Abstract
Based on Himawari-8 Sea Surface Temperature (SST) data and the semi-automatic Topographic Position Index (TPI)-based mapping method, this study maps the significant coastal upwelling in the northern South China Sea (NSCS). The results show that the Minnan coastal upwelling mainly occurs within 100 km off the south coast of Fujian; the Yuedong coastal upwelling appears to the east of Pearl River Estuary, limited to the area shallower than 40 m; and the Qiongdong coastal upwelling occurs most frequently in the area shallower than 75 m off the east coast of Hainan Island. Based on the results, this paper quantitatively describes the temporal and spatial variations of upwelling duration, influence area, upwelling SST anomaly, and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) increase. Different coastal upwelling regions in the NSCS are significantly different in characteristics. The Qiongdong coastal upwelling has the longest duration and occurs most frequently, the Yuedong coastal upwelling has the largest influence area and Chl-a increase, and the Minnan coastal upwelling is quite strong in the NSCS.
1. Introduction
The South China Sea (SCS) with a maximum depth deeper than 5000 m is a large semi-enclosed tropical marginal sea in the northwest Pacific Ocean. The SCS has a broad continental shelf with the depth shallower than 200 m, and its isobaths are parallel to the coastline on the whole (Figure 1). The SCS is situated in the monsoon regime with prevailing northeasterly and southwesterly winds in winter and summer, respectively [1]. As a result, the coast of the northern South China Sea (NSCS) features seasonal coastal upwelling during the boreal summer [2]. Hu and Wang [3] reviewed the studies of upwelling in the China seas and summarized their characteristics and new progresses. They pointed out that the coastal upwelling in the NSCS mainly occurs off south coast of Fujian (called Minnan coastal upwelling hereafter), east coast of Guangdong (called Yuedong coastal upwelling hereafter), and east coast of Hainan Island (called Qiongdong coastal upwelling hereafter), and the coastal upwelling is mainly driven by the southwesterly monsoon in boreal summer. Since Hu and Wang [3], there have been some studies on the upwelling in the SCS using the remotely sensed data [4,5,6,7,8]. Combining the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) sea surface temperature (SST) data with the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) wind field data, Xie et al. [4] studied the variability and long-term tendency of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling, showing that the Qiongdong coastal upwelling has a weakening trend in most recent 30 years. Kok et al. [5] used the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) SST data and the ECMWF wind data to discuss the inter-monthly variation and the formation mechanism of the upwelling along the coastline of the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia (ECPM), showing that Ekman pumping contributes to about more than half of the total upwelling transport along the entire coastline of the ECPM. Based on in situ data, MODIS SST and simulation model, Shu et al. [6] revealed the inter-annual variability of the coastal upwelling in the NSCS and pointed out that in addition to local wind, large-scale currents and the thermocline depth on the shelf are also the cause of inter-annual variability of upwelling intensity. Li et al. [7] analyzed the vertical structure and the formation mechanism of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling using MODIS SST data and in situ data, indicating that El Niño has an impact on the annual variation of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling. Based on Hadley Centre Global Sea Ice and Sea Surface Temperature (HadISST) data and other remotely sensed data, Wang and Wu [8] analyzed the inter-annual variability of the upwelling off Vietnam and its relationship with El Niño, showing that El Niño could weaken the SCS upwelling under certain circumstance.
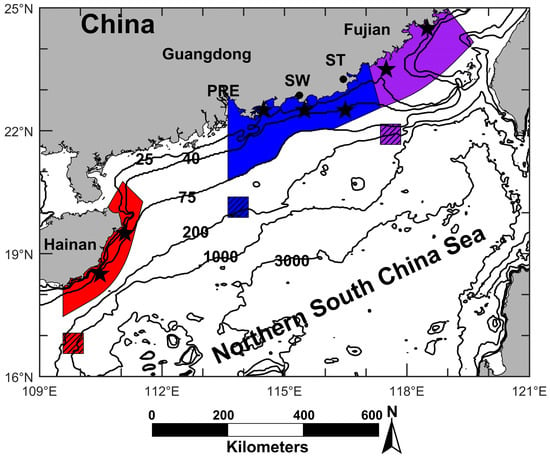
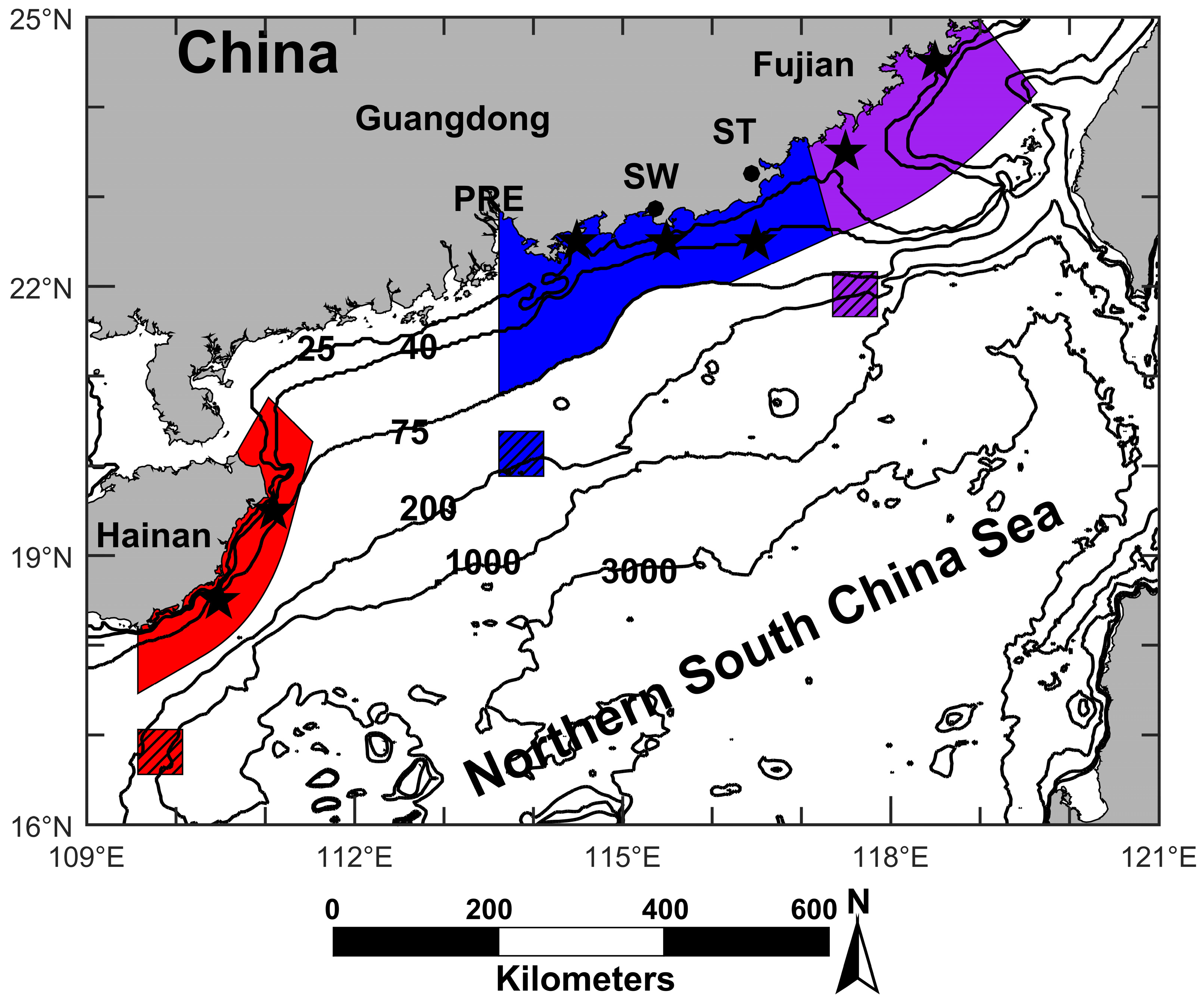
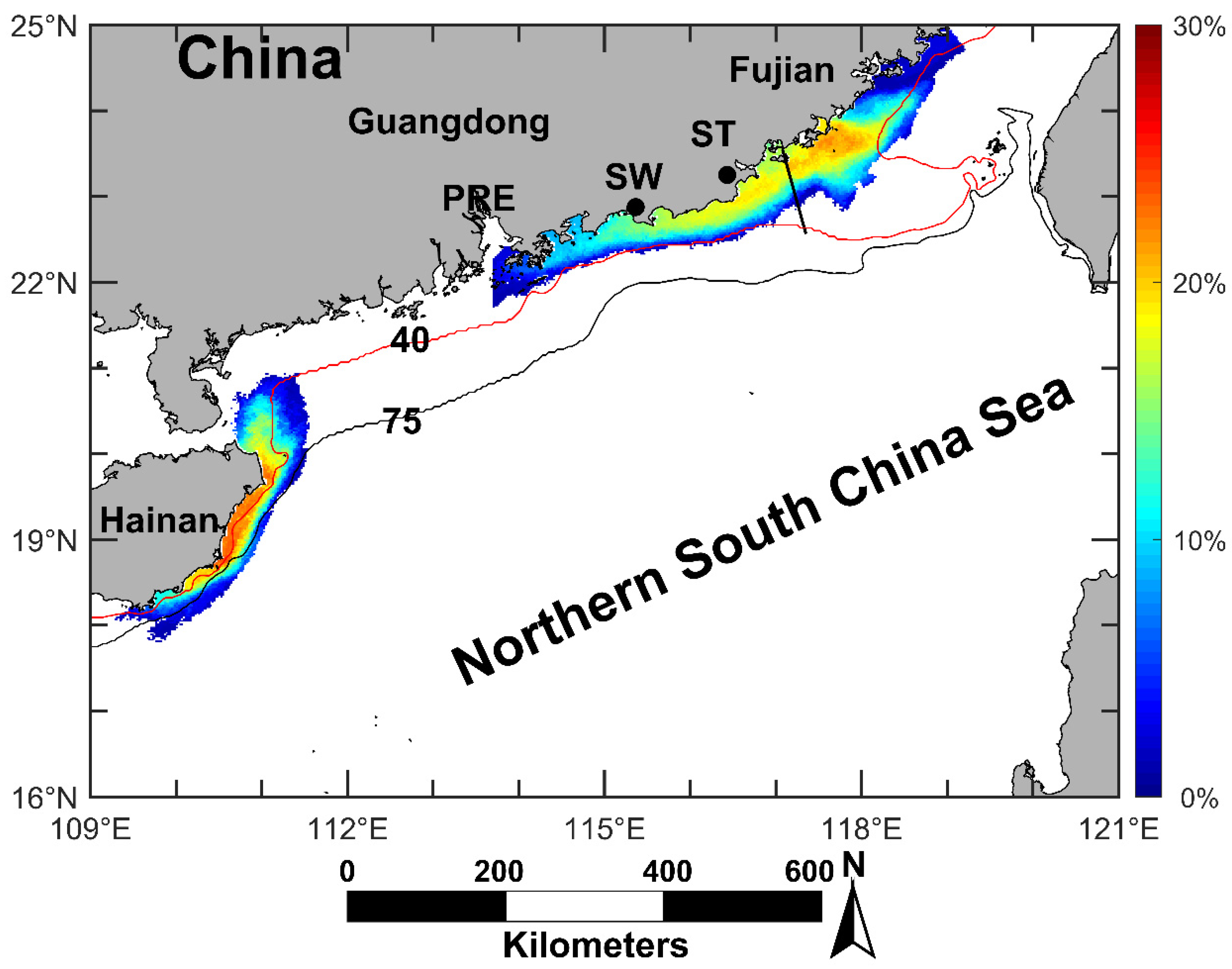
Figure 1.
Topography of northern South China Sea (NSCS). PRE: Pearl River Estuary, SW: Shanwei, ST: Shantou. Purple: occurrence region of the Minnan coastal upwelling (MNCU); Blue: occurrence region of the Yuedong coastal upwelling (YDCU); Red: occurrence region of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling (QDCU). Purple shadow: the reference location of the MNCU; Blue shadow: the reference location of the YDCU; Red shadow: the reference location of the QDCU. Stars: upwelling index calculation stations. The depth contours are in meters.
Most previous studies focused on a particular upwelling event in a certain area or qualitatively described the inter-monthly or inter-annual variation of upwelling using remotely sensed data. Although it is imperative to quantify upwelling in the SCS [9], there are rarely quantitative analyses of upwelling frequency, duration, and influence area. There are few studies comparing the characteristics of different upwelling regions in the NSCS. Using Himawari-8 high-resolution SST data and the Climate Forecast System version2 (CFSv2) wind field data, this study aims to map and investigate spatial and temporal variations of significant coastal upwelling in the NSCS during the boreal summers (May to September) of 2016–2019. Specifically, the objectives of this study include the following: (1) quantitatively map spatial and temporal variations of significant coastal upwelling; (2) identify areas with frequent coastal upwelling; and (3) examine the characteristics of different coastal upwelling regions. In this study, we defined that a significant coastal upwelling event must have an SST signature that lasts a substantial duration (≥5 days) and a relatively large cold area (>1000 km2) (detailed below).
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study focuses on three known coastal upwelling regions in the NSCS (Figure 1). According to [10], the influence area of the Minnan coastal upwelling is limited to 100–150 km offshore the south coast of Fujian (purple area in Figure 1). The Yuedong coastal upwelling usually occurs to the east of Pearl River Estuary (PRE), and its influence area may extend to the area shallower than 75 m (blue area in Figure 1) [11]. The main influence area of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling is located 20–50 km offshore east and northeast of Hainan Island (red area in Figure 1) [12].
