Abstract
This work describes a study using multi-view hyperspectral imagery to retrieve sediment filling factor through inversion of a modified version of the Hapke radiative transfer model. We collected multi-view hyperspectral imagery from a hyperspectral imaging system mounted atop a telescopic mast from multiple locations and viewing angles of a salt panne on a barrier island at the Virginia Coast Reserve Long-Term Ecological Research site. We also collected ground truth data, including sediment bulk density and moisture content, within the common field of view of the collected hyperspectral imagery. For samples below a density threshold for coherent effects, originally predicted by Hapke, the retrieved sediment filling factor correlates well with directly measured sediment bulk density (). The majority of collected samples satisfied this condition. The onset of the threshold occurs at significantly higher filling factors than Hapke’s predictions for dry sediments because the salt panne sediment has significant moisture content. We applied our validated inversion model to successfully map sediment filling factor across the common region of overlap of the multi-view hyperspectral imagery of the salt panne.
1. Introduction
Retrieval of properties of Earth sediments and planetary regoliths from spectral remote sensing has been explored extensively [1,2,3,4]. Radiative transfer models have been a centerpiece of these studies with the Hapke model [1] having been among the more frequently used models in past studies. Hapke’s Isotropic Multiple Scattering Approximation (IMSA) [1] model and his later Modified IMSA (MIMSA) [1,5] have been widely used, especially to model the interaction of light with granular sediments [6,7,8,9]. Jacquemoud et al. [6] investigated laboratory spectral data for 26 different soil samples of varying soil type by inverting an an early version of IMSA predating Hapke’s adjustment of the model for the effects of porosity [10]. Their inversion of IMSA retrieved the single scattering albedo, single scattering phase function parameters, and opposition effect width parameter using spectral data from a multi-spectral sensor and spectrometer. In [7], Wu et al. inverted the MIMSA model to retrieve parameters for four different types of desert environments using Multi-Angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) [11] data. Their modeling efforts also included Hapke’s correction for macroscopic roughness [12]. Bachmann et al. [8] inverted laboratory hyperspectral goniometer data of the Algodones Dunes to jointly retrieve sediment filling factor and single scattering albedo and validated the results in the laboratory with direct measurements of sediment bulk density. This multi-stage optimization procedure also optimized other model parameters such as those parameterizing the phase function, and opposition effect. Eon, Bachmann, and Gerace [9] built on this approach extending it to multi-view hyperspectral imagery of the Algodones Dunes obtained by the NASA G-LiHT hyperspectral imaging (HSI) system [13]. Since roughly one-third of of the land surface on Earth is either desert or a similar arid environment [14], where granular sediments predominate, radiative transfer models that describe surfaces with significant granular content can play an important role in remote sensing analysis and in the inversion of surface parameters.
The IMSA model also has been used widely in astronomy, particularly for planetary studies [15,16,17] as well in studies of asteroids and comets [18,19,20,21] associated with recent and future NASA and JAXA probes [16,19,21]. Protopapa et al. [15], for example, applied the Hapke IMSA model to the inversion of Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA) spectral imagery of Pluto from the Ralph instrument onboard the New Horizons probe [22] to retrieve abundances of ice, tholin, and mixtures of ice and ice. They made a number of simplifying assumptions in their model, using a single-lobe Henyey–Greenstein phase function and fixing many of the free parameters of the Hapke model to reasonable values obtained in previous studies. They also combined the IMSA model with an areal linear mixture model and an equivalent slab model [1] that linked the single scattering albedo to optical constants and average particle size, optimizing over the particle size and mixture fraction. Ciarniello et al. [16] used a version of the IMSA model based on disk-integrated reflectance [1] to analyze Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) [23] hyperspectral data of Rhea from the Cassini mission [24]. They optimized the parameters of the opposition effect scale and width parameter, a two-parameter Henyey–Greenstein function, as well as Hapke’s surface roughness correction [12] using a grid search. They likewise combined their model with an equivalent slab model and a mixture model; however, they considered three different types of mixtures: areal, intimate, and intraparticle, with best results obtained using the latter. Lederer et al. [18] used the Hapke model to analyze disk-integrated reflectance of the asteroid Itokawa from ground-based multi-spectral observations. Their model similarly focused on the phase function, opposition effect, and surface roughness parameters. Since their study was published in the same year as Hapke’s improvement to IMSA incorporating porosity explicitly [10], they only considered porosity in terms of the width parameter of the opposition effect. In a study of an asteroid from multiple ground-based telescopes, Ishiguro et al. [19] similarly used the IMSA in a comparative study of models for the phase function. Their approach used a single lobe Henyey–Greenstein function as well as the Hapke surface roughness correction and opposition effect factors for disk-integrated reflectance. Their optimization found comparable local minima for different roughness values due to the more limited nature of the input data which were based solely on V band observations. Similar challenges appear in the study of Li et al. [20], who used the Hapke model to study surface properties of Comet 9P/Tempel 1 from High Resolution Instrument (HRI) and Medium Resolution Instrument (MRI) multispectral imagery acquired during the Deep Impact Mission [25]. Due to the limited sampling of phase angle geometries in their data, they fixed a number of the Hapke free parameters, varying only roughness and single scattering albedo during optimization. A later study by Fink [21] extended this same work to derive surface optical constants again using an equivalent slab model [1].
Inversion of surface properties has served as a central theme in application of the Hapke model and variants. Hapke’s IMSA solution to the radiative transfer equation accounts for influences such as macroscopic surface roughness [12,26], sediment filling factor (the fraction of volume occupied by particles) [1,10], and grain size distribution [1,10,27], as well as intrinsic properties of materials such as single scattering albedo [1]. Extensions of the Hapke model also have considered methods to include the influence of pore water in sediment [28]. A central focus of this paper is the inversion of a variant of the IMSA model to retrieve the sediment filling factor. In practical terms, the sediment filling factor is directly proportional to a commonly used geotechnical property, the sediment bulk density, which is a critical parameter in a variety of civil engineering applications as well as scientific analyses of sediments. In the coastal zone, sediment bulk density is a contributing factor to models analyzing erosion and coastal change [29] and parameters such as bulk density, among others, contribute to sediment strength, an important factor in assessment of substrate bearing strength [30]. As we discuss in more detail later in this article, sediment filling factor, or equivalently porosity (the complementary void space in the medium), contributes to the observed reflectance at the sensor. Indeed, in IMSA, Hapke derived an explicit form of the radiative transfer equation and its solution that directly incorporates the effect of the filling factor of the granular medium [1,10]. Porosity can have a significant effect on the reflectance of granular materials as has been demonstrated both theoretically and empirically [1,10], although there is some evidence to suggest that the degree of impact may depend on the material properties of the sediment. In a limited test of three different mineral types, for example, Helfenstein and Shepard, found preliminary evidence that minerals with very high albedo may show less effect than those with a lower albedo [31]. However, in the general case, even modest changes in sediment density can have a significant impact. In [32], for example, we analyzed sand sediments from a lacustrine evironment. For these samples, a change in density of resulted in a consistent change in reflectance of . For comparison, in this work, the change in bulk density from the largest to smallest measured at our salt panne site spanned a range of . In some of our other past work, we have also observed similar effects on observed reflectance from changes in density (see, for example, Figure 9 in [33]).
In our earlier study with lacustrine sediments, we also took measurements of directional reflectance and found that, for a progression of changes in sediment density prepared via air pluviation [34] and covering a range of just , we observed significant shifts in the angular distribution of scattered light, which became progressively more forward scattering and less diffuse with increasing density [32]. Theoretical predictions developed by Hapke for model grain size distributions also predict [1] that the width of the opposition effect, the peak distribution around the retro-reflectance direction, should be directly dependent on the product of the sediment filling factor and another nonlinear but monotonically increasing function of the sediment filling factor ) [33], described in greater detail below.
Our recent work has investigated ways to improve both the optimization of the inversion of this complex radiative transfer model as well as to develop incremental improvements [8,9] to overcome limitations, such as the assumption of isotropic multiple scatter, which underlie Hapke’s Isotropic Multiple Scattering Approximation (IMSA) [1,2].
In our earlier laboratory studies [8,9], we showed that our modified Hapke model solution could more robustly be inverted to retrieve the sediment filling factor, especially in wavelength ranges, such as the short-wave infra-red (SWIR) where signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is typically lower [8]. Sediment filling factor has been defined as the fractional volume occupied by particles [1,8,9,10,27]:
where is the number density of particles of type i per unit volume and the associated particle volume, while N is the average number of particles per unit volume and V the average volume occupied by a particle. The absence of particle material, known as the sediment porosity, P, the factor so frequently described in the geophysical and geotechnical literature, represents the void space in the material and is just the complement of the filling factor [1] defined in Equation (1):
Hapke showed that, to properly account for the effects of filling factor, the radiative transfer equation must be modified to include a “porosity coefficient” [1] (distinct from the porosity defined in Equation (2)), which depends nonlinearly on the filling factor , and the approximate solutions to the radiative transfer equation developed by Hapke, therefore, also depend explictly on [1,10]. An approximate form of derived by Hapke takes the form [1]:
The porosity coefficient defined in Equation (3) appears explicitly in Hapke’s radiative transfer equation and IMSA solution. The filling factor must, therefore, be regarded as a fundamental parameter of such models.
