Abstract
Total variation (TV) is an effective super-resolution method to improve the azimuth resolution and preserve the contour information of the target in airborne radar imaging. However, the computational complexity is very high because of the matrix inversion, reaching . In this paper, a Gohberg–Semencul (GS) representation based fast TV (GSFTV) method is proposed to make up for the shortcoming. The proposed GSFTV method fist utilizes a one-dimensional TV norm as the regular term under regularization framework, which is conducive to achieve super-resolution while preserving the target contour. Then, aiming at the very high computational complexity caused by matrix inversion when minimizing the TV regularization problem, we use the low displacement rank feature of Toeplitz matrix to achieve fast inversion through GS representation. This reduces the computational complexity from to , benefiting efficiency improvement for airborne radar imaging. Finally, the simulation and real data processing results demonstrate that the proposed GSFTV method can simultaneously improve the resolution and preserve the target contour. Moreover, the very high computational efficiency of the proposed GSFTV method is tested by hardware platform.
1. Introduction
Airborne radar plays an important role in many fields for its all-day and all-weather imaging ability [1,2]. In general, airborne radar collects the echo through antenna scanning along with the platform movement. In range direction, the antenna continuously transmits a large bandwidth signal. After pulse compression, the range resolution is negatively correlated with the bandwidth, i.e.,
where is range resolution, c is light speed and B is the bandwidth of transmitted signal. Therefore, high range resolution can be achieved with large bandwidth signals. In azimuth, the resolution is limited to antenna size. According to Rayleigh criterion, the adjacent targets with an interval less than Rayleigh distance (RD) cannot be distinguished, where RD is the space between the peak of the antenna pattern and the first zero-crossing [3,4]. In order to distinguish adjacent targets with small spacing, radar needs to emit a narrow beam. However, narrower beams require a larger antenna aperture. Due to platform limitations, the antenna aperture of airborne radar is usually limited, resulting in lower azimuth resolution.
The application of super-resolution technology can make the resolution break Rayleigh limit [5,6], which makes it possible to improve the azimuth resolution without increasing the aperture of airborne radar. In fact, many super-resolution methods have been proposed in recent years. In [7], the Tikhonov regularization (TREGU) method was proposed to improve the resolution. However, this method encounters over smoothing, which makes the improvement of resolution limited. In [8], truncated singular value decomposition (TSVD) was utilized. This method suppresses the noise amplification by truncating small singular values, but its performance is poor in the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Iterative adaptive approach (IAA) can further suppresses noise, but it suffers from high computational complexity [9]. The sparse regularization method introduces the prior information of the target, and has a good effect of improving the resolution of the sparse target [10,11]. However, all of the above methods only consider the improvement of resolving ability, and do not consider the preservation of target contour information. Total variation (TV) method, which introduces the gradient constraint of targets, can effectively preserve the contour of targets. Recently, TV method has been widely used in imaging restor and radar imaging [12,13,14]. In [15], we proposed a one-dimensional TV method to improve the azimuth resolution of airborne radar. Unlike optical image restoration, in airborne radar imaging, range resolution has been improved by pulse compression, so the proposed TV method only introduces azimuth TV norm. The experiments show that the TV method can preserve the target contour information of airborne radar. However, the computational complexity is very high due to matrix inversion, and the computational complexity is . For airborne radar imaging, the azimuth samples N is determined by scanning range , scanning speed and pulse repetition frequency (PRF), i.e.,
Usually, N is large, which leads to the inefficiency of the algorithm. Therefore, it is necessary to study how to realize fast inversion to reduce the computational complexity.
In recent years, many researches have devoted to solve the problem of high computational complexity caused by matrix inversion. These methods utilized the special structure of coefficient matrix to achieve fast inversion, the computational complexity then can be decreased [16,17,18]. In previous research, we have found that the coefficient matrix of TV method has an approximate Toeplitz structure, which makes it possible to achieve fast inversion using the Toeplitz structure. In fact, literature [19] indicated the concepts of displacement structure and displacement rank, as well as revealing that the operation can be compressed by using a Toeplitz matrix. Subsequent research has proven that the displacement rank of a Toeplitz matrix is very small and, so, its inverse matrix also has a displacement structure, showing that the inversion of Toeplitz matrix can be fast realized [20]. Utilizing the low displacement rank features of Toeplitz matrices, the fast inversion of Toeplitz matrix has been achieved using Gohberg–Semencul (GS) representation [21,22].
In this paper, a GS representation based fast TV (GSFTV) method is proposed realize fast super-resolution imaging as well as preserve the contour information in airborne radar imaging. Firstly, the received signal of airborne radar is analyzed. It can be found that the azimuth echo can be modeled as a convolution of target scattering and antenna pattern. Secondly, the azimuth gradient constraint of the target is introduced in the regularization framework to transform the super-resolution problem into a TV regularization problem, and the TV regularization problem is solved by split Bregman algorithm (SBA). Thirdly, to solve the problem of high computational complexity caused by matrix inversion, we approximate the coefficient matrix to Toeplitz matrix, and use GS representation to realize fast inversion. The computational complexity will be decreased from to . Then we will prove that the error caused by the approximation is quite small and can be ignored through numerical analysis. Finally, the performance of the proposed GSFTV is demonstrated by experiments.
The reminder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 analyzes the received signal and models the echo model of airborne radar imaging. In Section 3, the traditional TV method is reviewed and the computational complexity is analyzed. In Section 4, the proposed GSFTV is deduced in detail. In Section 5, some experiments are conducted to verify the superior performance of the proposed GSFTV method. The conclusion is discussed in Section 6.
