Abstract
Since its economic reform and opening-up, China has undergone unprecedented urbanization, where massive areas of rural land have been converted into urban use. Urban land development plays an important role in dynamic urban economic development. This study aims to contribute to the understanding of urban land development and its mechanisms in China. We conceptualized the mechanism of urban land development from multiple perspectives based on a case study in Jiangsu Province. We employed the methods of global and local spatial auto-correlation detection and spatial lag model to analyze the provincial land use conveyance and survey data from 2004 to 2008 and 2009 to 2012 to understand the dynamics of urban land development. The results show that urban land development varies significantly across different time periods, spatial scales, and regions in Jiangsu. Higher absolute urban land development mainly occurred in Sunan, expanding to Subei and Suzhong, while faster development occurred mainly in Subei, where the initial bases were lower but had strong economic growth potential. The regression analysis shows that market activities and administrative levels had played a more critical role in driving urban land development, which suggests that rapid urban land development has institutional and market foundations. Urban land development was not only a consequence of economic development but also a strategy of local governments to stimulate and govern the urban economy. This study enriches the literature on urban dynamics by providing an institutional understanding of rapid urban land development in a transitional economy.
1. Introduction
The launch of economic reforms in China in the late 1970s has given rise to unprecedented urbanization. The urbanized population increased from 17.9% to 54.8% between 1978 and 2014 [1], meaning that almost 10 million people had moved to cities each year. In the process of urbanization [2], the flow of rural migrants, land use change, rural industrialization, the roles of state power, and globalization have been the focus of many studies [3,4,5,6]. Significant attention has been placed on rapid urban land expansion owing to a large area of cultivated land having been occupied, threatening the country’s food security [7].
With the help of geographic information systems and remote sensing techniques, existing literature has advanced the understanding of the patterns, mechanisms, and effects of urban growth and land use expansion in China [8,9]. Urban land expansion in China has resulted from industrialization, land commodification, and infrastructure development in the context of rapid economic growth [1,10,11]. Furthermore, physical factors such as geology, geomorphology, elevation, and slope restrict urban land development [12] and changes in social and economic conditions play a decisive role in land use change and urban land growth [13,14]. Other location-specific factors have been considered, including industrial restructuring [15], foreign direct investment (FDI) [16], and traditional culture [17]. Liu et al. showed that urban land development in China was largely driven by demographic changes, economic growth, foreign investment, and changes in land use policies and regulations [18]. Recently, Jiang et al. reported on the relative importance of urban land rent, urban wages, FDI in urban land development and loss of agricultural land in China [19].
However, the perspective gained from econometric analysis focusing on land demand does not provide a complete picture [20]. Local governments also play an important role in urban land development by controlling land supply [21,22,23]. Related failures of land use regulation and land governance have been extensively discussed [24]. Land supply is manipulated by local governments to attract investment and expand local revenue [24,25,26]. Urban land development is a result of seeking profit by multiple stakeholders in the land development process, including officials, developers, and land occupiers [20,22]. Several case studies provide the “big picture” of institutional factors driving urban land development in China. The process was conceptualized as government-engineered and land-centered urbanization [27]. Recent studies have focused on the political economy of urban development in China, especially within the framework of neo-liberalization, to investigate the motivation behind land commodification [28]. Some studies paid particular attention to the roles of different levels of government in the process of urban land development.
In the context of China’s socio-economic transition, the dynamics of urban land development are sophisticated and vary both territorially and temporarily. Therefore, there is a need for more conceptual and empirical studies to fully consider the interweaved factors of land market mechanisms, land finance, and land use policies [29,30]. Subsequently, we establish a conceptual framework with full consideration of land demand and supply, as well as factors such as spatial spill-over effects and the natural environment using spatial econometric modeling to scrutinize the patterns of urban land development and its mechanism in provincial China.
The outline of this work is as follows: the next section conceptualizes the mechanism of urban land development in China, followed by a description of the research methodology. The fourth and fifth sections discuss the changing spatial patterns and the mechanism of urban land development in Jiangsu Province. Conclusions are presented in the last section.
2. Understanding the Dynamics of Urban Land Development in China
2.1. Land Demand Factors
China has been experiencing urbanization and industrialization at an unprecedented rate over the last three decades. In order to adapt to economic globalization, China reshuffled its resource distribution from a centrally planned economy to market regulations and market-oriented economy. More specifically, the state relaxed its budget control over the economy, investment, prices, and state-owned enterprises. Marketization further intensified in the early 2000s as China joined the World Trade Organization regarded as one of the most important aspects of China’s economic reform [30]. Along with deepening reforms and opening-up, the Chinese economy has gradually been integrated into the global production network. FDI played a critical role in accelerating urban and regional economic development.
