The Impact of Electricity Grid Development on Economic Growth and Energy Consumption in Anhui Province: A Seemingly Unrelated Regression-Based Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
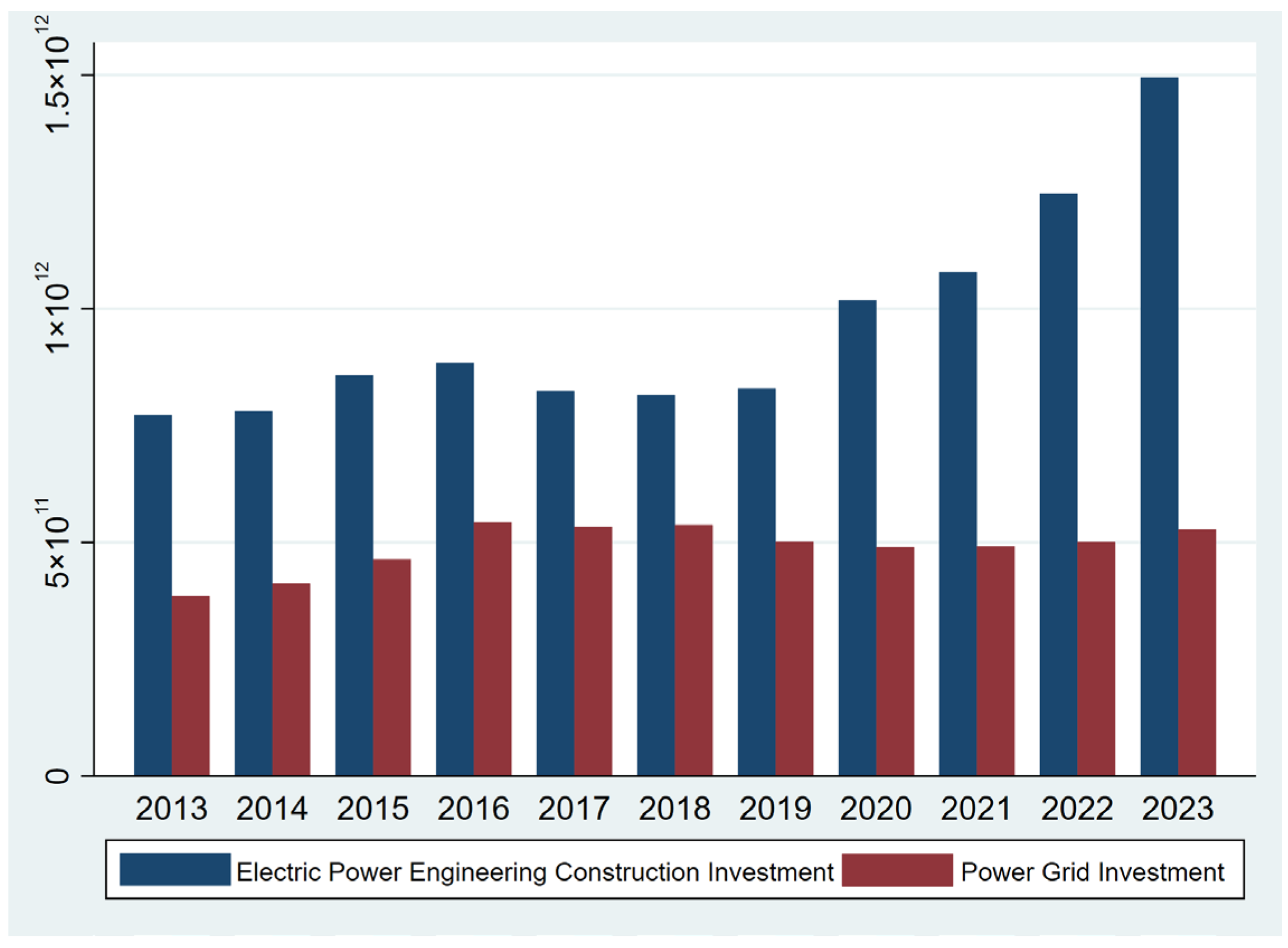
2.1. Development of the Power Grid in China
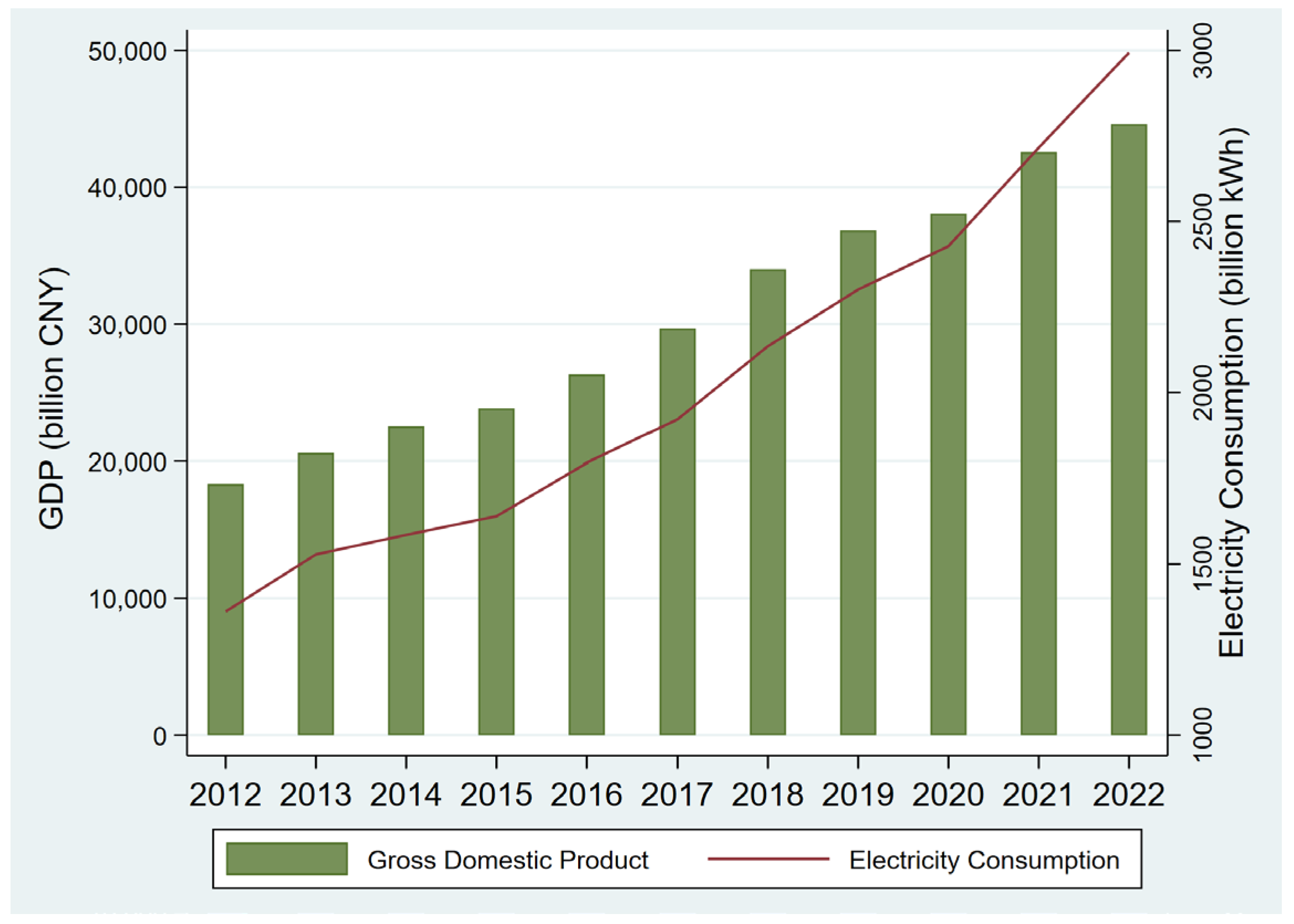
2.2. Development of the Power Grid in Anhui Province
2.3. Existing Research
3. Methodology and Data
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Analysis of the Elasticities of Electricity Infrastructure to Energy and Output Consumption
4.2. The Analysis of the Elasticities of Electricity Infrastructure to Energy Intensity
5. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, J.; Ghanadan, R. Electricity reform in developing and transition countries: A reappraisal. Energy 2006, 31, 815–844. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.; Severnini, E. Short- and long-run impacts of rural electrification: Evidence from the historical rollout of the U.S. power grid. J. Dev. Econ. 2020, 143, 102412. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, M. Managing electric power system transition in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5660–5677. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lin, B.; Zhang, Y. Sulfur dioxide emission reduction of power plants in China: Current policies and implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q.; Che, Y. The impacts on CO2 emission reduction and haze by coal resource tax reform based on dynamic CGE model. Resour. Policy 2018, 58, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Z.; Lilin, P.; Qiannan, F.; Yingjie, Z. Trans-regional electricity transmission in China: Status, issues and strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 572–583. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, W.; Wei, W. Transregional electricity transmission and carbon emissions: Evidence from ultra-high voltage transmission projects in China. Energy Econ. 2023, 123, 106751. [Google Scholar]
- Aschauer, D.A. Is public expenditure productive? J. Monet. Econ. 1989, 23, 177–200. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, M.J.; Álvarez, I. Network infrastructure spillover in private productive sectors: Evidence from Spanish high capacity roads. Appl. Econ. 2007, 39, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Konno, A.; Kato, H.; Takeuchi, W.; Kiguchi, R. Global evidence on productivity effects of road infrastructure incorporating spatial spillover effects. Transp. Policy 2021, 103, 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, T.B.; Dalgaard, C.J. Power outages and economic growth in Africa. Energy Econ. 2013, 38, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciulyte-Sniukiene, A.; Butkus, M. Does infrastructure development contribute to EU countries’ economic growth? Sustainability 2022, 14, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Das, D.K.; Guo, W.; Wei, W. Does power grid infrastructure stimulate regional economic growth? Energy Policy 2021, 155, 112296. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Duflo, E.; Qian, N. On the road: Access to transportation infrastructure and economic growth in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2020, 145, 102442. [Google Scholar]
