Abstract
Landslides recurrently impact the Italian territory, producing huge economic losses and casualties. Because of this, there is a large demand for monitoring tools to support landslide management strategies. Among the variety of remote sensing techniques, Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) has become one of the most widely applied for landslide studies. This work reviews a variety of InSAR-related applications for landslide studies in Italy. More than 250 papers were analyzed in this review. The first application dates back to 1999. The average production of InSAR-related papers for landslide studies is around 12 per year, with a peak of 37 papers in 2015. Almost 70% of the papers are written by authors in academia. InSAR is used (i) for landslide back analysis (3% of the papers); (ii) for landslide characterization (40% of the papers); (iii) as input for landslide models (7% of the papers); (iv) to update landslide inventories (15% of the papers); (v) for landslide mapping (32% of the papers), and (vi) for monitoring (3% of the papers). Sixty-eight percent of the authors validated the satellite results with ground information or other remote sensing data. Although well-known limitations exist, this bibliographic overview confirms that InSAR is a consolidated tool for many landslide-related applications.
1. Introduction
Landslides are responsible for huge human and economic losses worldwide, producing direct and indirect impacts on the population and the local communities. Italy is one of the European countries that is most severely and frequently hit by landslides, primarily triggered by heavy rainfalls [1] and favored by its peculiar geological, morphological, and tectonic setting.
The Italian landslide inventory (IFFI, Inventario Fenomeni Franosi Italiani) includes more than 480,000 phenomena collected since 1999. The IFFI database covers almost 7% of the entire national territory [2]. Known and most-of-all unknown or newly activated landslides have a considerable impact on regional and local entities, posing a frequent and not totally forecastable risk to the population [3]. Brunetti et al. [1] reported that, in a 60-year time span between 1950 and 2009, more than 6000 people were killed by landslides with an average of 16 deadly events per year. Some events such as the 1963 Vajont outburst, the 1987 Val di Pola landslide, or the 1998 Sarno mudslides caused thousands of victims [4,5,6]. All the Italian regions are hit by landslides with different temporal frequency. Guzzetti [7] collected thousands of events causing casualties and reported that Veneto (including almost 2000 victims for the Vajont outburst), Campania, and Lombardy are the regions that paid the highest human cost. Landslide typology and occurrence are strongly related to the geological and tectonic setting. Overall, rockfalls, rockslides, and rock avalanches in the Alpine arc and fast flows originated in volcanic ashes in the Campania region are the most hazardous and impactful phenomena [7].
This brief overview of the economic and social impact of landslides in Italy shows the strong need for proper monitoring tools that could support landslide risk management procedures and long-term risk reduction practices.
The motion of a landslide can be analyzed by using ground-based and remotely sensed data [8]. The first group includes all the techniques exploiting instruments or sensors directly connected to the terrain or installed on buildings/objects. In this case, the monitoring results are the direct reflection of the motion undergone by the field instrumentation. The second group relies on the use of no-contact techniques, e.g., on the use of active or passive sensors that receive and record a signal interacting with the landslide surface or with objects involved by the landslide motion. The emitting/receiving sensor can be ground-based or mounted on a drone, an aircraft, or a satellite.
In the last decade, Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) techniques have become widely used and broadly recognized tools for landslide mapping and monitoring. This is mainly due to the development of D-InSAR (Differential Interferometry) techniques that are based on the analysis of a couple of radar images acquired by an SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) sensor. The primary goal of such techniques is to derive an interferogram that expresses the phase difference for each image pixel between two passages of the satellite on the same area. By using multiple SAR images and the interferograms derived, it is possible to retrieve the temporal evolution of ground displacements over time. The time series of deformation are extracted from those pixels of an SAR image maintaining an optimal level of coherence (i.e., how stable the signal is) through the whole monitoring period. The selection of these pixels can be performed by using various algorithms [9] usually grouped in Point-like (or Persistent) Scatterers Interferometry (PSI [10]) and Distributed Scatterers Interferometry (DSI [11]) approaches. The final output of these multi-temporal Advanced Differential InSAR (A-DInSAR) analyses is a deformation map composed of thousands/millions of points, each one characterized by a value of annual velocity and by a time series of displacement. This product is extremely useful for landslide studies, since it grants millimeter accuracy and medium-to-high temporal and spatial resolution [12]. For a technical description of InSAR methodologies, we refer to [9,13,14]. In this document, we use “InSAR” to refer to every type of interferometric technique (whether it is Differential or Advanced).
Some authors have already set up the scene for the application of remote sensing data for landslide studies. Mantovani et al. [15], Metternicht et al. [16], Tofani et al. [17], and Scaioni et al. [18] are all valuable examples of review papers describing the exploitation of remote sensing data in landslide best practices. Wasowski and Bovenga [19] proposed a comprehensive work on the use of interferometric products for landslide studies, highlighting the advantages and limitations of the technique. InSAR has some widely recognized limiting factors such as (i) geometrical effects, (ii) snow cover, (iii) phase aliasing, and (iv) the presence of vegetation or variable land cover. Despite its drawbacks, the interferometric approach has some clear advantages: (i) great cost/benefit ratio, (ii) a wide area coverage combined with millimeter accuracy, (ii) temporal repetitiveness (up to 6 days with Sentinel-1 images), (iii) all-weather and day/night acquisitions, (iv) data coverage in inaccessible areas, and (v) the possibility of back analyzing phenomena from 1992 (the first year of acquisition of the C-band satellite ERS 1). All these characteristics led to a wide exploitation of interferometric products over the last 10 years. The diffusion of InSAR products was certainly eased by the recent launch of the Sentinel-1 constellation, which granted free access to radar images with a regular acquisition plan entirely dedicated to scientific purposes [20].
This review is neither focused on technical aspects, nor on a general presentation of the InSAR advantages and limitations. This paper is aimed to illustrate the role of satellite interferometry for landslide monitoring and mapping in Italy, highlighting current applications and future perspectives. Italy was chosen for several reasons: (i) it is one of the most landslide-prone countries in Europe [21]; (ii) the country registers relevant human and economic losses related to landslide events every year [22]; (iii) as a consequence of the previous points, the request for landslide monitoring and mapping tools is very high (including InSAR data) [17]; (iv) Italy has been the testing ground for several innovative InSAR applications since early 2000; (v) many InSAR providers and InSAR-based research centers are located in Italy, which is the primary target for their research activities; (vi) InSAR is a well-established technique in Italy, being utilized with standardized procedures for many years by both scientists and end users; (vii) three Italian regions are running landslide monitoring services based on InSAR data, and a nationwide ground motion service will be implemented in the future. Therefore, Italy is one of the best sample use cases to illustrate the past and current state of the InSAR technique applied to landslide studies.
This review aims to testify where and how InSAR has been profitably used to study landslides in Italy and to propose a temporal overview of InSAR-related studies over the last 20 years. Moreover, the review illustrates the most common InSAR applications for landslide studies with a focus on the evolution of the applications, following the technological advancements of the processing techniques and of the acquisition capabilities of the radar sensors.
2. Data Collection
In this review work, we exploited the Google Scholar (GS) engine to collect all the possible scientific contributions, where the authors exploited the InSAR technique to study landslides. We collected original articles, book chapters, conference proceedings, and extended abstracts written in English and published by international journals after peer review.
The data collection is based on the following searching criteria. The base level is constituted by the region name in Italian and in English for those regions with a commonly used translation, e.g., Toscana/Tuscany. Each regional name is connected to a double level of keywords. The first level comprises the type of application, such as “landslide monitoring,” “landslide mapping,” and “landslide detection.” The second level includes the keywords related to the technique or algorithm of analysis, such as “satellite interferometry,” “InSAR” (and other derived acronyms such as A-DInSAR or D-InSAR), “SBAS” (Small Baseline Subset), “PSI” (Persistent Scatterers Interferometry), and other widely recognized acronyms as “SqueeSAR,” “IPTA” (Interferometric Point Target Analysis), or “CPT” (Coherent Pixels Technique).
Google Scholar has been chosen because it is considered a “superset of Web of Science (WOS) and Scopus, with substantial extra coverage” [23]. Martín-Martín et al. [23] report that the database of articles included in the category Earth Sciences and Technology has a correspondence of 95% between GS and WOS. The 5% difference is related to the fact that GS includes non-journal sources, such as theses. GS is a powerful tool to analyze the existing literature in one specific field, as in our case, but it can overestimate the number of citations of a single author. Thus, it should be used with caution when the aim is to quantify authors/journals metrics [24]. GS certainly is less automatized than WOS, but is a free source of information as complete as other databases [24].
The articles are stored in different folders connected to a summary table with different fields, such as:
- The title of the document;
- Region;
- Toponym and municipality (for small scale works, we focused on the province or region);
- First author;
- Affiliation of the first author;
- Year of publication;
- Digital object identifier (DOI), when available;
- Type of InSAR approach and algorithm;
- Satellite and band;
- Type of landslide monitored;
- Type of application. (We defined 5 classes: (1) back-analysis, (2) characterization, (3) landslide inventory update, (4) mapping, and (5) monitoring. An article can be assigned to multiple applications. A description of each class is given in Section 5.)
3. Temporal Evolution of the Scientific Production
A total of 253 documents was collected for this review. The first documents date back to early 2000, and the most recent ones were published in September 2019 (the end of the articles’ collection).
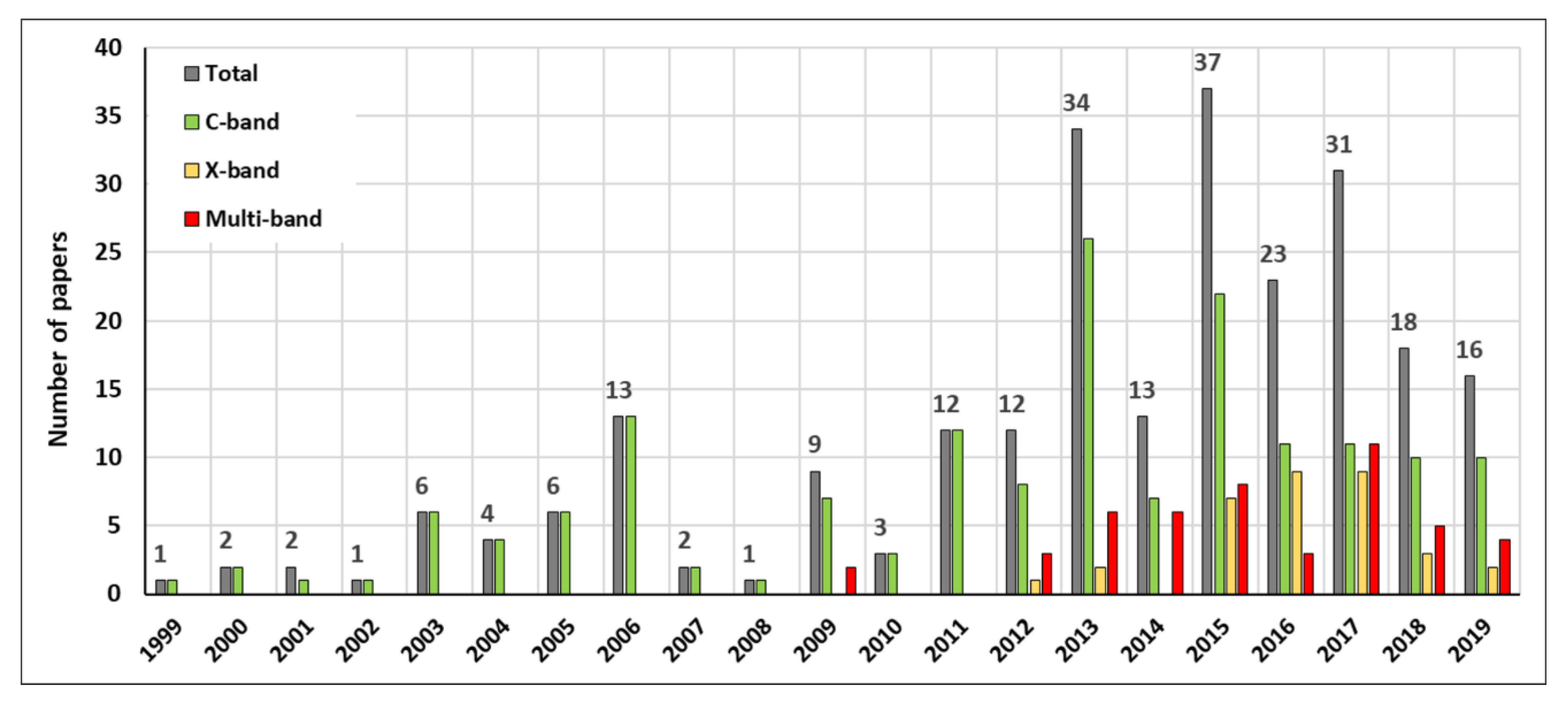
Figure 1 shows the temporal distribution of the scientific papers, with respect to the acquisition band of the sensor. Due to the unavailability of other satellite platforms, all the papers published before 2009 focus on C-band and before 2003 to ERS 1/2 images only.