2. Signal Model of Airborne Radar Imaging
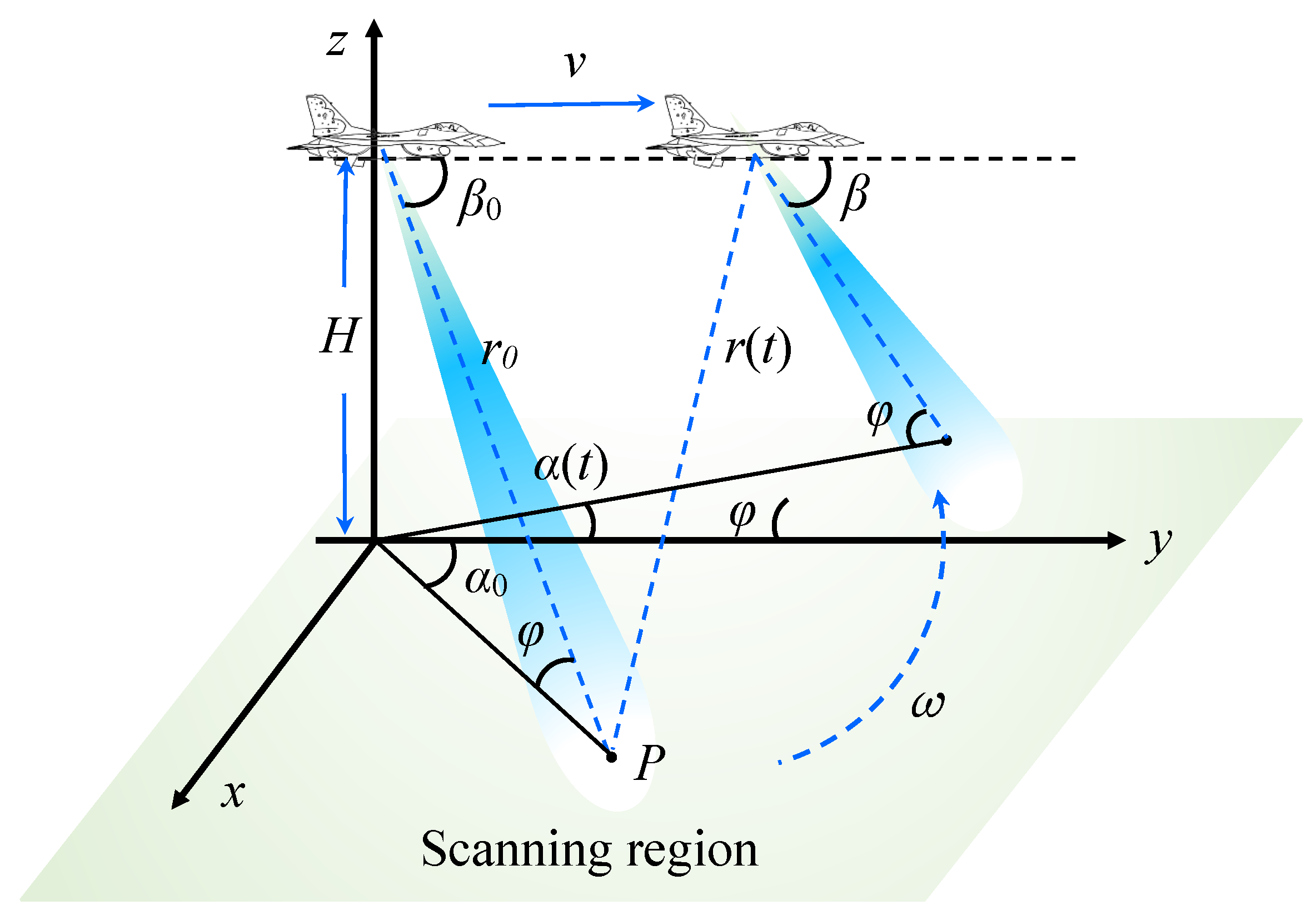
Airborne radar scans the imaging region along with the movement of the aircraft. The schematic diagram of airborne radar imaging is shown in Figure 1. The aircraft flies at altitude H and speed v. is the scanning speed of the antenna and is pitching angle. When the antenna is scanning the target P, we define the azimuthal angle is , and the distance between the target and the radar is . After time t, the radar moving distance is . At this time, the distance between radar and target P is , and the azimuth angle of the radar beam is with .
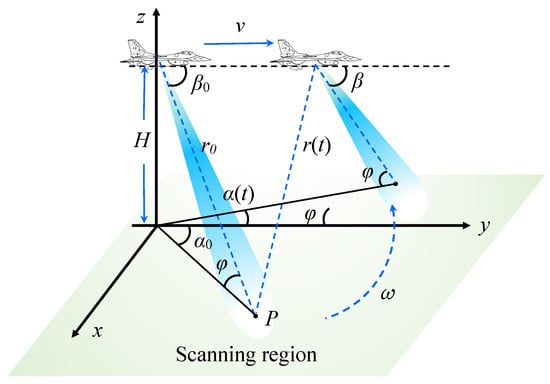
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of airborne radar scanning imaging.
According to the trigonometric relation, the range history at time t can be obtained as
where .
It can be approximated as
In practical applications, since the time for the antenna beam to sweep across the target is very short and the radar has a large working distance, the quadratic term in (4) is very small and can be ignored. Thus the range history can be finally approximated as
Considering both the range resolution and working distance, the radar transmits linear frequency modulated (LFM) signal, i.e.,
where rect is a rectangle window, is the fast time, is carry frequency and is chirp rate. After antenna scanning, the received signal is
where is the target scattering distribution, represents the modulation effect of antenna pattern and is time delay.
Matched filtering is a widely utilized technology to obtain high range resolution. After matched filtering, the received signal becomes
For airborne radar, antenna scanning is accompanied by platform movement, which results in the echo of the same range unit being dispersed in different units. Therefore, range walk correction is needed to eliminate the influence of platform motion. After that, the received echo can be modeled as a convolution of antenna pattern and target scattering distribution [3,23], i.e.,
where is the noise and is the convolution matrix structured by antenna pattern, i.e.,
Based on the convolution model of airborne radar imaging, the target distribution can be recovered by deconvolution, but this process is extremely ill-posed.
3. One-Dimensional TV Method
Aiming at the ill-posedness of deconvolution, the one-dimensional TV method is used to relax the ill-posedness, and the computational complexity is analyzed.
3.1. Deduction of the Method
TV method has been widely used in imaging restoration because it has a good effect in contour preservation. In airborne radar imaging, an one-dimensional TV method is proposed since the range resolution has been improved by matched filtering. The one-dimensional TV method requires minimizing following optimization problem,
where is regularization parameter.
For minimizing (10) using SBA, a variable is employed to decouple the and , i.e.,
We obtain a constrained optimization problem (11). Usually, it can be transformed into unconstrained optimization problem, i.e.,
where is a positive parameter.
Then based on Bregman distance, the iteration strategy is obtained [3],
It can be minimized by cross iteration:
where , , and
3.2. Analysis of Computational Complexity
Traditional TV method achieves super-resolution by iterating (14) to (16). However, the main computational complexity comes from (14). As for (15) and (16), they only cover simple basic operation, and their computational complexities are inappreciable compared with (14).
For (14), the iterations is K. First, we need to calculate one and , for which the computational complexities are and , respectively; where can be calculated by an N-point fast Fourier transform (FFT) as is a circular matrix. Secondly, for each iteration, the computational complexity of is . The computational complexity of is . Finally, the main computational complexity of traditional TV method is .
It can be seen that the computational complexity of traditional TV method is quite high, which will seriously affect the real-time performance of the algorithm in practical application.
4. Proposed GSFTV Method
To decrease the computational complexity of traditional TV method, the proposed GSFTV method is deduced in this section.
4.1. GSFTV Method
In view of the high computational complexity of tradition TV method comes from (14), we rewrite it as
where
and
From the structure of , we can obtain that the matrix also has Toeplitz structure. As for , it also can be regarded as a Toeplitz matrix by approximation, i.e.,
By approximation, has the Toeplitz structure, its inversion thus can be fast obtained by GS representation. The Levinson–Durbin algorithm is first utilized to obtain the autoregressive coefficients and prediction error from the YuleWalker-AR equations:
Then we can obtain that
Constructing matrixes
According to GS representation, the inversion of can be fast calculated, i.e.,
Finally, (19) can be obtained, i.e.,
As a result, the inversion of is avoid, and can be obtained by multiplying a matrix with a vector. We would indicate that the product of matrix and vector can be achieved by fast Fourier transform (FFT).
Define
According to the special structure of and , it can be seen that and can be obtained by intercepting the first N rows and the N to rows of and , respectively. Therefore, the multiplication of and a vector can be obtained by intercepting the 1 to N elements of the FFT of and the vector. As for the multiplication of and a vector, it can be obtained by the N to elements of the FFT of and the vector, where . In the same way, also can be obtained by two FFTs and truncations.
4.2. Analysis of Computational Complexity
The proposed GSFTV method realizes fast inversion of matrix by GS representation, that is, the target scattering distribution is estimated by iterating (27). Above analysis have indicated that it can be calculated by four-times operations of Toeplitz and vector, so the computational complexity is . Before that, the autoregressive coefficients and prediction error need to be obtained by Levinson–Durbin algorithm, and the computational complexity is . As a result, the computational complexity of the proposed GSFTV method is .
