Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Characteristics during the 2018 Typhoon Maria from GPS Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Date and Method
2.1. Typhoon Information
2.2. GPS Observations
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Ionospheric Disturbance Characteristics
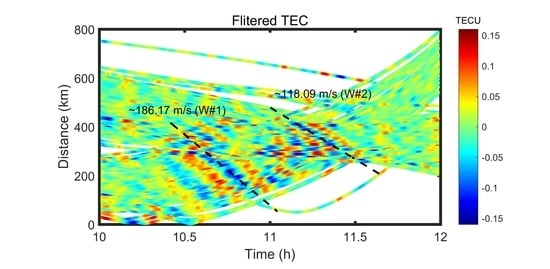
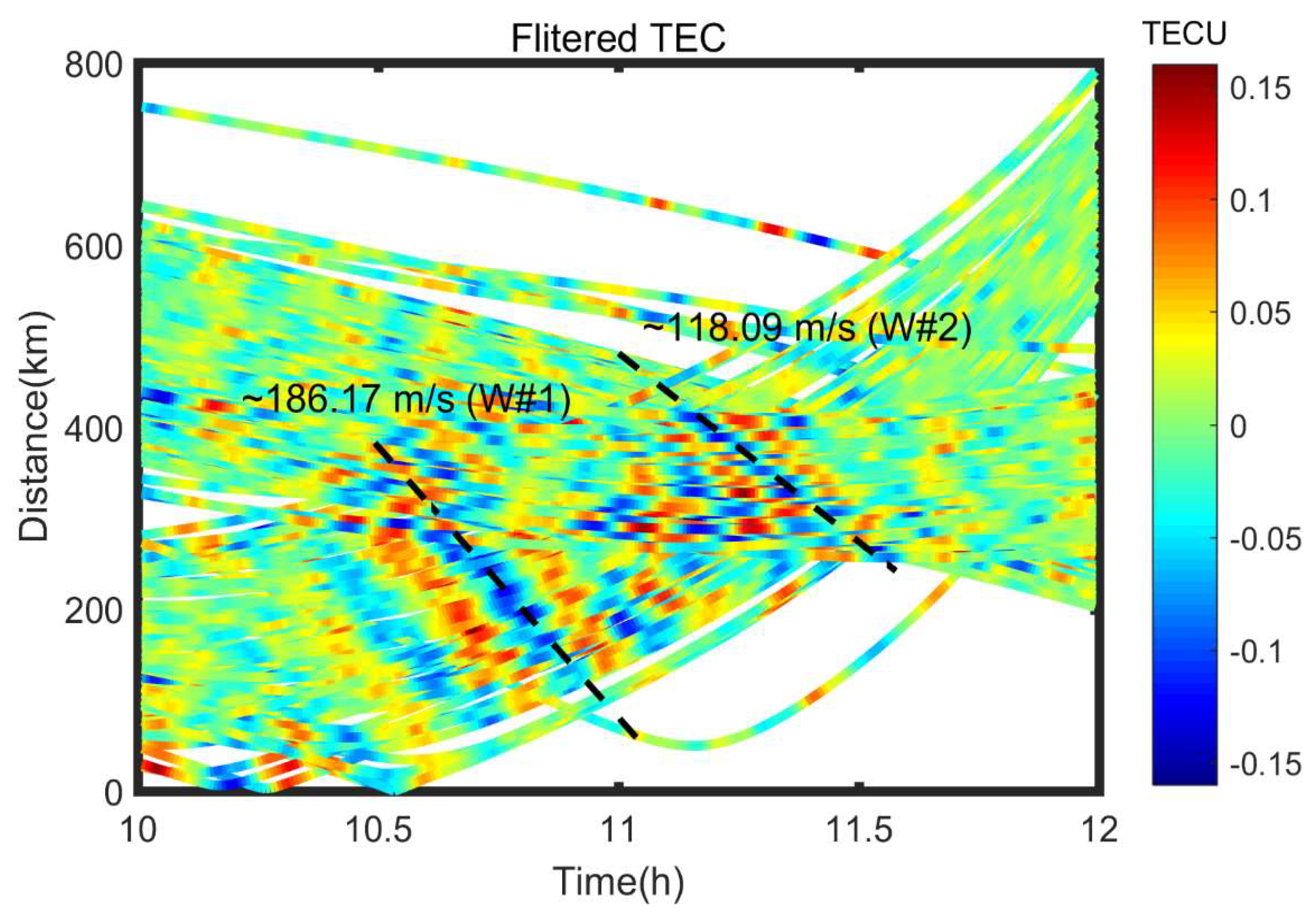
3.2. Disturbance Propagation Velocity
3.3. Disturbance Azimuth Variation
3.4. Disturbance Spectrum Characteristics
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazimirovsky, E.; Herraiz, M.; Morena, B.A.D.L. Effects on the Ionosphere Due to Phenomena Occurring Below it. Surv. Geophys. 2003, 24, 139–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishbeth, H. F-region links with the lower atmosphere? J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Voeykov, S.V.; Ishin, A.B.; Perevalova, N.P.; Ruzhin, Y.Y. Variations in the total electron content during the powerful typhoon of August 5–11, 2006, near the southeastern coast of China. Geomagn. Aeron. 2008, 48, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.I.; Kunitsyn, V.E. Regional features of atmospheric manifestations of tropical cyclones according to ground-based GPS network data. Geomagn. Aeron. 2012, 52, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.J. An apparent ionospheric response to the passage of hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. 1958, 63, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Chen, S. On the detection of acoustic-gravity waves generated by typhoon by use of real time HF Doppler frequency shift sounding system. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.K. Small-Scale Wind Disturbances Observed by the MU Radar during the Passage of Typhoon Kelly. J. Atmos. Sci. 1993, 50, 518–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, D.; Sojka, J.; Eccles, J.V.; Schunk, R.W. Typhoon Melor and ionospheric weather in the Asian sector: A case study. Radio Sci. 2012, 47, RS0L05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yungang, W.; Tian, M.; Jisheng, W. A case study of the variation of ionospheric parameter during typhoons at Xiamen. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2010, 68, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.S. Chronic or Permanent Coupling (CoP Coupling) between the lower and upper Martian atmospheres. Geophys. Res. Abs. 2005, 7, 05855. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.T.; Mao, T.; Zhao, X.K.; Wang, Y.G. Medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances induced by typhoon Chan-hom over China. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 2223–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Mao, T. GPS detection of the ionospheric disturbances over China due to impacts of typhoon Rammasum and Matmo. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 122, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kuo, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhai, C. A clear link connecting the troposphere and ionosphere: Ionospheric reponses to the 2015 Typhoon Dujuan. J. Geodesy 2017, 91, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Yue, J.; Tsai, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, C. Concentric traveling ionosphere disturbances triggered by Super Typhoon Meranti (2016). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G. Two-mode ionospheric disturbances following the 2005 Northern California offshore earthquake from GPS measurements. J. Geophys. Res.Space Phys. 2018, 123, 8587–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Jin, S. Ionospheric Rayleigh wave disturbances following the 2018 Alaska earthquake from GPS observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Monte Moreno, E.; Hernández-Pajares, M. ADDTID: An alternative tool for studying earthquake / tsunami signatures in the ionosphere. Case of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.G.; Jin, R.; Li, J.H. Pattern and evolution of seismo-ionospheric disturbances following the 2011 Tohoku earthquakes from GPS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 119, 7914–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.G.; Jin, R.; Li, D. GPS detection of ionospheric Rayleigh wave and its source following the 2012 Haida Gwaii earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Liu, Z.; Xia, P.; Dai, W. Cycle slip detection and repair for undifferenced GPS observations under high ionospheric activity. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, M.N.; Heki, K. Coseismic ionospheric disturbance of the large strike-slip earthquakes in North Sumatra in 2012: Mw dependence of the disturbance amplitudes. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 200, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.G.; Occhipinti, G.; Jin, R. GNSS ionospheric seismology: Recent observation evidences and characteristics. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 147, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Jin, S. Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Characteristics during the 2018 Typhoon Maria from GPS Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040746
Wen Y, Jin S. Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Characteristics during the 2018 Typhoon Maria from GPS Observations. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040746
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yiduo, and Shuanggen Jin. 2020. "Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Characteristics during the 2018 Typhoon Maria from GPS Observations" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040746
APA StyleWen, Y., & Jin, S. (2020). Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Characteristics during the 2018 Typhoon Maria from GPS Observations. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040746