Abstract
The Brazil–Malvinas Confluence (BMC) is one of the most dynamical regions of the global ocean. Its variability is dominated by the mesoscale, mainly expressed by the presence of meanders and eddies, which are understood to be local regulators of air-sea interaction processes. The objective of this work is to study the local modulation of air-sea interaction variables by the presence of either a warm (ED1) and a cold core (ED2) eddy, present in the BMC, during September to November 2013. The translation and lifespans of both eddies were determined using satellite-derived sea level anomaly (SLA) data. Time series of satellite-derived surface wind data, as well as these and other meteorological variables, retrieved from ERA5 reanalysis at the eddies’ successive positions in time, allowed us to investigate the temporal modulation of the lower atmosphere by the eddies’ presence along their translation and lifespan. The reanalysis data indicate a mean increase of 78% in sensible and 55% in latent heat fluxes along the warm eddy trajectory in comparison to the surrounding ocean of the study region. Over the cold core eddy, on the other hand, we noticed a mean reduction of 49% and 25% in sensible and latent heat fluxes, respectively, compared to the adjacent ocean. Additionally, a field campaign observed both eddies and the lower atmosphere from ship-borne observations before, during and after crossing both eddies in the study region during October 2013. The presence of the eddies was imprinted on several surface meteorological variables depending on the sea surface temperature (SST) in the eddy cores. In situ oceanographic and meteorological data, together with high frequency micrometeorological data, were also used here to demonstrate that the local, rather than the large scale forcing of the eddies on the atmosphere above, is, as expected, the principal driver of air-sea interaction when transient atmospheric systems are stable (not actively varying) in the study region. We also make use of the in situ data to show the differences (biases) between bulk heat flux estimates (used on atmospheric reanalysis products) and eddy covariance measurements (taken as “sea truth”) of both sensible and latent heat fluxes. The findings demonstrate the importance of short-term changes (minutes to hours) in both the atmosphere and the ocean in contributing to these biases. We conclude by emphasizing the importance of the mesoscale oceanographic structures in the BMC on impacting local air-sea heat fluxes and the marine atmospheric boundary layer stability, especially under large scale, high-pressure atmospheric conditions.
1. Introduction
The dynamically active Brazil–Malvinas Confluence (BMC) region [1] is characterized by the confluence of the Brazil (warm, saltier) and Malvinas (cold, less salty) currents and has its variability mostly dominated by the ocean’s mesoscale, especially eddies and meanders. The importance of the BMC eddies on the across-front distribution of ocean’s properties such as heat, salt, nutrients, chlorophyll and others, is recently becoming well understood [2,3,4].
Although at the large scale in extra tropical latitudes we expect to have a negative correlation between sea surface temperature (SST) and both the air-sea heat fluxes and the wind magnitude, the opposite happens along frontal regions of the world’s ocean and at the BMC [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Among the several reasons why the lower atmosphere may be locally forced by the surface action of the ocean’s mesoscale, especially eddies, the humidity and air-sea temperature difference caused on the air above when the wind blows over oceanic fronts leads to a modification on the MABL stability and the air-sea heat fluxes [5]. The first descriptions of the MABL modulation by the ocean’s surface processes were made in the Equatorial Pacific Ocean [11,12,13]. Two hypotheses explain the phenomenon: (i) the hydrostatic balance modulation hypothesis, where the surface winds are related to the Sea Level Pressure (SLP) variations. In this case, a lower SLP would be located over warmer waters while a higher SLP would be located over colder waters. As a consequence, high SLP would be associated to stronger winds and occurring over regions of higher SST gradients [11]; (ii) the static stability modulation hypothesis, where the MABL stability may adjust to the ocean’s mesoscale dynamics in regions of oceanographic fronts. As a consequence, positive SST anomalies would induce changes on the MABL static stability. In the presence of warmer waters, the air buoyancy and turbulence would increase and the vertical wind shear in the MABL would be reduced. We would then expect stronger winds at the sea surface. Negative SST anomalies, on the other hand, would imply in less turbulence and weaker winds at the sea surface, with a stable and stratified MABL [13].
The presence of large SST gradients and high mesoscale variability of the BMC are key factors to promote a positive correlation between SST and wind magnitude at the sea level [5,6]. When analyzing the BMC at the synoptic meteorological scale during observational campaigns, the air-sea latent heat fluxes (Hl) ranged from more than 100 W m−2 over the warm Brazil Current to less than 20 W m−2 over the cold Malvinas Current. Sensible heat fluxes (H) follow the same pattern but generally with amplitudes ranging in an order of magnitude lower. At the meteorological synoptic scale, larger heat fluxes and higher differences between the SST and the air temperature (SST-Tair) tend to be coincident with strong bursts of surface winds and independent of season [10,14,15,16].
The Southwestern Atlantic Ocean where the BMC is located is an important region for cyclogenesis with at least three cyclogenetic regions located from the northern portion of the Antarctic Peninsula to the La Plata River basin [17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Distinct forcing mechanisms for cyclogenesis north and south of the 35 °S parallel are identified [18] and a seasonal cycle is markedly important north of this latitude. Observational data collected during some in situ campaigns are often used to demonstrate that the intense SST gradients present at the BMC are important local forcing mechanisms for modulating the MABL and, consequently, the cyclogenesis in this part of the world’s ocean [15,16,24,25,26].
When transient atmospheric systems such as fronts or cyclones are not present at the BMC and persistent atmospheric high-pressure systems dominate the weather, heat is transferred from the ocean to the atmosphere over the warm waters of the Brazil Current. That causes convection that sustains a well-mixed MABL, with strong winds along the entire air column within the MABL. Air temperature and humidity, as well as both H and Hl, are also higher on the warm side of the oceanographic front compared to the cold side. On the cold side of the BMC over waters carried by the Malvinas Current and in the absence of transient systems, the atmosphere tends to be cooler, drier and characterized by weaker winds at the sea surface, with a pronounced vertical shear inside the MABL. H and Hl tend to be always low on the cold side of the front, and may be negative in some cases (heat transferred from the atmosphere to the ocean). The MABL is often stable on the cold side of the BMC front whereas it is unstable on the warm side [10,15,16,24,25,26].
When large scale, transient atmospheric systems cross the South Atlantic in mid to high latitudes, and the local modulation of the MABL by the SST tends to be suppressed. Observations performed in a wide range of synoptic atmospheric conditions at sea demonstrated that the warm and cold advection of air masses in the BMC are a prominent mechanism to modify the MABL stability on both sides of the oceanographic front [24]. The different phases of the synoptic cycle in the atmosphere lead to different patterns of thermal advection at the BMC, causing different patterns of adjustment of the MABL to the SST heterogeneity. Some characteristics of the MABL observed near the sea surface in the BMC, such as the large moisture accumulation in that layer and a very strong vertical stratification, may contribute to making the air-sea heat flux bulk parameterizations fail [24]. A combination of observational and modeling data indicate that both the hydrostatic balance and the static stability are equally important modulation mechanisms for controlling the MABL stability in the BMC region. Important effects, such as an unbalanced Coriolis force and turbulence/friction effects, may be relevant in the study area when atmospheric disturbances caused by the passage of atmospheric fronts occur [25].
The impact of the local forcing of the lower atmosphere by ocean eddies is an interesting aspect to be considered when using numerical models to predict both the weather and the climate [9,16]. The lack of in situ observations, however, jeopardizes our knowledge on the subject [27]. In this study our main objective is to describe the local modulation of two eddies (one warm and one cold core) in the BMC and their impact on the lower atmosphere along the eddies’ lifespans. We used here the Radon transform, a new method developed by Oliveira and Polito [28] to locate and track the eddies along their life span. After that, we retrieved wind magnitude data from to satellite-borne scatterometers as well as other atmospheric data from atmospheric reanalysis, collocated with the successive positions along the eddies’ trajectories. These data produced different time series, used to assess the impact of the two eddies on the lower atmosphere above them.
In complement to that, we also used direct measurements from an in situ campaign performed between 14–20 October 2013 to investigate the air-sea coupling along a ship track north, within and south of the eddies’ location during that period. Fortunately, during this particular campaign the observed synoptic condition of the atmosphere (a well-stablished high-pressure center) did not change abruptly. This large-scale atmospheric condition facilitated the interpretation of the local modulation of the lower atmosphere by the eddies’ surface signal during the sampling period. We organized the paper as follows: Section 2 describes the used material and methods; Section 3 presents the results and discussion. In Section 4 we draw our conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eddies Identification and Tracking
Two well-established ocean eddies, one with a warm core and the other cold cored (ED1 and ED2, respectively) were identified in satellite SST and sea level anomaly (SLA) maps of the BMC during October 2013 (Figure 1). During their lifespans, the mean diameters of ED1 and ED2, as estimated from their surface signature with respect to surrounding waters in SLA maps, were 104 km (ED1 varied between 86–122 km and ED2 varied between 95 and 114 km). These structures were present in the study region when the Brazilian Navy Polar Ship, Almirante Maximiano, was at port before a planned field campaign aimed to collect air-sea interaction data in the BMC, so we could later direct the ship toward them for in situ sampling (Section 2.3 of this paper). Once we had both ED1 and ED2 positions clearly identified from the in situ temperature and salinity data after the field campaign, a backward and forward tracking approach was performed with the Radon transform method, using altimetry data. As a result, we successfully followed ED1 and ED2’s cores and defined their trajectories and life span periods.
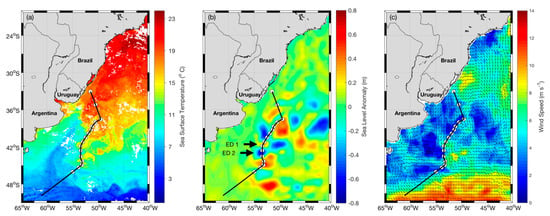
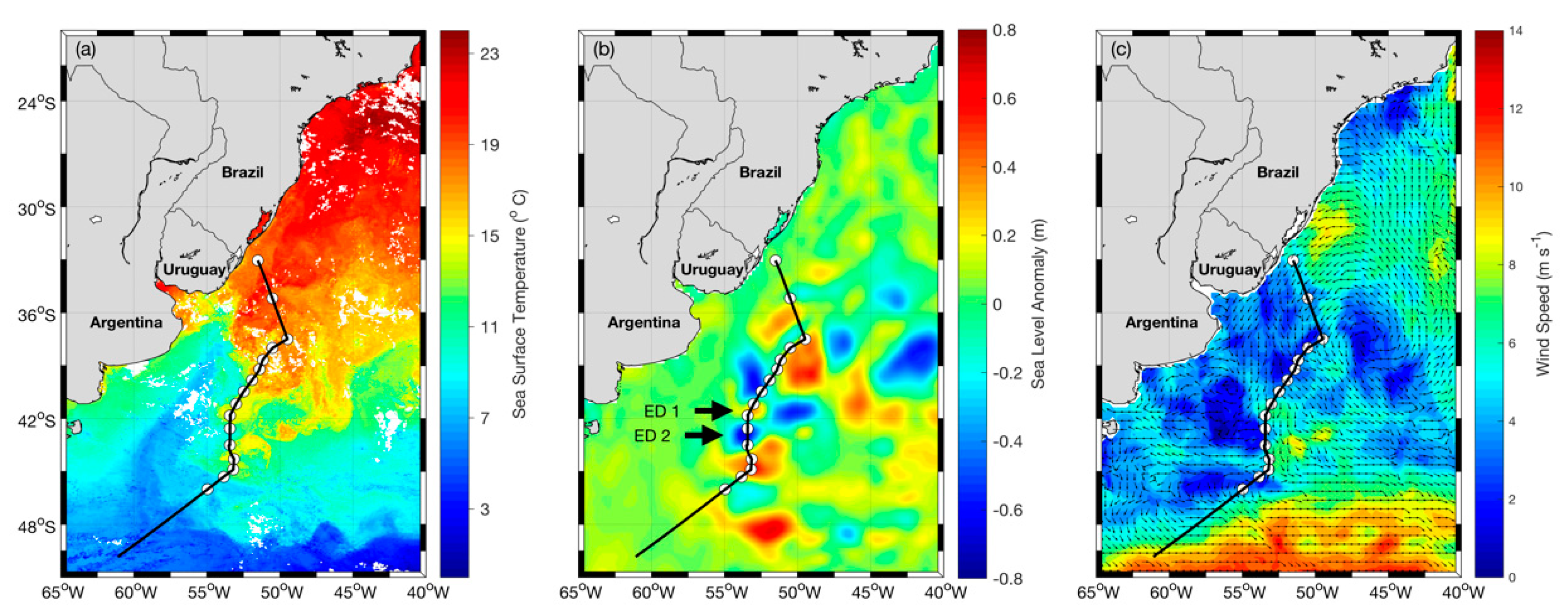
Figure 1.
Mean maps: (a) sea surface temperature (SST), (b) sea level anomaly (SLA) and (c) surface wind of the Brazil–Malvinas Current (BMC), respectively, representing these variables’ mean fields during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. The black line represents the ship’s track. White dots represent the coincident radiosonde and XBT/CTD launching positions. SST is an 8-day mean of MODIS image between 16–23 October 2013; SLA is a daily composite of 17 October 2013 and wind is an ASCAT 3-day mean between 16–18 October 2013. Warm core eddy (ED1) and cold core eddy (ED2) locations are indicated by the black arrows.