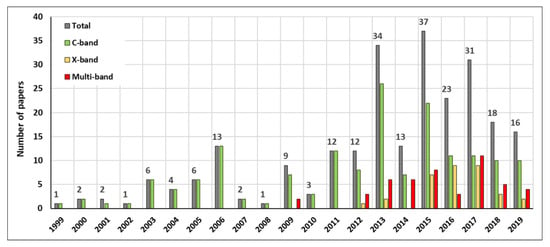
Figure 1.
Scientific papers published per year from 1999 to 2019 subdivided for satellite acquisition band. Multi-band refers to different combinations between C-, X-, and L-band SAR images.
The first example of a multi-temporal InSAR application for landslide detection was published in 1999. Ferretti et al. [25] introduced the concept behind the Permanent Scatterer approach, by presenting a case study of the Ancona landslide (Marche region, central Italy), repeatedly reactivated following intense rainfall events [26].
In the following 10 years, PSI products derived from ERS 1/2 C-band images were exploited to monitor landslides in 45 different scientific works and 14 different Italian regions. The first application of a multi-band approach was proposed by Nitti et al. [27]. These authors analyzed Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed data by means of the Stable Point Interferometry over Urbanized Areas (SPINUA) algorithm [28]. The goal was to map and characterize landslides in some municipalities of the Lombardy region (Northern Italy).
In the decade 1999–2009, the average scientific production was 4.5 articles/year (with a peak of 13 in 2006). In the following 10 years (2009–2019), this number was significantly raised to 19.7 papers/year (with a peak of 34 in 2013 and 37 in 2015), an increment of over 300%. This is clearly due to the increased awareness, within the scientific community and among end users, of InSAR capabilities. The spreading of InSAR applications was fostered by the technical evolution of algorithms, the launch of new C- and X-band satellites, and, in recent years, the increased computational capability offered by cloud computing services [29]. The distribution of the ERS 1/2, Envisat, and COSMO-SkyMed interferometric products derived in the framework of the PST-A project (Piano Straordinario di Telerilevamento—Special Plan of Remote Sensing of the Environment [30]) certainly ensured a better and wider downstream of InSAR applications.
C-band images are the most widely adopted for InSAR-related landslide applications in Italy. This is due to different factors, such as (i) the longer temporal coverage, (ii) the wider area capability, (iii) the better performances in peri-urban areas, (iv) the recent launch of the Sentinel-1 constellation, and (v) the free access to the PST-A products. X-band sensors, mainly COSMO-SkyMed, are starting to be used more often, as shown by the growth of applications in the last five years. This is related to the high value offered by X-band data in urban areas, and for single infrastructures monitoring. L-band images are less frequently used; this is probably due to, e.g., the long revisit time of the first L-band constellations and the image availability policy.
4. Spatial Distribution of the InSAR Applications
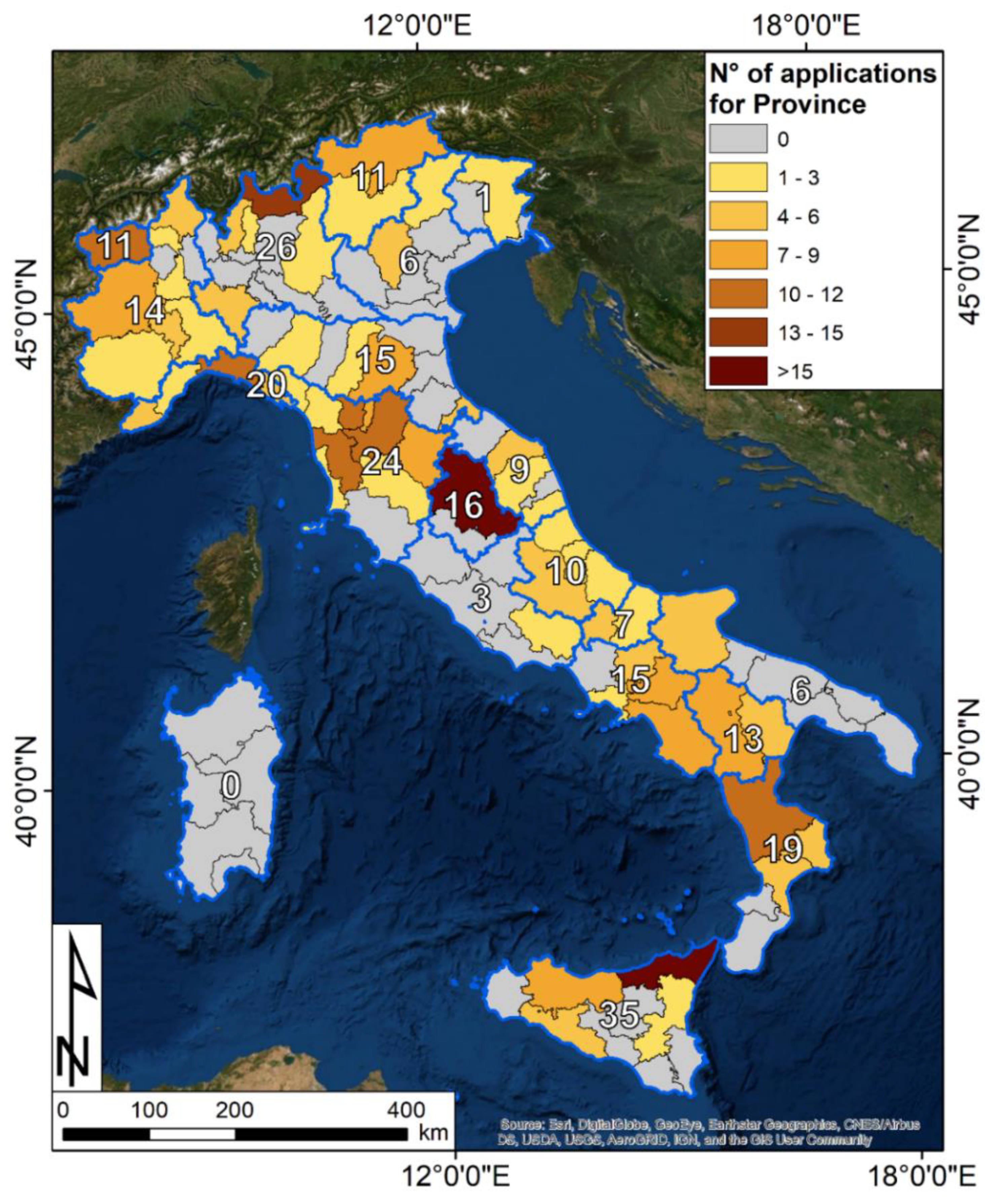
Figure 2 presents the regional and provincial distribution of the papers collected. It is worth noting that multiple provinces can be the target of a single study. This is true for basin-scale works and for articles showing multiple case studies. The Arno River Basin, including five different Tuscan provinces, is an example of this [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Video S1 proposes an additional visual interpretation of the temporal evolution of the scientific production at regional scale.
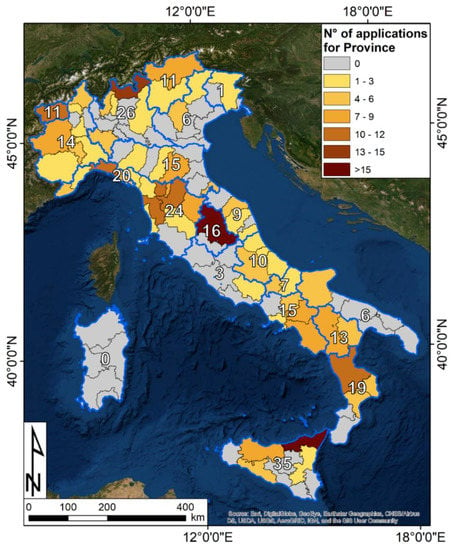
Figure 2.
Distribution of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)-related applications for landslide studies in Italy in the period 1999–2019. The total number of applications for each region is included as well. Multiple provinces and regions can be the target of a single work. National-scale applications are excluded. The background image is an ESRI World Imagery Map.
InSAR has been applied for landslide studies in all Italian regions except for Sardinia. The regions with the highest number of applications are Sicily (35), Lombardy (26), and Tuscany (24). Of course, the lack of applications does not imply a lower level of attention paid to landslides. Although uncommon, some Italian provinces have an almost flat morphology (such as Southern Apulia or some coastal provinces along the Adriatic coast). In other areas, where landslides can occur or have occurred, interferometric products have simply not been chosen because of regional and local policies, due to, e.g., a lack of awareness of existing InSAR technologies, or technical aspects related to the landslide location and typology. Another factor is the inhomogeneous distribution of available radar imagery; for instance, Sardinia was covered by only a few ERS 1/2 and COSMO frames before the launch of Sentinel-1.
Messina (19) and Perugia (16) are the two Italian provinces with the highest number of InSAR-related applications. In the last 10 years, the province of Messina has been periodically affected by intense rainfall events that triggered several landslides and caused severe damage and casualties. Most of the applications have been used in the municipalities of Giampilieri (e.g., [39,40,41]) and San Fratello (e.g., [40,42,43,44,45,46]) or in the Nebrodi range in general (e.g., [47,48,49,50,51,52]). In the Perugia province, the Ivancich roto-translational landslide (Assisi municipality) has been widely studied with the aid of interferometric products [53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60].
Sondrio (Lombardia, Northern Italy) is another province where interferometric data were frequently used (15 papers published). This Alpine region is characterized by the presence of several active landslides ranging between flank-scale Deep Seated Gravitational Slope Deformations (DSGSD) to rockfalls and rockslides [60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. One of the first applications of InSAR to assess the state of activity of a rockslide comes from this province (Ruinon landslide, Santa Caterina Valfurva municipality [67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79]).
InSAR data have been widely used for landslide monitoring along the Alpine Arc, such as in the Valle d’Aosta and Trentino-Alto Adige regions. Although different from a geological point of view, the current morphology of both regions was shaped by post-glacial processes. Large DSGSD and complex landslides, as well as rockfalls and rockslides, are led by the combination of glacial debuttressing, post-glacial erosion, and current climatic regimes. In Valle d’Aosta, InSAR has been exploited for regional and basin-to-valley-scale landslide mapping [70,71,72,73,74], as well as for single landslide characterization and monitoring. The Bosmatto complex landslide is an example of such an approach [75]. In Trentino-Alto Adige, the Corvara complex landslide (Bolzano Province) has been widely studied by means of InSAR. Corner reflectors, specifically designed for the installation in a high mountain environment, were deployed on the landslide to increase the number and quality of measurement points [76,77,78,79]. A unique application of satellite interferometry comes from the Adige River Valley (Lavini di Marco site, Trento Province [80]), where InSAR was used to study slope buckling.
Piedmont is a region where landslides related to Alpine dynamics and shallow processes in hilly landscapes coexist. Verbania, Torino, and Cuneo are mountain provinces where InSAR data were exploited for landslide mapping [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85]. The Langhe and Oltrepò Pavese Hills were the target of InSAR analyses as well [86,87,88].
The whole Apennine Arc registers hundreds of landslides every year. The Apennines are particularly prone to landslides, because of their geological and geomorphological evolution. Although they have less energy of the relief with respect to the Alps, Apennines are dominated from North to South by clayey formations. Neotectonics, land use changes, and agricultural practices are other unfavorable conditions. Landslide characteristics differ locally, but their impact along the Apennine Arc produces considerable economic and human losses.
In the Northern Apennines, Emilia Romagna and Liguria are two of the Italian regions paying a high price in terms of landslide impact. In these regions, InSAR techniques were a possible mitigation solution. In Emilia-Romagna, satellite-derived products were used for landslide mapping in the provinces of Bologna and Modena [89,90,91] and for single-site studies, such as the San Leo (Rimini Province [92]) and Berceto (Parma Province [93]) landslides. InSAR data were employed in Liguria to characterize and estimate the motion of single landslides such as Castagnola (La Spezia Province [94]), Lemeglio (Genova Province [95]), and Santo Stefano d’Aveto (Genova Province [96]).
As a result of the high seismicity of some sectors of the Central Apennines, earthquakes are not negligible triggering factors for landslides. Thus, satellite interferometry was used to map moving slopes after mainshocks, such as the 2016 Amatrice earthquake, which heavily impacted Marche, Lazio, and Abruzzo [97,98,99], or the 2009 Aquila earthquake [100]. In the Central Apennines, InSAR has been also used for classical landslide mapping, such as in the Maiella relief [101,102], in the Biferno Valley (Campobasso Province, Southern Molise [103]), and in Northern Molise [104,105]. Other authors exploited the satellite interferometric data for single-site characterization, as in the case of the Mt. Frascare DSGSD (Macerata Province, Marche region [106]) or for the Ancona (Marche region [107]) and Agnone (Isernia Province, Molise region [108]) landslides.
