How Does the “Civilized City” Selection Affect Environmental Governance Performance? A Spatial DID Approach Based on Prefecture-Level Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Considerations and Development of Hypotheses
- (1)
- The Technological Progress Effect
- (2)
- The Public Participation Effect
2.2. Sample Selection and Data Sources
2.3. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Autocorrelation Test
3.2. Spatial Panel Model Selection
3.3. Parallel Trend Test
3.4. Empirical Results
3.5. Regression Results of Spatial Lag Variables
3.6. Spatial Effect Decomposition
3.7. Robustness Tests
3.7.1. Replacing the Spatial Weight Matrix
3.7.2. Controlling for Other Policy Effects
4. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L. Research on the Promotion Tournament Model of Chinese Local Officials. Econ. Res. J. 2007, 7, 36–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, F.; Du, Y.; Wang, M. The Driving Force for Transforming Economic Development Mode and Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction. Econ. Res. J. 2008, 6, 4–11+36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.; Gao, N. Personnel Changes, Legal Environment, and Local Environmental Pollution. Manag. World 2014, 6, 65–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, D.; Zhang, J. ‘Effortless Perfection’: Do Chinese cities manipulate air pollution data? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmé, G.R.; Goldkorn, J. Civilising China; The Australian National University: Canberra, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Greenstone, M.; Hanna, R. Environmental regulations, air and water pollution, and infant mortality in India. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 3038–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Wu, Y. Formal institutions, informal institutions, and firms’ environmental innovation: An application of the fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis method. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.M.; Kaneko, S. Can environmental quality spread through institutions? Energy Policy 2013, 56, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, J.; Wang, E.; Hu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Economic growth and pollutant emissions in China: A spatial econometric analysis. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottenrott, H.; Rexhäuser, S. Policy-induced environmental technology and inventive efforts: Is there a crowding out? Ind. Innov. 2015, 22, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Hua, H.; Dong, Z.; Hao, C. Environmental performance index at the provincial level for China 2006–2011. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xiao, H.; Ding, J.; Ma, S. Impact of performance contest on local transformation and development in China: Empirical study of the National Civilized City program. Growth Change 2021, 53, 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Ge, G.; Hao, Y.; Hao, H. The impact of government intervention on corporate environmental performance: Evidence from China’s national civilized city award. Financ. Res. Lett. 2021, 39, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, K.C.; Xie, D.C.; Yeh, C.P.; Lan, H.R.; Cui, Z.X. Chinese national civilized city and corporate social responsibility: Will civilized city promote corporate social responsibility? Appl. Econ. Lett. 2022, 29, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, W. Does urban civilization improve corporate environmental performance? A quasi-natural experiment from China. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Feng, D.; Liu, F. Can government-led civilized city construction promote green innovation? Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 81783–81800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ye, J. Can civilized city construction facilitate green total factor productivity? A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s pilot civilized city. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 68, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hong, Y. Effects of civilized cities commendation on urban green innovation: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Appl. Econ. 2023, 55, 4060–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, Y. “Civilized City” Selection and Pollution Control: A Quasi-Natural Experiment. J. Financ. Econ. 2020, 46, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhang, M.; Hou, S. Analysis of spatial correlation characteristics and key factors of regional environmental governance efficiency in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 27, 3989–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. How Does Award Evaluation Promote Pollution Control? Evidence from the Evaluation of Civilized Cities. Public Adm. Rev. 2020, 13, 151–169+213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Hu, K.; Chen, J. Does Urban Civilization Promote High-Quality Enterprise Development? From the Perspective of Environmental Regulation and Transaction Costs. Ind. Econ. Res. 2019, 6, 27–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, F. Adaptive Social Mobilization in Grassroots Policy Implementation: Administrative Control and Multilateral Participation. Chin. Soc. Sci. 2018, 11, 135–155+205–206. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Yuan, J.; Zeng, W. Analysis of China’s Industrial Environmental Kuznets Curve: Empirical Research Based on a Spatial Panel Model. China Ind. Econ. 2010, 6, 65–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Spatial Effects of FDI on Energy Intensity in China. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2007, 1, 101–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, Z. The Impact of Urban Renewal on Spatial–Temporal Changes in the Human Settlement Environment in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land 2024, 13, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Chen, H. Urban Civilization, Transaction Costs, and the “Fourth Profit Source” of Enterprises: Evidence Based on National Civilized Cities and Private Listed Companies. China Ind. Econ. 2015, 7, 114–129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Research on the Green Innovation Effect of Environmental Information Disclosure: A Quasi-Natural Experiment Based on the “Ambient Air Quality Standard”. J. Financ. Res. 2021, 10, 134–152. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2010, 65, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Lv, Z. Spillover Effects of Economic Globalization on CO2 Emissions: A Spatial Panel Approach. Energy Econ. 2018, 73, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubara, M.; Kopczewska, K. Akaike information criterion in choosing the optimal k-nearest neighbours of the spatial weight matrix. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2024, 19, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hou, L. How does Civilized city Rating Promote Labor Inflow?—Quasi-natural experimental evidence from prefecture-level cities. Ind. Econ. Res. 2021, 3, 43–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q. The driving effect of state-level new areas on regional economic growth: Based on the empirical evidence of 70 large and medium-sized cities. Chin. Ind. Econ. 2020, 7, 43–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, H. Low-carbon pilot policy and development path in urban agglomerations of China: Mechanism analysis and stage identification. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