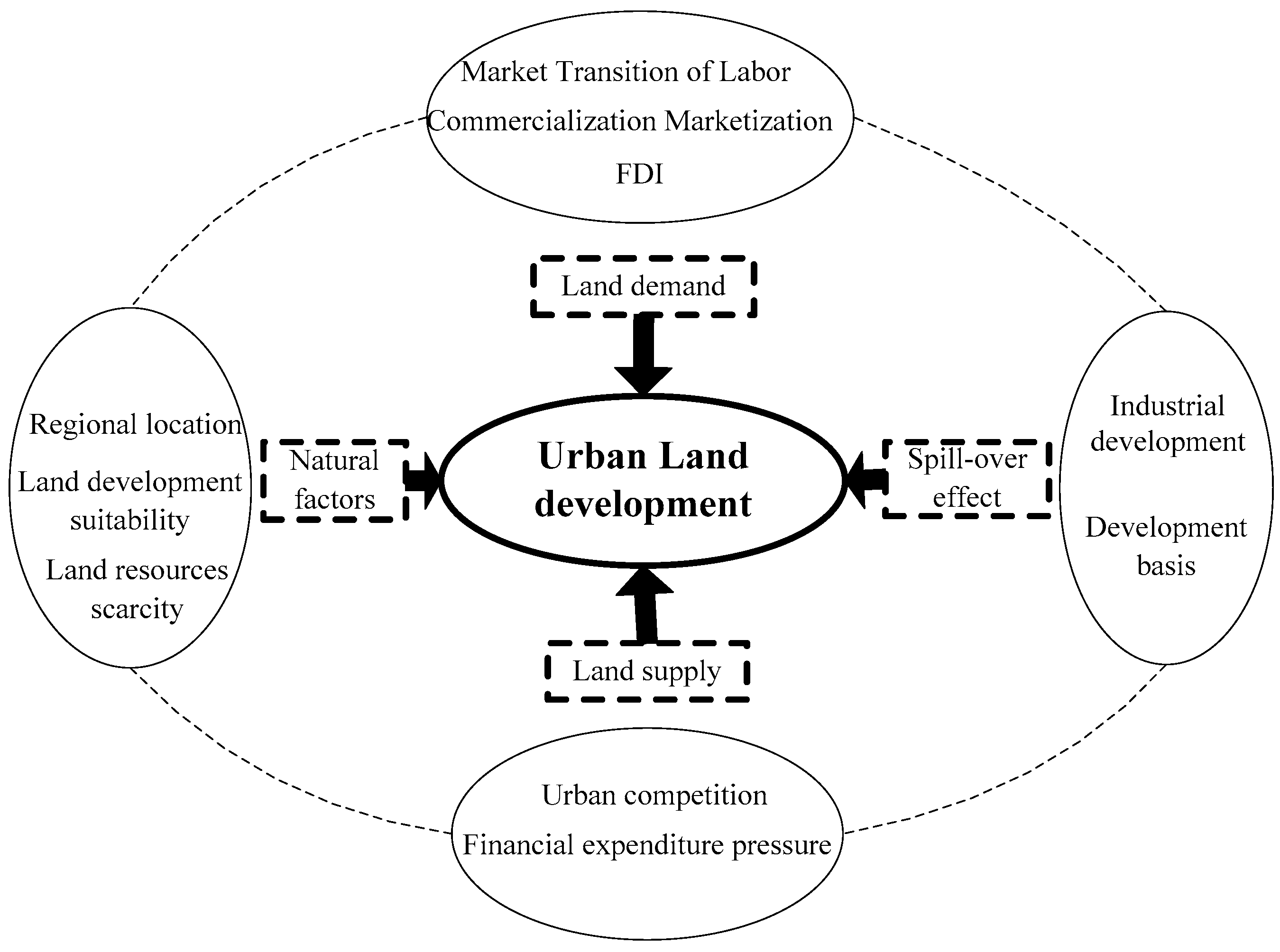
Marketization and the subsequent economic globalization significantly boosted China’s urbanization and industrialization that increased the demand for land development. Meanwhile, urban governments have been competing to improve local infrastructures, highway transport networks, high-speed rails, and airports, as well as to establish various industrial parks and tax-free zones to attract FDI and global resources. Moreover, many new towns and large residential areas have been developed to accommodate the growing urbanized population. Subsequently, the establishment and development of the land market in the early 2000s promoted urban land development dramatically. Marketization of land use catered to land user demands from foreign investors and local businesses [31]. Therefore, we used marketization and globalization indicators to represent the land demand factors of urban land development (Figure 1).
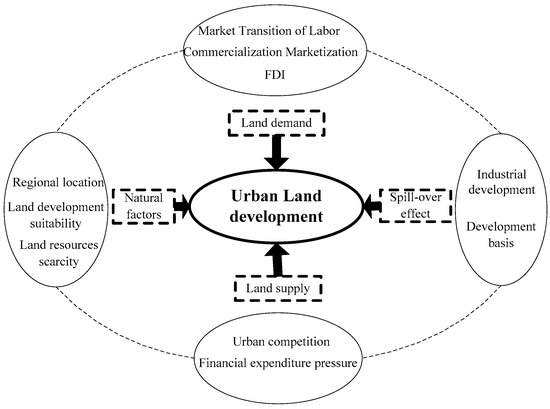
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework for understanding urban land development in urban China.
2.2. Land Supply Factors
Along with the rapid economic growth since the late 1970s, the Chinese governance structure has been decentralized significantly, which has transformed the central-local relations and the priorities of local governments [32]. Alongside economic decentralization, financial decentralization was accomplished by the tax-sharing system implemented in 1994, after which there was a so-called “mismatch” in the financial system, as local governments collected a 40–60% of the tax base, while taking spending 50–70% expenditure in China [26]. Nonetheless, under the cadre promotion system, the political system remains highly centralized. The government at the higher level assigns economic targets to lower-level governments, and local chief officials are promoted mainly based on their economic performance. Consequently, local officials are responsible for and have interests in promoting urban economic development by building local infrastructure, encouraging local businesses, and attracting foreign investment.
Land commodification, along with land and housing reforms in the late 1990s, extended dramatically in urban China. The property sector has become the engine of economic growth and revenue capturing. Various “growth coalitions” were formed by local chief officials and land developers [33]. Moreover, local governments fiercely compete for resources and investments by setting up preferential policies of taxation and land prices, which further complicate urban land development [34]. However, land, as a key input for industrial and commercial development, is yet to be fully marketized in China [35]. Under the current land administration system, local governments can claim agricultural land from rural collectives at low prices to lease to the developers in the land market at either low prices to attract industrial projects or high prices to develop commercial properties [27,32,35]. Subsequently, local governments monopolized land supply and used it as an instrument for developing industrial projects or revenue capturing. Therefore, we used financial expenditure pressure and urban competition to represent the land supply factors of urban land development (Figure 1) in our case study.
2.3. Spill-Over Factors
Urban land development is manifested by the demand of urban socio-economic development, and the scale of the urban economy would generate spill-over effects from urban land development. The speed and intensity of urban land expansion are greatly affected by the foundation and level of urban and regional economic development [36]. With the development of the urban economy, the improvement of residents’ income level, and continuously changing social conditions, people would require improved living standards, environment, and transportation. Hence, there would be an increased demand for entertainment facilities and amenities, resulting in continual restructuring and expansion of urban land development [37]. Particularly, in the process of industrialization, various production factors are driven by agglomeration and scale economies, and they gradually concentrate in urban areas and other favorable geographic locations. Larger economic sectors and production scale further enhance the agglomeration effects of large cities, followed by the continuous expansion of construction land and urban space [38].
Meanwhile, along with the economic expansion, urban governments are eager to promote the relocation of industries from city centers to peripheral areas to prepare for the developing service economy; this is a strategy for upgrading the industrial structure while reducing the secondary industry and promoting the tertiary. Nonetheless, increased land prices in central city areas have forced relatively low value-added sectors to move to city peripheries, where land rent is affordable and transport facilities are in good condition. Consequently, factory workers and a series of support service facilities also move to the suburbs, resulting in urban land development gradually spreading to the periphery of cities [39].
