Abstract
Coal is an important energy resource in the world, especially in China. Extensive coal exploitation seriously damaged the grassland and its fragile ecosystem. However, temporal and spatial impact laws of open-pit coal exploitation on Landscape Ecological Health (LEH) of semi-arid grasslands are still not clear. Therefore, the main objective of this paper is to study impact of Large-scale Open-pit Coal Base (LOCB) on the LEH of semi-arid grasslands from the perspectives of temporal and spatial. Taking Shengli LOCB of Xilinguole grassland in Inner Mongolia as an example, we demonstrate a conceptual model of LOCB impact on LEH of semi-arid grasslands, and establish a research system called landscape Index-pattern Evolution-Driving force-Spatial statistics (IEDS). A complete process integrated from investigation, monitoring, and evaluation to the analysis of impact laws was developed. Result indicated that coal mining causes gradual increase of landscape patches, landscape fragmentation, gradual decline of landscape connectivity, complexity and irregularity of landscape shape, enhancement of landscape heterogeneity and complexity, gradual decline of landscape stability, gradual decrease of grassland landscape and annual increase of unhealthy grassland landscape. The LEH of grassland basically belongs to the state of slight deterioration. In the past 15 years, the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of LEH in the study area are similar. This study provides scientific reference for ecological disturbance research, environmental protection, landscape planning, restoration and renovation of ecological environment in mining areas. At the same time, future research should integrate geological, hydrological, soil, vegetation, microorganisms, animals, climate, and other perspectives to study the impact of mining on landscape ecology deeply.
1. Introduction
Coal is the most important energy resource in China [1]. Since economic reform and expansion, the demand for mineral and fossil fuel resources is growing due to China’s social and economic development. This stimulated rapid development of coal mining industry, which, in turn, promoted the rapid development of the social economy [2]. To further meet China’s energy needs, the Chinese government is focusing on building 14 large-scale coal bases during the 12th Five-Year Plan period. In 2015, the coal production of China’s large-scale coal bases accounted for 93% of the total coal production [3]. From a worldwide perspective, mining areas are present on all continents except Antarctica. The biggest impact on the landscape, however, was made by mining of the past 250 years, since the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries [4]. In the 20th century, the availability of industrial mining technologies, such as bucket-wheel excavators or conveyor bridge systems, enhanced the complete modification of landscapes on a regional scale in practically all large mining districts of the world [5]. The problem of landscape transformations due to human activities has been present in the literature for over a hundred years and has undergone successive stages of scientific diagnosis—from ascertaining the fact of transformations and their description, through classifying the forms and processes, to the quantitative and qualitative recognition of transformations [4]. Therefore, mining activities have caused a wide range of significant impacts on the landscapes not only in China [6,7], but also in Europe [4,8,9,10,11,12], Asia [13,14,15,16], Americas [17,18,19], Africa [20,21], and Oceania [22,23]. It follows that large-scale coal exploitation activities, often lead to severe disturbances of regional landscape ecology. Coal mining areas nowadays represent the most typical and degraded ecosystem of the terrestrial biosphere [24]. In particular, open-pit mining operations replace the former dynamic equilibrium of the landscape ecology, eventually resulting in the new ecosystem development. Large-scale open-pit coal mines affect all landscape components and functions [25]: gradual evolution of the landscape is interrupted, original ecosystems are removed, and biodiversity is significantly reduced. At the same time, landscape functions and recreational potential, as well as its aesthetic value, is degraded [26]. Impact of coal mining, as a temporary large-scale project developed to satisfy human needs, on landscape ecology is difficult to accurately identify, both in time and space. However, if the impact of mining activities on landscape ecology can be identified, then cost of human, material, and financial resources in the process of ecological restoration can be greatly reduced, which will eventually help to achieve more satisfactory ecological benefits.
The proposition of Landscape Ecological Health (LEH) discusses health problems of landscape ecology, which is seriously polluted and degraded or even gradually disappeared under the interference of extensive human activities. LEH originates from natural health [27,28], land health [29], ecological medicine [30] and ecosystem health (EH) [31]. At present, there is still no consensus on the appropriate definition of EH [32,33]. Due to the impact of EH, the concept of LEH has no authoritative meaning. Many scholars have defined it from different research perspectives [34]. Ferguson [35] firstly extended the concept of health to the landscape level, considering landscape health as a “dynamic balance” state, where the regulation and feedback mechanism maintains the automatic regulation function of the whole landscape. Rapport et al. [36,37] argue that a healthy landscape simply needs to be able to provide a satisfactory range of ecological services. Cao Yu et al. [38] defined a healthy landscape as holding two characteristics. First, under the condition of active human intervention, the impact of human activities will not lead to landscape disorder in maintaining its own stable structure and normal function. Second, with the passage of time, the evolution and development of landscape will not affect or damage the orderly, healthy, and sustainable development of adjacent landscapes and human socio-economic systems. Bojie Fu et al. [39] hold that LEH refers to the stability and sustainability of the rich ecosystem services provided by different types of ecosystems within a certain space-time range and on the premise of maintaining their own health. This means that a healthy landscape has the ability to maintain its spatial structure and ecological process, its self-regulation and renewal, the ability to restore to stress in time, and can ensure the sustainable and optimal supply of ecosystem services. LEH is the basis and an ideal end point of ecological environmental management and is a cornerstone of sustainable development [38].
Natural vegetation in the semi-arid areas mainly consists of grassland, which is characterized by drought, poor soil as well as by high potential evaporation capacity, short plant growth, low biomass, simple biological chains, slow material circulation, ecosystem energy conversion and fragile ecological ecosystem [40,41]. Grassland degradation is very serious in these areas. Xilingole Grassland is one of the four natural grasslands in China and the only National Grassland Nature Reserve listed in the United Nations Human and Biosphere Protection Network in China [42,43]. Situated in the hinterland of Xilinguole grassland, Xilinhot is a typical mining city with simultaneous exploration of coal, petroleum, heavy metals and other mineral resources. Driven by human disturbance such as high-intensity energy development, urban expansion, industrial development and overgrazing, grassland landscape pattern, process and functions are gradually changing, and LEH becomes more and more problematic. The contradiction between mankind, land, and ecological environment is serious in Xilinhot City. Therefore, taking Shengli Coal Base of Xilinhot City as an example, we studies how open-pit mining impacts on LEH of semi-arid grasslands. Our goal was not only to perform theoretical studies of these phenomena, but also to demonstrate practical significance of our results in order to maintain sustainable and healthy development of this and similar regions.
In addition to landscape, the region impacted by mining also focuses on: (1) impact of waste produced during mining and mineral processing on the environment [44]; (2) impact of heavy metals due to coal mining on regional ecological environment as well as on human or animal health [45,46,47]; (3) impact of coal mining on ecosystem services [48]; (4) mining impact on land use in general [49]; (5) impact of atmospheric dust produced by mining on the surrounding areas [50], etc. However, all existing research dose not discuss impact of mining on LEH, especially on LEH of semi-arid grasslands. Current research methods require a lot of manpower, materials, and financial resources to conduct on-site sampling, analysis, or surveys. Yet, they failed to perform macro- and micro-research as well as time- and space-dependent multi-scale and multi-angle analyses. During the past decades, remote sensing technology is coming into an important and necessary tool for large-scale ecological monitoring and impact assessment. This method, being simultaneously a multi-platform and multi-band, offers many advantages such as multi-platform, multi-band, multi-field of view, multi-temporal, multi-angle, and multi-polarization. Integration of remote sensing with geographical information systems can further strengthen the capabilities of environmental impact assessment of mining activities at both regional and global scales.
The objectives of this study were: (1) to summarize a conceptual model of the impact of Large-scale Open-pit Coal Base (LOCB) on the LEH of semi-arid grasslands; (2) to build a framework to study the impact of LOCB on the LEH of semi-arid grasslands; and (3) to study the impact of Shengli LOCB in Xilinhot on the LEH of semi-arid grasslands indepth. The significance of this study was to provide references to study the impact of human disturbance on LEH, as well as to optimize landscape pattern of large coal bases and to manage the regional ecological environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Conceptual Model of the LOCB Impact on LEH of Semi-Arid Grasslands
Types of disturbance landscapes formed during open-pit coal mining are excavation, occupied, piled-up types [51]. The excavation type landscapes are typically open-pits formed during direct coal excavation. Piled-up landscapes mainly refer to dump sites. Occupied landscapes include coal preparation and washing plants, coal conveyance stacks, roads, industrial squares, etc., developed and constructed specifically for coal development. Impact of all these open-pit mines on grasslands is visible defined as ”Dominant Impact“ in this study.
The biggest impact of open-pit coal mining on ecology is topology change. As open-pit elevation is continuously reduced, surrounding surface and ground waters accumulate in these pits, indirectly affecting ecological functions of the landscape of a surrounding grassland. High topography and unstable geological structures of the dump sites can easily lead to soil erosion and affect the ecological function of the landscape of surrounding grasslands. Dust is formed during coal excavation, transportation, and production. Heavy metals in this dust also affect grassland landscape functions. In this work, process of reducing the ecological function of grassland landscape around open-pit coal mines is called ”Recessive Impact”.