2.2. Himawari-8 Data
Himawari-8 is a geostationary meteorological satellite launched by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) in October 2014 [13]. Himawari-8 is capable of providing near real-time geophysical products (such as SST, sea surface chlorophyll-a, and aerosol properties) at a temporal resolution of 10-mins full-disk frequency [13]. This study used Himawari-8 SST product, with a spatial resolution of ≈2 km, which was processed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) based on a quasi-physical SST algorithm and a Bayesian cloud screen method [14]. Kurihara [14] compared Himawari-8 SSTs from June to September 2015 with the drifting and tropical moored buoy data, showing good agreement between the Himawari-8 SST and the buoy data.
Specifically, we used daily Himawari-8 SST data for the upwelling mapping. The SST data were processed to Level 3, with the highest quality levels of 4 and 5 deemed cloud-free, representing skin SST according to the GHRSST (Group for High-Resolution Sea Surface Temperature) standard and format. In addition, we also used a daily chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) product, which was processed by the JAXA to Level 3 using the algorithm developed in [15]. The spatial resolution of the Chl-a data is ≈5 km.
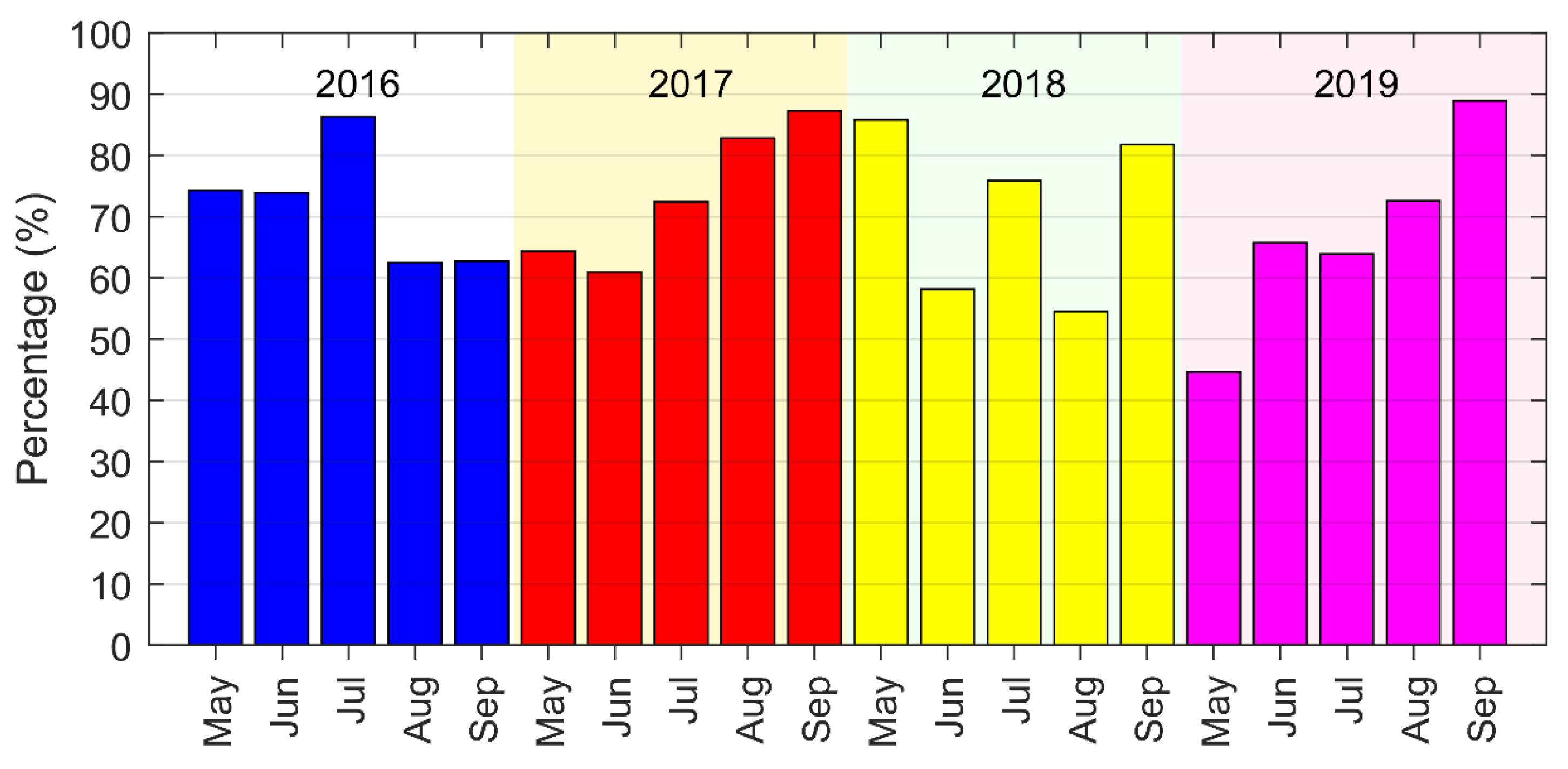
It should be noted that despite the high frequency Himawari-8 data with a 10-min temporal resolution having minimized the data gaps caused by the cloud coverage, there were still some days when the upwelling regions were completely or partially covered by cloud. Figure 2 shows the percentage of each month when the pixels were free from cloud influence. In most cases, the percentages were more than 60%. Half of the months, the percentage were more than 70%; and about one-third of the months, the percentage were more than 80%. Nevertheless, during persistent cloud cover, some significant upwelling events could not be identified in this study.
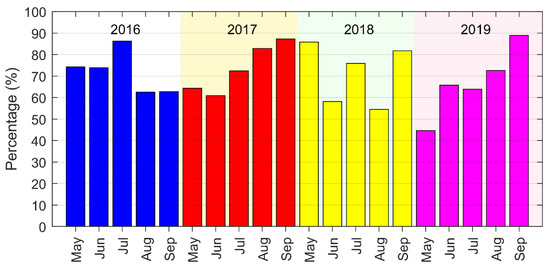
Figure 2.
The percentage of the month a pixel is free from cloud influence, spatially averaged across the entire study region. The percentage was calculated from the daily images of the corresponding month.
2.3. CFSv2 Wind Field Data
This study used CFSv2 wind field data from the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) [16] to calculate upwelling index and wind stress curl. In this study, wind field data with a spatial resolution of 0.5° × 0.5° and a time resolution of 6 h from May 2016 to September 2019 were used to calculate the upwelling index.
2.4. Mapping the Upwelling Area
The first step of mapping an upwelling area is to calculate the Topographic Position Index (TPI) from an SST image (Figure 3a,b). TPI is a local-based algorithm that calculates the difference between the center cell and its neighbors, which is usually used to classify landform types [17]. As a result, the TPI calculated from an SST image represents local SST anomaly. The TPI method has been successfully used to map the ocean currents [18,19]. Similarly, the TPI method is also applicable for mapping the upwelling signature of negative SST anomaly [20,21]. TPI parameter from an SST image can be calculated by the following equation:
where x and y are the positions of the center cell, and WD(x, y) is the mean SST within a nominated window surrounding the center cell. Previous studies [19,21] indicated that the TPI works best when its window size is larger than the typical width of the feature of interest. In this study, we used a circle window with a diameter of 200 km (100 Himawari-8 cells), which was deemed larger than the width of individual upwelling area in the NSCS.
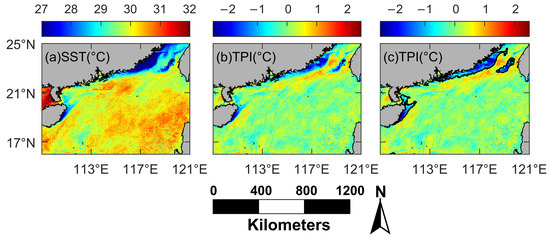
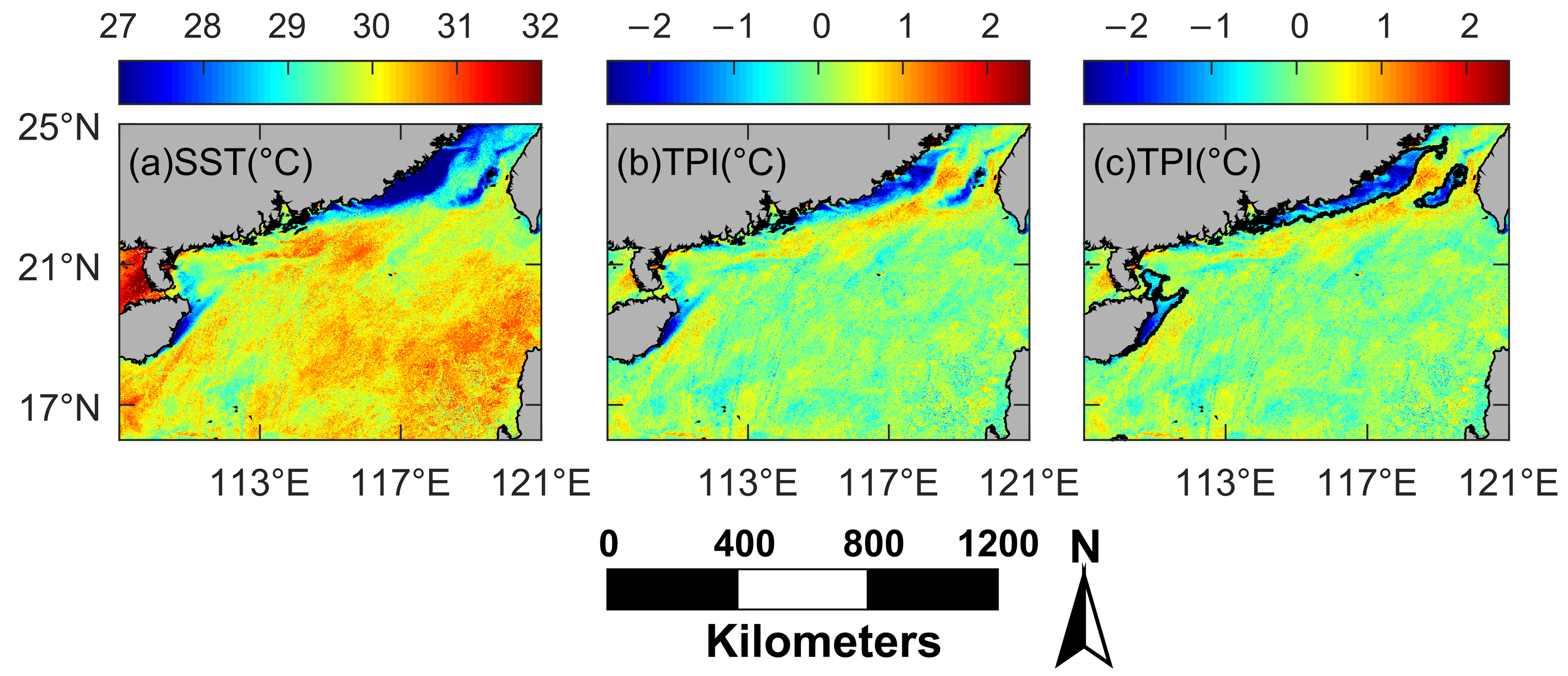
Figure 3.
Upwelling region calculation process. (a) The Himawari-8 Sea Surface Temperature (SST) image on 17 July 2016; (b) Topographic Position Index (TPI) calculated from SST image; (c) upwelling region calculated by TPI (the region within black solid line).
In the second step, areas of negative TPI values were selected using a pre-defined threshold (Φ), satisfying the following condition:
where S_SD(TPI) is the standard deviation of the TPI image. Next, we further select only those areas that have an areal extent greater than 1000 km2 as suitable upwelling candidates, because this threshold is part of the definition of a significant coastal upwelling event that does not include smaller and patchier individual upwelling areas.
It is assumed that an upwelling area should have a reasonably large local SST anomaly. The local SST anomaly of an upwelling candidate was calculated using the equation below:
where SSTc is the mean SST value of an upwelling candidate, and SSTb is the mean SST value of a 20 km buffer around (but excluding) the upwelling candidate [21]. Only when the local SST anomaly of an upwelling candidate is larger than a threshold (Ψ), we consider that the upwelling indeed occurs at the location (e.g., Figure 3c), for example:
The selection of appropriate Φ and Ψ values is important for the upwelling mapping. For this study, a Φ value between 0.5 and 1.0 may be suitable because the TPI values such calculated indicate the lower part of the “valley” on a surface [17], which in this case is considered as the upwelling area. According to [22], SST in the coastal upwelling is usually 1–2 °C lower than that in the open ocean. However, we consider that the local SST anomaly should be lower when compared to the 20 km buffer around the upwelling area. For this study, we also consider that a Ψ value between 0.5 and 1.0 °C may be suitable to evaluate the local SST anomaly between an upwelling candidate and its 20 km buffer.