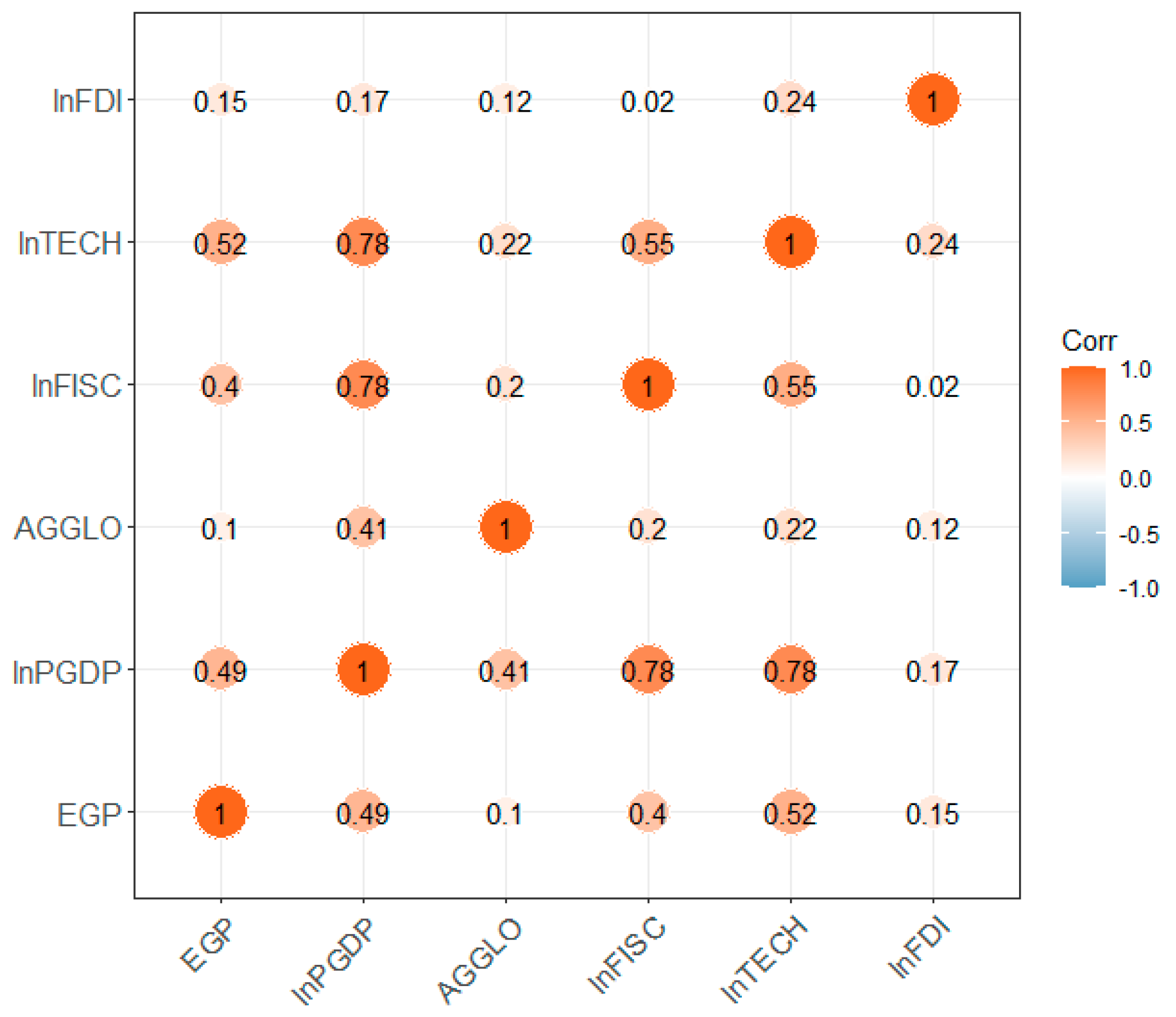
| Variables | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGP | 0.302 | 0.069 | 0.022 | 0.999 |
| DID | 0.200 | 0.400 | 0 | 1 |
| lnPGDP | 9.930 | 0.800 | 7.545 | 12.363 |
| AGGLO | 0.928 | 0.286 | 0.144 | 1.948 |
| lnFISC | 1.140 | 0.595 | −0.648 | 3.469 |
| lnTECH | 4.060 | 1.946 | 0 | 9.801 |
| lnFDI | −0.214 | 1.778 | −11.513 | 3.626 |
| Year | Moran’s I index | Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 0.077 | 2.467 ** | 0.014 |
| 2004 | 0.109 | 3.372 *** | 0.001 |
| 2005 | 0.108 | 3.371 *** | 0.001 |
| 2006 | 0.057 | 1.777 * | 0.076 |
| 2007 | 0.090 | 2.688 *** | 0.007 |
| 2008 | 0.082 | 2.462 ** | 0.014 |
| 2009 | 0.092 | 2.779 *** | 0.006 |
| 2010 | 0.093 | 2.809 *** | 0.005 |
| 2011 | 0.105 | 3.129 *** | 0.002 |
| 2012 | 0.112 | 3.307 *** | 0.001 |
| 2013 | 0.117 | 3.417 *** | 0.001 |
| 2014 | 0.108 | 3.166 *** | 0.002 |
| 2015 | 0.200 | 5.560 *** | 0.000 |
| 2016 | 0.207 | 5.746 *** | 0.000 |
| 2017 | 0.196 | 5.418 *** | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.182 | 5.038 *** | 0.000 |
| 2019 | 0.175 | 4.821 *** | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.158 | 4.308 *** | 0.000 |
| Statistic | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LM Test | LM-ERR | 41.636 *** | 0.000 |
| Robust LM-ERR | 64.846 *** | 0.000 | |
| LM-LAG | 0.395 | 0.530 | |
| Robust LM-LAG | 23.605 *** | 0.000 | |
| LR Test | SDM → SAR | 60.700 *** | 0.000 |
| SDM → SEM | 66.800 *** | 0.000 | |
| Wald Test | SDM → SAR | 61.030 *** | 0.000 |
| SDM → SEM | 67.010 *** | 0.000 |
| Statistic | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HausmanTest | 31.330 *** | 0.000 | |
| LR Joint Significance Test | time vs. both | 10,017.17 *** | 0.000 |
| ind vs. both | 82.650 *** | 0.000 |
| Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t − 14 | −0.001 | t − 5 | −0.000 | t + 4 | 0.008 * |
| (−0.114) | (−0.018) | (1.944) | |||
| t − 13 | −0.001 | t − 4 | −0.000 | t + 5 | 0.011 ** |
| (−0.150) | (−0.044) | (2.489) | |||
| t − 12 | −0.001 | t − 3 | −0.002 | t + 6 | 0.018 *** |
| (−0.355) | (−0.471) | (3.772) | |||
| t − 11 | −0.002 | t − 2 | −0.000 | t + 7 | 0.021 *** |
| (−0.380) | (−0.009) | (4.121) | |||
| t − 10 | −0.003 | t − 1 | −0.000 | t + 8 | 0.025 *** |
| (−0.725) | (−0.005) | (4.217) | |||
| t − 9 | −0.002 | t | 0.003 | t + 9 | 0.044 *** |
| (−0.574) | (0.747) | (4.427) | |||
| t − 8 | −0.001 | t + 1 | 0.006 | t + 10 | 0.052 *** |
| (−0.168) | (1.463) | (4.522) | |||
| t − 7 | 0.000 | t + 2 | 0.006 | t + 11 | 0.051 *** |
| (0.049) | (1.514) | (4.256) | |||
| t − 6 | −0.000 | t + 3 | 0.005 | t + 12 | 0.063 *** |
| (−0.101) | (1.149) | (3.558) |
| DID Model | SDM-DID Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| DID | 0.008 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 * | 0.006 * |
| (6.571) | (5.794) | (1.784) | (1.826) | |
| lnPGDP | −0.009 | 0.011 * | ||
| (−1.326) | (1.688) | |||
| AGGLO | 0.004 | 0.0004 | ||
| (0.632) | (0.092) | |||
| lnFISC | −0.015 *** | −0.014 *** | ||
| (−5.425) | (−2.953) | |||
| lnTECH | 0.003 *** | 0.002 *** | ||
| (6.063) | (6.827) | |||
| lnFDI | −0.001 ** | −0.001 *** | ||
| (−2.343) | (−3.388) | |||
| W*DID | 0.010 *** | 0.008 *** | ||
| (4.386) | (5.083) | |||
| W*lnPGDP | −0.039 *** | |||
| (−3.824) | ||||
| W*AGGLO | 0.007 | |||
| (1.517) | ||||
| W*lnFISC | 0.002 | |||
| (0.864) | ||||
| W*lnTECH | 0.003 ** | |||