The Radon transform is particularly efficient at identifying eddies with diameters between 100 to 500 km. The criteria used to detect and follow ocean eddies supposes a circular geometry of a two-dimensional target described by a particular oceanic variable (SLA, for instance). The transform computes how circularly symmetric a given, individual mesoscale feature, such as an eddy, is in a two-dimensional field. The circular symmetry is given by a measure of how constant the Radon transform is with respect to different rotation angles. A sensitivity parameter is used in order to quantify the eddy’s deformation from symmetry, allowing the detection of non-symmetrical eddies.
Oliveira and Polito [28] describe that the Radon transform method is effective on detecting ocean eddies with respect to other ocean features, reporting that the major advantage in comparison to other automatic detection methods is owed to its capacity of detecting eddies in different (satellite) datasets and variables. Another method for automatically detecting and following ocean eddies is the objective method using the Okubo–Weiss parameter [29,30,31]. The parameter relates the normal and shear components of the strain to compute the relative dominance between strain and vorticity and is generally fed by SLA data. Oliveira and Polito [28] presented a comparison between their method and another ten eddy detection methods, including the Okubo–Weiss, listing a series of negative and positive points among the distinct methods. The Radon transform, for instance, presents versatility and is amplitude-independent, although requiring previous knowledge of the eddy size range in order to be effective. According to the authors, the Okubo–Weiss method was used for supporting the first global statistics of eddies in the ocean [32], but is noisy and can promote false positives. Cross-checking was made when the features were visually detectable to validate the eddies’ positions using the automatic method.
Once the Radon transform method defines a particular feature as an eddy, it provides its core position through successive days. In this work, the method was applied to the daily, multi-mission altimeter, gridded SLA product processed by the Seal Level Thematic Center (SL-TAC). The data are distributed at level 4, 1/4° spatial resolution (~25 km at 41 °S) by the European Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (https://marine.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 10 January 2021).
The identification and precise location of both ED1 and ED2 eddies in October 2013 were made using a combination of satellite SST, SLA and wind data (Figure 1), as well as using surface temperature and salinity data collected by the ship’s thermosalinographer (SeaBird SBE45) during the time when the ship crossed the structures (Section 2.3). The eddy diameters, as estimated by the maximum SST gradients with respect to surrounding waters using thermosalinographer data obtained in October 2013, were about 150 km for ED1 and 130 km for ED2. These diameters are larger than the ones estimated using SLA data, but both estimates are consistent to the diameters of other geostrophically-balanced eddies reported for the mean latitude (41 °S) of the study region [3,4,32,33]. ED1 and ED2 diameters balanced are also within the range of automatic identification by the Radon transform and several times larger than the spatial resolution of the SLA, satellite-derived wind and reanalysis data used here, thus allowing their identification on these different datasets.
2.2. Satellite-Derived Wind Magnitudes and Atmospheric Reanalysis Time Series
One of the main objectives of this research is to assess the ability of ED1 and ED2, SST signals to locally modulate the surface winds, the air-sea heat fluxes, the MABL stability and other lower atmosphere parameters in the study region along their trajectories. Once both ED1 and ED2 daily positions along their life spans were obtained by the method described before, we extracted satellite-derived surface wind magnitude data at those positions in successive days from two different scatterometers: (i) the ASCAT onboard the EUMETSAT MetOp-A satellite and (ii) the WindSat Polarimetric Radiometer (WindSat) onboard the Coriolis satellite. Both wind data sets are processed and distributed at level 3, 1/4° spatial resolution (~25 km at 41 °S) by Remote Sensing Systems (http://www.remss.com/, accessed on 10 January 2021). Both instruments use completely different technologies to provide wind magnitude data and are considered totally independent products. WindSat itself also provides different wind magnitude data, but we only used the ones based on the scatterometer’s low frequency channels.
The ERA5 atmospheric reanalysis data were used here to both describe the surface atmospheric conditions of our study area during the INTERCONF-32 field campaign (14–20 October 2013, see Section 3.2) and to extract important surface variables at the consecutive positions and times along ED1 and ED2 trajectories during their life spans (ED1 between 22 September and 13 November 2013; ED2 between 13 September and 1 November 2013). We also extracted ERA5 data from a fixed location outside ED1 and ED2 for the time range 13 September–13 November 2013 that covered both eddies’ life spans. This location is centered at 45 °S, 42 °W inside the Zapiola Rise (ZR), a known topographic feature in the Southwestern Atlantic’s Argentine Basin, and was used here as a time-synchronous reference site for the meteorological variability of the atmosphere in this location with respect to the eddies’ locations. Volkov and Fu [33] describe that the ZR sustains an anti-cyclonic, eddy-driven gyre of barotropic circulation, controlled by the bottom friction. In the center of this gyre, the mesoscale flow, as measured by the Eddy Kinetic Energy and geostrophy, tends to be small [34,35,36]. Our hypothesis is that this region, located close to where ED1 and ED2 existed, is subject to the same large-scale meteorological variability that affected the MABL above the eddies along their trajectories, although not being affected by an eventual local forcing caused by the eddies’ presence. In this case, a significant difference between the time series of ZR with respect to ED1 and ED2 can be expected.
ERA5 is the latest reanalysis product of the European Center for Medium Range Weather Forecast (ECMWF) and offers a range of meteorological and oceanographic variables at 30 km, 1 h spatial and temporal resolutions (https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/reanalysis-datasets/era5, accessed on 10 January 2021). For this work, the variables extracted along the eddies’ trajectories and for ZR from the global ERA5 data set were: atmospheric sea level pressure (SLP); surface level wind magnitude, dew point and air temperatures; SST; and air-sea sensible and latent heat fluxes.
2.3. The INTERCONF-32 Campaign
The Brazilian National Institute for Space Research (INPE), in collaboration with the Brazilian Antarctic Program (PROANTAR) sustains a long-term series of field campaigns aimed to better understand the synoptic scale, air-sea coupling mechanisms at the BMC [15,16,24,25,26]. Although supported by many projects, most field campaigns are maintained under the umbrella of a scientific initiative called INTERCONF (Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction in the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence Region), which is at the present date leaded by the virtual Brazilian National Institute of the Cryosphere (INCT Criosfera). The major drive for the INTERCONF campaigns is the fact that, together with the high oceanic mesoscale variability typically expressed by the SST, SLA and chlorophyll concentration fields [3,4], the Subtropical to Subantarctic environments of the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean are also very dynamical from a meteorological viewpoint [15,16,18,19,20,21,24,25,26].
For this study, standard meteorological and oceanographic, together with micrometeorological, data were collected during the INTERCONF-32 research cruise in the BMC by the Brazilian Navy, Polar Vessel Almirante Maximiano. The vessel is the same formerly used in other INTERCONF campaigns described by Pezzi et al. [10], Santini et al. [16] and Hackerott et al. [26], for example. The INTERCONF-32 campaign was explicitly designed to sample a train of warm and cold core eddies (including ED1 and ED2), detected in the BMC previously to the ship’s departure from port. The entire campaign was performed between 14 to 20 October 2013. ED1 and ED2 were crossed and sampled between 16 and 17 October 2013. Figure 1 presents the ship’s track performed to cross ED1, ED2 and other mesoscale structures found in the study region.
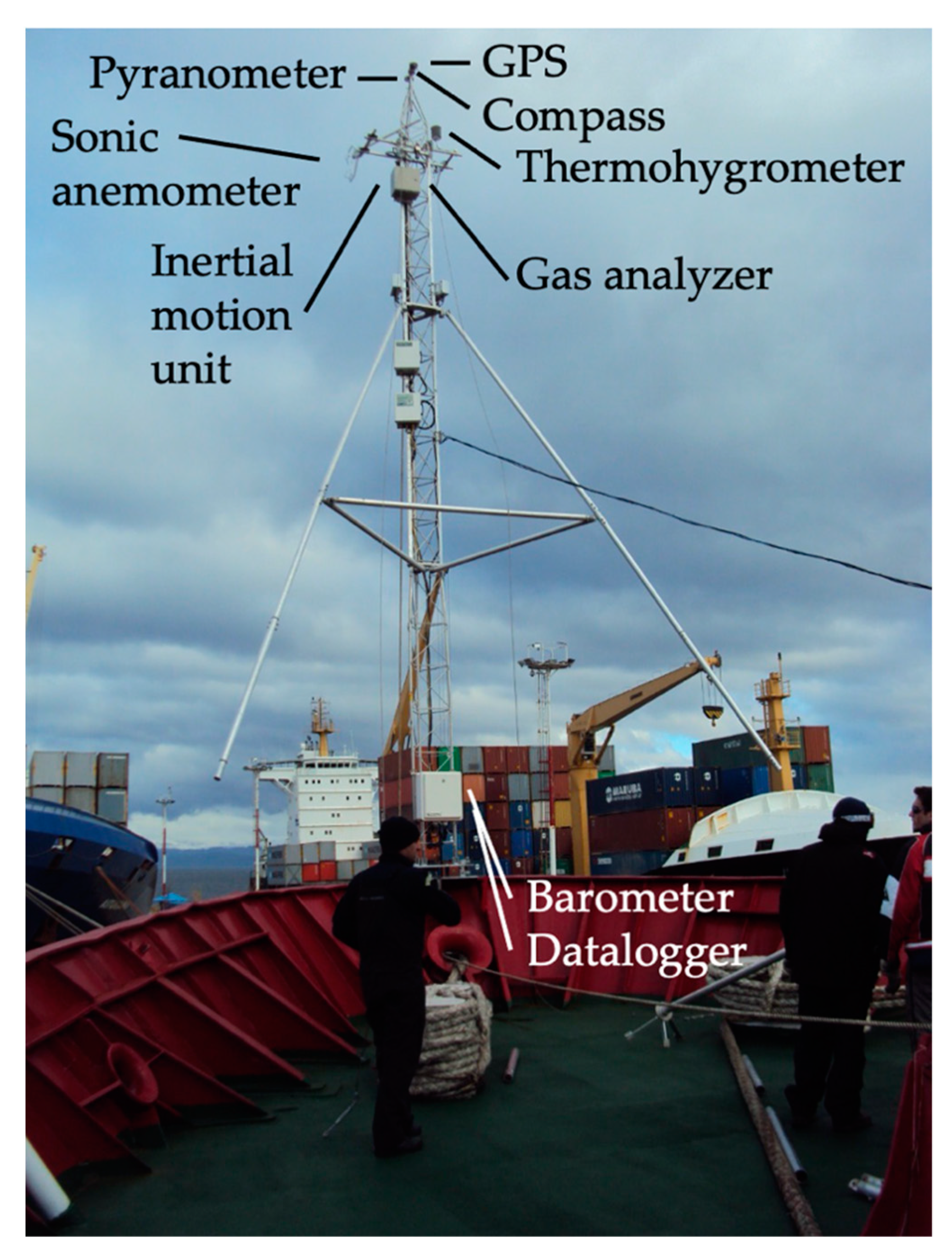
When still at port before the INTERCONF-32 campaign started, we installed a micrometeorological tower at the ship’s bow. The tower was mounted following procedures previously adopted in other INTERCONF campaigns [10,16,26]. The instruments installed in the tower included a (water vapor, CO2) gas analyzer, a three-dimensional sonic anemometer, a 3-axis inertial motion unit (IMU), a magnetic compass, a GPS and other meteorological sensors. All data were collected and stored by a Campbell Sci. CR3000 datalogger. Table 1 and Figure 2 present our micrometeorological tower and the instruments used here. In order to perform high-frequency measurements of water vapor concentrations (later used to compute the latent heat fluxes between the ocean and the atmosphere), a closed-path LI-COR LI-7200 gas analyzer was employed. The gas analyzer was equipped with a 1 m insulated tube aimed to reduce the chances for sorption processes that occur at the tube walls as suggested by Fratini et al. [37].

Table 1.
Meteorological instruments of the micrometeorological tower used during the INTERCONF-32 campaign.
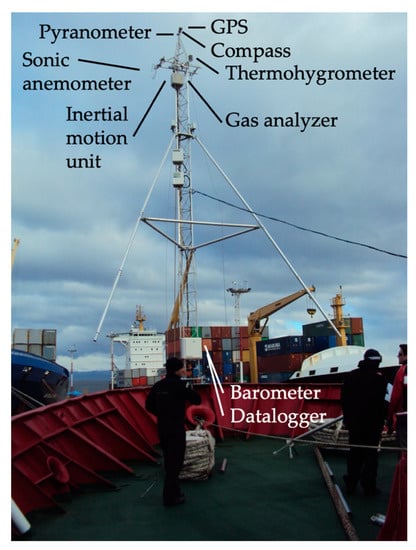
Figure 2.
Micrometeorological tower with sensors mounted on the Polar Ship Almirante Maximiano’s bow. The tower is 9 m tall and the upper sensors are about 15 m above the sea level. The micrometeorological data used in this study were obtained with these instruments.