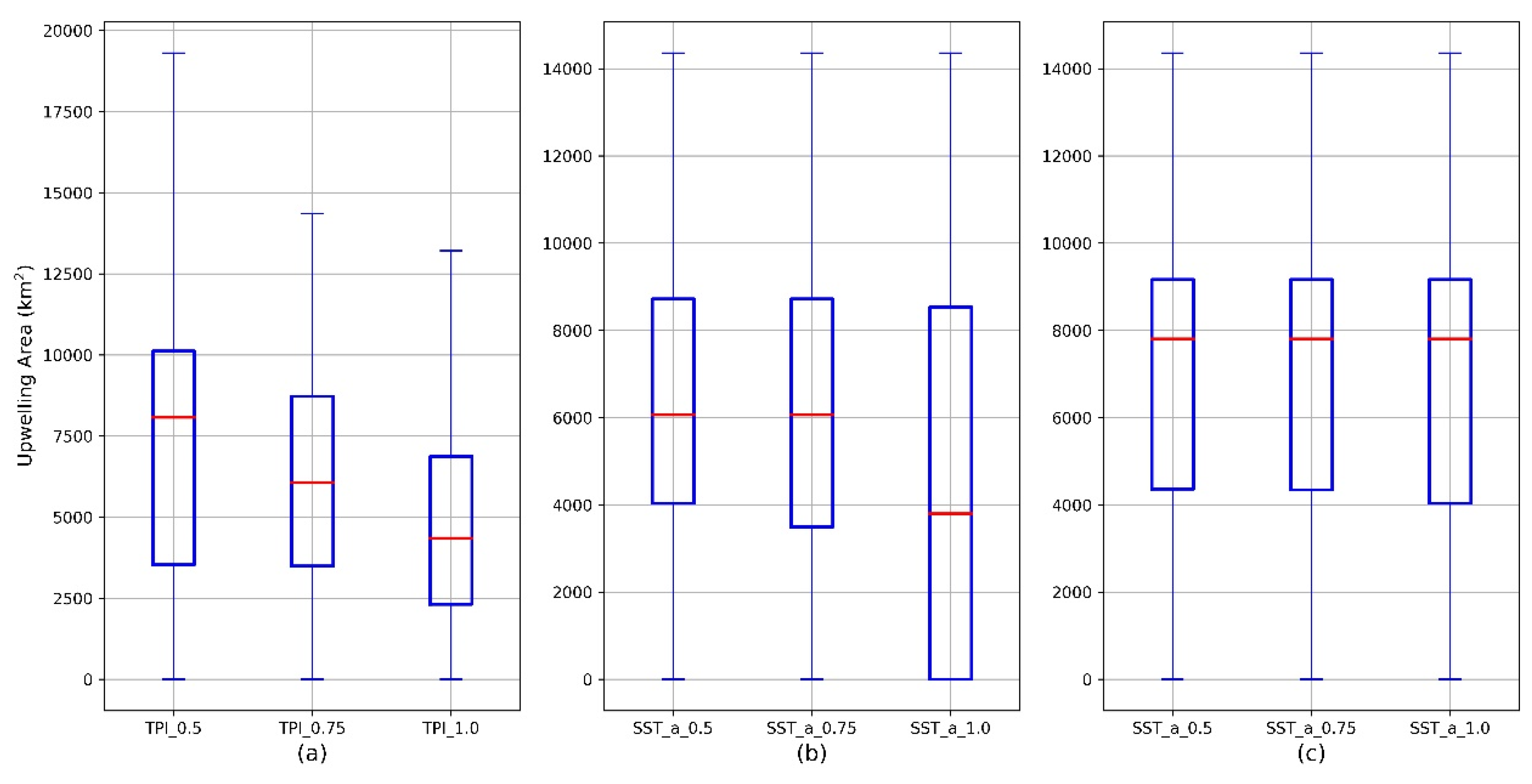
To determine the most appropriate Φ and Ψ values, we conducted two sensitivity analyses for the mapping of the Qiongdong upwelling in the year 2016. In the first one, we kept Ψ as a constant (Ψ = 0.75 °C) while varying Φ values from 0.5 to 0.75 and to 1.0. In the second one, we kept Φ as a constant (Φ = 0.75) while varying Ψ values from 0.5 °C to 0.75 °C and to 1.0 °C. Note that all other parameters remained constant in the sensitivity analyses. The results of the sensitivity analyses are summarized in Figure 4. Out of the 153 days in 2016, between May and September, the Qiongdong upwelling area was entirely covered by the Himawari-8 SST data in 92 days. It is clear that the mapped upwelling area was sensitive to the Φ parameter (Figure 4a). Varying Φ value from 0.5 to 0.75 and from 0.75 to 1.0 resulted in ≈20–25% change of the upwelling area on average. Among the three Ψ values, using the Ψ value of 1.0 °C failed to identify upwelling (i.e., upwelling area = 0) in 32 days when the upwelling was otherwise identified using the Ψ value of 0.5 °C. This is clearly reflected in Figure 4b. However, after removing these 32 days from the statistics, the upwelling areas from the remaining 60 days were not sensitive to the Ψ parameter (Figure 4c). Consequently, the sensitivity analyses indicate that the upwelling mapping is sensitive to the selection of Φ threshold, but only sensitive to the specific Ψ threshold of 1.0 °C.
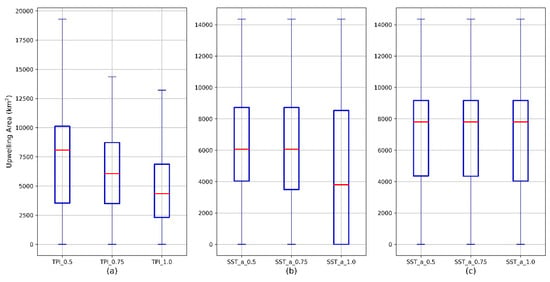
Figure 4.
The summarized results of the sensitivity analyses of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling mapping in 2016 to the Φ and Ψ values, displayed as boxplots. (a) Ψ = 0.75 °C, Φ varies in (0.5, 0.75, 1.0), n = 92; (b) Φ = 0.75, Ψ varies in (0.5 °C, 0.75 °C, 1.0 °C), n = 92; (c) Φ = 0.75, Ψ varies in (0.5 °C, 0.75 °C, 1.0 °C), n = 60. The blue box indicates the range between the first (25th percentile) and the third (75th percentile) quantiles. The solid red line indicates the median. The two caps indicate the data range.
In this study, we thus select Φ = 0.75 because it was not only used in previous upwelling studies [20,21] but also would yield intermediate mapping results according to the above sensitivity analyses. In terms of Ψ, Ψ = 1.0 °C is not appropriate according to the above sensitivity analyses. Between 0.5 and 0.75 °C, we selected Ψ = 0.75 °C, as this would yield a slightly more conservative mapping result.
It usually takes several days for upwelling to uplift cold water from deep to the sea surface. The surface influence of upwelling also requires several more days to be completely dispersed (e.g., [12,21]). In addition, a cold SST signature of short duration (e.g., 2–3 days) could be due to the influence of confounding oceanographic phenomena such as the horizontal advection. Therefore, in this study, to increase the confidence of mapping the real occurrence of a significant upwelling event, we defined that a significant upwelling event must last more than 5 days. As a result, a significant upwelling event was identified by satisfying one of the following three criteria:
(1) Upwelling occurred for ≥5 consecutive days;
(2) Upwelling occurred for the first 2 consecutive days, followed by 1 day of “absence of upwelling”, then followed by ≥2 consecutive days of upwelling occurrence;
(3) Upwelling occurred for the first 3 consecutive days, followed by 1 day of “absence of upwelling”, then followed by ≥1 day of upwelling occurrence.
The criteria only allow one such “absence of upwelling” day within a ≥5 days upwelling event. The “absence of upwelling” in criteria 2 and 3 is either due to “no data” caused by the cloud coverage or due to the temporary subsiding of the upwelling on that day. In this study, the cloud coverage was the most likely cause of the “absence of upwelling”. Note that these “absence of upwelling” days were not included in the subsequent calculations of upwelling statistics of influence area, Chl-a increase, and SST anomaly.
2.5. Upwelling Index and Wind Stress Curl Calculation Method
The offshore Ekman transport and the Ekman pumping are major influence factors for the coastal upwelling. In this study, we used upwelling index and wind stress curl to represent the offshore Ekman transport [23,24,25,26] and the Ekman pumping [4,5,10,27], respectively.
Upwelling index (UI) and wind stress curl (Curlz) were calculated using the following equations:
where is the wind stress, and are the meridional and zonal components of , respectively, ρa is the air density (1.22 kg m−3), ρw is the seawater density (1026 kg m−3), Cd is the drag coefficient, f is the Coriolis parameter (s−1), α is the wind direction, β is the shoreline orientation, and V is the wind speed.
The Coriolis parameter varies with the latitude. It was calculated by the following equation:
where ω is the angular velocity of the earth, φ is the latitude.
The drag coefficient varies with wind speed, and it was calculated by the following equation [28]:
Based on these equations, we used CFSv2 wind data to calculate the upwelling index and wind stress curl. A positive upwelling index or wind stress curl indicates the occurrence of upwelling. The value of the upwelling index is often used to estimate the coastal upwelling strength. Similarly, the value of wind stress curl is an index for the Ekman pumping, which can be also regarded as another index of upwelling strength.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
In this paper, we presented four different upwelling characteristics (upwelling duration, influence area, SST anomaly, and Chl-a increase). The upwelling duration is the lasting time of a significant upwelling event. The influence area was calculated as the areal extent of the mapped upwelling area. The SST anomaly (SST_A) was calculated using Equation (10) as the difference of mean SST of upwelling region (SSTup) and the mean SST of reference location (SSTref). The Chl-a increase was calculated by Equation (11), where Chl-a_I is the Chl-a increase in the upwelling region in a certain month, Chl-aup is the mean Chl-a in the upwelling influence area mapped by TPI, and Chl-anup is the mean Chl-a in the upwelling region (e.g., the purple, blue, and red areas in Figure 1) on the non-upwelling days of that month. The Chl-a increase can be regarded as an index of the ecological impact of upwelling.
To examine the upwelling’s temporal variation, we conducted the following temporal statistics for the four upwelling characteristics, i.e., influence area, SST anomaly, Chl-a increase, and upwelling index. Here, the following apply:
(1) The monthly mean values in the individual years 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, respectively, were calculated from the daily values of the corresponding month in the specific year;
(2) The monthly mean values of all years combined were calculated from the daily values in the corresponding month regardless of the year;
(3) The annual mean was calculated from the daily values in the corresponding year.
Note here that only the day that upwelling occurred was the daily value adopted to calculate the monthly mean or annual mean. We only consider May–September of each year as the temporal range of our study. Therefore, the annual mean is actually the mean value of May–September of each year.
3. Results
3.1. Upwelling Events
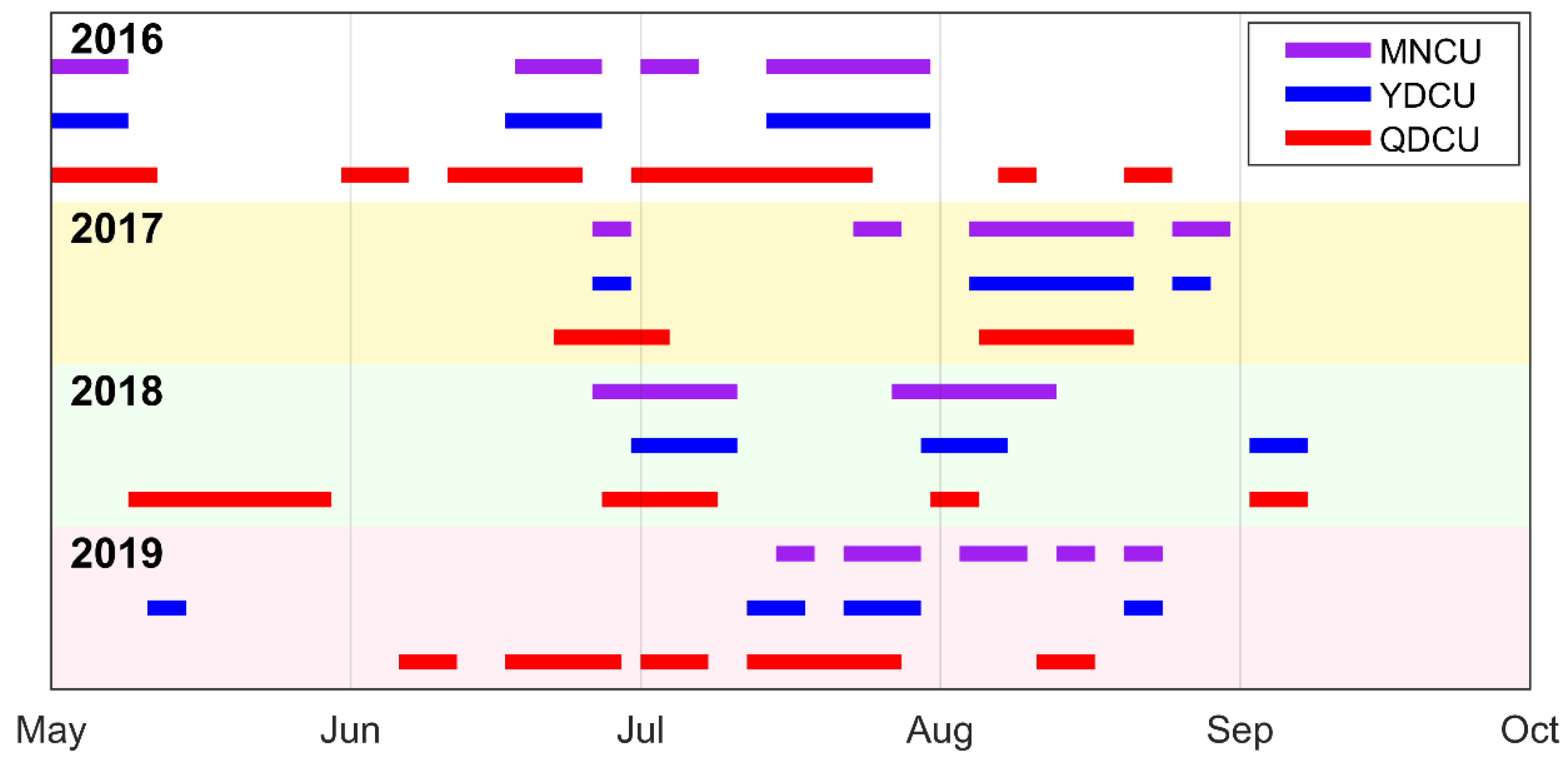
The upwelling events identified during 2016–2019 are shown in Figure 5, and the duration of upwelling is shown in Figure 6. During the boreal summers of 2016–2019, the Qiongdong coastal upwelling (QDCU) occurred most frequently, with 17 upwelling events from 2016 to 2019. The total duration of the QDCU was the longest (194 days). The mean duration of each event was about 11 days, with the longest single event lasting for 26 days (30 June 2016–25 July 2016; Figure 5). The frequency of the Yuedong coastal upwelling (YDCU) was the lowest, with only 13 upwelling events from 2016 to 2019. The total duration of the YDCU events was the shortest (120 days), averaged ≈9 days, and the longest single event lasted for 18 days (14 July 2016–31 July 2016; Figure 5). There were 15 Minnan coastal upwelling (MNCU) events during the boreal summers of 2016–2019, totaling 145 days. The mean duration of each event was about 10 days, with the longest single event lasting for 18 days (14 July 2016–31 July 2016; 4 August 2017–21 August 2017; and 27 July 2018–13 August 2018; Figure 5). The YDCU and the MNCU often occurred concurrently, which amounted to 104 days, accounting for 86.7% and 71.7% of total duration of the YDCU and the MNCU, respectively.
