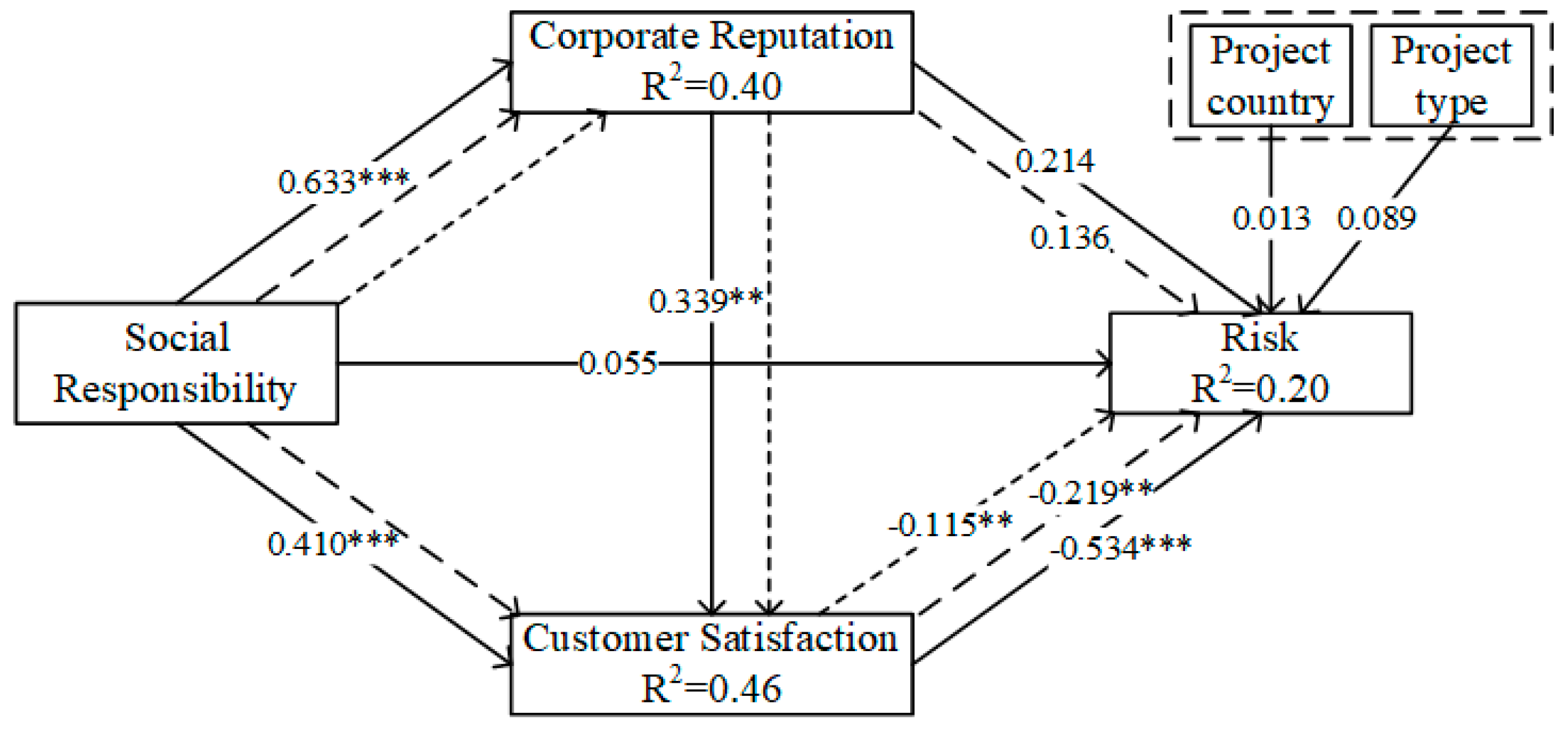
According to Table 5, customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects (H3c: β = −0.219, p < 0.01), supporting H3c. Furthermore, corporate reputation has no mediation effect between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects (H2c: β = 0.136, p > 0.05), H2c is not supported. The results also confirm that corporate reputation and customer satisfaction have a chain mediating role between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects (H4b: β = −0.115, p < 0.01); thus, H4b is supported. Finally, as shown in Figure 3, the results also indicate that the two control variables—project country and project type—have no significant effect on the risk of international construction projects.