- Dinlersoz, E.M.; Fu, Z. Infrastructure investment and growth in China: A quantitative assessment. J. Dev. Econ. 2022, 158, 102916. [Google Scholar]
- Bluhm, R.; Dreher, A.; Fuchs, A.; Parks, B.C.; Strange, A.M.; Tierney, M.J. Connective financing: Chinese infrastructure projects and the diffusion of economic activity in developing countries. J. Urban Econ. 2025, 145, 103730. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, S.; Novosad, P. Rural roads and local economic development. Am. Econ. Rev. 2020, 110, 797–823. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L. The role of transport infrastructure in economic growth: Empirical evidence in the UK. Transp. Policy 2023, 133, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Fernald, J.G. Roads to prosperity? Assessing the link between public capital and productivity. Am. Econ. Rev. 1999, 89, 619–638. [Google Scholar]
- Dinkelman, T. The Effects of Rural Electrification on Employment: New Evidence from South Africa. Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 3078–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Kaygusuz, K. Energy services and energy poverty for sustainable rural development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 936–947. [Google Scholar]
- Oyedepo, S.O. Energy and sustainable development in Nigeria: The way forward. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2012, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, C.B.; Lederman, D. Agricultural productivity and its determinants: Revisiting international experiences. Estud. Econ. 2004, 31, 133–163. [Google Scholar]
- Fedderke, J.W.; Perkins, P.; Luiz, J.M. Infrastructural investment in long-run economic growth: South Africa 1875–2001. World Dev. 2006, 34, 1037–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, D. Does electrification cause industrial development? Grid expansion and firm turnover in Indonesia. J. Dev. Econ. 2024, 167, 103234. [Google Scholar]
- Burlig, F.; Preonas, L. Out of the darkness and into the light? Development effects of rural electrification. J. Political Econ. 2024, 132, 2937–2971. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.J.; Zhang, N.; Mao, Y.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Tian, X.T.; Zhong, W. A review of the transformation from urban centralized heating system to integrated energy system in smart city. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 240, 122272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, B. Power infrastructure quality and manufacturing productivity in Africa: A firm level analysis. Energy Policy 2013, 61, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Esfahani, H.S.; Ramirez, M.T. Institutions, infrastructure, and economic growth. J. Dev. Econ. 2003, 70, 443–477. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, D. Impact of infrastructure on productivity: Case of Indian registered manufacturing. Indian Econ. Rev. 2003, 38, 95–113. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, S. Infrastructure and development: A critical appraisal of the macro-level literature. J. Dev. Stud. 2011, 47, 683–708. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Huang, S. How Much Infrastructure Is Too Much? A New Approach and Evidence from China. World Dev. 2014, 56, 272–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Cai, W.; Guo, Y.; Bai, C.; Yang, L. Decoupling relationship between energy consumption and economic growth in China’s provinces from the perspective of resource security. Resour. Policy 2020, 68, 101693. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, J.T. Jobs! Electricity shortages and unemployment in Africa. J. Dev. Econ. 2024, 167, 103231. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M.P. The Bad, the Weak, and the Ugly: Avoiding the Pitfalls of Instrumental Variables Estimation. 2006. Available online: http://ssrn.com/abstract=843185 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Tan, R.; Liu, K.; Lin, B. Transportation infrastructure development and China’s energy intensive industries—A road development perspective. Energy 2018, 149, 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Demetriades, P.O.; Mamuneas, T.P. Intertemporal Output and Employment Effects of Public Infrastructure Capital: Evidence from 12 OECD Economies. Econ. J. 2000, 110, 687–712. [Google Scholar]
- Kratena, K. Technical Change, Investment and Energy Intensity. Econ. Syst. Res. 2007, 19, 295–314. [Google Scholar]
- Berndt, E.R.; Fuss, M.A. Economic Capacity Utilization and Productivity Measurement for Multi-Product Firms with Multiple Quasi-Fixed Inputs; NBER Working Papers; National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, M.A. The restricted profit function and the application of the generalised Leontief and the translog functional forms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1997, 49, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, M.B. Additive General Error Models for Production, Cost, and Derived Demand or Share Systems. J. Political Econ. 1987, 95, 737–757. [Google Scholar]
- Castells, A.; Solé-Ollé, A. The regional allocation of infrastructure investment: The role of equity, efficiency and political factors. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2005, 49, 1165–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, J. Accounting and determinants analysis of China’s provincial total factor productivity considering carbon emissions. China Econ. Rev. 2021, 65, 101576. [Google Scholar]
- Chakir, R.; Le Gallo, J. Predicting land use allocation in France: A spatial panel data analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 92, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susaeta, A.; Lal, P.; Carter, D.R.; Alavalapati, J. Modeling nonindustrial private forest landowner behavior in face of woody bioenergy markets. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 46, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T. Impacts of Transport Infrastructure on Productivity and Economic Growth: Recent Advances and Research Challenges. Transp. Rev. 2013, 33, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achour, H.; Belloumi, M. Investigating the causal relationship between transport infrastructure, transport energy consumption and economic growth in Tunisia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 988–998. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| y | Output. |