2.4. Natural Factors
Cities and towns are usually proclaimed in superior natural geographic environments. The formation, direction, and scale of land development are therefore closely related to natural geographic factors. An intertwined series of natural factors including geography, geology, topography, geomorphology, and resources constitute the material basis for urban development. Furthermore, the characteristics of the physical-geographical environment directly reveal the potential and cost of urban land development. With the progress of science and technology, engineering abilities have overcome many natural limitations, which have led to urban land development over a short period of time, largely driven by social and economic factors. Nonetheless, the natural geographic environment is still considered a factor in urban land expansion. Natural foundation and background conditions are important as both promoters and restrictors of urban land expansion [40]. Urban land expansion is affected by the underlying surface which has topographical constraints in the process of cities’ formation and development. Hence, cities’ topography and geomorphology have a profound influence on urban form and spatial structure [41]. Zhang Li regarded terrain conditions as an important natural factor that influences urban land expansion in China [42]. In this study, we composed a comprehensive index reflecting the availability of land resources and the suitability of land development to analyze the role of natural factors in urban land development (Figure 1).
3. Study Area and Data Collection
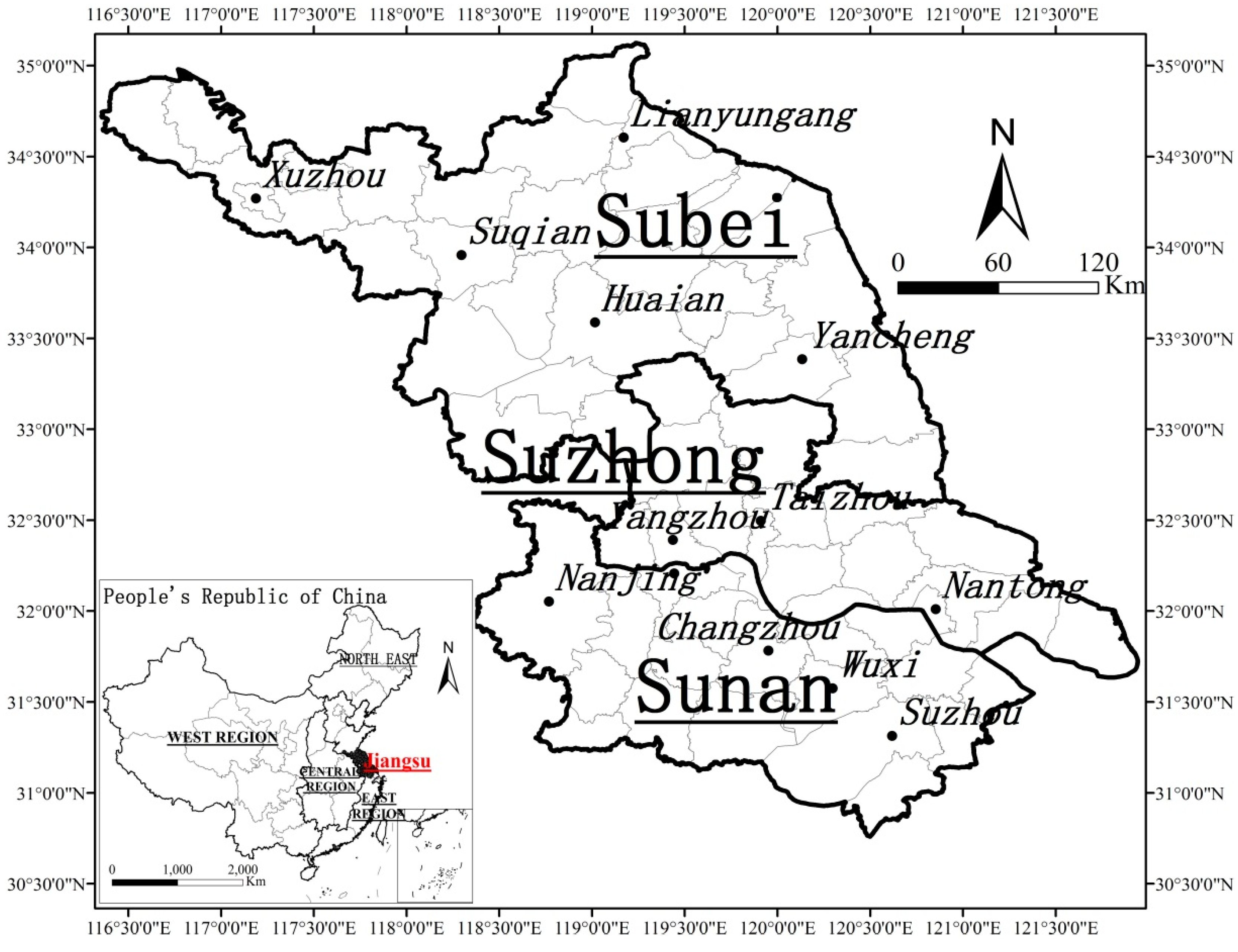
Since its reform and opening-up, China has undergone rapid economic growth and urbanization. The dynamics of urban and regional development together with the transitional institutions resulted in various challenges to land governance, which has drawn the attention of the scientific community. Jiangsu Province is the ideal location to study urban land development in provincial China for the following reasons. Located in the Lower Yangtze River Delta, Jiangsu is one of China’s most developed provinces with the fastest economic growth and highest marketization level. However, Jiangsu has also recently encountered problems of environmental degradation and unbalanced development, which are of concern to the general public, researchers, and government officials. Moreover, Jiangsu has an unequal political culture in that local officials have an entrepreneurial outlook for developing urban and regional economies [43,44,45]. In 2015, Jiangsu covered an area of 102,600 km2, with a population of 79.76 million. Its gross domestic product (GDP) per capita reached $14,114, belonging to the high-income economy group according to the World Bank criteria. Only accounting for 1.06% of land area, the province has attracted 20% of China’s FDI. Along with its rapid economic growth, the province has been experiencing dramatic land use restructuring due to industrialization and urbanization. According to the differences in natural characteristics and the economic development level, Jiangsu Province is divided into three sub-regions. The southern area (Sunan) includes Nanjing (provincial capital), Zhenjiang, Changzhou, Wuxi, and Suzhou; the middle area (Suzhong) includes Nantong, Taizhou, and Yangzhou; the northern area (Subei) includes Xuzhou, Lianyungang, Suqian, Huai’an, and Yancheng (Figure 2). There is a large regional disparity among the sub-regions, in which Sunan has traditionally been the most developed one followed by Suzhong and Subei.