Campania, Basilicata, and Calabria are located along the Southern Apennines, and were the testing ground for successful InSAR studies. In Campania, some authors handled the InSAR results for landslide mapping and detection at the regional and provincial scale, aiming for the update of landslide inventories [109,110,111,112,113]. Single landslide studies were produced as well, such as for the Moio della Civitella (Salerno Province [114,115]) and Calitri (Avellino Province [116,117]) landslides.
Basilicata region proposes some interesting landslide case studies from the Province of Potenza and Matera. Authors focus their analysis on the Montescaglioso [118,119,120], Maratea [121], Avigliano [122], and Costa della Gaveta [123] landslides.
Cosenza is the Calabrian province with the highest number of published research articles, 12 in total. InSAR was applied for landslide mapping and characterization in some municipalities, such as Lungro [124,125], Verbicaro [126,127], and Cerzeto [128]. Other relevant examples of single landslide characterization come from Gimigliano (Catanzaro Province [129]) and Papanice (Crotone municipality [130]). In addition, satellite interferometric products were exploited for landslide mapping and a state of activity assessment at the province and basin scale [131,132,133,134,135,136].
5. Statistical Evaluation of the Database
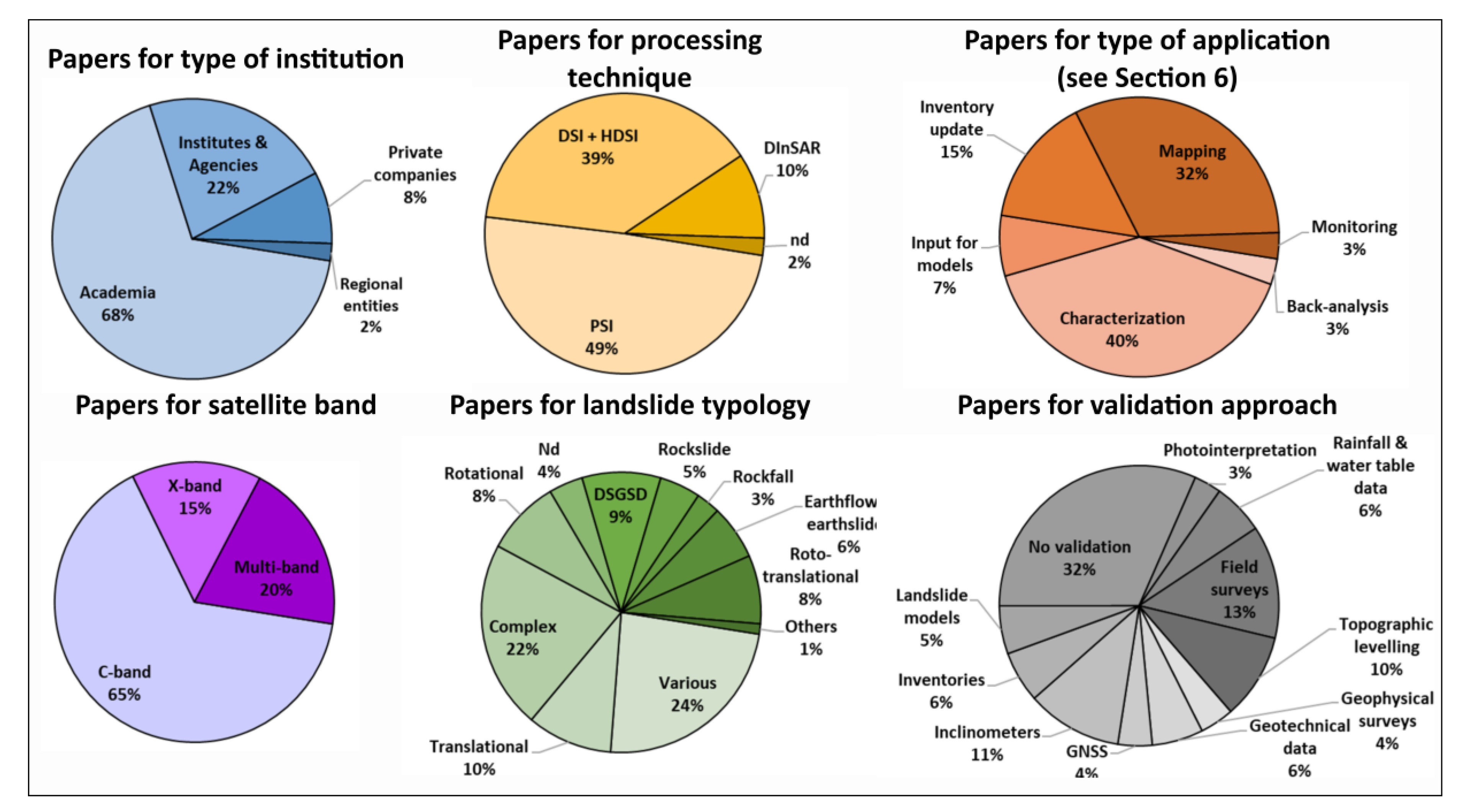
Figure 3 presents some significant statistics extracted from the database of scientific articles considered in this review work.
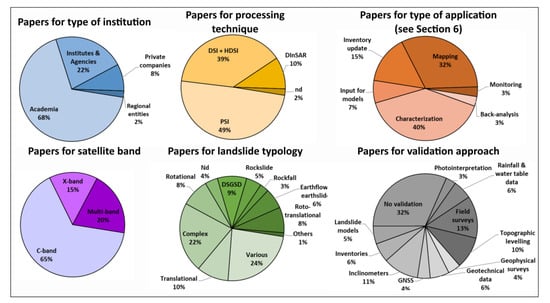
Figure 3.
Pie charts showing significant statistics extracted from the review database.
The largest part of the papers has as first author a researcher belonging to the academic world (68% of the total) or to national institutes and agencies (22% of the total). Just a few papers are presented by private companies (InSAR providers and consultants) or by members of regional institutions. Twenty percent of the papers comes from non-Italian universities or research centers, mainly from Spain and secondly from Austria, China, Great Britain, Japan, and Switzerland.
By the point of view of the processing technique used to select the radar targets, 49% of the authors have applied a Persistent Scatterer Approach (PSI), based on point-like targets. Thirty-nine percent of the authors performed an analysis based on distributed or homogeneously distributed scatterers (DSI or HDSI). Ten percent of the authors used classical differential interferometric approaches; this is the case of the early applications or of the works aimed to map landslides in non-urban areas (e.g., [104,121]).
Seventy-five percent of the authors used C-band data to perform their analysis. On one side, this is related to the availability of such radar images in the decade 1999–2009 (Figure 1). On the other side, C-band performs better outside of urban areas and in landslide mapping activities at the basin to regional scale. X-band is preferred when the target landslide is directly involving an urban area and where building-scale analysis is required. Twenty percent of the authors opted for multi-band approaches, a few involving L-band images as well (e.g., [88,97]).
Many different landslide typologies have been the target for InSAR analysis. It is worth recalling that InSAR is able to detect the motion of extremely slow to slow phenomena to avoid phase aliasing. Many authors (24% of the total) did not focus on a specific landslide typology. This is the case of mapping and inventory update activities at regional to municipal scale or of those works including multiple case studies. The most analyzed landslide typologies are complex (22% of the total), DSGSD (9%), rotational (8%), and roto-translational (8%). These numbers are clearly an expression of the abovementioned limitation of the InSAR technique when dealing with fast motions. Moreover, it is common to have parts of or entire villages located on the top of large slope deformations, which are the ideal target for an InSAR analysis.
Validation is an important task for many authors, as testified by the percentage (68%) of papers presenting at least one approach to validate the satellite results. The most common validation practices include ground surveys, aimed to collect geomorphological evidence or damage catalogues (13% of the total). Inclinometers (11% of the total) and topographic leveling (10% of the total) are other trusted sources of validation data.
6. How InSAR Products Have Been Used for Landslide Studies in Italy
With the aim of providing a comprehensive overview of InSAR applications in Italy, we defined six macro-classes of data usage:
- Back-analysis: Satellite radar images are analyzed in response to the occurrence of a highly impactful and damaging landslide. InSAR is used to reconstruct the recent history and evolution of the landslide, as well as to investigate possible motion precursors before its catastrophic failure.
- Characterization: The activity focuses on a single landslide, where the classical geomorphological analysis, supported by ground survey evidence and in situ measurements, is integrated with interferometric results. Commonly, multi-band and multi-sensor data are used to cover the largest temporal span possible, reconstructing the evolution of the landslide. Such activity is mainly focused on the evaluation of the potential risk posed by the landslide, assessing its behavior and the possibility of a future failure.
- Input for models: Satellite evidence can become the input for different kind of models, depending on the working scale and on the landslide typology. For example, interferometric data can be used as inputs for landslide susceptibility refinement or for landslide model calibration and validation. This activity emphasizes the high interoperability of InSAR data with models and ancillary data in general.
- Landslide inventory update: One of the most useful features of InSAR products is the wide-area coverage coupled with millimeter accuracy. This potential is exploited for landslide inventory refinement, where landslide databases are available. This activity comprises the definition of the state of activity of known landslides, information to be used for urban planning, and risk management purposes, including the identification of stable areas for relocation [128];
- Mapping: This activity aimed to show what is moving in an area. Interferometric data are a valuable support to detect the motion of new and unknown landslides within the technical boundaries of the technique, in terms of maximum measurable displacement and considering the land coverage.
- Monitoring: The most advanced application of interferometric products, relying on a frequently updated processing plan. This activity is possible thanks to the low revisiting time of the most recent satellite constellations, such as Sentinel-1 (6 days) or COSMO-SkyMed (4–16 days). Satellite monitoring cannot be considered as a real-time product for obvious reasons, but, for some landslide types, a bi-weekly update frequency is enough to follow their evolution. Indeed, some authors refer to this activity as “near-real-time monitoring.”
This classification is subjective and reflects the points of view of the authors of this review paper. Many articles were connected to multiple classes since different data exploitation methodologies have been applied. The percentages of papers for each category are shown in Figure 3. Some considerations, supported by study cases for each usage category, are proposed in the following sections.
6.1. Back-Analysis
When a landslide occurs, one of the first questions asked to experts and scientists is: Did the landslide show any precursory sign that could have been used to forecast its occurrence? The answer is not immediate if in-situ deformation monitoring systems are not available. Thanks to the possibility to back-track the target deformation over the past 28 years, satellite interferometry is a very good answer to this question.
Post-failure reconstruction of landslide behavior using InSAR data is a rather new application in Italy. This is due to (i) landslide type, as many landslides in Italy are connected to intense rainfall events that trigger newly or reactivated fast to very fast landslides, whose pre-failure can be considered instantaneous by the point of view of satellite interferometry; (ii) unfavorable morphology and land use of the slope; and (iii) the fact that InSAR is sometimes not a priority for some geohazard risk management entities, and it is not well integrated in risk management practices. It is worth recalling that the Italian Civil Protection usually requests interferometric analysis in the case of damaging landslide events (when technically feasible). Raspini et al. [128] showed that satellite interferometry has been used in every phase of the Civil Protection cycle, starting from prevention to recovery. Infante et al. [137] used InSAR to monitor strategic buildings in the framework of civil protection activities.
Nutricato et al. [138] analyzed a set of COSMO-SkyMed images with the SPINUA algorithm [28] in order to reconstruct the recent history of a slope affected by landslide whose runout interrupted the underlying railway line along the Ligurian coast, causing the derailment of a train. The PSI analysis confirmed the motion of the upper portion of the slope, in the proximity of the crown of the landslide, some years before its failure.
In February 2010, a large complex rotational landslide affected the eastward part of the town of San Fratello in the Nebrodi Mountains (Northern Sicily), and caused severe damage to tens of buildings. Bardi et al. [42] investigated the pre- and post-event behavior of the landslide combining satellite- and ground-based interferometric data. On the one hand, Envisat and RADARSAT-1 InSAR products confirmed the motion of the central portion of the landslide five years before its failure. On the other hand, COSMO-SkyMed InSAR data and Ground-Based Interferometry (GBInSAR) deformation maps allowed for the detection of residual motions in the whole crown area of the February 2010 failure. This approach was followed by Frodella et al. [92] in the case of the San Leo rockfall event of 27 February 2014. In this case, GBInSAR and InSAR measurements were integrated with terrestrial laser scanning data.
Confuorto et al. [130] characterized the pre- and post-failure evolution of the Papanice landslide (Crotone Province, Calabria), which occurred on 23 February 2012. Two different stacks of TerraSAR-X images were analyzed using the Coherent Pixel Technique-Temporal Sublook Coherence (CPT-TSC) and SBAS techniques. The interferometric analysis was supported by rainfall data, geomorphological evidence collected during ground surveys and slope stability analysis. This compound study allowed the authors to visualize the pre-failure evolution of the landslide and to highlight the activation of a landslide sector which was incorrectly considered stable.