| x | Variable input. In the short run, producers can only change variable inputs. |
| P | The price of an output. |
| W | The price of a variable input. |
| Z | The price of an invariable input, which functions with a one-period lag and involves adjustment costs. In the long run, adjustment costs will become zero. |
| E | Energy is the variable input. |
| L | Labor is the variable input. |
| K | Capital is the invariable input. In the long run, producers can change this invariable input. |
| Ei | Electricity infrastructure is the invariable input. |
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 165 | 19.976 | 18.411 | 4.257 | 120.131 |
| K | 165 | 6.178 | 5.597 | 1.285 | 33.794 |
| Py | 165 | 100.703 | 4.169 | 93.94 | 107.980 |
| E | 165 | 8.010 | 5.880 | 1.734 | 27.718 |
| We | 165 | 101.138 | 5.369 | 93.46 | 111.520 |
| L | 165 | 34.951 | 33.917 | 10.324 | 183.289 |
| Wl | 165 | 65,775.903 | 18,529.411 | 35,062 | 112,019 |
| Ei | 165 | 1.173 | 0.949 | 0.148 | 5.509 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Adjustment for Infrastructure Utilization Rate | With Adjustment for Infrastructure Utilization Rate | |||||
| Output | Energy | Labor | Output | Energy | Labor | |
| Variables | Equation | Equation | Equation | Equation | Equation | Equation |
| Kt−1 | 3.160 *** | −0.194 *** | −2.323 *** | 3.280 *** | −0.178 *** | −2.586 *** |
| (27.71) | (−6.40) | (−6.42) | (27.39) | (−5.49) | (−5.92) | |
| Eit−1 | −2.016 ** | −0.830 *** | 7.773 ** | −3.632 *** | −1.137 *** | 11.13 ** |
| (−2.68) | (−4.16) | (3.03) | (−3.74) | (−4.33) | (2.85) | |
| PyWe | −0.000733 | −0.0599 | ||||
| (−0.00) | (−0.22) | |||||
| Kt−1Eit−1 | 0.365 * | 0.299 * | ||||
| (2.51) | (1.99) | |||||
| −0.0123 | 0.0343 | |||||
| (−0.13) | (0.36) | |||||
| WeWe | −0.00125 | 0.0281 | ||||
| (−0.01) | (0.21) | |||||
| PyPy | 0.00395 | 0.0337 | ||||
| (0.03) | (0.25) | |||||
| Kt−1Kt−1 | −0.0107 | −0.00753 | ||||
| (−0.90) | (−0.58) | |||||
| Eit−1Eit−1 | −1.514 ** | −1.412 ** | ||||
| (−2.83) | (−2.59) | |||||
| Py | −0.238 | −0.123 | −0.266 | −0.115 | ||
| (−0.90) | (−1.74) | (−1.03) | (−1.65) | |||
| We | 0.0877 | 0.0784 | 0.107 | 0.0730 | ||
| (0.43) | (1.44) | (0.54) | (1.35) | |||
| Constant | 21.29 ** | 0.981 | −40.86 *** | 22.19 ** | ||
| (2.89) | (0.50) | (−6.29) | (3.11) | |||
| Time fixed effect | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| City fixed effect | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Observations | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| R-squared | 0.987 | 0.990 | 0.989 | 0.987 | 0.990 | 0.990 |