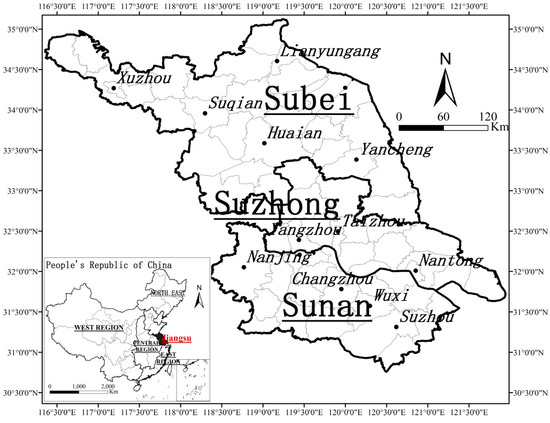
Figure 2.
Location of Jiangsu Province, with its three sub-regions, in China.
Data used in studying urban land development usually come from two sources in China [46]. The first source is remote sensing data such as Landsat TM/ETM satellite images. The interpreted data can explicitly deliver spatial information of urban expansion. However, the data cannot provide detailed land use/land cover changes between different land use types because of their low resolution. The second source is land utilization conveyance data compiled by the Chinese Ministry of Land and Resources (MLR). The MLR updates the data set annually and records the details of the changes in land use types at the county level. The land use types are classified into three major categories, namely agricultural land, construction land, and unused land, each of which has several sub-categories. For example, construction land includes urban and township settlements, rural settlements, industrial/mining sites, transportation land, and land for water conservation facilities. In this study, we used land utilization conveyance data to study urban land development in Jiangsu Province. Urban/township settlements and industrial/transportation land introduced here were regarded as urban land. This is because the data not only offer greater detail regarding changes in land use types but also are statistically consistent with socio-economic data from the statistics department, which is helpful for our quantitative analysis of the urban land development mechanisms.
In 2004, further land market reforms were implemented and the land exchange and reservation center were established under the MLR to secure land market development. Therefore, land leasing, which had been conducted using an administrative approach in the past, had to be conducted through market approaches such as auctioning and bidding. The reform has deeply impacted the pattern of land development in urban China. For this reason, we selected 2004–2012 as the study period and use the construction land for urban development. The second national land use survey in 2008 slightly changed its classification system of land use types, which resulted in statistical gaps. Therefore, we divided the study period into two sub-periods, 2004–2008 and 2009–2012. We further collected socio-economic data on labor, capital, industries, and FDI, amongst others, from Jiangsu Statistical Yearbooks (2005–2013) [47] for modeling the driving factors of urban land development in this province. Social and economic data used in this study, such as GDP, FDI, foreign trade, the output value of three industries, and employed population, come from Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook and Statistics Bulletin of the National Economic and Social Development.
4. Changing Patterns of Urban Land Development in Jiangsu Province
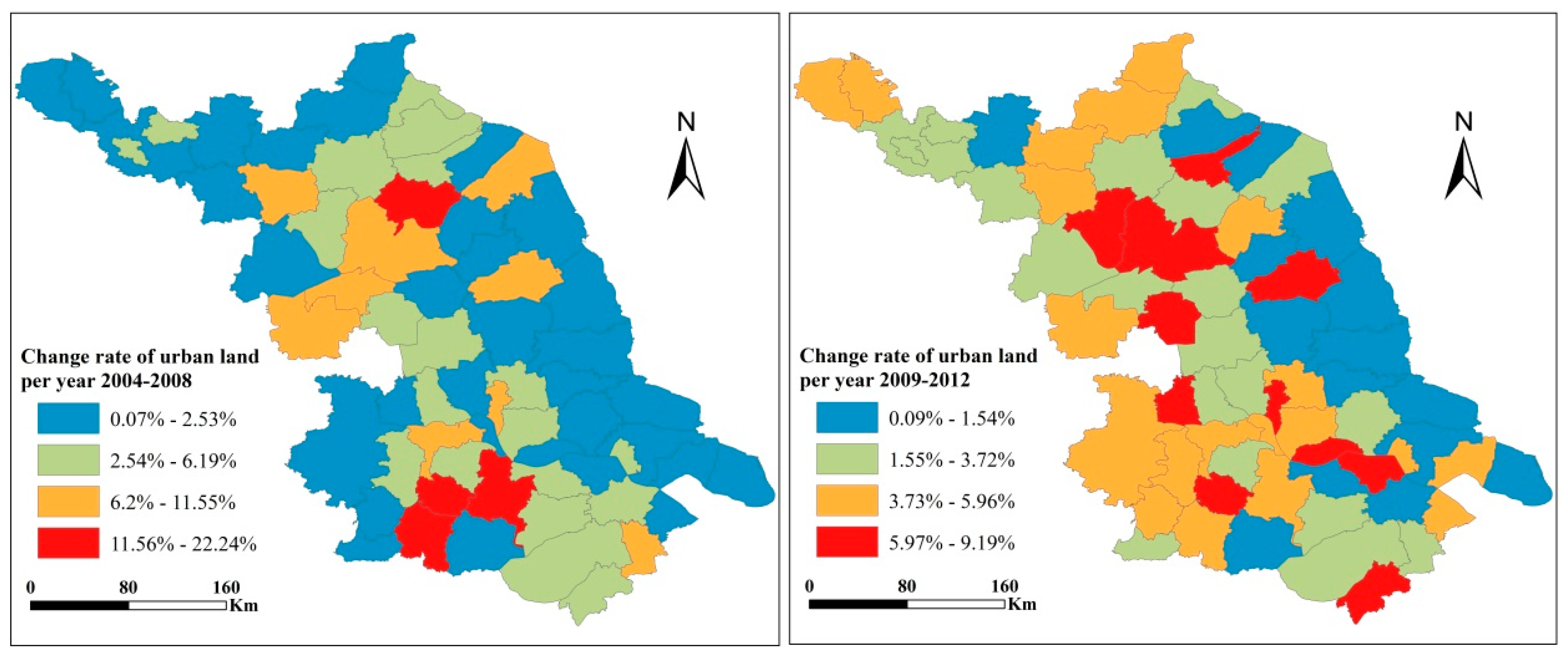
To explore the general pattern of urban land development in Jiangsu Province, we first analyzed the average change in land use from 2004 to 2012. At the provincial level from 2004 to 2008, urban land increased by 9430 ha with an average annual growth rate of 4.53% (Table 1). The rapid increase in urban land reflected the simultaneous rapid economic growth and urbanization in Jiangsu. From 2009 to 2012, urban land increased by 23,350 ha per year, with a slightly lower annual growth rate of 3.92%. At the municipal level, there were significant spatial variations in urban land development between the two study periods. In general, the rate of urban land development in Sunan was higher than that in both Suzhong and Subei. However, although Subei lagged behind Suzhong economically, its urban land development was higher than that of Suzhong in both study periods.