2.2. Research Area
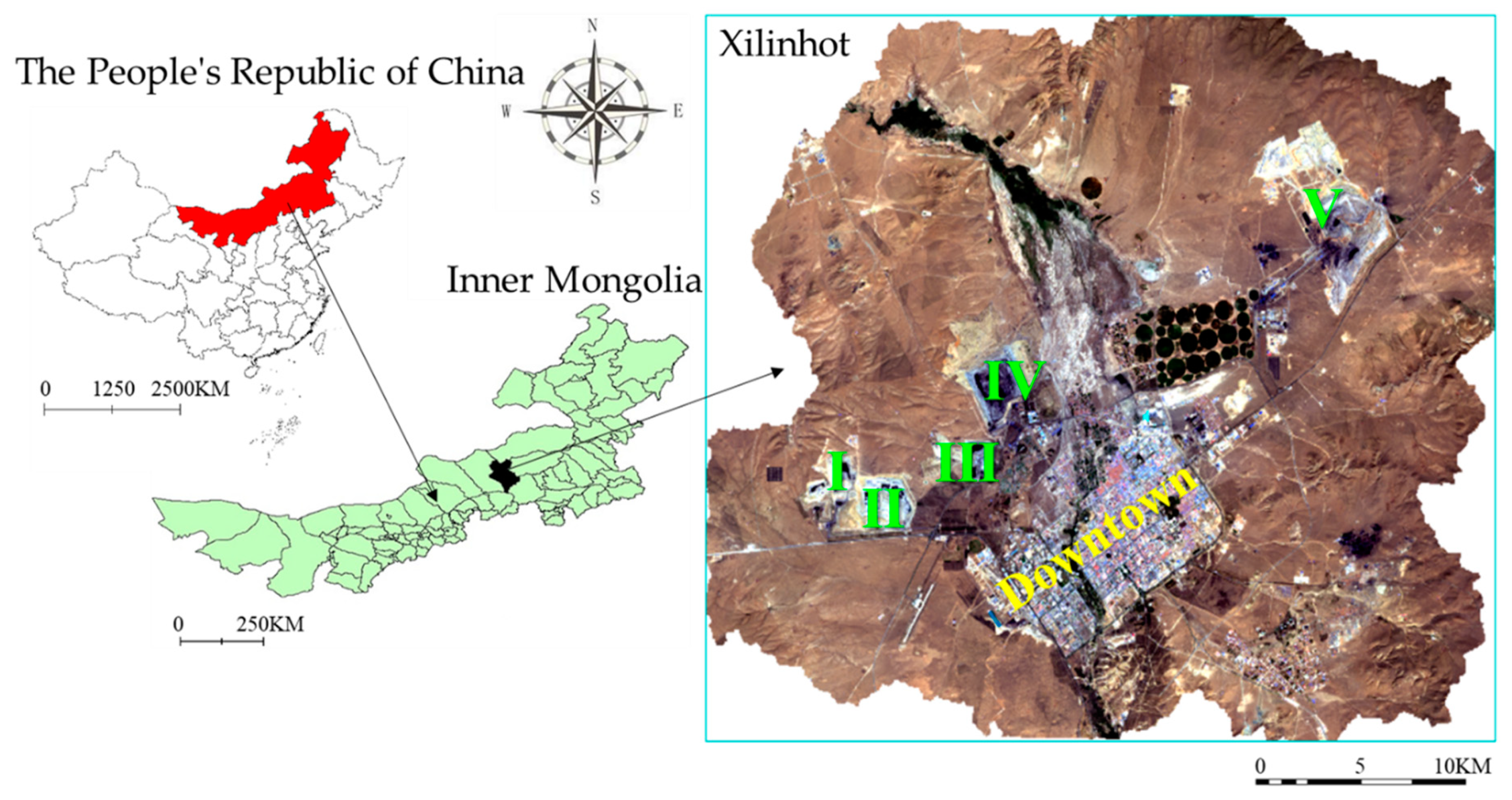
Our research area was Shengli mining area in the northern suburbs of Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Figure 1). This area belongs to the Mengdong LOCB, which is one of the 14 LOCBs in China. Geographical coordinates of this region are 43°02′–44°52′ latitude, 115°18′–117°06′ east longitude, and 970–1202 m elevation. This area is located in the mid-latitude westerly air zone and is characterized by the semi-arid continental climate in the middle temperate zone. Average annual rainfall is 294.74 mm, with an average annual potential evaporation of 1794.64 mm. Potential evaporation refers to the evaporation capacity rather than actual evaporation. Xilin River is the largest river in the research area; it is 268 km distance and is currently a seasonal river.
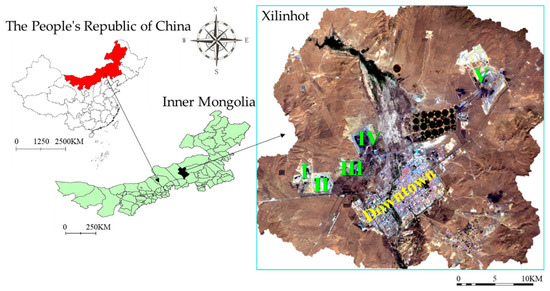
Figure 1.
Location of the Research Area. I: Open-pit Germanium Mine; II: West No. 2 Open-pit Mine; III: West No. 3 Open-pit Mine; IV: No. 1 Open-pit Mine; V: East No. 2 Open-pit Mine.
2.3. Data Source and Processing
We selected six Landsat data sets dated as 8 July 2002, 17 August 2005, 8 July 2008, 2 August 2011, 25 July 2014, 17 July 2017 [52]. The spatial resolution of remote sensing image is 30 m per pixel [53]. Radiation calibration, FLAASH atmospheric correction, image registration, and image clipping were preprocessed. Supervised classification and visual correction methods were used to obtain Landscape Patterns Evolution (LPE) maps. Landscape Pattern Indexes (LPIs) were calculated by the Fragstats standard algorithm. LEH assessment results over the years were obtained using an index system method [54]. Data on China’s raw coal production and total coal consumption were downloaded from the National Bureau of Statistics website (http://www.stats.gov.cn/).
2.4. Analysis Method
2.4.1. Landscape Pattern Index (LPI)
According to the main impact of LOCB on landscape pattern of semi-arid grasslands, LPIs can be divided into three levels: landscape pattern fragmentation, connectivity, and diversity. The impact of mining on grassland LEH was analyzed using Fragmentation-Connectivity-Diversity (FCD) framework. Aggregation, contagion and landscape shape indices (AI, CONTAG, and LSI, respectively) were selected to reflect landscape pattern fragmentation. Patch cohesion and connectivity indices (COHESION and CONNECT, respectively) were used to reflect connectivity. Shannon’s diversity and evenness indices (SHDI and SHEI, respectively) as well as patch number (NP) were implemented to reflect diversity status of the study area (Table 1).

Table 1.
The landscape ecological significance of each landscape pattern indices.
2.4.2. Landscape Patterns Evolution (LPE)
In this study, landscape type change and grassland occupation by main landscape types were used to analyze the evolution of landscape pattern in the study area. Grassland occupation by main landscape types is computed using transfer matrix method. Transfer matrix can comprehensively and specifically describe structural characteristics of LPE and its direction. Its mathematical form is:
where A represents the area of landscape type; n represents the number of landscape types; i, j represents the landscape types at the beginning and end of the research period, respectively.
2.4.3. Driving Forces (DF)
Dynamic changes of LEH are mainly driven by natural and human factors. Because the scope of our study area is relatively small, difference of natural DFs (e.g., climate, soil, plant diversity, etc.) are small as well. At the same time, our study area is located at the northern border of China, which is an area populated by Mongolians. Their population growth is very slow, and their cultural concepts are very similar. Progress and development in science, technology, economy, and other aspects are relatively slow as well. Therefore, according to the characteristics of the research, we selected elevation, slope, aspect, and distance to the nearest water landscape (WATER) as natural DFs. Distance to the nearest mining landscape (MINE), distance to the nearest town construction land landscape (TOWN), distance to the nearest industries and storage land landscape (INDU), distance to the nearest agricultural landscape (AGRI) and distance to the nearest road network landscape (ROAD) were chosen as human DFs.
DF of LEH change in semi-arid grasslands was studied using geographic detection method [55,56]. The formula of geographic detection model is described as Equation (2):
where h = 1,..., L is the stratification of variable Y or factor X; Nh and N are the unit number of layer h and whole region; and σ2 are the variance of Y values of layer h and whole region, respectively. q represents the size of the driving force. The range of q is [0,1]. The larger the q value, the more obvious the driving force is.
2.4.4. Spatial Statistical Analysis (SSA)
In this study, Spatial Change Analysis and Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) are used to implement Spatial Statistical Analysis. Spatial distribution of the ecological impacts of open-pit mining and vegetation reconstruction can be identified by EOF method and verified by field investigations [57]. The formula of the EOF method is described as Equation (3):
where i is a vector which represents a spatial location. pi is a time series of the i pixel in original data. pcji (j = 1,…, d) is the value of the i pixel corresponding to time j on PC which is the principal component matrix of original time-space data. EOFj (j = 1,…, d) is the j column of temporal empirical orthogonal function (EOF) matrix, which is coming from the variance matrix of the original time-space data and d is the dimension of temporal variation types.
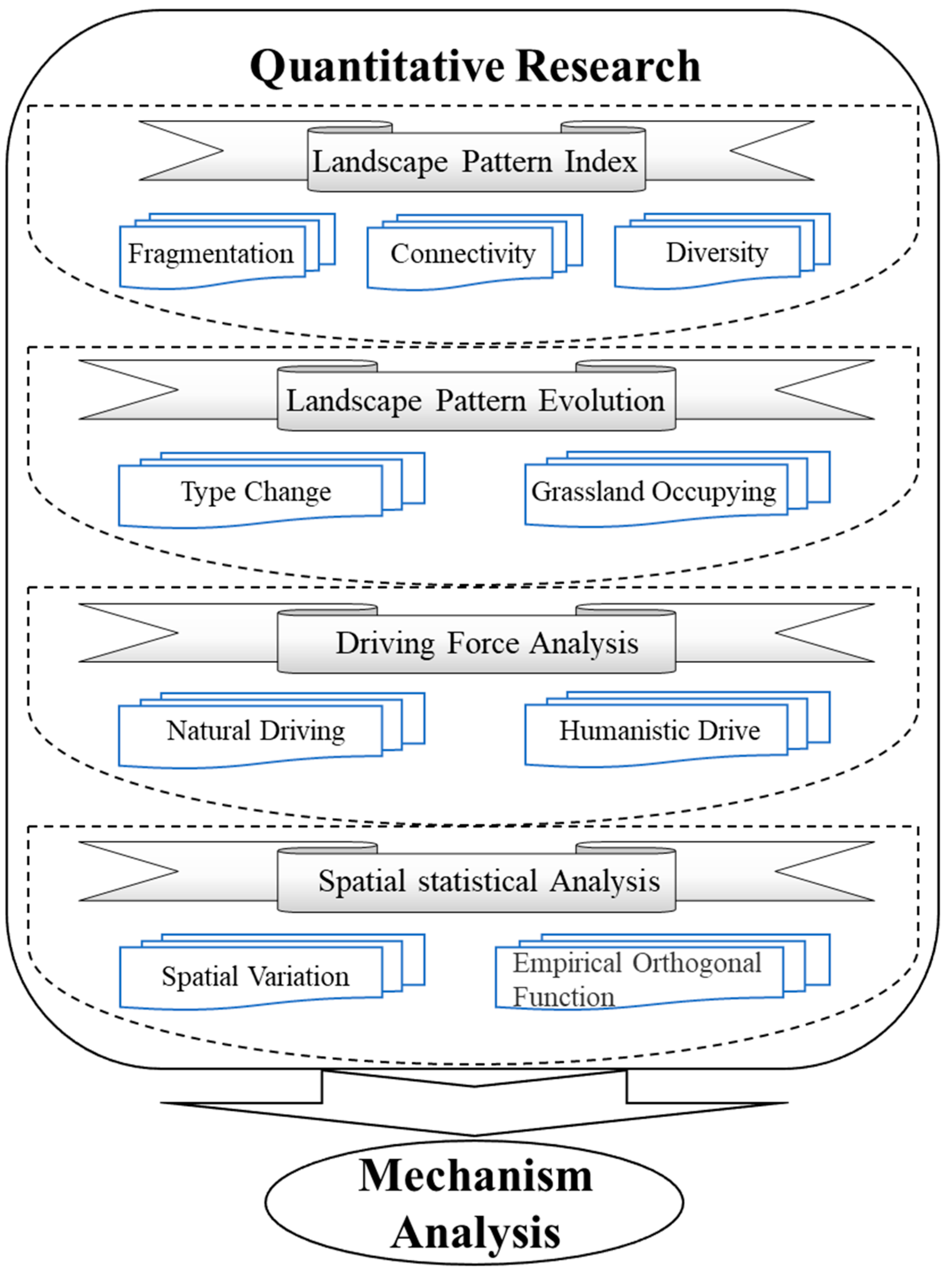
Thus, to study coal exploitation impact on LEH from multiple perspectives, this study used LEH assessment as a basis and constructed landscape Index-pattern Evolution-Driving force-Spatial statistical (IEDS) comprehensive research framework (Figure 2) by combining all four methods (LPI, LPE, DF and SSA) with the goal to take advantages of their individual strengths.