InSAR is a powerful technique for ground motion assessment when the velocity of the phenomenon of interest does not exceed the phase unwrapping limits imposed by the nature of the radar signal. Some authors overcame this limitation by applying amplitude-based techniques, which allowed for the reconstruction of the sin-event deformation field. Manconi et al. [139] and Raspini et al. [118] applied, for the first time in Italy, the pixel-offset amplitude tracking to reconstruct the deformation field of the large complex landslide of Montescaglioso (Basilicata region). This approach was followed by Solari et al. [140] in the case of the Ponzano landslide (Abruzzo region). X-band images were the input for the pixel-offset analysis. Amplitude-based investigations were supported by multi-interferometric products and geomorphological evidence collected during ground surveys.
6.2. Landslide Characterization
Single studies aimed to the recognition of the spatial and temporal pattern of a landslide are the most common applications of InSAR in Italy. Satellite data are the perfect support for landslide characterization activities, where an on-site measurement network has been already deployed, or where the motion of the landslide is known or supposed, and additional information is required.
One of the very first applications of DInSAR for landslide characterization comes from Northeastern Sicily [141]. The Randazzo landslide (Catania Province) was the target for an integrated analysis between ERS1/2-derived interferograms, topographic surveys, inclinometric data, and groundwater level measures. Although in the early stages of the technique, satellite interferometry provided useful information for the landslide state of activity, confirmed by ground evidence.
The Assisi–Ivancich landslide is an example of a known hazard whose activity has been determined by several authors using satellite interferometry [54] and references therein. This roto-translational landslide affects a part of the urban area of the city of Assisi [58]. Castaldo et al. [58,59] report that the landslide motion is constant over time (with an average deformation rate around 1 cm/yr), regardless of the water table fluctuations. Its activity appears to be controlled by viscous factors. The landslide motion over time has been characterized by means of different radar sensors (both C- and X-band), and of various processing techniques. The satellite analysis was supported by ground measures, e.g., inclinometers, and by other remote sensing sources, e.g., Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data.
In synthesis, landslide characterization is based on:
- One or more interferometric datasets, including multi-band approaches (e.g., [56,95,108,142,143]);
- Geotechnical parameters of the landslide mass and bedrock (e.g., [80,95,144,145]);
- Ground survey evidence and geomorphological features, such as ground fissures, cracks or trenches, and/or building damage (e.g., [45,66,146,147,148]);
- In situ measurements, such as inclinometers (e.g., [96,149,150,151]);
- Additional remote sensing monitoring tools, such as topographic levelling techniques, TLS (Terrestrial Laser Scanning), or GBInSAR (e.g., [76,92,148,151]);
- Geophysical surveys data, such as seismic or geoelectrical surveys (e.g., [122,152]);
- Photogrammetry (e.g., [108,153]);
- Thermography (e.g., [144,154]);
- Rainfall data, hydrogeological conditions, and water table fluctuations (e.g., [123,155]).
6.3. InSAR Data as Inputs for Models
Satellite-derived displacement information has been used by some authors as input or calibration for models. InSAR is a precious resource where in situ measurements are unavailable or where the working scale does not allow for the acquisition of thousands of point-like data. Models usually require high-quality inputs, a requirement fulfilled by InSAR products, which can reach millimetric accuracy in the estimation of annual velocity.
Our bibliographic review revealed that there are two main areas where InSAR is used as input for models: single landslide modelling or basin-scale susceptibility modeling.
The first activity is aimed to the quantification of the landslide kinematic, for assessing the current landslide behavior and forecasting its future evolution [156]. A good coverage of InSAR measurement points allows for the detection of landslide sectors with different velocities. This information is fundamental for the proper definition of the model boundaries, and for the identification of different kinematic areas (e.g., [121]). InSAR can provide a temporal overview of landslide behavior several years before the time of the analysis. Multi-temporal InSAR results are used to optimize time-dependent landslide models, and as a starting point to forecast the future evolution of the phenomenon on the basis of viscosity/creep models (e.g., [58]).
The goal of landslide susceptibility is to produce maps indicating the propensity of an area to generate landslides [157]. Hundreds of types of numerical susceptibility models exist, more or less complex and based on different input data, parameters, and validation methodologies. For a review of susceptibility models, we refer to [158]. Some authors proposed landslide susceptibility models refined by means of InSAR data. For example, Ciampalini et al. [51] presented a methodology for susceptibility map refinement in the Nebrodi Range (Northern Sicily), based on X-band SqueeSAR ascending and descending datasets. First, line of sight velocity was projected along the slope. An empirical contingency matrix that considers the susceptibility degree, and the projected velocities are then used to integrate the two datasets. As a result, the prediction capability of the Random Forest algorithm used the generate the landslide susceptibility map was improved. A similar approach was recently followed in the case of the Sorrentina Peninsula (Campania region [159]).
In recent years, InSAR results have been used for a further model purpose: as input for the calculation of fragility curves for concrete and masonry buildings. The fragility curves represent the probability of exceeding a given damage as a function of ground displacements. Satellite-derived deformation is used to tune the fragility curves and to provide velocity measures for each damaged building whose state of conservation is assessed through ground surveys. This engineering methodology has been applied to landslide studies supported by interferometric results by, e.g., Peduto et al. [160], Del Soldato et al. [161], and Infante et al. [162].
6.4. Landslide Inventory Update and the State of Activity Definition
Thanks to the wide-area coverage, InSAR is the perfect tool to update and modify the boundaries and the state of activity of known landslides. Considering the impact of these phenomena in the Italian Peninsula, regional and national catalogs already exist; the IFFI database is an example [2]. However, a constant update is needed to improve risk management activities. The update of landslide inventories is a demanding task, especially where databases of events or high-resolution optical images are lacking. For this reason, InSAR was chosen by some authors as a support for landslide inventory updates and, most of all, for the definition of landslides’ state of activity.
One of the first examples comes from the Arno River Basin (Tuscany region), the testing ground of the SLAM (Service for LAndslides Monitoring) project, funded by the European Space Agency [32,33]. In the following years, many applications were proposed in different Italian regions, such as Molise [103], Calabria [131,133], Sicily [51,163], Tuscany [164], Emilia Romagna [165], and Lombardia [166], and at the basin scale, as in the case of the Liri-Garigliano and Vulturno basins [112,167].
The update of landslide inventories is a complex activity that requires both ancillary information, i.e., geomorphological maps, orthophotos or preexisting inventories, and expertise in the field. This activity cannot be automatized, and it always requires the support of InSAR experts. All the intrinsic uncertainties of the interferometric technique and the distribution of measurement points within a landslide area must be taken into account. Since InSAR is an opportunistic technique, i.e., able to derive information only from well-defined objects (the PS/DS), the update of landslide inventories will be more precise in urban or peri-urban areas. The expert judgment is relevant, especially where the point density is low, and where the support of ancillary information is required.
Landslide activity matrices are a useful tool to estimate the state of activity of landslides. The activity matrix approach exploits multi-temporal InSAR datasets as indicators of activity and intensity of landslide processes [126]. Different versions of activity matrices were developed in recent years [84,103,126,130,131,132,133]. All these approaches are aimed to the evaluation of the temporal evolution of landslides, highlighting reactivation and stabilization cycles.
6.5. Landslide Mapping
Where landslide inventories are not complete or outdated, InSAR can support the classical landslide mapping activities conducted by means of digital orthophotos or satellite optical images.
DSGSD landslides are flank-scale phenomena with very slow annual deformation rates (usually below 1 cm/year [168]), whose contour is sometimes unknown or not included in landslide inventories. InSAR was used to support DSGSD mapping activities in the Lombardia [65,66] and Valle d’Aosta [71,72,169] regions in the Alps, in Abruzzo [170] and the Marche [106] regions in the Central Apennines, and in the Palermo Province (Sicily [171]). In particular, the Valle d’Aosta DSGSD inventory was produced starting from ERS 1/2, and Envisat interferometric results obtained in the frame of the PST-A project [30]. DSGSD monographies connecting InSAR data and geomorphological features were the outputs of such activity [169].
Slow-moving landslides along the Apennines were the target of several InSAR mapping applications. Going from north to south, some valuable examples come from the Provinces of Bologna and Modena (Emilia Romagna region [91]), the Maiella Massif [101,102], the Daunia (Puglia region [172,173]), the Northern Molise region [104,174] and the Crati Valley (Calabria region [135]).
Some authors used InSAR as a mapping tool in response to earthquakes, such as the 1997 Umbria–Marche event [175], the 2009 Aquila earthquake [100], and the 2016–2017 Central Italy sequence [97,98,99]. Other authors evaluated the presence of active landslides along main transportation routes, such as in the Isarco Valley (Trentino Alto Adige region [176]), or in the Cosenza and Crotone Provinces (Calabria region [136]).
Recently, some authors proposed new techniques to semi-automatically extract clusters of moving points, focusing on active (and potentially unknown) landslides. These “hot-spot” approaches are useful for landslide mapping activities when the working scale requires the analysis of millions of measurement points. The concept has been developed by Bianchini et al. [132] and further improved by Barra et al. [177]. In Italy, the hot-spot mapping approach has been applied in the Valle d’Aosta [73,74] and Tuscany [178,179,180] regions. More complex clustering approaches were proposed by Milone & Scepi in the Avellino (Campania region) area (CLARA, Clustering LARge Application algorithm [181]) and by Lu et al. [35,37,182] for the Arno River Basin and the Volterra municipality (Tuscany region). The principal component analysis was applied by Bordoni et al. [85] for landslide mapping in the alpine sector of the Piemonte region.
6.6. Landslide Monitoring
The term “monitoring” can have different facets. Some authors use “monitoring” to indicate the analysis of multi-temporal InSAR datasets that are not updated and refer to a defined time period. In this review, these applications can fall into the categories “back-analysis” or “landslide characterization.” For the authors, “monitoring” refers to the most novel applications of satellite interferometry, focused on time series data mining and near-real-time approaches. It is worth recalling that, as defined by the Decree of the President of the Council of Ministers (DPCM) of 27 February 2004, any monitoring activity with a temporal update of less than 30 days is considered real-time.
Interferometric data can evidence accelerations and temporal changes relevant for the detection of a modified behavior of the landslide, potentially leading to its failure [183,184].
A satellite monitoring system requires a dedicated processing platform (with high capacity requirements) and an algorithm able to detect time series changes. Some authors have worked on the definition of methods applied in Italian case studies to highlight such temporal shifts.
Cigna et al. [185] proposed a manual classification of time series to identify trend changes induced by ground motion. The same author improved this methodology by proposing a semi-automatic method, based on the definition of two statistical indexes (Deviation Indexes, DI) able to quantify the trend differences before and after a breaking time defined by the user [186]. Berti et al. [89] further automatized this process and developed a standalone application able to classify a set of time series according to their temporal pattern: (i) uncorrelated, (ii) linear, (iii) bilinear, (iv) quadratic, and (v) discontinuous. The software was tested on Envisat InSAR products and applied in some municipalities affected by landslides in the Emilian Apennine.
These tools were developed when satellites had long repeat pass times and a real monitoring service based on such methods that could not be deployed. Recently, the launch of the Sentinel-1 constellation greatly reduces the temporal acquisition frequency, up to 6 days. This factor, altogether with the open policy on data distribution and the wide-area capabilities, made Sentinel-1 images the perfect candidates for the launch of the first satellite monitoring systems. This could not be possible without the consolidation of processing algorithms and the availability of cloud computing services.
The Tuscany region is the first worldwide example of such services. Sentinel-1-derived InSAR products are used for the early detection of landslides and other ground motions [187]. Raspini et al. [155] showed that it is now possible to detect landslide temporal changes accordingly to external triggering factors, e.g., an intense rainfall event. The main limitation of this method is related to the magnitude of the acceleration. Indeed, if the trend change exceeds the phase unwrapping capability of the deformation model applied, phase aliasing cannot be avoided, and the acceleration cannot be properly detected.
Table 1 proposes a summary of the reference papers used in this review to present each class.

Table 1.
Summary of the reference papers for each category of InSAR application. For the complete reference list, we refer to the six sub-sections of Chapter 6.
7. Final Remarks
This paper presents an overview of the temporal and spatial distribution of scientific papers related to satellite interferometric analysis of landslides along the Italian Peninsula. More than 250 papers were analyzed to provide a 20-year overview of the most common and uncommon applications of satellite interferometry. Moreover, emphasis was given to the early applications and to the most recent advancements (Table 2).

Table 2.
Summary of the pioneering applications and of the most recent advancements of InSAR for landslide studies in Italy.
The case studies proposed by Chapter 5 confirmed the potential of InSAR for landslide detection, mapping, and monitoring. InSAR has some intrinsic limitations that must be always taken into account when analyzing landslides. Among many, the most important are as follows:
- The spatial sampling of measures. The density of measurement points over an area is uneven. Due to the dependency of radar coherence on the dielectric characteristics of the ground, vegetated, smooth and snow-covered surfaces have null to very low density of points. This is an unsolvable issue that can limit the number of landslides to be investigated, or the amount of information obtainable for a single phenomenon.