Table 1.
The increasing areas and percentages of urban land development in Jiangsu Province (unit: 1000 ha).
Figure 3 shows the patterns of urban land development at a finer scale, at the county-level, in Jiangsu Province, in both study periods. Several general patterns could be observed: (1) The higher rate of urban land development mainly concentrated in the city centers of Nanjing, Suzhou, Wuxi, and other economically developed cities, while cities and counties with lower economic development had a lower rate of urban land development. (2) Fast expansion rates were mainly distributed in the counties and municipal districts located in Suqian and Yancheng prefectures of Subei, where the initial bases were relatively low but have had greater economic potential in recent years.
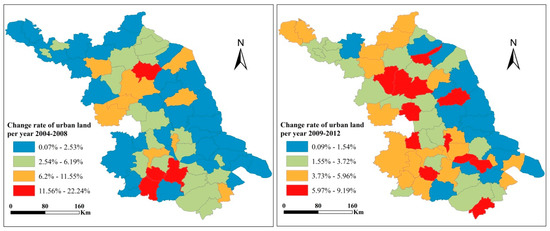
Figure 3.
Patterns of changing urban land development in Jiangsu Province over the two study periods.
5. Urban Land Development Restructuring: Spatial Auto-Correlation Analysis
In order to find the spatial characteristics of changing urban land development in Jiangsu Province, spatial auto-correlation analysis was performed. The annual rate of urban land development at the county level was used to detect the degree of spatial clustering. The Getis–Ord General G(d) and Getis–Ord indices were used to analyze spatial auto-correlations and hotspots of urban land development [44].
The G(d) index is a global statistical tool that was used to detect the overall pattern and trends of spatial clustering of urban land development over the study region and is calculated as follows:
The G-statistic () indicates whether the county-level units’ urban land development with high or low values tended to cluster in a specific area. The method is also known as the hot spots analysis, used to assess the emergence of urban land development clusters within the spatial context of neighboring features and to compare local values with global values. is calculated as follows:
where j ≠ I, and the subscripts refer to the N sub-regions of an area; xj represents an observation for sub-region j; and is a symmetric binary (0 or 1) spatial weight matrix, with 1 representing each unit that is within distance d of a given case i. Inclusion of d in the definition of the statistic is not essential, but it highlights the fact that the technique can be used to search for clusters at different spatial distances by varying the d values. If the change in the urban land development of a city and of its neighboring cities is high, then city is located within a hotspot. The local sum of total land use change of a city and its neighboring cities is compared to the sum of all cities. A Z-score () was used to test whether there was a significant difference between the local sum and expected land use change of a random distribution. The Z-score was transformed as follows:
where E(.) and Var(.) denote the expected value and variance of the statistic , respectively.
The observed values of G for urban land change were 3.32 × 10−2 and 3.02 × 10−2 in two study periods, 2004–2008 and 2009–2012, respectively (Table 2). Both were significant at p < 0.01, confirming that urban land development in Jiangsu exhibits significant spatial dependence. Z[G(d)] also showed that land expansion over the two study periods had positive spatial auto-correlations across Jiangsu. However, the Z-score decreased from 28.93 to 21.76, indicating the decreasing trend of spatial clustering in urban land development in Jiangsu.

Table 2.
The Global Getis–Ord G value of urban land expansion in Jiangsu Province during the two study periods.
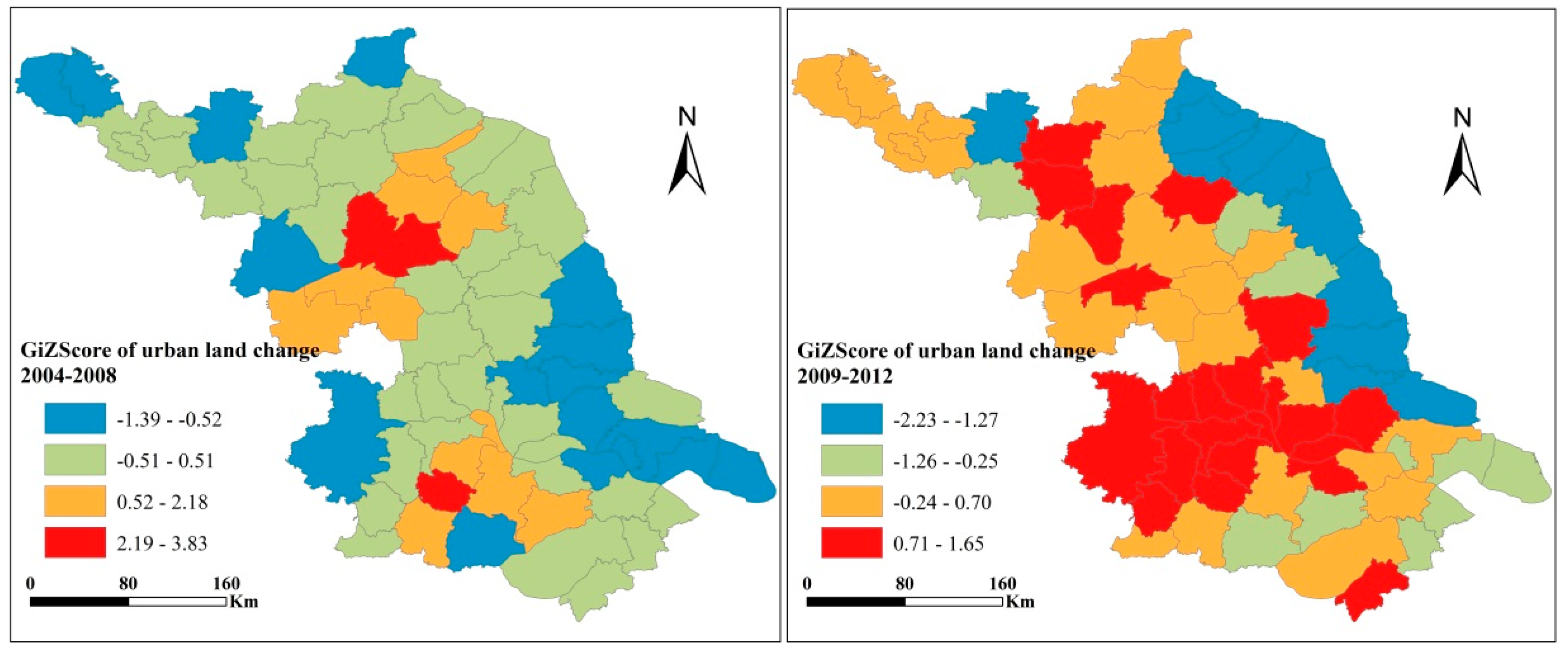
The distribution of the hot spot analysis of Z[] is depicted in Figure 4. The value was divided into four groups by a natural break, from hottest to coldest. The findings show that the hotspots of urban land development are found in core counties in Sunan and Huai’an county in Subei. In general, urban land development in counties along the coast and in Suzhong tends to cluster in low urban land development area, which suggests an uneven pattern of urban land development across the province. However, the pattern changed significantly in the second time period (2009–2012) as more hot spots were detected. Hot spots of urban land development not only emerged in the developed south but also appeared in the less developed north. The results suggest that there was massive urban land development in the region. The spatial cluster of urban land development partly demonstrated the interregional competition in economic development and the imperatives of political promotion.
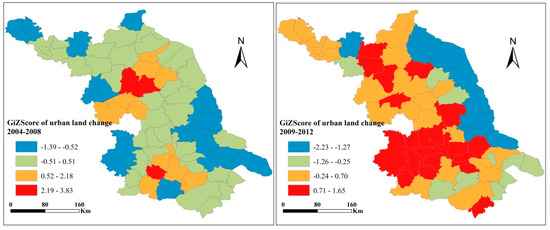
Figure 4.
Hotspot analysis using the Getis–Ord Gi values for the change rate of land area per year in Jiangsu Province during the two study periods.