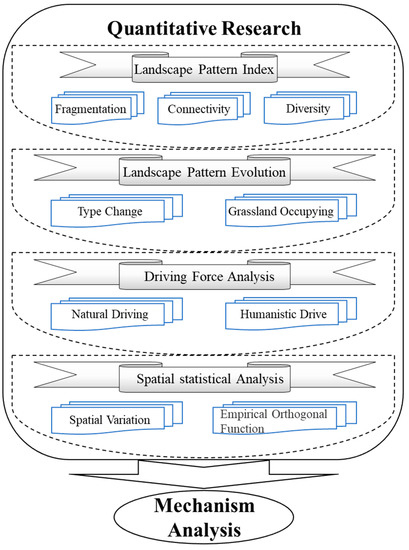
Figure 2.
Research system (landscape Index-pattern Evolution-Driving force-Spatial statistics; IEDS) of the impact of Large-scale Open-pit Coal Base (LOCB) on Landscape Ecological Health (LEH) of semi-arid grasslands.
3. Results
3.1. Landscape Pattern Index
Fragmentation: AI and CONTAG were decreasing, which indicates that the landscape in the study area has been in the process of fragmentation, which will eventually destroy the ecological functions. The increase of LSI indicates that the landscape shape became more complex and irregular, and that landscape edge was growing. At the same, patches became more and more discrete, and interaction between patches and matrix was enhanced (Table 2). As area associated with artificial disturbance patches (e.g., mining and town landscape patches) expanded, grassland patches became more and more isolated from each other. Thus, the probability of successful bio-diffusion might decrease, which in turn, might reduce the population. The worst-case scenario is the extinction of the corresponding species and the disappearance of the whole landscape.

Table 2.
Landscape pattern index (LPI) of the study area over the years.
Connectivity: COHESION and CONNECT are becoming smaller and smaller, and landscape connectivity in the study area is decreasing (Table 2). Expansion of mining landscape, town landscape patches and fragmentation of the road network built on former grasslands resulted in decrease of amount and sizes of grassland patches as well as fragmentation of the overall landscape, which might lead to the continuous decline of landscape connectivity. This change might affect some basic ecological processes, including species diffusion and migration, source-sink dynamics, invasion control, network design of ecological protection areas and ecological restoration [58].
Diversity: NP increased four-fold in the past 15 years, which indicates that the number of patches in the study area is increasing with the total landscape area remaining unchanged. SHDI and SHEI are increasing, which indicates that the number of patch types in the landscape is increasing. At the same time, the proportion of patch areas remains balanced, and heterogeneity and complexity of the landscape are increasing. Additionally, the interaction intensity of different landscape types is increasing, and landscape stability is decreasing (Table 2). Landscape pattern diversity index increase also confirms increasing landscape fragmentation as well as dispersion of landscape patches and decline of landscape connectivity.
For grasslands, human disturbances lead to a gradual increase of a number of grassland landscape patches, fragmentation of the landscape, gradual decline in landscape connectivity, gradual increase in landscape pattern diversity, complex and irregular landscape shapes. Human disturbances also cause more and more dispersed landscape patches, increase of landscape heterogeneity and complexity as well as the gradual decline of landscape stability. However, the expansion of town landscape patches increases human habitat areas. At the same time, construction of roads enhances connectivity between these habitats. Therefore, these habitats and corridors associated with them should be constructed from the perspective of ecological protection.
3.2. Landscape Patterns Evolution
3.2.1. Analysis of Landscape Type Change
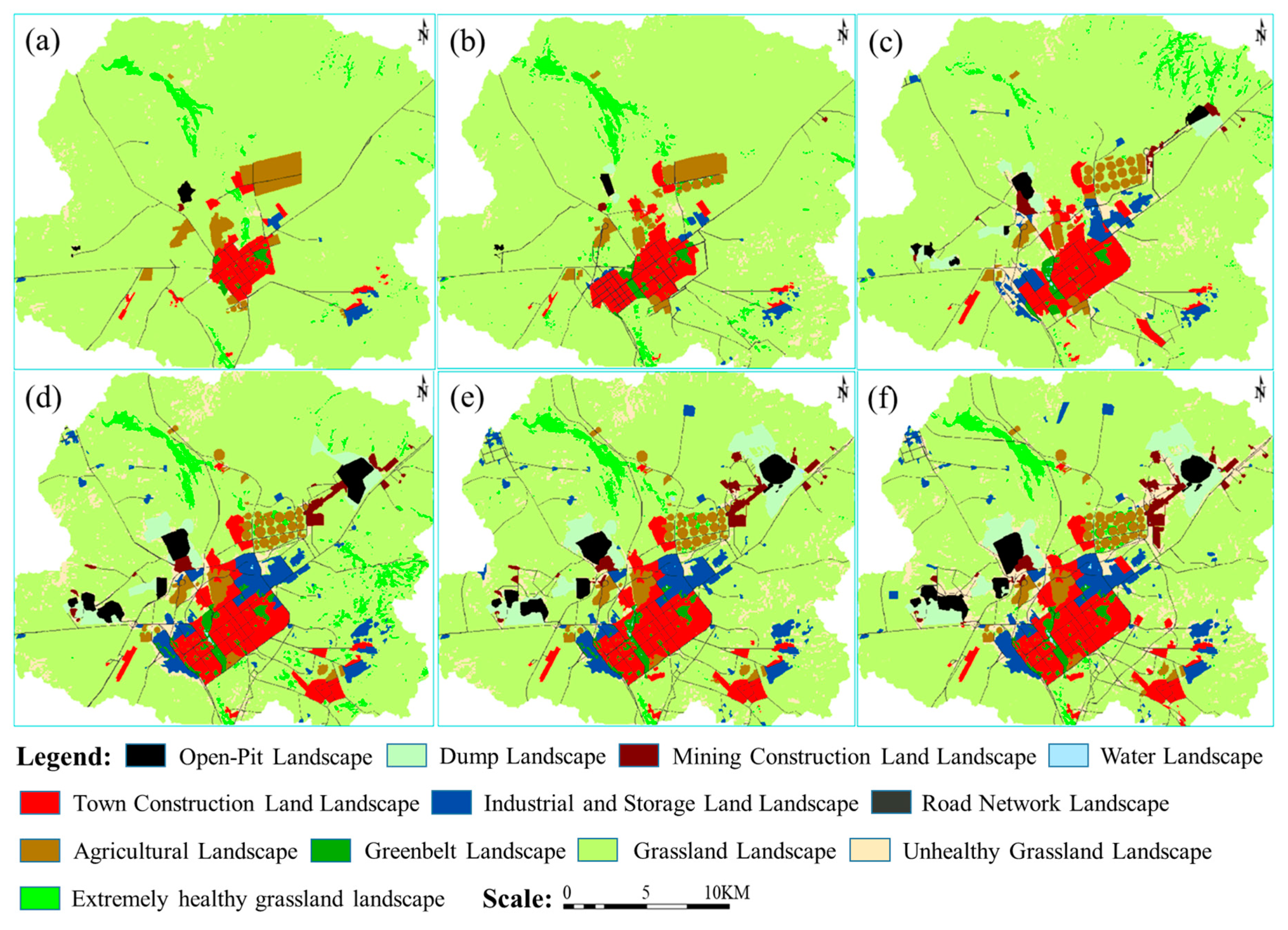
The healthy grassland landscape has strong vitality, stable landscape structure, capable of gradual recovery in the absence of external disturbances, and sustainable ecosystem service functions. The natural breakpoint method was used to classify the grassland landscape: very healthy grassland landscape (>0.6); healthy grassland landscape (0.4–0.6); unhealthy grassland landscape (<0.3) [54]. Extremely healthy grassland landscape is mainly distributed in the wetlands of Xilin River Basin (Figure 3). Some low-lying catchment areas in this region reached a very healthy state. Unhealthy grassland landscape is mainly located around industrial and mining production and living areas. This rule became more and more obvious with the time progress. Because of overgrazing, some grasslands, located far from human disturbance areas, also demonstrate an unhealthy state. However, because of grazing work prohibition by the Xilinhot Municipal Government, the number of unhealthy grassland landscapes caused by overgrazing gradually decreases.
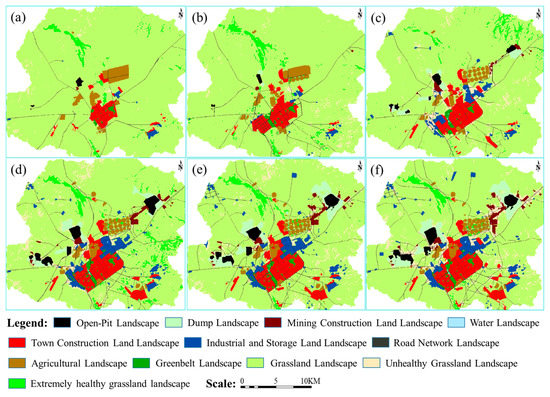
Figure 3.
Landscape pattern classification maps of the study area in (a) 2002, (b) 2005, (c) 2008, (d) 2011, (e) 2014 and (f) 2017.
