The Impact of Digital Village Construction on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture: An Empirical Study Based on Panel Data from 53 Counties in Fujian Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Construction of the Indicator System
3.1.1. Explanatory Variables
3.1.2. Explained Variables
3.1.3. Control Variables
3.1.4. Data Sources
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Entropy Method
3.2.2. Biomass Conversion Method
3.2.3. DEA-SBM Models Incorporating Non-Expected Output
3.2.4. Spatial Measurement Models
4. Results
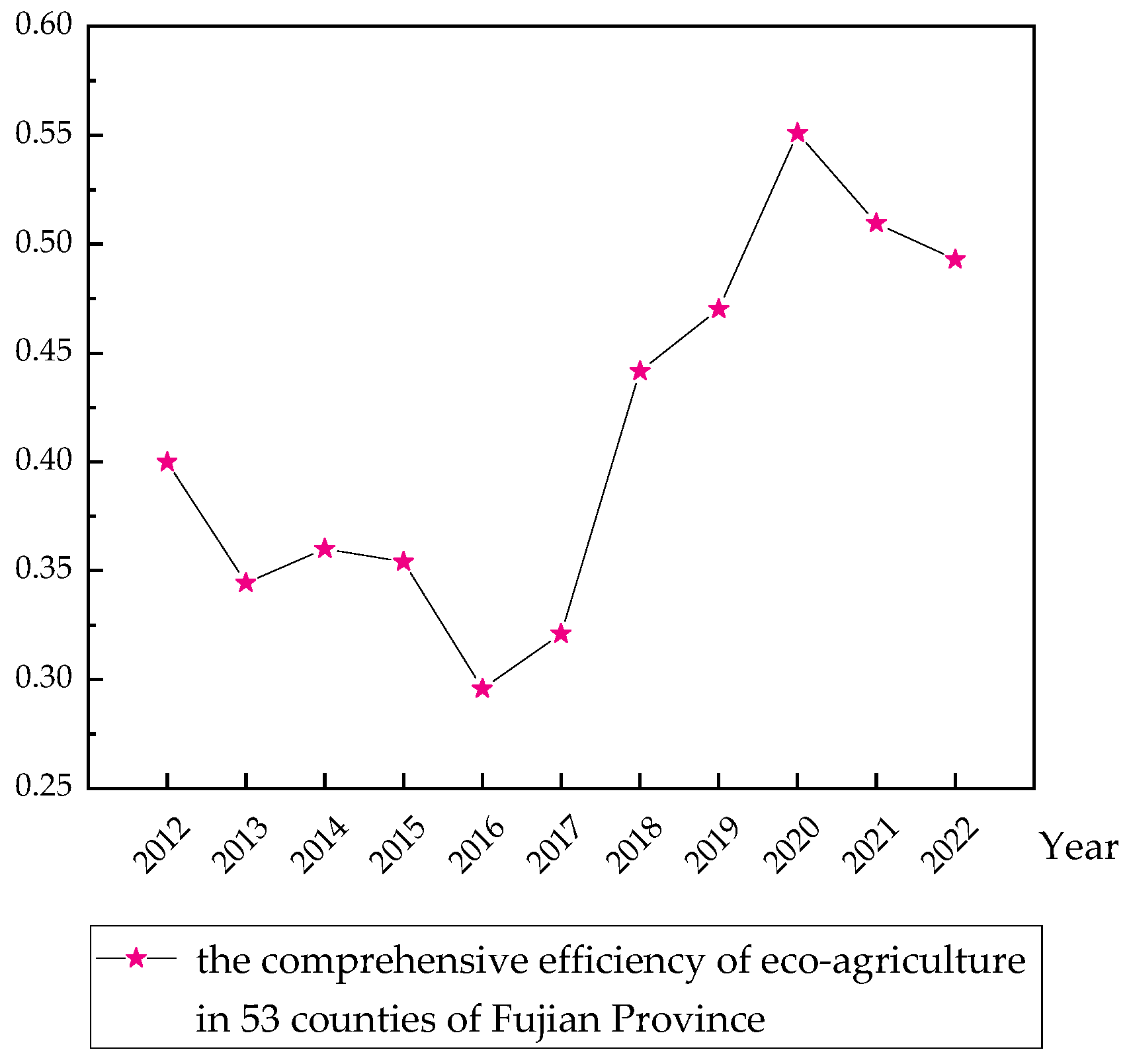
4.1. Measurement of the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture
4.2. Measurement of the Level of Digital Village Construction
4.3. Analysis of the Impact of Digital Village Construction on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture
4.3.1. Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.3.2. Analysis of Spatial Measurement Results
4.3.3. Spatial Spillover Effects
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDM | Spatial Durbin model |
| SAR | Spatial autoregressive model |
References
- Guan, Y. Study on the Index System for Constructing Eco-province—A case study on Fujian Province. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2002, 18, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, J. Reflections on Policies for Building an Ecological Province in Fujian Province. Fujian Forum (Humanit. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2005, 25, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, S. Reform of Agricultural Production Mode in China under the Background of Digital Economy:Mechanism, Contradiction and Solution. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 43, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Li, Y.; Ren, K. Actual Contradictions and Optimization Paths of Digital Rural Construction in the Perspective of Multiple Policy Relations. J. Yunnan Natl. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 40, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lyu, P. Digital Village Construction: Goals, Achievements, and Challenges. Econ. Manag. 2022, 36, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhao, W. Mechanism and Path of Digital Rural Construction Boosting the Modernization of Chinese–style Agriculture. J. South China Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2024, 23, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Song, Y.; Lin, X.; Fu, C. Some Humble Opinions on China’s Digital Village Construction. China’s Rural. Econ. 2021, 37, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, H. Construction of the Evaluation Index Systemfor the Digital Villages in China and its Practical Utility. J. Yunnan Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 55, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M. The Theory and Practice of Modern Ecological Agriculture in China. People’s Forum·Acad. Front. 2019, 8, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Chu, S. Digital Village Construction, Rural Consumption Upgrading, and High-Quality Economic Development. J. South-Cent. Univ. Natl. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2025, 45, 136–144+186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eanes, F.R.; Singh, A.S.; Bulla, B.R.; Ranjan, P.; Prokopy, L.S.; Fales, M.; Wickerham, B.; Doran, P.J. Midwestern US farmers perceive crop advisers as conduits of information on agricultural conservation practices. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, M.; Ma, C. Triple Play and Rural Informatization: International Experience and Inspiration. Intell. Mag. 2012, 31, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philbeck, T.; Davis, N. The fourth industrial revolution. J. Int. Aff. 2018, 72, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, K. Practical analysis of digital village construction: Progress, patterns and path optimisation. Stud. Social. Chin. Charact. 