4.3. Results of fsQCA
This study adopted fsQCA to investigate the synergistic effect of multiple factors on the risk of international construction projects. Data calibration, necessary condition analysis, truth table construction, and causal condition analysis are necessary steps in the data analysis process. First, this study performed data calibration, using 95% as the full membership threshold, 50% as the turning point for maximum ambiguity, and 5% as the non-membership threshold [80]. Second, there was an assessment of whether any of the causal conditions might be necessary. On the basis of the QCA method, a condition is considered necessary for the occurrence of the result when the consistency level is greater than 0.9 [75]. As shown in Table 6, the results indicate that none of the variables are a necessary condition for causing a high degree of risk in international construction projects. However, it is observed that the presence of the condition of customer satisfaction is necessary to reduce risk in international construction projects.

Table 6.
Analysis of necessary conditions.
Next, by specifying a consistency threshold of 0.8 and a number-of-cases threshold of 1, a truth table is constructed to generate different combinations of causal conditions sufficient to achieve low risk in international construction projects. Finally, this study uses standard analysis to obtain “intermediate solutions” to identify causal patterns that lead to low risk in international construction projects. Table 7 and Figure 4 summarize the results of the intermediate solutions for low risk. As shown in Table 7, the consistency levels of the individual and overall solutions of the four configurations presented in the table are above the level of 0.75 [81], and most of the coverage values are between 0.228 and 0.647 [72]. This implies that the model is informative [82].

Table 7.
Intermediate solutions for low risk in international construction projects.
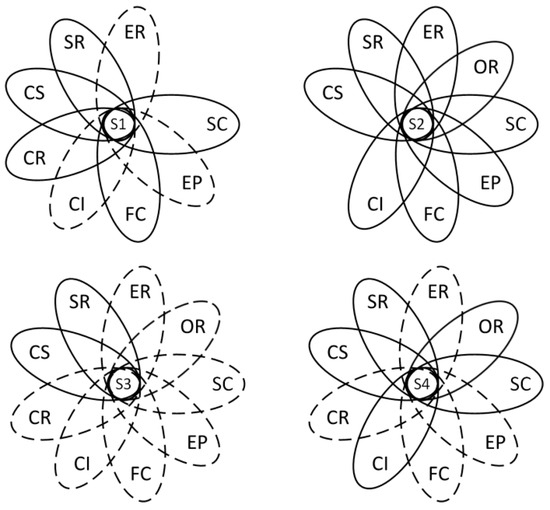
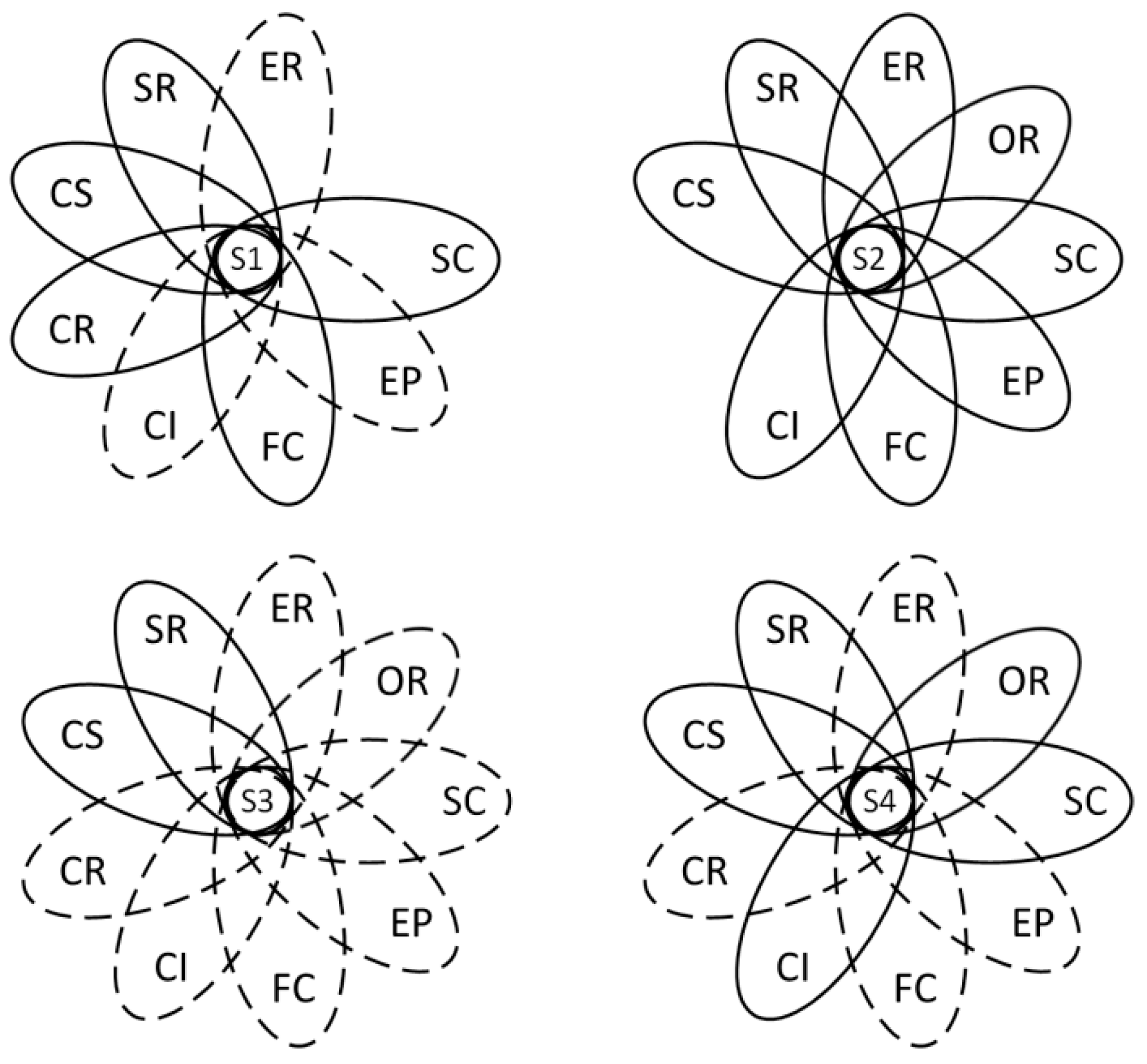
Figure 4.
Causal configurations for low risk in international construction projects. Note: An ellipse with a solid line indicates the presence of a condition, while an ellipse with a dashed line indicates the absence or negation of a condition. If the condition is not relevant to the configuration, no ellipse is displayed.
Solution 1 shows that in international construction projects, shareholder rights and customer satisfaction are core conditions for risk mitigation, and supply chain management, fair competition, and corporate reputation are peripheral conditions. The raw coverage shows that this solution explains 23.2% of the sample. Solution 2 shows that in international construction projects, shareholder rights, employee rights, owner rights, and customer satisfaction are core conditions for risk mitigation, and supply chain management, environmental protection, fair competition, and community involvement and development are peripheral conditions. The raw coverage