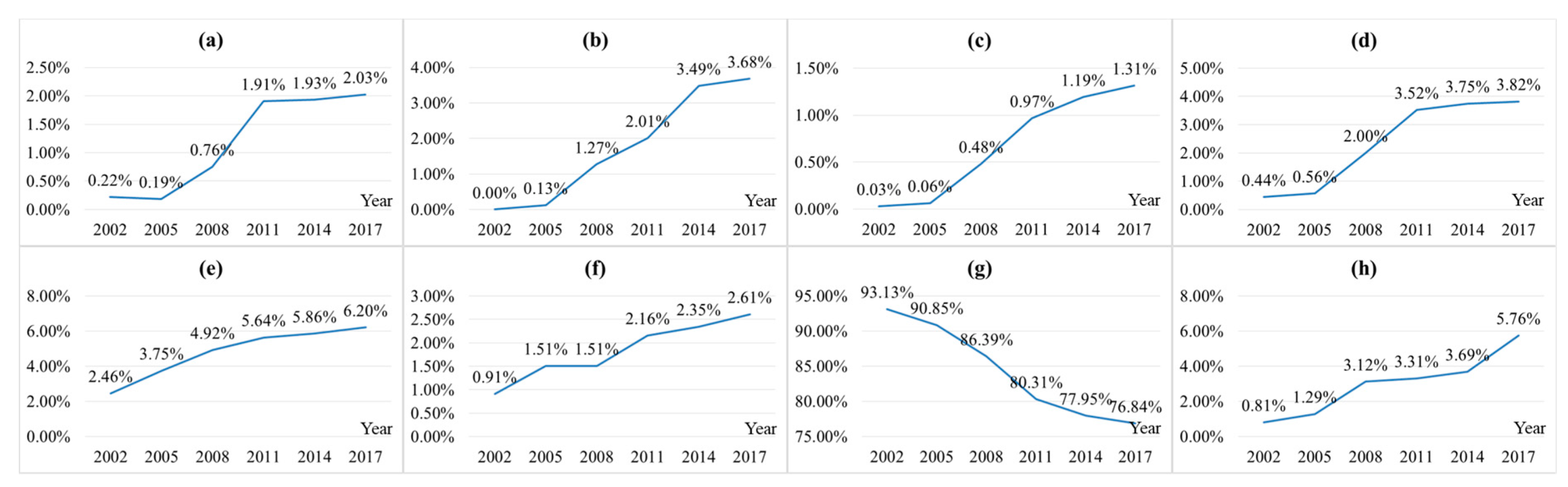
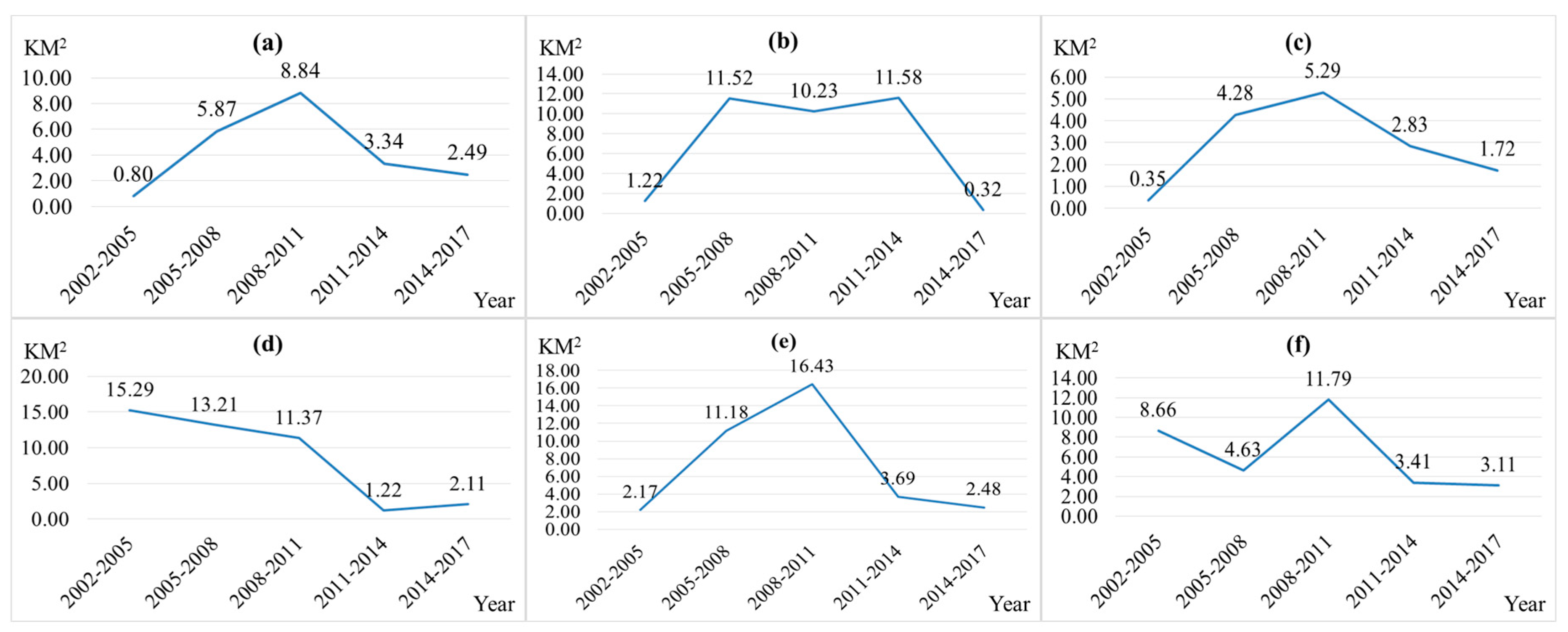
Open-pit landscape increased 10 times in the past 15 years (Figure 4). However, strangely, during 2002 and 2005, open-pit landscape decreased and mostly because prior to 2003 Shengli Coalfield was developed by local small coal kilns. Mining mode of small coal kilns is extremely extensive and offers significant economic benefits. However, it does not take into account or pays any attention to ecological protection. In 2003, Shengli Coalfield was taken over by the National Energy Group and other large-scale state-owned energy groups to carry out planned green mining. The green mining plan includes a dumping site and an industrial square, both of which located directly inside the mining area. While guaranteeing the coal production, large-scale energy groups have tried their best to implement the land reclamation and ecological reconstruction in the mining area. In 2002, there was no dump landscape in the study area. In the following 15 years, 37.63 KM2 dump landscape was constructed. Mining construction landscape has increased 44-fold in the past 15 years. Area of town construction on former landscape increased from 25.13 km2 in 2002 to 63.36 km2 in 2017. It expanded linearly and increased 2.5 times. Industrial storage and road network landscapes increased annually from 4.46 and 9.32 km2 to 39.04 and 26.67 km2, respectively, in the last 15 years. Because of coal mining, town expansion, industrial development, and road construction, the total grassland area decreased from 951.18 km2 in 2002 to 784.85 km2 in 2017. At the same time, unhealthy grassland landscape increased from 8.28 km2 in 2002 to 58.78 km2 in 2017. However, the percentage of grassland landscape in the study area remains over 75%. Therefore, the grassland landscape is the matrix of the study area.
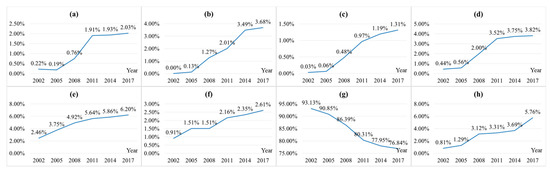
Figure 4.
The area ratio of (a) Open-pit Landscape, (b) Dump Landscape, (c) Mining Construction Land Landscape, (d) Industrial and Storage Land Landscape, (e) Town Construction Land Landscape, (f) Road Network Landscape, (g) Grassland Landscape, (h) Unhealthy Grassland Landscape.
3.2.2. Analysis of Grassland Occupation by Main Landscape Types
Landscape types conversion from 2002–2005, 2005–2008, 2008–2011, 2011–2014 and 2014–2017 were obtained using transfer matrix. We also paid attention to areas associated with open-pit and dumping landscapes, with mining and town construction, as well as with industrial storage and road network landscapes in each stage (Figure 5). From 2002 to 2017, Mining landscape, including open-pit, dumping, and mining construction landscapes, occupies the largest area of the grassland: 2.37, 21.67, 24.36, 17.75 and 4.53 km2, respectively. Mining landscape occupied the largest part of the grassland during the 2005–2014 decade, in particular during the 2008–2011 period. At the same time, industrial storage landscape is similar to the mining landscape because main industrial types in Xilinhot are deep coal processing, thermal power generation, cement industry (which uses coal gangue as a raw material) as well as other industries related to the coal industry. Therefore, coal development led to regional industry expansion. Part of the grassland occupied by town construction landscape decreased annually. At the same time, town expansion rate decreased annually. Road network landscape includes town roads, highways, pastoral roads, special roads for mining areas, civil and special railways for mining areas, etc. Therefore, the expansion of the road network landscape was affected by many factors. Thus, areas occupied by grasslands also fluctuated.
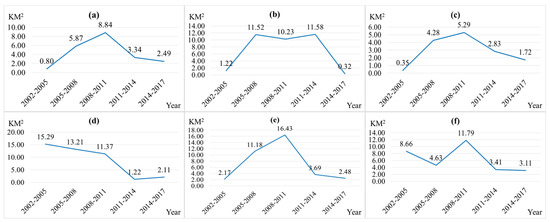
Figure 5.
The area of grassland occupied by (a) Open-pit Landscape, (b) Dump Landscape, (c) Mining Construction Land Landscape, (d) Town Construction Land Landscape, (e) Industrial and Storage Land Landscape, (f) Road Network Landscape (Note: All values in this figure represent changes presented rather than cumulated values).
3.3. Driving Forces
Six-year q values of MINE (distance to the nearest mining landscape), WATER (distance to the nearest water landscape), TOWN (distance to the nearest town construction land landscape), INDU (distance to the nearest industries and storage land landscape), and AGRI (distance to the nearest agricultural landscape) exceed 0.79 (Table 3). Thus, all these factors strongly affect LEH spatial distribution and change in the study area. Over the years, q of ROAD (distance to the nearest road network landscape) ranged from 0.787 to 0.4577. Thus, ROAD had a strong impact on LEH spatial distribution and change in the study area. Unhealthy grassland landscape is mainly distributed around mining and town landscapes. Water landscape mainly surrounds extremely healthy grassland landscapes. Vegetation coverage is extremely high, and the ecological conditions are the best. This distribution pattern was especially obvious in 2017. Over the years, q of elevation ranged from 0.2039 to 0.3608. Thus, elevation had only some, yet still distinct, impact on LEH spatial distribution and change in the study area. Field results demonstrated that LEH of catchment areas (e.g., as wetlands) is better, while ecological conditions in mountains are worse due to the soil erosion by wind. In these areas, q values of slopes and aspects are <0.06. Thus, two DFs do not significantly affect LEH spatial distribution and change in the study area.

Table 3.
q values of driving factors of LEH in the study area over the years.
Thus, judging by the q values averaged over the years, we conclude that DFs affecting the spatial distribution and change of grassland LEH in the study area are water, open-pit mine, town, agriculture, industry, road network, and elevation.
Remarks: MINE denotes distance to the nearest mining landscape, WATER denotes distance to the nearest water landscape, TOWN denotes distance to the nearest town construction land landscape, INDU denotes distance to the nearest industries and storage land landscape, AGRI denotes distance to the nearest agricultural landscape, and ROAD denotes distance to the nearest road network landscape.
