Assessing the Applicability of Mobile Laser Scanning for Mapping Forest Roads in the Republic of Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Descriptions
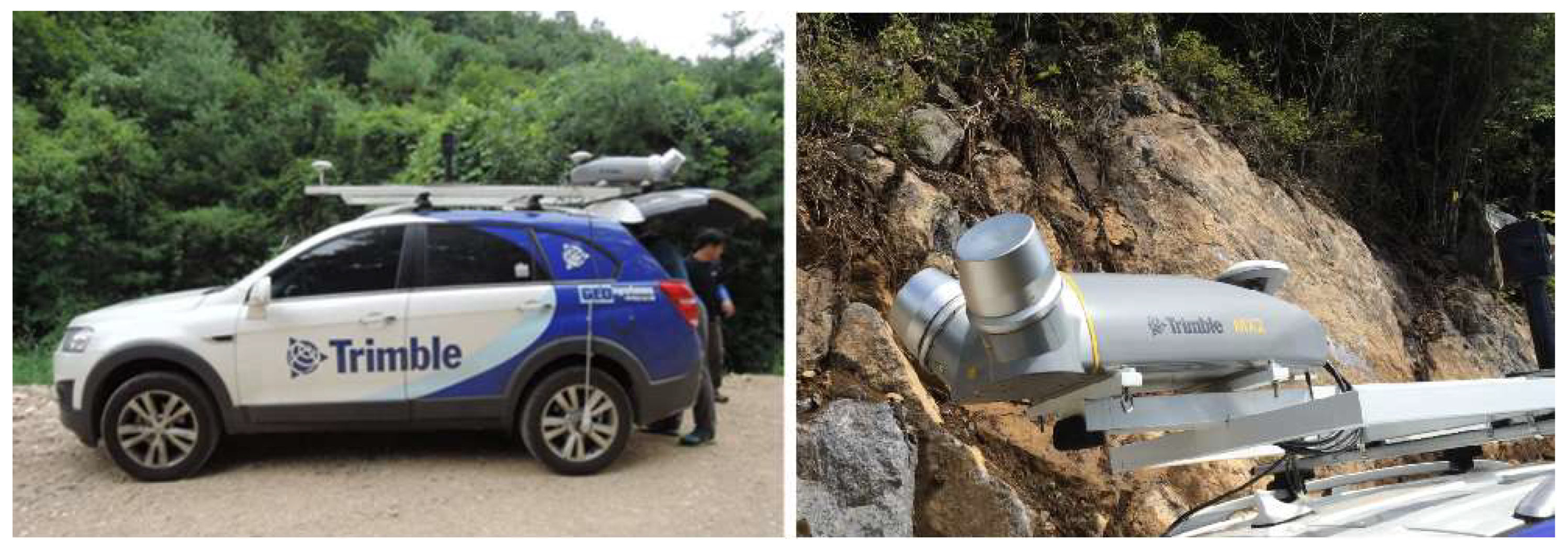
2.2. Collection and Mapping of MLS Data
2.3. Collection and Mapping of TS and GNSS Data
2.4. Comparison of the Relative Positional Accuracy on MLS, TS, and GNSS Data
2.5. Comparison of the Mapping Time and Cost Using MLS, TS, and GNSS
3. Results
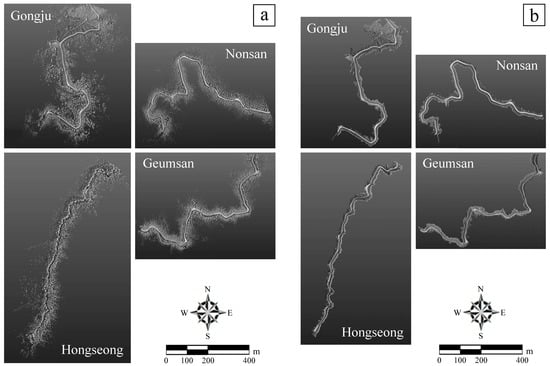
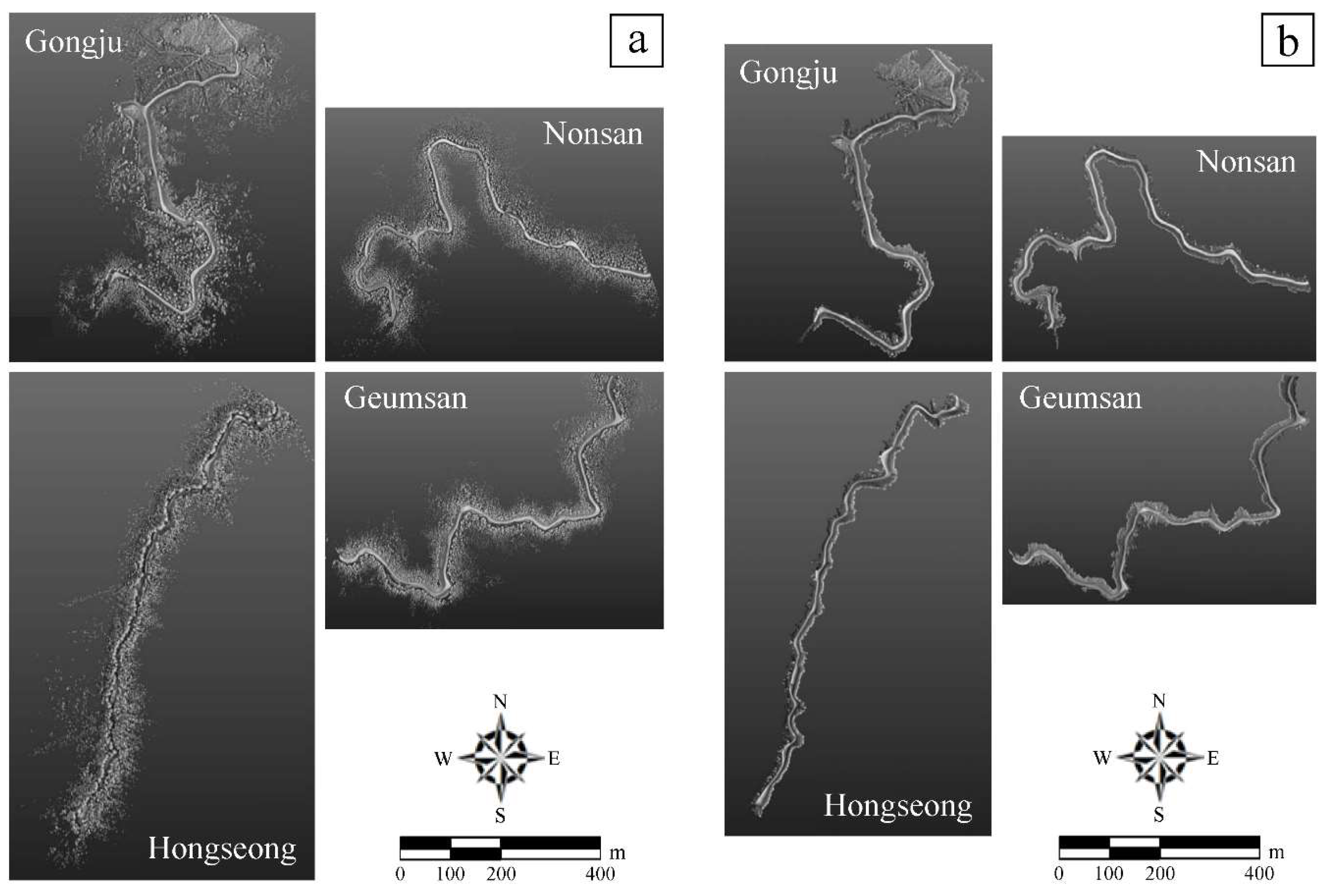
3.1. 3D Forest Road Maps Created Using MLS and The Degree of Precision Density
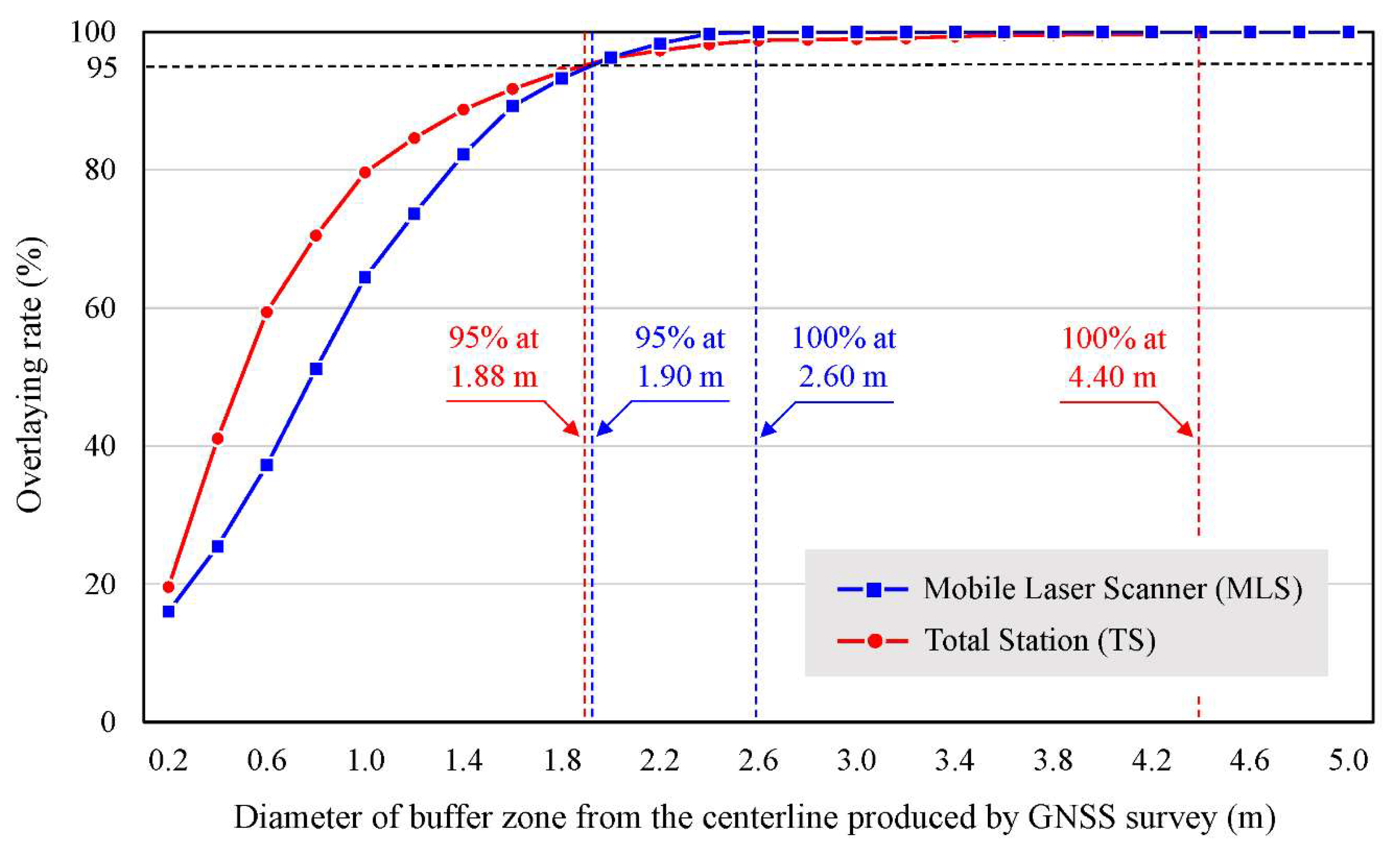
3.2. Relative Positional Accuracy Estimated from MLS, TS, and GNSS Data
3.3. Estimated Mapping Time and Cost Using MLS, TS, and GNSS
4. Discussion
4.1. Precision Density of Mapping by the MLS Survey
4.2. Relative Positional Accuracy of the MLS Map
4.3. Efficiency of MLS Mapping for Forest Road Inventory
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdi, E.; Sisakht, L.; Goushbor, L.; Soufi, H. Accuracy assessment of GPS and surveying technique in forest road mapping. Ann. For. Res. 2012, 55, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Talebi, M.; Majnounian, B.; Abdi, E.; Tehrani, F.B. Developing a GIS database for forest road management in Arasbaran forest, Iran. For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 11, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.A.; Dietterick, B.C.; Mastin, T.; Strohman, R. Forest roads mapped using LiDAR in steep forested terrain. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1120–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laschi, A.; Foderi, C.; Fabiano, F.; Neri, F.; Cambi, M.; Mariotti, B.; Marchi, E. Forest road planning, construction and maintenance to improve forest fire fighting: A review. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2019, 40, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kweon, H. Comparisons of estimated circuity factor of forest roads with different vertical heights in mountainous areas, Republic of Korea. Forests 2019, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kweon, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.-W.; Seo, J.I.; Rhee, H. Comparison of horizontal accuracy, shape similarity and cost of three different road mapping technique. Forests 2019, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, K.; Malinen, J.; Tokola, T. Forest road quality control using ALS data. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhle, J.; Höhle, M. Accuracy assessment of digital elevation models by means of robust statistical methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2009, 64, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stereńczak, K.; Kozak, J. Evaluation of digital terrain models generated from airborne laser scanning data under forest conditions. Scand. J. For. Res. 2011, 26, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, M.; Yurtseven, H.; Akburak, S.; Demir, M.; Cigizoglu, H.K.; Ozturk, T.; Eksi, M.; Akay, A.O. Short term moniterning of forest road pavement degradation using terrestrial laser scanning. Measurement 2017, 103, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.O.; Akgul, M.; Demir, M. Determination of temporal changes in forest road pavement with terrestrial laser scanner. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Hyyppa, J.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Yu, X. The use of a mobile scanning system for mapping large forest plots. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Agostino, M.; Lingua, A.; Piras, M. Rock face surveys using a LiDAR MMS. Ital. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 44, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R. An Object-based hierarchical method for change detection using unmanned aerial vehicle images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7911–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čerňava, J.; Mokroš, M.; Tuček, J.; Antal, M.; Slatkovská, Z. Processing chain for estimation of tree diameter from GNSS-IMU-based mobile laser scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, K.P.; Lapucha, D.; Cannon, M.E.; Martell, H. The use of GPS/INS in a highway inventory system. In Proceedings of the FIG XIX Congress, Helsinki, Finland, 10–19 May 1990; Volume 5, pp. 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, I. Method for Improving the Integrity of the Data from Land-Based Mobile Mapping System to Create Multipurpose Precise Road Map. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Seoul, Seoul-si, Korea, 2013. (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Grejner-Brzezinska, D.; Toth, C.; Yi, Y. On improving navigation accuracy of GPS/INS systems. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 4, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Gruen, A. 3D change detection at street level using mobile laser scanning point clouds and terrestrial images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 90, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Ji, S.; Shan, J.; Gong, J.; Liu, K. Line-based registration of panoramic images and LiDAR point clouds for mobile mapping. Sensors 2017, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Chapman, M.A. Mobile laser scanned point-clouds for road object detection and extraction: A review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y. A Study on Calibration Method of Vehicle-Based Mobile Mapping System. Master’s Thesis, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon-si, Korea, 2011. (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Khoramshahi, E.; Hakala, T.; Hyyppä, J.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, H. SLAM-aided stem mapping for forest inventory with small-footprint mobile LiDAR. Forests 2015, 6, 4588–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsman, M.; Holmgren, J.; Olofsson, K. tree stem diameter estimation from mobile laser scanning using and hyperspectral data. Sensors 2011, 11, 5158–5182. [Google Scholar]
- Buwens, S.; Bartholomeus, H.; Calders, K.; Lejeune, P. Forest inventory with terrestrial LiDAR: A Comparison of static and hand-held mobile laser scanning. Forests 2016, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korea Forest Service (KFS). Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/DRF/MDRFLawService.do?OC=foalaw&ID=10317 (accessed on 5 August 2019).
- Trimble Korea. Available online: https://geospatial.trimble.com (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Spectra. Available online: https://spectrageospatial.com/ (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Kagawa, Y.; Sekimoto, Y.; Shibasaki, R. Comparative study of positional accuracy evaluation of line data. In Proceedings of the 20th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Hong Kong, China, 22–25 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ömer, M.; Ayhan, C. Accuracy and cost comparison of spatial data acquisition methods for the development of geographical information systems. J. Geogr. Reg. Plan. 2009, 2, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Kweon, H.; Choi, Y.; Yeom, I.; Lee, J. Evaluation of horizontal position accuracy in forest road completion drawing. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 37, 471–479, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yurtseven, H.; Akgul, M.; Akay, A.O. High accuracy monitoring system to estimate forest road surface degradation on horizontal curves. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velkamp, R.C. Shape matching: Similarity measures and algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications, Genova, Italy, 7–11 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Balenović, I.; Gašparović, M.; Milas, A.S.; Seletković, A.B. Accuracy assessment of digital terrain models of lowland pedunculate oak forests derived from airborne laser scanning and photogrammetry. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2018, 39, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Arastounia, M. Automated recognition of railroad infrastructure in rural areas from LIDAR data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14916–14938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, M.; Sui, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, N. Recovering missing tracjectory data for mobile laser scanning systems. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Index | Study Area | Road Length Surveyed (m) | Altitude above Sea Level (m) | Construction Year | Forest Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | |||||
| A | Gongju | 1022 | 439.1 | 450.8 | 2017 | Mixed forest |
| B | Nonsan | 1015 | 127.9 | 190.6 | 2017 | Mixed forest |
| C | Hongseoung | 1019 | 135.4 | 154.7 | 2018 | Mixed forest |
| D | Geumsan | 1019 | 424.5 | 459.2 | 2017 | Mixed forest |
| Mobile Laser Scanning (MLS) Trimble MX2 | |
|---|---|
| Type | Single or dual SLM-250 Class 1 lasers |
| Range | Up to 250 m |
| Accuracy | ±1 cm at 50 m |
| Scanner FOV | 360 degrees |
| Scan rate | Dual laser head: 2 × 20 Hz (1200 rpm) |
| Maximum effective measurement rate | Single laser head: 36,000 points per second Dual laser head: 72,000 points per second |
| Pulse rate | Dual laser head: 2 × 36 kHz |
| TS (Nikon NPL 352) | GNSS (Trimble R8) | |
|---|---|---|
| Operating temperature | –40 to +60 °C | –40 to +65 °C |
| Distance measurement | 1.6 to 200 m | - |
| Weight | 5.5 kg | 1.52 kg |
| Accuracy | x : 3 mm y : 3 mm z : 3 mm | x : 8 mm y : 8 mm z : 15 mm |
| Study Road | Number of Point Data (point/km) | Point Data Loss by Excluding Vegetation Information (point/km, %) | Forest Road Area in the Final 3D Map (m2/km) | Unit Point Number in the Final 3D Map (point/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial 3D Map | Final 3D Map | ||||
| Gongju | 26,310,704 | 9,729,385 | 16,581,319 (63.0) | 12,427.4 | 782.9 |
| Nonsan | 33,920,193 | 10,174,684 | 23,745,509 (70.0) | 13,480.0 | 754.8 |
| Hongseong | 36,070,736 | 8,971,478 | 27,099,258 (75.1) | 12,360.8 | 725.8 |