shows that the solution explains 41.4% of the sample. Solution 3 indicates that in international construction projects, shareholder rights and customer satisfaction are core conditions for risk mitigation, and the raw coverage shows that this solution explains 28.2% of the sample. Solution 4 shows that in international construction projects, shareholder rights and customer satisfaction are core conditions for risk mitigation, and customer rights, supply chain management, community involvement and development are peripheral conditions for risk mitigation; in addition, the raw coverage shows that this solution explains 17.2% of the sample. As can be seen from the four solutions above, shareholder rights and customer satisfaction are the core conditions for mitigating risks in international construction projects. This study also tested the robustness of the fsQCA results by adjusting the consistency threshold from 0.80 to 0.85 with all other treatments unchanged. This result shows that the configuration paths, the core condition, and the peripheral condition have not essentially changed, further suggesting that the results of the study are robust.
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of the Results
By adopting PLS-SEM, this study validates the research hypotheses between social responsibility, corporate reputation, customer satisfaction, and risk in international construction projects. In addition, by using fsQCA, this study proposes four configuration paths to reduce the risk of international construction projects. The main findings are as follows.
First, in international construction projects, social responsibility has no direct impact on risk. While many studies have shown that practicing social responsibility can have beneficial effects on construction enterprises, this study argues that these potential benefits are often not immediately apparent. Through interviews, we also found that the implementation of social responsibility lays the foundation for the survival of international construction enterprises in the host country and improves the competitiveness of the project by, for example, reducing employee turnover, enhancing technological advantage, and attracting customer investment. However, the risks faced by international construction projects are complex and varied, and this study finds that improving project competitiveness by implementing social responsibility is not sufficient to effectively reduce these risks. Moreover, for companies with limited resources and capabilities, the excessive pursuit of social responsibility is, rather, a burden [83]. In addition, international construction projects are usually larger in scale, more technically and organizationally complex, and involve multiple countries and regions, each with different cultural, legal, and social needs. Therefore, if international construction enterprises fail to accurately match the local needs of their projects, their socially responsible behavior may be ineffective or even counterproductive.