3.4. Spatial Statistical Analysis
3.4.1. Spatial Change Analysis of Landscape Ecological Health
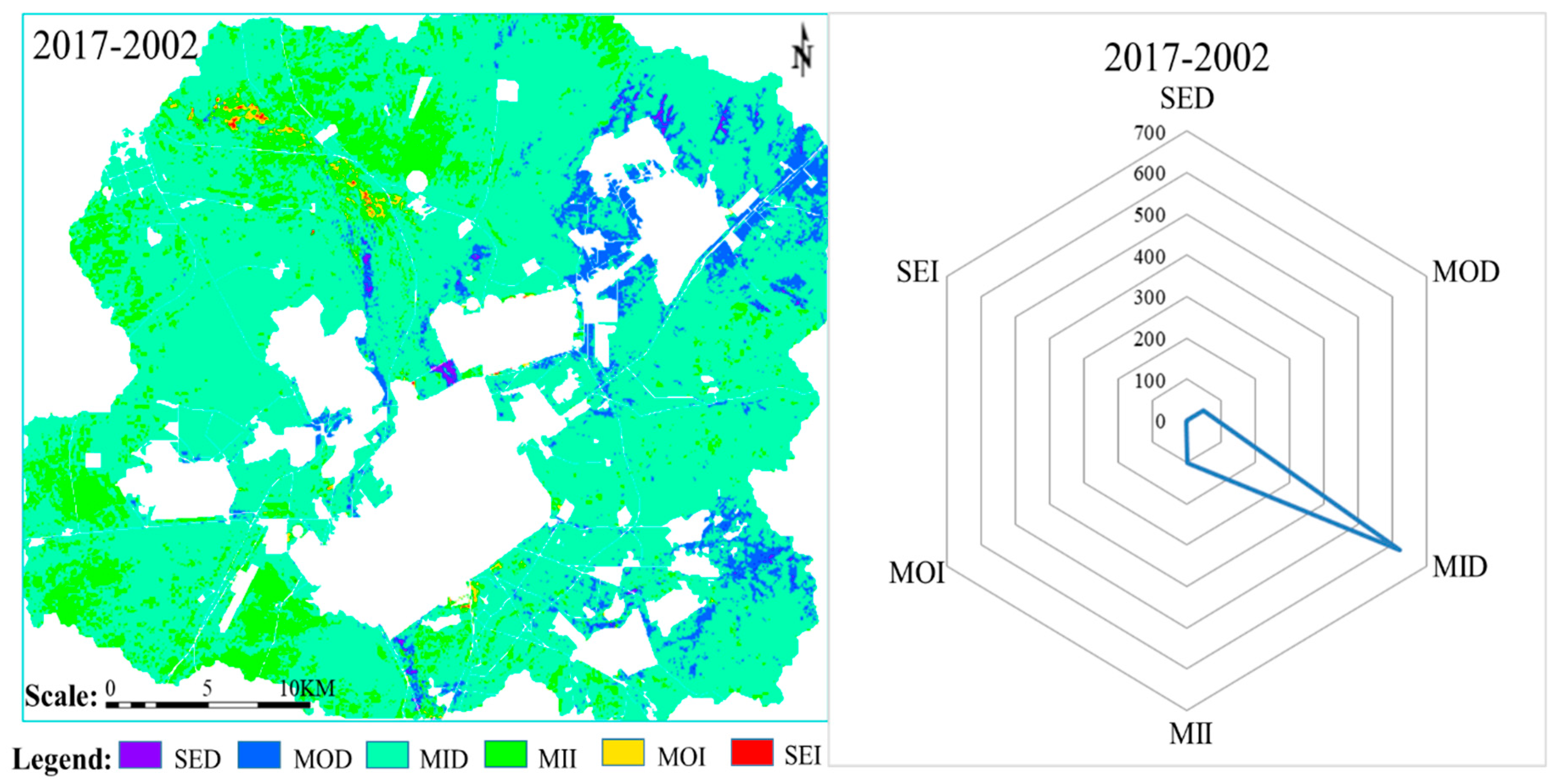
To further study LEH spatial changes in Shengli LOCB, LEH assessment maps of 2002 and 2017 were first superimposed, and then 2017 results were subtracted from 2002 results. LEH change from better (i.e., higher LEH evaluation value) to worse (i.e., lower LEH evaluation value) status is defined as ”deterioration”; change from worse to better is defined as ”improved”. LEH changes in Shengli LOCB were classified and are shown in Table 4. Trend and radar maps of LEH changes in the study area are shown in Figure 6.

Table 4.
Classification of LEH changes in the study area.
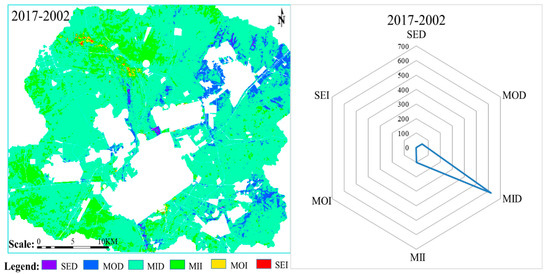
Figure 6.
Landscape ecological health changes in the study area from 2002 to 2017.
The area with improved LEH in Shengli LOCB was 106.44 km2 from 2002 to 2017, which accounts for 10.42% of the total area. The area with deteriorated LEH was 671.72 km2, which accounted for 65.77% of the total area. From 2002 to 2017, the grassland landscape in the study area slightly deteriorated. Thus, during this time, large area of grassland landscape was in a slightly deteriorated state. Moderate and severe deterioration areas were mainly distributed around the landscapes associated with mining, industrial storage, and town construction, especially around East No. 2 open-pit mine.
3.4.2. Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF)
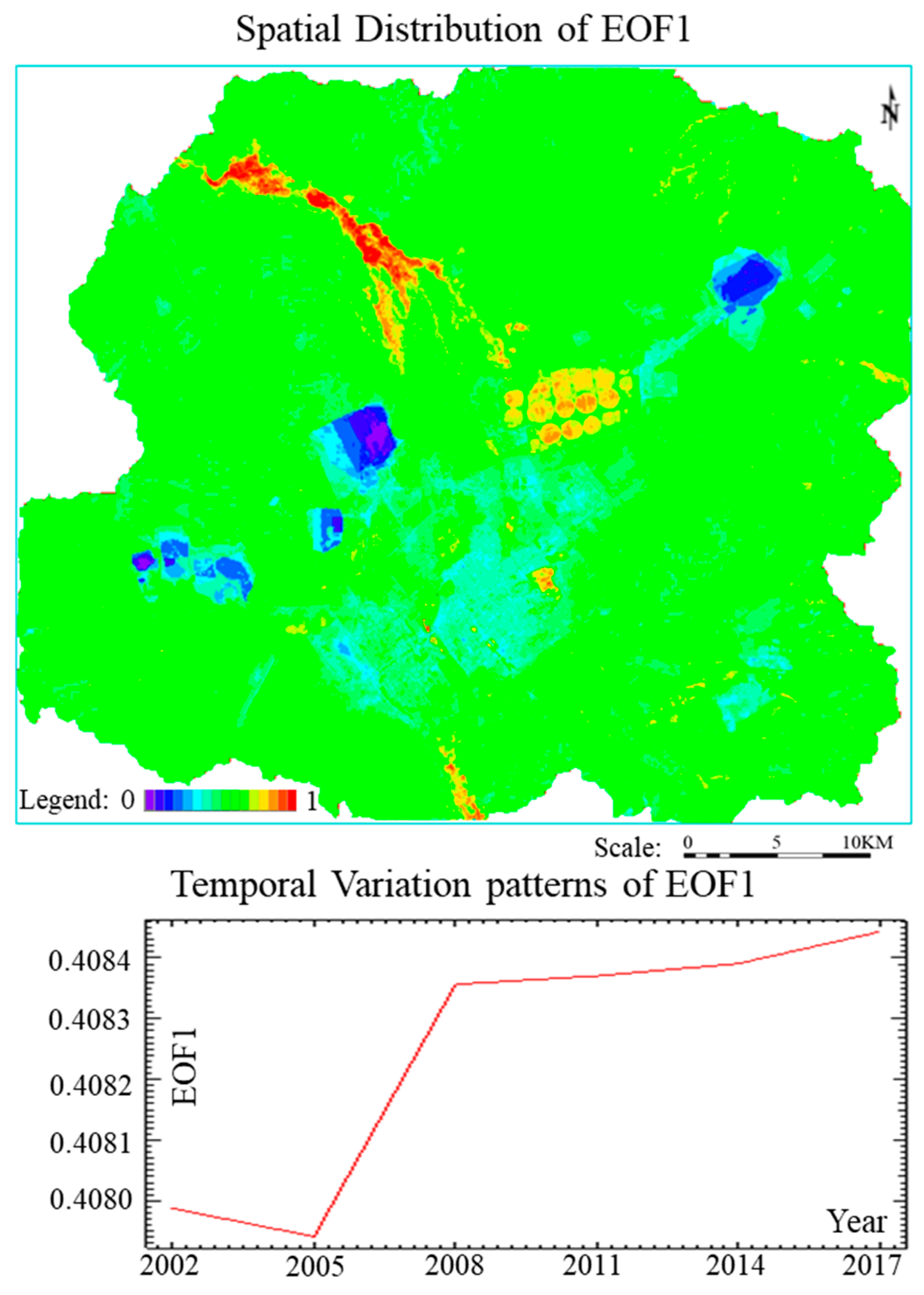
Time series data of LEH in mining area not only contain spatial distribution information on LEH, but on LEH changes, with time. Six EOF results were obtained from LEH in 2002, 2005, 2008, 2011, 2014, and 2017. Because EOF principle is similar to the principal component analysis, EOF results also have principal component analysis characteristics. The regularity of the evolution type reflected by the obtained EOF becomes weaker, the randomness becomes stronger and closer to the EOF background noise. According to the calculation and statistics, the contribution rate of EOF1 (The first mode of EOF) obtained in this study reached 99.89%. In the past 15 years, the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of LEH in the study area are similar. EOF1 can be used as a feature to represent the change form of LEH in the whole study area. Through in-depth study of EOF1, main characteristics of regional LEH can be obtained. The variance contribution rate of EOF2 (The second mode of EOF) is 0.11%. At the same time, the variance contribution rate of the last four EOFs is less than 0.00001%. Therefore, the last five EOFs can be disregarded.
Time coefficients of EOF1, ranging from 0.407941 to 0.408443, are all positive and increase with time. Therefore, the spatial distribution of EOF1 becomes more significant with time (Figure 7). Spatial distribution map of EOF1 shows that areas with high EOF1 values are mainly distributed in catchment areas of landscapes associated with wetlands, agriculture, green space, and grasslands of the Xilin River Basin. These areas have a common feature-high soil water content. Soil water in the agricultural and green space landscapes mainly comes from irrigation. Soil water in the catchment areas of wetland and grassland landscapes of the Xilin River Basin mainly comes from the natural river and topographic catchment waters. EOF1 values of landscapes associated with town construction, industrial storage, mining, and road network are low. EOF1 value of external dump landscape is generally higher than that of the internal dump landscape mostly because the construction time of the external dump landscape is long. Its artificial maintenance time is also long. Thus, overall ecological conditions are better. Therefore, artificial ecological restoration promotes the healthy development of landscape ecology.
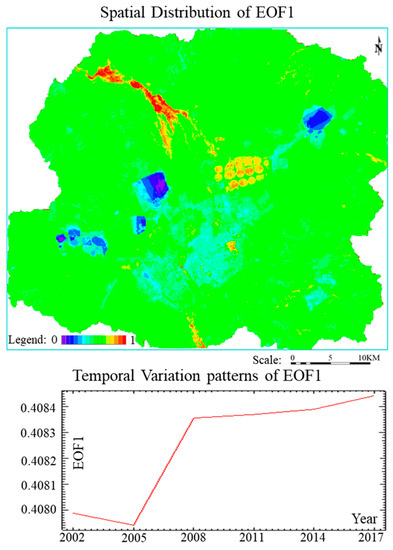
Figure 7.
Spatial Distribution and Time Variation of empirical orthogonal function 1 (EOF1).