Interregional competition in Subei may be not as intensive as that in the south because of its poor marketization and low degree of economic development. Moreover, as developed regions, the county-level cities in Sunan expanded more rapidly and reduced the opportunity for urban land development in the surrounding cities. The speed of urban land development was slower in the counties and municipal districts in Subei and Suzhong, respectively. They tend to cluster around the “cold spots” resulting from geographic constraints and relatively poor foundation, leading to the slower pace of urban land development (Figure 4).
6. Driving Factors of Urban Land Development: Market Mechanisms and Local Government Initiatives
6.1. Model Specifications and Selection of Variables
The spatial Getis–Ord statistic shows that there was a significant spatial correlation of urban land development in Jiangsu Province in the two study periods. Therefore, we employed the spatial lag model (SLM) to identify the determinants of urban land development by controlling these spatial effects. The SLM was defined as follows:
where y is the change in urban land development at the county level in 2004–2008 and 2009–2012, in Jiangsu; W is the n × n spatial weight matrix, reflecting the spatial trends of the variable; Wy is the first-order lag space dependent variable; ρ is the coefficient of spatial lag term; X is the exogenous variables observed value; β is the variable regression coefficient; and ε is the error term. We used OpenGeoda software version (Spatial Analysis Laboratory Department of Geography University of ILLinois, Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Champaign, IL, USA) to generate the weight matrix with a first-order Rook contiguity. The independent variable matrix is the logarithm of the influence factors and calculated as follows:
A series of exploratory variables were used to conceptualize urban land development as a result of the INTERACTION of factors from land demand, land supply, spill-over effects, and the natural environment (Table 3).

Table 3.
Definitions of dependent and independent variables used in this study.
Since the early 1980s, under the market-oriented reform, China’s economic development has been highly reliant on increasing market development, private sectors, and FDI (foreign direct investment). Therefore, the land demand has expanded significantly, calling for increasing urban land development. Therefore, labor marketization (the proportion of employment in the non-state sector), production marketization (the proportion of output value in non-state-owned enterprises), FDI, and international trade development were selected to reflect the demand for residential land, industrial land, and infrastructure by migrants and enterprises flooding into urban areas.
Furthermore, the land supply plays a significant role in urban land development considering the political-economic context of land supply in China. The fiscal and political decentralization greatly influenced land development politics. Local governments have monopolized the rights to transform land for urban land use from rural collectives, after which the land becomes collateral to mobilize banking loans and serves as a means of capital accumulation. Local governments further rely on land sales to earn land conveyance fees to compensate for insufficient tax revenues and alleviate financial pressure. Furthermore, cities compete through land supply policies to attract FDI and inward private investment to boost economic growth. Subsequently, we used administrative levels and financial constraints to represent land supply factors in urban land development.
The spill-over effect of urban land development is mainly reflected in the following aspects: High living standards and wages are major factors attracting migrants to urban areas in China. Along with more than three decades of rapid economic development, industrial infrastructure upgrades (i.e., reducing secondary industries, promoting tertiary industries, and vacating the cage for new bird) are the priorities for local governments. Therefore, some production and processing enterprises have moved to the outskirts and less developed parts of the cities where land prices are lower and regulations are fewer. In this study, we used GDP per capita and industrial structure to represent the spill-over effects of urban land development that have positive relations.
Lastly, natural factors are the foundation of urban land development, even though humans have the capacity to overcome various geographic constraints for land development. In this study, we used the following variables: suitability of land development, land location (the degree of economic suitability of land to be developed), and scarcity of land resources to represent the natural factors of urban land development.