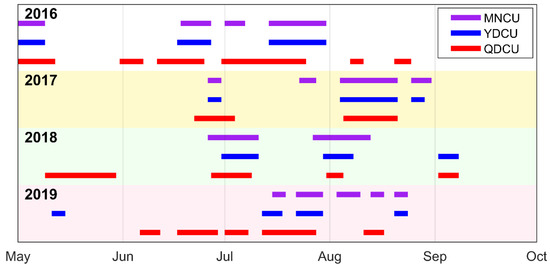
Figure 5.
Time series of significant upwelling events in summers of 2016–2019. Purple (blue/red) bars represent the upwelling events off Minnan (Yuedong/Qiongdong) coast. The length of a bar indicates the duration of the event. Purple: Minnan coastal upwelling (MNCU), blue: Yuedong coastal upwelling (YDCU), red: Qiongdong coastal upwelling (QDCU).
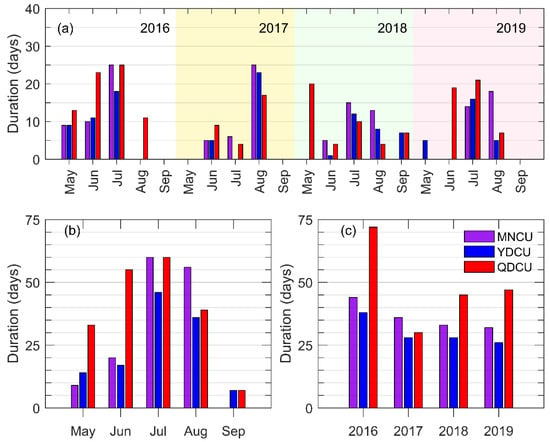
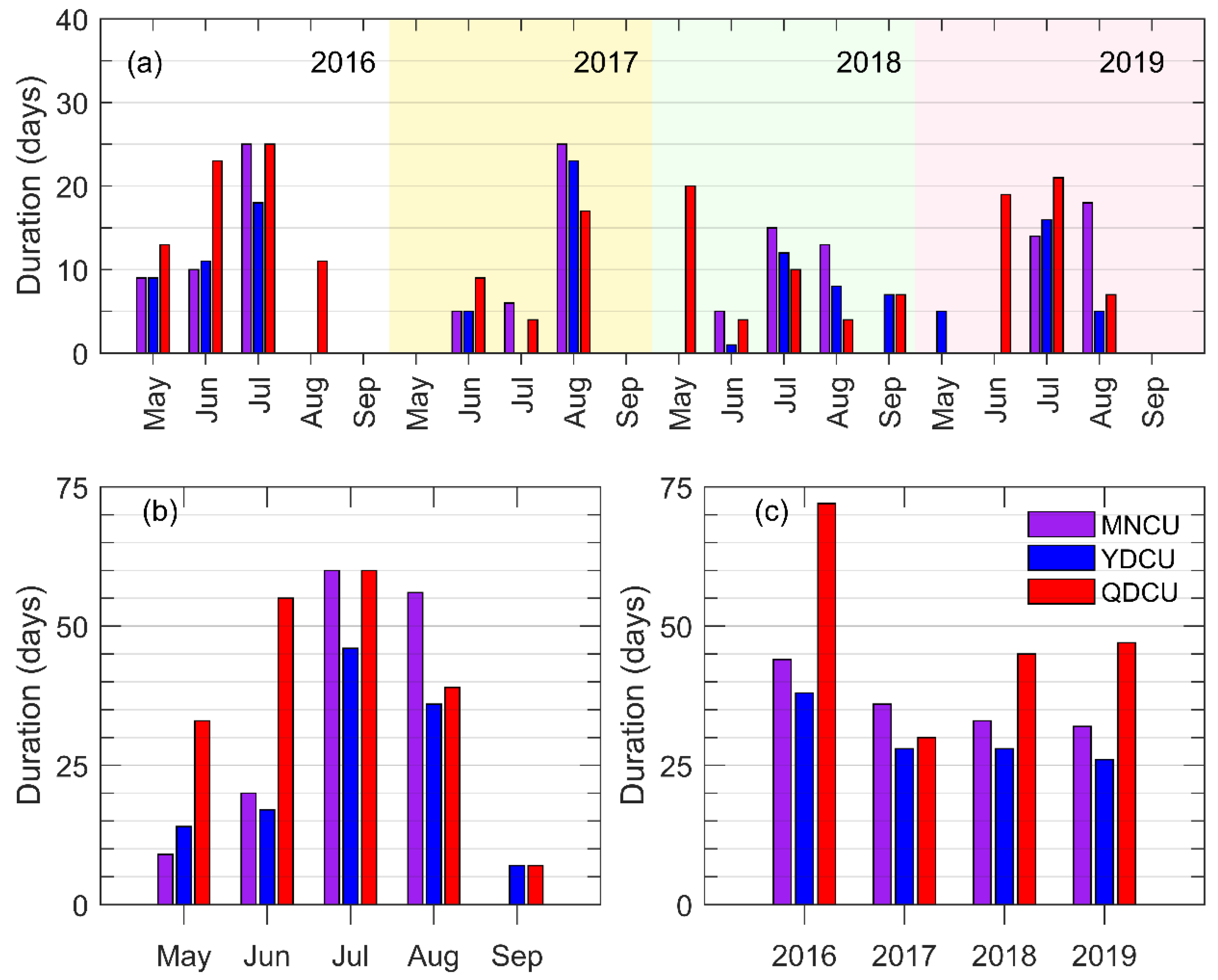
Figure 6.
The inter-monthly variation and the inter-annual variation of upwelling’s duration. (a) The upwelling duration in each month during the boreal summers of 2016–2019; (b) the monthly mean upwelling duration regardless of the year; (c) the total upwelling duration in May–September of each year.
There is significant inter-monthly variation of upwelling duration. During the boreal summers of 2016–2019, the coastal upwelling in the NSCS occurred mainly in June, July, and August (Figure 6b), while the upwelling rarely occurred in September. In general, the duration increases from May to July and then decreases to minimum in September (Figure 6b). As for the inter-annual variation, the duration was the longest in 2016 (Figure 6c). The durations of the MNCU and the YDCU decreased from 2016 to 2019, while the duration of the QDCU was the shortest in 2017 (Figure 6c).
3.2. Spatial Variation of Coastal Upwelling in the NSCS
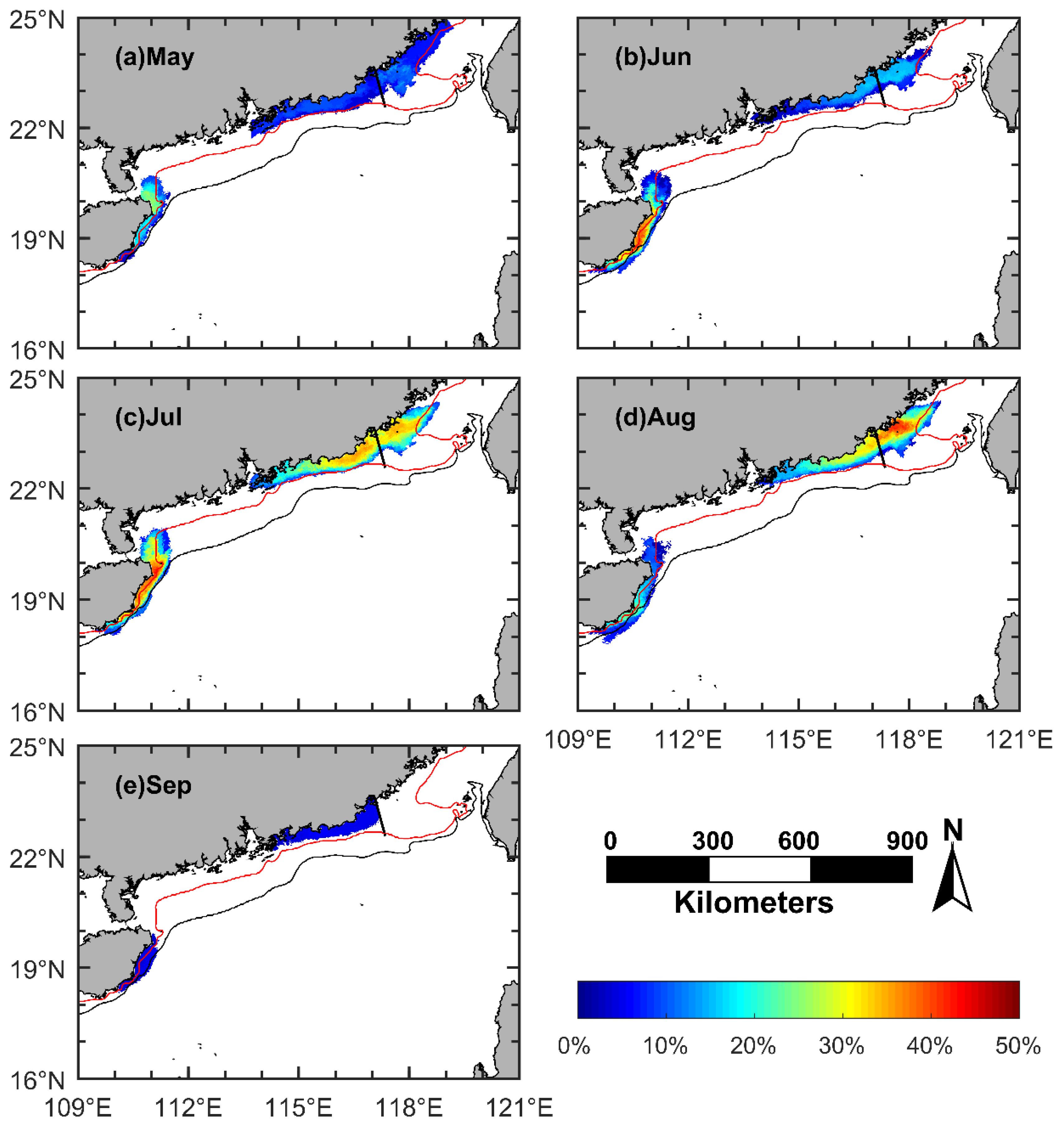
The frequency of occurrence and the influence area of the coastal upwelling during the boreal summers of 2016–2019 mapped by the TPI method are shown in Figure 7. The frequency of occurrence of upwelling is the ratio of the upwelling duration to the total days of corresponding month.
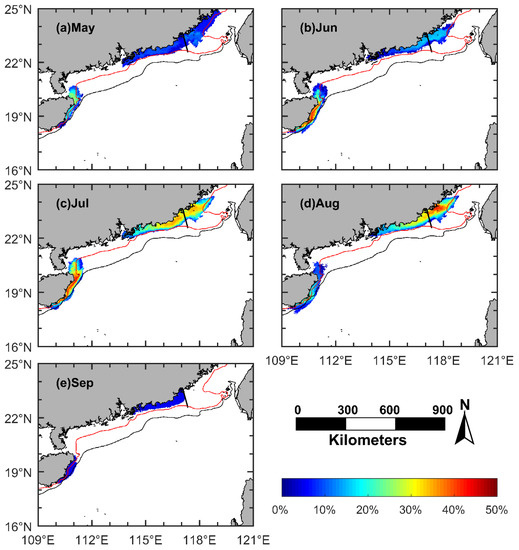
Figure 7.