Second, from the analysis of the results, consistent with most of the previous studies, fulfilling social responsibility can enhance corporate reputation [15,40]. However, the increase in corporate reputation has no effect on risk in international construction projects, contrary to the findings of Boubaker et al. [84]. This study posits that the fulfillment of social responsibility may enhance corporate reputation in the short term, but the formation of a good corporate reputation requires long-term efforts [85]. Although most studies have shown that good corporate reputation mitigates risk [42,43], the reputation accumulated in the short term by performing social responsibility may not be sufficient to reduce the risk faced by international construction projects. Furthermore, through interviews, this study found that, influenced by project characteristics, international construction enterprises undertake projects in different country regions and that the corporate reputation established by implementing social responsibility in one place is seldom recognized and disseminated in other regions.
Third, in this study, it can be seen that fulfilling social responsibility can improve customer satisfaction, and customer satisfaction has a significant negative effect on risk in international construction projects. Customers are more satisfied with the quality, service, and pricing of projects delivered by international construction enterprises that actively fulfill social responsibility. Such enterprises are also more likely to gain the recognition of existing customers, thereby obtaining new customers recommended by these existing customers. This provides them with a more favorable market position in the host country, thereby reducing the risks associated with international construction projects. Analysis of the chained mediating effect of corporate reputation and customer satisfaction reveals that fulfilling social responsibility contributes to economic, social, and environmental development, as well as to the progress of local communities [86]; enhances the local recognition and reputation of the enterprise [14]; and further enhances customer satisfaction [15], thereby reducing the risk of international construction projects.
Finally, the fsQCA results further elucidate the configuration effects, enhancing the understanding of how multiple factors interact to mitigate risks. Based on the fsQCA results, customer satisfaction is a necessary condition for reducing risk in international construction projects. This finding further validates the results of the PLS-SEM analysis. Furthermore, solutions 1, 2, 3, and 4 show that the active fulfillment of social responsibility in relation to shareholders is a core condition for reducing risk in international construction projects. It has been pointed out that the company’s participation in social responsibility activities not only maximizes shareholder value but also ensures the long-term survival of the company [13]. This study further confirms the view that managers protecting the interests of shareholders will reduce the risks faced by the firm [87]. In addition, the four configuration paths also indicate that the active fulfillment of social responsibilities related to employees, suppliers, subcontractors, government, and the community can also contribute to the reduction of risk in international construction projects. The importance of stakeholders, such as employees, suppliers, subcontractors, governments, and the community, in reducing risk in international construction projects is related to the combination of variables in different configuration paths.
5.2. Theoretical Contribution
This study enriches the research on social responsibility in international construction projects. First, this study proposes a conceptual framework for social responsibility in international construction projects based on stakeholder theory, which provides a useful reference for international construction project managers to develop social responsibility strategies. Second, this study expands the application of signaling theory in practice. The study found that in international construction projects, social responsibility, as a signal to stakeholders, positively affects customer perceptions and enhances customer satisfaction. This study also confirms that improving customer satisfaction mitigates the risk shocks faced by international construction projects. Third, this study uses fsQCA to identify shareholder rights as a core factor in mitigating risk in international construction projects, providing useful recommendations for international construction enterprises to mitigate project risk in the future. Finally, this study proposes four configuration paths for mitigating risks in international construction projects based on the results of fsQCA, which provides a useful reference for international construction project managers to develop the next stage of social responsibility action plans.
5.3. Practical Implication
This study provides guidance for international construction enterprises to better formulate social responsibility plans, build a good corporate image, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce risks in international construction projects. International construction enterprises are able to achieve improved corporate reputation and customer satisfaction, reduce project risks, and ultimately, contribute to the successful delivery of international construction projects by fulfilling social responsibilities based on their resources and capabilities. In international construction projects, the project manager is the primary person in charge. In order to mitigate the impact of risks faced by international construction projects in the host country, project managers should actively carry out social responsibility actions to establish a good relationship with customers and enhance customer satisfaction. Project managers should fully understand customers’ needs and expectations, establish a customer-centered service system, and provide customers with valuable products and services through effective communication and research. In addition, project managers should protect shareholders’ rights by providing them with timely and accurate information and reports, as well as stable financial returns, when developing social responsibility programs. Beyond protecting the interests of customers and shareholders, international construction project managers should also develop a detailed social responsibility plan and perform proactive social responsibility actions to protect the interests of stakeholders such as employees, suppliers, and local residents.
