RAINBOW: An Operational Oriented Combined IR-Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instrumentation and Methods
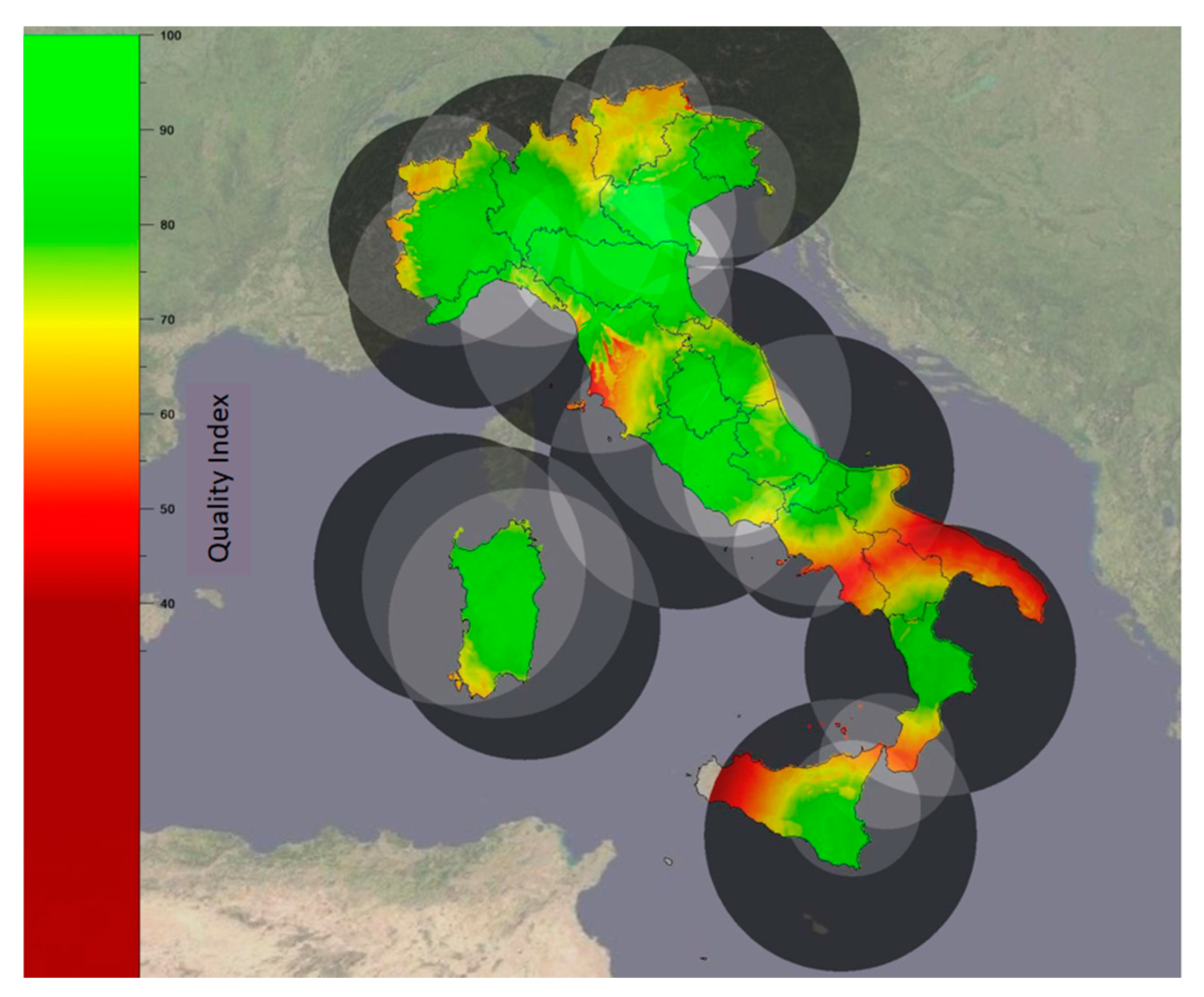
2.1. IT GR Network
2.2. SEVIRI Radiometer
2.3. P-IN-SEVIRI
2.4. GRISO
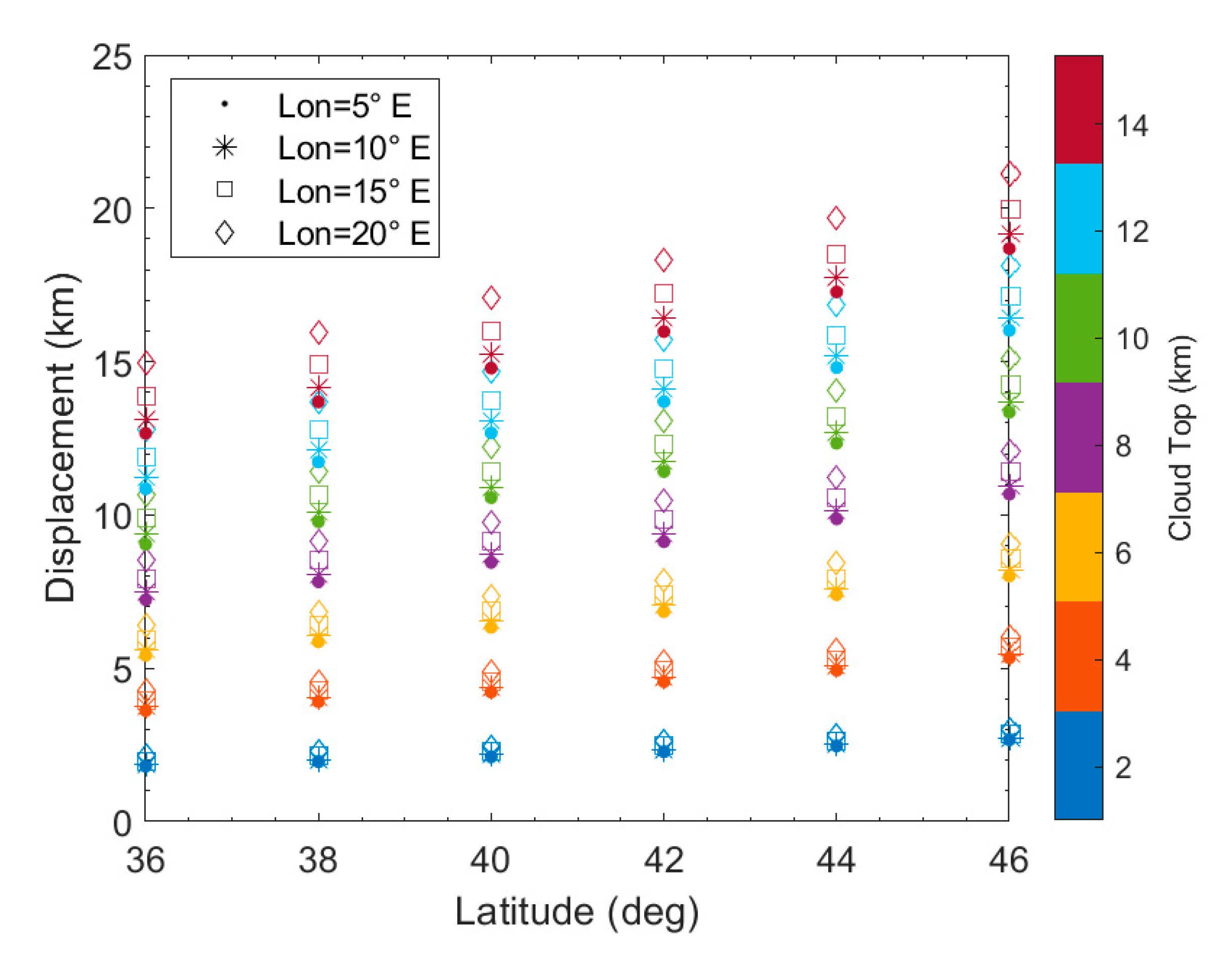
2.5. Parallax Correction
2.6. RAINBOW Algorithm
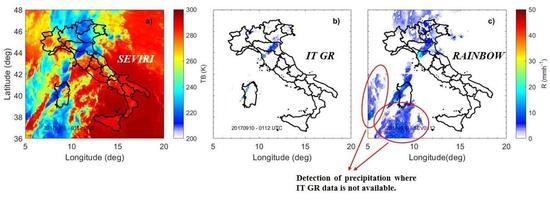
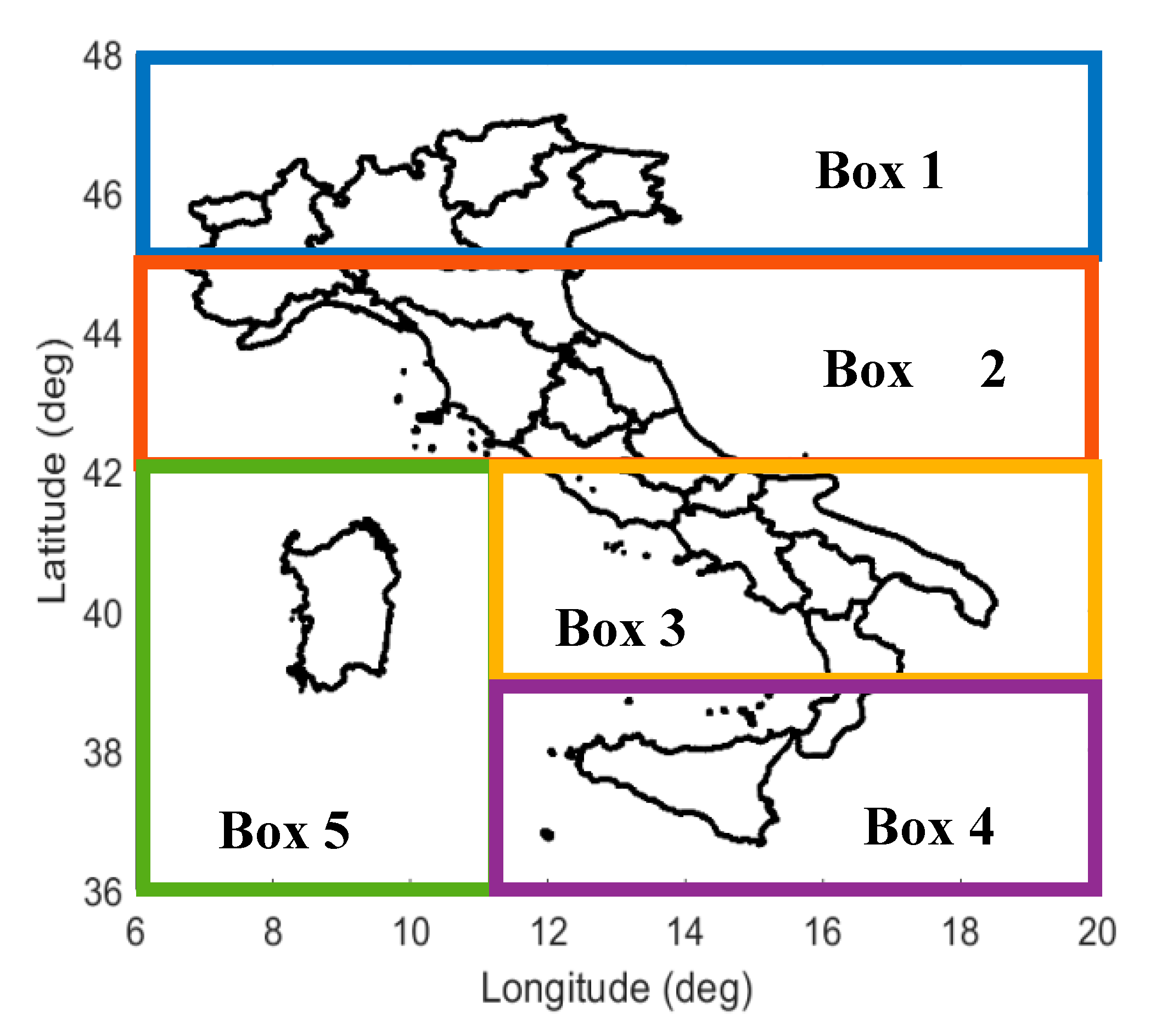
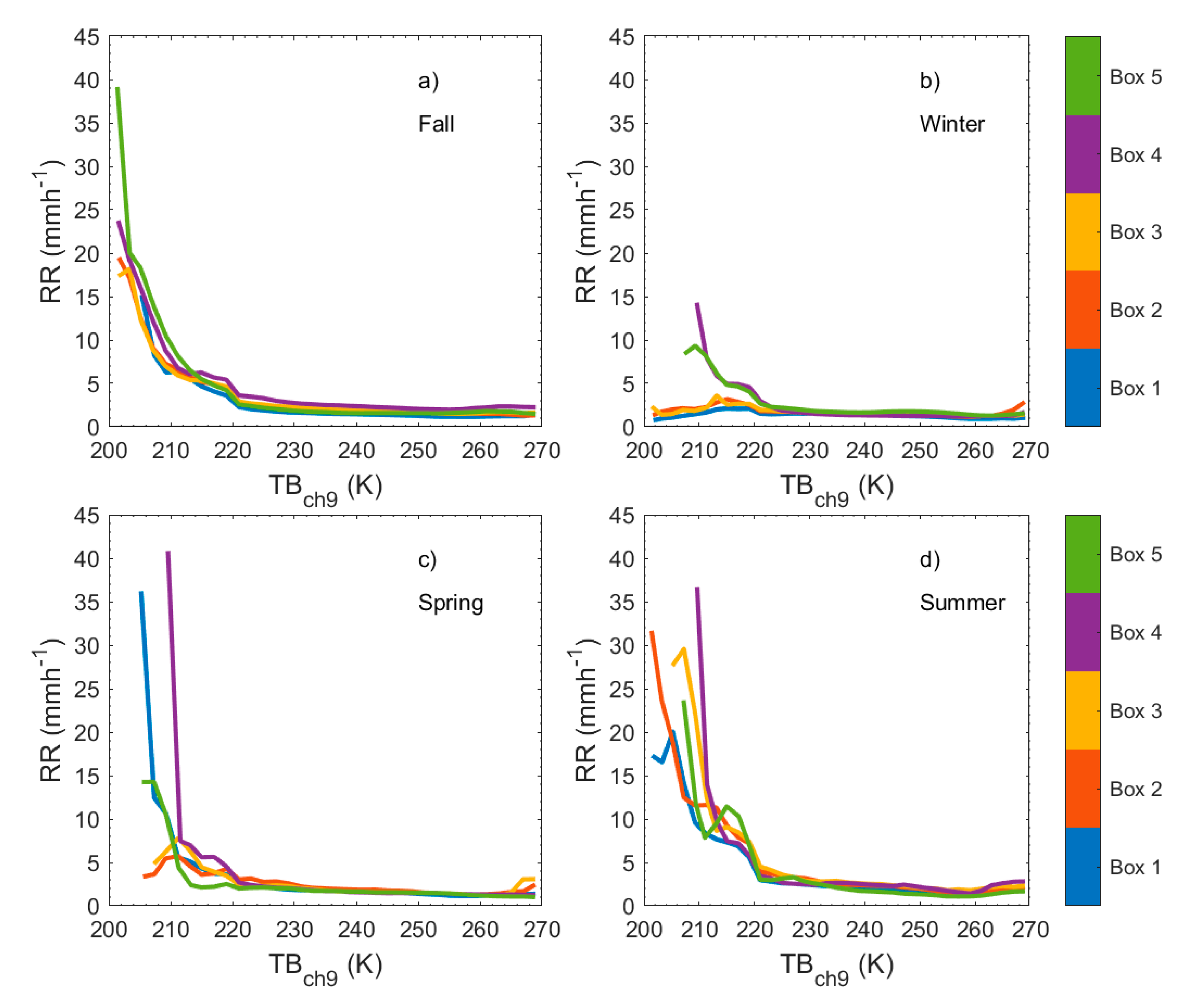
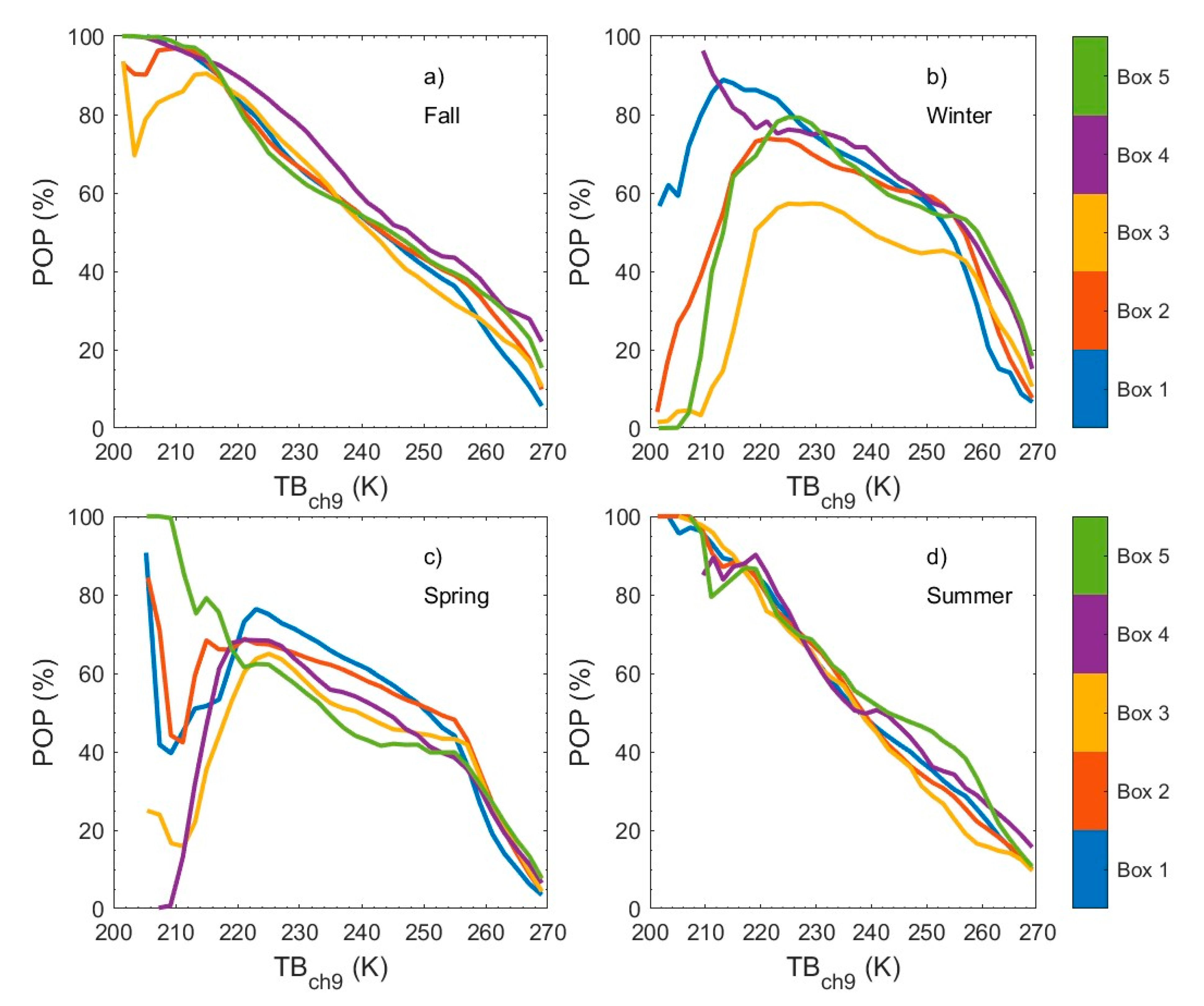
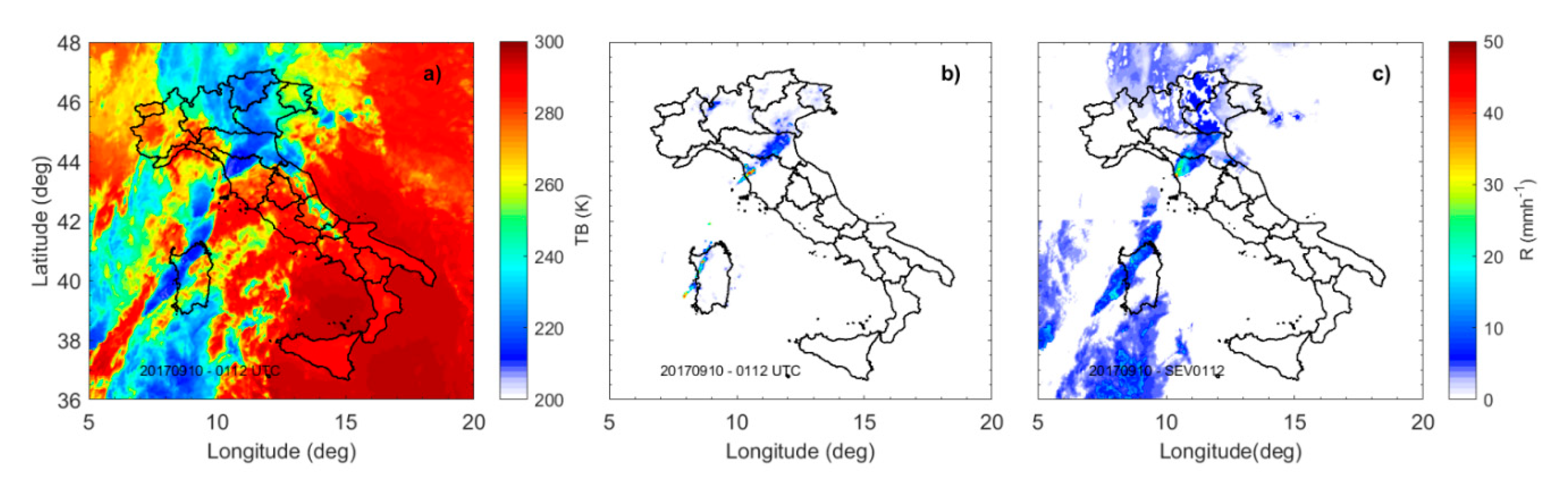
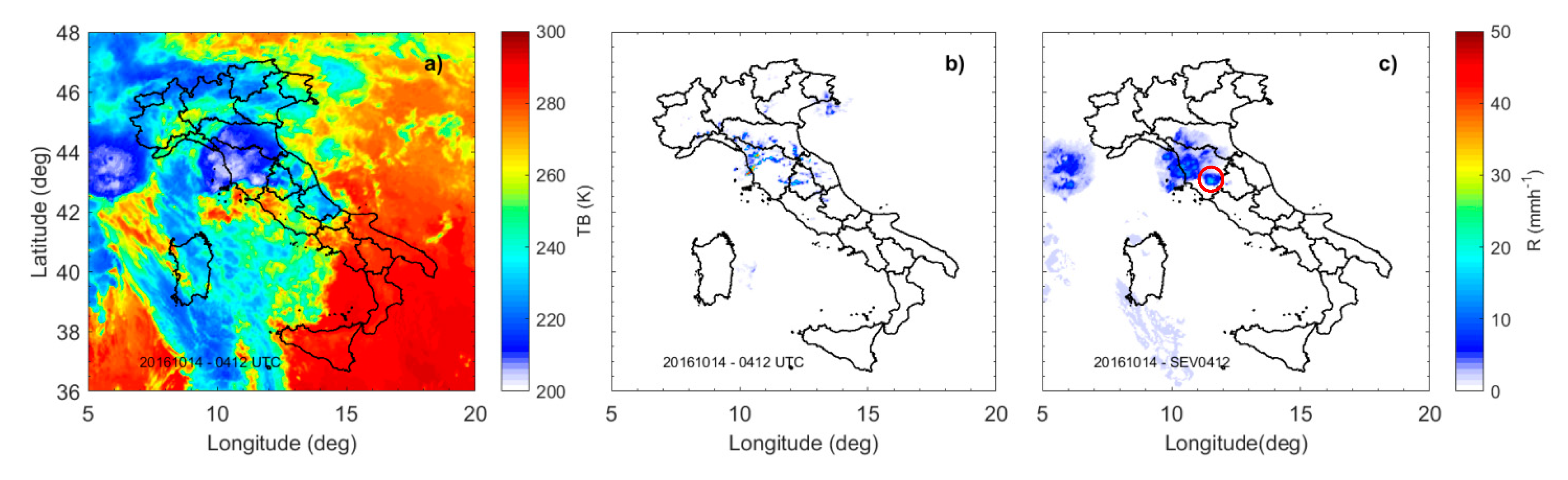
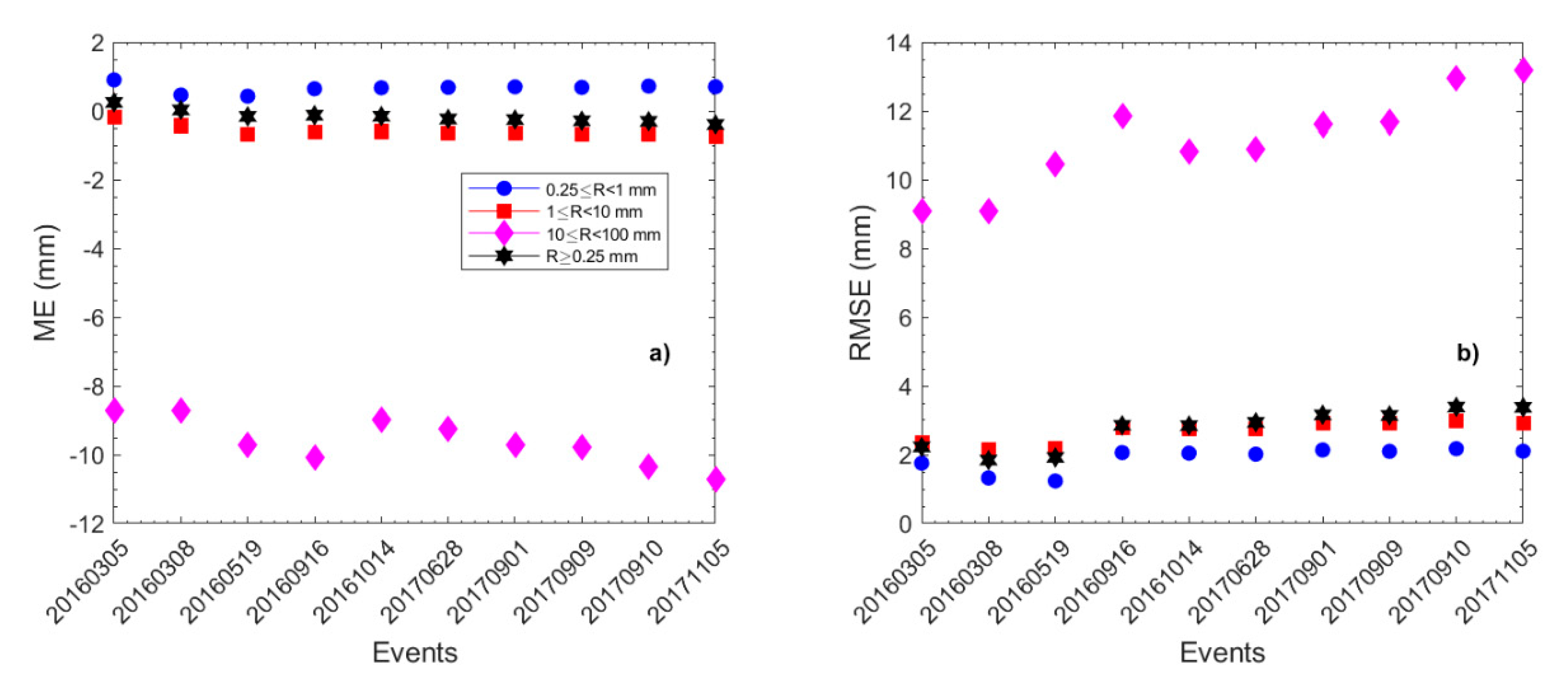
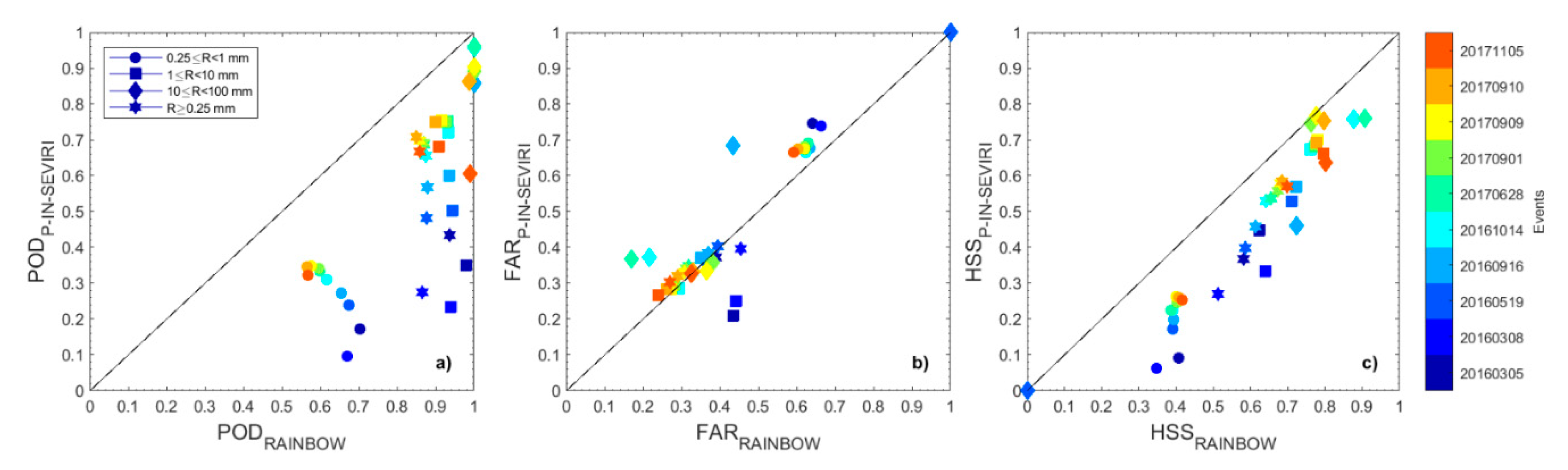
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-521-62384-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kirstetter, P.-E.; Delrieu, G.; Boudevillain, B.; Obled, C. Toward an error model for radar quantitative precipitation estimation in the Cévennes–Vivarais region, France. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulpiani, G.; Montopoli, M.; Passeri, L.D.; Gioia, A.G.; Giordano, P.; Marzano, F.S. On the use of Dual-Polarized C-Band radar for operational rainfall retrieval in mountainous areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Anagnostou, E.; Anagnostou, M.N.; Kalogiros, J.; Casella, D.; Marra, A.C.; Panegrossi, G.; Sano, P. Passive microwave rainfall error analysis using high-resolution X-Band Dual-Polarization radar observations in complex terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Thoss, A.; Dybbroe, A.; Michelson, D.B. Precipitation analysis using the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit in support of nowcasting applications. Meteorol. Appl. 2002, 9, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Kummerow, C.D. The Remote Sensing of Clouds and Precipitation from Space: A Review. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 3742–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Matsui, T.; Chern, J.; Mohr, K.; Kummerow, C.; Randel, D. Global precipitation estimates from cross-track passive microwave observations using a physically based retrieval scheme. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levizzani, V.; Cattani, E. Satellite remote sensing of precipitation and the terrestrial water cycle in a changing climate. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkin, P.A.; Meisner, B.N. The relationship between large-scale convective rainfall and cold cloud over the Western Hemisphere during 1982-84. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rickenbach, T.M. Cloud-top evolution of tropical oceanic squall lines from radar reflectivity and infrared satellite data. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2951–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorati, R.; Alberoni, P.P.; Levizzani, V.; Nanni, S. IR-based satellite and radar rainfall estimates of convective storms over northern Italy. Meteorol. Appl. 2000, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levizzani, V.; Schmetz, J.; Lutz, H.J.; Kerkmann, J.; Alberoni, P.P.; Cervino, M. Precipitation estimations from geostationary orbit and prospects for METEOSAT Second Generation. Meteorol. Appl. 2001, 8, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazri, M.; Ameur, S.; Brucker, J.M.; Testud, J.; Hamadache, B.; Hameg, S.; Ouallouche, F.; Mohia, Y. Identification of raining clouds using a method based on optical and microphysical cloud properties from Meteosat second generation daytime and nighttime data. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capacci, D.; Porcù, F. Evaluation of a satellite multispectral VIS–IR daytime statistical rain-rate classifier and comparison with passive microwave rainfall estimates. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnlein, M.; Thies, B.; Nauß, T.; Bendix, J. Rainfall-rate assignment using MSG SEVIRI Data—A promising approach to spaceborne rainfall-rate retrieval for midlatitudes. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1477–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnlein, M.; Appelhans, T.; Thies, B.; Nauß, T. Precipitation estimates from MSG SEVIRI daytime, nighttime, and twilight data with random forests. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 2457–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feidas, H.; Giannakos, A. Identifying precipitating clouds in Greece using multispectral infrared Meteosat Second Generation satellite data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, B.; Nauß, T.; Bendix, J. Precipitation process and rainfall intensity differentiation using Meteosat Second Generation Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager data. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, E.N.; Kummerow, C. Stratiform and convective classification of rainfall using SSM/I 85-GHz brightness temperature observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1997, 14, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.; Marcos, C.; Sancho, J. The convective rainfall rate from cloud physical properties algorithm for meteosat second-generation satellites: Microphysical basis and intercomparisons using an object-based method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurczyk, A.; Szturc, J.; Otop, I.; Ośródka, K.; Struzik, P. Quality-based combination of multi-source precipitation data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NWC SAF. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document for the Precipitation Product Processors of the NWC/GEO. 2019. Available online: http://www.nwcsaf.org/Downloads/GEO/2018/Documents/Scientific_Docs/NWC-CDOP2-GEO-AEMET-SCI-ATBD-Precipitation_v2.1.