4.3. Selection of Parameters
Each regularization method need to determine the regularization parameter . In this paper, the regularization parameter is determined by combining maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation and noise estimation.
In radar imaging, usually the noise is Gaussian noise. With the assumption of Gaussian noise, we can obtain the likelihood function
where is the noise variance.
Let , then the target scattering distribution can be obtained by MAP estimation:
i.e.,
It can be found that (30) is equivalent to (10) when . Therefore, the regularization parameter can be determined by estimating the noise variance . In this paper, the variance is estimated by the method proposed in literature [24]. As for the parameter , a small means high resolution improvement, but poor contour preservation. In the research, the setting of between and works well.
4.4. Evaluation of Computational Efficiency
Utilizing GS representation, the computational complexity is decreased significantly. For comparison, the complexity is compared with some traditional super-resolution methods, including TSVD [8], IAA [9], sparse [25] and TV methods [15]. The computational complexities and the typical parameter values of different methods are listed in Table 1, where is the truncation parameter of TSVD, K is iterations.

Table 1.
Computational complexities of different methods.
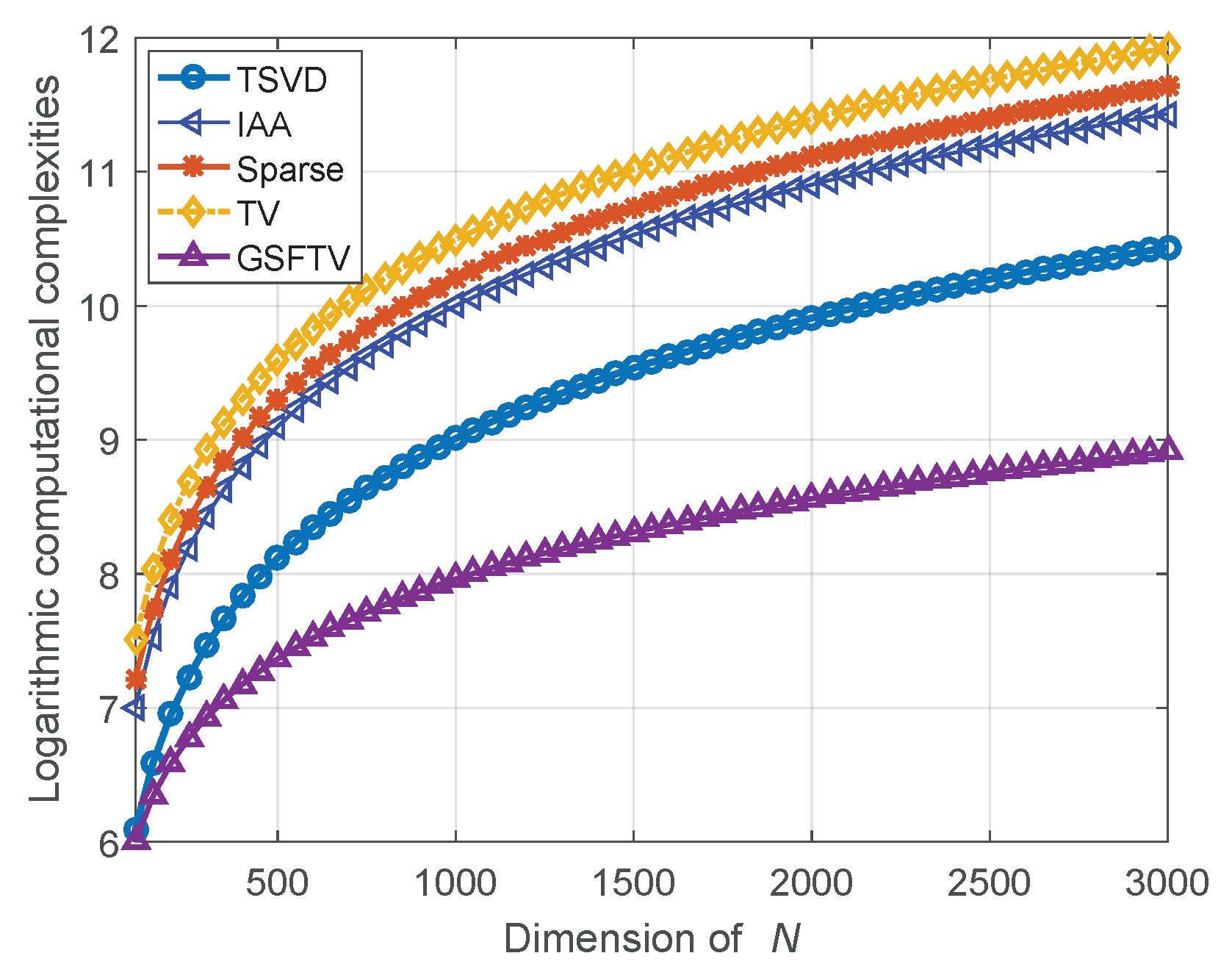
The logarithmic computational complexity curves are shown in Figure 2. It shows that the computational complexity of the proposed GSFTV method is much lower than that of other methods. Typically, when , the proposed GSFTV method improves the computational efficiency by 11, , and times, as compared with the TSVD, IAA, sparse and TV methods.
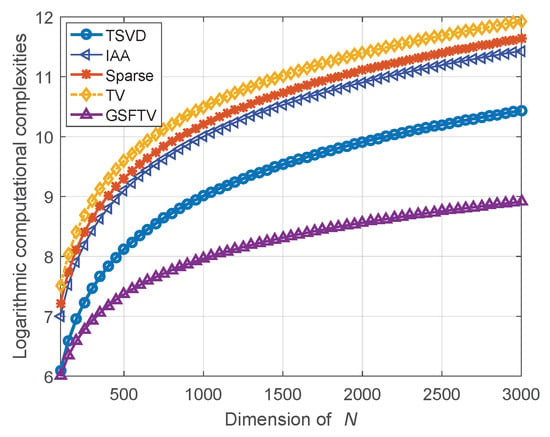
Figure 2.
Logarithmic computational complexity curves.
