Potential Associations between Low-Level Jets and Intraseasonal and Semi-Diurnal Variations in Coastal Chlorophyll—A over the Beibuwan Gulf, South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multi-Satellite Datasets
2.2. Identification of LLJs
2.3. Difference Significance Test
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation of Summer LLJs over the BBG
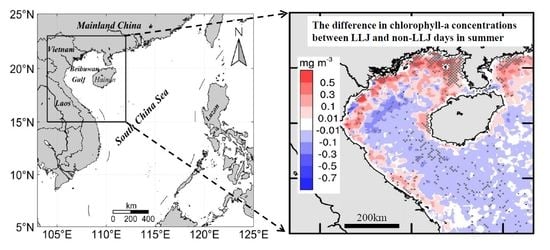
3.2. Biophysical Differences between LLJs and Non-LLJs Days in Coastal Regions
3.3. Potential Drivers of LLJs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, I.S.; Antoine, D.; Darecki, M.; Gorringe, P.; Pettersson, L.; Ruddick, K.; Santoleri, R.; Siegel, H.; Vincent, P.; Wernand, M.R.; et al. Remote sensing of shelf sea ecosystems: State of the art and perspectives. J. Southeast Asian Stud. 2008, 24, 2905–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.A.; Liu, K.K.; Macdonald, R. Continental margin exchanges. In Ocean Biogeochemistry: The Role of the Ocean Carbon Cycle in Global Change; Global Change—The IGBP Series; Fasham, M.J.R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 53–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.L.; Kawamura, H.; Doan-Nhu, H.; Takahashi, W. Remote sensing oceanography of a harmful algal bloom off the coast of southeastern Vietnam. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2004, 109, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largier, J.L.; Lawrence, C.A.; Roughan, M.; Kaplan, D.M.; Dever, E.P.; Dorman, C.E.; Kudela, R.M.; Bollens, S.M.; Wilkerson, F.P.; Dugdale, R.C.; et al. West: A northern california study of the role of wind-driven transport in the productivity of coastal plankton communities. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2006, 53, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, J.; Tweddle, J.F.; Mattias Green, J.A.; Palmer, M.R.; Kim, Y.N.; Hickman, A.E.; Holligan, P.M.; Mark Moore, C.; Rippeth, T.P.; Simpson, J.H.; et al. Spring-neap modulation of internal tide mixing and vertical nitrate fluxes at a shelf edge in summer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.H.; Kedong, Y.; Lee, J.H.W.; Gan, J.P.; Liu, H.B. Physical–biological coupling in the Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Wong, C.K.; Lie, A.A.Y.; Yung, Y.K. Size structure and pigment composition of phytoplankton communities in different hydrographic zones in Hong Kong’s coastal seas. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2015, 95, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.; Hong, Y.G.; Yin, J.P.; Dong, J.D.; Wang, Y.S. Evolution of the sink and source of dissolved inorganic nitrogen with salinity as a tracer during summer in the Pearl River Estuary. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, R.H.; Black, B.D.; Li, Z. An upwelling case study on florida’s west coast. J. Geophy. Res. Ocean 2000, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, A. Ecological Geography of the Sea, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; p. 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafstall, J.; Dengler, M.; Brandt, P.; Bange, H. Tidal-induced mixing and diapycnal nutrient fluxes in the mauritanian upwelling region. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.J. Shelf-sea ecosystems. In Analysis of Marine Ecosystems; Longhurst, A.R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1980; pp. 159–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ward, B.A.; Waniek, J.J. Phytoplankton growth conditions during autumn and winter in the Irminger sea, North Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 334, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, J.A.; Schollaert, S.E.; O’Reilly, J.E. Climatological phytoplankton chlorophyll and sea surface temperature patterns in continental shelf and slope waters off the northeast U.S. coast. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botsford, L.W.; Lawrence, C.A.; Dever, E.P.; Hastings, A.; Largier, J. Effects of variable winds on biological productivity on continental shelves in coastal upwelling systems. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2006, 53, 3116–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Waniek, J.J. Factors affecting chlorophyll a concentration in the central Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 474, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Ning, X.R.; Cai, Y.M. Distribution characteristies of size-fractionated chlorophyll-a and productivity of phytoplankton in the Beibu Gulf. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1998, 20, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, D.S.V.; Hoekstra, P. Dispersal of suspended sediments in the turbid and highly stratified red river plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, D.S.V. Water and sediment dynamics in the red river mouth and adjacent coastal zone. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 29, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Pan, J.; Adam, T.D. Influence of monsoonal winds on chlorophyll-α distribution in the Beibu Gulf. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, Q.; Lin, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Yan, J. The role of Qiongzhou Strait in the seasonal variation of the South China Sea circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, J. On the mechanism of the cyclonic circulation in the Gulf of Tonkin in the summer. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C09029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Huang, Q.; Long, X. Three-dimensional numerical model study of the residual current in the South China Sea. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.; Chao, S.Y.; Shaw, P.T.; Gong, G.