| Geumsan | 37,813,718 | 17,237,514 | 20,576,204 (54.4) | 13,797.7 | 1249.3 |
| Mean | 33,528,838 | 11,528,265 | 22,000,573 (65.6) | 13,016.5 | 878.2 |
| Study Road | Road Length (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS | MLS | MLS–GNSS | TS | TS–GNSS | |
| Gongju | 1022.2 | 1022.3 | 0.1 | 1025.1 | 2.9 |
| Nonsan | 1015.1 | 1015.8 | 0.7 | 1019.8 | 4.7 |
| Hongseong | 1019.2 | 1019.7 | 0.5 | 1021.3 | 2.1 |
| Geumsan | 1019.4 | 1019.6 | 0.2 | 1023.2 | 3.8 |
| Mean | 0.4 | 3.4 | |||
| Survey Method | Total (n = 200) | Gongju (n = 50) | Nonsan (n = 50) | Hongseong (n = 50) | Geumsan (n = 50) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| MLS | 0.802 | 0.473 | 0.685 | 0.328 | 0.745 | 0.364 | 0.961 | 0.481 | 0.817 | 0.631 |
| TS | 0.716 | 0.593 | 0.553 | 0.401 | 0.815 | 0.642 | 0.868 | 0.724 | 0.625 | 0.501 |
| t | 1.778 | 1.801 | –0.833 | 0.828 | 1.796 | |||||
| p | 0.076 | 0.074 | 0.406 | 0.409 | 0.076 | |||||
| Survey Method | Work | Labor | Working time (min/km) | Labor Cost | Equipment Cost * (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit (USD/h) | Total (USD) | ||||||
| MLS | Field survey | 1 professional 1 assistant | 32 | 20.5 10.1 | 32.0 | 143.2 | 175.2 |
| Mapping | 1 technician | 64 | 15.2 | ||||
| TS | Field survey | 1 professional 2 assistants | 195 | 20.5 10.1 | 155.1 | 46.8 | 201.9 |
| Mapping | 1 technician | 118 | 15.2 | ||||
| GNSS | Field survey | 1 professional | 128 | 20.5 | 56.2 | 26.3 | 82.5 |
| Mapping | 1 technician | 60 | 15.2 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kweon, H.; Seo, J.I.; Lee, J.-W. Assessing the Applicability of Mobile Laser Scanning for Mapping Forest Roads in the Republic of Korea. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091502
Kweon H, Seo JI, Lee J-W. Assessing the Applicability of Mobile Laser Scanning for Mapping Forest Roads in the Republic of Korea. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(9):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091502
Chicago/Turabian StyleKweon, Hyeongkeun, Jung Il Seo, and Joon-Woo Lee. 2020. "Assessing the Applicability of Mobile Laser Scanning for Mapping Forest Roads in the Republic of Korea" Remote Sensing 12, no. 9: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091502
APA StyleKweon, H., Seo, J. I., & Lee, J.-W. (2020). Assessing the Applicability of Mobile Laser Scanning for Mapping Forest Roads in the Republic of Korea. Remote Sensing, 12(9), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091502