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Kummerow, C.D.; Tanelli, S.; Takahashi, N.; Furukawa, K.; Klein, M.; Levizzani, V. Plans for Future Missions. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Advances in Global Change Research; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C.D., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 67, pp. 99–119. ISBN 978-3-030-24567-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, F.; Pasternak, F.; Davancens, R.; Baldit, E.; Luitot, C.; Penquer, A.; Calvel, B.; Buil, C. Overview of IASI-NG the new generation of infrared atmospheric sounder. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Space Optics—ICSO, Tenerife, Spain, 6–10 October 2014; Cugny, B., Sodnik, Z., Karafolas, N., Eds.; SPIE: Tenerife, Spain, 2017; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Andrey-Andrés, J.; Fourrié, N.; Guidard, V.; Armante, R.; Brunel, P.; Crevoisier, C.; Tournier, B. A simulated observation database to assess the impact of the IASI-NG hyperspectral infrared sounder. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mugnai, A.; Cooper, H.J.; Smith, E.A.; Tripoli, G.J. Simulation of microwave brightness temperatures of an evolving hailstorm at SSM/I frequencies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1990, 71, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilheit, T.; Adler, R.; Avery, S.; Barrett, E.; Bauer, P.; Berg, W.; Chang, A.; Ferriday, J.; Grody, N.; Goodman, S.; et al. Algorithms for the retrieval of rainfall from passive microwave measurements. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 11, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Grody, N.C. Retrieval of Ice cloud parameters using a microwave imaging radiometer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Petty, G.W. The sensitivity of microwave remote sensing observations of precipitation to ice particle size distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Moreau, E.; Di Michele, S. Hydrometeor retrieval accuracy using microwave window and sounding channel observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1016–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Kniveton, D.R.; Todd, M.C.; Bellerby, T.J. Satellite rainfall estimation using combined passive microwave and infrared algorithms. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1088–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, F.S.; Palmacci, M.; Cimini, D.; Giuliani, G.; Turk, F.J. Multivariate statistical integration of Satellite infrared and microwave radiometric measurements for rainfall retrieval at the geostationary scale. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1018–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Huffman, G. Global precipitation measurement: Global precipitation measurement. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Turk, F.J.; Petersen, W.; Hou, A.Y.; García-Ortega, E.; Machado, L.A.T.; Angelis, C.F.; Salio, P.; Kidd, C.; Huffman, G.J.; et al. Global precipitation measurement: Methods, datasets and applications. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, M.; Hossain, F. (Eds.) Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-90-481-2914-0. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Kachi, M.; Arai, Y.; Tashima, T.; Masaki, T.; Kawamoto, N.; et al. Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) products in the GPM Era. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Advances in Global Change Research; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C.D., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 67, pp. 355–373. ISBN 978-3-030-24567-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, K.-L.; Karbalee, N.; Braithwaite, D. Improving PERSIANN-CCS Using Passive Microwave Rainfall Estimation. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Advances in Global Change Research; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C.D., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 67, pp. 375–391. ISBN 978-3-030-24567-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kuligowski, R.J.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Improvements to the GOES-R Rainfall Rate Algorithm. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Gupta, H.V.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Estimation of physical variables from multichannel remotely sensed imagery using a neural network: Application to rainfall estimation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite–based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.-L.; Joyce, R.J.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J.; et al. Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission (IMERG). In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Advances in Global Change Research; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C.D., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 67, pp. 343–353. ISBN 978-3-030-24567-2. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, R.F.; Negri, A.J.; Keehn, P.R.; Hakkarinen, I.M. Estimation of monthly rainfall over japan and surrounding waters from a combination of low-orbit microwave and geosynchronous IR data. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1993, 32, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levizzani, V.; Porcú, F.; Marzano, F.S.; Mugnai, A.; Smith, E.A.; Prodi, F. Investigating a SSM/I microwave algorithm to calibrate Meteosat infrared instantaneous rainrate estimates. Meteorol. Appl. 1996, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcú, F.; Borga, M.; Prodi, F. Rainfall estimation by combining radar and infrared satellite data for nowcasting purposes. Meteorol. Appl. 1999, 6, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerby, T.; Todd, M.; Kniveton, D.; Kidd, C. Rainfall estimation from a combination of TRMM precipitation radar and GOES multispectral satellite imagery through the use of an artificial neural network. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 2115–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.C.; Kidd, C.; Kniveton, D.; Bellerby, T.J. A combined satellite infrared and passive microwave technique for estimation of small-scale rainfall. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, F.J.; Miller, S.D. Toward improved characterization of remotely sensed precipitation regimes with MODIS/AMSR-E blended data techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Global Precipitation Map Using Satellite-Borne Microwave Radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerby, T.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. LMODEL: A Satellite Precipitation Methodology Using Cloud Development Modeling. Part I: Algorithm Construction and Calibration. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kidd, C.; Bauer, P.; Turk, J.; Huffman, G.J.; Joyce, R.; Hsu, K.-L.; Braithwaite, D. Intercomparison of high-resolution precipitation products over Northwest Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paola, F.; Casella, D.; Dietrich, S.; Mugnai, A.; Ricciardelli, E.; Romano, F.; Sanò, P. Combined MW-IR Precipitation Evolving Technique (PET) of convective rain fields. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 3557–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porcú, F.; Caracciolo, C.; Prodi, F. Cloud systems leading to flood events in Europe: An overview and classification. Meteorol. Appl. 2003, 10, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglietta, M.M.; Laviola, S.; Malvaldi, A.; Conte, D.; Levizzani, V.; Price, C. Analysis of tropical-like cyclones over the Mediterranean Sea through a combined modeling and satellite approach: TLC ANALYSIS THROUGH A COMBINED APPROACH. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2400–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzato, A.; Davolio, S.; Miglietta, M.M.; Pucillo, A.; Setvák, M. 12 September 2012: A supercell outbreak in NE Italy? Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panegrossi, G.; Casella, D.; Dietrich, S.; Marra, A.C.; Sano, P.; Mugnai, A.; Baldini, L.; Roberto, N.; Adirosi, E.; Cremonini, R.; et al. Use of the GPM constellation for monitoring heavy precipitation events over the Mediterranean Region. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2733–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, N.; Adirosi, E.; Baldini, L.; Casella, D.; Dietrich, S.; Gatlin, P.; Panegrossi, G.; Petracca, M.; Sanò, P.; Tokay, A. Multi-sensor analysis of convective activity in central Italy during the HyMeX SOP 1.1. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestro, F.; Rebora, N.; Giannoni, F.; Cavallo, A.; Ferraris, L. The flash flood of the Bisagno Creek on 9th October 2014: An “unfortunate” combination of spatial and temporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestro, F.; Rebora, N.; Rossi, L.; Dolia, D.; Gabellani, S.; Pignone, F.; Trasforini, E.; Rudari, R.; De Angeli, S.; Masciulli, C. What if the 25 October 2011 event that struck Cinque Terre (Liguria) had happened in Genoa, Italy? Flooding scenarios, hazard mapping anddamage estimation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marra, A.C.; Porcù, F.; Baldini, L.; Petracca, M.; Casella, D.; Dietrich, S.; Mugnai, A.; Sanò, P.; Vulpiani, G.; Panegrossi, G. Observational analysis of an exceptionally intense hailstorm over the Mediterranean area: Role of the GPM Core Observatory. Atmos. Res. 2017, 192, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puca, S.; Porcu, F.; Rinollo, A.; Vulpiani, G.; Baguis, P.; Balabanova, S.; Campione, E.; Ertürk, A.; Gabellani, S.; Iwanski, R.; et al. The validation service of the hydrological SAF geostationary and polar satellite precipitation products. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 871–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Hagen, M.; Einfalt, T. A Quality control concept for radar reflectivity, polarimetric parameters, and Doppler Velocity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 865–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joss, J.; Lee, R. The Application of Radar–gauge comparisons to operational precipitation profile corrections. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 2612–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, U.; Joss, J. Mesobeta profiles to extrapolate radar precipitation measurements above the alps to the ground level. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, L.D.; Rutledge, S.A.; Ahijevych, D.A.; Keenan, T.D. Correcting propagation effects in C-Band polarimetric radar observations of tropical convection using differential propagation phase. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1405–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Testud, J.; Le Bouar, E.; Obligis, E.; Ali-Mehenni, M. The Rain Profiling Algorithm Applied to Polarimetric Weather Radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 332–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulpiani, G.; Tabary, P.; Parent du Chatelet, J.; Marzano, F.S. Comparison of advanced radar polarimetric techniques for operational attenuation correction at C Band. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1118–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisologo, I.; Vulpiani, G.; Abon, C.C.; David, C.P.C.; Bronstert, A.; Heistermann, M. Polarimetric rainfall retrieval from a C-Band weather radar in a tropical environment (The Philippines). Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 50, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinollo, A.; Vulpiani, G.; Puca, S.; Pagliara, P.; Kaňák, J.; Lábó, E.; Okon, L.; Roulin, E.; Baguis, P.; Cattani, E.; et al. Definition and impact of a quality index for radar-based reference measurements in the H-SAF precipitation product validation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2695–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petracca, M.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Porcù, F.; Vulpiani, G.; Sebastianelli, S.; Puca, S. Validation of GPM Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) Rainfall Products over Italy. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastianelli, S.; Russo, F.; Napolitano, F.; Baldini, L. On precipitation measurements collected by a weather radar and a rain gauge network. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabary, P. The new french operational radar rainfall product. Part I: Methodology. Weather Forecasting 2007, 22, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins Costa do Amaral, L.; Barbieri, S.; Vila, D.; Puca, S.; Vulpiani, G.; Panegrossi, G.; Biscaro, T.; Sanò, P.; Petracca, M.; Marra, A.; et al. Assessment of Ground-reference data and validation of the H-SAF precipitation products in Brazil. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vulpiani, G.; Baldini, L.; Roberto, N. Characterization of Mediterranean hail-bearing storms using an operational polarimetric X-band radar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4681–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmetz, J.; Pili, P.; Tjemkes, S.; Just, D.; Kerkmann, J.; Rota, S.; Ratier, A. Supplement to an introduction to Meteosat Second Generation (MSG): SEVIRI CALIBRATION. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2002, 83, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnai, A.; Casella, D.; Cattani, E.; Dietrich, S.; Laviola, S.; Levizzani, V.; Panegrossi, G.; Petracca, M.; Sanò, P.; Di Paola, F.; et al. Precipitation products from the hydrology SAF. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1959–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turk, F.J.; Rohaly, G.; Hawkins, J.; Smith, E.A.; Marzano, F.S.; Mugnai, A.; Levizzani, V. Meteorological applications of precipitation estimation from combined SSM/I, TRMM and geostationary satellite data. In Microwave Radiometry and Remote Sensing of the Earth’s Surface and Atmosphere; Pampaloni, P., Paloscia, S., Eds.; VSP International Science Publisher: Florence, Italy, 2000; pp. 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, F.J.; Sohn, B.-J.; Oh, H.-J.; Ebert, E.E.; Levizzani, V.; Smith, E.A. Validating a rapid-update satellite precipitation analysis across telescoping space and time scales. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2009, 105, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignone, F.; Rebora, N.; Silvestro, F.; Castelli, F. GRISO (Generatore Random di Interpolazioni Spaziali da Osservazioni Incerte)-Piogge; 2010; p. 353. [Google Scholar]