2023, 29, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wang, J. International experience and inspiration in digital village construction. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Jiang, J. Study on the spatial and temporal evolution of agro-ecological efficiency and influencing factors in major food–producing areas. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2024, 40, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Lu, R.; Du, F. Spatial–temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency in Counties of Yunnan Province. Agric. Resour. Reg. China 2024, 45, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xiong, J.; Li, W. Evolution and driving factors of spatial correlation network of agricultural eco–efficiency in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 3199–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Measurement and spatial–temporal characteristics of agricultural eco–efficiency in a typical North–South Transition Zone from 2001 to 2018. Ecol. Sci. 2023, 42, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H. Comprehensive Measurement of Agroecological Efficiency Based on DEA Modelling. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2019, 35, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Qi, Q.; Han, J. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Agricultural Eco–efficiency in China. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2018, 38, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, H. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Eco–efficiency in China. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2022, 38, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Deng, C.; Ye, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency in Hainan Province. J. Trop. Crops 2025, 46, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Zhang, S.; Tang, C. Spatio–temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Eco–efficiency in Guangdong Province Under “Dual Carbon” Target. Agric. Resour. Reg. China 2023, 44, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Tao, J. Analysis of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of Carbon Source and Carbon Sink. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Basset–Mens, C.; Ledgard, S.; Boyes, M. Eco–efficiency of intensification scenarios for milk production in New Zealand. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez–Limón, J.A.; Picazo–Tadeo, A.J.; Reig–Martínez, E. Eco–efficiency assessment of olive farms in Andalusia. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, N.; Arsenault, N.; Tyedmers, P. Scenario modeling potential eco–efficiency gains from a transition to organic agriculture: Life cycle perspectives on Canadian canola, corn, soy, and wheat production. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qian, Z.; Shi, R. Research Hotspots and Trends of Agriculture Eco–efficiency in China. Agric. Resour. Reg. China 2023, 44, 20–31. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=N5Mfx_KcSpKEoqKJ9Ae5Hzc1L4xv6e5Wn8WSjA3Zu0oYdne70f0IahyVPb4sD3U2F3zGSAZZjBjbb7C2RicgeR5AKXhEfHmn4gpxqC5k9lMmHHjW5NYEdzcAobzD6r0GqIuhKKBK7alLQ22l_AzvvVkcw4owiptgAkRG6KXeYE2XpK5VEps2Zw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Lin, E.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q. Systematic Review and Analysis of Eco–Efficiency: A Comparative Perspective Between Chinese and English Literatures. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2019, 35, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dang, G.; Tang, X. Spatial–temporal Differences and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Eco–efficiency in China Based on SBM–Tobit Model. J. Southwest For. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2022, 6, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, Z.; Liu, Y. Measurement of agro-ecological efficiency and influencing factors in ethnic areas. J. South-Cent. Univ. Natl. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2021, 41, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Yue, Y. The Impact of Digital Economy on the Ecological Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. People’s Yellow River 2023, 45, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Hou, Y.; Tan, J. How does digital village construction influences carbon emission? The case of China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chong, Y.; Yu, H.; Ye, X.; Li, G. Digital financial development and ecological footprint: Evidence from green–biased technology innovation and environmental inclusion. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Chen, S.; Wan, S.; Liang, C.; Ma, Y. Digital financial inclusion and economic green growth: Evidence from counties covered by China’s national key ecological functional zones. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1467542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Pang, Q.; Zhang, C. Impacts of Digital Economy on Provincial Green Water Resourcesuse Efficiency Based on System Gmm Model Tests. Resour. Ind. 2025, 27, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Gong, Y. Spatial spillover effects of digital rural construction on carbon emissions from agriculture. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Pang, W. Impact of digital economy development on ecological well–being performance. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2023, 38, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of the effect of digital economy on the improvement of ecological welfare performance. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2024, 40, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Lyu, H. Digital Technology Enabling Rural Industry Modernisation in Ethnic Areas: Mechanisms, Dilemmas and Practical Paths. Agric. Econ. 2023, 43, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Embedding Digital Technology in Rural Society: Application Scenarios, Practical Dilemmas and Optimization Strategies. Mod. City Res. 2024, 39, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L. Realization Path of Digital Technology Enabling High–Quality Agricultural Development. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2022, 44, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G. Study on the Influence Effect of Economic and Technological Development Zones on the Spatial Structure of Urban Economy–Taking Beijing as an Example. Explor. Econ. Issues 2006, 27, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Study on the spatial spillover effects of the digital economy and high–quality agricultural development. Product. Res. 2023, 38, 70–74+95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, P. Institutional pressure and group behavior in corporate green technology diffusion. Chin. Soft Sci. 2024, 39, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, F.; He, J.; Zhu, H. Did the “Belt and Road” Initiative Promotes China’s Technology Diffusion—An Analysis Based on High–tech Industry. J. Technol. Econ. 2023, 42, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dubin, R.A. Spatial autocorrelation: A primer. J. Hous. Econ. 1998, 7, 304–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Eco–Efficiency in Yangtze River Delta. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, China, 17 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Wan, H. The spatial characteristics of digital village development and farmers’ income increase effect: An empirical analysis based on Digital Rural County Index and CHFS. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 2041–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, H. Digital Countryside Construction: Underlying Logic, Practical Errors and Optimization Path. China’s Rural. Econ. 2023, 39, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The General Office of the Communist Party of China Central Committee and the General Office of the State Council issued the “Outline of the Digital Rural Development Strategy”. Available online: https://www.chinacourt.org/article/detail/2019/05/id/3922058.shtml (accessed on 16 May 2019).