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact Types of Open-Pit Coal Mining on Grassland Landscape Ecological Health
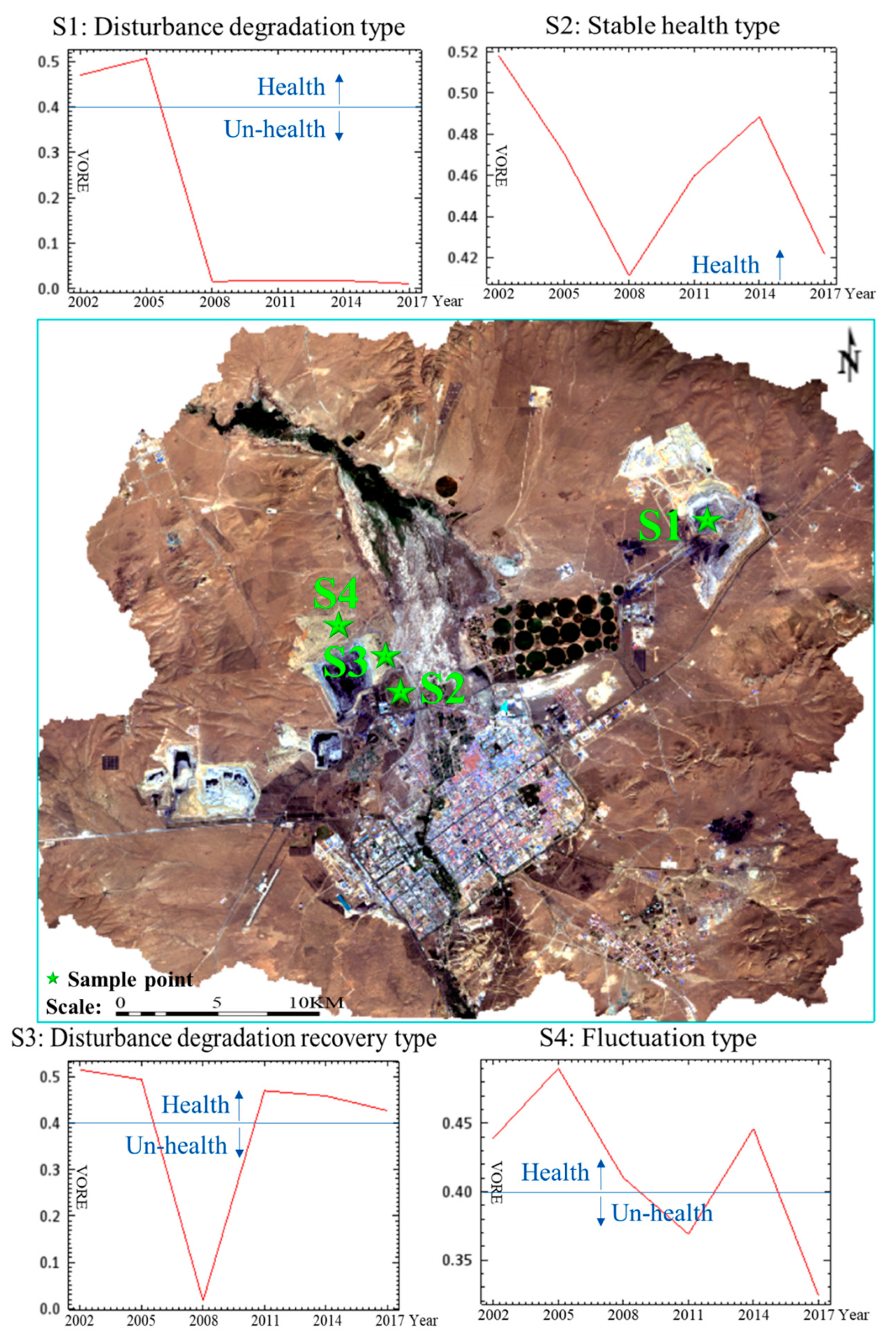
According to the development mode of LOCB, the disturbance landscape type formed in the process of open-pit coal mining and the evolution process of LEH in the study area, the impact of LOCB on healthy grassland is divided into four types: disturbance degradation, disturbance degradation recovery, stable health, and fluctuation types. Disturbance degradation type refers to the direct degradation of healthy grasslands into the unhealthy landscape because of open-pit coal development. Example include: damage of healthy grassland by open-pit mining (point S1 in Figure 8, which corresponds to the mining pit of Shengli East No.2 Open-pit Mine), coal gangue accumulation and storage in healthy grasslands, damage of healthy grasslands by long-term compaction due to the heavy machinery operations, etc. In the past, it was difficult to restore grasslands to their healthier states by just self-restoration measures, which typically require significant scientific and artificial restoration efforts. In general, stable health type implies a healthy state even though it is affected by the open-pit coal development. Healthy dumping landscape is one of such examples. For example, S2 point in Figure 8 is a dump south from the Shengli No. 1 open-pit mine. Dumping landscape is a typical piled-up one. However, it maintains its health all the time because of careful manual maintenance or good background conditions. Disturbance degradation recovery typically refers to unhealthy landscapes, which were directly degraded because of open-pit coal exploitation, but later became restored and converted into healthy grasslands by artificial restoration or grassland self-restoration. The most typical example is the internal dump landscape. Example of an external dump landscape is S3 point in Figure 8, which is an actual internal dumping site of the Shengli No. 1 open-pit mine. It was changed from healthy grassland to the open-pit landscape but then restored to become a healthy grassland landscape after mining stopped. Fluctuation type means that under the impact of open-pit coal development, the health situation is extremely unstable, which is always free from health and unhealthy. A typical example of this situation is the S4 point in Figure 8, which is dumping site of the Shengli No. 1 open-pit mine. Since the dumping site of the Shengli No. 1 open-pit mine is located far from the industrial development and the city, it is not well maintained and is left to be in a self-sustaining state.
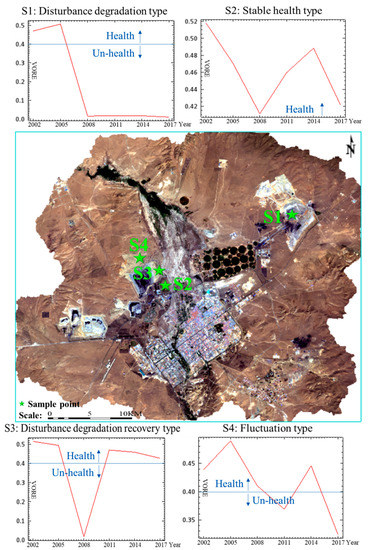
Figure 8.
The evolution types of grassland landscape ecological health under the disturbance of coal exploitation.
4.2. Construction of Multi-Scale Ecological Health Monitoring System in Mining Areas
Mining areas worldwide impact ecological health differently. It is desirable to predict these impacts in advance to reduce future restoration cost, which will involve developing the corresponding plans in advance. All of this is indeed done in advance to reduce the negative impacts of coal mines on the ecological environment. Currently, both photogrammetry and remote sensing technology are very mature and well-developed methods, are widely used for environmental and disaster monitoring. Development of multi-scale and large-scale monitoring system as well as a network of mine ecological environment health and disaster, covering all aspects of this system (from macro to micro, from the surface to the bottom) will greatly benefit global ecological environment protection and restoration (Table 5).

Table 5.
Multi-scale ecological monitoring in the mining area.
Although ecological health at different spatial scales are closely related, non-deductibility of these scales determines that the ecological health on large scales can neither be reduced linearly to small scales nor simply accumulated on small scales. Therefore, research on mining impact on ecological health should be carried out at a multi-scale. At the same time, although research objects of ecological health at different scales have different emphases, they are not completely separated from each other: a lot of links exist between them. A comprehensive study on the coordination and organic integration of ecological health at multi-scales, as well as ways and methods of transformation between these scales, are the key scientific issues needed to be addressed during comprehensive study and analysis of ecological health in mining areas [34].
4.3. Impact of Governmental Macro-Policies on Ecology of Semi-Arid Grasslands
4.3.1. Coal Development and Recovery Policy
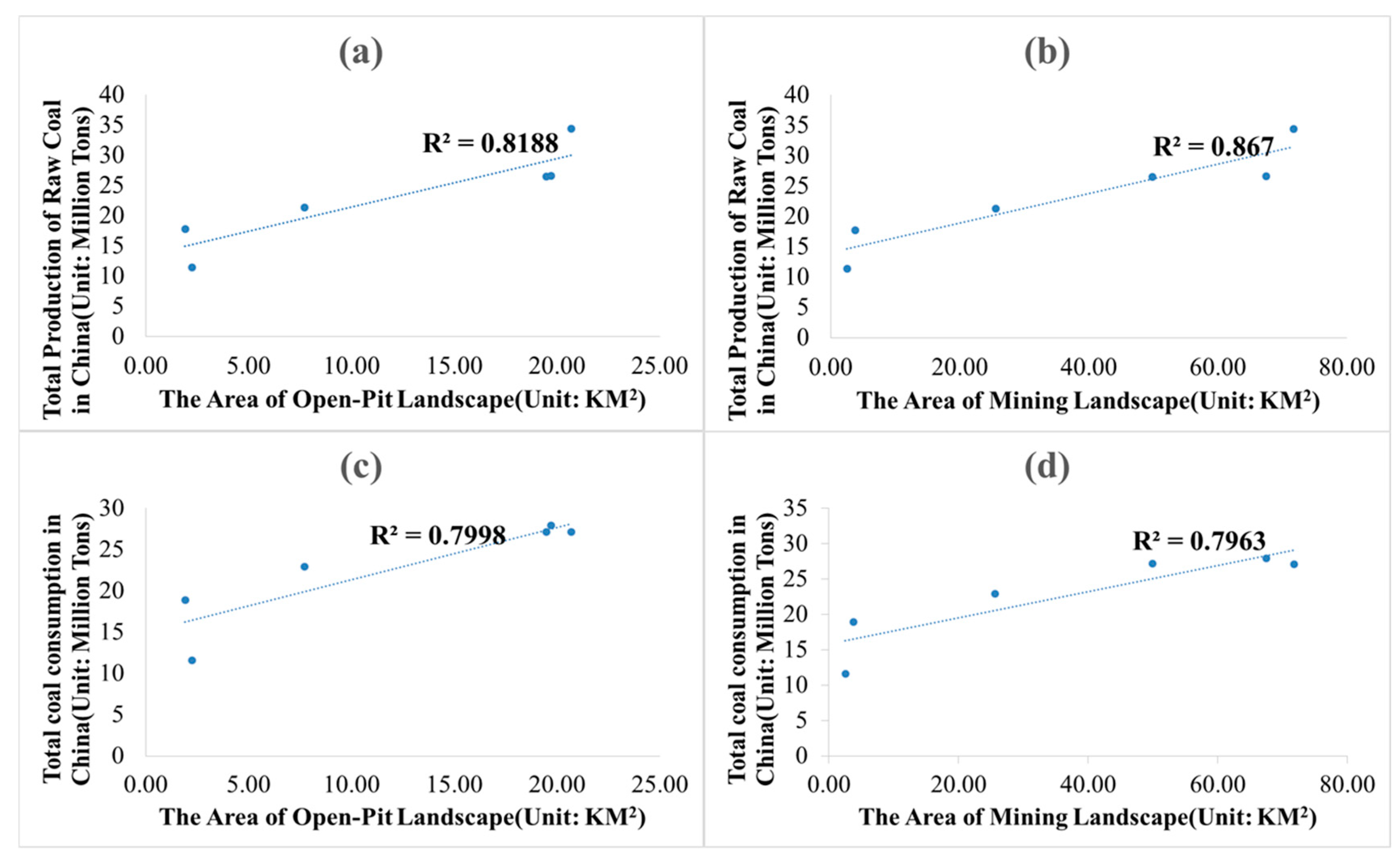
We analyzed the area of open-pit and mining landscapes, taking into account the correlation between China’s raw and total coal consumption. Correlation coefficients (R2) of these correlations were 0.8188, 0.867, 0.7998, and 0.7963, respectively (Figure 9). Judging by the results of Chinese government coal policy implemented in 2002–2011, coal industry entered the supernormal rapid development stage. In 2011–2017, the 12th Five-Year Plan was introduced, and the coal industry adjusted its industrial structure to continuously improve industrial concentration. It is an important period for the coal industry to change from quantity growth to quality. As can be seen from Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, areas of open-pit landscapes expanded rapidly from 2002 to 2011, and reached their peaks between 2008 and 2011. Expansion rate significantly slowed down after 2011. Thus, China’s coal production is closely related to national policies. Five coal mines in this area are state-owned enterprises, and their annual coal production plans are controlled by the state. Without national and market demand, no mining efforts (from organizations and/or individuals) are undertaken.