Once at sea, the micrometeorological observations were automatically taken at the 20 Hz frequency. Eddy Covariance (EC) and bulk, air-sea heat fluxes calculations (Equation (1) to Equation (4) of Section 2.4) were made to represent each 30 min-window period and the data were later interpolated to a 1-h interval to be presented here. For the bulk calculations we also used SST data collected by the ship’s thermosalinographer and surface current data from a Teledyne 75 kHz Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) located at about 5 m depth in the ship’s hull. This last equipment provided us the surface current data used to derive the real, not relative (measured by the micrometeorological tower’s sonic anemometer) sea level surface winds that are used in our bulk calculations [16].
Our micrometeorological measurements permit the computations of turbulent heat, momentum and gas (water vapor and CO2) fluxes between the ocean and atmosphere. In this study, however, we only focused on the sensible and latent heat fluxes as well as on their equivalent bulk parametrizations for the same period and positions. In order to perform a correction for three-dimensional (3D) movements of the ship when at sea making the measurements, the 3D linear accelerations, angular rates and geographical position of the ship were measured at the same frequency employed to measure the primary micrometeorological data, following the method described by Edson et al. [38] and Miller et al. [39]. The three-axis components of the wind vector were measured by the sonic anemometer. In order to avoid flow distortions caused by the ships’ structure on the vertical component of the wind vector, the sonic anemometer was fixed in a 1 m long metal bar installed perpendicularly to the (vertical) mechanical structure of the micrometeorological towers and forward to the ship’s bow. This installation procedure is of maximum necessity when estimating ocean-atmosphere fluxes with the necessary accuracy [16].
The inertial data obtained by the IMU during the INTERCONF-32 cruise were corrected using the method described by Santini et al. [16]. The correction is made by comparing the cruise data obtained from the IMU with a robust gyratory balancing device (Schenck E4) able to precisely account for 3D accelerations in respect to a fixed reference. Eventual errors were subsequently subtracted from the in situ data. Aiming to have the in situ sonic anemometer’s wind data corrected for the ship’s 3D movements, we followed the method proposed by Miller et al. [36] and recently detailed by Hackerott et al. [26] and Santini et al. [16]. The method uses the angular velocities (rad s−1) and accelerations (m s−2) in combination with the ship’s heading and velocity data. The last two variables were registered by the GPS also installed in our micrometeorological tower. The sonic anemometer was located at 16 m in relation to the sea surface. The distance of the anemometer in respect to the sea surface is an important variable for the vertical wind data correction.
All the micrometeorological data used in the EC computation were corrected and filtered following the method described by Fujitani [40]. The method is widely used in air-sea heat flux calculations [10,16,41,42,43,44,45]. After these procedures, the in situ data collected during the INTERCONF-32 campaign were then ready to be applied to both the EC and the parameterization methods (fully described in Section 2.4).
Following the methodology used in previous INTERCONF campaigns to study the synoptic-scale, air-sea coupling in the BMC region [10,14,15,16,24,25,26], 16 radiosonde launchings were made underway from the ship’s helicopter deck during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. On most of the radiosonde launching positions (Figure 1) we also deployed Expendable Bathy-Thermographs (XBTs) or performed Conductivity-Temperature-Depth (CTD) casts aiming to measure the water temperature profile in respect to depth. These measurements provide the mixed layer depth, useful for further studies of the air-sea coupling in the area. During the research cruise, the vessel slowed down to a mean speed of 10 knots (~5.1 m s−1) to permit the synchronous launching of XBTs, CTDs and radiosondes.
We later combined radiosonde with XBT/CTD data for generating a transect of (air and water) temperature and meridional wind against depth (in the ocean) and height (in the atmosphere). This transect represents a “snapshot” of the air-sea coupling at the meteorological synoptic scale along the ship’s track seen in Figure 1.
2.4. Bulk Parameterization and Eddy Covariance Measurements of Air-Sea Heat Fluxes
The most common way to estimate the air-sea heat fluxes using surface observational data is through parameterization methods, also known as bulk formulae. The more accepted bulk algorithm is the COARE (Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Response Experiment) [46], with the latest version being COARE 3.5 [38]. The data used for the bulk calculations are generally taken from the automatic weather stations onboard the vessels, from the corrected winds of a sonic anemometer and/or from surface current (ADCP) data. Here we followed Santini et al. [16] and used ADCP data. SST data were taken by from the thermosalinograph. Bulk-derived sensible (Hb) and latent (Hlb) heat fluxes are given by:
where is the air density, is the air specific heat, and are the heat and humidity transference coefficients, respectively, is the air potential temperature, U is the surface relative wind vector, SSTskin is the skin sea surface temperature as corrected from the thermosalinographer’s SST using the COARE 3.5 warm layer correction algorithm [38], is the specific humidity at the sea surface and is the specific humidity.
Although bulk parameterizations are well accepted, when micrometeorological data can be gathered at sea, the Eddy Covariance (EC) method can provide direct and more accurate measurements of the air-sea heat fluxes. For this study the turbulent, air-sea sensible (HEC) and latent (HlEC) heat fluxes were computed from high frequency (20 Hz) meteorological data as [47,48]:
where is the dry air density, is the water evaporation latent heat, , and are the air virtual temperature, the vertical component of the wind velocity and the water mixing ratio fluctuations, respectively, with respect to their averages.
Aiming to infer the MABL stratification (a measure of stability) from surface data, the Monin–Obukhov stability parameter (ζ) was used here. The parameter is described as [48]:
where z is the measurement height, d is the displacement of z in respect to the zero-plane, and L is the Obukov length that relates thermal, dynamical and buoyance processes from the original micrometeorological parameters. ζ can be used to point out situations when the EC method may not be accurate [16]. Generally, that is caused by a failure in the air-sea turbulence transfer owing to the large stability of the MABL in the interface with the ocean.
In order to accurately compute the air-sea heat fluxes using shipborne micrometeorological data, a series of corrections aiming to suppress the effect of the ships’ movements should be applied to the three-dimensional wind data collected by the sonic anemometer. The corrections use the angular velocities and accelerations combined with the vessels’ heading and velocity data registered by a GPS, also installed in our micrometeorological tower [16,26,39]. In order to improve accuracy, an additional calibration was also performed in the inertial unit data using a fixed system [16]. All micrometeorological data were synchronized in space and time to the ship’ position coordinates.
The EC method, however, has a practical limitation: it is only recommended to be used for estimating sensible and latent, air-sea (or land) fluxes under unstable to quasi-neutral MABL conditions. When the MABL presents a stable (ζ > 0.2) condition, the fluxes tend to be suppressed and inaccurate [16,49,50,51]. Owing to that, in this work we simply discharged the EC data computed under MABL stable conditions. Having the time series of bulk and EC air-sea, sensible and latent heat fluxes in hands, we also computed the differences (biases) found between those variables during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. The (Hb − HEC) and (Hlb − HlEC) differences are indicators of the high-frequency ocean and atmospheric perturbations present in our study area [16].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Eddies Identification and Tracking
Maps of SST, SLA and wind magnitude of the BMC during the INTERCONF-32 campaign are presented in Figure 1. The maps are satellite derived, daily (SLA) or temporal averages of 3-day winds (ASCAT) to 8-day (SST) means centered in 17 October 2013. The maps indicate the presence of ED1 and ED2 that were sampled by the ship when crossing the eddies in 16 and 17 October, respectively. The positions of these two structures on those dates are also marked in Figure 3. The SST and SLA images show that in latitudes south of 42 °S, we see the well-known Brazil Current retroflection region in the BMC [52] and a fully developed warm core eddy associated to the retroflection, centered at about 45 °S, 53 °W. Eddies ED1 and ED2, at the time of the crossing by the ship during the INTERCONF-32 campaign, were both north of that position. The wind map (Figure 4a–i) indicate a clear zonal gradient in the vicinity of the positions where the eddies were located along the ship’s trajectory.
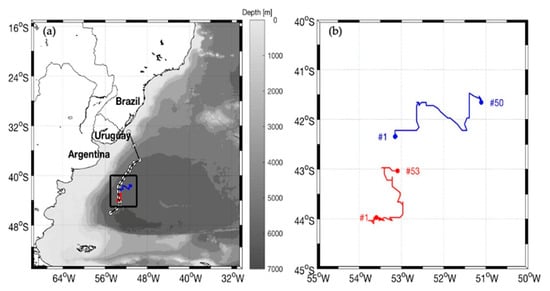
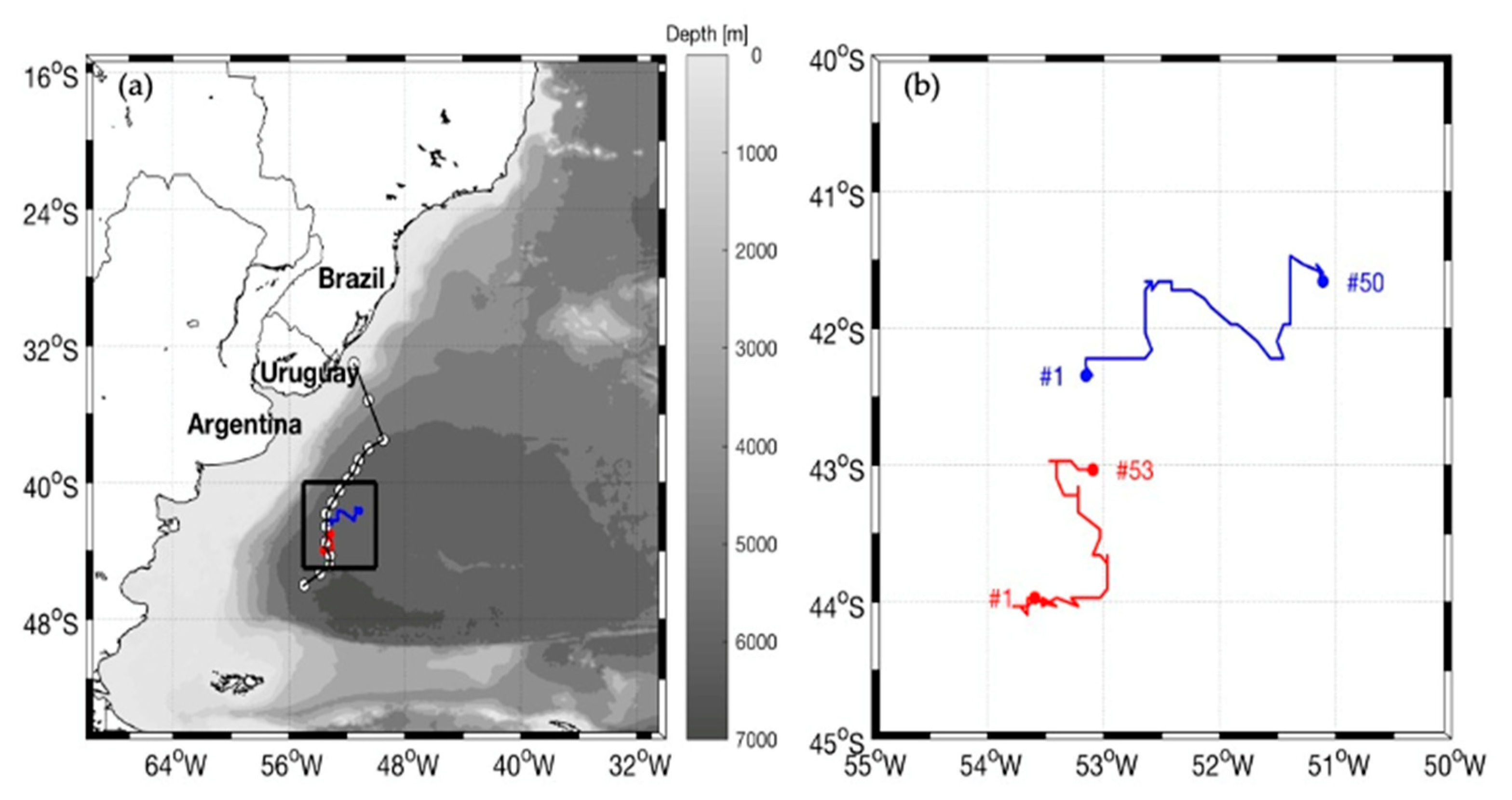
Figure 3.
(a) Translational trajectories of the ED1 (22 September to 13 November 2013, red line) and ED2 (13 September to 1 November 2013, blue line) superimposed onto the bathymetry (m) of the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. The ship’s track during the INTERCONF-32 campaign with the radiosonde and XBT/CTD launching positions (white circles) between 16–18 October 2013 are also shown. (b) Zoomed trajectories of ED1 and ED2 in the BMC: circles and triangles indicate the initial and final positions of the eddies, respectively. During their lifespans, SLA data indicated that ED1 diameters varied between 86 (day 1) and 122 km (day 53); ED2 diameters varied between 95 (day 1) and 114 km (day 50).