Because the filling factor and bulk density are directly proportional:
where is the bulk density, which includes both sediment and void space of the sediment in gm/cm , and is the mass density of particle type i and the fraction of particle type i, inversion of radiative transfer models, such as those due to Hapke, provides information about this directly measurable geotechnical parameter, the bulk density. If accurately retrieved from remote sensing imagery, therefore, the filling factor will be linearly proportional to the measured bulk density in the field or laboratory provided that the total density of particles is reasonably constant within a region of interest. In this case, from Equation (4), the slope will be the inverse of the total particle density.
In past work, we have developed methods to invert both the Hapke model and a modified form of the Hapke model that we developed [8,9] in order to specifically retrieve the sediment filling factor from multi-view hyperspectral data. Initially, we had focused on laboratory studies, using hyperspectral bi-conical reflectance factor (BCRF) [35,36,37,38] data derived from the Goniometer of the Rochester Institute of Technology-Two (GRIT-T) [8,39] to demonstrate the feasibility of the approach. Our method relied on the observation that single particle properties such as the single scattering phase function are intrinsic properties of particles with a distribution depending only on the phase angle g, i.e., the relative angle between illumination and observation direction [8]. BCRF measurements over the full observation hemisphere with GRIT-T acquired at two different illumination geometries provided the input data for a multi-stage optimization procedure, which ultimately ensured consistency of the inverted phase function distribution in phase angle g between the measurements acquired at the two illumination geometries [8]. A brief summary of our inversion approach appears in Section 2.
Our first application of our approach to inverting our modified form of the Hapke radiative transfer solution used multi-view and multi-temporal imagery from NASA G-LiHT imagery acquired in the Algodones Dunes. Compared to our earlier laboratory-focused study [8], a key innovation of this study using G-LiHT [9] was a method that we developed to use remote sensing time series imagery, the more typical situation encountered in practical remote sensing applications in which a full sampling of the hemispherical conical reflectance factor (HCRF) [35,36,37,38] observation hemisphere is by no means guaranteed, and the illumination geometry typically varies from one acquisition time to the next. Specifically, we replaced the optimization that ensured a self-consistent single-scattering phase function over two full BCRF scans in the earlier laboratory study [8] with an optimization that ensured consistency of the single-scattering phase function between a spectral pixel and its neighbors [9]. Our enhanced approach, which is applicable to any remote sensing time series, demonstrated a retrieval of sediment filling factor that was consistent with nearby ground truth measurements [9]; however, in that earlier study, the available ground truth was not directly within the overlapping field of view of the multi-view, multi-temporal G-LiHT hyperspectral imagery used. In the present study, we address this shortcoming using multi-view, multi-temporal hyperspectral imagery acquired from a mast-mounted hyperspectral imaging (HSI) system [40] and contemporaneous ground truth collected by us during a field campaign at the Virginia Coast Reserve (VCR) [41] Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) [42] site in July 2018. In our present study, the ground truth that we collected provides a large number of validation points within the field of view, and we find good correlation in the retrieved sediment filling factor with the directly measured field sediment bulk density.
In this paper, we review the theoretical basis of the Hapke radiative transfer model, the modifications made by us to the model, as well as our inversion procedure (Section 2.2). In Section 2.3, we describe the field campaign that provided the hyperspectral imagery and ground truth data collected to support validation of our inversion procedure to retrieve sediment filling factor as well as its relationship to the measured sediment density. Section 3 summarizes our inversion results and accuracy using our validation data, Section 4 provides a discussion, and Section 5 discusses the conclusions drawn.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Methods: Overview
In this section, we describe our approach to retrieving the sediment filling factor from multi-view hyperspectral imagery. We begin by discussing the underlying theory of the Hapke radiative transfer model and our approach to model inversion, which is based on an optimization scheme that we developed and described previously in [8,9]. We then describe the field data collection campaign conducted in a salt panne environment on a barrier island at the VCR LTER, including the hyperspectral imaging system used to collect the imagery and the ground truth data used in validating the retrieval of sediment filling factor from the multi-view hyperspectral imagery.
2.2. Methods: Theory and Retrieval Methodology
The IMSA solution to the equation of radiative transfer equation was proposed by Hapke [1]. Our approach to the inversion of a modified form of Hapke’s solution jointly retrieves the filling factor and the single scattering albedo and relies on the key observation that the single scattering phase function, is invariant to the absolute illumination geometry [8,9], with a geometric dependence only on the phase angle g. Hapke’s IMSA solution to the radiative transfer equation has the form:
where and represent the direction cosines for incident and scattered light, is the single scattering albedo, and is the nonlinear porosity factor previously mentioned. is a scale factor for the shadow hiding opposition effect (SHOE), modeled by the function [1]. The second term in Equation (5), , is the isotropic multiple scattering component of the original Hapke model, dependent on the Ambartsumian–Chandrasekhar H-functions [1]. Because of the separation of terms that describe single- and multiple-scattering, the Hapke solution to the radiative transfer equation can be reorganized to solve for the single scattering phase function and other factors related to the SHOE in terms of a scaled version of the observed reflectance and the multiple scattering term [8,9]:
Our multi-stage optimization procedure [8,9] makes an initial estimate of the best filling factor and single scattering albedo that satisfy Equation (6) and minimizes the difference over the two data sets (illumination conditions):
To improve convergence and numerical stability, we also use regularization by adding additional terms that penalize very large values of and [8]. To implement this, we add two terms to Equation (7): , where and are constants [8]. When optimization is complete, we then enter a second stage of optimization which compares the resulting estimated quantities with a forward model using a three-parameter Henyey–Greenstein single scattering phase function in order to optimize the Henyey–Greenstein constants ,, and c and simultaneously optimize other free parameters such as and the width parameter of the SHOE distribution function (here g is the phase angle). This second stage optimization procedure also yields a separate estimate of the isolated single scattering phase function . In this second-stage optimization step, we let take the form with a free parameter to be optimized; we have based this choice on the fact that, for most prototypical grain size distributions that Hapke solved analytically [1], the form of is always proportional to [8], as noted earlier. With the phase function , , , , and the three constants of the three-parameter Henyey–Greenstein, , , and c, now fixed, our method then re-optimizes a modified version of Equation (6) using this time for :
Equation (8) also includes an additional factor, that we originally introduced to remove the assumption of isotropic multiple scattering [8] with serving as a scale parameter to be optimized. Although not derived from first principles, the addition of this factor can be thought of as introducing the directional dependence of single scattering at the last scattering event in the multiple scattering pathway [8]. This final stage of optimization again uses the regularization terms discussed earlier and now searches over a three-parameter space which re-optimizes the filling factor , the single scattering albedo , as well as the new scale parameter for Equation (8) again minimizing Equation (7). In each stage of our multi-stage optimization procedure, we use the Nelder–Mead simplex optimization method [43]. Further details of the overall approach can be found in [8,9].
It is important to emphasize that the two data sets reflected in the subscript indices of Equation (7) for each optimization stage represent two data sets that are formed from: (1) all views of a given hyperspectral pixel in a scene and (2) all views of the immediately neighboring hyperspectral pixels. We apply this process to each pixel of the scene. This is the same method that we developed in our previous study using hyperspectral imagery of the Algodones Dunes [9], where we first extended our laboratory-based inversion of hyperspectral goniometer data [8] to multi-view hyperspectral imagery. In the present work, for the first time, we directly compare the filling factor inversion with in situ ground truth measurements of sediment bulk density within the field-of-view of the multi-view hyperspectral imagery.
2.3. Methods: Field Survey
2.3.1. Methods: Experimental Design and Instrumentation
In July 2018, we undertook a field campaign on Hog Island, VA, USA at the VCR LTER. The campaign focused on hyperspectral imaging of both salt marsh vegetation and sediments as well as ground truth data collection. We dedicated one phase of the campaign to the acquisition of coordinated multi-view hyperspectral imagery and ground truth data within the field of view of the imagery in order to evaluate the accuracy of the inversion methodology described in Section 2.2. Since our focus in this phase of the campaign, therefore, was on validating our ability to accurately retrieve sediment filling factor, we selected a site where there would be minimal variation in other underlying variables such as moisture content, surface roughness, and composition. In a laboratory setting, we have far greater control of these other sources of variation in the sediment. In this field setting, the salt panne offered a site with minimal variation in moisture content and both a relatively uniform surface texture and composition.
To collect imagery during the campaign, we used our state-of-the-art hyperspectral imaging system [40]. The hyperspectral imager, a Headwall VNIR Micro-hyperspec High Efficiency E-series [44] (Headwall Photonics, Bolton, MA, USA), is a pushbroom system providing spectral measurements from 400 to 1000 nm with 371 spectral bands and 1600 across-track spatial pixels. The HSI sensor resides within a maritime-rated General Dynamics Vector 20 pan-tilt unit [45] (General Dynamics, Reston, VA, USA). The pan-tilt unit scan covers the range from −34 to 34 in pitch, and −175 to 175 in yaw. The imaging system also hosts a Vectornav VN-300 IMU-GPS [46] (VectorNav Technologies, Dallas, TX, USA) to provide pointing information and GPS time-stamps. In the field, the HSI system is placed on top of a BlueSky AL-3 (15 m) telescopic mast [47] (BlueSky Mast, Largo, FL, USA), which can be raised up to 15 m above the ground [40]. The pan-tilt unit integrated into the telescopic mast is capable of imaging a scene from multiple viewing geometries, which allows us to perform HCRF measurements from the imaging sensor [40].