| (2.340) | ||||
| W*lnFDI | 0.002 *** | |||
| (3.209) | ||||
| ρ | 0.126 *** | 0.115 *** | ||
| (3.503) | (3.888) | |||
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DID | 0.006 * | 0.010 *** | 0.016 *** |
| (1.881) | (5.683) | (3.427) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.010 | −0.042 *** | −0.032 *** |
| (1.598) | (−3.847) | (−5.180) | |
| AGGLO | 0.001 | 0.008 * | 0.009 ** |
| (0.139) | (1.671) | (1.984) | |
| lnFISC | −0.014 *** | 0.0004 | −0.014 *** |
| (−2.912) | (0.208) | (−3.287) | |
| lnTECH | 0.002 *** | 0.004 ** | 0.006 *** |
| (8.727) | (2.495) | (3.949) | |
| lnFDI | −0.001 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.001 ** |
| (−3.250) | (3.208) | (2.385) |
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DID | 0.006 * | 0.028 *** | 0.034 *** |
| (1.730) | (4.778) | (6.169) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.005 | −0.053 *** | −0.048 *** |
| (1.005) | (−2.986) | (−3.483) | |
| AGGLO | −0.001 | 0.031 *** | 0.030 *** |
| (−0.223) | (2.809) | (2.639) | |
| lnFISC | −0.014 *** | −0.0004 | −0.014 *** |
| (−2.919) | (−0.118) | (−5.431) | |
| lnTECH | 0.002 *** | 0.005 | 0.007 ** |
| (5.725) | (1.488) | (2.132) | |
| lnFDI | −0.001 ** | 0.002 * | 0.001 |
| (−2.564) | (1.714) | (1.276) |
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DID | 0.006 * | 0.014 *** | 0.020 *** |
| (1.794) | (6.940) | (6.057) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.004 | −0.029 *** | −0.025 *** |
| (0.892) | (−3.273) | (−4.729) | |
| AGGLO | −0.0000 | 0.014 ** | 0.014 ** |
| (−0.013) | (2.165) | (2.057) | |
| lnFISC | −0.015 *** | 0.005 | −0.010 *** |
| (−2.864) | (1.441) | (−3.782) | |
| lnTECH | 0.002 *** | 0.003 ** | 0.005 *** |
| (7.829) | (2.115) | (3.694) | |
| lnFDI | −0.001 *** | 0.001 | −0.0002 |
| (−2.722) | (0.784) | (−0.329) |
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DID | 0.005 * | 0.009 *** | 0.014 *** |
| (1.661) | (5.188) | (3.253) | |
| DT | 0.009 *** | −0.005 *** | 0.004 |
| (4.585) | (−2.976) | (1.375) | |
| ZH | 0.002 ** | 0.003 | 0.005 * |
| (2.056) | (1.434) | (1.817) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.011 * | −0.044 *** | −0.033 *** |
| (1.819) | (−4.055) | (−4.850) | |
| AGGLO | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| (0.211) | (1.043) | (1.200) | |
| lnFISC | −0.015 *** | 0.001 | −0.014 *** |
| (−3.171) | (0.553) | (−3.378) | |
| lnTECH | 0.002 *** | 0.004 ** | 0.006 *** |
| (8.617) | (2.455) | (3.859) | |
| lnFDI | −0.001 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.001 ** |
| (−3.267) | (3.017) | (2.166) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, W.; Yang, R.; You, W. How Does the “Civilized City” Selection Affect Environmental Governance Performance? A Spatial DID Approach Based on Prefecture-Level Cities. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093812
Ou W, Yang R, You W. How Does the “Civilized City” Selection Affect Environmental Governance Performance? A Spatial DID Approach Based on Prefecture-Level Cities. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093812
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Weixing, Ruirui Yang, and Wanhai You. 2025. "How Does the “Civilized City” Selection Affect Environmental Governance Performance? A Spatial DID Approach Based on Prefecture-Level Cities" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093812
APA StyleOu, W., Yang, R., & You, W. (2025). How Does the “Civilized City” Selection Affect Environmental Governance Performance? A Spatial DID Approach Based on Prefecture-Level Cities. Sustainability, 17(9), 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093812