The monthly frequency of occurrence and the influence area of the coastal upwelling in the northern South China Sea (NSCS), generated by combining the daily upwelling maps in the corresponding month regardless of the year. (a) May; (b) June; (c) July; (d) August; (e) September. Red line: 40 m isobath; black line: 75 m isobath; black solid line: boundary between the Minnan coastal upwelling and the Yuedong coastal upwelling.
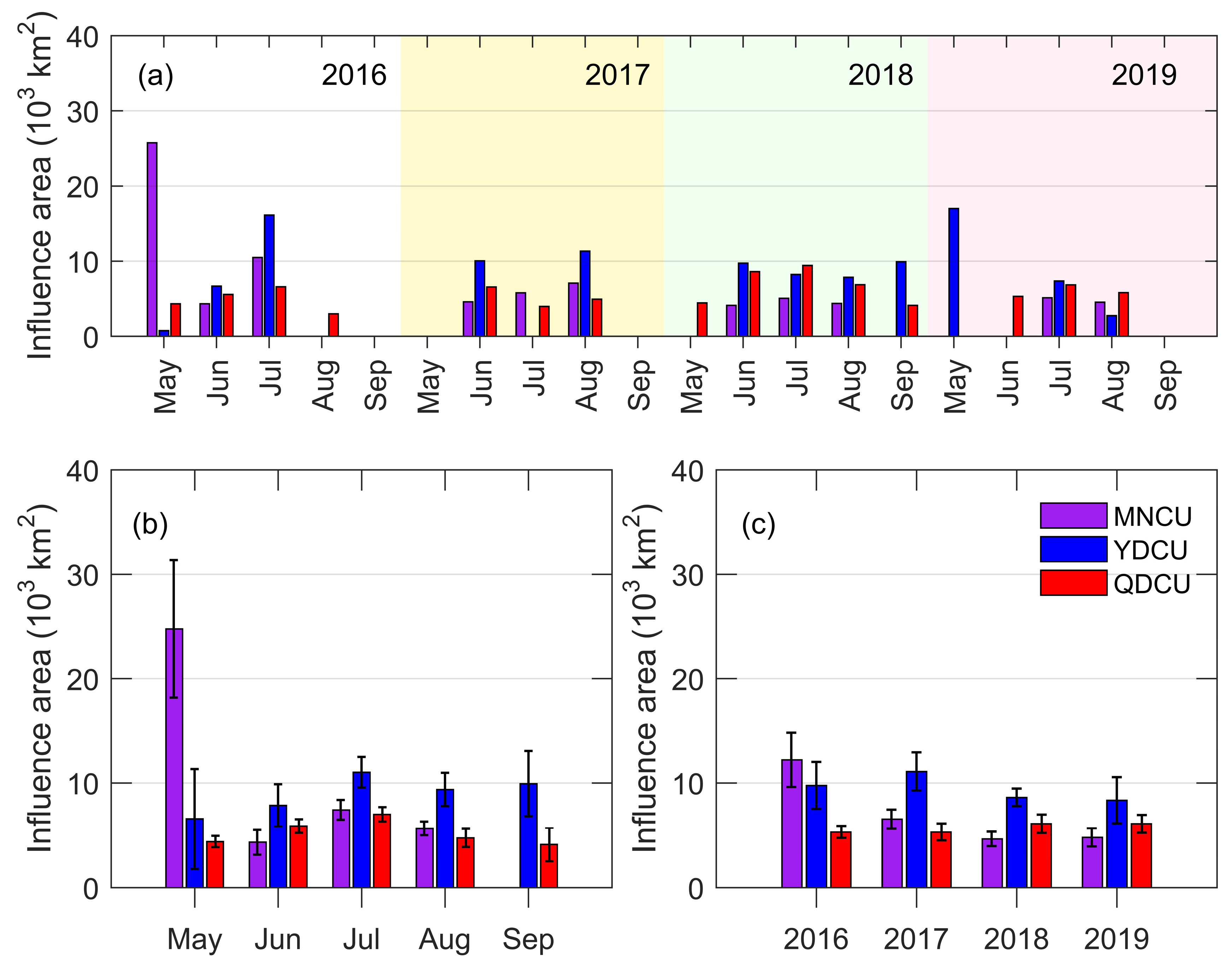
The Minnan coastal upwelling mainly occurs off the south coast of Fujian. Only in May 2016 was the upwelling extended to the middle coast of Fujian, with the largest influence area of 2.6 × 104 km2 (Figure 8a). However, there was no MNCU event in May of 2017–2019 or in September during the four years (Figure 5 and Figure 6a). Except for the upwelling event that occurred in May 2016, the influence area of the MNCU was all limited to within 100 km offshore of the southern Fujian. The influence area of the MNCU varies from June to August. The largest influence area, about 7.4 × 103 km2, appears in July, which is statistically larger than that in June or in August. The mean influence area of the MNCU from June to August is 5.8 × 103 km2 (Figure 8b).
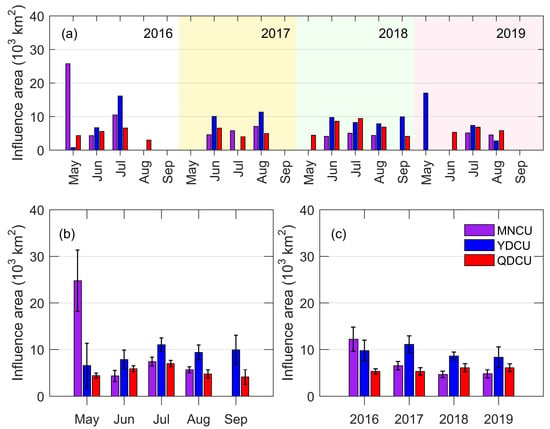
Figure 8.
The inter-monthly and inter-annual variations of the upwelling’s influence area (unit: km2) in the NSCS from 2016 to 2019. (a) The monthly mean of the influence area for the individual year in 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019; (b) the monthly mean of the influence area regardless of the year; (c) the annual mean of the influence area. The error bars in (b,c) are 95% confidence intervals.
The Yuedong coastal upwelling mainly occurs to the east of PRE, covering the whole coastal area east of Guangdong. The YDCU occurs most frequently to the east of Shanwei in July and August. Near the PRE, the influence area of the YDCU is not far away from the coastline, with its outer edge along the 40 m isobath. From the PRE to Shantou, the influence area extends to about 80 km offshore. The influence area of the YDCU increases from May (≈6.6 × 103 km2) and reaches the maximum in July (≈1.1 × 104 km2). The mean influence area from May to September is 8.9 × 103 km2 (Figure 8b).
There is statistically significant inter-monthly variation in the influence area of the Qiongdong coastal upwelling (Figure 7 and Figure 8b). The QDCU in May is mainly located off the southeast, east, and northeast coasts of Hainan Island. From June to August, it occurs off the east and northeast coasts of Hainan Island, and it is limited to the area shallower than 75 m. In September, the influence area shrinks to the east coast of Hainan Island, and it is also limited to the area shallower than 75 m. The influence area of the QDCU increases from May (≈4.4 × 103 km2), reaches the maximum in July (≈7.0 × 103 km2), and then decreases to minimum in September (≈4.1 × 103 km2), with a mean area of 5.2 × 103 km2 (Figure 8b).
As a result of the long coastline, the influence area of the YDCU was the largest in most cases among the three coastal upwelling regions (Figure 8). The influence area of the MNCU decreased from 2016 to 2019, being ≈1.3 × 104 km2 in 2016 while ≈4.8 × 103 km2 in 2019 (Figure 8c). The influence area of the YDCU increased from 2016 (≈9.5 × 103 km2), reached the maximum in 2017 (≈1.1 × 104 km2), and then decreased to a minimum in 2019 (≈8.3 × 103 km2). The influence area of the QDCU did not vary much from 2016 to 2019, ranging from ≈5.3 × 103 km2 in 2016 and 2017 and ≈6.1 × 103 km2 in 2018 and 2019 (Figure 8c).
3.3. Variation of Upwelling SST Anomaly in the NSCS
We chose three locations (0.5 degree × 0.5 degree) in the open ocean as the reference locations for the three upwelling regions (Figure 1). These three reference locations are deemed to be free from the upwelling influence because they are located further offshore from the three upwelling regions. The upwelling SST anomaly is calculated by Equation (10), which can be regarded as an index of upwelling strength. The results are shown in Figure 9.
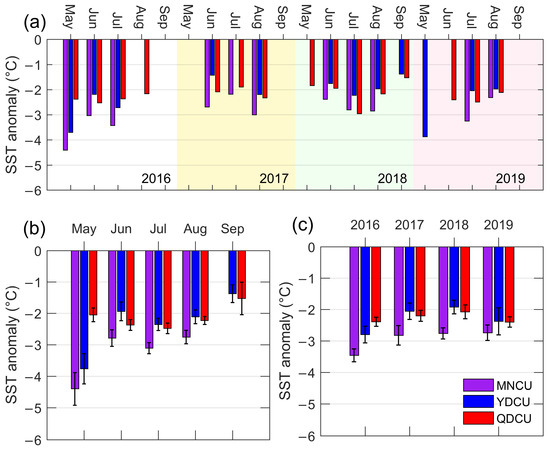
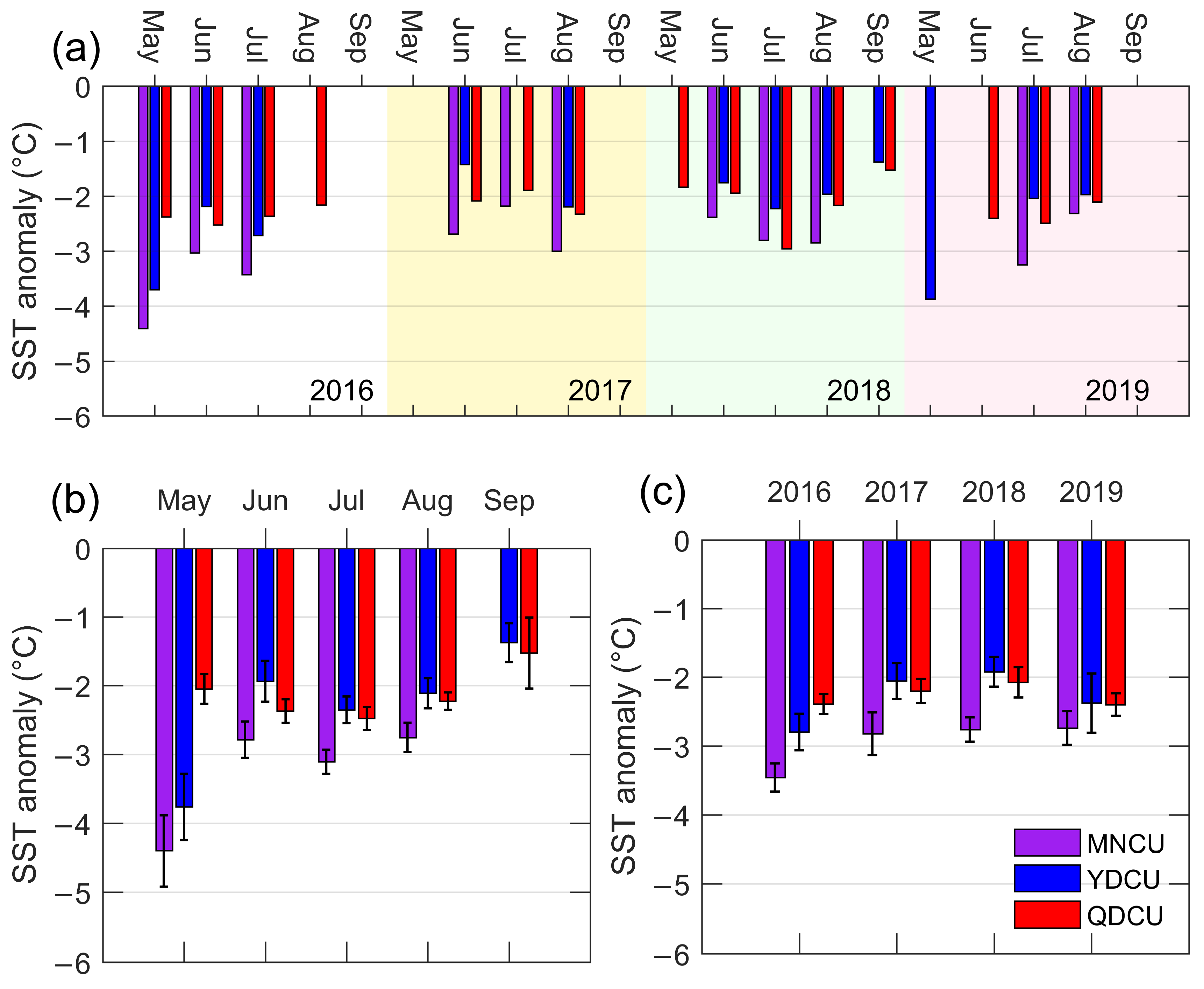
Figure 9.
The inter-monthly and the inter-annual variations of the coastal upwelling’s SST_A (unit: °C) in the NSCS from 2016 to 2019. (a) The monthly mean of upwelling SST_A for the individual years 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019; (b) the monthly mean of the upwelling SST_A regardless of the year; (c) the annual mean of the upwelling SST_A. The error bars in (b,c) are 95% confidence intervals.