- The geometric effects. Foreshortening, layover, and shadowing are common geometric distortions in mountainous areas. Depending on the slope orientation with respect to the LOS of the sensor, some landslides could be detected, whereas others could not be in any case monitored. Thus, it is fundamental to know a priori whether our target landslides are measurable or not. The creation of a visibility map for the area of interest is a simple but effective way to estimate this before data processing [73,88].
- The one-dimensional nature of the results. InSAR provides the estimate of one component of the real displacement vector, i.e., along the LOS direction. This implies that the 3D motion of a landslide can be viewed from only one point of view. Since the kinematic of a landslide is complex, a good practice is to derive the vertical and the east-to-west horizontal components of motion from double geometry InSAR data [e.g., 96].
- The kinematic of the landslide. In a noise-free situation, the radar signal should not change by more than a quarter-wavelength (e.g., 14 mm for C-band sensors) between two consecutive samples. Due to noise, this threshold is in reality lower. Because of this, landslides characterized by non-linear deformation rates higher than 2 mm/day are challenging targets for InSAR. InSAR processing based on linear phase unwrapping would not be able to capture such motions. Higher order deformation models may be applied to solve the phase ambiguity for single applications [189].
For a more comprehensive review of InSAR limitations for landslide studies, we refer to Wasowski & Bovenga [19] and to Bovenga et al. [190].
Although these well-known (and sometimes predictable) limitations exist, the interferometric technique is a reliable choice for many landslide-related applications, such as the following:
- Landslide mapping over wide areas. As seen in Section 6.5, it is possible to retrieve reliable information about the presence of landslides over entire basins or regions. The analysis is limited to certain landslide types, i.e., extremely slow and very slow landslides, according to the Cruden & Varnes classification [191]. Moreover, the quality of the results depends on the land cover, the presence of snow or geometric effects. Nevertheless, InSAR is useful when no other ground or remotely sensed information is available or where it is impossible to gather them. In Italy, InSAR gave positive responses for landslide mapping in both Alpine and Apennine contexts.
- Landslide state of activity estimation. InSAR is becoming a reliable and recognized tool to assess the multi-temporal behavior of landslides, including the evaluation of their state of activity. This line of research is relevant for land planners since the presence of an active landslide forbids the construction of new structures. Landslide databases sometimes lack information about the current activity of landslides, limiting the correct management of a territory. InSAR is the right tool to provide such information and to be included in regional/national landslide-related policies. The Tuscany region is an example of this [152,164].
- Landslide characterization. One of the more powerful characteristics of InSAR is its multi-scale capability. With proper processing configurations and according to the satellite band, it can be profitably employed from the continental to the local scale. In the second case, it is the perfect complement for in situ motion instruments and for use as input for landslide models.
- Back-analysis. Nowadays, an InSAR database can cover a 28-year time span with different satellite images acquired by multi-band sensors. This is a relevant feature for the post-collapse reconstruction of the landslide behavior.
Considering that InSAR is used not only for research purposes, but also to produce outputs for national or regional entities, data validation is a common request and requirement. Validation is the process to evaluate the applicability and detection capability of the InSAR products through an independent assessment, i.e., by using external data not connected to the data production. In the context of InSAR, validation is aimed to demonstrate the completeness and reliability of satellite measurements. Almost 70% of the revised paper highlighted the need for validation data of various types, ranging from classical in situ instruments to other remote sensing monitoring tools, such as GNSS, GBInSAR, or TLS (cfr. Section 6.3 and Figure 3). Validation was performed at a single landslide scale and when managing a large InSAR dataset. For example, Di Martire et al. [192] validated the results of the national interferometric coverage produced in the frame of the PST-A project. These authors proposed a validation approach known as the Landslide Detection Integrated System (LaDIS, [188]). Two hundred forty-nine sites were chosen as field validation targets affected by landslides. LaDIS is based on the comparison between landslide inventories derived from field survey evidence and satellite data. The coincidence between satellite data and ground truth is evaluated in four classes, ranging from 1—total coincidence—to 4—no coincidence [192].
8. Future Perspectives
InSAR is growing in popularity in the last years, especially outside of the academic world. The increasing attention paid to such data from different non-research entities is a clear evidence of this. In a wider context, the possible future evolutions and new advancements include the following:
- The increase of repeat pass time offered by the latest radar constellations allows and will allow for a better temporal definition of the landslide behavior over time. This opens new lines of research for time series data mining algorithms, and for the back-analysis of landslide events. The latter activity is certainly aided by the capability to construct 28-year-long time series. Moreover, some authors have already exploited InSAR as a calibration tool for landslide models, and we expect that, with a larger diffusion of such data, this activity will increase in the future.
- The increasing diffusion of InSAR products over wide areas will stimulate the integration of radar and optical results for the improvements of available landslide inventories. Moreover, the all-weather acquisition of radar satellites can be exploited to map landslides connected to a specific event in the areas of the world where cloud coverage is a recurrent issue. The future launch of the Radar Observing System for Europe L (ROSE-L) constellation by the European Space Agency will certainly offer new capabilities for landslide mapping and for InSAR analysis in general [193].
- The wide area capability and the level of accuracy of InSAR results have allowed some scientists to develop integrated approaches for qualitative and quantitative landslide risk assessment. In our opinion, this line of research has much room for improvement. Moreover, it is expected that InSAR will be integrated in civil protection practices and in landslide risk management chains.
- The Sentinel-1 constellation opened new horizons for landslide studies, allowing for the development of near-real-time monitoring systems, as testified by the example of the Tuscany region [187]. Such applications encourage a different use of InSAR data, trying to forecast rather than back-analyze or map landslides. On the one hand, these approaches surely carry a great potential for landslide risk management and civil protection activities. On the other hand, this data requires the continuous control of InSAR experts; such activity produces complex outputs that need to be interpreted before being disseminated to stakeholders. Moreover, as intrinsic for a novel near-real-time tool, the number of false positives is not negligible, and should be taken into account with proper data management and dissemination strategies.
- Italy is collecting user requirements for the future national ground motion service (GMS) based on Sentinel-1 and COSMO-SkyMed PSI and DSI products. The project is designed as the Mirror Copernicus Downstream Service and is one of the expected products of the Italian Space Economy Strategic Plan [194]. This service follows the examples of previously launched GMSs, such as InSAR Norway [195] and the German Ground Motion Service [196]. Such services are of pivotal importance for landslide mapping activities at a national and regional scale. Moreover, the GMSs are currently used and will continue to be used by researchers, public entities, and private companies to assess the status of known and unknown landslides. Depending on the temporal update of the data and on the target phenomenon, the services could be used for landslide mapping or monitoring activities.
- In 2017, the Copernicus User Forum and the Copernicus Committee unanimously approved the addition of the European Ground Motion Survey (EGMS) to the Copernicus Land Monitoring Service’ product portfolio [197]. The idea of the EGMS started in November 2016, when the EGMS Task Force began to develop the EGMS White Paper [198], which is considered the conceptual framework for the current project. Over the next few years, the EGMS will deliver consistent, regular, standardized, harmonized, and reliable information regarding natural and anthropogenic ground motion phenomena (including landslides) over Europe. Considering the successful experiences and the frequency of impactful landslide events, such service will constitute a reliable baseline for landslide studies, hopefully guaranteeing a wider uptake of satellite interferometric data.
- Despite the maturity of the interferometric techniques, the repeat pass time is still a major hurdle for the use of satellite InSAR as tool for systematic monitoring, especially when dealing with very short period events, such as landslide accelerations. Geological processes with strong deformation magnitudes with respect to the temporal sampling may yield aliased results or be missed altogether. In this scenario, another promising opportunity is represented by geosynchronous satellite, whose observing capability can provide a novel set of measurements, specifically InSAR at high temporal resolution (e.g., 1–12 h). This can be a game changer for solid earth applications. Hydroterra is an example of a project exploring such new InSAR horizons [199]. Hydroterra is currently a phase 0 candidate mission for the 10th Earth Explorer Programme of the ESA. The aim of the project is to observe key processes of the daily water cycle by placing a single SAR satellite in geosynchronous orbit. The Mediterranean, the Alpine Arc, Sahel, and other African regions would be covered from a geosynchronous orbit slot positioned over Africa. The main science goals are to improve the prediction capability of intense rainfall and related flooding and landslides, improving the understanding of the diurnal water cycle. These goals will be supported by providing estimates of soil moisture, integrated atmospheric water vapor changes, flood extent, and information on snow melt. Secondarily, rapid response imaging of ground motion will enable new science applications and near-real-time services.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/12/8/1351/s1, Video S1: GIF of the temporal evolution of interferometric applications for landslide studies in Italy. GIF created using the bar chart race of Flourish Studio and Screencast-O-Matic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and writing, L.S.; bibliographic review and creation of the database, L.S., M.D.S., A.B., and P.C.; methodology and figures preparation, S.B. and F.R.; review and homogenization, N.C. and M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been partially funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness through the DEMOS project “Deformation monitoring using Sentinel-1 data” (Ref: CGL2017-83704-P).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
- Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Luciani, S.; Valigi, D.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides in Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigila, A.; Iadanza, C.; Spizzichino, D. Quality assessment of the Italian Landslide Inventory using GIS processing. Landslides 2010, 7, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, P.; Bianchi, C.; Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F. Societal landslide and flood risk in Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barla, G.; Paronuzzi, P. The 1963 Vajont Landslide: 50th Anniversary. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2013, 46, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Chen, H.; Lee, C.F. Replay of the 1987 Val Pola landslide, Italian alps. Geomorphology 2004, 60, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Dal Negro, P. Observations and modelling of soil slip-debris flow initiation processes in pyroclastic deposits: The Sarno 1998 event. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F. Landslide fatalities and the evaluation of landslide risk in Italy. Eng. Geol. 2000, 58, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.G.; Park, H.J.; Catani, F.; Simoni, A.; Berti, M. Landslide prediction, monitoring and early warning: A concise review of state-of-the-art. Geosci. J. 2017, 21, 1033–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P.; Berthier, E.; Raucoules, D.; Casson, B.; Grandjean, P.; Pambrun, C.; Varel, E. Remote-sensing techniques for analysing landslide kinematics: A review. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2007, 178, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chang, N.B.; Li, S. Applications of SAR interferometry in earth and environmental science research. Sensors 2009, 9, 1876–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, A.; Calò, F. A review of interferometric synthetic aperture RADAR (InSAR) multi-track approaches for the retrieval of Earth’s surface displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, F.; Soeters, R.; Van Westen, C.J. Remote sensing techniques for landslide studies and hazard zonation in Europe. Geomorphology 1996, 15, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.; Hurni, L.; Gogu, R. Remote sensing of landslides: An analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems for hazard assessment in mountainous environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaioni, M.; Longoni, L.; Melillo, V.; Papini, M. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: An overview of recent achievements and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9600–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Segoni, S.; Agostini, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Use of remote sensing for landslide studies in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F. Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite Multi Temporal Interferometry: Current issues and future perspectives. Eng. Geol. 2014, 174, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucci, A.; Ferretti, A.; Guarnieri, A.M.; Rocca, F. Sentinel 1 SAR interferometry applications: The outlook for sub millimeter measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Mateos, R.M.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Grandjean, G.; Poyiadji, E.; Maftei, R.; Filipciuc, T.-C.; Auflič, M.J.; Jež, J.; Podolszki, L. Landslide databases in the Geological Surveys of Europe. Landslides 2018, 15, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, U.; Blum, P.; Da Silva, P.F.; Andersen, P.; Pilz, J.; Chalov, S.R.; Malet, J.-P.; Auflič, N.J.; Andres, N.; Poyiadji, E.; et al. Fatal landslides in Europe. Landslides 2016, 13, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martí, A.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Thelwall, M.; López-Cózar, E.D. Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus: A systematic comparison of citations in 252 subject categories. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevi, G.; Moed, H.; Bar-Ilan, J. Suitability of Google Scholar as a source of scientific information and as a source of data for scientific evaluation—Review of the literature. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; Stein, T.I., Ed.; IEEE Publications: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Agostini, A.; Tofani, V.; Nolesini, T.; Gigli, G.; Tanteri, L.; Rosi, A.; Cardellini, S.; Casagli, N. A new appraisal of the Ancona landslide based on geotechnical investigations and stability modelling. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2014, 47, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, D.O.; Bovenga, F.; Nutricato, R.; Rana, F.; D’Aprile, C.; Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Chiaradia, M.T.; Ober, G.; Candela, L. C- and X-band Multi-pass InSAR analysis over alpine areas (ITALY). In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XV, Proceeding of SPIE Remote Sensing, Berlin, Germany, 31 August–3 September 2019; Bruzzone, L., Notarnicola, C., Posa, F., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bovenga, F.; Nutricato, R.; Guerriero, A.R.L.; Chiaradia, M.T. SPINUA: A flexible processing chain for ERS/ENVISAT long term interferometry. In Proceedings of the ESA-ENVISAT Symposium, Salzburg, Austria, 6–10 September 2004; Lacoste, H., Ouwehand, L., Eds.; ESA Publications Division: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zinno, I.; Bonano, M.; Buonanno, S.; Casu, F.; De Luca, C.; Manunta, M.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. National Scale Surface Deformation Time Series Generation through Advanced DInSAR Processing of Sentinel-1 Data within a Cloud Computing Environment. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2018, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Ferretti, A.; Minati, F.; Falco, S.; Trillo, F.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Malvarosa, F.; Mammone, C.; Vecchioli, F.; et al. Analysis of surface deformations over the whole Italian territory by interferometric processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, D.; Farina, P.; Gontier, E.; Fumagalli, A.; Moretti, S. Integration of Permanent Scatterers analysis and high resolution optical images within landslide risk analysis. In Proceedings of the FRINGE 2003 Workshop, Advances in SAR interferometry from ERS and ENVISAT missions, Frascati, Italy, 20 August 2003; ESA Publications Division: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, P.; Moretti, S.; Colombo, D.; Fumagalli, A.; Manunta, P. Landslide risk analysis by means of remote sensing techniques: Results from the ESA/SLAM project. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS 2004, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, P.; Colombo, D.; Fumagalli, A.; Marks, F.; Moretti, S. Permanent Scatterers for landslide investigations: Outcomes from the ESA-SLAM project. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Falorni, G.; Farina, P. Integration of remote sensing techniques in different stages of landslide response. In Progress in Landslide Science; Sassa, K., Fukuoka, H., Wang, F., Wang, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry Hotspot and Cluster Analysis (PSI-HCA) for detection of extremely slow-moving landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugioni, M.; Mazzanti, B.; Montini, G.; Sulli, L. Use of SAR interferometry for landslide analysis in the Arno river basin. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Daehne, A.; Travelletti, J.; Casagli, N.; Corsini, A.; Malet, J.P. Innovative techniques for the detection and characterization of the kinematics of slow-moving landslides. In Mountain Risks: From Prediction to Management and Governance; Van Asch, T., Corominas, J., Greiving, S., Malet, J.-P., Sterlacchini, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Del Ventisette, C.; Gigli, G.; Tofani, V.; Lu, P.; Casagli, N. Radar technologies for landslide detection, monitoring, early warning and emergency management. In Modern Technologies for Landslide Monitoring and Prediction; Scaioni, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 209–232. [Google Scholar]
- Raspini, F.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Landslide mapping using SqueeSAR data: Giampilieri (Italy) case study. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Frodella, W.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. The effectiveness of high-resolution LiDAR data combined with PSInSAR data in landslide study. Landslides 2016, 13, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Tofani, V.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Lu, P.; Morelli, S. TXT-tool 2.039-3.1: Satellite Remote Sensing Techniques for Landslides Detection and Mapping. In Landslide Dynamics: ISDR-ICL Landslide Interactive Teaching Tools; Sassa, K., Guzzetti, F., Yamagishi, H., Arbanas, Ž., Casagli, N., McSaveney, M., Dang, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 235–254. [Google Scholar]
- Del Ventisette, C.; Ciampalini, A.; Manunta, M.; Calò, F.; Paglia, L.; Ardizzone, F.; Mondini, A.C.; Reichenbach, P.; Mateos, R.M.; Bianchini, S.; et al. Exploitation of large archives of ERS and ENVISAT C-band SAR data to characterize ground deformations. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3896–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, F.; Frodella, W.; Ciampalini, A.; Bianchini, S.; Del Ventisette, C.; Gigli, G.; Fanti, R.; Moretti, S.; Basile, G.; Casagli, N. Integration between ground based and satellite SAR data in landslide mapping: The San Fratello case study. Geomorphology 2014, 223, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Tapete, D.; Ciampalini, A.; Di Traglia, F.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Multi-temporal evaluation of landslide-induced movements and damage assessment in San Fratello (Italy) by means of C-and X-band PSI data. In Mathematics of Planet Earth; Golden, K., Lewis, M., Nishiura, Y., Tribbia, J., Zubelli, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampalini, A.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Frodella, W.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Analysis of building deformation in landslide area using multisensor PSInSAR™ technique. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2014, 33, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bardi, F.; Di Traglia, F.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Multi-temporal evaluation of landslide movements and impacts on buildings in San Fratello (Italy) by means of C-band and X-band PSI data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2015, 172, 3043–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F. DORIS project: The European downstream service for landslides and subsidence risk management. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3018–3021. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Moretti, S. Landslide back monitoring and forecasting by using PSInSAR technique: The case of Naso (Sicily, Southern Italy). Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. A 2015, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Frodella, W.; Bardi, F.; Lagomarsino, D.; Di Traglia, F.; Moretti, S.; Proietti, C.; Pagliara, P.; et al. Remote sensing as tool for development of landslide databases: The case of the Messina Province (Italy) geodatabase. Geomorphology 2015, 249, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Lagomarsino, D.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Landslide susceptibility map refinement using PSInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Ciampalini, A.; Bianchini, S.; Bardi, F.; Di Traglia, F.; Basile, G.; Moretti, S. Updated landslide inventory of the area between the Furiano and Rosmarino creeks (Sicily, Italy). J. Maps 2016, 12, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Lagomarsino, D.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. How to improve the accuracy of landslide susceptibility maps using PSInSAR data. In Proceedings of the Workshop on World Landslide Forum, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 29 May–2 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 965–971. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetti, F.; Manunta, M.; Ardizzone, F.; Pepe, A.; Cardinali, M.; Zeni, G.; Reichenbach, P.; Lanari, R. Analysis of ground deformation detected using the SBAS-DInSAR technique in Umbria, Central Italy. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2009, 166, 1425–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radicioni, F.; Stoppini, A.; Brigante, R.; Fornaro, G.; Bovenga, F.; Nitti, D.O. Long-term GNSS and SAR data comparison for the deformation monitoring of the Assisi landslide. In Proceedings of the FIG Working Week 2012, Knowing to Manage the Territory, Protect the Environment, Evaluate the Cultural Heritage, Rome, Italy, 6–10 May 2012; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bonano, M.; Calo, F.; Manunta, M.; Paglia, L.; Zeni, G. Long-term Analysis of Landslides via SBAS-DInSAR. In Landslide Science and Practice: Volume 2: Early Warning, Instrumentation and Monitoring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Bovenga, F.; Nitti, D.O.; Fornaro, G.; Radicioni, F.; Stoppini, A.; Brigante, R. Using C/X-band SAR interferometry and GNSS measurements for the Assisi landslide analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4083–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Castaldo, R.; Lollino, P.; Tizzani, P.; Guzzetti, F.; Lanari, R.; Angeli, M.G.; Pontoni, F.; Manunta, M. Enhanced landslide investigations through advanced DInSAR techniques: The Ivancich case study, Assisi, Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; Tizzani, P.; Lollino, P.; Calò, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Lanari, R.; Guzzetti, F.; Manunta, M. Landslide kinematical analysis through inverse numerical modelling and differential SAR interferometry. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2015, 172, 3067–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; Tizzani, P.; Lollino, P.; Calò, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Manunta, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Lanari, R. The Ivancich active landslide process (Assisi, Central Italy) analysed via numerical modeling jointly optimized by DInSAR and inclinometric data. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 2; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1513–1517. [Google Scholar]
- De Novellis, V.; Castaldo, R.; Lollino, P.; Manunta, M.; Tizzani, P. Advanced three-dimensional finite element modeling of a slow landslide through the exploitation of dinsar measurements and in situ surveys. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Crosta, G.B.; Ferretti, A.; Ambrosi, C. Monitoring and assessing the state of activity of slope instabilities by the Permanent Scatterers Technique. In Landslides from Massive Rock Slope Failure; Evans, S.G., Scarascia Mugnozza, G., Strom, A., Hermanns, R.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 175–194. [Google Scholar]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.; Allievi, J. Damage to buildings in large slope rock instabilities monitored with the PSInSAR™ technique. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4753–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agliardi, F.; Crosta, G.B. Long-and short-term controls on the Spriana rockslide (Central Alps, Italy). In Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Yin, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Del Ventisette, C.; Righini, G.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Multitemporal landslides inventory map updating using spaceborne SAR analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2014, 30, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, A.; Del Conte, S.; Novali, F.; Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B. Recent advances in satellite radar data processing and their support to the characterization of DSGSDs in the alps. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 2; Lollino, G., Giordan, D., Crosta, G.B., Corominas, J., Azzam, R., Wasowski, J., Sciarra, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 609–612. [Google Scholar]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Rossini, M.; Allievi, J. Activity and kinematic behaviour of deep-seated landslides from PS-InSAR displacement rate measurements. Landslides 2018, 15, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, H.; Nagler, T.; Rocca, F.; Prati, C.; Mazzotti, A.; Keusen, H.; Liener, S.; Tarchi, D. InSAR techniques and applications for monitoring landslides and subsidence. In Proceedings of the Geoinformation for Europeanwide Integration, 22nd EARSeL Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 4–6 June 2002; pp. 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Strozzi, T.; Farina, P.; Corsini, A.; Ambrosi, C.; Thüring, M.; Zilger, J.; Wiesmann, A.; Wegmüller, A.; Werner, C. Survey and monitoring of landslide displacements by means of L-band satellite SAR interferometry. Landslides 2005, 2, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Agliardi, F.; Rivolta, C.; Alberti, S.; Dei Cas, L. Long-term evolution and early warning strategies for complex rockslides by real-time monitoring. Landslides 2017, 14, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölbling, D.; Füreder, P.; Antolini, F.; Cigna, F.; Casagli, N.; Lang, S. A semi-automated object-based approach for landslide detection validated by persistent scatterer interferometry measures and landslide inventories. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1310–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignetti, M.; Manconi, A.; Manunta, M.; Giordan, D.; De Luca, C.; Allasia, P.; Ardizzone, F. Taking advantage of the esa G-pod service to study ground deformation processes in high mountain areas: A Valle d’Aosta case study, northern Italy. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordan, D.; Cignetti, M.; Bertolo, D. The Use of Morpho-Structural Domains for the Characterization of Deep-Seated Gravitational Slope Deformations in Valle d’Aosta. In Proceedings of the Workshop on World Landslide Forum, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 29 May–2 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Montalti, R.; Bianchini, S.; Raspini, F.; Thuegaz, P.; Bertolo, D.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. A Sentinel-1 based hot-spot analysis: Landslide mapping in north-western Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7898–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Bianchini, S.; Franceschini, R.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Thuegaz, P.; Bertolo, D.; Crosetto, M.; Catani, F. Satellite interferometric data for landslide intensity evaluation in mountainous regions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2020, 87, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T.; Tofani, V.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Bertolo, D.; Thuegaz, P.; Casagli, N. Combination of GNSS, satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR remote sensing monitoring to improve the understanding of a large landslide in high alpine environment. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iasio, C.; Novali, F.; Corsini, A.; Mulas, M.; Branzanti, M.; Benedetti, E.; Tamburini, A.; Mair, V. COSMO SkyMed high frequency-high resolution monitoring of an alpine slow landslide, Corvara in Badia, Northern Italy. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 7577–7580. [Google Scholar]