| Short-Term Elasticity | Long-Term Elasticity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | Area (km2)/ Population (Million) | Electricity to Energy | Electricity to Output | Electricity to Energy | Electricity to Output |
| Bozhou | 8429/670 | −0.101 | −0.099 | −0.725 | 3.462 |
| Lu’an | 15,351/581 | −0.052 | −0.079 | −0.377 | 2.746 |
| Hefei | 11,496/800 | −0.067 | −0.064 | −0.480 | 2.247 |
| Anqing | 13,528/523 | −0.075 | −0.072 | −0.537 | 2.524 |
| Xuancheng | 12,340/275 | −0.084 | −0.133 | −0.603 | 4.640 |
| Suzhou | 9787/658 | −0.070 | −0.098 | −0.508 | 3.428 |
| Huainan | 5650/387 | −0.237 | −0.445 | −1.711 | 15.502 |
| Chuzhou | 13,433/453 | −0.174 | −0.244 | −1.258 | 8.522 |
| Wuhu | 6026/387 | −0.091 | −0.091 | −0.659 | 3.172 |
| Huaibei | 2732/218 | −0.136 | −0.182 | −0.982 | 6.349 |
| Tongling | 2992/168 | −0.143 | −0.162 | −1.031 | 5.641 |
| Bengbu | 5959/386 | −0.418 | −0.581 | −3.015 | 20.258 |
| Ma’anshan | 4049/226 | −0.151 | −0.110 | −1.089 | 3.822 |
| Fuyang | 10,118/1074 | −0.140 | −0.502 | −1.010 | 17.499 |
| Huangshan | 9678/147 | −0.100 | −0.093 | −0.720 | 3.237 |
| Average | −0.136 | −0.197 | −0.980 | 6.870 | |
| Short-Term Elasticity | Long-Term Elasticity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | Area (km2)/ Population (Million) | Electricity to Energy Intensity | Electricity to Energy Intensity |
| Bozhou | 8429/670 | −0.001 | −4.187 |
| Lu’an | 15,351/581 | 0.027 | −3.123 |
| Hefei | 11,496/800 | −0.002 | −2.727 |
| Anqing | 13,528/523 | −0.002 | −3.061 |
| Xuancheng | 12,340/275 | 0.049 | −5.243 |
| Suzhou | 9787/658 | 0.028 | −3.936 |
| Huainan | 5650/387 | 0.207 | −17.213 |
| Chuzhou | 13,433/453 | 0.070 | −9.780 |
| Wuhu | 6026/387 | −0.000 | −3.831 |
| Huaibei | 2732/218 | 0.046 | −7.332 |
| Tongling | 2992/168 | 0.019 | −6.672 |
| Bengbu | 5959/386 | 0.163 | −23.273 |
| Ma’anshan | 4049/226 | −0.041 | −4.910 |
| Fuyang | 10,118/1074 | 0.362 | −18.508 |
| Huangshan | 9678/147 | −0.007 | −3.957 |
| Average | 0.061 | −7.850 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Gao, X.; Li, R.; Hou, K.; Song, Y.; Lu, Z. The Impact of Electricity Grid Development on Economic Growth and Energy Consumption in Anhui Province: A Seemingly Unrelated Regression-Based Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073193
Shi X, Gao X, Li R, Hou K, Song Y, Lu Z. The Impact of Electricity Grid Development on Economic Growth and Energy Consumption in Anhui Province: A Seemingly Unrelated Regression-Based Analysis. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073193
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xiaomin, Xiang Gao, Rong Li, Ke Hou, Yang Song, and Zhongjiang Lu. 2025. "The Impact of Electricity Grid Development on Economic Growth and Energy Consumption in Anhui Province: A Seemingly Unrelated Regression-Based Analysis" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073193
APA StyleShi, X., Gao, X., Li, R., Hou, K., Song, Y., & Lu, Z. (2025). The Impact of Electricity Grid Development on Economic Growth and Energy Consumption in Anhui Province: A Seemingly Unrelated Regression-Based Analysis. Sustainability, 17(7), 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073193