2.3.2. Methods: Data Acquisition
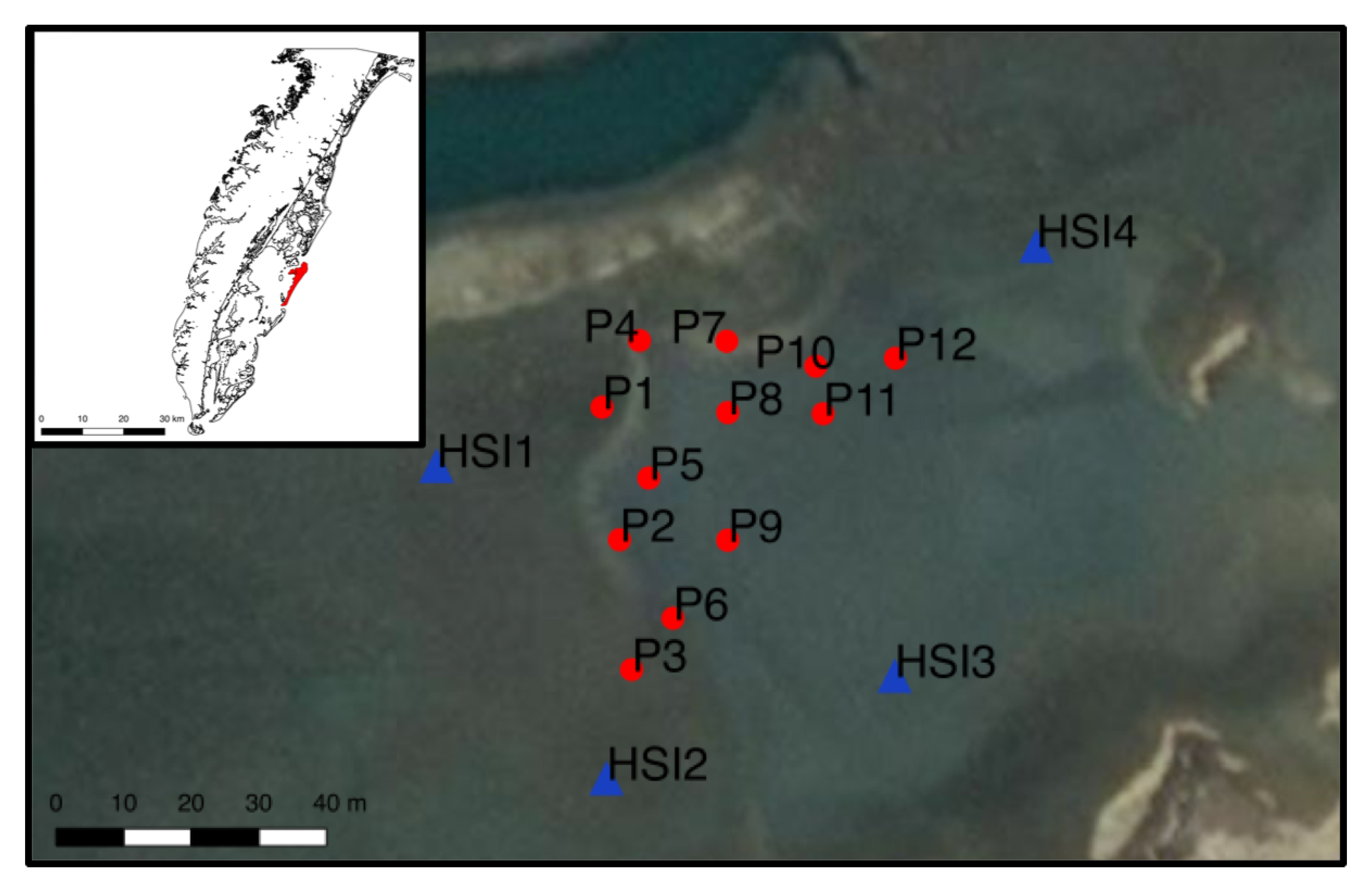
The work detailed in this paper was conducted in July 2018, in the back-barrier salt marshes on Hog Island, a well-studied barrier island that is part of the VCR LTER site [41,42]. The region of interest (ROI) of this study is a salt panne environment, which is a water-retaining tidal flat typically located within brackish marshes. The area of study on Hog Island, VA, USA is shown in Figure 1. During the 2018 field survey, we collected extensive ground reference data, including bulk density, and overlapping hyperspectral imagery from our ground-based HSI system. In this study, we used this bulk density data set, the right-most column of Table 1, to rigorously validate the initial approach to retrieving sediment fill factor that we had developed in our previous studies [8,9].
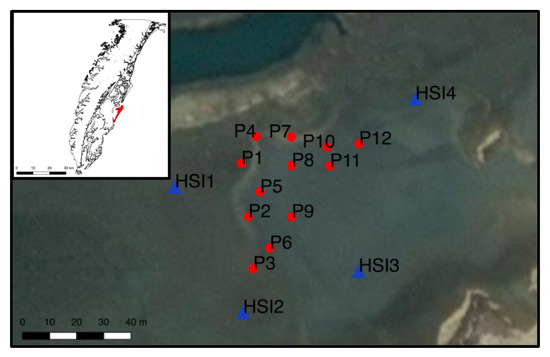
Figure 1.
Site Map of the Delmarva Peninsula, VA, USA along with the barrier islands, which are part of the VCR LTER, with Hog Island shown in red. The salt panne study site during the 2018 field campaign was on the southern part of Hog Island. The figure shows the location of in situ measurements that were taken during the field survey in 2018; P1–12 (in red) are the field survey points and HSI1–4 (in blue) are the positions of the mast-based HSI system.

Table 1.
The moisture content and bulk density data collected during the 2018 field survey.
Table 1 summarizes the dry bulk density measurements along with the soil moisture content (SMC) collected at the salt panne site during the field campaign. Following ASTM standard D2216-10 [48], we determined SMC by comparing the wet sample weight of sediment samples acquired at each test site to the dry weight of the sample after drying. The dry bulk density and moisture content ground truth measurements in Table 1 are based on a cylindrical core sample of diameter cm extracted to a depth of cm. To obtain dry bulk density, we take the ratio of the mass of the sample after drying in an oven at 60 degrees Celsius for 24 hr, , to the known volume, , of the core sample: . is the difference between , which is the combined mass of the sample plus a laboratory sample holder, and , which is the mass of the empty sample holder: . From this, the dry bulk density is:
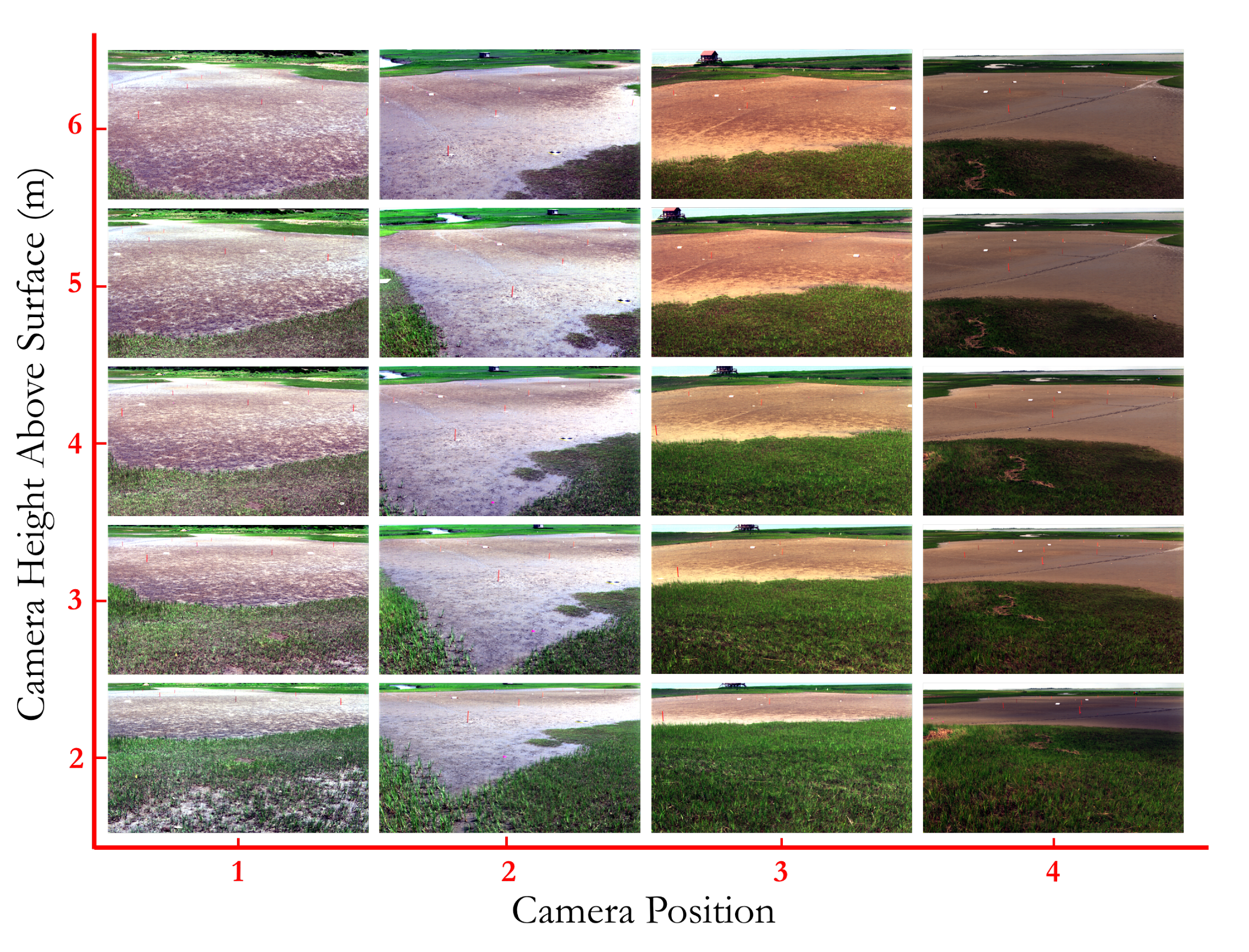
Our ground–based system acquired hyperspectral imagery at four different locations around the salt panne, and at five different heights (2 m to 6 m at approximately 1 m increments). Red-Green-Blue (RGB) images derived from the hyperspectral imagery of the salt panne appear in Figure 2, which shows the twenty hyperspectral scenes collected in this manner and used in this study. The captured hyperspectral imagery had a ground sampling distance (GSD) ranging between 0.5 to 20 cm. The HSI system was characterized in our lab at RIT using a LabSphere Helios Integrating Sphere (LabSphere, North Sutton, NH, USA), which is coupled to an on-board calibrated spectrometer to determine a calibration of the Headwall system to convert the raw digital numbers (DN) to spectral radiance (Wmnmsr) [40]. The placement of Spectralon® (LabSphere, North Sutton, NH, USA) panels within the scene enabled the conversion of the imagery into surface reflectance. Using a Garmin RTK GPS TRM55971 (Garmin International, Inc., Olathe, KS, USA), we also conducted GPS surveys of fiducials within the scene, which allowed us to geo-register the images, and also measure the view geometries of the sensor.