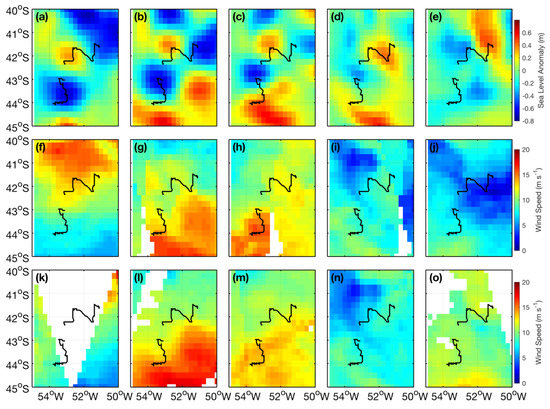
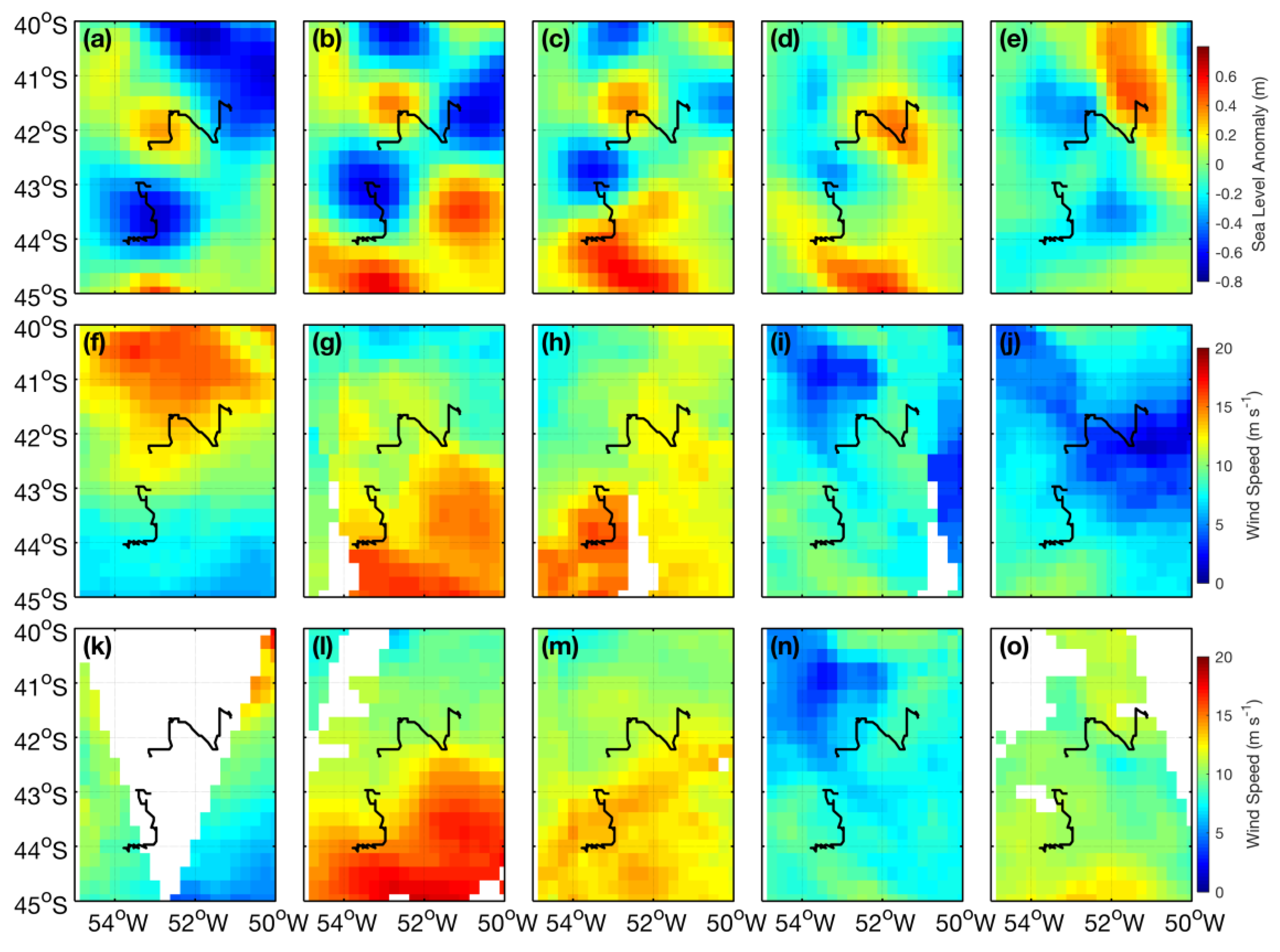
Figure 4.
SLA (a–e), ASCAT (f–i) and WindSat (k–o) wind magnitude maps of the BMC throughout ED1 and ED2 life spans. Columns from left to right indicate consecutive dates in 1 October, 11 October, 21 October, 31 October and 10 November 2013, respectively. ED1 and ED2 translational trajectories (Figure 3) are also represented here.
3.2. Satellite-Derived Wind Magnitudes and Atmospheric Reanalysis Time Series
Figure 3 presents the track of the Polar Vessel Almirante Maximiano during the INTERCONF-32 campaign together with the translation trajectories performed by ED1 and ED1 during their life span periods. As quoted before, the eddies’ trajectories were obtained using the Radon transform methodology [28]. The warm core eddy ED1 lasted for 53 days (22 September to 13 November 2013) in the BMC while the cold core eddy ED2 lasted 50 days (13 September to 1 November 2013). These life span periods and translation trajectories are fully compatible to what is expected with eddies in the BMC [4,10,33]. As reported early on this text, both ED1 and ED2 trajectories were intercepted by the Polar Ship Almirante Maximiano’s track in 16 and 17 October 2013. By then, their SST and surface salinity signals obtained from thermosalinographer data indicate that the eddies were distinctive structures with respect to neighboring waters.
Figure 4 presents the SLA and wind magnitude maps taken from both ASCAT and WindSat instruments in the BMC during the ED1 and ED2 life spans. For space reasons, only maps at each 10 days during October–November 2013 (1 October, 11 October, 21 October, 31 October and 10 November) are displayed here. The maps show the displacement of SLA positive and negative anomalies associated to the displacement of ED1 and ED2, respectively. We also notice interesting coincidences between regions of high SLA gradients and high lateral wind magnitude gradients, especially at the vicinity of ED1 and ED2 trajectories.
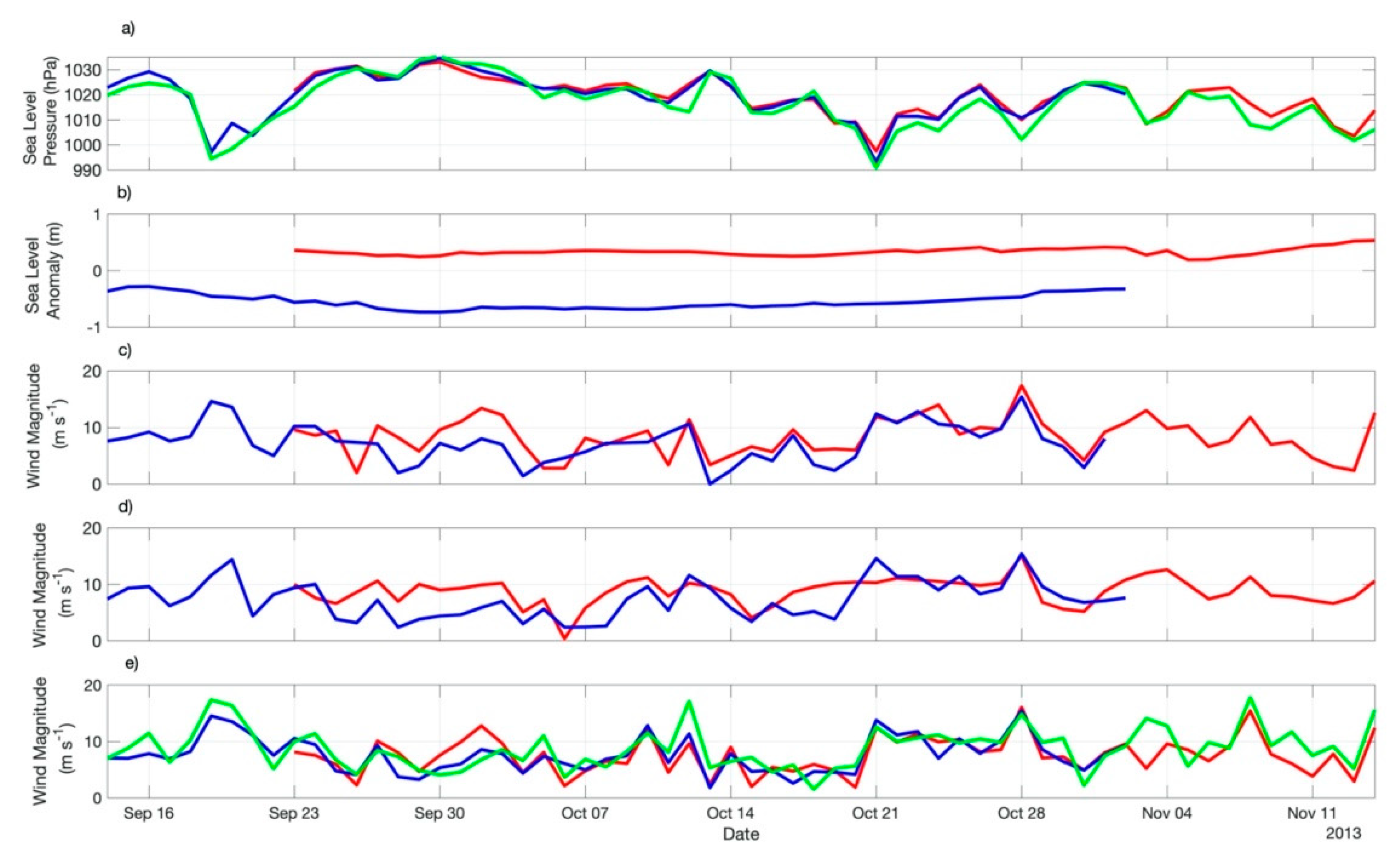
Using data taken from the diurnal maps at the consecutive positions of ED1 and ED2 during their life spans, as well as at 45 °S, 42 °W (Zapiola Rise) Figure 5 and Figure 6 display the time series of the satellite-derived SLA and wind magnitude data together with SLP, wind magnitude, air temperature, dew point temperature, SST, SST-Tair difference, and air-sea sensible and latent heat fluxes retrieved from the ERA5 data set. Satellite-derived winds were taken from both ASCAT and WindSat. These scatterometers are independent and different instruments, measuring winds at different spatial and temporal resolutions. Their measurements are also expected to be different from ERA5 data. Therefore, small differences in the wind estimates were naturally expected to occur among the three data sets used here to estimate the wind magnitudes along the successive positions performed by ED1 and ED2 during their life spans.
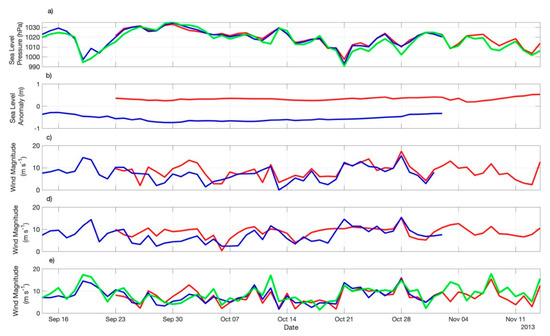
Figure 5.
Time series of (a) ERA5 sea level pressure; (b) Sea level anomaly; (c) ASCAT wind magnitude; (d) WindSat wind magnitude; (e) ERA5 wind magnitude of both ED1 (red lines) and ED2 (blue lines) measured along their trajectories during their life spans. The green lines represent the time series of the same variables derived from ERA5 reanalysis at the neutral region of the Zapiola Rise (45 °S, 42 °W) during the same period when both eddies were tracked.