- Xu, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhai, J.; Kon, F. Impact of Digital Rural Construction on Development and Upgrading of Forestry Industry of 26 Counties in Mountainous Regions of Zhejiang Province. For. Sci. 2024, 60, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Y. Research on Human Capital Structure Effect of Digital Economy Development. Econ. Manag. Stud. 2022, 43, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Xu, Z. Modernization of China’s Ecological Environment Governance System and Governance Capacity: Theoretical Analysis, Practical Evaluation and Research Prospect. J. Manag. 2022, 35, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Zhu, Z. The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Labor Income Share from the Perspective of Space Analysis Based on Static and Dynamic Space Durbin Model. Explor. Econ. Issues 2022, 43, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Qi, C.; Zeng, G.; Yang, J. Evaluation and Spatiotemporal Characteristics Analysis of the Development Level of China’s Digital Village Construction. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2024, 40, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Yang, J. Study on Effect of Land Use Structure, Economic Development and Land Carbon Emission––A case Study of Urumqi. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2017, 38, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, D.; Luo, G.; Peng, Y. Spatial Variance of Farmland Carbon Emission Factors Based on Stirpat and GWR Models. Resour. Ind. 2019, 21, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks–based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Luo, L.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F. Influence of Forest Resource Development Project on the Urban–Rural Income Gap in Old Revolutionary Regions. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2023, 59, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, F. Study on the Influencing Factors and Ecological Improvement of Agricultural Productivity in Fujian Mountainous Counties under the Perspective of Farmers’ Behaviour. Agric. Econ. 2021, 41, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Cai, B.; Zhang, M. Analysis of Differences in Development Levels and Obstacles of Digital Villages in Regional Municipalities of Fujian Province. Straits Sci. 2024, 40, 139–144+152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Chen, J.; Hou, J. The Impact of Digital Rural Construction the Quality of Agricultural Development. China Bus. Mark. 2025, 39, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhong, Z. Regional Differences of Digital Rural Construction in China and Driving Factors. Trop. Geogr. 2025, 45, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K. Evaluation of Agricultural Eco–efficiency in Fujian Province and Exploration of Paths to Improvement. Seed Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Explanation of Secondary Indicators | Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Information Infrastructure | Fixed telephone penetration rate | Total fixed telephone subscribers as a proportion of the household population | % |
| Digital Industry Development | Development level of the tertiary industry | Tertiary value added | CNY 10,000 |
| Digital Science and Technology Agriculture | Degree of agricultural mechanization | Area covered by digital agricultural mechanization technologies. | Hectares |
| Digital Life Services | Health technology employees | Number of health technology practitioners | People |
| Digital Financial Services | Financial loans | The year-end outstanding balance of financial institution loans | CNY 10,000 |