In addition, the main participants in international engineering projects include owners, designers, contractors, and engineers. In order to better fulfill social responsibility, enhance customer satisfaction, and mitigate risks, project participants can carry out the following measures. First, when selecting contractors, owners should prioritize those contractors with good social responsibility records and clearly express social responsibility needs to them, which will enable contractors to perform better social responsibility actions [22]. Secondly, the designers can design for environmental protection according to the owner’s social responsibility needs and integrate the host country’s cultural elements into the design. During the design process, designers should also give full consideration to the project’s impact on the environment and use sustainable building materials and energy-saving technologies to reduce the consumption of natural resources and reduce damage to the ecological environment [88]. Thirdly, the contractor should ensure the quality of the project while delivering it on time. During the construction process, the contractor should strictly follow the construction safety codes to ensure the safety of construction workers. The contractor should implement effective environmental protection measures to minimize the impact of construction on the surrounding environment [89]. Finally, the engineers should strictly supervise the quality of the project during the construction process to ensure that the project meets the design requirements and safety standards [90]. To help owners and contractors make reasonable decisions, engineers should provide them with accurate and comprehensive engineering information and professional advice. By actively carrying out the above social responsibility actions, international engineering project participants can reduce project risks while allowing the project to develop in a sustainable direction.
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
This study also has some limitations that provide direction for future research. First, this study only examined the mediating roles of corporate reputation and customer satisfaction, and further research is needed to determine whether there are other variables that influence the relationship between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects. Second, this study used the snowball sampling method to collect data; snowball sampling relies on the subjective selection of initial contacts, which may result in the sample being biased toward individuals who are similar to the initial contacts, thus losing representativeness. In future research, the snowball sampling method can be combined with the stratified sampling method when collecting data to improve the representativeness and diversity of the sample. Third, the data of this study mainly come from international construction projects undertaken by Chinese international construction enterprises, but these projects are widely distributed and involve multiple countries and cultural backgrounds; therefore, the results are still somewhat generalizable and can provide reference for international construction enterprises in other countries. However, the sample of this study cannot cover the current situation of all international construction projects. Future research can establish a database of international construction projects that includes multiple countries and regions in order to accurately reveal various phenomena and patterns in international construction projects. Finally, the cross-sectional data collected in this study only reflect the situation at a particular point in time and cannot capture the trend of changes in the variables over time. Future research can adopt a longitudinal tracking design to track the changes in the same group of study subjects at different points in time, thus providing a deeper understanding of the dynamic relationship between variables and improving the validity of the study.
6. Conclusions
This study analyzes the risk mitigation effects of social responsibility in international construction projects using two data analysis tools—PLS-SEM and fsQCA—and using corporate reputation and customer satisfaction as mediating variables. The results of PLS-SEM show that social responsibility has no direct effect on risk in international construction projects. However, risk in international construction projects can be significantly reduced by the mediating variable of customer satisfaction or by the sequential mediating variables of corporate reputation and customer satisfaction. The results of fsQCA show that customer satisfaction is a necessary condition for risk reduction. Using the truth table algorithm, this study produces four configuration paths that will decrease risk in international construction projects. By further analyzing the fsQCA results, this study concludes that the active implementation of social responsibility related to shareholders is a core condition for reducing risk in international construction projects. Fulfilling social responsibility in relation to employees, suppliers, subcontractors, governments, and the community also plays an important role, to varying degrees, in different configuration paths to reduce risk in international construction projects. This study expands the application of stakeholder theory and signaling theory in practice. The findings reveal the mechanism of influence between social responsibility and risk in international construction projects and provide useful insights for international construction enterprises to better carry out social responsibility actions and mitigate project risks.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, review and editing were performed by L.L., X.D. (Xiaopeng Deng), N.Z. and M.C. The first draft of the manuscript was written by X.D. (Xiaoxu Dang); all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC72171048, NSFC-71771052, and NSFC-72101053) and the Shaanxi Provincial Department of Transportation Scientific Research Project (Grant No. 20–07R).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
References