4.5. Evaluation of Approximated Error
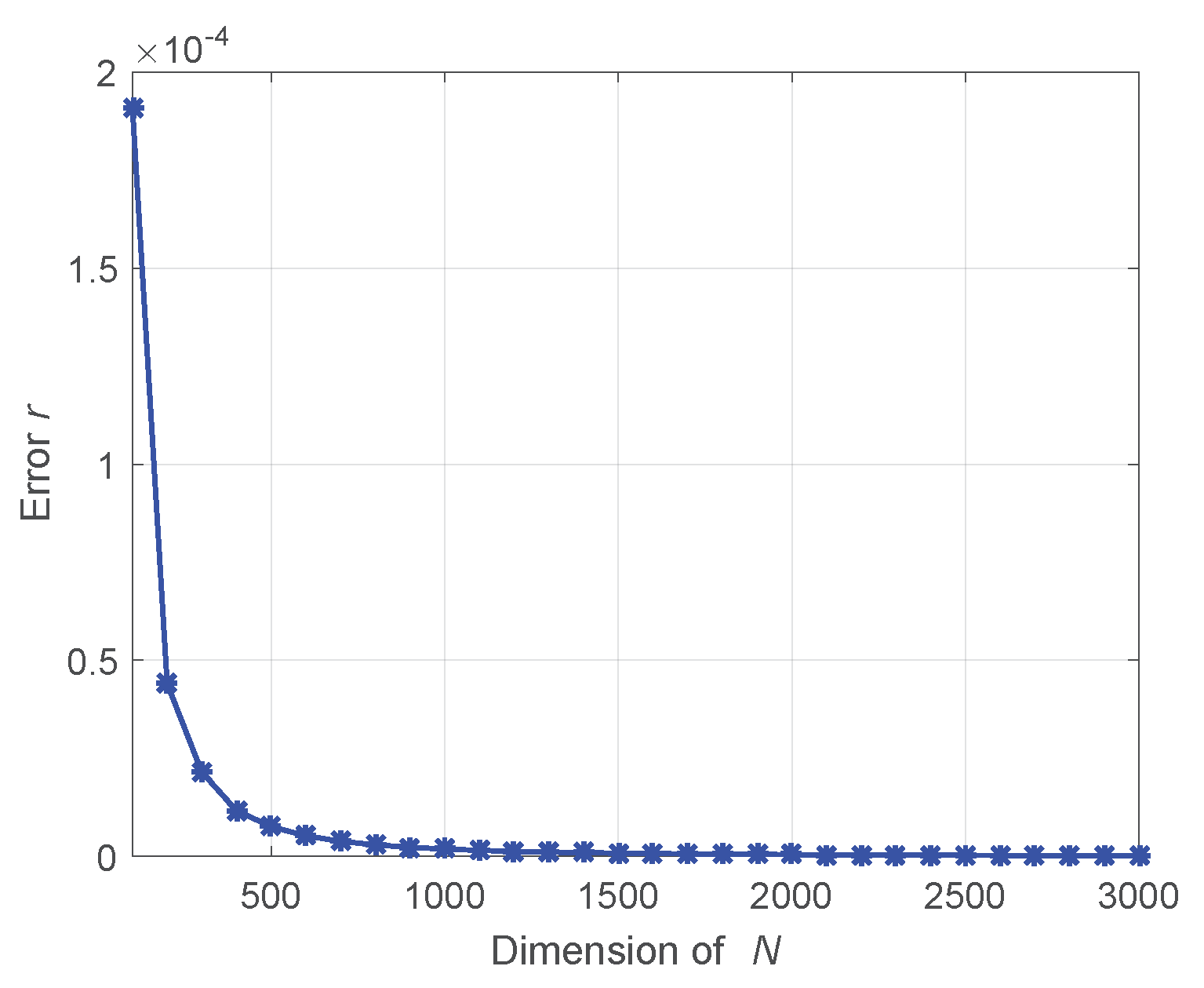
The logarithmic computational complexity curves demonstrate the great advantage of the proposed GSFTV method in computational complexity. However, in order to decrease the computational complexity, some approximations are also made, that is, is approximated by , which makes becomes . The error caused by the approximation is evaluated. The error is defined a
where r is the approximated error. The error curve with different N is shown in Figure 3. It shows that the approximated error is extremely small. Even when , the error lower than . And the error decreases with the increase of N. In radar imaging, usually the azimuth samples N is large, so the error can be ignored in practice.
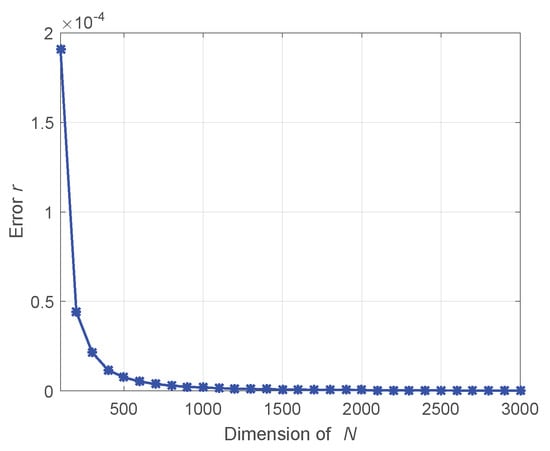
Figure 3.
Approximated error with different N.
5. Performance Verification
In this section, the performance of the proposed GSFTV method is demonstrated by experiments. We first conduct simulation and process real data on personal computer to demonstrate the performance of resolution improvement and contour preservation. Then, based on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), a hardware platform is built to evaluate the efficiency of the proposed GSFTV method.
5.1. Simulation
Considering both the resolution improvement and contour preservation, the real scene of the simulation covers two adjacent targets and one isolated target, as Figure 4 shows. The centers of the targets are located at , and , respectively. The width of them is . For the radar system, we assume that the radar works on X-band. The antenna pattern is a function, and its beamwidth is . Scanning region is , and PRF is 1000 Hz.
Figure 4.
Real scene of simulation.
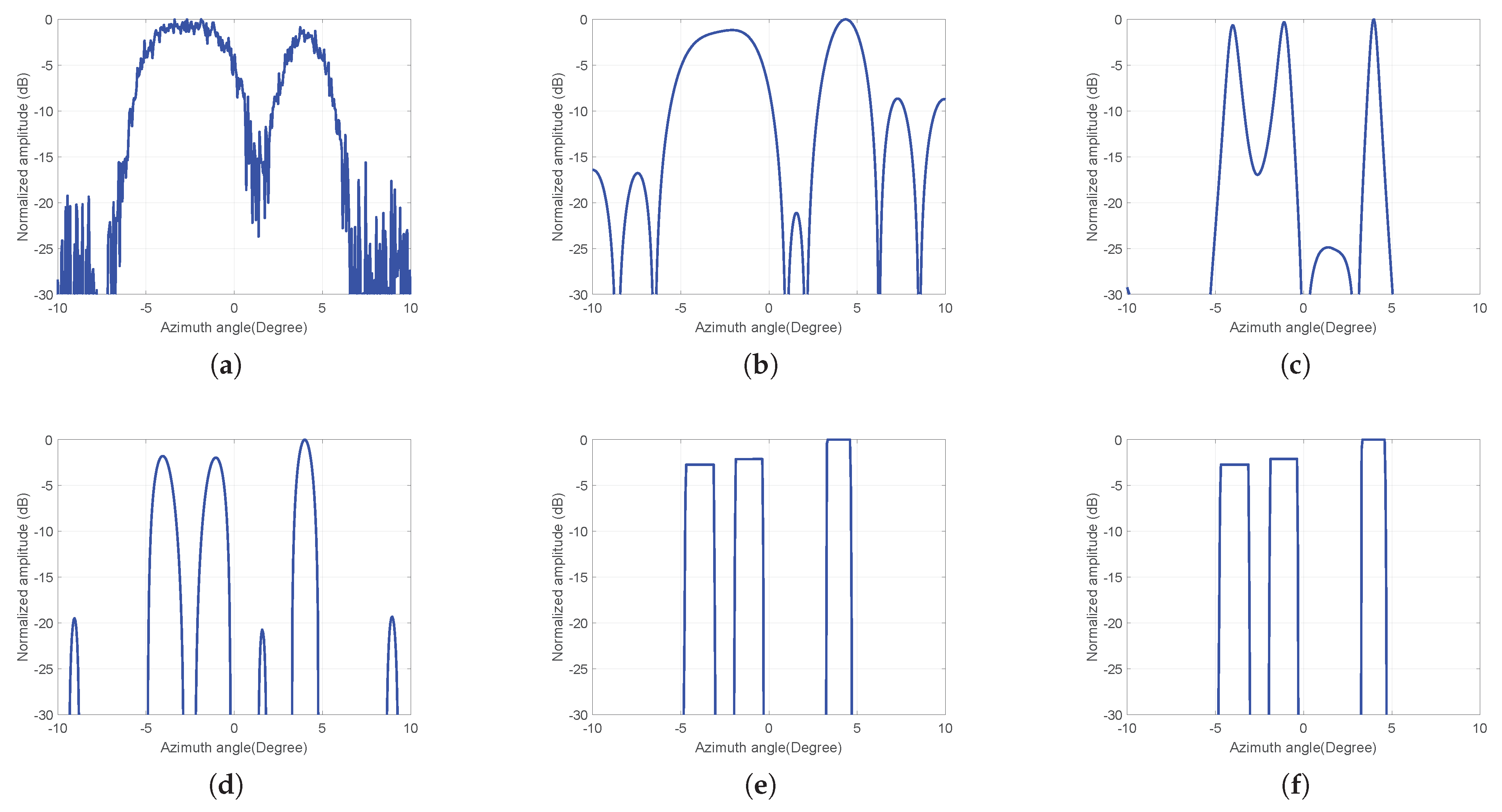
The left two adjacent targets are used to test the distinguishable ability. From the parameters, it can be seen that the interval of the adjacent targets is less than the beamwidth. So according to Rayleigh criterion, they will not be distinguished in real-beam echo. The real-beam echo is shown in Figure 5a. It can be seen that the isolated targets is distinguishable, but the adjacent targets are not. Certainly, in order to be close to practical application, white Gaussian noise is added in Figure 5a, and the SNR is 20 dB. The processed results of TSVD, IAA, Sparse, TV and GSFTV methods are shown in Figure 5b–f. It shows that TSVD smoothes the noise but cannot distinguish the adjacent targets. IAA and sparse methods can distinguish the adjacent targets, however, the contour information of targets cannot be preserved. TV and GSFTV can not only distinguish adjacent targets, but also preserve contour information.