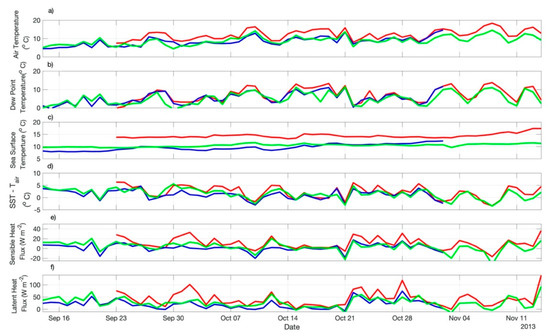
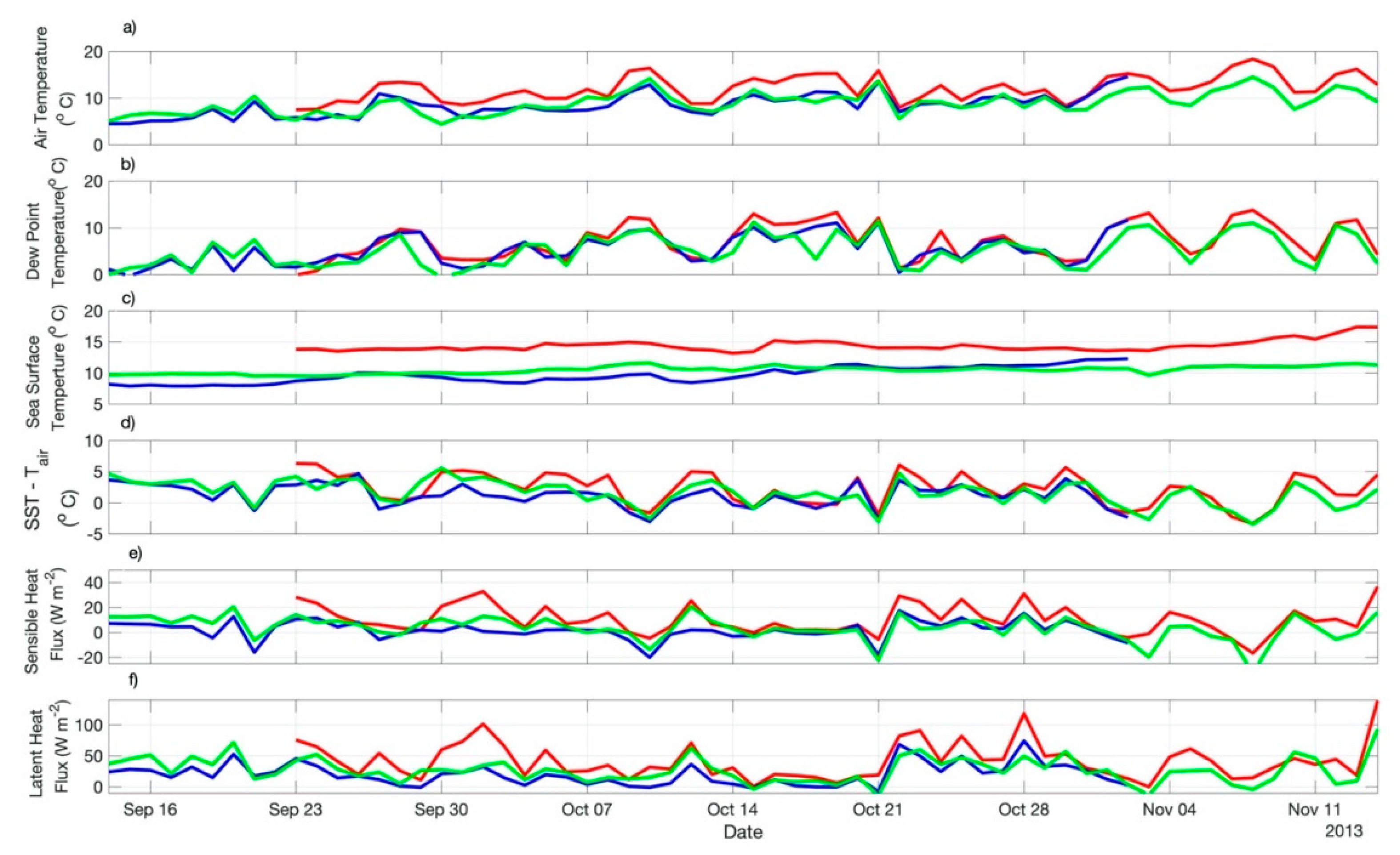
Figure 6.
Time series of ERA5: (a) the sea level air temperature (Tair); (b) dew point temperature; (c) SST; (d) SST-Tair; (e) air-sea sensible heat flux; (f) air-sea latent heat flux of both ED1 (red lines) and ED2 (blue lines) measured along their trajectories during their lifespans. The green lines represent the time series of the same variables derived from ERA5 reanalysis at the neutral region of the Zapiola Rise (45 °S, 42 °W) during the same period when both eddies were tracked.
Figure 5a presents the SLP time series taken from ERA5 data along ED1 and ED2 trajectories and at the ZR location. As expected, owing to the geographical proximity of both trajectories and the position of ZR, they are pretty much coincident. Table 2 indicates that the mean SLP on top of ED1 and ED2 was 1019.7 to 1019.8 (±7.6 to ±8.8) hPa throughout their life spans. The variability of the SLP is coincident between the eddies’ time series and the one obtained for the ZR. The 3 to 5-day cycles seen in the time series are indicative of the large-scale changes in the atmosphere caused by the passage of transient systems commonly passing over the South Atlantic at periods previously reported between 3 to 6-days [18,19].

Table 2.
Temporal averages and standard deviations of ERA5 and satellite air-sea interaction variables obtained along ED1 and ED2 trajectories and over the eddies during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. The variables in this table are: Air temperature (Tair), dew point temperature (Td), sea surface temperature (SST), SST-Tair difference, bulk sensible heat flux (Hb), eddy covariance sensible heat flux (HEC), bulk latent heat flux (Hlb), eddy covariance latent heat flux (HlEC), sea level pressure (SLP), sea level anomaly (SLA), ERA5, ASCAT and WindSat wind magnitudes.
The altimetry SLA time series taken over the eddies’ cores along their trajectories are presented in Figure 5b. The time series, together with averages presented in Table 2 attest to the expected difference on the eddies’ SLA signal owing to the fact that they were warm (positive SLA) and cold (negative SLA) cored. Mean (±std.) SLA values were 0.3 ± 0.07 m (ED1) and −0.5 ± 0.13 m (ED2).
Figure 5c,d and represents the ASCAT and WindSat wind magnitude time series throughout the eddies life spans, respectively. Although the different data sets, owing to the different natures of their instruments or outputs, as well as different temporal and spatial resolutions and accuracies, tend to show a reasonable indication that ED1, for having a characteristically higher SST signal in respect to its neighboring waters and to ED2 (Figure 5c), imprints a higher wind magnitude signal in the lower atmosphere along its translation in the BMC region. The opposite occurs to ED2, a cold core eddy, which suggests it impacts the lower atmosphere by reducing the wind magnitude. The average values of wind magnitudes computed for the eddies’ life span periods seen in Table 2 indicate that the (scatterrometer-measured) wind intensities were 0.6 to 0.7 m s−1 higher on top of ED1 than on top of ED2. This result is expected as a clear indication of local modulation of the near surface winds by the eddies SST signals throughout their life spans and had been already reported for the BMC and other frontal regions of the world’s ocean [5,6,7,8,9,10].
Figure 5e presents the ERA5 wind magnitudes of ED1, ED2 and ZR. Consistently to the satellite estimates, ERA5 wind magnitudes are higher over ED1 than over ED2, suggesting the local modulation of the winds by the SST along the eddies’ trajectories. The ZR series, however, indicate that the wind modulation may occur only in cases of weaker large-scale winds blowing over the entire region. In Figure 5e we only notice a pronounced increase of wind magnitudes over ED1 with respect to ZR during a couple of days after 30 September 2013 when winds blowing at the ZR location were weaker than 10 m s−1.
A simple explanation for the positive correlation between SST and wind magnitude (the SST locally forcing the winds), when occurring, is this: when the wind blows over an increased SST, a situation typically found in the ocean’s frontal regions where the mesoscale variability is dominant, there is an increase in the momentum mixing inside the MABL and upper level, stronger winds descend toward the ocean’s surface, consequently increasing the near surface winds [5,9]. This is consistent to the static stability modulation hypothesis [13]. When the wind blows over a decreased SST, the MABL turbulence is diminished and the wind magnitudes are lower. Our Figure 5c displays ERA5 wind magnitude time series and, although clearly showing that higher winds are associated to higher SST (Figure 6c) in the beginning of the series, presents a mean wind magnitude (and std.) computed over all the series virtually equal between ED1 and ED1 (Table 2).
The time series of several air-sea interaction variables retrieved from ERA5 along ED1 and ED2 trajectories and at the ZR position are presented in Figure 6. It is clear that all the variables, most of the time during the eddies’ life spans, were modulated by the presence of both mesoscale structures. The SST-Tair difference, an empirical measure of the MABL stability [10,14,15,16], was always higher over ED1 in relation to ED2 throughout the time series. That resulted in an average difference of 1 °C higher along ED1 translation in relation to ED2 translation (Table 2). ERA5 (bulk) heat fluxes indicated the same: both Hb and Hlb were consistently higher on top of ED1 than on top of ED2 along their trajectories. Hb and Hlb averaged (±std.) 10.3 ± 11.44 W m−2 and 41.5 ± 29.55 W m−2, respectively over ED1 and 1.9 ± 7.44 W m−2 and 19.9 ± 18.02 W m−2, respectively over ED2 (Table 2).
It is expected, however, as we observed here, that Hb magnitudes should to be smaller than those of Hlb [40,41]. It is also expected, most of the time, that Hb and Hlb are positive on warm core eddies (that is, the eddy’s surface loses heat to the atmosphere) and negative on cold core eddies (that is, the eddy’s surface gains heat from the atmosphere). That was reported for the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean (SWA) in recent works [8,10,16]. Short-term perturbations of both meteorological and oceanographic variables, especially caused by strong wind bursts, strong SST contrasts and abrupt changes in the SST-Tair difference can disrupt the expected response of the air-sea heat fluxes on top of mesoscale structures [10,16], as we notice during specific periods of time in our time series seen in Figure 6.
Table 3 and Table 4 resume the differences between the air-sea sensible and latent (bulk) heat fluxes obtained from the ERA5 reanalysis along ED1 and ED2 trajectories and at the ZR location. The differences are presented in the form of mean and standard deviation of the Hb and Hlb series, complemented with the important variables Tair and SST. The statistics for these variables (Table 3) confirm the expected higher (lower) mean SST along ED1′s (ED2′s) trajectories with comparison to the mean SST of the neutral waters (ZR), where no eddies are present. On the average, Hb and Hlb were higher (lower) along ED1 (ED2) trajectory with respect to ZR. Table 4 indicates a mean increase of 37% in Tair and SST in the magnitudes of ED1′s variables, resulting in a mean increase of 78% (Hb) and 55% (Hlb) in the air-sea heat fluxes along ED1′s trajectory with respect to the neutral waters. Over ED2, on the other hand, Table 4 shows that a reduction of 6% and 8% in Tair and SST, respectively, resulted in a decrease of 49% and 25% in Hb and Hlb, respectively, in respect to ZR. These numbers indicate the importance of the eddies studied here on locally modifying the heat fluxes at the air-sea interface along their translation in the BMC region.

Table 3.
Temporal averages and standard deviations of ERA5 air-sea interaction variables obtained along ED1 and ED2 trajectories and at the neutral region of the Zapiola Rise (45 °S, 42 °W) during period of the eddies’ lifespans. The variables in this table are: air temperature (Tair), sea surface temperature (SST), bulk sensible heat flux (Hb) and bulk latent heat flux (Hlb).

Table 4.
Percentual discrepancies between the temporal averages of ERA5 air-sea interaction variables obtained along ED1 and ED2 trajectories and at the neutral region of the Zapiola Rise (45 °S, 42 °W) during period of the eddies’ lifespans. The variables in this table are: air temperature (Tair), sea surface temperature (SST), bulk sensible heat flux (Hb) and bulk latent heat flux (Hlb).
Bharti et al. [53] recently presented a study on the air-sea fluxes of heat and momentum for the Southern Ocean, in a region south of Australia between ~42–53 °S. The authors used eddy covariance, inertial dissipation and COARE 3.5 to compute heat fluxes on a track covered by the R/V Investigator that covered both a cold core and a warm core eddy. When describing the air-sea heat fluxes obtained within the warm-core eddy, Bharti et al. [53] reported that the structure responded for an increase of 187% and 79% on the sensible and latent heat fluxes, respectively, in relation to the average of all data collected during the in situ campaign. The numbers are quite impressive, indicating a strong modulation of the lower atmosphere above oceanic mesoscale structures in a latitude range comparable to the one of this work. The authors also described a substantial decrease, with respect to the mean conditions, on the air-sea sensible and latent heat fluxes during the passage of six extratropical cyclones that traveled in the area during their experiment.
Leyba et al. [8] provide a comprehensive study on the impact of ocean eddies on the lower atmosphere at the SWA. They used NCEP-CFSR reanalysis SST, Hb and Hlb data and also reported an increase (decrease) of all variables inside warm (cold) core eddies. The authors, nevertheless, describe that the BMC region is distinct of other areas of the SWA because its cold core eddies in general are sources of heat to the atmosphere, contrary to what is expected and occurs in the rest of the SWA. As an explanation, eddy-pumping is induced which, according to Leyba et al. [8], is not strong enough to effectively cool down the waters at the center of BMC’s cold-cored eddies. These cyclonic structures trap warm waters inside during their shedding phase in the subtropical region of the SWA. As a result, the eddy-pumping mechanism is not very effective to modify the SST and, consequently, the air-sea heat fluxes.