- Gao, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Deng, X. Retention in Challenging International Construction Assignments: Role of Expatriate Resilience. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 04023158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Competency Model for International Engineering Project Manager through MADM Method: The Chinese Context. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, H.; Ma, H.; Shi, J.J. Governance of Social Responsibility in International Infrastructure Megaprojects. Front. Eng. Manag. 2022, 9, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, A.; Cui, Q. Predictive Risk Modeling for Major Transportation Projects Using Historical Data. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.K.; Jha, K.N. Critical Risk Factors in International Construction Projects: An Indian Perspective. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2020, 27, 1169–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayegh, S.M.; Manjikian, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Abouelyousr, A.; Jabbour, R. Risk Identification and Assessment in Sustainable Construction Projects in the UAE. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2021, 21, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yang, L.; Cai, H. Risk Assessment and Management via Multi-Source Information Fusion for Undersea Tunnel Construction. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Dulaimi, M.F.; Aguria, M.Y. Risk Management Framework for Construction Projects in Developing Countries. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2004, 22, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.A.E.; Hussein, R.M. Innovation Management Framework for Achieving Sustainability through Managing Risks of Innovative Solutions during the Design Process. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2024, 22, 1870–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Li, Q. Compliance Management of Overseas Operation of Chinese Construction Companies. Chin. J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 23, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.W.; Zhang, F.; Fang, D.; Peña-Mora, F.; Liao, P.-C. Corporate Social Responsibility on Disaster Resilience Issues by International Contractors. J. Manag. Eng. 2021, 37, 04020089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.; Hoejmose, S.; Kastrinaki, Z. Corporate Philanthropy and Risk Management: An Investigation of Reinsurance and Charitable Giving in Insurance Firms. Bus. Ethics Q. 2017, 27, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwowski, M.; Raulinajtys-Grzybek, M. The Application of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Actions for Mitigation of Environmental, Social, Corporate Governance (ESG) and Reputational Risk in Integrated Reports. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Wang, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, N.; Mao, H.; Wang, X. The Influence of CSR to Financial Performance in International Engineering Contracting Enterprises: Evidence from China. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Islam, R.; Pitafi, A.H.; Xiaobei, L.; Rehmani, M.; Irfan, M.; Mubarak, M.S. The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Customer Loyalty: The Mediating Role of Corporate Reputation, Customer Satisfaction, and Trust. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Oo, B.L.; Lim, B.T.H. Drivers, Motivations, and Barriers to the Implementation of Corporate Social Responsibility Practices by Construction Enterprises: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 563–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Good, V.; Sardashti, H.; Peloza, J. Beyond Warm Glow: The Risk-Mitigating Effect of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). J. Bus. Ethics 2021, 171, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.Y.; Danish, R.Q.; Asrar-ul-Haq, M. How Corporate Social Responsibility Boosts Firm Financial Performance: The Mediating Role of Corporate Image and Customer Satisfaction. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Khan, A.; Rahman, A. Corporate Social Responsibility’s Influence on Firm Risk and Firm Performance: The Mediating Role of Firm Reputation. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 2991–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, H.R. Social Responsibilities of the Businessman; Haper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S. Zeitgeist or Chameleon? A Quantitative Analysis of CSR Definitions. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Oo, B.L.; Lim, B.T.H. Key practices and impact factors of corporate social responsibility implementation: Evidence from construction firms. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 2124–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqershy, M.T.; Shi, Q. Barriers to social responsibility implementation in belt and road mega infrastructure projects: A hybrid fuzzy DEMATEL-ISM-MICMAC approach. Buildings 2023, 13, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Lu, W.; Flanagan, R.; Chau, K.W. Corporate Social Responsibility “Glocalisation”: Evidence from the International Construction Business. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Y.; Zhao, X.-J.; Davidson, K.; Zuo, J. A Corporate Social Responsibility Indicator System for Construction Enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 29–30, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandage, R.V.; Mantha, S.S.; Rane, S.B.; Bhoola, V. Analysis of Interactions among Barriers in Project Risk Management. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2018, 14, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Hwang, B.-G.; Deng, X.; Zhao, X. Identifying Political Risk Management Strategies in International Construction Projects. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1016384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.Y.Y.; Hoang, V.T.P. Political, Economic, and Legal Risks Faced in International Projects: Case Study of Vietnam. J. Prof. Issues Eng. Educ. Pract. 2010, 136, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Wang, M.; Deng, X.; Zhang, N.; Mao, H.; He, P. What Drives the Fulfillment of Social Responsibility among International Construction Contractors? Stakeholder Perspective. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2024, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gao, S.; Liao, P.; Ganbat, T.; Chen, J. A Stakeholder-Based Risk Assessment and Intervention Framework for International Construction Projects: A Meta-Network Perspective. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2021, 14, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Deng, X.; Hwang, B.