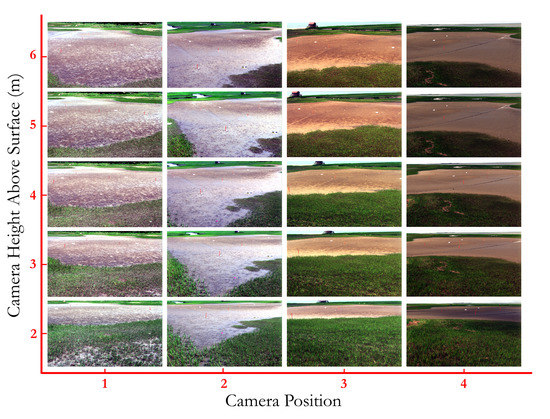
Figure 2.
Twenty hyperspectral scenes of the salt panne study site on Hog Island acquired from our mast-mounted hyperspectral imaging system. Imagery was acquired from five different heights (approximate height indicated on the y-legend above the surface and from four different locations around the salt panne identified in Figure 1).
2.4. Methods: Sources of Uncertainty
The uncertainties in , , and are small since the absolute uncertainty of the scale used is g, while the disposable sample holder masses were typically in the range of 5.6–5.8 g, and combined mass of dry sample and holder were typically in the range 103–112 g. The largest source of error in the dry bulk density stems from uncertainty in the core volume. The estimated absolute uncertainty in the height of the core, which is cm, contributes the most, while the estimated absolute uncertainty in diameter, cm, is not a significant factor. Calculation of the error in the volume assumes independent errors in diameter and height of the cylindrical sample volume adding in quadrature and, therefore, leading to an uncertainty in the volume of
From the uncertainty in volume in Equation (10), and the uncertainties in the masses, we then can determine the uncertainty in the dry bulk density in Equation (9), according to:
Because of the high-precision of the scale (low uncertainties in the mass), the second quadrature term in Equation (11) is negligible, meaning that for all of the sites the uncertainty in the bulk density is . Across all of the samples in Table 1, therefore, the absolute uncertainties in dry bulk density range from 0.021–0.023 .
Due to the high precision of the scale that we used, uncertainty in the soil moisture content is low. We determine soil moisture content by comparing the mass of the wet sample, , to the dry mass of the sample:
In Equation (12), analogous to dry mass, the wet mass is the difference between the combined mass of the sample holder and wet sample and the mass of the sample holder: . From this, we see that the uncertainty in SMC is:
Since the uncertainties in the masses are all the same in Equation (13) ( ), we found that the uncertainties in the soil moisture content were small with the range of values being , leading to for all measurements in Table 1.
Sources of uncertainty in the retrieved filling factor stem from several sources. As noted earlier, in prior work, we characterized the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and Noise Equivalent Spectral Radiance (NESR) of our hyperspectral imaging system using our state-of-the-art LabSphere Helios integrating sphere (see Figure 2 of [40]). In that analysis, we determined that peak SNR near full-daylight illumination levels is . SNR declines considerably at the ends of the wavelength range. For example, we found that at the smallest wavelengths near 0.4 m, the SNR drops to . These variations in SNR have an impact on our error budget in the results that we present in Section 3, specifically because our inversion methodology described in Section 2.2 incorporates all of the available wavelengths. Thus, in Section 3, in our statistical results comparing the retrieved fill factor against ground truth measurements of sediment bulk density, the error bars in our regression represent more than one source of uncertainty, including the noise of our hyperspectral imaging system. The purpose of including all wavelengths is two-fold. Firstly, there is no a priori reason to prefer one individual band over the others. More importantly, from an optimization perspective, we use a specific constraint that penalizes differences in the retrieved values of filling factor across wavelength [8,9]. The advantage of enforcing this constraint is that it uses the additional information available across all of the bands to limit the possible values of retrieved filling factors that could be minima obtainable by the optimization procedure, that is, the physical parameters such as filling factor that do not depend on wavelength should be consistent across all wavelengths. The disadvantage of using all of the wavelengths in our retrieval process, including those at the ends of the wavelength range, is the additional noise that this contributes to the overall optimization process since SNR is lower at the ends of the wavelength range.
Beyond system noise, an additional source of uncertainty in our retrievals, contributing to the errors bars in our regression in Section 3, results from the intrinsic limitations of the model itself. The original Hapke model, IMSA, as its name implies, makes the fundamental approximation of isotropic multiple scattering. In our modified version of the Hapke model [8,9], we have included an additional factor to be optimized which, as noted in Section 2.2, introduces anisotropy into the solution [8]. As noted earlier in Section 2.2, the additional factor is not derived from first-principles. Hapke’s alternative strategy for describing anisotropic multiple scattering, the MIMSA model later developed by him [1,5], took the approach of more accurately representing the phase function in terms of a Legendre polynomial expansion that must be fit in the multiple scattering terms of the radiative transfer equation and solution; however, even this approach involved approximation of radiometric quantities over the lower and upper scattering hemispheres in the spirit of a two-stream model.
In the present work, our approach also assumes that we could ignore surface roughness in our model. Since our study site, the salt panne, was a relatively flat and smooth surface, we chose not to include Hapke’s correction for surface roughness [12] in our model. In addition, limitations of the Hapke surface roughness correction have been identified in recent studies by us and others [26,49]. In [26], for example, we showed that the Hapke model does not faithfully reproduce the effects of sub-centimeter scale roughness, especially in the forward scattering direction. For the salt panne, including Hapke’s correction for macroscopic roughness, therefore, might introduce additional systematic error. On the other hand, omitting a correction for macroscopic roughness also potentially introduces a source of uncertainty since sub-centimeter scale roughness may not be accounted for, and this may contribute, therefore, to the size of the error bars in our regression. In the salt panne, roughness variations are small in scale and relate to factors such as small balls of sand resulting from crabs feeding on the surface and some variations in surface composition associated with proximity to a nearby tidal creek.
Another factor that contributes to the error budget in our regression in Section 3 is the number of points sampled on the observation hemisphere. Although our regression validation results in Section 3 demonstrate that we have developed a reasonably good model for retrieving sediment filling factor, the number of samples over the observation hemisphere and the range of phase angles covered determine how accurately the final solution can characterize parameters of the model. Beyond the geophysical variable of filling factor, parameters such as those parameterizing the Henyey–Greenstein phase function will be more accurate with greater sampling over phase angle.