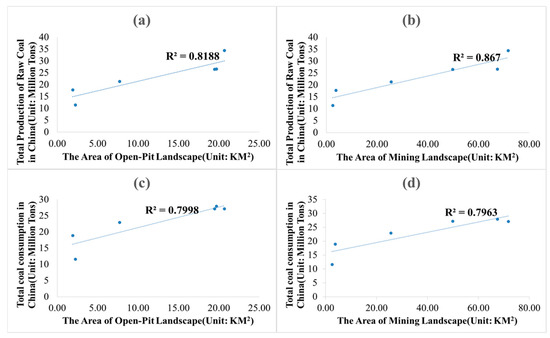
Figure 9.
Correlation analysis of (a) open-pit mining landscape area and (b) mining landscape area with a total production of raw coal. Correlation analysis of (c) open-pit mining landscape area and (d) mining landscape area with total coal consumption in China over the Years.
It is generally acknowledged that coal exploitation damages the ecological environment. Therefore, Chinese government implemented policies of synergistic utilization of resources and ecological restoration. These policies include the Land Reclamation Regulations implemented in January 1989, the Land Reclamation Regulations implemented in 2011 as well as several policies implemented in 2013 (Technical Specifications for the Protection and Restoration of Mine Ecological Environment and the Protection and Restoration of Mine Ecological Environment). In China, the reclamation rate of mine land increased from 1% to 48% by the end of 2015 [3]. Thus, significant progress was achieved to reclaim lands affected by mining. Driven by the national policy, dumps were constructed steadily for 15 years. In 2002, there were no dumps. In 2017, the total area of the dump landscape accounted for 52.45% of the total area of the mining landscape. In addition, ecological restoration of open-pit mines was implemented.
4.3.2. Grassland Grazing Management Policy
The life cycle of a coal mine typically lasts from several decades to several years. Town, industry, and roads only consume a small fraction of the grassland. Impact of grazing on the grassland ecology is the most direct, severe and long-lasting. For thousands of years, nomadism was the basic economic lifestyle of the grassland people [59]. However, the ”tragedy of the commons“ theory points out that each herder will increase the number of sheep to raise. This group behavior (and, as a result, number of sheep increase) will lead to rapid deterioration of the grassland as well as to unregulated and open disaster of public resource utilization [60].
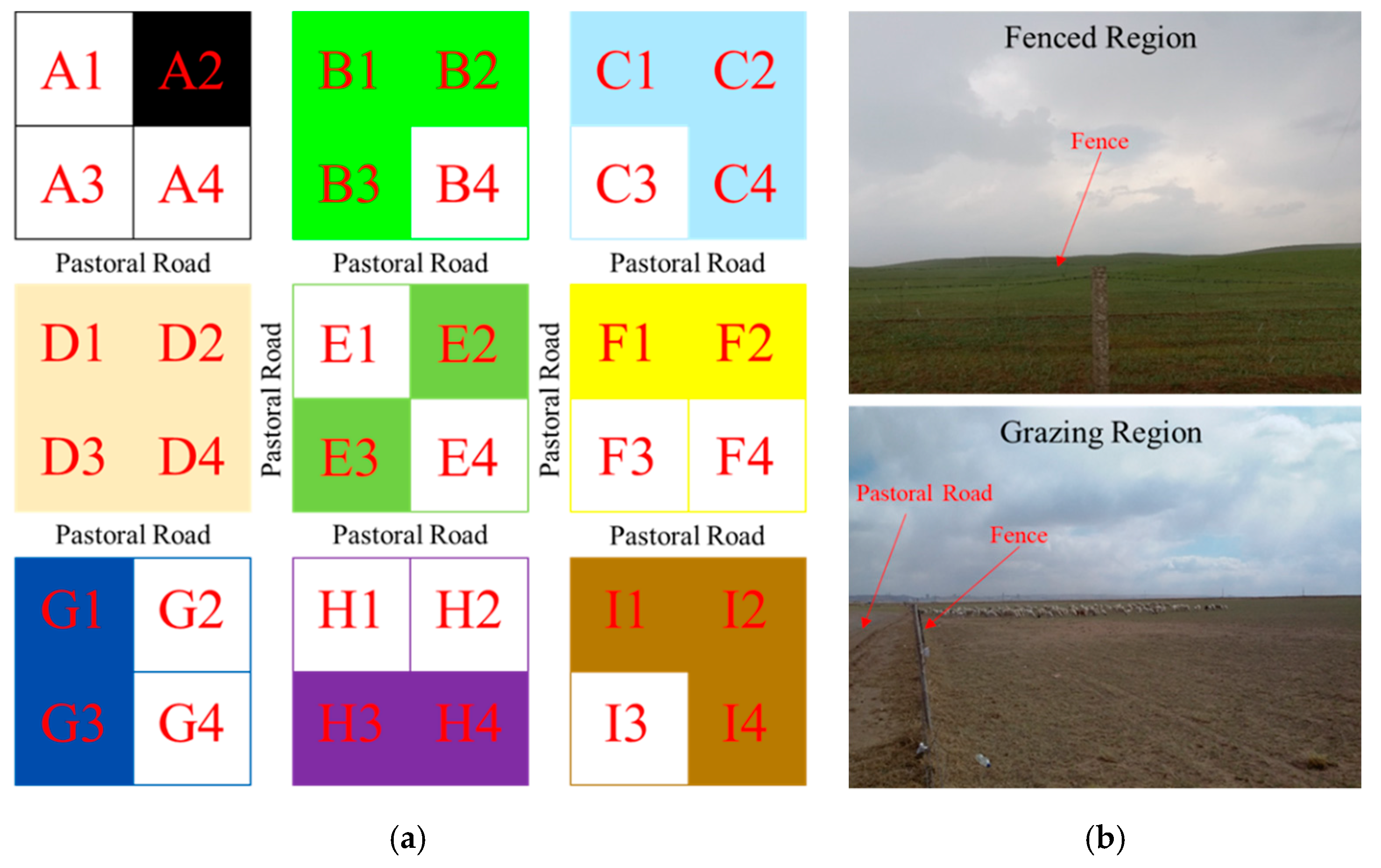
In order to avoid this ”tragedy of the commons”, in the 1990s, under the intervention of the Chinese central and local government, pastures began to be contracted out to the households [61]. Site survey (Figure 10a) visualizes the way sheep farmers manage family ranches. Lots from A to I schematically represent ranches of nine families. Herdsmen use fences to enclose their own pastures and to divide their farms into small pieces. Typically, 4–6 small areas exist, which might be undivided and randomly distributed. Typically, herdsmen choose their grazing pastures every year and leave remaining areas as ”grassland fenced”. Figure 10a shows grazing and fencing regions filled with and without color, respectively. Fencing regions typically have high vegetation coverage and excellent ecological conditions. Ecological conditions of grasslands, constantly being exposed to livestock grazing and foot traffic, is obviously poor in grazing regions (Figure 10b). Establishment of fences ignores ecological externalities. A series of negative externalities, such as disturbances to the internal balance of ecosystems and fragmentation, is entirely assumed by nature. This ‘’fence effect” has a serious impact on wildlife activities such as water intake, foraging, and migration associated with pastoral areas. It also affects natural selection and reproduction, which is not beneficial for biodiversity. It also destroys the food chain of grasslands, which is detrimental to grassland ecosystem stability. “”Fence effect“” also makes the ecological quality of grassland pastoral areas uneven and conflicts with the traditional Grazing Methods of nomadic peoples. This also affects the lifestyle of herdsmen [62].
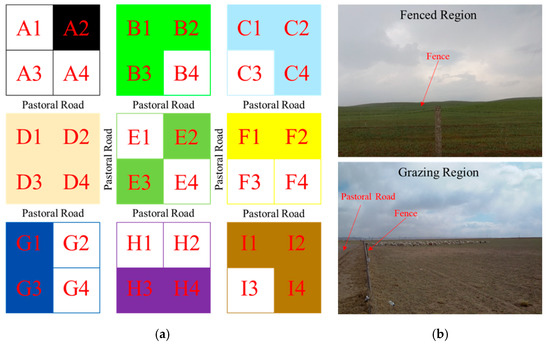
Figure 10.
(a) Conceptual model diagram of Chinese pastoralists managing family pastures under the “Household Contract Responsibility System”. (b) Photographs of fenced (top) and grazing (bottom) regions in the study area.
Chinese government implements the “Household Contract Responsibility System”, in which the right to use pasture is contracted out to the household, while the pasture is divided by herdsman fences. The impact of this grassland management system (or mode of use) on a multi-scale of the ecological health needs further investigation. In addition, under the existing grassland management system, methods to fully protect grassland ecology also represent a scientific issue that needs to be studied in detail. The scale of this study is relatively small. In broader spatial and temporal scales, regional ecology will also be affected by changes of climate, geology, geomorphology, hydrology, population, policy, random overgrazing, coal mining, urban expansion, industrial development, etc. Accurate clarification of various factors affecting grassland LEH is very important and urgent and needs to be studied in the future.
4.4. Advantages of Landscape Index-Pattern Evolution-Driving Force-Spatial Statistical (IEDS) Research Framework
During open-pit coal mine development in semi-arid grassland areas, landscape undergoes significant changes due to excavation, additional developments (such as industrial areas and power plants), all of which consume grasslands areas surrounding excavation sites. Grasslands also shrink because they are used as storage for mining waste and as road sites. Thus, all these activities result in the increase of fragmentation around open-pit mines. Connectivity between these fragments is reduced, while the number of plaques is increased. At the same time, diversity of landscape patterns and their heterogeneity are amplified, and proportions of various landscape types are constantly changing [63]. Therefore, such territories can be characterized using various LPIs to reflect temporal changes in landscape structure as well as the spatial layout and landscape patterns [64].
Open-pit mining will inevitably affect landscape pattern, which, in some cases, might lead to disastrous outcomes. As a special geographical area, LPE of the mining area is a dynamic spatial-temporal process driven by resource exploitation, which is a comprehensive reflection of the mining impact on the regional ecosystem. Thus, it is very important to study the LPE of mining areas to understand how mining impacts regional ecosystems [65].
LPE is only a description of the phenomena, which is insufficient to explain the LEH change mechanism. To fully understand and control LEH changes, DFs causing these changes must be identified. Their driving mechanisms must be explored as well [66]. DFs of LEH changes are very important to uncover the causes, basic processes, and internal mechanisms as well as to predict future directions and consequences of LEH changes.
LPIs, LPE, and DFs are all from the macro level to study the change law of quantity with time, which can’t reflect the spatial impact law. SSA can better understand geographical and ecological phenomena and accurately determine their causes. On the landscape scale, time-varying patterns determined by heterogeneous nature of LEH and by its influencing factors are always different. The key to rational utilization of natural resources and ecological protection is determination of their spatial and temporal distribution patterns.
Therefore, the IEDS research framework can more fully and deeply study the impact of open-pit mining on semi-arid grasslands’ LEH. This study believes that the IEDS research framework can be extended to other semi-arid grassland open-pit mines in the world for empirical research.