-G.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, N. Developing the Framework of Tacit Knowledge Externalization in International Construction Projects. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 3691–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Yan, P. Risk Paths in International Construction Projects: Case Study from Chinese Contractors. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2016, 142, 05016002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatjuthamard, P.; Treepongkaruna, S.; Jiraporn, P.; Jiraporn, N. Does Firm-level Political Risk Influence Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? Evidence from Earnings Conference Calls. Financ. Rev. 2021, 56, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, C.; Si, C. The real effect of mandatory CSR disclosure: Evidence of corporate tax avoidance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 179, 121646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barauskaite, G.; Streimikiene, D. Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance of Companies: The Puzzle of Concepts, Definitions and Assessment Methods. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, G.; Kang, H. Risk Management and Corporate Social Responsibility. Strateg. Manag. J. 2021, 42, 202–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-S.; Chiu, C.-J.; Yang, C.-F.; Pai, D.-C. The Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Brand Performance: The Mediating Effect of Industrial Brand Equity and Corporate Reputation. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 95, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peloza, J. Using Corporate Social Responsibility as Insurance for Financial Performance. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2006, 48, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, E.; Kantur, D.; Maden, C.; Telci, E.E. Investigating the Mediating Role of Corporate Reputation on the Relationship between Corporate Social Responsibility and Multiple Stakeholder Outcomes. Qual. Quant. 2016, 50, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.K.; Bui, H.M. The Role of Corporate Social Responsibility Activities in Employees’ Perception of Brand Reputation and Brand Equity. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, M.R.; Vosta, L.N.; Mahyari, H.K.; Pool, J.K. Social Responsibility Influence on Customer Trust in Hotels: Mediating Effects of Reputation and Word-of-Mouth. Tourism Rev. 2017, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, D.; Miller, D.R.; Smith, D. Let Me Make It Up to You: Understanding the Mitigative Ability of Corporate Social Responsibility Following Product Recalls. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 157, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, W. Corporate Social Responsibility, Firm Performance, and Firm Risk: The Role of Firm Reputation. Asia Pac. J. Account. Econ. 2021, 28, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L.; Rust, R.T.; Varki, S. Customer Delight: Foundations, Findings, and Managerial Insight. J. Retail. 1997, 73, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, S.J.; Pavelin, S. Corporate Reputation and Social Performance: The Importance of Fit. J. Manag. Stud. 2006, 43, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Shamim, A.; Park, J. Impacts of Cruise Industry Corporate Social Responsibility Reputation on Customers’ Loyalty: Mediating Role of Trust and Identification. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 92, 102706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Han, H.; Radic, A.; Tariq, B. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) as a Customer Satisfaction and Retention Strategy in the Chain Restaurant Sector. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2020, 45, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.Q.T. Corporate Social Responsibility and Bank’s Performance under the Mediating Role of Customer Satisfaction and Bank Reputation. Emerg. Sci. J. 2022, 6, 1409–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C. Corporate Social Responsibility on Customer Behaviour: The Mediating Role of Corporate Image and Customer Satisfaction. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2020, 31, 742–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.-N.; Nguyen, H.T.N. Achieving Customer Satisfaction through Product–Service Systems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 247, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Sandanayake, M.; Miao, P.; Shi, Y.; Yap, P.-S. Sustainability considerations of green buildings: A detailed overview on current advancements and future considerations. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvari, H.; Chan, D.W.; Alaeos, A.K.F.; Olawumi, T.O.; Aldaud, A.A.A. Critical success factors for managing construction small and medium-sized enterprises in developing countries of Middle East: Evidence from Iranian construction enterprises. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 103152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, S.; Eggert, A.; Garnefeld, I. Modeling the Impact of Corporate Reputation on Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Using Partial Least Squares. In Handbook of Partial Least Squares: Concepts, Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 515–534. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.; Leblanc, G. Corporate Image and Corporate Reputation in Customers’ Retention Decisions in Services. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2001, 8, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, S.P.; Sofian, S.; Saeidi, P.; Saeidi, S.P.; Saaeidi, S.A. How Does Corporate Social Responsibility Contribute to Firm Financial Performance? The Mediating Role of Competitive Advantage, Reputation, and Customer Satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Salamzadeh, Y.; Iqbal, Q.; Yang, S. The Impact of Customer Relationship Management and Company Reputation on Customer Loyalty: The Mediating Role of Customer Satisfaction. J. Relat. Mark. 2020, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, G.; Dikmen, I.; Tanyer, A.M.; Birgonul, M.T. Ontology for Relating Risk and Vulnerability to Cost Overrun in International Projects. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2011, 25, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Low, S.P.