- Schlögel, R.; Thiebes, B.; Mulas, M.; Cuozzo, G.; Notarnicola, C.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Mair, V.; Corsini, A. Multi-temporal X-Band radar interferometry using corner reflectors: Application and validation at the Corvara Landslide (Dolomites, Italy). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Schlögel, R.; Bruzzone, L.; Cuozzo, G. Integration of PSI, MAI, and Intensity-Based Sub-Pixel Offset Tracking Results for Landslide Monitoring with X-Band Corner Reflectors—Italian Alps (Corvara). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Schlögel, R.; Kofler, C.; Cuozzo, G.; Rutzinger, M.; Zieher, T.; Toschi, I.; Remondino, F.; Mejia-Aguilar, A.; Thiebes, B.; et al. Sentinel-1 and ground-based sensors for continuous monitoring of the Corvara Landslide (South Tyrol, Italy). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasi, P.; Verrucci, L.; Campedel, P.; Veronese, L.; Pettinelli, E.; Ribacchi, R. Buckling of high natural slopes: The case of Lavini di Marco (Trento-Italy). Eng. Geol. 2009, 109, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanteri, L.; Colombo, A. The integration between satellite data and conventional monitoring system in order to update the Arpa Piemonte landslide inventory. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Meisina, C.; Notti, D.; Zucca, F.; Ceriani, M.; Colombo, A.; Poggi, F.; Roccati, A.; Zaccone, A. The use of PSInSAR™ and SqueeSAR™ techniques for updating landslide inventories. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Vassileva, M.; Giulio Tonolo, F.; Riccardi, P.; Lecci, D.; Boccardo, P.; Chiesa, G. Satellite SAR interferometric techniques in support to emergency mapping. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Bordoni, M.; Colombo, A.; Lanteri, L.; Meisina, C. Landslide state of activity maps by combining multi-temporal A-DInSAR (LAMBDA). Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Bonì, R.; Colombo, A.; Lanteri, L.; Meisina, C. A methodology for ground motion area detection (GMA-D) using A-DInSAR time series in landslide investigations. Catena 2018, 163, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisina, C.; Zucca, F.; Notti, D.; Colombo, A.; Cucchi, A.; Savio, G.; Giannico, C.; Bianchi, M. Geological interpretation of PSInSAR data at regional scale. Sensors 2006, 8, 7469–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notti, D.; Herrera, G.; Bianchini, S.; Meisina, C.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Zucca, F. A methodology for improving landslide PSI data analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2186–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Calò, F.; Cigna, F.; Manunta, M.; Herrera, G.; Berti, M.; Meisina, C.; Tapete, D.; Zucca, F. A user-oriented methodology for DInSAR time series analysis and interpretation: Landslides and subsidence case studies. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2015, 172, 3081–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, M.; Corsini, A.; Franceschini, S.; Iannacone, J.P. Automated classifcation of Persistent Scatterers Interferometry time series. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, B.; Schmidt, D.; Simoni, A. The influence of external digital elevation models on PS-InSAR and SBAS results: Implications for the analysis of deformation signals caused by slow moving landslides in the northern apennines (Italy). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2618–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, B.; Simoni, A.; Mulas, M.; Corsini, A.; Schmidt, D. Deformation responses of slow moving landslides to seasonal rainfall in the Northern Apennines, measured by InSAR. Geomorphology 2018, 308, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodella, W.; Ciampalini, A.; Gigli, G.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Nocentini, M.; Scardigli, C.; Casagli, N. Synergic use of satellite and ground based remote sensing methods for monitoring the San Leo rock cliff (Northern Italy). Geomorphology 2016, 264, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, A.; Farina, P.; Antonello, G.; Barbieri, M.; Casagli, N.; Coren, F.; Guerri, L.; Ronchetti, F.; Sterzai, P.; Tarchi, D. Space-borne and ground-based SAR interferometry as tools for landslide hazard management in civil protection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 2351–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Integration of remote sensing techniques for intensity zonation within a landslide area: A case study in the northern Apennines, Italy. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevasco, A.; Termini, F.; Valentino, R.; Meisina, C.; Bonì, R.; Bordoni, M.; Chella, G.P.; De Vita, P. Residual mechanisms and kinematics of the relict Lemeglio coastal landslide (Liguria, northwestern Italy). Geomorphology 2018, 320, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Raspini, F.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) technique for landslide characterization and monitoring. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Fielding, E.J.; Liang, C.; Milillo, P.; Bekaert, D.; Dreger, D.; Salzer, J. Coseismic deformation and triggered landslides of the 2016 Mw 6.2 Amatrice earthquake in Italy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcari, M.; Montuori, A.; Bignami, C.; Moro, M.; Stramondo, S.; Tolomei, C. Using multi-band InSAR data for detecting local deformation phenomena induced by the 2016–2017 Central Italy seismic sequence. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Devoti, R.; Fubelli, G.; Aringoli, D.; Bignami, C.; Galvani, A.; Moro, M.; Polcari, M.; Saroli, M.; Sepe, V.; et al. Step-like displacements of a deep seated gravitational slope deformation observed during the 2016–2017 seismic events in Central Italy. Eng. Geol. 2018, 246, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Cigna, F.; Bianchini, S.; Hölbling, D.; Füreder, P.; Righini, G.; Del Conte, S.; Friedl, B.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Iasio, C.; et al. Landslide mapping and monitoring by using radar and optical remote sensing: Examples from the EC-FP7 project SAFER. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, A.; Mazzanti, P.; Bozzano, F.; Perissin, D. Advanced characterization of a landslide-prone area by satellite a-DInSAR. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory; Lollino, G., Manconi, A., Guzzetti, F., Culshaw, M., Bobrowsky, P.T., Luino, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzano, F.; Mazzanti, P.; Perissin, D.; Rocca, A.; De Pari, P.; Discenza, M.E. Basin scale assessment of landslides geomorphological setting by advanced InSAR analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righini, G.; Pancioli, V.; Casagli, N. Updating landslide inventory maps using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 2068–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Mazzanti, P.; Esposito, C.; Crosetto, M.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. First insights on the potential of Sentinel-1 for landslides detection. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Devanthéry, N.; Cuevas González, M.; Barra, A.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry using Sentinel-1 data. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences Congress (ISPRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 12–19 July 2016; Volume 41, pp. 835–839. [Google Scholar]
- Tolomei, C.; Taramelli, A.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M.; Aringoli, D.; Salvi, S. Analysis of the deep-seated gravitational slope deformations over Mt. Frascare (Central Italy) with geomorphological assessment and DInSAR approaches. Geomorphology 2013, 201, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzielli, M.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. Risk analysis for the Ancona landslide—I: Characterization of landslide kinematics. Landslides 2015, 12, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Riquelme, A.; Bianchini, S.; Tomás, R.; Di Martire, D.; De Vita, P.; Moretti, S.; Calcaterra, D. Multisource data integration to investigate one century of evolution for the Agnone landslide (Molise, southern Italy). Landslides 2018, 15, 2113–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardo, G.; Ventura, G.; Terranova, C.; Matano, F.; Nardò, S. Ground deformation due to tectonic, hydrothermal, gravity, hydrogeological, and anthropic processes in the Campania Region (Southern Italy) from Permanent Scatterers Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L.; Peduto, D.; Pisciotta, G.; Arena, L.; Ferlisi, S.; Fornaro, G. The combination of DInSAR and facility damage data for the updating of slow-moving landslide inventory maps at medium scale. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Arena, L.; Calvello, M.; Anzalone, R.; Cascini, L. Evaluating the state of activity of slow-moving landslides by means of DInSAR data and statistical analyses. In Proceedings of the XVI ECSMGE Geotechnical Engineering for Infrastructure and Development Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 13–17 September 2015; Winter, M.G., Smith, D.M., Eldred, P.J.L., Toll, D.G., Eds.; ICE Publishing: London, United Kingdom, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 1843–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Calvello, M.; Peduto, D.; Arena, L. Combined use of statistical and DInSAR data analyses to define the state of activity of slow-moving landslides. Landslides 2017, 14, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, L.; Confuorto, P.; Calcaterra, D.; Guadagno, F.M.; Revellino, P.; Di Martire, D. PS-driven inventory of town-damaging landslides in the Benevento, Avellino and Salerno Provinces, southern Italy. J. Maps 2019, 15, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Confuorto, P.; Di Martire, D.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Use of DInSAR data for multi-level vulnerability assessment of urban settings affected by slow-moving and intermittent landslides. Procedia Eng. 2016, 158, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Di Martire, D.; Confuorto, P.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D.; Tomàs, R.; Duro, J.; Centolanza, G. Multi-temporal assessment of building damage on a landslide-affected area by interferometric data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry (RTSI), Modena, Italy, 11–13 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Calò, F.; Calcaterra, D.; Iodice, A.; Parise, M.; Ramondini, M. Assessing the activity of a large landslide in southern Italy by ground-monitoring and SAR interferometric techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3512–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martire, D.; De Luca, G.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Landslide-related PS data interpretation by means of different techniques. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Raspini, F.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Conte, S.; Lombardi, L.; Nocentini, M.; Gigli, G.; Ferretti, A.; Casagli, N. Exploitation of amplitude and phase of satellite SAR images for landslide mapping: The case of Montescaglioso (South Italy). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14576–14596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carla, T.; Raspini, F.; Intrieri, E.; Casagli, N. A simple method to help determine landslide susceptibility from spaceborne InSAR data: The Montescaglioso case study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzano, F.; Caporossi, P.; Esposito, C.; Martino, S.; Mazzanti, P.; Moretto, S.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G.; Rizzo, A.M. Mechanism of the Montescaglioso landslide (Southern Italy) inferred by geological survey and remote sensing. In Proceedings of the Workshop on World Landslide Forum, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 29 May–2 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Costantini, M.; Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Pietranera, L.; Rizzo, V. Use of differential SAR interferometry in monitoring and modelling large slope instability at Maratea (Basilicata, Italy). Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamita, G.; Serlenga, V.; Stabile, T.A.; Gallipoli, M.R.; Bellanova, J.; Bonano, M.; Casu, F.; Vignola, L.; Piscitelli, S.; Perrone, A. An integrated geophysical approach for urban underground characterization: The Avigliano town (southern Italy) case study. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novellino, A.; Cigna, F.; Sowter, A.; Syafiudin, M.F.; Di Martire, D.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Intermittent small baseline subset (ISBAS) InSAR analysis to monitor landslides in Costa Della Gaveta, Southern Italy. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3536–3539. [Google Scholar]
- Antronico, L.; Borrelli, L.; Peduto, D.; Fornaro, G.; Gullà, G.; Paglia, L.; Zeni, G. Conventional and innovative techniques for the monitoring of displacements in landslide affected area. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Gullà, G.; Peduto, D.; Borrelli, L.; Antronico, L.; Fornaro, G. Geometric and kinematic characterization of landslides affecting urban areas: The Lungro case study (Calabria, Southern Italy). Landslides 2017, 14, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Bianchini, S.; Casagli, N. How to assess landslide activity and intensity with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI): The PSI-based matrix approach. Landslides 2013, 10, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlisi, S.; Peduto, D.; Gullà, G.; Nicodemo, G.; Borrelli, L.; Fornaro, G. The use of DInSAR data for the analysis of building damage induced by slow-moving landslides. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 2; Lollino, G., Giordan, D., Crosta, G.B., Corominas, J., Azzam, R., Wasowski, J., Sciarra, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1835–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Raspini, F.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Ventisette, C.; Farina, P.; Ferrigno, F.; Solari, L.; Casagli, N. The contribution of satellite SAR-derived displacement measurements in landslide risk management practices. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Cigna, F.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Monitoring landslide-induced displacements with TerraSAR-X persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI): Gimigliano case study in Calabria region (Italy). Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confuorto, P.; Di Martire, D.; Centolanza, G.; Iglesias, R.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Novellino, A.; Plank, S.; Ramondini, M.; Thuro, K.; Calcaterra, D. Post-failure evolution analysis of a rainfall-triggered landslide by multi-temporal interferometry SAR approaches integrated with geotechnical analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Bianchini, S.; Righini, G.; Proietti, C.; Casagli, N. Updating landslide inventory maps in mountain areas by means of Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) and photo-interpretation: Central Calabria (Italy) case study. In Proceedings of the Mountain Risks: Bringing Science to Society, Florence, Italy, 24–26 November 2010; Malet, J.P., Glade, T., Casagli, N., Eds.; CERG Editions. pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, S.; Cigna, F.; Righini, G.; Proietti, C.; Casagli, N. Landslide hotspot mapping by means of persistent scatterer interferometry. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Cigna, F.; Casagli, N. Improving Landslide Inventory with Persistent Scatterers in Calabria, Italy. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Confuorto, P.; Plank, S.; Di Martire, D.; Ramondini, M.; Thuro, K.; Calcaterra, D. Slow-Moving landslide monitoring with Multi-Temporal TerraSAR-X data by means of DInSAR tech-niques in Crotone province (Southern Italy). In Proceedings of the FRINGE’15: Advances in the Science and Applications of SAR Interferometry and Sentinel-1 InSAR Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 March 2015; Ouwehand, L., Ed.; ESA Publication SP-731: Frascati, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cianflone, G.; Tolomei, C.; Brunori, C.A.; Monna, S.; Dominici, R. Landslides and subsidence assessment in the Crati Valley (Southern Italy) using insar data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappo, N.; Peduto, D.; Mavrouli, O.; van Westen, C.J.; Gullà, G. Slow-moving landslides interacting with the road network: Analysis of damage using ancillary data, in situ surveys and multi-source monitoring data. Eng. Geol. 2019, 260, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Tessitore, S.; Confuorto, P.; Sepe, C.; Calcaterra, D.; Di Martire, D.; Ramondini, M. Monitoring of Strategic Buildings in Civil Protection Activities via Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2019, 34, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Bovenga, F.; Refice, A.; Wasowski, J.; Chiaradia, M.T.; Milillo, G. COSMO-SkyMed multi-temporal SAR interferometry over liguria region for environmental monitoring and risk management. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1405–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Manconi, A.; Casu, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Bonano, M.; Cardinali, M.; De Luca, C.; Gueguen, E.; Marchesini, I.; Parise, M.; Vennari, C.; et al. Brief communication: Rapid mapping of landslide events: The 3 December 2013 Montescaglioso landslide, Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Raspini, F.; Del Soldato, M.