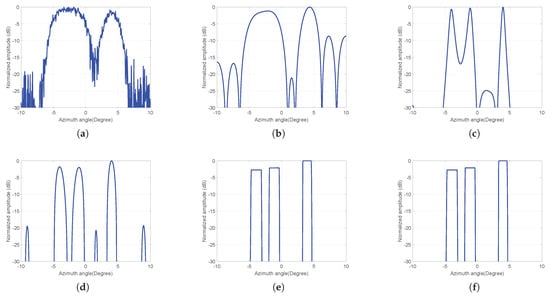
Figure 5.
Processed results of the simulation. (a) Real beam echo, (b) truncated singular value decomposition (TSVD), (c) iterative adaptive approach (IAA), (d) Sparse, (e) total variation (TV), (f) Gohberg–Semencul (GS) representation based fast TV (GSFTV).
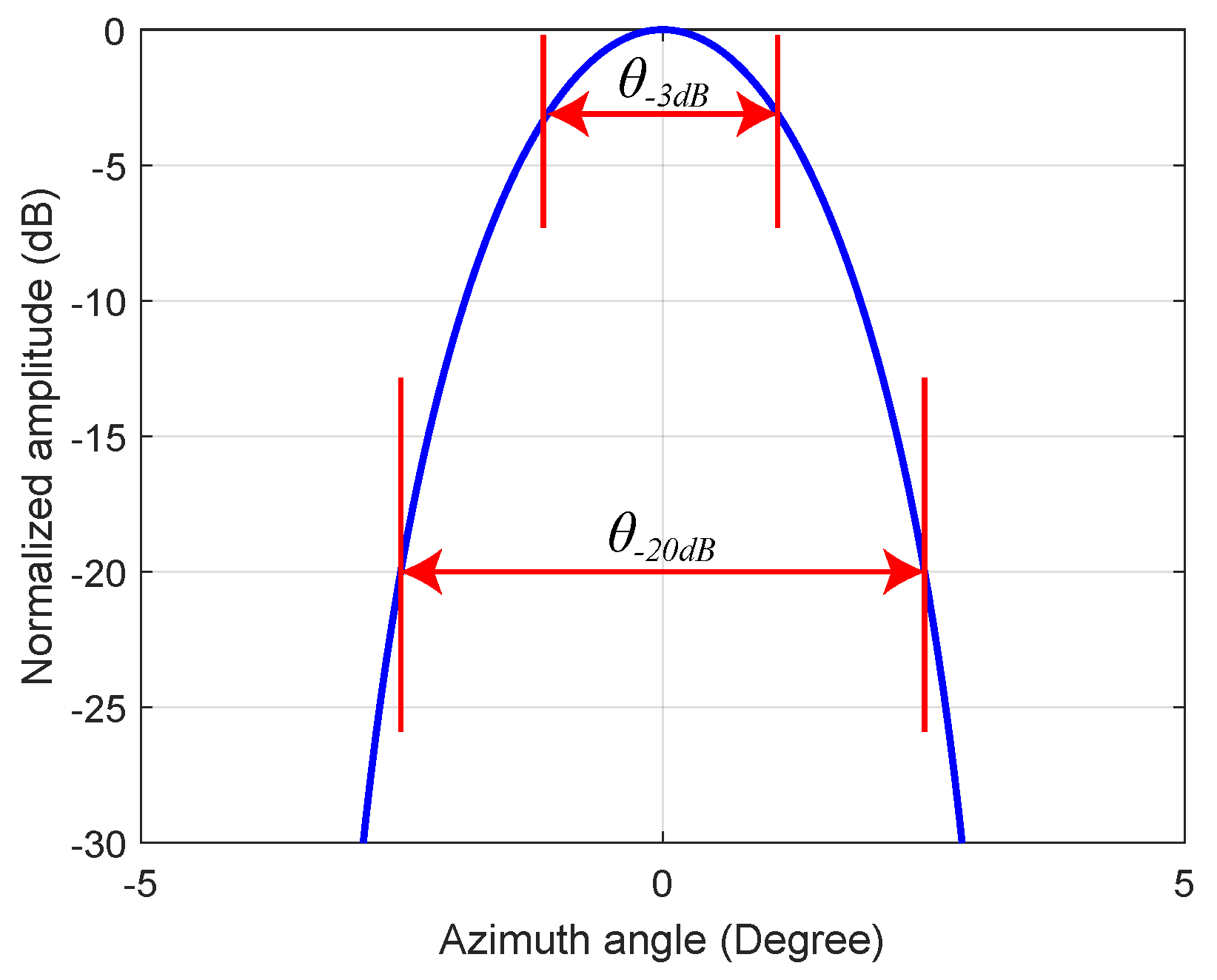
Intuitively, it can be found that TV and GSFTV methods can distinguish adjacent targets while preserving the target contour. Further, the isolated target is employed to verify the performance of contour preservation. For the purpose, we define the contour fidelity coefficient (CFC) as
where is CFC, and denotes the beam width at dB and dB, respectively. The definition of CFC can be visually seen in Figure 6. It can be known that the larger , the better the contour preservation ability.
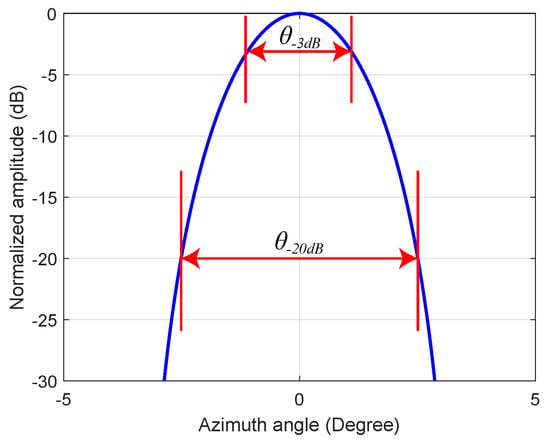
Figure 6.
Definition of contour fidelity coefficient (CFC).