3.3. The INTERCONF-32 Campaign
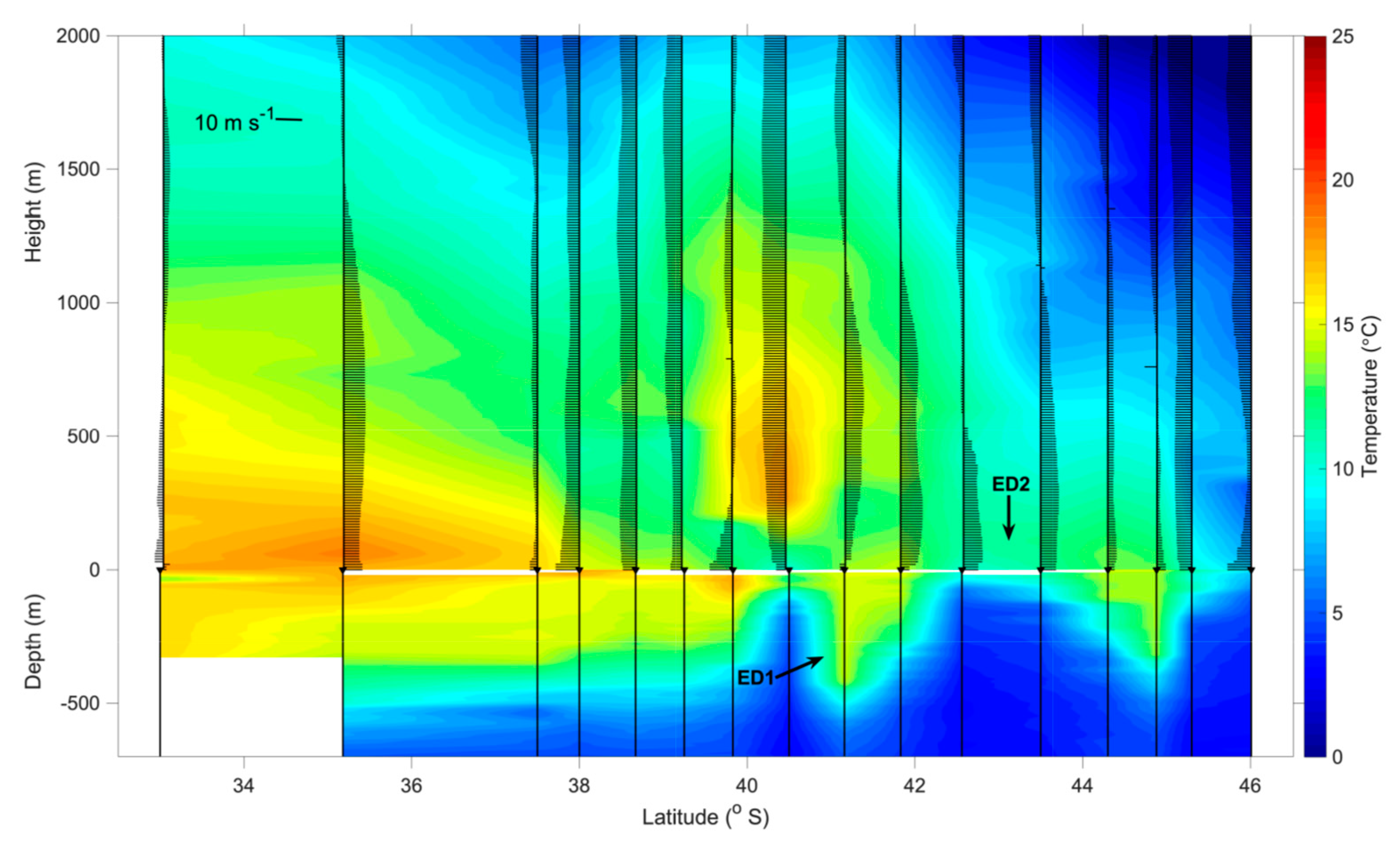
The synoptic characteristics of the coupled air-sea system in the BMC observed during the INTERCONF-32 campaign are seen in Figure 7. The figure presents a transect of the vertical distribution of the meridional component of the wind superimposed onto the ocean and air temperature as function of depth and height, along the ship’s track between 16 and 18 October 2013. The meridional component of the wind is used here following Pezzi et al. [14,15] for visual purposes only. Nevertheless, the vertical distribution of this wind component is a good indication of the wind shear in the MABL, indicating either a well-mixed, unstable and turbulent (where the meridional component of the wind is uniform with respect to height) or a stratified, stable MABL (where the meridional component of the wind is variable, increasing with height).
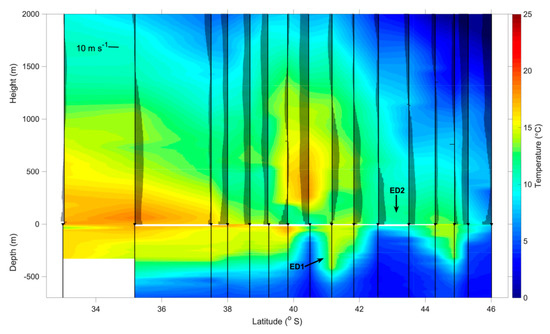
Figure 7.
Synoptic characteristics of the coupled air-sea system in the BMC observed during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. Water temperatures were obtained from a combination of XBT and CTD data while the air temperature and the meridional component of the wind were obtained from radiosondes launched along the ship’s trajectory (Figure 1). ED1 and ED2 positions in 16 and 17 October 2013, respectively, are denoted by the black arrows.
The water temperature distribution (Figure 7) shows the (expected) high variability of the oceanic mixing layer in the BMC. Warm waters carried by the Brazil Current, as well as the ones contained within the warm core eddies, produce a deepening of the thermocline to about 400 m. The presence of cold waters from the Malvinas Current, as well as from the cold core eddies causes a shoaling of the thermocline to depths between 80 to 30 m.
As previously described for our study region [8,10,14,15,16], we also observed that the wind magnitude along the entire MABL tends to be vertically constant over warm waters, indicating a well-mixed, turbulent and unstable MABL. A vertical wind shear tends to occur on top of cold waters (indicating a stable MABL) when no atmospheric transient systems are crossing the South Atlantic. In addition, a well-defined modulation of the near-surface air temperature can be seen (Figure 7) by the contrasting SSTs of the warm Brazil (higher Tair) and cold Malvinas waters (lower Tair). In the presence of the eddies and meanders over the course of the ship’s track, the MABL is shown to vary between unstable to stable conditions, with their associated sea level air temperature patterns. A more detailed explanation on the MABL stability follows later in this text considering the SST-Tair difference and the Monin–Obukhov stability parameter ζ.
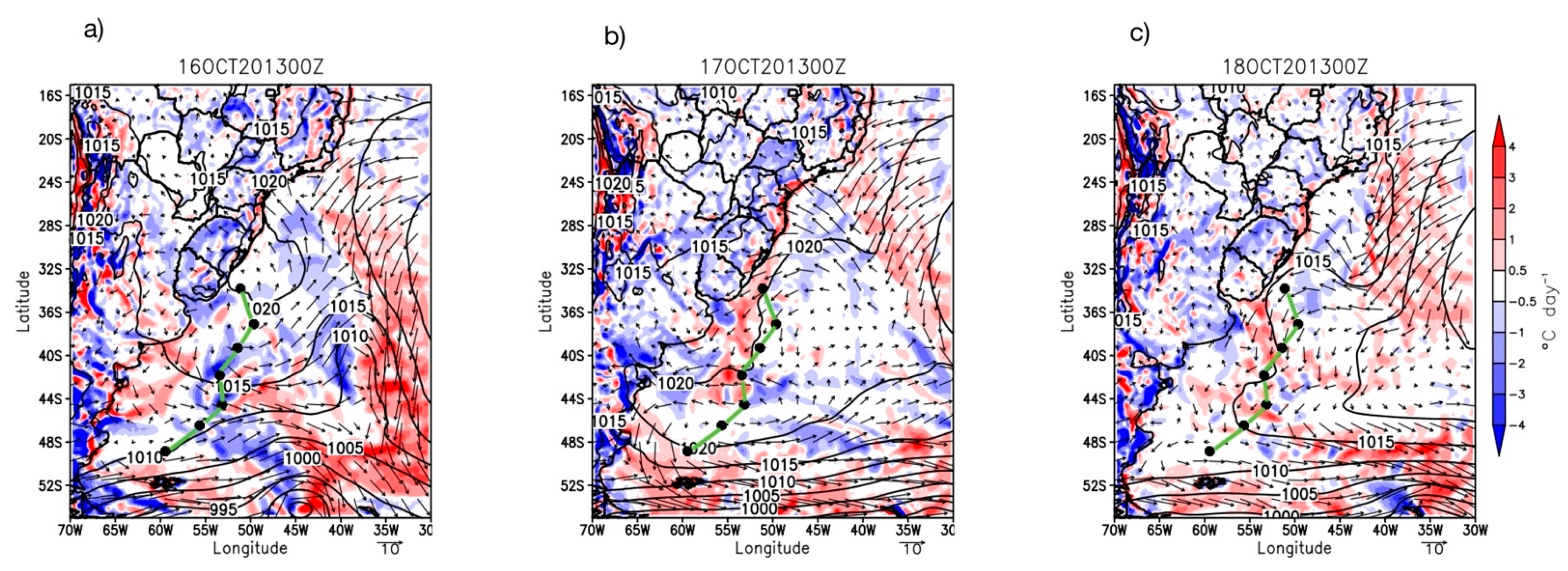
The weather maps of our study region during the INTERCONF-32 campaign are seen in Figure 8. These are derived from ERA5 data at midnight between 16 to 18 October 2013. These days were selected to be displayed because they generally represent the weather patterns of the whole INTERCONF-32 campaign in the BMC and cover the ED1 and ED2 sampling days. During 16 and 17 October, the ship followed its track under an atmospheric high-pressure condition. The associated atmospheric circulation during these days promoted winds blowing from northeast with a weak warm advection. The evolution of the high-pressure system on 17 October caused a reduction of the surface wind magnitude and a change in the wind direction which began to blow from the south-southwest. Throughout the later hours of the day, the propagation of the high-pressure system to the east caused a weak intensification of the northernly winds on the descending branch of the system, bringing a warm advection pattern to the vicinity of the ship’s location.
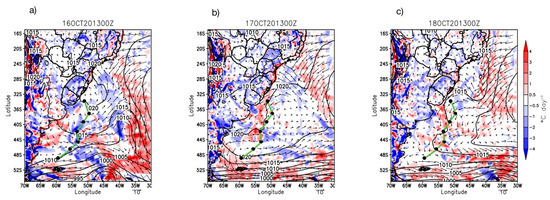
Figure 8.
ERA5 weather maps at 00Z during days 16 (a), 17 (b) and 18 (c) October 2013. Black lines represent the atmospheric pressure (hPa), the black arrows represent the surface wind vectors (m s−1) and the color scale from red to blues represent the thermal advection from warm to cold (°C day−1). The black dots represent the ship’s position in the study area at 00Z every day during the entire INTERCONF-32 campaign (14–20 October 2013) along the ship’s track (green line).
During 18 October 2013 we observed an atmospheric transition to a low-pressure system. After a short period characterized by weak winds, they changed direction and started blowing from south, causing a cold advection of the atmosphere over the study region. The sequential weather maps after 18 October 2013 (not shown), however, indicated that the establishment of this low-pressure system was not relevant to substantially change the air-sea coupling mechanisms reported here for the whole INTERCONF-32 campaign.
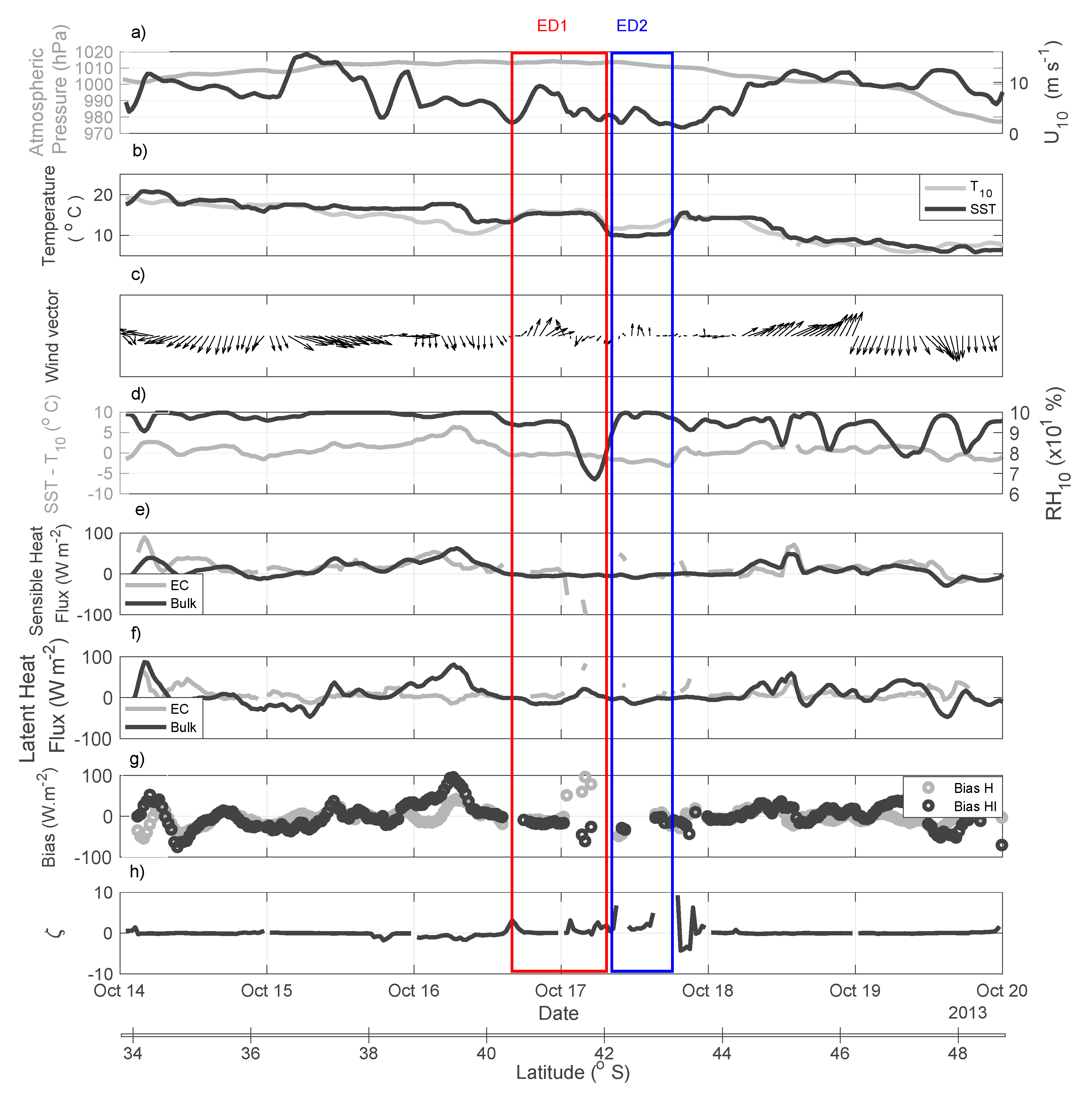
The time series of several meteorological parameters collected by the instruments installed on the ships’s micrometeorological tower, as well as SST data collected by the ship’s thermosalinographer, are displayed in Figure 9. The figure also includes time series of the derived variables (i) the sensible (Hbulk, HEC) and latent (Hlbulk, HlEC) heat fluxes estimated through bulk parameterization and measured directly using the EC method; (ii) the SST-Tair difference; (iii) the Hbulk − HEC and Hlbulk − HlEC differences (biases) and (iv) the Monin–Obukhov stability parameter ζ. Also indicated are the periods and latitudes when and where the eddies ED1 and ED2 were sampled. Figure 9 is complemented by Table 2 where we can see the average (and standard deviation) of all variables computed from measurements made at both eddies.