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X. Developing competitive advantages in political risk management for international construction enterprises. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2014, 140, 04014040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Deng, X.; Hwang, B.G.; Zhao, X. Improving quantitative assessment of political risk in international construction projects: The case of Chinese construction companies. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 04019083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, L.; McIver, R.P.; Liu, X.; Pan, A. Mixed-Ownership Reform and Private Firms’ Corporate Social Responsibility Practices: Evidence from China. Bus. Soc. 2020, 61, 389–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombrun, C.J.; Gardberg, N.A.; Sever, J.M. The Reputation QuotientSM: A Multi-Stakeholder Measure of Corporate Reputation. J. Brand Manag. 2000, 7, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbreath, J.; Shum, P. Do Customer Satisfaction and Reputation Mediate the CSR–FP Link? Evidence from Australia. Aust. J. Manag. 2012, 37, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L.; Parasuraman, A. The behavioral consequences of service quality. J. Mark. 1996, 60, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Han, S.H. Which Risk Management Is Most Crucial for Controlling Project Cost? J. Manag. Eng. 2017, 33, 04017029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nay, S.; Hoyle, R.H. Three Approaches to Using Lengthy Ordinal Scales in Structural Equation Models: Parceling, Latent Scoring, and Shortening Scales. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 2010, 34, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishton, J.M.; Widaman, K.F. Unidimensional Versus Domain Representative Parceling of Questionnaire Items: An Empirical Example. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1994, 54, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandalos, D.L.; Finney, S.J. Item Parceling Issues in Structural Equation Modeling. In New Developments and Techniques in Structural Equation Modeling; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 289–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bentler, P.M.; Chou, C.-P. Practical Issues in Structural Modeling. Sociol. Methods Res. 1987, 16, 78–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. J. Market. Theory. Prac. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzl, C.; Roldan, J.L.; Cepeda, G. Mediation Analysis in Partial Least Squares Path Modeling: Helping Researchers Discuss More Sophisticated Models. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 1849–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodside, A.G. Moving beyond Multiple Regression Analysis to Algorithms: Calling for Adoption of a Paradigm Shift from Symmetric to Asymmetric Thinking in Data Analysis and Crafting Theory. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiss, P.C. Building better causal theories: A fuzzy set approach to typologies in organization research. Acad. Manag. J. 2011, 54, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusa, R.; Duda, J.; Suder, M. Explaining SME performance with fsQCA: The role of entrepreneurial orientation, entrepreneur motivation, and opportunity perception. J. Innov. Knowl. 2021, 6, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, L. Pressure, State and Response: Configurational Analysis of Organizational Resilience in Tourism Businesses Following the COVID-19 Pandemic Crisis. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulland, J. Use of Partial Least Squares (PLS) in Strategic Management Research: A Review of Four Recent Studies. Strat. Mgmt. J. 1999, 20, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Mod. Methods Bus. Res. 1998, 295, 295–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzels, M.; Odekerken-Schröder, G.; Van Oppen, C. Using PLS path modeling for assessing hierarchical construct models: Guidelines and impirical illustration. MIS Q. 2009, 33, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallmuenzer, A.; Kraus, S.; Peters, M.; Steiner, J.; Cheng, C.-F. Entrepreneurship in Tourism Firms: A Mixed-Methods Analysis of Performance Driver Configurations. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C. Redesigning Social Inquiry: Fuzzy Sets and Beyond; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chuah, S.H.-W.; Tseng, M.-L.; Wu, K.-J.; Cheng, C.-F. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Sharing Economy in B2B Context in China: Findings from PLS-SEM and fsQCA. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, N.; Sethi, S.P. Does CSR Reduce Idiosyncratic Risk? Roles of Operational Efficiency and AI Innovation. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2021, 30, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, S.; Cellier, A.; Manita, R.; Saeed, A. Does Corporate Social Responsibility Reduce Financial Distress Risk? Econ. Model. 2020, 91, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberg, S.; Schwaiger, M.; Ringle, C.M. What’s important for relationship management? The mediating roles of relational trust and satisfaction for loyalty of cooperative banks’ customers. J. Mark. Anal. 2022, 10, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaciak, A.; Halaburda, M.; Bernaciak, A. The Construction Industry as the Subject of Implementing Corporate Social Responsibility (the Case of Poland). Sustainability 2021, 13, 9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoutsa Wamba, L.; Braune, E.; Hikkerova, L. Does Shareholder-Oriented Corporate Governance Reduce Firm Risk? Evidence from Listed European Companies. J. Appl. Account. Res. 2018, 19, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, C.C.; Bungau, T.; Prada, I.F.; Prada, M.F. Green buildings as a necessity for sustainable environment development: Dilemmas and challenges. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauashdh, A.; Jailani, J.; Rahman, I.A.; AL-fadhali, N. Strategic approaches towards achieving sustainable and effective building maintenance practices in maintenance-managed buildings: A combination of expert interviews and a literature review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Guo, M. Evaluating the engineering-procurement-construction approach and whole process engineering consulting mode in construction projects. IJST-T. Civ. Eng. 2023, 47, 2533–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).