The isolated target is employed to evaluate the contour preservation ability. The CFCs of the results processed by different methods are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that TSVD, RL, IAA and sparse methods have poor performance in contour preservation. Contrarily, the TV and GSFTV methods can greatly preserve the contour information of the targets. As for the GSFTV and TV methods, we can see that their CFCs are the same. Therefore, the proposed GSFTV method has no performance loss compared with the traditional TV method.

Table 2.
CFCs of simulation results.
In addition, we calculate the error between the processed results of TV and GSFTV to measure the error caused by the approximation. The error is defined as
where is the error between the results of GSFTV and TV methods, and are the estimation of GSFTV and TV methods, respectively. We calculate that for this simulation, . It can be seen that the error between the processed results of GSFTV and TV is very small and negligible, which proves that the approximation used in this paper will hardly cause performance degradation.
5.2. Real Data Verification
After simulation, two group of real data are processed to further verify the performance of the proposed GSFTV method.
5.2.1. Real Data 1
A airborne real data (We named it real data 1 for convenience) is processed to further demonstrate the performance of contour preservation in practice. The parameters of the experiment is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
System parameters of the real data.
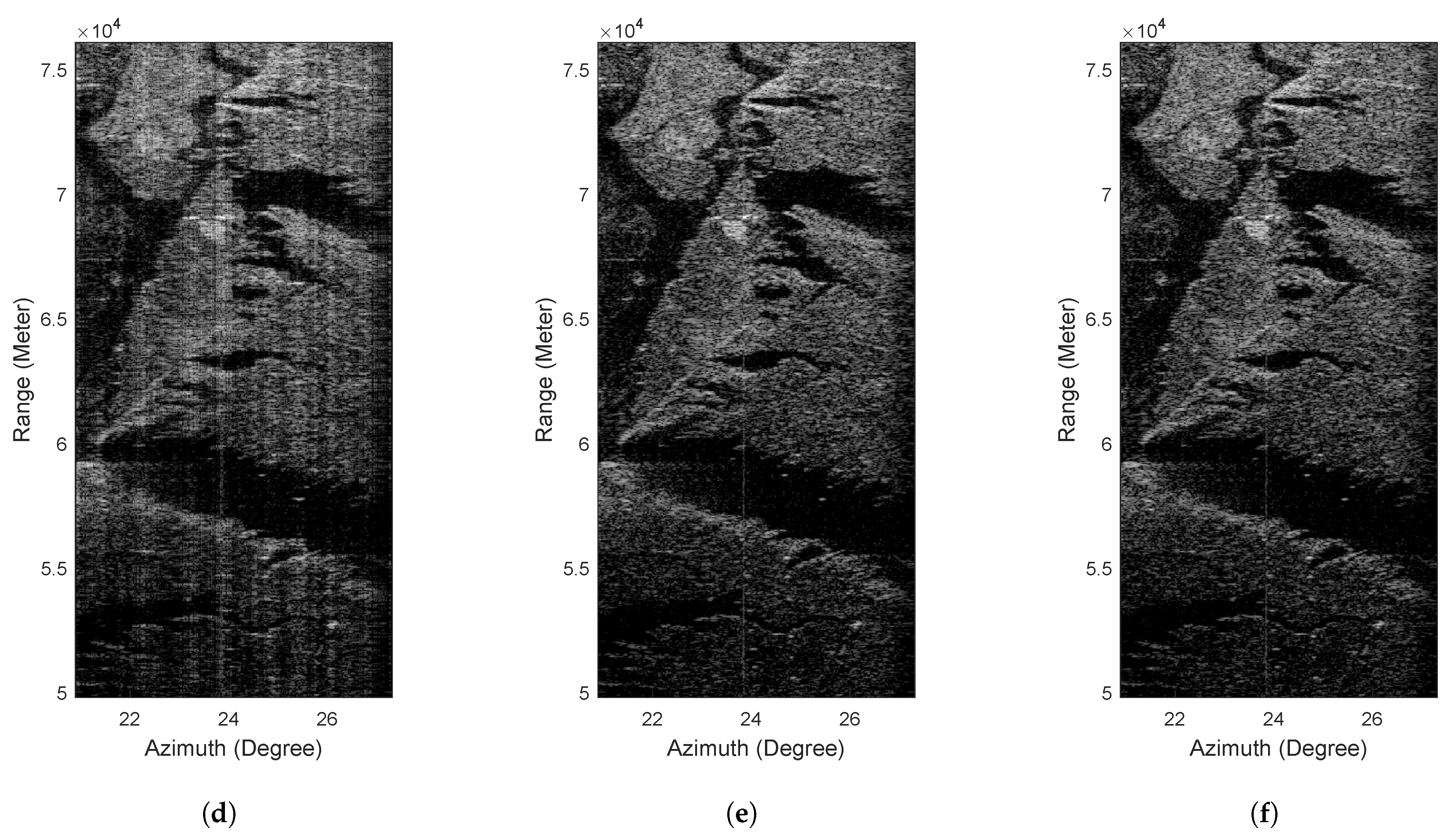
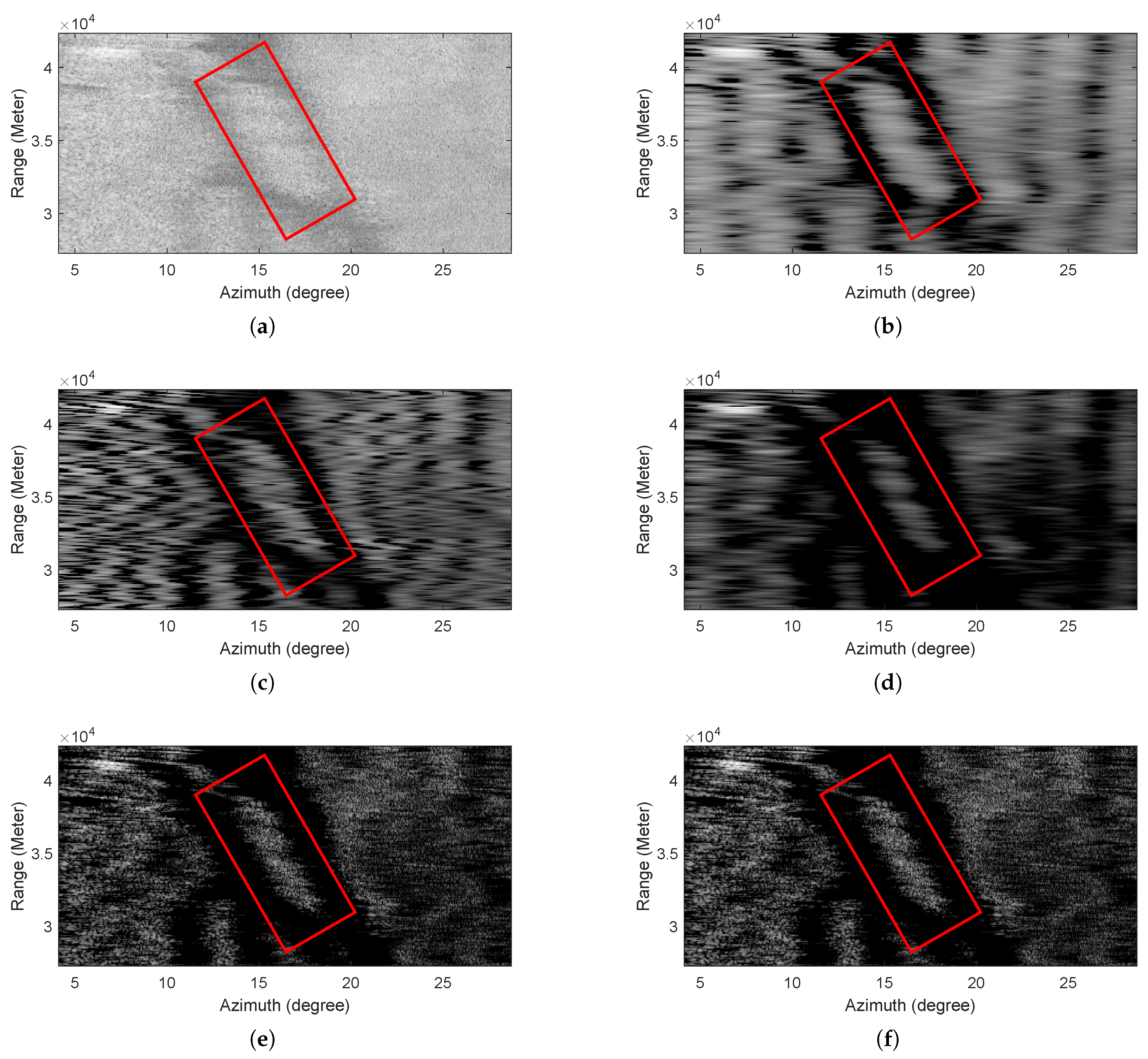
The experiment was carried out in a bay with an obvious island. The real beam echo received by the radar is shown in Figure 7a, in which the island is marked with a red rectangle box. It can be seen that the resolution of the real beam echo is very low, the contours of island and land are blurred, and the noise level is high.