6.2. Results of the Regression Analysis
Before conducting the regression analysis, we analyzed the correlations between 11 variables and incorporated the highly correlated variables into three different models to reduce multi-collinearity. Table 4 presents the correlation coefficients between different variables. We take the logarithm transformation to consider the nonlinear relationships between the dependent and independent variables. The log-transformation can also reduce the impacts of outliers on model estimations. All dependent variables, except LF and RL, are positively correlated with the index of urban land change. The relationships between LF and PGDP, MTL and PGDP, LIT and LF, LF and IAIS are moderately correlated with a correlation coefficient greater than 0.62. Other correlation coefficients are fairly small. Table 4 shows the correlation matrix between the independent variables and the change in urban land use. Three models for the two study periods were derived to eliminate the inter-correlation between independent variables and analyze the impacts of the factors of land demand, land supply, spill-over effects, and the natural environment on changes in urban land development in Jiangsu Province.

Table 4.
Correlation coefficient matrix.
The land demand indicators, except for labor marketization, were significantly correlated with urban land development, suggesting that the development of market activities played a critical role in driving urban land development. Interestingly, the labor factor had a positive and elastic effect ranging from 0.035 to −0.01, but not a significant correlation with urban land development in the first period and a slightly negative and significant correlation in the second. Along with the advancement of Jiangsu’s urbanization level and economy, the role of labor resources in urban development was marginalized. What is really scarce for advancing urban economies in relatively developed areas such as Jiangsu is skilled labor and human capital. Moreover, housing prices are continually increasing in most cities, which prevent migrants from poor provinces from settling. In the second period of this study, production marketization played a negative role in land urbanization; the effect of action is 0.224, which suggests that local governments’ strategies for upgrading industries have led to the retreat of small and middle-sized enterprises from city centers to peripheral areas or other poor provinces. In general, international trade consistently contributed to urban land development in Jiangsu Province in two study periods because Jiangsu is characterized as an export-oriented economy in China. Indeed, globalization has supplied Jiangsu with a large market and foreign firms, especially transnational corporations. Globalized cities may experience a higher rate of urban land development to build industrial parks and high-grade residential areas [10].
Regarding the land supply factors, administrative levels of local governments played a significant role in urban land development in Jiangsu Province. The Chinese land management system is a hybrid between centralization and decentralization. Although the location of supply is controlled by the lower levels of the government, the extent of land supply is controlled by a top-down land quota system. The quota allocation corresponds to the administrative level, suggesting that higher administrative level cities control the land quota of lower levels. Moreover, higher-level cities are usually big cities, which may also affect the results. The effect strength is more than 0.4 in two periods. Because of data limitations, we used indirect factors to represent the motivations of urban governments for land revenue. The factor of financial constraint was positively, but not significantly, correlated with urban land development in both study periods, suggesting that revenue capture was not a major factor in urban governments’ promotion of urban land development in Jiangsu. It also echoes the literature in that, compared to revenue capture, economic growth is more important in local officials’ terms of office.
In the 21st century, the development of urban economy in Jiangsu Province has been accompanied by the adjustment and upgrading of industrial structures. As a result of continuously rising land prices in the city center and the government’s industrial policies, low-end industries were forced to move to suburbs and less developed cities with relatively lower land rent and labor costs. Correspondingly, employment and a series of ancillary service facilities were also transferred. Selected indicators of spill-over effects were correlated with urban land development in two periods (Table 5). Along with the advancement of urban economy, urban populations demand higher living standards, better environment and larger number of recreational facilities and amenities that further promote urban land development.

Table 5.
Regression analysis results from the spatial lag model for the rate of change for urban land in Jiangsu Province in the two study periods.
Location had a positive and significant correlation with urban land development, whereas the scarcity of land resources was negatively correlated with urban land development. This was because of the expansion of urban land located on the outskirts of urban areas with high-quality cultivated land. The central government has established strict regulations to protect farmland, which has a significant impact on local urban land development. However, the suitability of land development only had a positive and significant correlation with urban land development in the second study period, which further highlights the land resource scarcity. In general, natural factors played important roles in urban land development in Jiangsu Province, which confirms our assumptions.
7. Conclusions
Urban land development has accompanied China’s rapid economic development since its reform and opening-up in the early 1980s. This study built a ground-specific conceptual framework to understand the dynamics of urban development in China and analyze the spatio-temporal patterns and its driving factors in the process of China’s economic transition. The empirical study was conducted in a developed province, Jiangsu. Based on the official land use conveyance data from 2004 to 2012, we explored the patterns of urban land development at different spatial scales and argued that urban land development in Jiangsu Province was driven by the interaction of four factors: land demand, land supply, spill-over effects, and the natural environment. The analysis and the case study captured the main characteristics of urban land development in the context of economic transition in developed provincial China.
From 2004 to 2008, urban land increased by 9430 ha, with an average annual growth rate of 4.53%, while from 2009 to 2012 urban land increased by 23,350 ha per year, with a slightly lower annual growth rate of 3.92%. The rapid increase of urban land reflected the dynamics of the urban economy and urbanization in Jiangsu. Significant spatial variations in urban land development were observed at the county level. Higher urban land development was also observed mainly in the sub-region of Sunan, expanding to Subei and Suzhong, while more rapid changes in urban land development were mainly distributed in the counties and cities located in Subei, where the initial bases were lower but have had greater economic potential in recent years.
Among the land demand indicators, except for labor marketization, production marketization, FDI, and international trade were significantly correlated with urban land development in both study periods in Jiangsu Province. This suggests that the development of market activities played a critical role in driving urban land development. With regards to the land supply factors, administrative levels of local government played a significant role in urban land development in Jiangsu because of the hierarchal nature of the land supply system in China. Selected indicators for spill-over effects were correlated with urban land development in the two periods. In general, the natural factors played important roles in urban land development, confirming our assumptions. The results therefore show that the conceptual framework built in this research could adequately explain urban land development in Jiangsu Province. The regression analysis further implied that rapid urban land development has institutional and market foundations and it was not only a consequence of economic development but also regarded as a strategy to develop the urban economy.