During 2016–2019, the Minnan coastal upwelling was quite strong, with its overall mean SST_A of −2.87 °C (Figure 9b), calculated from the daily SST_A values in June, July, and August of 2016–2019. We used only June, July, and August to calculate the overall mean SST_A, because the coastal upwelling in the NSCS occurred most frequently from June to August (Figure 5 and Figure 6b). The Qiongdong coastal upwelling and the Yuedong coastal upwelling had the overall mean SST_A of −2.36 °C and −2.13 °C, respectively.
During the boreal summers of 2016–2019, the inter-monthly pattern of SST_A was similar to that of the upwelling’s influence area. Except for the MNCU and the YDCU events that occurred in May 2016, the coastal upwelling intensified from May, peaked in July, and then weakened to its minimum in September (Figure 9b). The SST_A differences among these months are generally statistically significant. In terms of the inter-annual variation (Figure 9c), the MNCU’s mean SST_A was ≈−3.6 °C in 2016 and reduced to ≈−2.8 °C during 2017–2019. The SST_A differences between 2016 and the next years are statistically significant (Figure 9c). The YDCU was the strongest in 2016 (≈−2.8 °C), but it was the weakest in 2018 (≈−1.9 °C). The SST_A differences between 2016 and 2017 (between 2016 and 2018) are statistically significant. The QDCU was strong in both 2016 and 2019 (≈−2.4 °C) but weakened from 2016 to 2018 (≈−2.1 °C).
3.4. The Chl-a Increase of the Coastal Upwelling in the NSCS
Upwelling often uplifts nutrient-rich deeper water to the surface or subsurface layer, resulting in the increase of Chl-a concentration in the upwelling areas. In this study, we used Equation (11) to calculate the magnitude of such an increase. The results are shown in Figure 10.
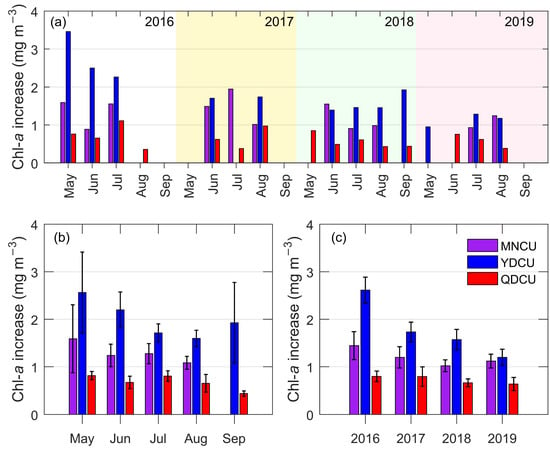
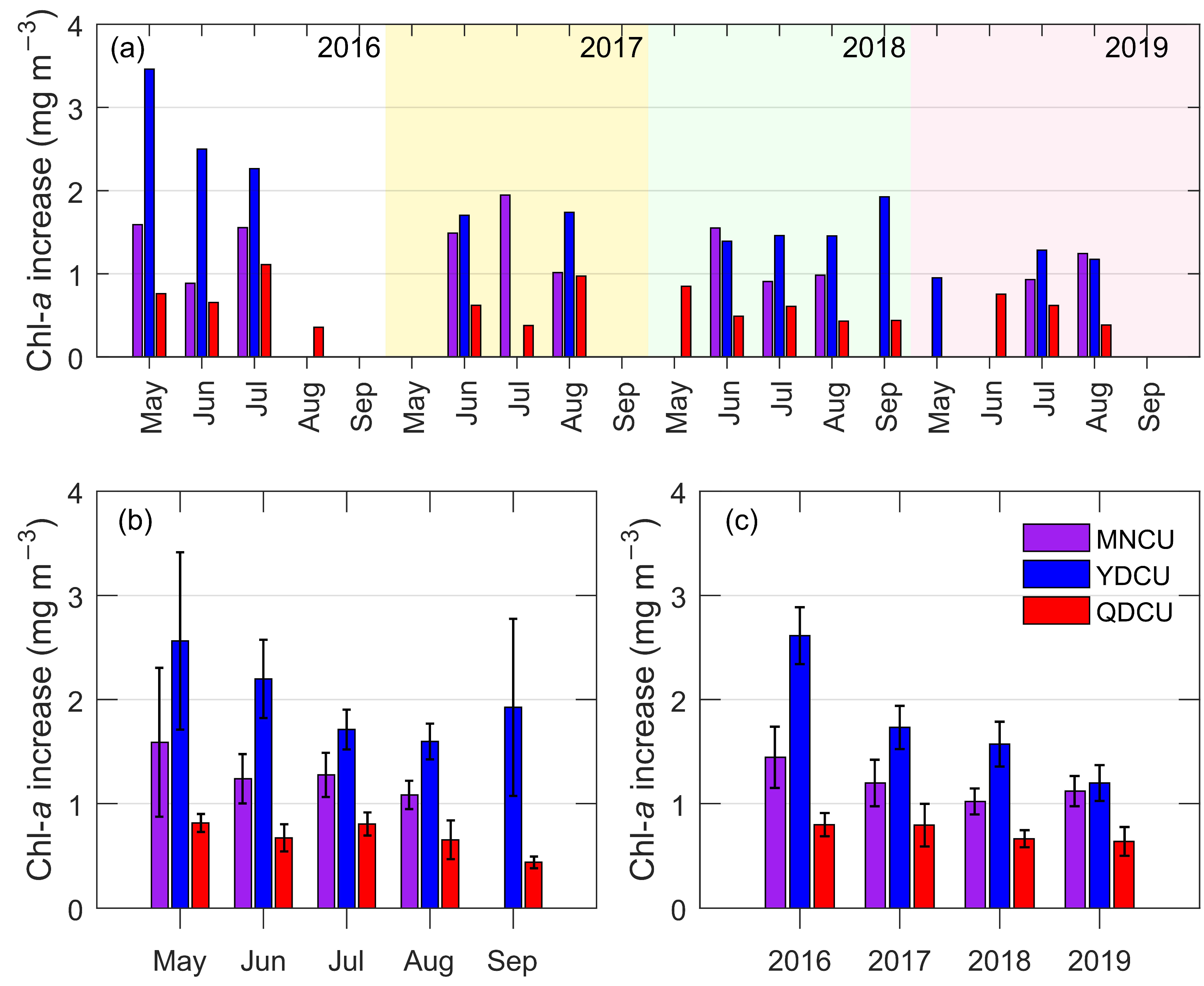
Figure 10.
The inter-monthly and the inter-annual variations of the coastal upwelling’s Chl-a increase (unit: mg m−3) in the NSCS from 2016 to 2019. (a) The monthly mean of upwelling’s Chl-a increase for the individual years 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019; (b) the monthly mean of the upwelling’s Chl-a increase regardless of the year; (c) the annual mean of the upwelling’s Chl-a increase. The error bars in (b,c) are 95% confidence intervals.
The Chl-a increase in the Yuedong coastal upwelling was the highest in the NSCS during the boreal summers of 2016–2019, with an overall mean Chl-a increase of 1.74 mg m−3. In contrast, the overall mean Chl-a increases of the Minnan coastal upwelling and the Qiongdong coastal upwelling were 1.28 mg m−3 and 0.66 mg m−3, respectively. The Chl-a increase of the YDCU reduces from May, reaches the minimum in August, and then rises again in September (Figure 10b). The patterns of the inter-monthly variation of Chl-a increase of the MNCU and the QDCU are similar to those of the SST_A (and other characteristics). The largest Chl-a increase in the MNCU or in the QDCU occurs in May, followed by July (Figure 10b). After July, the Chl-a increase reduces to a minimum in September. In terms of the inter-annual variation, the Chl-a increase was the largest in 2016 (Figure 10c). From 2016 to 2019, the Chl-a increase of the YDCU reduced gradually. However, for either the MNCU or the QDCU, the inter-annual variation of the Chl-a increase is not statistically significant.
4. Discussion
4.1. Upwelling Index and Upwelling Mechanisms in the NSCS
In this study, we used upwelling index and wind stress curl to discuss the mechanisms of coastal upwelling. Two points along the east coast of Hainan Island, three points along the east coast of Guangdong, and two points along the south coast of Fujian were selected to calculate their wind-driven upwelling index (the stars in Figure 1). The upwelling index for each region was calculated by averaging the index of the selected points in each region. The wind stress curl was calculated by the wind field for the whole NSCS region. Figure 11 shows the variations of upwelling index and Figure 12 shows the patterns of wind vectors and wind stress curl.
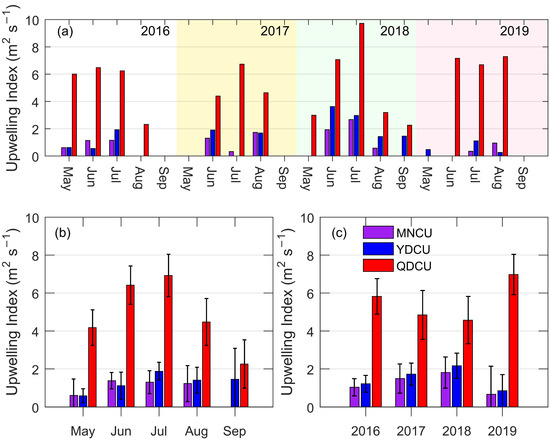
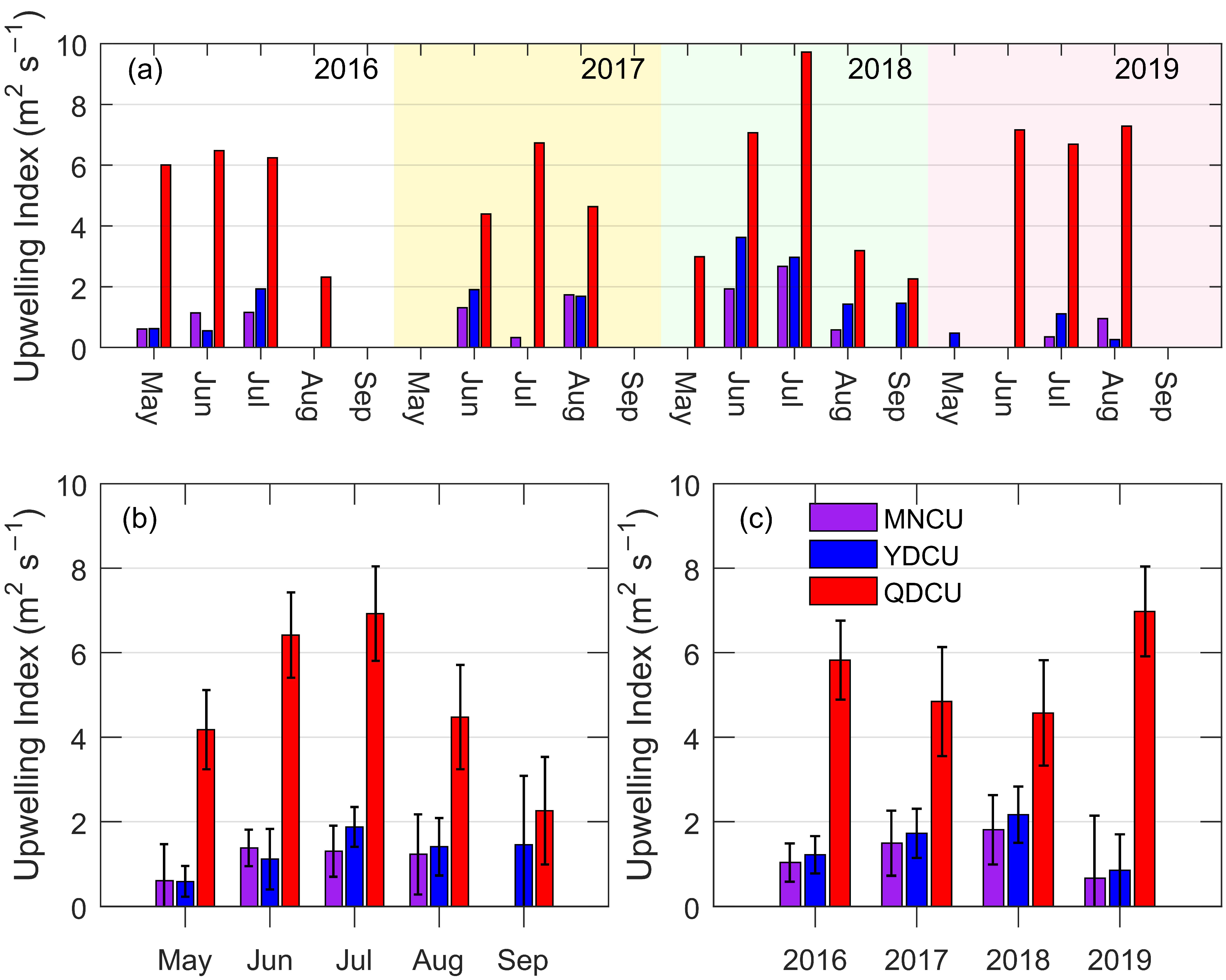
Figure 11.
The inter-monthly and inter-annual variations of the upwelling index (m2 s−1) in the NSCS from 2016 to 2019. (a) The monthly mean of upwelling index for the individual years 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019; (b) the monthly mean of the upwelling index regardless of the year; (c) the annual mean of the upwelling index. The error bars in (b,c) are 95% confidence intervals.