5. Conclusions
LEH of LOCB is a space-time distribution problem. Comprehensive application of 3S (Remote Sensing, Geographic Information System, Global Navigation Satellite System) technology to quickly obtain and accurately analyze basic data to dynamically monitor macro-LEH status became an important direction of a quantitative assessment of LEH. Taking Shengli LOCB of Xilinguole grasslands as an example, the conceptual model of the impact of LOCB on LEH of semi-arid grasslands was presented in this paper. Our work also established IEDS research framework to assess LOCB impact on LEH of semi-arid grasslands. Our results showed that: (1) Human disturbances lead to gradual increase in the number of grassland landscape patches, landscape fragmentations, gradual decline in landscape connectivity, gradual increase in landscape pattern diversity, complex and irregular landscape shapes, more and more dispersed landscape patches, increased landscape heterogeneity and complexity, and gradual decline in landscape stability. (2) Grassland landscape is the matrix of the study area. Landscapes related to mining, towns, industrial storage, and road networks expand every year by occupying a large number of grasslands, which results in a gradual decrease of overall grassland areas, as well as in increase of a number of unhealthy grassland areas. (3) DFs affecting spatial distribution and change of grassland LEH in our study area were water, mine, town, agriculture, industry, road network, and elevation. We demonstrated that open-pit coal development significantly affects grassland LEH. (4) Overall, LEH of grassland in our study area slightly deteriorated over the past 15 years. (5) In the past 15 years, the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of LEH in the study area are similar. Regional LEH with high water content is excellent, while regional LEH affected by human disturbances is poor. This work demonstrates new ideas and methods to study LEH as well as the impact of mining on the ecological environment. Our study provides scientific reference for the protection, planning, restoration, and renovation of ecological environment in mining areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W. and S.L.; Data curation, Z.W.; Formal analysis, Z.W.; Funding acquisition, S.L. and Z.B.; Investigation, Z.W.; Methodology, Z.W. and Q.L.; Project administration, S.L. and Z.B.; Resources, Z.W.; Software, Z.W.; Supervision, Z.W.; Validation, Z.W., S.L., Q.L., and Z.B.; Visualization, Z.W.; Writing—original draft, Z.W.; Writing—review & editing, Z.B.”.
Funding
This research is supported by “China National Key R&D and Design Project 2016YFC0501107” and “China National Science and Technology Foundation Work Project 2014FY110800”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ottmar, E. King Coal and the queen of subsidies. Science 2015, 349, 1286–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z. Introduction of Mine Ecology; Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission of China, National Energy Administration of China. 13th Five-Year Plan for Coal Industry Development; National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC): Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dulias, R. Environmental Science and Engineering the Impact of Mining on the Landscape; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttl, R.F.; Gerwin, W. Landscape and ecosystem development after disturbance by mining. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Rosner, H.-J.; Hagensieker, R.; Dieball, S. Multi-method dynamical reconstruction of the ecological impact of copper mining on Chinese historical landscapes. Ecol. Model. 2015, 303, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Pang, J.W.; Qi, S.Z.; Li, Y.P.; Han, C.C.; Liu, T.X.; Huang, L.M. Impacts of coal mining subsidence on the surface landscape in Longkou city, Shandong Province of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Popelková, R.; Mulková, M. The mining landscape of the Ostrava-Karviná coalfield: Processes of landscape change from the 1830s to the beginning of the 21st century. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larondelle, N.; Haase, D. Valuing post-mining landscapes using an ecosystem services approach—An example from Germany. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žibret, G.; Gosar, M.; Miler, M.; Alijagić, J. Impacts of mining and smelting activities on environment and landscape degradation—Slovenian case studies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4457–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrstener, E.; Biester, H.; Bigler, C.; Lidberg, W.; Meyer-Jacob, C.; Rydberg, J.; Bindler, R. Environmental footprint of small-scale, historical mining and metallurgy in the Swedish boreal forest landscape: The Moshyttan blast furnace as microcosm. Holocene 2019, 29, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Merino, L.; Cortizas, A.M.; Reher, G.S.; López-Sáez, J.A.; Mighall, T.M.; Bindler, R. Reconstructing the impact of human activities in a NW Iberian Roman mining landscape for the last 2500 years. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 50, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaviya, S.; Munsi, M.; Oinam, G.; Joshi, P.K. Landscape approach for quantifying land use land cover change (1972–2006) and habitat diversity in a mining area in Central India (Bokaro, Jharkhand). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upgupta, S. Fragmented landscapes of east bokaro coalfields: A remote sensing based approach highlighting forestland dynamics. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makineci, E.; Gungor, B.S.; Kumbasli, M. Natural plant revegetation on reclaimed coal mine landscapes in Agacli-Istanbul. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 3248–3259. [Google Scholar]
- Knabb, K.A.; Erel, Y.; Tirosh, O.; Rittenour, T.; Laparidou, S.; Najjar, M.; Levy, T.E. Environmental impacts of ancient copper mining and metallurgy: Multi-proxy investigation of human-landscape dynamics in the Faynan valley, southern Jordan. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 74, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ji, W. Relating landscape characteristics to non-point source pollution in mine waste-located watersheds using geospatial techniques. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 82, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T. Landscape restoration following phosphate mining: 30 years of co-evolution of science, industry and regulation. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.A.; Wood, P.B.; Strager, M.P.; Mazzarella, C. Impacts of mountaintop mining on terrestrial ecosystem integrity: Identifying landscape thresholds for avian species in the central Appalachians, United States. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, P.J.; Krüger, R. Restoring degraded landscapes in lowland Namaqualand: Lessons from the mining experience and from regional ecological dynamics. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 70, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festin, E.S.; Tigabu, M.; Chileshe, M.N.; Syampungani, S.; Odén, P.C. Progresses in restoration of post-mining landscape in Africa. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbett, M.; Mulligan, D.; Audet, P. Recent advances in restoration ecology: Examining the modern Australian agro-ecological and post-mining landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 163, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, D.; Audet, P.; Mulligan, D. Examining the Australian context for post-mined land rehabilitation: Reconciling a paradigm for the development of natural and novel ecosystems among post-disturbance landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 163, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, G. Major ecological and environmental problems and the ecological reconstruction technologies of the coal mining areas in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Sklenicka, P.; Prikryl, I.; Svoboda, I.; Lhota, T. Non-productive principles of landscape rehabilitation after long-term opencast mining in north-west Bohemia. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2004, 104, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J.; Sklenicka, P. Restoration of areas affected by mining. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 43, 0–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.L.; Brinkley, W.; Romolini, M. Environmental stewardship footprint research: Linking human agency and ecosystem health in the Puget Sound region. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, P.; Conti, L. Links among Human Health, Animal Health, and Ecosystem Health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2013, 34, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, A. Wilderness as a land laboratory. Living Wilderness 1941, 6, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rapport, D.J.; Thorpe, C.; Regier, H.A. Ecosystem Medicine. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 1979, 60, 180–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.J. An ecological comparison of the McHarg method with other planning initiatives in the Great Lakes Basin. Landsc. Plan. 1982, 9, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hua, O.; Niu, H. Ecosystem Health: Concept Analysis. Resour. Sci. 2005, 27, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation for regional ecosystem health: Methodology and research progress. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 4877–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.K. The Concept of Landscape Health. J. Environ. Manag. 1994, 40, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J.; Regier, H.A.; Hutchinson, T.C. Ecosystem Behavior under Stress. Am. Nat. 1985, 125, 617–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D. Dimensions of Ecosystem Health. Ecosystem Health: Principles and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Khasbagan; Song, D. A review on the concept, characteristic and assessment of landscape health. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Ma, K.; Wang, Y. Principles and Applications of Landscape Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Ho, T. Study on regional air quality impact from a chemical plant emergency shutdown. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Ho, T. New insight of ozone pollution impact from flare emissions of chemical plant start-up operations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Land Use/Land Cover Change and Carbon Cycle in Xilin River Basin of Inner Mongolia Based on Remote Sensing and GIS. Institute of Remote Sensing Applied Technology; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y. Study on the Change of Grassland in Xilinguole Supported by 3S; Inner Mongolia Normal University: Hohehot, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.; Miao, X.; Lei, S.; Wang, W.; Struthers, S.; Chen, S.E. The Challenges of Reusing Mining and Mineral-Processing Wastes. Science 2012, 337, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Verma, V.K.; Naskar, A.K.; Sharma, C.S.; Mukherjee, D.P. Bioavailability of Metals in Soil and Health Risk Assessment for Populations Near an Indian Chromite Mine Area. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2014, 20, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Árvay, J.; Demková, L.; Hauptvogl, M.; Michalko, M.; Bajčan, D.; Stanovič, R.; Tomáš, J.; Hrstková, M.; Trebichalský, P. Assessment of environmental and health risks in former polymetallic ore mining and smelting area, Slovakia: Spatial distribution and accumulation of mercury in four different ecosystems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Sahakyan, L.; Belyaeva, O.; Asmaryan, S.; Saghatelyan, A. Continuous impact of mining activities on soil heavy metals levels and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Yan, C.; Xiu, L.; Feng, K. The impact of mining changes on surrounding lands and ecosystem service value in the Southern Slope of Qilian Mountains. Ecol. Complex. 2018, 36, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonter, L.J.; Moran, C.J.; Barrett, D.J.; Soares-Filho, B.S. Processes of land use change in mining regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisquert, D.S.; Castejón, J.M.P.; Fernández, G.G. The impact of atmospheric dust deposition and trace elements levels on the villages surrounding the former mining areas in a semi-arid environment (SE Spain). Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.G.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, Z.K. The Changes of Landscape Structure and the Principes of Land Reclamation in the Antaibao Opencast Area. Resour. Ind. 2006, 8, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, S.; Bian, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. Study of the desertification index based on the albedo-MSAVI feature space for semi-arid steppe region. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.J.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Shen, L.D.; Wang, H.B.; Li, L.G. An approach to examining performances of cool/hot sources in mitigating/enhancing land surface temperature under different temperature backgrounds based on landsat 8 image. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, S.; He, B.J.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Peng, S.; Duo, L. Assessment of Landscape Ecological Health: A Case Study of a Mining City in a Semi-Arid Steppe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhang, T.L.; Fu, B.J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Ren, L.; Bian, Z. Time–space characterization of vegetation in a semiarid mining area using empirical orthogonal function decomposition of MODIS NDVI time series. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. Landscape Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M. On the nomadic pattern of nomadic people in the historical period. Res. Chin. Econ. Hist. 2003, 4, 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, G. The tragedy of the commons. Science 1968, 162, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, L. Grassland management: How to further improve the grassland household contract system. Chin. Rural Econ. 2007, 12, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.G.; Tang, K.H.; Lu, Y.L. Fence Effect: Property Division and Integrity of Grassland Ecosystem. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 24, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Ecological restoration and sustainable landscape design of mining wastelands. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2003, 24, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Landscape Reconstruction and Recreation of Damaged Land in Opencast Coal Mine: A Review. Adv. Earth Sci. 2016, 31, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.; Zhang, Y. Land Use Changes in Xuzhou Coal Mining Area. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2006, 61, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.S.; Wa, Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Song, J. Research Progresses on Driving Forces of the Changes of Landscape Pattern. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).