- Feidas, H.; Porcu, F.; Puca, S.; Rinollo, A.; Lagouvardos, C.; Kotroni, V. Validation of the H-SAF precipitation product H03 over Greece using rain gauge data. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 377–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; de Rosnay, P.; Bell, B.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; Abdalla, S.; Alonso-Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bechtold, P.; et al. Operational Global Reanalysis: Progress, Future Directions and Synergies with NWP. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/18765 (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.P.; Poli, P.; Brugge, R.; Fielding, M.; Fuentes, M.; Kallberg, P.W.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A. The ERA-Interim Archive Version 2.0. 2011. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/8174 (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Tang, C.; Dai, C.; Wu, X.; Wei, H. The Global Distribution of Cirrus Clouds Reflectance Based on MODIS Level-3 Data. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, D. (Ed.) Cirrus; Oxford University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-19-513072-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmi, P. Recommendations on the Verification of local Weather Forecasts. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/node/11401 (accessed on 30 July 2020).




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Adderio, L.P.; Puca, S.; Vulpiani, G.; Petracca, M.; Sanò, P.; Dietrich, S. RAINBOW: An Operational Oriented Combined IR-Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152444
D’Adderio LP, Puca S, Vulpiani G, Petracca M, Sanò P, Dietrich S. RAINBOW: An Operational Oriented Combined IR-Algorithm. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(15):2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152444
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Adderio, Leo Pio, Silvia Puca, Gianfranco Vulpiani, Marco Petracca, Paolo Sanò, and Stefano Dietrich. 2020. "RAINBOW: An Operational Oriented Combined IR-Algorithm" Remote Sensing 12, no. 15: 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152444
APA StyleD’Adderio, L. P., Puca, S., Vulpiani, G., Petracca, M., Sanò, P., & Dietrich, S. (2020). RAINBOW: An Operational Oriented Combined IR-Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 12(15), 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12152444