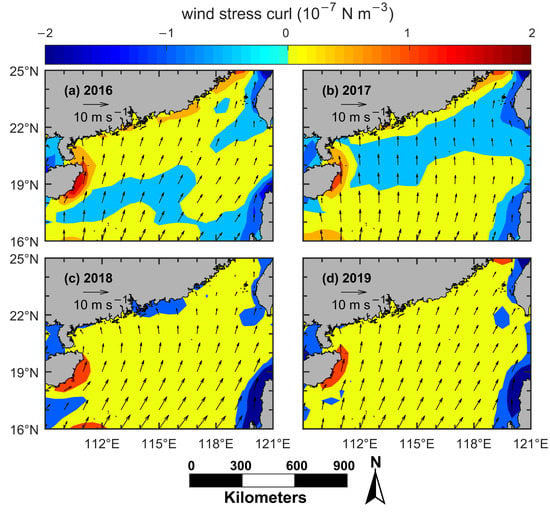
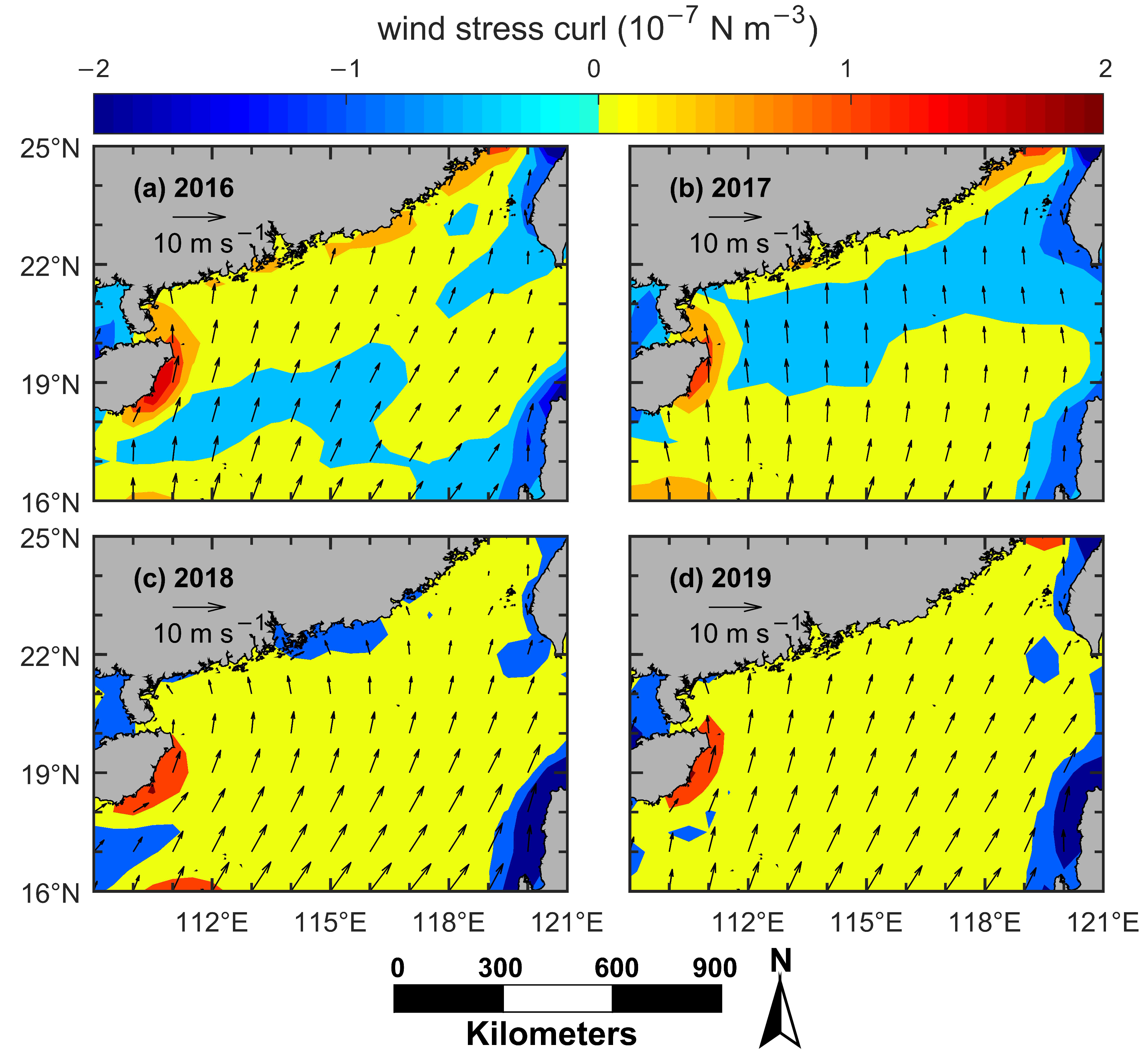
Figure 12.
Boreal summer average sea surface wind (arrows, m s−1) and wind stress curl (color, N m−3) for 2016 (a), 2017 (b), 2018 (c), and 2019 (d). Note that the boreal summer excludes the months of May and September.
During each upwelling event, the upwelling index was positive on average. For the Qiongdong coastal upwelling, the upwelling index increases from May, reaches a maximum in July, and then decreases to a minimum in September (Figure 11b). The differences in upwelling index between June/July and the other months are statistically significant. For the Yuedong coastal upwelling, the upwelling index is the smallest in May and the largest in July. The difference between these two months is statistically significant. For the Minnan coastal upwelling, the upwelling index is also higher in June–August than that in May. However, the differences are not statistically significant. In general, the inter-monthly pattern of the upwelling index is similar to that of the upwelling SST_A or other characteristics Figure 9a and Figure 11a).
Since May and September are the monsoon transition seasons, Figure 12 only shows the mean wind field and wind stress curl from June to August each year. The wind stress curl off the east coast of Hainan Island was much larger than that off the east coast of Guangdong or off south coast of Fujian from 2016 to 2019. That is to say, during 2016–2019, the wind stress curl was also an important cause of Qiongdong coastal upwelling. As for the Yuedong coastal upwelling and the Minnan coastal upwelling, the wind stress curl was ≈0 or negative in most cases, which means that the wind stress curl did not induce upwelling or even induced downwelling during 2016–2019.
The value of upwelling index is determined by the wind speed and wind direction. The wind speed along the east coast of Hainan Island in June–August during 2016–2019 was much larger than that along the east coast of Guangdong or along the south coast of Fujian (Figure 12). Therefore, the upwelling index of the QDCU was much larger than that of the MNCU or the YDCU during 2016–2019 (Figure 11). Moreover, in the QDCU occurrence region, the wind stress curl also contributed to the upwelling generation. However, the SST_A and the Chl-a increase of the QDCU were actually smaller than (or similar to) those of the MNCU or the YDCU (Figure 9 and Figure 10). Meanwhile, the temporal pattern of the upwelling index of the QDCU was similar to that of the SST_A or the Chl-a increase, indicating that the summer southwesterly monsoon was the main mechanism for the QDCU. However, in the MNCU and the YDCU, the temporal pattern of the upwelling index was different from that of SST_A or Chl-a increase, which may indicate that there were other factors contributing to the formation of these two coastal upwelling regions. It has been found that the coastal upwelling occurs off Shantou coast during wind relaxation [29], indicating that in addition to the local wind, there are other factors (e.g., topography, thermocline depth on the shelf) contributing to the formation of the MNCU or the YDCU [6,30]. Moreover, according to the in situ observations, the MNCU and the YDCU can uplift the deeper water to the layer of 10 m [31]. However, east of Hainan Island, the upwelling is strong in the layer of 30–50 m [32]. Consequently, despite a much larger upwelling index of the QDCU, the SST_A and Chl-a increase of the QDCU were both smaller (or similar) compared to those of the MNCU or the YDCU.
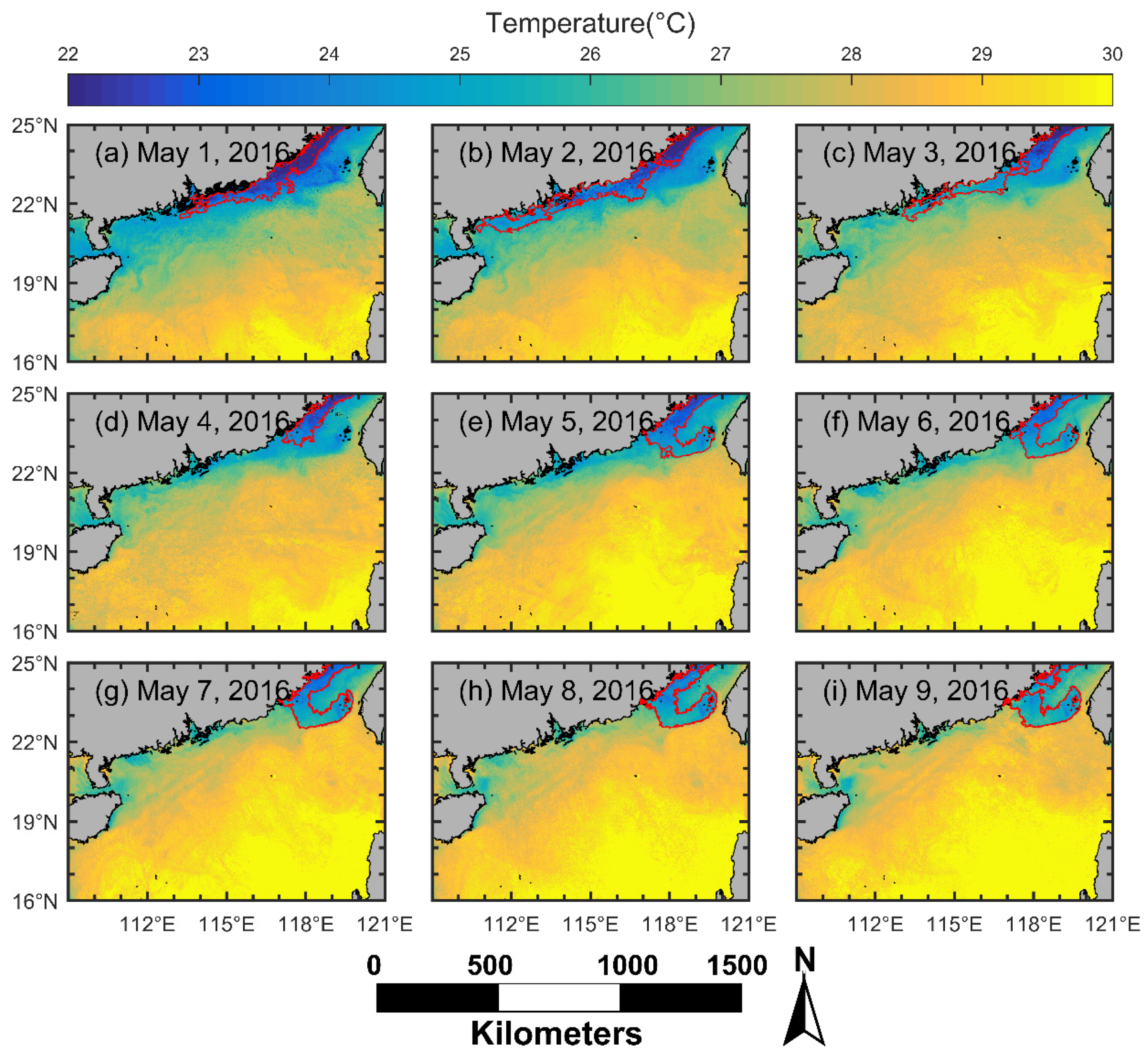
The significant upwelling event that occurred off the south coast of Fujian between May 1 and 9, 2016 (Figure 5) was unusually strong, with a mean SST_A of ≈−4.40 °C (Figure 9a) and its influence area (2.6 × 104 km2, Figure 8a) extending to mid-shelf off the Fujian coast (Figure 7a). Indeed, as shown in Figure 13, during this upwelling event, the entire Fujian’s south coast featured low SST, and this low-temperature area extended to east of Guangdong or the Taiwan Bank. However, the mean upwelling index of this event was only 0.61 m2 s−1 (Figure 11a), which was much lower than the overall mean upwelling index of the Minnan coastal upwelling (1.16 m2 s−1) during the boreal summers of 2016–2019. Therefore, we believe that the alongshore wind was not the only factor inducing this upwelling event; besides, the offshore wind may be one factor for flow–topography interaction that resulted in this phenomenon. The detailed mechanism of this upwelling event is not clear and requires further study.
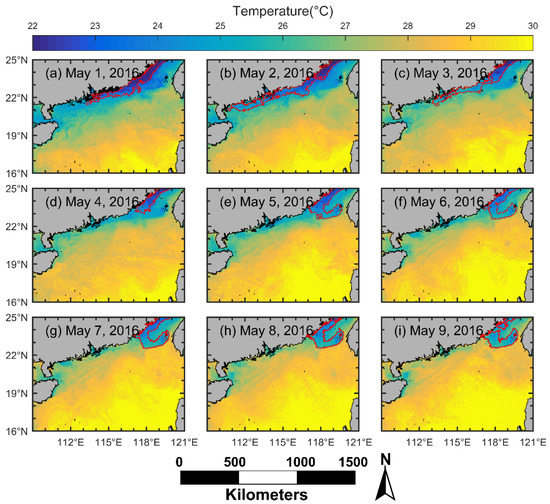
Figure 13.
SST in the NSCS from 1 May to 9 May 2016. (a–i) represent the SST on 1 May to 9 May 2016, respectively. The areas within the red line are the low-temperature areas mapped by the TPI method (also the upwelling candidate).