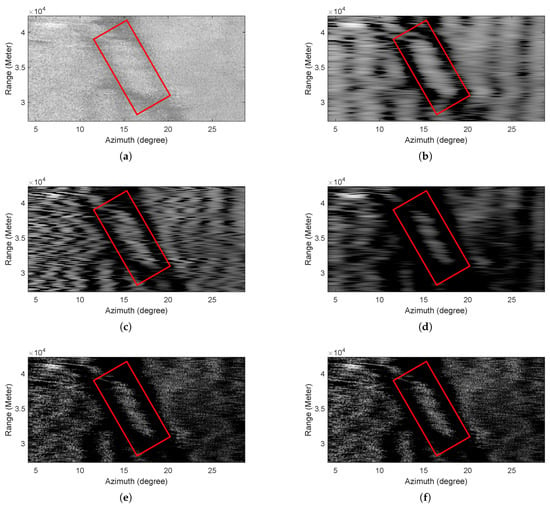
Figure 7.
Real data 1 results. (a) Real-beam echo, (b) TSVD, (c) IAA, (d) Sparse, (e) TV, (f) GSFTV.
The processed results of different methods are illustrated in Figure 7b–f. Figure 7c,d show that TSVD, IAA and sparse methods can improve the resolution and suppress the noise partly, but the performance of contour preservation is very poor. It is obvious that the edges of land and island are rather blurred in the results of these methods. By contraries, the TV and GSFTV methods achieve high resolution improvement. As shown in Figure 7e,f, the contours of land and island are more clear than that of Figure 7b–d.
To quantitatively evaluate the results of different methods, we introduce image entropy to quantitatively evaluate the quality of the results processed by different methods. According to the principle of minimum entropy, the smaller the image entropy means the clearer the image [26]. The image entropies of above processed results are shown in Table 4. It can be seen that the entropies of the results of TV and GSFTV are smaller than that of TSVD, IAA and sparse methods. This also proves that the results of TV and GSFTV methods are clearer than those of other methods. More importantly, compared with Figure 7e,f, it can be found that the proposed GSFTV method has almost no performance loss compared with the traditional TV method.

Table 4.
Entropies of real data 1.
Besides, as with simulation, the error between the results of GSFTV and TV methods is . It can be seen that the error caused by the approximation in this paper is very small and can be ignored.
5.2.2. Real Data 2
Another airborne data (We named it real data 2 for convenience) was processed to further verify the performance of the proposed GSFTV method. The target area of this experiment includes land and gully. The main parameters are consistent with Table 3, the difference is that the scanning range is ∼.
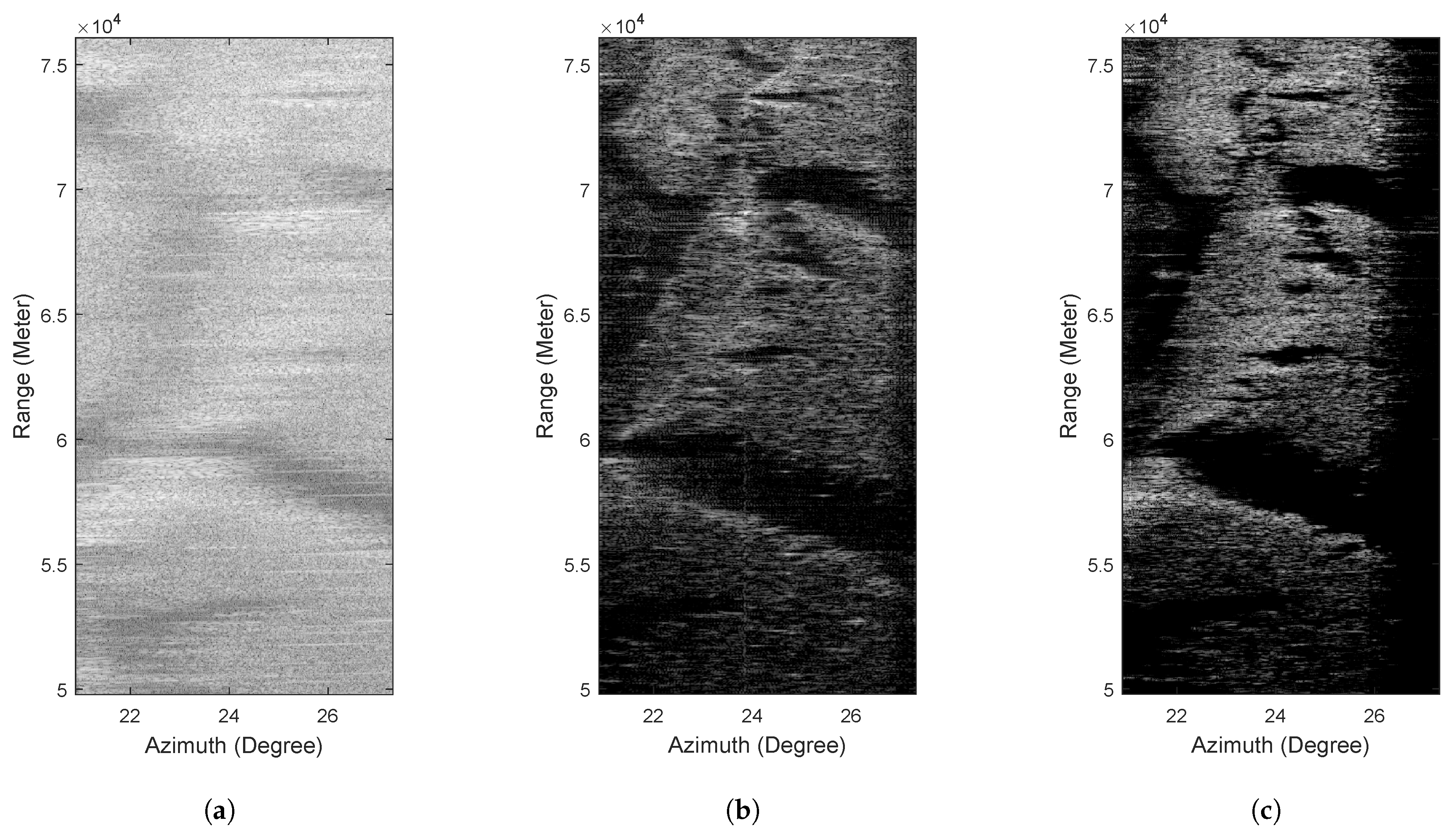
The processed results are shown in Figure 8, where Figure 8a is the real-beam echo with low SNR, from which we can hardly see the shape of the target. Figure 8b–f are the processed results of different methods. It can be seen that TSVD, IAA and sparse methods can improve the resolution to a certain extent, but the improvement of resolution is limited, and the contor of land is blurred, as Figure 8b–d shows. Figure 8e,f illustrate that TV and GSFTV have superior super-resolution performance, and the contour of the land is clearly visible.