Land is considered one of the most important factors in the literature of urban growth. In the market economy, land development is mainly regarded as a consequence of the expansion of economic activities. Our analysis suggests that land development in China is much more complex owing to the country’s distinctive land ownership and land management system. Particularly, under the vertical control of land supply management, it favors the cities with rapid economic growth, while the other cities seek alternative channels to support project development, which may result in a much more complicated landscape of urban land development in contemporary China. By highlighting these institutional factors, this study contributes to the understanding of urban land development as a result of both market-oriented development and governance strategies of levels of government. However, because of fierce urban competition, land supply and land price are usually used as tools to attract investment and over-supply and informal land development are serious concerns for sustainable development in the long term. Therefore, land use efficiency and land use policies should be reviewed to counteract the land-centered urbanization in China.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by Science and Technology Service Network Initiative of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-STS-ZDTP-011) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20161088). We would also like to thank Zhifeng Jin for his help on data acquisition and insightful suggestions on revising the draft version and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author Contributions
Qingke Yang contributed to data processing and analysis; Xuejun Duan designed the research and provided guidance on manuscript writing; Qingke Yang and Lei Wang wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bai, X.M.; Shi, P.J.; Liu, Y.S. Realizing China’s urban dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.W. Crossing the 50 Percent Population Rubicon: Can China Urbanize to Prosperity? Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2012, 53, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.C. Urban transformation in China, 1949–2000: A review and research agenda. Environ. Plan. A 2002, 34, 1545–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.F.; Wong, K.Y.; Feng, Z.Q. State-sponsored and spontaneous urbanization in the Pearl River Delta of south China, 1980–1998. Urban Geogr. 2002, 23, 674–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Ma, L.J.C. China’s urbanization levels: Reconstructing a baseline from the fifth population census. China Q. 2003, 173, 176–196. [Google Scholar]
- Pannell, C.W. China’s continuing urban transition. Environ. Plan. A 2002, 34, 1571–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.A. Patterns of Federal Urban Spending Central Cities and their Suburbs, 1983–1992. Urban Aff. Rev. 1995, 31, 184–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wei, Y.H.D. Modeling spatial variations of urban growth patterns in Chinese cities: The case of Nanjing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 91, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Qu, Y.; Chen, L. Spatiotemporal variation analysis of driving forces of urban land spatial expansion using logistic regression: A case study of port towns in Taicang City, China. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, R. Land use change and economic growth in urban China: A structural equation analysis. Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 2880–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.H.F.; Wei, Y.H.D. Modeling determinants of urban growth in Dongguan, China: A spatial logistic approach. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; van de Steeg, J.; Veldkamp, A.; Willemen, L. From land cover change to land function dynamics: A major challenge to improve land characterization. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jin, C.; Li, F.; Liu, H. Land Use Change in Sanjiang Plain and Its Driving Forces Analysis since 1954. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Cao, G. Progress in Urban Land Expansion and Its Driving Forces. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, G.; Xu, Y. Interactive Relationship between Land Use Change and Industrial Change. Resour. Sci. 2005, 27, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.Z. Land use Change Mechanism in Shenzhen City. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2000, 55, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.; Zhang, Y. Role of traditional cultural factors in land use changes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2002, 24, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Jiang, X.S. Financial Risks of Land Financing by Local Governments—Case Study of a Developed Area in East China. China Land Sci. 2005, 19, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Deng, X.; Seto, K.C. Multi-level modeling of urban expansion and cultivated land conversion for urban hotspot counties in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, C.P. Explaining Land Use Change in a Guangdong County: The Supply Side of the Story. China Q. 2011, 207, 626–648. [Google Scholar]
- Cartier, C. ‘Zone Fever’, the Arable Land Debate, and Real Estate Speculation: China’s evolving land use regime and its geographical contradictions. J. Contemp. China 2001, 10, 445–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S. Urban expansion in contemporary China: What can we learn from a small town? Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.-R.; Wang, H.-K. Dilemmas of local governance under the development zone fever in China: A case study of the Suzhou region. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Ho, S.P.S. The state, land system, and land development processes in contemporary China. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2005, 95, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Land Expansion in China during the Economic Reform Era. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2005, 34, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Su, F.; Liu, M.; Cao, G. Land Leasing and Local Public Finance in China’s Regional Development: Evidence from Prefecture-level Cities. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 2217–2236. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z. Fiscal decentralization, political centralization, and urban land development in China. Urban Geogr. 2015, 37, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S. Reproducing spaces of chinese urbanisation: New city-based and land-centred urban transformation. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 1827–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wei, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Yenneti, K. Urban Land Expansion and Structural Change in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10281–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, Y.D.; He, C.; Li, H. Urban land expansion under economic transition in China: A multi-level modeling analysis. Habitat Int. 2015, 47, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.M. A transitional institution for the emerging land market in urban China. Urban Stud. 2005, 42, 1369–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. Urban Infrastructure Financing and Economic Performance in China. Urban Geogr. 2010, 31, 648–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. Local developmental state and order in China’s urban development during transition. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2004, 28, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Zhou, L.A. Political turnover and economic performance: The incentive role of personnel control in China. J. Public Econ. 2005, 89, 1743–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Yi, F. Urbanization of Capital or Capitalization on Urban Land? Land Development and Local Public Finance in Urbanizing China. Urban Geogr. 2011, 32, 50–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Yang, G. An Analysis of Driving Forces of Urban Land Expansion—A Case Study of Hubei Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 13, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.L.; Yu, T.F.; Li, W.M. China’s Urbanization: Structure, Process, Mechanism; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Uchida, E. Growth, population and industrialization, and urban land expansion of China. J. Urban Econ. 2008, 63, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chang, K.-T.; Karacsonyi, D.; Zhang, X. Comparing urban land expansion and its driving factors in Shenzhen and Dongguan, China. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.N.; Zhang, X.L. A Study on the Impetus Mechanism and Models of Urban Spatial Expansion. Areal Res. Dev. 1997, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.Z.; Liu, S.Z. The Geomorphological Factors of Influence on Urban Distribution and Construction in China. J. Southwest Teach. Univ. 1990, 15, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lei, J.; Li, X.; Gao, C. The Features and Influencing Factors of Urban Expansion in China during 1997–2007. Prog. Geogr. 2011, 30, 607–614. [Google Scholar]
- Oi, J.C. Rural China Takes off: Institutional Foundations of Economic Reform; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; pp. 1215–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wong, C.; Duan, X. Urban growth and spatial restructuring patterns: The case of Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Environ. Plan. B 2016, 43, 515–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.D.; Fan, C.C. Regional Inequality in China: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Prof. Geogr. 2000, 52, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wei, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Economic transition and urban land expansion in Provincial China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Statistics of Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook (2005–2013); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).