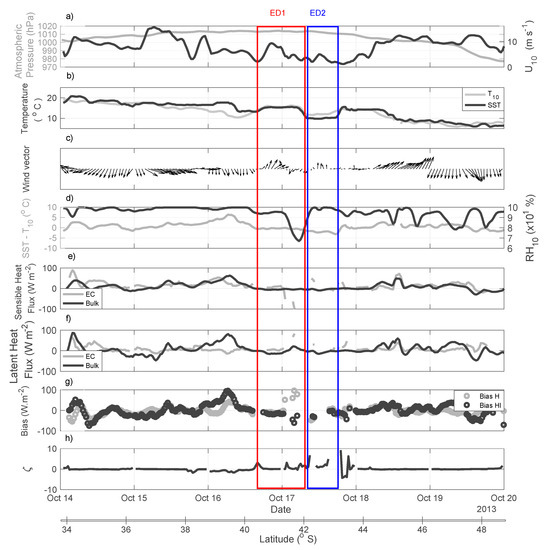
Figure 9.
Time series of meteorological and derived heat flux variables measured or computed along the ship’s track during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. (a) SLP (grey line) and the wind magnitude at 10 m level (U10, black line); (b) T10 (grey line) and SST; (c) wind vector; (d) SST-T10 (grey line) and relative humidity at 10 m level (RH10, black line); (e) HEC (grey line) and Hbulk (black line); (f) HlEC (grey line) and Hlbulk (black line); (g) Hb-HEC (grey line) and Hlb-HlEC biases (black line); (h) Monin–Obukhov stability parameter ζ.
The time series of SLP (Figure 9a) registered along the ship’s route indicate that a high-pressure system was dominant over the time both ED1 and ED2 were observed, decaying from about 1000–1010 hPa to about 980 hPa at the end of the series. Figure 9a also shows that the lowest values of the wind magnitude (U10) occurred during the time when and just after the ship was sampling the cold core of ED2.
Figure 9b indicates that T10 is well synchronized with SST in the period 17–18 October, when the ship’s track crossed ED1 and ED2. This implies that warm (cold) surface waters of ED1 (ED2) were important on modifying the surface air temperature in respect to surrounding areas outside the eddies, an important result showing the local modulation of these eddies in the lower levels of the atmosphere. The direct relationship between SST and wind magnitude in the presence of ocean eddies is an active area of research and new results indicate that the BMC region is an important region for the MABL modulation by the ocean’s mesoscale variability and its eddies [5,8,10,16,27,54,55]. In agreement with these studies, our observations indicate that eddies ED1 and ED2 also promoted a marked local imprint in the lower atmosphere at the meteorological synoptic scale. A simultaneous peak of maximum U10 (~10 m s−1) also occurred when the ship was crossing the warm core eddy, ED1. The surface wind vectors also indicate a weakening in magnitude, with no extreme changes in the wind direction during the time when the ship crossed ED1 toward ED2 (Figure 9c).
Figure 9d shows a relatively steady difference in SST-Tair (±2 °C) throughout the entire series. At the ED1 and ED2 locations, the difference is close to zero. Relative humidity, however, presented a minimum of about 65% rapidly changing to a maximum (100%) in the boundary between ED1 and ED2. Although not obvious in the Hbulk time series, the rapid RH10 change between the warm and cold core eddies was mirrored by the HEC (Figure 9e). During most of time series, the sensible and latent heat fluxes ranged between ± 20 W m−2 (Figure 9e,f). Extreme peaks reached between 80–100 W m−2. Biases between EC and bulk for both sensible and latent heat fluxes (Figure 9g), in agreement to other recent findings in the BMC region [16], tended to be high when episodes such these occur: (i) rapid changes in the wind magnitude; (ii) rapid changes of the SST-Tair difference; (iii) rapid changes in the RH10 and (iv) rapid changes in the SST pattern caused by the presence of mesoscale structures.
As also recently reported [16], the positive stability condition of the MABL represented by (Monin–Obukhov stability parameter) ζ > 0 seen during ED1 and ED2 sampling (Figure 9h) caused major biases between the EC and bulk estimates (Figure 9g). In cases of ζ > 0, there is a suppression of the intensity of the air-sea turbulent fluxes and a failure in the calculations due to non-realistic heat and humidity turbulent transfer coefficients [16,50,56].
The importance of measuring and/or estimating accurately the air-sea heat fluxes is widely known [38,39,46,57,58,59]. Bulk parameterizations such as the COARE 3.5 [38] used here are commonly applied in most weather and climate prediction models for estimating the air-sea heat fluxes [30]. Nonetheless, the accuracy of these estimations, especially in high latitudes, depend upon the SST variability, the winds and the MABL stability [59,60,61]. The heat fluxes estimated by the bulk formulae are generally accurate when H varies between −50 to 50 W m−2 with wind magnitudes between 4 and 16 m s−1 and during unstable MABL conditions [60]. In addition, it is expected that in high latitudes and when the winds are very weak (<4 m s−1) or very strong (>20 m s−1), the heat fluxes estimated by the bulk formulae may present enhanced errors [61]. These errors may also be associated with a high SST-Tair difference [16,59].
The results presented in Figure 9 are important to describe two major points: (i) our in situ observations are able to demonstrate in situ the local forcing of the MABL by the presence of mesoscale structures in the BMC in a “stable” atmospheric situation (when no transient systems were present) and (ii) major differences between directly measured (EC) and bulk parameterizations of air-sea heat fluxes in an oceanic region, particularly those dominated by the mesoscale activity corroborate the necessity of constraining the spatial and temporal variability of the ocean-atmosphere system, in agreement to previous studies [16,59,60,61].
The air-sea heat fluxes over ED1 and ED2, as measured by the EC method, were directly influenced by the atmospheric stability condition occurring during 16–18 October 2013 during the INTERCONF-32 campaign. This stability was a consequence of the displacement of the high-pressure atmospheric system already reported here (Figure 8). The MABL stability has a primary role on the modulation of the air-sea heat fluxes, causing large uncertainties when stable or nearly neutral (ζ ~ 0) atmospheric conditions predominate [16,49,50,51]. As reported earlier on in this text, as part of data pre-processing, all data sampled when positive stability (ζ > 0.2) occurred were removed from our analysis aiming not to bring uncertainties into our dataset. The remaining observational data, although more precise on the methodological viewpoint, contributed to an unexpected result: the warm core eddy ED1 absorbed sensible heat from the atmosphere (HEC = −10.3 W m−2) and the cold core eddy ED2 lost sensible heat to the atmosphere (HEC = 16.3 W m−2). Although Leyba et al. [8] reported that the difference from expectations on the case of BMC cold core eddies as sources of heat fluxes to the atmosphere is owed to the nature of their shedding process and the eddy-pumping, we believe that abrupt changes in the atmosphere’s dynamics are also an important mechanism not to be neglected.
In the case of ED1, towards the end of the sampling campaign in 18 October 2013 (Figure 8c) a change in the atmospheric advection condition induced a MABL warmer than the ocean’s surface causing an intensification of the negative HEC. The changes in the advection pattern, on the other hand, caused a cooling on the MABL over ED2, consequently imposing an intensification of the HEC to the atmosphere. Although somehow inhibited by the atmospheric stability condition that persisted over the INTERCONF-32 campaign, HlEC were positive over both eddies (ED1 = 15.2 W m−2; ED2 = 14.2 W m−2). Here again, the unexpected results may be attributed to the high pressure atmospheric system transition that acted directly modifying the MABL stability during the sampling period. The change in the atmospheric advection pattern, on the other hand, acted changing the humidity content of the MABL thus modulating the latent heat fluxes in short time scales.
3.4. Comparing ERA5 and In Situ Measurements of Heat Fluxes over ED1 and ED2
In this section we make a brief exercise of comparing the results presented in Figure 5 and Figure 8 as well as in Table 2. The direct dataset comparisons are not necessarily obvious because of the different methods, accuracies and spatial/temporal resolutions used by ERA5 reanalysis and during the ship-based field campaign.
When looking at the air-sea heat flux results obtained from the ERA5 data set we notice that both ED1 and ED2, on average during their life spans, can be considered as sources of sensible and latent heat (positive Hb, Hlb) from the ocean to the atmosphere (Table 2). However, as expected, the warm core eddy ED1 offers around five (two) times more sensible (latent) heat to the atmosphere in comparison to the cold core eddy ED2.
During the INTERCONF-32 campaign, bulk sensible heat fluxes (Hb) of both eddies were negative on average. Bulk latent heat fluxes, however, on average presented contrary results to what we would expect: negative Hlb for ED1 and positive Hlb for ED2. It is fair to assume that these results were associated to the synoptic atmospheric conditions acting over the study region during the days when both eddies were sampled. Although fairly stable (high SLP) during the overall INTERCONF-32 campaign, during 17–18 October 2013 we experienced a change in the atmospheric advection pattern leading to a prevailing negative advection (Figure 9c) that may have modulated the specific humidity at the air-sea interface. As a consequence of that, the atmosphere becomes saturated in the air-sea interface causing an inversion of the Hlb signal. The opposite occurs over ED2.
During the INTERCONF-32 campaign the observed EC heat fluxes, as quoted before, are dependent on the MABL stability. A very stable MABL (ζ > 0.2) results in poor EC estimates. As we removed the data associated to these conditions from our analysis, we tended to keep only negative sensible heat fluxes (HEC) for ED1 (Table 2), while the opposite occurred at ED2. The latent heat fluxes (HEC) of both ED1 and ED2 were positive, with higher values associated to the warm core eddy.
In general, we also notice that during the INTERCONF-32 campaign, the bulk and EC heat fluxes time series (Figure 9e,f) are consistently similar except during high-frequency episodes of wind magnitude bursts and/or SST-Tair difference changes related to subtle changes in the MABL stability occur [16].
4. Conclusions
In this paper we used in situ, satellite and ERA5 reanalysis data to investigate the local modulation of the MABL caused by the presence of two contrasting ocean eddies in the BMC. Using a novel tracking technique, we followed both warm (ED1) and cold cored (ED2) eddies throughout their observed life spans between September and November 2013. The eddies were shown to modify surface meteorological variables and air-sea fluxes along their trajectories and lifetimes. Their core SST was found to be a predominant forcing mechanism towards atmospheric modulation. ERA5 data obtained along ED1′s trajectory indicated that the eddy’s presence sustained a mean increase of 78% and 55% in sensible and latent air-sea heat fluxes, respectively, with respect to waters inside the Zapiola Rise, a region nearly free from mesoscale activity in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. A mean reduction of 49% (25%) in sensible (latent) air-sea heat fluxes was found over ED2 during its trajectory in comparison to the neutral waters of the Zapiola Rise.
A ship-based field campaign was especially designed to sample the mesoscale eddies within the study region. In situ measurements of several meteorological and oceanographic variables were taken simultaneously in the BMC between 14–20 October 2013. Besides the standard atmospheric measurements, we were able to directly measure the air-sea heat fluxes at high frequency (20 Hz) using the EC method. For the first time, we compare these direct air-sea flux measurements to the COARE 3.5 bulk parameterization in the region and also specifically over the warm and cold cored eddies. Large discrepancies, of up to 100 W m−2 (Figure 9), are found between the comparisons indicating the inaccuracies in determining bulk heat fluxes in such energetic regions characterized by strong temperature fronts.