3. Results
3.1. Spectral Analysis
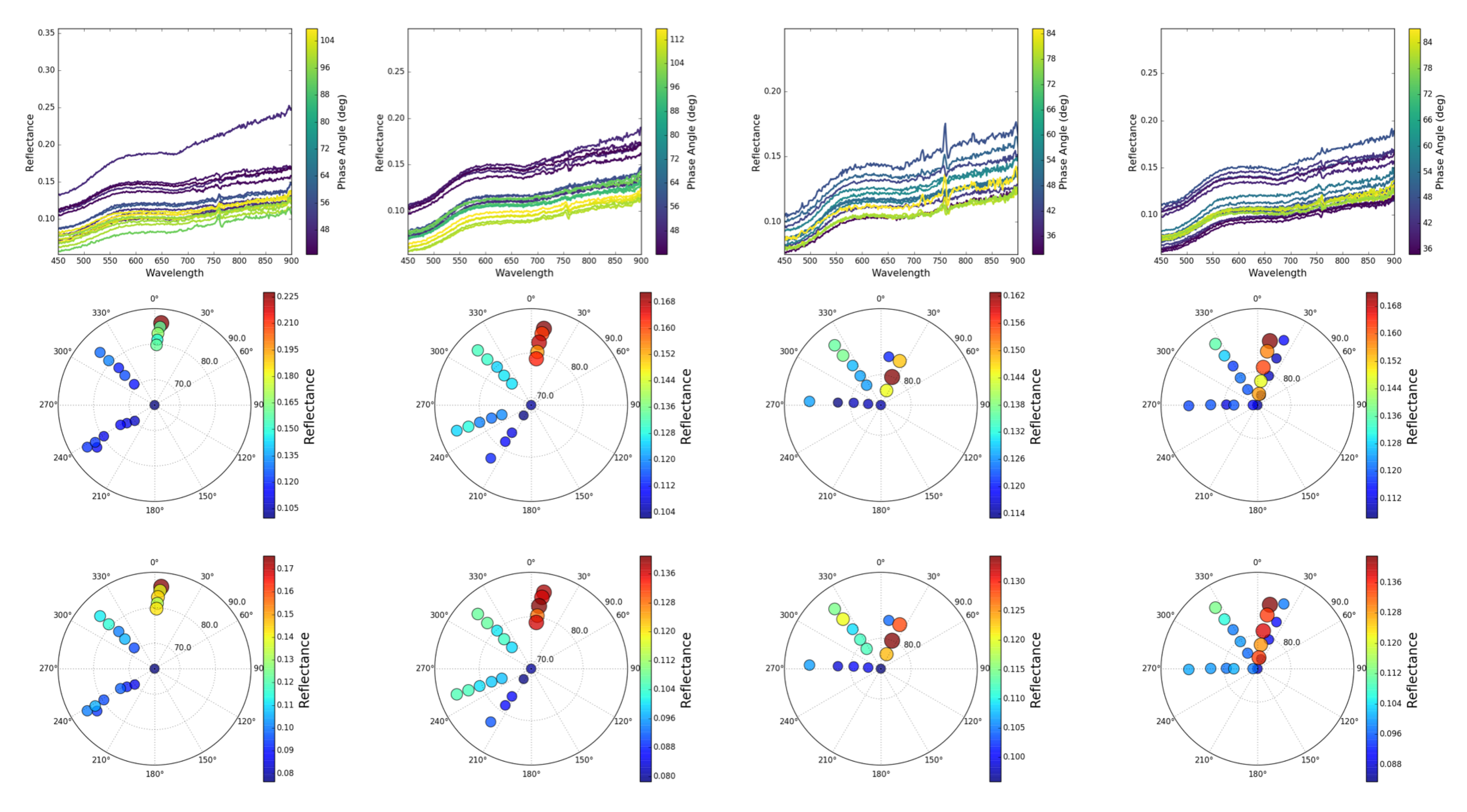
The key to our overall approach is the representation of the angular dependence of spectral reflectance obtainable from multi-view hyperspectral imagery. Figure 3 illustrates the spectral library and polar plots representing their angular distribution for four different locations around the salt panne. The angular plots show that the HCRF [35,36,37,38] has been sampled across the twenty scenes shown in Figure 2. The spectral library plots show the reflectance in the visible and near–infrared (400–1000 nm) wavelength region for different solar and view geometries used in imaging with our mast-based HSI system. The spectral libraries for the sediment, which is a mixture of sand, silt, and clay, are consistent with observations from our previous studies, with the reflectance increasing with wavelength in the VIS–NIR region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The overall amplitude/magnitude of the reflectance values are slightly lower than our previous experiments [8,9] due to significant soil moisture content in our area of study, the salt panne. The high water content within the ROI is illustrated in the SMC values shown in Table 1, with the average SMC being approximately 20%. The varying view geometries described in Section 2.3.2 along with the varying solar illumination geometry ensured that the hyperspectral imagery of our ROI covered a wide range of phase angles from 30 deg to 130 deg. Thus, both forward scattering and backward scattering of the target pixels were sampled throughout all pixels in our ROI.
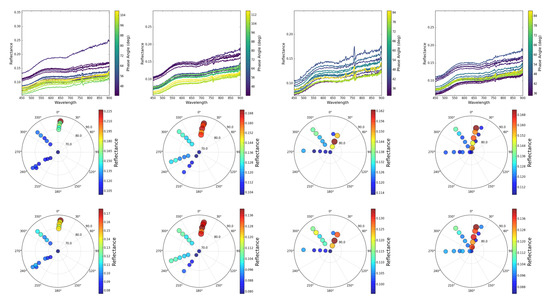
Figure 3.
(Top row) Spectral reflectance data for four locations (ground truth positions P2, P5, P7, and P11 shown in Figure 1) around the salt panne site. Spectral plot colors represent the phase angle between solar and view directions (see colorbars). (Middle and bottom row) Plots of the angular distribution of the viewing geometry which represent samples of the HCRF for 807 nm (middle row) and 551 nm (bottom row).
Figure 3 also shows the corresponding polar plots of the sampled HCRF at wavelengths 807 nm and 551 nm, respectively. The plots are a composite of 10–14 different looks from the HSI sensor for four of the positions shown in Figure 1, positions P2, P5, P7, and P11. In addition to showing the spectral reflectance curves, the top row of Figure 3 also color-codes the reflectance curves by phase angle, showing that a large fraction of the views were in the backscatter direction (phase angle ), while a few of the views are in the forward scattering direction (phase angle ). Although the salt-panne was imaged at 20 different positions, the ground-reference points shown were not all in view for all 20 different HSI images collected. The sensor-zenith angles are all greater than 70 deg for the different looks due to the unique setup of our mast-based HSI system. The high sensor zenith angle is in stark contrast to traditional airborne and space-borne platforms, which typically collect data at or near nadir–looking directions. The sampled HCRF distributions for pixels within the salt panne are fairly different from each other, which is illustrated in both the spectral library and polar plots in Figure 3. This demonstrates the influence of the view-geometry as well as the geophysical properties of the sediment on the reflectance.