| Rural Quality of Life | Per capita disposable income | Per capita disposable income of rural residents | CNY |
| Total retail sales of consumer goods | Total retail sales of consumer goods | CNY 10,000 |
| Input and Output Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Variables | Unit (of Measure) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Facility agricultural land inputs | Based on data on total area occupied by facility agriculture | Hectares |
| Farmland inputs | Based on data on total sown area of crops | Thousand hectares | |
| Labor force inputs | Employees of the unit at the end of the year | People | |
| Agricultural machinery inputs | Based on data on total power of agricultural machinery | Kilowatts | |
| Expected output | Added value of the primary industry in agriculture | Based on data on value added in the primary sector | CNY 10,000 |
| Non-expected output | Carbon emissions from agriculture | In terms of total grain production | kg |
| Variable Type | Variable Name | Indicators of Measurement | Variable Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanatory variable | Eco-agriculture | Comprehensive efficiency of eco-agriculture | lnagri |
| Explained variable | Digital village construction | Level of digital village construction | lndigit |
| Control variables | Level of economic development | Gross regional product | lngdp |
| Number of administrative divisions | Number of townships | lntown | |
| Level of agricultural development | Value added of agricultural production | lnadd | |
| Size of the oilseed industry | Oilseed production | lnoil |
| County | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lianjiang | 1.23 | 1.28 | 1.24 | 1.22 | 1.37 | 1.54 | 1.33 | 1.34 | 1.43 | 1.46 | 1.56 | 1.36 |
| Luoyuan | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.03 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 1.34 | 1.43 | 1.51 | 1.58 | 1.62 | 1.19 |
| Dongshan | 1.77 | 1.75 | 1.71 | 1.88 | 1.87 | 1.12 | 1.38 | 1.32 | 1.28 | 1.29 | 0.22 | 1.42 |
| Guangze | 1.15 | 1.16 | 1.36 | 1.30 | 1.17 | 1.02 | 1.20 | 1.19 | 1.13 | 1.10 | 0.52 | 1.12 |
| Region | Average Level of Digital Village Construction |
|---|---|
| Southern region | 0.0422 |
| Northern region | 0.0153 |
| Central region | 0.0423 |
| Western region | 0.0180 |
| Eastern region | 0.0183 |
| Whole province | 0.0277 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 0.403 *** | 4.214 | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.236 *** | 2.470 | 0.007 |
| 2019 | 0.246 *** | 2.560 | 0.005 |
| 2020 | 0.221 ** | 2.315 | 0.010 |
| 2021 | 0.203 ** | 2.154 | 0.016 |
| 2022 | 0.228 *** | 2.403 | 0.008 |
| Year | Counties Where Different Agglomerations Are Located (Number) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-H | L-H | L-L | H-L | |
| 2012 | Youxi, Luoyuan, Lianjiang, Pingtan, Zhao’an, Fuqing (6) | Shaowu, Shaxian, Zhangping, Minhou, Wuyishan, Dehua, Yongchun, Minqing, Nanjing, Xianyou, Zhangpu, Yong’an, Yunxiao (13) | Shunchang, Hui’an, Fuding, Songxi, Liancheng, Fu’an, Mingxi, Pinghe, Jianning, Anxi, Jian’ou, Shouning, Xiapu, Shishi, Gutian, Ninghua, Nan’an, Zhouning, Wuping, Changting, Qingliu, Zhenrong, Zhenghe, Pingnan, Shanghang, Jinjiang (26) | Datian, Hua’an, Guangze, Dongshan, Yongtai, Pucheng, Taining, Jiangle (8) |
| 2017 | Luoyuan, Lianjiang, Yongtai, Minqing (4) | Youxi, Hui’an, Shaowu, Minhou, Wuyishan, Nanjing, Zhangpu, Gutian, Jinjiang, Yunxiao, Fuqing (11) | Shunchang, Fuding, Songxi, Datian, Zhangping, Liancheng, Fu’an, Mingxi, Dehua, Yongchun, Pucheng, Jianning, Anxi, Jian’ou, Xianyou, Shouning, Taining, Chongle, Zhao’an, Yong’an, Ninghua, Nan’an, Zhouning, Wuping, Changting, Qingliu, Zhengrong, Zhenghe, Pingnan, Shanghang (30) | Shaxian, Hua’an, Guangze, Dongshan, Pinghe, Pingtan, Xiapu, Shishi (8) |