Our results demonstrate that the intense SST gradients imposed by both warm and cold core eddies studied here were the major local forcing mechanism for modulating the MABL at the atmospheric synoptic scale. This variability is clearly observed because, during the field campaign, no transient atmospheric systems crossed the BMC region. For the first time in the known literature, we present the differences between directly measured (EC) and bulk parameterizations of air-sea heat fluxes over both warm and cold core eddies of the BMC. The differences were mainly caused by rapid changes in the wind magnitude, in enhanced SST-Tair differences, in the relative humidity and, in the SST pattern caused by the presence of the mesoscale structures studied here. During the observations over the eddies, however, the positive stability condition of the MABL also contribute to cause major biases between the EC and bulk estimates. This condition tends to promote a suppression of the intensity of the air-sea turbulent fluxes and a failure in the EC and bulk calculations.
This paper contributes to a better understanding of the lower atmosphere and the MABL modulation by ocean eddies in the BMC, attesting the importance of the use of in situ, meteorological and oceanographic data, assessed in synergy with remote sensing and reanalysis data for such a task.
The lack of in situ measurements to assess the real contribution of warm core eddies in the extratropical regions of the world ocean is acknowledged as a cause of the present lack of understanding on the atmospheric response to oceanic mesoscale structures [27]. Contrary to what is expected in the extratropics, warm eddies, for instance, can reverse the direction of the air-sea flows, normally expected to be from the atmosphere to the ocean when the heat flows are negatively correlated with SST [27]. Our results may be taken into consideration to improve both weather and climate prediction models in the region of South America and the South Atlantic Ocean.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.; methodology, R.S., M.S. and F.O.; software, M.S. and F.O.; validation, R.S., L.P. and S.S.; formal analysis, R.S., M.S. and F.O.; investigation, R.S., L.P. and S.S.; resources, R.S. and L.P.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.; writing—review and editing, R.S. and S.S.; visualization, R.S.; supervision, R.S.; project administration, R.S. and L.P.; funding acquisition, R.S. and L.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Brazilian agencies CNPq, CAPES and FAPERGS to the following projects: (i) National Institute for Science and Technology of the Cryosphere (CNPq 704222/2009 + FAPERGS 17/2551-0000518-0); (ii) Use and Development of the BESM Model for Studying the Ocean-Atmosphere-Cryosphere in high and medium latitudes (CAPES 88887-145668/2017-00); (iii) Antarctic Modeling and Observation System (CNPq/PROANTAR 443013/2018-7) and (iv) Biocomplexity and Physical-Chemical-Biological Interactions in Multiple Scales in the Southwest Atlantic (CNPq/PROANTAR 442695/2018-7). L.P. is partly funded through a CNPq Scientific Productivity Fellow (CNPq/304858/2019-6). S.S. acknowledges support from the Swedish Research Council (VR 2019-04400) and a Wallenberg Academy Fellowship grant (WAF 2015.0186).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors also would like to thank NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center OceanColorWEB, Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service, the Remote Sensing Systems and the National Centers for Environmental Prediction for providing the satellite and weather analysis data used in this work. We thank the Brazilian Navy, the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations (MCTI) and the Brazilian Antarctic Program (PROANTAR) for making the INTERCONF-32 campaign possible and enjoyable. We also acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Witter, D.L.; Richmann, J.G. GEOSAT altimeter observations of the surface circulation of the Southern Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 877–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzoli, S.; Simionato, C. Baroclinic instabilities and forced oscillations in the Brazil/Malvinas Confluence front. Deep-Sea Res. 1990, 37, 1053–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.A.E.; Sarma, Y.V.B.; Mata, M.M.; Garcia, V.M.T. Chlorophyll variability and eddies in the Brazil–Malvinas Confluence region. Deep-Sea Res. 2004, 51, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.B.; Mata, M.M.; Garcia, C.A.; Kampel, M.; Oliveira, E.N.; Lorenzzetti, J.A. Multi-sensor satellite and in situ measurements of a warm core ocean eddy south of the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, R.J.; DeSzoeke, S.P.; Xie, S.-P.; O’Neill, L.; Seo, H.; Song, Q.; Cornillon, P.; Spall, M.; Minobe, S. Air-sea interaction over ocean fronts and eddies. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2008, 45, 274–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Xie, S.-P. Coupled ocean–atmosphere interaction at oceanic mesoscales. Oceanography 2010, 23, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Veley, P.; Backeberg, B. Wind changes above warm Agulhas Current eddies. Ocean. Sci. 2016, 12, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyba, I.M.; Saraceno, M.; Solman, S.A. Air-sea fluxes associated to mesoscale eddies in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean and their dependence on different regional conditions. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 2491–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentemann, C.L.; Clayson, C.A.; Brown, S.; Lee, T.; Parfitt, R.; Ferrar, J.T.; Bourassa, M.; Minnett, P.; Seo, H.; Gille, S.T.; et al. FluxSat: Measuring the ocean-atmosphere turbulent exchange of heat and moisture from space. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzi, L.P.; Souza, R.B.; Santini, M.F.; Miller, A.J.; Carvalho, J.T.; Parise, C.K.; Quadro, M.F.; Rosa, E.B.; Justino, F.; Sutil, U.A.; et al. Oceanic eddy-induced modifications on the air-sea heat and CO2 fluxes in the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence. Sci. Rep. 2020. in revision. [Google Scholar]
- Lindzen, R.S.; Nigam, S. On the role of sea surface temperature gradients in forcing low-level winds and convergence in the tropics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 2418–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.P.; McPhaden, M.J.; Wallace, J.M. The influence of sea surface temperature on surface wind in the eastern equatorial Pacific: Weekly to monthly variability. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Mitchell, T.P.; Deser, C.J. The influence of sea-surface temperature on surface wind in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific: Weekly to monthly variability. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzi, L.P.; Souza, R.B.; Dourado, M.S.; Garcia, C.A.E.; Mata, M.M.; Silva Dias, M.A.F. Ocean-atmosphere in situ observations at the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzi, L.P.; Souza, R.B.; Acevedo, O.; Wainer, I.E.K.; Mata, M.M.; Garcia, C.A.E.; Camargo, R. Multi-year measurements of the Oceanic and Atmospheric Boundary Layers at the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence Region. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, M.F.; Souza, R.B.; Pezzi, L.P.; Swart, S. Observations of air-sea heat fluxes in the southwestern Atlantic under high-frequency ocean and atmospheric perturbations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 4226–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokinaga, H.; Tanimoto, Y.; Xie, S.P. SST-induced wind variations over Brazil/Malvinas Confluence: Satellite and in-situ observations. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3470–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramcianinov, C.B.; Hodges, K.I.; Camargo, R. The properties and genesis environments of South Atlantic cyclones. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4115–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.A.; Rao, V.B. Surface cyclogenesis over South America. Mon. Weather Rev. 1991, 119, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboita, M.S.; da Rocha, R.P.; Ambrizzi, T.; Sugahara, S. South Atlantic Ocean cyclogenesis climatology simulated by regional climate model (RegCM3). Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Pinto, J.R.; da Rocha, R.P. The energy cycle and structural evolution of cyclones over southeastern South America in three case studies. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.L.; Braun, A. A Climatology of Subtropical Cyclones in the South Atlantic. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7328–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzo, L.F.; da Rocha, R.P.; Reboita, M.S.; Sugahara, S. Subtropical Cyclones over the Southwestern South Atlantic: Climatological aspects and case study. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 8543–8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, O.C.; Pezzi, L.P.; Souza, R.B.; Anabor, V.; Degrazia, G.A. Atmospheric boundary layer adjustment to the synoptic cycle at the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence, South Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Camargo, R.; Todesco, E.; Pezzi, L.P.; Souza, R.B. Modulation mechanisms of marine atmospheric boundary layer at the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6266–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackerott, J.A.; Pezzi, L.P.; Bakhoday Paskyabi, M.; Oliveira, A.P.; Reuder, J.; Souza, R.B.; Camargo, R. The role of roughness and stability on the momentum flux in the Marine Atmospheric Surface Layer: A study on the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 3914–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S.; Aono, K.; Fukui, S. Local atmospheric response to warm mesoscale ocean eddies in the Kuroshio-Oyashio Confluence region. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.S.C.; Polito, P.S. Mesoscale eddy detection in satellite imagery of the oceans using the Radon transform. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, S.A.; Thomas, A.C. A census of oceanic anticyclonic eddies in the Gulf of Alaska. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2008, 55, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.L.; Oey, L.Y. Analysis of STCC eddies using the Okubo–Weiss parameter on model and satellite data. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenger, I.; Gruber, N.; Knutti, R.; Münnich, M. Imprint of Southern Ocean eddies on winds, clouds and rainfall. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.; Schlax, M.G.; Samelson, R.M.; Szoeke, R.A. Global observations of large oceanic eddies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, l15606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, C.A.D.; Olson, D.B.; Podestá, G. Statistics of Brazil Current rings observed from AVHRR: 1993 to 1998. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 58-1–58-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, D.L.; Fu, L.-L. The role of vorticity fluxes in the dynamics of the Zapiola Anticlyclone. Geophys. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, M.; Provost, C.; Zajaczkovski, U. Long-term variation in the anticyclonic ocean circulation over the Zapiola Rise as observed by satellite altimetry: Evidence of possible collapses. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2009, 56, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.R.; Piola, A.R.; Mata, M.M.; Soares, I.D. Brazil Current surface circulation and energetics observed from drifting buoys. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, F.; Ibrom, A.; Arriga, N.; Burba, G.; Papale, D. Relative humidity effects of water vapour fluxes measured with closed-path eddy-covariance systems with short sampling lines. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 165, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, J.B.; Jampana, V.; Weller, R.A.; Bigorre, S.P.; Plueddemann, A.J.; Fairall, C.W.; Miller, S.D.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D.; Hersbach, H. On the Exchange of Momentum over the Open Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1589–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Hristov, T.S.; Edson, J.B.; Friehe, C.A. Platform motion effects on measurements of turbulence and air-sea exchange over the open ocean. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, T. Direct measurement of turbulent fluxes over the sea during AMTEX. Pap. Meteorol. Geophys. 1981, 32, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, J.B.; Hinton, A.A.; Prada, K.E.; Hare, J.E.; Fairall, C.W. Direct covariance flux estimates from mobile platforms at sea. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGilis, W.R.; Edson, J.B.; Hare, J.E.; Fairall, C.W. Direct covariance air–sea CO2 fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 16729–16745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Marandino, C.; Saltzman, E.S. Ship-based measurement of air–sea CO2 exchange by eddy covariance. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flügge, M.; Edson, J.B.; Reuder, J. Sensor movement correction for direct turbulence measurements in the marine atmospheric boundary layer. Energy Procedia 2012, 24, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.G.N.; Miller, S.D.; Acevedo, O.C. Using empirical mode decomposition to filter out non-turbulent contributions to air–sea fluxes. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2016, 163, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Rogers, D.P.; Edson, J.B.; Young, G.S. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes for Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere Coupled-Ocean Atmosphere Response Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 3747–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; 666p. [Google Scholar]
- Aubinet, M.; Vesala, T.; Papale, D. (Eds.) Eddy Covariance: A Practical Guide to Measurement and Data Analysis; Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-94-007-2351-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pattey, E.; Strachan, I.B.; Desjardins, R.L. Measuring nighttime CO2 flux over terrestrial ecosystems using eddy covariance and nocturnal boundary layer methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusup, Y.; Liu, H. Effects of atmospheric surface layer stability on turbulent fluxes of heat and water vapor across the water-atmosphere interface. J. Hidrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2835–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jia, L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, C. Optimizing window length for turbulent heat flux calculations from airborne eddy covariance measurements under near neutral to unstable atmospheric stability conditions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeckis, R.; Gordon, A.L. Satellite observations of the Brazil and Falkland Currents—1975 to 1976 and 1978. Deep-Sea Res. 1982, 29, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, V.; Fairall, C.W.; Blomquist, B.W.; Huang, Y.; Protat, A.; Sullivan, P.P.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J. Air-sea heat and momentum fluxes in the Southern Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 12426–12443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas Bôas, A.B.; Sato, O.T.; Chaigneau, A.; Castelão, G.P. The signature of mesoscale eddies on the air-sea turbulent heat fluxes in the South Atlantic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, C.; Swart, S. Significant atmospheric boundary layer change observed above an Agulhas Current warm cored eddy. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 3659657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouin, M.-N.; Caniaux, G.; Traullé, O.; Legain, D.; Le Moigne, P. Long-term heat exchanges over a Mediterranean lagoon. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D23104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, J.R. Providing the Best Turbulent Heat Flux Estimates from Eddy Correlation and Bulk Methods Using DYNAMO Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist, B.W.; Huebert, B.J.; Fairall, C.W.; Bariteau, L.; Edson, J.B.; Hare, J.E.; McGillis, W.R. Advances in Air-Sea CO2 Flux Measurement by Eddy Correlation. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2014, 152, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, B.J.; Miller, S.D. Automated underway eddy covariance system for air-sea momentum, heat, and CO2 fluxes in the Southern Ocean. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2016, 33, 635–652. [Google Scholar]
- Bourassa, M.A.; Gille, S.T.; Bitz, C.; Carlson, D.; Cerovecki, I.; Clayson, C.A.; Cronin, M.F.; Drennan, W.M.; Fairall, C.W.; Hoffman, R.N.; et al. High-latitude ocean and sea ice surface fluxes: Challenges for climate research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.; Hare, J.; Edson, J.; Mcgilllis, W. Parameterization and micrometeorological measurement of air-sea gas transfer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2000, 96, 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).