3.2. Inversion Retrieval
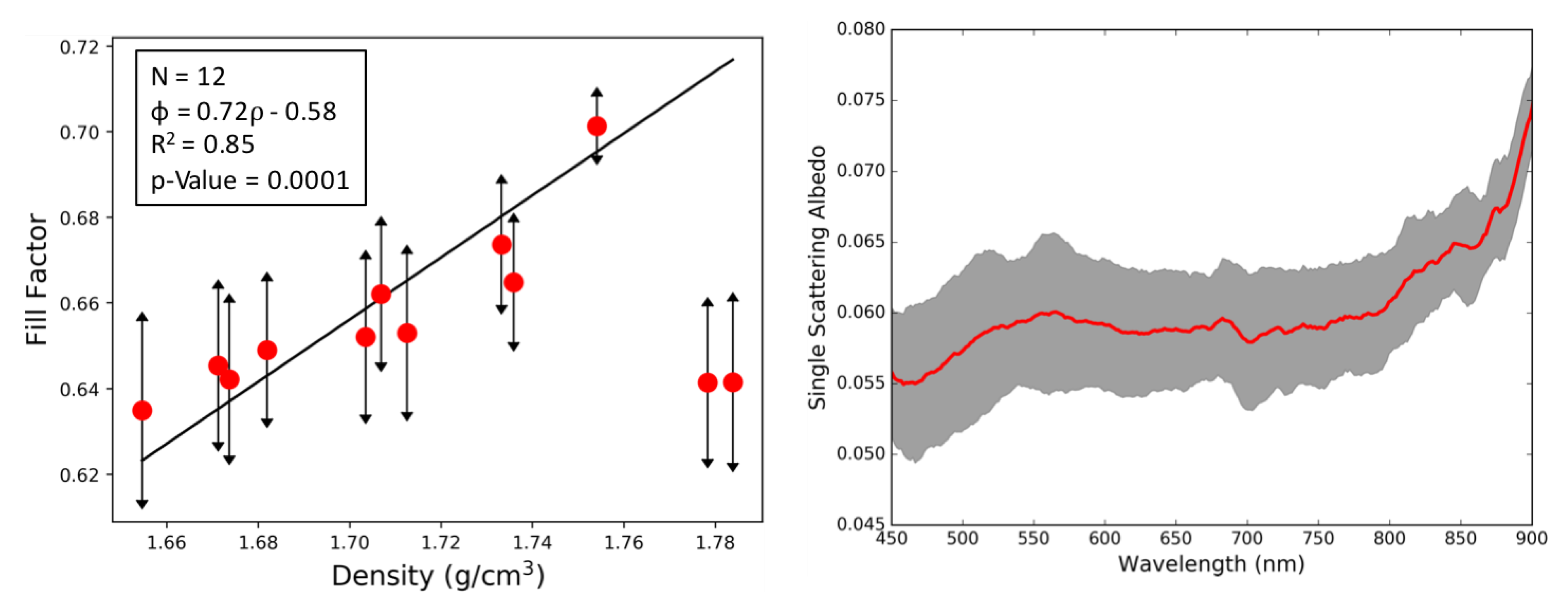
In this study, we used the set of hyperspectral images (Section 2.3.2) collected from our HSI system to derive the filling factor and single scattering albedo (SSA) by inversion of our modified Hapke model [8,9] (Section 2.2). The range of phase angles for each pixel within the salt panne provided us with satisfactory information about the scene to perform inversion of the modified Hapke model. In the inversion procedure, we assumed that neighboring/adjacent pixels had the same geophysical properties. Since the HSI system provided imagery at very high spatial resolutions (0.5 to 20 cm), it was a reasonable assumption for the inversion process. As a result, the spectra at a particular pixel formed one set while the spectra from adjacent pixels served as the second input data set required for inversion of the model using Equations (6)–(8). Figure 4 shows the retrieved filling factor versus the measured bulk density for 12 of our ground reference points that were spaced throughout the salt panne and fell with the overlap zone of our hyperspectral imagery acquired from the four locations and five mast heights described in Section 2.3.2. The final filling factor shown in Figure 4 was an average of the filling factors obtained at each wavelength by the inversion process, since the filling factor, a physical property of the medium, does not depend on wavelength. In Figure 4, the uncertainties shown for the filling factor represent the standard deviation of the retrieved filling factors across wavelength during the inversion. While our inversion procedure imposes a regularization penalty that tends to force the retrieved results for the filling factor across wavelength toward a common value [8,9], there is still some residual variance with wavelength when the optimization is completed. The inversion of the Hapke model shows moderately good correlation between the retrieved filling factor and measured density, with an R value of 0.85. The R value was calculated by ignoring the last two density points (1.778 and 1.784 g/cm). The low values in retrieved filling factor at these two high densities can be attributed to the onset of “coherent effects”, originally predicted by Hapke [1,10], within the sediment where the model is no longer valid. According to Hapke, the coherent effect arises when the separation between sediment particles is comparable to the wavelength, occurring when particles are closely packed [1,10] and coming into contact. When this occurs, groups of particles that are clustered begin to act like larger single particles which would have larger void space if the medium were composed of such larger single particles. Hapke’s predicted threshold for the onset of coherent effects depends on the ratio of the wavelength to the average particle diameter according to [1,10]:
Given typical grain size distributions observed at the VCR LTER during past experiments [30,50], in a salt panne region such as ours in the present study at the VCR LTER, a reasonable estimate for average grain size would be ∼ 100 m. This, combined with the wavelength range of our Headwall imaging system, 0.4–1.0 m, would ordinarily imply a threshold for coherent effects, in the range ∼ 0.508–0.517, depending on wavelength. This range is significantly lower than the retrieved values seen in Figure 4; however, the presence of relatively high moisture content that we recorded in the salt panne (Table 1) violates the conditions under which the threshold in Equation (14) was derived: Hapke’s derivation assumed the space between particles was a void [1,10]. Thus, while it is still reasonable to anticipate a threshold for coherent effects, the presence of water in the pore space likely implies a higher filling factor than that described in Equation (14). Not surprisingly, due to the high moisture content in the salt panne, the filling factor values in general were also higher compared to those observed in our previous studies in a desert environment, the Algodones Dunes [9].
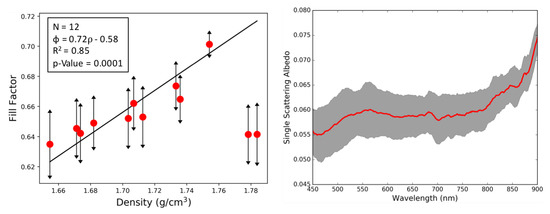
Figure 4.
(Left) Retrieved filling factor vs. sediment dry bulk density measured in the field for the twelve ground truth sites. The two highest densities appear to be above an expected threshold beyond which reflectance should decrease due to coherent effects originally predicted by Hapke. Omitting these two points, the remaining points below the threshold show a good correlation between retrieved filling factor and sediment bulk density (R = 0.85); (Right) jointly retrieved single scattering albedo (SSA) vs. wavelength: the average SSA is computed over the inversions performed for the twelve ground truth sites, with the standard deviation shown in grey for each wavelength.
Figure 4 also displays the averaged SSA (shown in red) for all twelve ground points, and the standard deviation of the SSA estimates is shown in gray for each wavelength. The SSA is generally dependent on the optical properties of the medium. The derived SSA values from the panne were significantly lower than those that we have seen in our previous studies [8,9]. Both the high values of the filling factor and low value of the SSA can be attributed to the high presence of water within the salt panne.
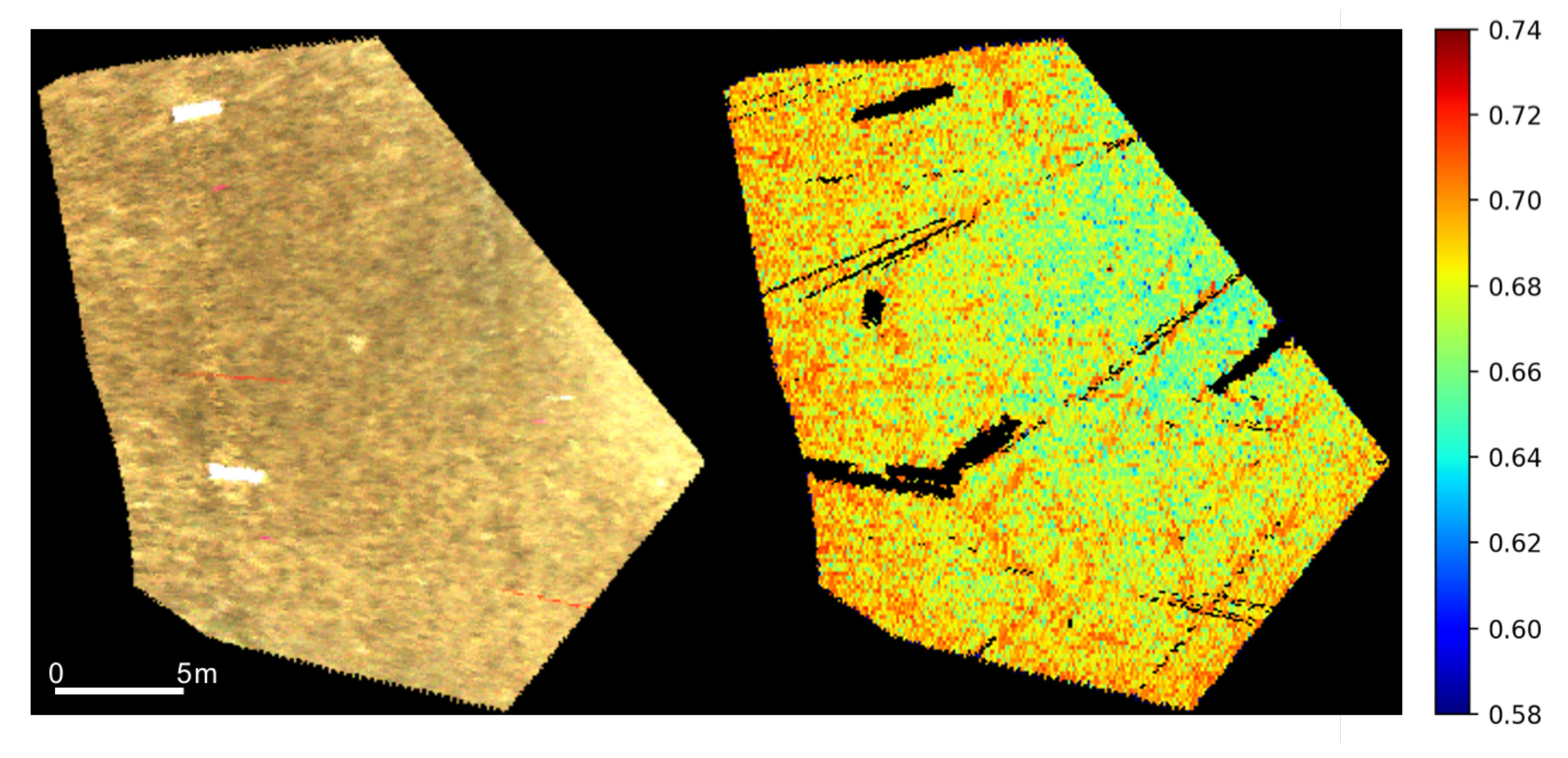
After validating the inversion methodology using the ground reference points, as summarized in Figure 4, we applied the same inversion procedure to map the filling factor across a large section of the panne within the overlap region of the hyperspectral scenes. The presence of fiducials within the salt panne enabled the georegistration of the HSI images using a third–order polynomial equation. The instrument design and collection method of the system produced varying GSD for each along-track pixel captured. The HSI images were resampled to a common GSD of 10 cm using cubic interpolation. The overlap area of the HSI images was a 30 m by 30 m region in the middle of the salt panne, which is shown in Figure 5. The retrieved filling factor over the 30 m by 30 m is also shown in Figure 5. The filling factor values over the ROI, similar to Figure 4, were high due to the presence of moisture.