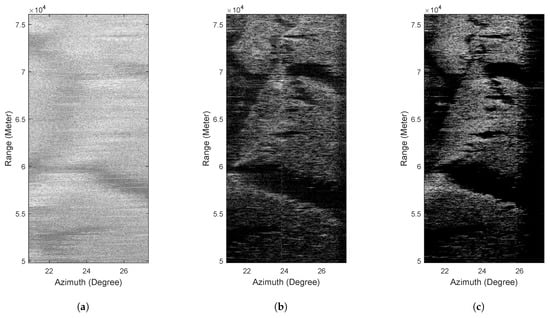

Figure 8.
Real data 2 results. (a) Real-beam echo, (b) TSVD, (c) IAA, (d) Sparse, (e) TV, (f) GSFTV.
The entropy of above results are shown in Table 5. From the table, we can get the same conclusion as Table 4.

Table 5.
Entropies of real data 2.
Similarly, we calculate the error between the results of TV and GSFTV methods as , indicating that the error caused by the approximation can be ignored.
5.3. Hardware Testing
Section 4.4 has demonstrated the very low computational complexity of the proposed GSFTV method in theory. In practice, the computing time is also limited by hardware conditions. So in this subsection, a hardware platform based on FPGA is built to verify the high computational efficiency of the proposed GSFTV method in practice.
The chip is core TMS320c6678 produced by Texas Instruments Company. The main frequency is 1 GHz and the memory is 4 G. For above real data, the dimensions of the data are and , respectively, where denotes M range samples and N azimuth samples. The computing times of different methods are shown in Table 6. It shows that the computing time of the proposed GSFTV method is much less than that of other methods. It can be seen that for the above two groups of measured data, the computational efficiency of the proposed GSFTV is about 244 times and 189 times of that of TV method respectively, which indicates that the computational advantage of the proposed GSFTV mainly depends on the number of azimuth samples. The more the number of azimuth samples, the greater the computational advantage of the proposed GSFTV.

Table 6.
Computing time of different methods.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, a GSFTV method was proposed to solve the problem of low azimuth resolution in airborne radar imaging. The proposed GSFTV method can efficiently improve the azimuth resolution and break the Rayleigh limit. In this process, the contour information of target is preserved. So its processed result is more clear than other traditional methods. Besides, utilizing the GS representation, the computational complexity of each iteration is decreased from to , which greatly increases the computing efficiency in practice. Although we make some approximations in order to realize the acceleration, we also proved that these approximations can be ignored.
Through simulation and real data processing, we demonstrated that the proposed GSFTV method almost no performance degradation compared with traditional TV method. Hardware test results show that the efficiency of the proposed GSFTV is much higher than that of the traditional TV method, and the more the number of azimuth points, the greater the computing advantage of the proposed GSFTV method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z.; methodology, Q.Z., Y.Z. (Yin Zhang), Y.Z. (Yongchao Zhang); software, Q.Z.; validation, Q.Z. and Y.Z. (Yin Zhang); formal analysis, Q.Z.; investigation, Q.Z.; resources, Q.Z., Y.Z. (Yongchao Zhang), Y.H. and J.Y.; data curation, Q.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, Q.Z.; visualization, Q.Z.; supervision, Y.Z. (Yin Zhang); project administration, Y.Z. (Yin Zhang); funding acquisition, Y.Z. (Yin Zhang), Y.Z. (Yongchao Zhang), Y.H. and J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61671117, 61901090 and 61901092.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
I exclude this statement because the study did not report any data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Esposito, C.; Berardino, P.; Natale, A.; Perna, S. On the Frequency Sweep Rate Estimation in Airborne FMCW SAR Systems. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigber, A.; Scheiber, R.; Jager, M.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Nannini, M.; Aguilera, E.; Baumgartner, S.; et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications. Proc. IEEE 2012, 101, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, J.; Yi, Q.; Li, W.; Yang, J. TV-Sparse Super-Resolution Method for Radar Forward-Looking Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6534–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, F. Recovery of partially corrupted SAR images by super-resolution based on spectrum extrapolation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 14, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, F. Beating the Rayleigh limit: Orbital-angular-momentum-based super-resolution diffraction tomography. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 033205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Superresolution via sparsity constraints. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1992, 23, 1309–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Kim, K.T. Compressive sensing based SAR imaging and autofocus using improved Tikhonov regularization. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 19, 5529–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennarelli, G.; Soldovieri, F. A linear inverse scattering algorithm for radar imaging in multipath environments. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.; Reddy, T.S. MST radar signal processing using iterative adaptive approach. Geosci. Lett. 2018, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Fast Split Bregman Based Deconvolution Algorithm for Airborne Radar Imaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.; Yu, G. Super-resolution with sparse mixing estimators. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, V.H.; Bouzerdoum, A.; Phung, S.L. Compressive Radar Imaging of Stationary Indoor Targets with Low-Rank Plus Jointly Sparse and Total Variation Regularizations. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4598–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnevskiy, V.; Gass, T.; Szekely, G.; Tanner, C.; Goksel, O. Isotropic total variation regularization of displacements in parametric image registration. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2016, 36, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tuo, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. A tv forward-looking super-resolution imaging method based on tsvd strategy for scanning radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4517–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, J. Total variation superresolution method for radar forward-looking imaging. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 26–29 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, R.W.; Zha, H. A look-ahead algorithm for the solution of general Hankel systems. Numer. Math. 1993, 64, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Super-resolution surface mapping for scanning radar: Inverse filtering based on the fast iterative adaptive approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glentis, G.O.; Jakobsson, A. Time-recursive IAA spectral estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2010, 18, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailath, T. Some new algorithms for recursive estimation in constant linear systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1973, 19, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitmead, R.R.; Anderson, B.D.O. Asymptotically fast solution of Toeplitz and related systems of linear equations. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 1980, 34, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glentis, G.O.; Jakobsson, A. Efficient implementation of iterative adaptive approach spectral estimation techniques. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 4154–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Rowe, W.; Xu, L.; Glentis, G.O.; Li, J. Fast missing-data IAA with application to notched spectrum SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Airborne forward-looking radar super-resolution imaging using iterative adaptive approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2044–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhu, F.; Ann, Heng, P. An efficient statistical method for image noise level estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: NW Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, J. Sparse with fast MM superresolution algorithm for radar forward-looking imaging. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 105247–105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; Mohammad, J. Optimal selection of annulus radius ratio to enhance heat transfer with minimum entropy generation in developing laminar forced convection of water-Al2O3 nanofluid flow. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 1850–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).