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tang, T.Y. Monsoon-forced chlorophyll distribution and primary production in the South China Sea: Observations and a numerical study. Deep Sea Res. Part I 2002, 49, 1387–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xian, T.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.F. Summer Monsoon Impacts on Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Middle of the South China Sea: Climatological Mean and Annual Variability. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2012, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Wang, H. The transport and deposition of dust and its impact on phytoplankton growth in the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhou, W.; Wang, G.; Cao, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, G.; Zhao, W. Comparison of Satellite-Derived Phytoplankton Size Classes Using In-Situ Measurements in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cham, D.D.; Son, N.T.; Minh, N.Q.; Thanh, N.T.; Dung, T.T. An analysis of shoreline changes using combined multitemporal remote sensing and digital evaluation model. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.L.; Kawamura, H.; Lee, M.A.; Dien, V.T. Seasonal and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentrations and water conditions in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Guo, F.; Huang, L.F.; Huang, F.P. Distribution characteristics of chlorophyll a content in the Beibu Gulf. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2014, 42, 144–146. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.M.; Tang, D.L. Offshore and nearshore chlorophyll increases induced by typhoon winds and subsequent terrestrial rainwater runoff. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 333, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Pan, D.; Mao, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chen, J. The effects of chlorophyll-a and SST in the South China Sea area by typhoon near last decade. SPIE Eur. Remote Sens. 2009, 7478, 74782E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.P.; Zhong, Z.; Jiang, J. Upper ocean response of the South China Sea to Typhoon Krovanh (2003). Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2009, 47, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Li, J.G.; Sun, L.; Wang, G.H.; Tan, D.L.; Huang, P.; Yan, H.; Gao, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.Q.; et al. Basin-wide responses of the South China Sea environment to Super Typhoon Mangkhut (2018). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Tang, D.L. Remote sensing analysis of impact of typhoon on environment in the sea area south of Hainan Island. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollerud, E.I.; Caracena, F.; Koch, S.E.; Jamison, B.D.; Hardesty, R.M.; Mccarty, B.J.; Kiemle, C.; Collander, R.S.; Bartels, D.L.; Albers, S. Mesoscale moisture transport by the Low-Level Jet during the IHOP field experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 3781–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berg, L.K.; Riihimaki, L.D.; Qian, Y.; Yan, H.P.; Huang, M.Y. The Low-Level Jet over the Southern Great Plains determined from observations and reanalyses and its impact on moisture transport. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 6682–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, R.W.; Yao, Y.; Yarosh, E.S.; Janowiak, J.E.; Mo, K.C. Influence of the great plains Low-Level Jet on summertime precipitation and moisture transport over the Central United States. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, A.J.; Rife, D.L.; Pinto, J.O.; Davis, C.A.; Hannan, J.R. Global precipitation extremes associated with diurnally varying Low-level Jets. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5065–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. Numerical simulations of spatial distributions and diurnal variations of Low-Level Jets in china during early summer. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5747–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, L.S.; Allwine, K.J.; Banta, R.M. Nocturnal low-level jet in a mountain basin complex. part II: Transport and diffusion of tracer under stable conditions. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Klein, P.M.; Xue, M.; Zhang, F.; Doughty, D.C.; Forkel, R.; Joseph, E.; Fuentes, J.D. Impact of the vertical mixing induced by Low-level Jets on boundary layer ozone concentration. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ahn, J.; Jiang, L.; Shi, W.; Son, S.; Park, Y.; Ryu, J. Ocean color products from the Korean Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Opt. Express 2013, 21, 3835–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Lu, C.-Y.; Hsu, T.-W.; Ho, C.-R. Diurnal to Seasonal Variations in Ocean Chlorophyll and Ocean Currents in the North of Taiwan Observed by Geostationary Ocean Color Imager and Coastal Radar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Analysis of ocean diurnal variations from the Korean Geostationary Ocean Color Imager measurements using the DINEOF method. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 180, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H. Ocean color estimation by Himawari-8/AHI. In Proceedings of the SPIE Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing, New Delhi, India, 4–7 April 2016; Volume 9878, p. 987810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Han, H.; Cho, S.; Park, Y.; Ahn, Y. Overview of geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) and GOCI data processing system (GDPS). Ocean Sci. J. 2012, 47, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Gentemann, C.L.; Smith, D.K.; Chelton, D. Satellite measurements of sea surface temperature through clouds. Science 2000, 288, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlon, C.; Rayner, N.; Robinson, I.; Poulter, D.J.S.; Casey, K.S.; Vazquez Cuervo, J.; Armstrong, E.; Bingham, A.; Arino, O.; Gentemann, C.; et al. The Global Ocean Data Assimilation Experiment High-resolution Sea Surface Temperature Pilot Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentemann, C.L.; Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. Accuracy of satellite sea surface temperatures at 7 and 11 GHz. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M. Improved global sea surface temperature analyses using optimum interpolation. J. Clim. 1994, 7, 929–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A. Assessment and quantification of meteorological data for implementation of weather radar in mountainous regions. Mausam 2016, 67, 789–802. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrazzaq, Z.T.; Hasan, R.H.; Aziz, N.A. Integrated TRMM Data and Standardized Precipitation Index to Monitor the Meteorological Drought. Civ. Eng. J. 2019, 5, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F.J.; Zheng, X.Y.; Fu, Y.F.; Zhou, S.X. TRMM-based Optical and Microphysical Features of Precipitating Clouds in Summer over the Yangtze-Huaihe River Valley, China. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.D. Climatology of the Low-Level Jet. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 833–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, C.D.; Bian, X.; Zhong, S. Low-Level Jet Climatology from Enhanced Rawinsonde Observations at a Site in the Southern Great Plains. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1363–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.; Zhang, F. Characteristics of coastal low-level jets over Beibu Gulf, China, during the early warm season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Hu, J.Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhu, J. Sectional features of temperature and salinity in Beibu Gulf during July–August, 2006. In Marine Scientific Research Papers in Beibu Gulf, 2nd ed.; Li, Y., Hu, J.Y., Eds.; The Ocean Publishing Company: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 85–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.G.; Qiao, F.L.; Wang, G.S.; Xia, C.S.; Yuan, Y.L. Upwelling off the west coast of Hainan Island in summer: Its detection and mechanisms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Qiao, F.L.; Xia, C.S.; Wang, G. The numerical investigation of seasonal variation of the cold water mass in the Beibu Gulf and its mechanisms. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.S.; Wu, G.D.; Ya, H.Z. Review of the circulation in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 138, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Kawamura, H.; Tang, D. Tidal front around the Hainan Island, northwest of the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Shan, H.; Li, Y.H. Seasonal variations of sea surface temperature, chlorophyll a and turbidity in Beibu Gulf, MODIS imagery study. J. Xiamen Univ. 2008, 47, 856–863. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Chen, P.; Yu, J.; Wu, Q. Environmental influence on the spatiotemporal variability of fishing grounds in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.J.; Sui, Y.; Tang, D.L.; Afanasyev, Y.D. A subsurface chlorophyll a bloom induced by typhoon in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, D.; Su, J. Generation and life cycle of the dipole in the South China Sea summer circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.P.; Chang, C.H.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D.X. Intraseasonal variability in the summer South China Sea: Wind jet, cold filament, and recirculations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Cai, S.; Cai, S.; Shang, X.; Peng, S.; Shu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xie, X.H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Advances in research of the mid-deep South China Sea circulation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Huang, Z.; Hu, J. Using TPI to Map Spatial and Temporal Variations of Significant Coastal Upwelling in the Northern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Han, H.J.; Heo, J.M.; Jeong, J.; Kwak, S. Ocean Color Algorithm Development Environment for High-Speed Data Processing of GOCI-II. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 7968–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Title 1 | LLJ Days | Non-LLJ Days |
|---|---|---|
| Region A | 1.33 | 0.63 |
| Region B | 0.83 | 0.64 |
| Region C | 0.10 | 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Tang, D.; Yan, H.; Ning, G.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y. Potential Associations between Low-Level Jets and Intraseasonal and Semi-Diurnal Variations in Coastal Chlorophyll—A over the Beibuwan Gulf, South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061194
Liu S, Tang D, Yan H, Ning G, Liu C, Yang Y. Potential Associations between Low-Level Jets and Intraseasonal and Semi-Diurnal Variations in Coastal Chlorophyll—A over the Beibuwan Gulf, South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061194
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuhong, Danling Tang, Hong Yan, Guicai Ning, Chengcheng Liu, and Yuanjian Yang. 2021. "Potential Associations between Low-Level Jets and Intraseasonal and Semi-Diurnal Variations in Coastal Chlorophyll—A over the Beibuwan Gulf, South China Sea" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061194
APA StyleLiu, S., Tang, D., Yan, H., Ning, G., Liu, C., & Yang, Y. (2021). Potential Associations between Low-Level Jets and Intraseasonal and Semi-Diurnal Variations in Coastal Chlorophyll—A over the Beibuwan Gulf, South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061194