4.2. Upwelling Characteristics
The frequency of occurrence and influence area of the coastal upwelling in the NSCS during the boreal summers of 2016–2019 are shown in Figure 14. The coastal upwelling occurs most frequently off the east coast of Hainan Island, east coast of Guangdong, and south coast of Fujian. However, it is too difficult to distinguish the Yuedong coastal upwelling from the Minnan coastal upwelling because of their spatial connection. Indeed, the occurrence time of YDCU coincides with that of the MNCU in most cases (Figure 5).
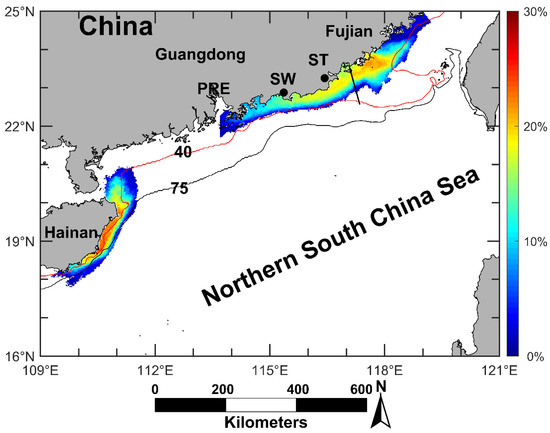
Figure 14.
The frequency of occurrence and influence area of significant coastal upwelling in the NSCS. The color represents the frequency of upwelling occurrence. Red line: 40 m isobath, black line: 75 m isobaths, black solid line: border between Minnan coastal upwelling and Yuedong coastal upwelling. (PRE: Pearl River Estuary, ST: Shantou, SW: Shanwei).
The correlation coefficients of the monthly characteristics (duration in Figure 6a, influence area in Figure 8a, SST_A in Figure 9a, Chl-a increase in Figure 10a, and upwelling index in Figure 11a) are shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 for the Minnan coastal upwelling, the Yuedong coastal upwelling, and the Qiongdong coastal upwelling, respectively. Most values of the correlation coefficients are larger than 0.5 or even larger than 0.7 (Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3). As mentioned above, there are other factors contributing to the formation of MNCU or YDCU. So, as for either the MNCU or the YDCU, some values of the correlation coefficients are less than 0.5 (Table 1 and Table 2, values with superscript “*”). However, for the QDCU, all the values of correlation coefficients are larger than 0.5, with the maximum value of ≈0.9. In general, most upwelling characteristics show moderate to high correlations with one another. Most of these correlations are statistically significant, especially the correlations of other three characteristics with SST_A. This indicates that the characteristics of the coastal upwelling in the NSCS have generally similar inter-monthly patterns. Generally speaking, the upwelling strength increases from May, reaches the maximum in July, and then decreases to a minimum in September. This is because the coastal upwellings in the NSCS are mainly wind-driven and thus follow the inter-monthly patterns of the summer monsoon, although there are still other factors driving the MNCU and the YDCU [6,29,30].

Table 1.
Correlation coefficients between characteristics of Minnan coastal upwelling (n = 20, p = 0.01).

Table 2.
Correlation coefficients between characteristics of Yuedong coastal upwelling (n = 20, p = 0.01).

Table 3.
Correlation coefficients between characteristics of Qiongdong coastal upwelling (n = 20, p = 0.01).
A four-year time series is not sufficient to examine the inter-annual variability of the upwelling characteristics. However, this study did show that the coastal upwelling in the NSCS was much stronger in 2016 than in 2017–2019. This finding is consistent with a previous upwelling study [6]. According to the Ocean Niño Index, there was a strong El Niño event in 2015–2016, and the strong El Niño condition was quickly transitioned into the La Niña condition during the summer of 2016. This might have contributed to the strongest upwelling activities detected in the summer season of 2016 (e.g., [4,6,8,21,33]).
The Yuedong coastal upwelling has a higher Chl-a increase than that of the Minnan coastal upwelling or the Qiongdong coastal upwelling. This is likely because that the YDCU brings the nutrient-rich Pearl River diluted water to the surface, and the interaction of Pearl River plume and the YDCU would also accumulate the nutrients in the nearshore area [34,35]. The temporal pattern of Chl-a increase of the YDCU is different from that of other characteristics, showing a decline from May to August (Figure 10b). This may be due to the flood season in the Pearl River beginning in early May (sometimes April), which lasts for about 4 months. In May and September, the diluted water enriches the Chl-a in the YDCU area, but in June–August, the strong southwesterly monsoon induces strong offshore Ekman transport, transporting the enriched water to the open ocean (far reaching the ≈21.5 °N, out of upwelling area) [36,37]. As a result, the Chl-a increase in June–August is less than that in May or September.
5. Conclusions
Previous upwelling studies in the NSCS have been generally point-specific, mostly focusing on a single zone. Although it is important to directly quantify the upwelling, there were few studies investigating the upwelling in the NSCS quantitatively [9]. This study focuses on three different coastal upwelling regions by mapping and comparing their upwelling characteristics. Based on the Himawari-8 SST data and the semi-automatic TPI based mapping method, this study identifies the areas in which the coastal upwelling occurs most frequently in the NSCS. Most importantly, this study quantitatively examines the spatial and temporal characteristics of significant coastal upwelling in the NSCS.
The key findings of this study are as follows:
- (1)
- Based on the Himawari-8 SST data, we have used the semi-automatic TPI based method to identify and map the significant coastal upwelling events and quantitatively analyze the characteristics of coastal upwelling in the NSCS. In general, the strength of the coastal upwelling in the NSCS increased from May, reached the maximum in July, and then decreased to its minimum in September during the boreal summers of 2016–2019. One notable exception to this general pattern is that the upwelling that occurred in May 2016 had unusually large upwelling strength in the Minnan and the Yuedong coastal upwelling regions. In addition, the upwelling strength was much stronger in 2016 than that in next three years, which may be due to the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation) effect.
- (2)
- The area in which upwelling occurs most frequently in the NSCS was specified. The Qiongdong coastal upwelling occurs most frequently off the east coast of Hainan Island, and it is limited to the area shallower than 75 m. The Yuedong coastal upwelling occurs most frequently east of Shanwei, and it is limited to the ≈80 km offshore area within the 40 m depth contour. The Minnan coastal upwelling occurs most frequently off the south coast of Fujian, and it is limited to the ≈100 km offshore area.
- (3)
- Different coastal upwelling regions in the NSCS are significantly different in characteristics. Mainly driven by the summer monsoon, the Qiongdong coastal upwelling had the longest duration and occurred most frequently during 2016–2019. As a result of the long coastline, the influence area of the Yuedong coastal upwelling is the largest in the NSCS. In addition, affected by the Pearl River diluted water, the Chl-a increase of the Yuedong coastal upwelling is much larger than that of the other two upwelling regions. In terms of upwelling strength, the Minnan coastal upwelling is quite strong in the NSCS.
- (4)
- The Minnan coastal upwelling and the Yuedong coastal upwelling share many characteristics in common. Especially, their formation mechanisms and temporal variability are similar. Due to the consistence of occurrence time and spatial connection of these two upwellings, it is difficult to distinguish them from one another only by using the SST data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.H. and J.H.; funding, J.H.; methodology, W.S., Z.H. and J.H.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S.; writing—review and editing, W.S., J.H. and Z.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91958203, 41776027 and 41730533). Z.H.’s visiting to Xiamen University was supported by the MEL Visiting Fellowship (MELRS1767).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets for this research are publicly available. The wind data are provided by National Centers for Environmental Information, NOAA via https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/data-access/model-data/model-datasets/climate-forecast-system-version2-cfsv2 accessed on 10 March 2021. The Himawari-8 SST and Chlorophyll-a data are provided by GHRSST and JAXA/EORC via https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ptree/index.html accessed on 10 March 2021. We appreciate the use of these publically available datasets.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate all the constructive comments from the Editor and four anonymous reviewers that have improved early version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hu, J.Y.; Kawamura, H.; Hong, H.S.; Qi, Y.Q. A review on the currents in the South China Sea: Seasonal circulation, South China Sea warm current and Kuroshio intrusion. J. Oceanogr. 2000, 56, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S.; Li, L. Summarization of study on upwelling system in the South China Sea. J. Oceangor. Taiwan Strait 2003, 22, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.Y.; Wang, X.H. Progress on upwelling studies in the China seas. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.L.; Zong, X.L.; Yin, X.F.; Li, M. The interannual variation and long term trend of Qiongdong Upwelling. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2016, 47, 43–51, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kok, P.H.; Mohd Akhir, M.F.; Tangang, F.; Husain, M.L. Spatiotemporal trends in the southwest monsoon wind-driven upwelling in the southwestern part of the South China Sea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.Q.; Wang, D.X.; Feng, M.; Geng, B.X.; Chen, J.; Yao, J.L.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Q.Y. The contribution of local wind and ocean circulation to the interannual variability in coastal upwelling intensity in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2018, 123, 6766–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gao, L.; Dong, X.; Pan, A.J.; Wang, W.B.; Wan, X.F. The interannual variation and preliminary analysis of upwelling in eastern Hainan Island in summer of 2014 and 2015. Haiyang Xuebao 2019, 41, 1–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Wu, C.R. Nonstationary El Niño teleconnection on the post-summer upwelling off Vietnam. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndah, A.B.; Becek, K.; Dagar, L. A review of coastal upwelling research in the South China Sea: Challenges, limitations and prospects. Int. J. Earth Atmos. Sci. 2016, 3, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.Y.; Qi, Y.Q.; Hua, Z.L. Numerical study on upwelling and its seasonal variation along Fujian and Zhejiang coast. J. Hohai Univ. 2007, 34, 464–470, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.X.; Lin, H.Y. Preliminary analysis for the summer upwelling in the continental shelf margin waters of east Guangdong. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 1990, 9, 16–23, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.Y.; Qi, Y.Q.; Yan, D.; Zhang, S.W.; Xie, L.L. Summer upwelling and thermal fronts in the northwestern South China Sea: Observational analysis of two mesoscale mapping surveys. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2015, 120, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An introduction of Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satelites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, Y.; Murakami, H.; Kachi, M. Sea surface temperature from the new Japanese geostationary meteorological Himawari-8 satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H. Ocean color estimation by Himawari-8/AHI. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9878, Remote Sensing of the Oceans and Inland Waters: Techniques, Applications, and Challenges, New Delhi, India, 4–7 April 2016; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2016; p. 987810. [Google Scholar]
- Sasa, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.R.; Wang, J.D.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.T.; Chuang, H.Y.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NECP climate forecast system version2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, A.D. Topographic Position and Landforms Analysis. In Proceedings of the ESRI International User Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Feng, M. Remotely sensed spatial and temporal variability of the Leeuwin Current using MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 166, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X. Quantitative mapping of the East Australian Current encroachment using time series Himawari-8 sea surface temperature data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.H. Mapping the spatial and temporal variability of the upwelling systems of the Australian south-eastern coast using 14-year of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hu, J.Y.; Shi, W.S. Mapping the coastal upwelling east of Taiwan using geostationary satellite data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.Y.; Qi, Y.Q.; Hua, Z.L. Numerical study on summer upwelling over northern continental shelf of South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2008, 3, 1–8, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A. Coastal Upwelling Indices, West Coast of North America, 1946–1971, NOM Tech. Rep. NMFS SSRF-671; Scientific Publications Office: Seattle, WA, USA, 1973; pp. 1–13.
- Wang, D.W.; Gouhier, T.C.; Menge, B.A.; Ganguly, A.R. Intensification and spatial homogenization of coastal upwelling under climate change. Nature 2015, 518, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, J.; Doubell, M.; Griffin, D.; Matthews, R.L.; Ward, T.M. Evidence of a large seasonal coastal upwelling system along the southern shelf of Australia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L09310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, R.; Alvarez, I.; Santos, F.; de Castro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. Has upwelling strengthened along worldwide coasts over 1982–2010? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.K.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Liu, G.M.; Wu, X.Y. Role of Ekman transport versus Ekman pumping in driving summer upwelling in the South China Sea. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2013, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, Y.; Iida, N.; Kawamura, H.; Ebuchi, N.; Jones, I.S.F. Wave dependence of sea-surface wind stress. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.P.; Cheung, A.; Guo, X.G.; Li, L. Intensified upwelling over a widened shelf in the northeastern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C09019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.X.; Shu, Y.Q.; Xue, H.J.; Hu, J.Y.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, W.; Zu, T.T.; Xu, J.D. Relative contributions of local wind and topography to the coastal upwelling intensity in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2014, 119, 2550–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.Z.; Wu, R.S.; Xu, J.D. Characteristics of upwelling in eastern Guangdong and southern Fujian coastal waters during 2006 summer. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2011, 30, 489–497, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, Z.Y.; Qi, Y.Q. Coastal upwelling off eastern Hainan Island observed in the summer of 2013. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2016, 35, 40–49, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.P.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D.X.; Liu, W.T. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2003, 108, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.Q.; Dai, M.H.; Kao, S.J.; Gan, J.P.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.F.; Zhai, W.D.; Wang, L. Nutrient dynamics and biological consumption in a large continental shelf system under the influence of both a river plume and coastal upwelling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.P.; Li, L.; Wang, D.X.; Guo, X.G. Interaction of a river plume with coastal upwelling in the northeastern South China Sea. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2009, 29, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, D. Responses of the river plume to the external forcing in Pearl River Estuary. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, R.X.; Zhu, P.L.; Ren, P.D. Seasonal variation of the Pearl River diluted water and its dynamical cause. Marin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 33, 36–44, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).