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Ferrigno, F.; Tucci, S.; Casagli, N. Satellite radar data for back-analyzing a landslide event: The Ponzano (Central Italy) case study. Landslides 2018, 15, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, V.; Tesauro, M. SAR interferometry and field data of Randazzo landslide (Eastern Sicily, Italy). Phys. Chem. Earth 2000, 25, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessari, G.; Floris, M.; Achilli, V.; Fabris, M.; Menin, A.; Monego, M. Testing Sentinel-1A data in landslide monitoring: A case study from North-Eastern Italian pre-Alps. In Proceedings of the Workshop on World Landslide Forum, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 29 May–2 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, B.; Simoni, A.; Schmidt, D.; Bertello, L. Using advanced InSAR techniques to monitor landslide deformations induced by tunneling in the Northern Apennines, Italy. Eng. Geol. 2017, 226, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; Spalluto, L.; Bovenga, F.; Fiore, A.; Miccoli, M.N.; Muzzicato, P.; Nitti, O.; Nutricato, R.; Pasquariello, G. Integration of persistent scatterer interferometry and ground data for landslide monitoring: The Pianello landslide (Bovino, Southern Italy). Landslides 2019, 16, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Vannocci, P.; Tofani, V.; Gigli, G.; Casagli, N. Landslide characterization using satellite interferometry (PSI), geotechnical investigations and numerical modelling: The case study of Ricasoli Village (Italy). Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolesini, T.; Frodella, W.; Bianchini, S.; Casagli, N. Detecting slope and urban potential unstable areas by means of multi-platform remote sensing techniques: The Volterra (Italy) case study. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confuorto, P.; Di Martire, D.; Infante, D.; Novellino, A.; Papa, R.; Calcaterra, D.; Ramondini, M. Monitoring of remedial works performance on landslide-affected areas through ground-and satellite-based techniques. Catena 2019, 178, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Montalti, R.; Ferretti, A.; Pellegrineschi, V.; Casagli, N. Monitoring Ground Instabilities Using SAR Satellite Data: A Practical Approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, C.; Crosta, G.B. Large sackung along major tectonic features in the Central Italian Alps. Eng. Geol. 2006, 83, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfo, L.; Brunetti, A.; Bozzano, F.; Bratus, A.; Busnardo, E.; Floris, M.; Genevois, R.; Mazzanti, P.; Saporito, F. The Ligosullo (UD, Italy) Landslide, Revisiting of Past Data and Prospects from Monitoring Activities. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 5; Lollino, G., Manconi, A., Guzzetti, F., Culshaw, M., Bobrowsky, P., Luino, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Delle Piane, L.; Perello, P.; Baietto, A.; Giorza, A.; Musso, A.; Gabriele, P.; Baster, I. Mature vs. active deep-seated landslides: A comparison through two case histories in the Alps. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 2189–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, A.; Del Conte, S.; Larini, G.; Lopardo, L.; Malaguti, C.; Vescovi, P. Application of SqueeSAR™ to the Characterization of Deep Seated Gravitational Slope Deformations: The Berceto Case Study (Parma, Italy). In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Schlögel, R.; Thiebes, B.; Toschi, I.; Zieher, T.; Darvishi, M.; Kofler, C. Sensor data integration for landslide monitoring—The LEMONADE concept. In Proceedings of the Workshop on World Landslide Forum, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 29 May–2 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Pappalardo, G.; Mineo, S.; Angrisani, A.C.; Di Martire, D.; Calcaterra, D. Combining field data with infrared thermography and DInSAR surveys to evaluate the activity of landslides: The case study of Randazzo Landslide (NE Sicily). Landslides 2018, 15, 2173–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Soldato, M.; Montalti, R.; Solari, L.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. Persistent Scatterers continuous streaming for landslide monitoring and mapping: The case of the Tuscany region (Italy). Landslides 2019, 16, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Asch, T.W.; Malet, J.P.; van Beek, L.P.; Amitrano, D. Techniques, issues and advances in numerical modelling of landslide hazard. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2007, 178, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Ardizzone, F.; Cardinali, M.; Galli, M. Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, P.; Rossi, M.; Malamud, B.D.; Mihir, M.; Guzzetti, F. A review of statistically-based landslide susceptibility models. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 180, 60–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinetti, C.; Bisson, M.; Tolomei, C.; Colini, L.; Galvani, A.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M.; Sepe, V. Landslide susceptibility mapping by remote sensing and geomorphological data: Case studies on the Sorrentina Peninsula (Southern Italy). GISci. Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 940–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Ferlisi, S.; Nicodemo, G.; Reale, D.; Pisciotta, G.; Gullà, G. Empirical fragility and vulnerability curves for buildings exposed to slow-moving landslides at medium and large scales. Landslides 2017, 14, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Poggi, F.; Raspini, F.; Tomás, R.; Fanti, R.; Casagli, N. Landslide-Induced Damage Probability Estimation Coupling InSAR and Field Survey Data by Fragility Curves. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Di Martire, D.; Confuorto, P.; Tessitore, S.; Tòmas, R.; Calcaterra, D.; Ramondini, M. Assessment of building behavior in slow-moving landslide-affected areas through DInSAR data and structural analysis. Eng. Struct. 2019, 199, 109638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Cigna, F.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Liguori, V.; Casagli, N. Integrated geomorphological mapping in the north-western sector of Agrigento (Italy). J. Maps 2012, 8, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Tofani, V.; Tanteri, L.; Tacconi Stefanelli, C.; Agostini, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. The new landslide inventory of Tuscany (Italy) updated with PS-InSAR: Geomorphological features and landslide distribution. Landslides 2018, 15, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangioni, S.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. Landslide inventory updating by means of Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI): The Setta basin (Italy) case study. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2015, 6, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonielli, B.; Mazzanti, P.; Rocca, A.; Bozzano, F.; Dei Cas, L. A-DInSAR Performance for Updating Landslide Inventory in Mountain Areas: An Example from Lombardy Region (Italy). Geosciences 2019, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Peduto, D. Advanced low-and full-resolution DInSAR map generation for slow-moving landslide analysis at different scales. Eng. Geol. 2010, 112, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P.; Agliardi, F. Deep seated gravitational slope deformations in the European Alps. Tectonophysics 2013, 605, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccolato, M.; Paganone, M. Grandi Frane Permanenti Complesse—Schede Monografiche di Frane in Valle d’Aosta Analizzate con Tecnica PS. Attività B2/C2 Rischi Idrogeologici e da Fenomeni Gravitative—Progetto Strategico Interreg IVa Risknat (In Italian). 2012. Available online: http://www.risknet-alcotra.org/rna/allegati/risknat-b2-c2-schede-frane-vda_1023.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Stramondo, S.; Saroli, M.; Moro, M.; Atzori, S.; Tolomei, C.; Salvi, S.; Lanari, R. Monitoring long-term ground movements and Deep Seated Gravitational Slope Deformations by InSAR time series: Cases studies in Italy. In Proceedings of the Fringe 2005 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 28 November–2 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cappadonia, C.; Confuorto, P.; Sepe, C.; Di Martire, D. Preliminary results of a geomorphological and DInSAR characterization of a recently identified Deep-Seated Gravitational Slope Deformation in Sicily (Southern Italy). Rend. Online Soc. Geol. Ital. 2019, 49, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Bovenga, F.; Refice, A.; Wasowski, J.; Chiaradia, M.T. C/X-band SAR interferometry applied to ground monitoring: Examples and new potential. In Proceedings of the SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XIII, Dresden, Germany, 25–26 September 2013; Notarnicola, C., Ed.; SPIE, International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8891, p. 88910C. [Google Scholar]
- Nutricato, R.; Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F.; Refice, A.; Pasquariello, G.; Nitti, D.O.; Chiaradia, M.T. C/X-band SAR interferometry used to monitor slope instability in Daunia, Italy. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Crosetto, M.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Luzi, G.; Crippa, B. Sentinel-1 data analysis for landslide detection and mapping: First experiences in Italy and Spain. In Proceedings of the Workshop on World Landslide Forum, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 29 May–2 June 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, M.; Saroli, M.; Salvi, S.; Stramondo, S.; Doumaz, F. The relationship between seismic deformation and deep-seated gravitational movements during the 1997 Umbria–Marche (Central Italy) earthquakes. Geomorphology 2007, 89, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoni, L.; Ronchetti, F.; Corsini, A.; Mongiovì, L. Interaction of extremely slow landslides with transport structures in the alpine glacial Isarco valley. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 2; Lollino, G., Giordan, D., Crosta, G.B., Corominas, J., Azzam, R., Wasowski, J., Sciarra, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Barra, A.; Solari, L.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Monserrat, O.; Bianchini, S.; Herrera, G.; Crosetto, M.; Sarro, R.; Alonso, E.G.; Mateos, R.M.; et al. A methodology to detect and update active deformation areas based on sentinel-1 SAR images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastonchi, L.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Luzi, G.; Solari, L.; Tofani, V. Satellite data to improve the knowledge of geohazards in world heritage sites. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalti, R.; Solari, L.; Bianchini, S.; Del Soldato, M.; Raspini, F.; Casagli, N. A Sentinel-1-based clustering analysis for geo-hazards mitigation at regional scale: A case study in Central Italy. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 2257–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Pagán, J.I.; Navarro, J.A.; Cano, M.; Pastor, J.L.; Riquelme, A.; Cuevas-González, M.; Crosetto, M.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; et al. Semi-automatic identification and pre-screening of geological–geotechnical deformational processes using persistent scatterer interferometry datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, G.; Scepi, G. A clustering approach for studying ground deformation trends in Campania region through PS-InSAR TM time series analysis. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Bai, S.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. Landslides detection through optimized hot spot analysis on persistent scatterers and distributed scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2019, 156, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrieri, E.; Carlà, T.; Gigli, G. Forecasting the time of failure of landslides at slope-scale: A literature review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 193, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T.; Intrieri, E.; Raspini, F.; Bardi, F.; Farina, P.; Ferretti, A.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Casagli, N. Perspectives on the prediction of catastrophic slope failures from satellite InSAR. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Del Ventisette, C.; Liguori, V.; Casagli, N.; Lasaponara, R.; Vlcko, J.; Meisina, C. Advanced radar-interpretation of InSAR time series for mapping and characterization of geological processes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D.; Casagli, N. Semi-automated extraction of Deviation Indexes (DI) from satellite Persistent Scatterers time series: Tests on sedimentary volcanism and tectonically-induced motions. Nonlinear Proc. Geophys. 2012, 19, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Novali, F.; Del Conte, S.; Rucci, A.; Ferretti, A.; Casagli, N. Continuous, semi-automatic monitoring of ground deformation using Sentinel-1 satellites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martire, D.; Tessitore, S.; Brancato, D.; Ciminelli, M.G.; Costabile, S.; Costantini, M.; Graziano, G.V.; Minati, F.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Landslide detection integrated system (LaDIS) based on in-situ and satellite SAR interferometry measurements. Catena 2016, 137, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Sunar, F.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E. Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 115, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Belmonte, A.; Refice, A.; Pasquariello, G.; Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Chiaradia, M.T. Performance analysis of satellite missions for multi-temporal SAR interferometry. Sensors 2018, 18, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruden, D.M.; Varnes, D.J. Landslides: Investigation and mitigation. In Chapter 3. Landslide Types and Processes; Transportation Research Board Special Report 247; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Di Martire, D.; Paci, M.; Confuorto, P.; Costabile, S.; Guastaferro, F.; Verta, A.; Calcaterra, D. A nation-wide system for landslide mapping and risk management in Italy: The second Not-ordinary Plan of Environmental Remote Sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2017, 63, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierdicca, N.; Davidson, M.; Chini, M.; Dierking, W.; Djavidnia, S.; Haarpaintner, J.; Hajduch, G.; Laurin, G.V.; Lavalle, M.; López-Martínez, C.; et al. The Copernicus L-band SAR mission ROSE-L (Radar Observing System for Europe). In Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring III; Notarnicola, C., Pierdicca, N., Bovenga, F., Santi, E., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 11154, p. 111540E. [Google Scholar]
- Comerci, V.; Vittori, E. The Need for a Standardized Methodology for Quantitative Assessment of Natural and Anthropogenic Land Subsidence: The Agosta (Italy) Gas Field Case. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehls, J.F.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Lauknes, T.R.; Stødle, D.; Moldestad, D.A. INSAR.No: A National Insar Deformation Mapping/Monitoring Service in Norway--From Concept To Operations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 5461–5464. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, A.C.; Frei, M.; Lege, T. A Copernicus downstream-service for the nationwide monitoring of surface displacements in Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Dehls, J.F.; Bredal, M.; Bishop, C.; Jøkulsson, G.; Gjøvik, L.P.; Frauenfelder, R.; Salazar, S.E.; Vöge, M.; et al. European Ground Motion Service: Service Implementation; Copernicus Land Monitoring Service: European Environment Agency, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020; Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/egms-specification-and-implementation-plan (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Frei, M.; Members of the EU-GMS Task Force. European Ground Motion Service (EU-GMS): A proposed Copernicus Service Element. 2017. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/egms-white-paper (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- G-CLASS Hydroterra: An Earth Explorer Mission for Water Cycle Science. Available online: https://www.nceo.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Stephen-Hobbs-G-CLASS-Hydroterra.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2020).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).