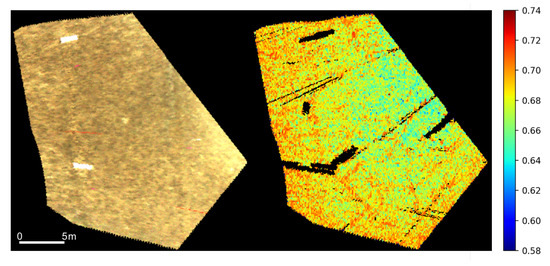
Figure 5.
(Left) One of the georeferenced hyperspectral scenes (shown: red, green, and blue channels at 641, 551, and 462 nm respectively) of the salt panne used in the inversion of the modified Hapke model; (Right) the corresponding retrieved filling factor for the same region.
4. Discussion
In most past studies, inversion of the large set of free parameters in the Hapke IMSA model used either laboratory observations and validation data [6,51,52,53], astronomical observational data from ground-based systems, or probes [15,16,18,19,21] for which direct corroborating ground truth is difficult to obtain, or combinations of these two types of data [2,54,55]. Even when the input data have been Earth remote sensing imagery, typically the Hapke model has been fit to the remote sensing imagery data, and it is an error in the reconstruction of the original spectral reflectance of the remote sensing imagery from the optimized Hapke parameters that has served as validation rather than direct comparison to physical measurements on the ground [7]. What sets our particular study apart is the fact that this is the first analysis, to our knowledge, in which sediment bulk density measured in situ in a field setting has been compared directly to sediment filling factor obtained from inversion of the Hapke model using input hyperspectral imagery of the validation locations. Even our own past analyses using this inversion scheme had used either inputs from laboratory-based hyperspectral BCRF measurements obtained from goniometer systems [39] with carefully controlled densities [8,9] or had been based on field hyperspectral imagery, but without ground truth directly within the field of view of the hyperspectral imaging system, but instead only in close proximity to the hyperspectral scenes [9]. While the latter retrieval was consistent with nearby ground truth [9], it was nevertheless not a direct test from ground truth. In this work, for the first time, we undertook a direct test of the ability to invert sediment filling factor from a modified version of the Hapke model with direct ground truth within the field of view to assess accuracy of the approach. The relatively good fit to the data ( = 0.85) and significance () of the regression between our retrieved sediment filling factor and the ground truth sediment bulk density suggest a good relationship between the two. As discussed earlier in Section 2.4, limiting factors in the regression include the fact that the retrieved filling factor is based on all of the available wavelengths in the hyperspectral data, which improves the optimization procedure [8,9], but leads to an overall greater level of noise since SNR falls dramatically towards the end of the wavelength range of our hyperspectral imaging system [40].
This work focused on the extraction of geophysical parameters, filling factor (decreasing porosity), and the single scattering albedo, through the inversion of a modified Hapke model [8,9] from imagery collected using a mast-based HSI system [40]. The area of study was a salt panne environment located in Hog Island, Virginia, USA, a barrier island in the VCR LTER [41,42]. In our past work [9], we had applied this inversion methodology to retrieve filling factor from imagery collected in a desert environment, the Algodones Dunes. The salt panne and the dunes are two exceedingly different environments. The dunes consisted of soil mainly composed of quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments [56]. On the other hand, the sediments within the salt panne consist mostly of sand, silt, and clay, with the highest percentage being sand. The average grain size distribution of the desert sediment was considerably larger than that of the salt panne in the present study. In addition, the amount of moisture was drastically higher in the salt panne compared to the dunes. The desert soil had almost no moisture at the surface, while the SMC for the salt panne was on average 20%. The smaller grain size distribution alongside the higher moisture level led to the sediments being more compact in the salt panne than in the dunes, resulting in a lower porosity or equivalently a higher filling factor. The higher SMC values of the salt panne in the present study are also reflected in the lower retrieved SSA of the salt panne sediments than that observed in our previous retrievals from both lab hyperspectral data and field hyperspectral imagery of the dune sediments [8,9].
The retrieved filling factor from our results in Figure 4 increases with density, except for the two highest density points, where we see the retrieved filling factor value drop drastically. This drop occurs because of the predicted effects of coherency [1,10]. Radiative transfer models, such as the one developed by Hapke [1], typically predict a correlation between reflectance and density, provided the material does not exhibit any “coherent effects” [1,10,33]. We start to see the effects of coherency when the separation between particles and wavelength are similar in size [1,10], i.e., as the particles begin to come into contact and form clusters resembling single larger particles. A medium with single larger particles has bigger voids meaning lower filling factor. The correlation between the density and reflectance ceases to exist at the onset of coherent effects [1,10,33]. In this study, we observed the effects of coherency at the highest field densities that we measured, (the two largest densities), as seen in our results in Figure 4, where sediments were much more closely packed, and, as Hapke predicted [1], the scattering from local groups of particles coming into contact begins to resemble the scattering of larger single particles, resulting in the retrieval of lower filling factor values, since, as just noted, larger single particles with bigger voids would have lower filling factor.
Below the onset of coherent effects, we found a good correlation between the retrieved filling factor from the HSI imagery and the measured bulk density from the field (, corroborating validation studies from our previous experiments in desert sediments [8,9]. These validation studies in our previous experiments were done by performing controlled laboratory measurements, however, not under the field conditions of the dunes since that earlier study did not have ground truth directly within the overlap zone of airborne hyperspectral imagery acquired at that site [9]. The experiments detailed in this study validate that this inversion methodology using our modified version of Hapke’s radiative transfer model can be applied, with confidence, to retrieve the filling factor from angular dependent data derived from remotely sensed HSI imagery.
5. Conclusions
We successfully validated our retrieval approach to retrieving sediment filling factor [8,9] for the first time with ground truth data obtained within the field of view of overlapping multi-view hyperspectral imagery. While this illustrates that the approach can be used successfully in realistic field settings, additional testing will be necessary over a wider variety of conditions in future work. Other sources of variation in the natural setting, such as macroscopic surface roughness, and variations in grain size distributions and composition, which can be addressed within the context of the Hapke model, must also be considered to ensure broad applicability. Similarly, soil moisture content must be successfully tested within the Hapke model framework, perhaps along the lines already proposed by Yang [28] or through an alternative method yet to be determined.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.E. and C.M.B.; methodology, R.S.E. and C.M.B.; validation, R.S.E., C.M.B., C.S.L., A.C.T. and S.G.; formal analysis, R.S.E. and C.M.B.; investigation, R.S.E., C.M.B., C.S.L., A.C.T., and S.G.; resources, C.M.B. and A.C.T.; data curation, R.S.E., C.S.L., C.M.B., and S.G.; writing–original draft preparation, R.S.E and C.M.B.; writing—review and editing, C.M.B., R.S.E., and A.C.T.; visualization, R.S.E.; supervision, C.M.B. and A.C.T.; project administration, C.M.B. and A.C.T.; funding acquisition, C.M.B. and A.C.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by an academic Grant from the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (Award #HM0476-17-1-2001, Project title: Hyperspectral Video Imaging and Mapping of Littoral Conditions), approved for public release, 20-006, and by an Explorer Grant from the National Geographic Society (Grant NGS-382R-18). The authors are also grateful for support provided by NSF DEB Grants #1237733 and #1832221 (VCR-LTER), which contributed to the fieldwork described in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hapke, B. Theory of Reflectance and Emittance Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-521-88349-8. [Google Scholar]
- Helfenstein, P.; Shepard, M.K. Testing the Hapke photometric model: Improved inversion and the porosity correction. Icarus 2011, 215, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Chabrillat, S.; Demattê, J.; Taylor, G.; Hill, J.; Whiting, M.; Sommer, S. Using imaging spectroscopy to study soil properties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S38–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniewski, J.; Verbrugghe, M. Influence of soil surface roughness on soil bidirectional reflectance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy: 5. The coherent backscatter opposition effect and anisotropic scattering. Icarus 2002, 157, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F.; Hanocq, J. Modeling spectral and bidirectional soil reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gong, P.; Liu, Q.; Chappell, A. Retrieving photometric properties of desert surfaces in China using the Hapke model and MISR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.; Eon, R.; Ambeau, B.; Harms, J.; Badura, G.; Griffo, C. Modeling and intercomparison of field and laboratory hyperspectral goniometer measurements with G-LiHT imagery of the Algodones Dunes. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 12, 012005-1–012005–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eon, R.; Bachmann, C.; Gerace, A. Retrieval of sediment fill factor by inversion of a modified Hapke model applied to sampled HCRF from airborne and satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy. 6. Effects of porosity. Icarus 2008, 195, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Beckert, J.C.; Reilly, T.H.; Bruegge, C.J.; Conel, J.E.; Kahn, R.A.; Martonchik, J.V.; Ackerman, T.P.; Davies, R.; Gerstl, S.A.; et al. Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument description and experiment overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy: 3. Correction for macroscopic roughness. Icarus 1984, 59, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.D.; Corp, L.A.; Nelson, R.F.; Middleton, E.M.; Morton, D.C.; McCorkel, J.T.; Masek, J.G.; Ranson, K.J.; Ly, V.; Montesano, P.M. NASA Goddard’s LiDAR, hyperspectral and thermal (G-LiHT) airborne imager. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4045–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.J.; Abrahams, A.D. Geomorphology of Desert Environments, Second Edition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapa, S.; Grundy, W.; Reuter, D.; Hamilton, D.; Dalle Ore, C.; Cook, J.; Cruikshank, D.; Schmitt, B.; Philippe, S.; Quirico, E.; et al. Pluto’s global surface composition through pixel-by-pixel Hapke modeling of New Horizons Ralph/LEISA data. Icarus 2017, 287, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarniello, M.; Capaccioni, F.; Filacchione, G.; Clark, R.; Cruikshank, D.; Cerroni, P.; Coradini, A.; Brown, R.H.; Buratti, B.; Tosi, F.; et al. Hapke modeling of Rhea surface properties through Cassini-VIMS spectra. Icarus 2011, 214, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, X. Retrieving the hydrous minerals on Mars by sparse unmixing and the Hapke model using MRO/CRISM data. Icarus 2017, 288, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, S.; Domingue, D.; Thomas-Osip, J.; Vilas, F.; Osip, D.; Leeds, S.; Jarvis, K. The 2004 Las Campanas/Lowell Observatory campaign II. Surface properties of Hayabusa target Asteroid 25143 Itokawa inferred from Hapke modeling. Earth Planets Space 2008, 60, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, M.; Kuroda, D.; Hasegawa, S.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Moskovitz, N.; Abe, S.; Pan, K.S.; Takahashi, J.; Takagi, Y.; et al. Optical properties of (162173) 1999 JU3: in preparation for the JAXA Hayabusa 2 sample return mission. Astrophys. J. 2014, 792, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; A’Hearn, M.F.; Belton, M.J.; Crockett, C.J.; Farnham, T.L.; Lisse, C.M.; McFadden, L.A.; Meech, K.J.; Sunshine, J.M.; Thomas, P.C.; et al. Deep Impact photometry of comet 9P/Tempel 1. Icarus 2007, 187, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, U. Considerations regarding the colors and low surface albedo of comets using the Hapke methodology. Icarus 2015, 252, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, D.C.; Stern, S.A.; Scherrer, J.; Jennings, D.E.; Baer, J.W.; Hanley, J.; Hardaway, L.; Lunsford, A.; McMuldroch, S.; Moore, J.; et al. Ralph: A visible/infrared imager for the New Horizons Pluto/Kuiper Belt mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 140, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.H.; Baines, K.H.; Bellucci, G.; Bibring, J.P.; Buratti, B.J.; Capaccioni, F.; Cerroni, P.; Clark, R.N.; Coradini, A.; Cruikshank, D.P.; et al. The Cassini visual and infrared mapping spectrometer (VIMS) investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 2004, 115, 111–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini Mission. Available online: https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/cassini/mission/spacecraft/cassini-orbiter/ (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Hampton, D.L.; Baer, J.W.; Huisjen, M.A.; Varner, C.C.; Delamere, A.; Wellnitz, D.D.; A’Hearn, M.F.; Klaasen, K.P. An overview of the instrument suite for the Deep Impact mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 117, 43–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badura, G.; Bachmann, C.M. Assessing Effects of Azimuthally Oriented Roughness on Directional Reflectance of Sand. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy: 4. The extinction coefficient and the opposition effect. Icarus 1986, 67, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Zhao, C.J.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, J.H. Extension of the Hapke bidirectional reflectance model to retrieve soil water content. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Jepsen, R.; Gotthard, D.; Lick, W. Effects of particle size and bulk density on erosion of quartz particles. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.M.; Nichols, C.R.; Montes, M.J.; Li, R.R.; Woodward, P.; Fusina, R.A.; Chen, W.; Mishra, V.; Kim, W.; Monty, J.; et al. Retrieval of substrate bearing strength from hyperspectral imagery during the Virginia Coast Reserve (VCR’07) multi-sensor campaign. Mar. Geod. 2010, 33, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, M.K.; Campbell, B.A. Shadows on a Planetary Surface and Implications for Photometric Roughness. Icarus 1998, 134, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.M.; Peck, D.S.; Ambeau, B.; Harms, J.; Schultz, M. Improved modeling of multiple scattering in hyperspectral BRDF of coastal sediments observed using the goniometer of the Rochester Institute of Technology (GRIT). Proc. SPIE 2015, 9611, 96110J-1–96110J-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.M.; Philpot, W.; Abelev, A.; Korwan, D. Phase angle dependence of sand density observable in hyperspectral reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D.C.F.; Pedroni, S.; Crippa, V. Maximum dry density of cohesionless soils by pluviation and by ASTM D 4253-83. A comparative study. Geotech. Test. J. 1992, 15, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemus, F.E.; Richmond, J.; Hsia, J.J. Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance; US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; Volume 160.
- Schaepman-Strub, G.; Schaepman, M.; Painter, T.H.; Dangel, S.; Martonchik, J.V. Reflectance quantities in optical remote sensing—Definitions and case studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doctor, K.Z.; Bachmann, C.M.; Gray, D.J.; Montes, M.J.; Fusina, R.A. Wavelength dependence of the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) of beach sands. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, F243–F255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, C.M.; Abelev, A.; Montes, M.J.; Philpot, W.; Gray, D.; Doctor, K.Z.; Fusina, R.A.; Mattis, G.; Chen, W.; Noble, S.D.; et al. Flexible field goniometer system: The goniometer for outdoor portable hyperspectral earth reflectance. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 036012-1–036012-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.D.; Bachmann, C.M.; Ambeau, B.; Faulring, J.W.; Ruiz Torres, A.J.; Badura, G.; Myers, E. Fully automated laboratory and field-portable goniometer used for performing accurate and precise multiangular reflectance measurements. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 046014-1–046014-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.; Eon, R.; Lapszynski, C.; Badura, G.; Vodacek, A.; Hoffman, M.; Mckeown, D.; Kremens, R.; Richardson, M.; Bauch, T.; et al. A Low-Rate Video Approach to Hyperspectral Imaging of Dynamic Scenes. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virginia Coast Reserve Long Term Ecological Research. Available online: https://www.vcrlter.virginia.edu/home2/ (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- National Science Foundation Long Term Ecological Research Network. Available online: https://lternet.edu/ (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headwall E-Series Specifications. Available online: https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/145999/June%202018%20Collateral/MicroHyperspec0418.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- General Dynamics Vector 20 Maritime Pan Tilt. Available online: https://www.gd-ots.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Vector-20-Stabilized-Maritime-Pan-Tilt-System-1.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Vectornav VN-300 GPS IMU. Available online: https://www.vectornav.com/products/vn-300 (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- BlueSky AL-3 (15m) Telescopic Mast. Available online: http://blueskymast.com/product/bsm3-w-l315-al3-000/ (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- ASTM Committee D-18 on Soil and Rock. Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labarre, S.; Jacquemoud, S.; Ferrari, C.; Delorme, A.; Derrien, A.; Grandin, R.; Jalludin, M.; Lemaître, F.; Métois, M.; Pierrot-Deseilligny, M.; et al. Retrieving soil surface roughness with the Hapke photometric model: Confrontation with the ground truth. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.M.; Fusina, R.A.; Montes, M.J.; Li, R.R.; Korwan, D.; Bennert, E.; Miller, W.; Gillis, D.; Nichols, C.; Fry, J.C. Virginia Coast Reserve 2007 Remote Sensing Experiment; NRL/MR/7230–12-9402; NAVAL RESEARCH LAB WASHINGTON DC REMOTE SENSING DIV: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cierniewski, J.; Kaźmierowski, C.; Królewicz, S. Evaluation of the Effects of Surface Roughness on the Relationship Between Soil BRF Data and Broadband Albedo. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, C.; Roush, T.; Pedrazzi, G.; Capaccioni, F. Visible and Near-Infrared (VNIR) reflectance spectroscopy of glassy igneous material: Spectral variation, retrieving optical constants and particle sizes by Hapke model. Icarus 2016, 266, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souchon, A.; Pinet, P.; Chevrel, S.; Daydou, Y.; Baratoux, D.; Kurita, K.; Shepard, M.; Helfenstein, P. An experimental study of Hapke’s modeling of natural granular surface samples. Icarus 2011, 215, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, M.K.; Helfenstein, P. A laboratory study of the bidirectional reflectance from particulate samples. Icarus 2011, 215, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingue, D.L.; Vilas, F.; Holsclaw, G.M.; Warell, J.; Izenberg, N.R.; Murchie, S.L.; Denevi, B.W.; Blewett, D.T.; McClintock, W.E.; Anderson, B.J.; et al. Whole-disk spectrophotometric properties of Mercury: Synthesis of MESSENGER and ground-based observations. Icarus 2010, 209, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Yeend, W.; Dohrenwend, J.; Gese, D. Mineral Resources of the North Algodones Dunes Wilderness Study Area (CDCA-360), Imperial County, California; Geological Survey: Menlo Park, CA, USA; Bureau of Mines: Denver, CO, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).