| 2022 | Luoyuan, Lianjiang, Fu’an, Pinghe, Yongtai, Minqing, Jian’ou, Xiapu, Zhao’an, Gutian (10) | Youxi, Fuding, Shaowu, Shaxian, Dongshan, Minhou, Wuyishan, Nanjing, Zhangpu, Jiangle, Zherong, Pingnan, Yunxiao, Fuqing (14) | Hui’an, Songxi, Datian, Hua’an, Liancheng, Mingxi, Dehua, Yongchun, Jianning, Anxi, Xianyou, Shouning, Yong’an, Ninghua, Nan’an, Zhou’ning, Wuping, Changting, Qingliu, Zhenghe, Shanghang, Jinjiang (22) | Shunchang, Guangze, Zhangping, Pingtan, Pucheng, Taining, Shishi (7) |
| Explanatory Variable | Statistics | LM | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Digital Village Construction | Spatial error estimation | 18.352 *** | 0.000 |
| Space lag estimation | 16.078 *** | 0.000 |
| Variables | SDM Model | SAR Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time-Fixed | Spatial-Fixed | Spatiotemporal Two-Way Fixed | Time-Fixed | Spatial-Fixed | Spatiotemporal Two-Way Fixed | |
| Spatial (rho) | 0.2095 *** | 0.2039 *** | 0.1107 ** | 0.2240 *** | 0.2015 *** | 0.1099 ** |
| lndigit | 0.2153 | 0.2223 | 0.0292 | 0.6723 | 0.2008 *** | 0.0342 |
| lngdp | −0.0421 ** | −0.0144 | −0.0063 | −0.0225 | 0.0813 | −0.0053 |
| lntown | −0.0586 *** | 0.0328 | 0.0499 | −0.0612 *** | 0.0173 | 0.0211 |
| lnadd | −0.0254 ** | 0.0316 * | −0.0253 ** | −0.0122 | −0.0333 ** | −0.0203 |
| lnoil | −0.0010 | 0.0451 ** | 0.0451 *** | −0.0073 | 0.0301 | 0.0366 * |
| R2 | 0.0936 | 0.0191 | 0.0028 | 0.0329 | 0.0026 | 0.0039 |
| Variables | Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDM Model | SAR Model | |||||
| Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Aggregate Effect | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Aggregate Effect | |
| lndigit | 0.2589 | 0.6527 | 0.9115 | 0.6946 * | 0.1954 ** | 0.8900 ** |
| lngdp | −0.0399 ** | 0.0586 * | 0.0187 | −0.0236 | −0.0068 | −0.0303 |
| lntown | −0.0609 *** | −0.0711 | −0.1320 | −0.0610 ** | −0.0170 *** | −0.0780 *** |
| lnadd | −0.0201 * | 0.1063 *** | 0.0862 *** | −0.0128 | −0.0037 | −0.0165 |
| lnoil | −0.0027 | −0.0383 * | −0.0410 *** | −0.0071 | −0.0019 | −0.0090 |
| R2 | 0.0936 | 0.0936 | 0.0936 *** | 0.0329 | 0.0329 | 0.0329 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, W.; Xue, Z.; Ma, G.; Zeng, F. The Impact of Digital Village Construction on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture: An Empirical Study Based on Panel Data from 53 Counties in Fujian Province. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093840
Lian W, Xue Z, Ma G, Zeng F. The Impact of Digital Village Construction on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture: An Empirical Study Based on Panel Data from 53 Counties in Fujian Province. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093840
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Wenqi, Zexi Xue, Gaiyan Ma, and Fangfang Zeng. 2025. "The Impact of Digital Village Construction on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture: An Empirical Study Based on Panel Data from 53 Counties in Fujian Province" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093840
APA StyleLian, W., Xue, Z., Ma, G., & Zeng, F. (2025). The Impact of Digital Village Construction on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Eco-Agriculture: An Empirical Study Based on Panel Data from 53 Counties in Fujian Province. Sustainability, 17(9), 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093840






