Consistency between Satellite Ocean Colour Products under High Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption in the Baltic Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
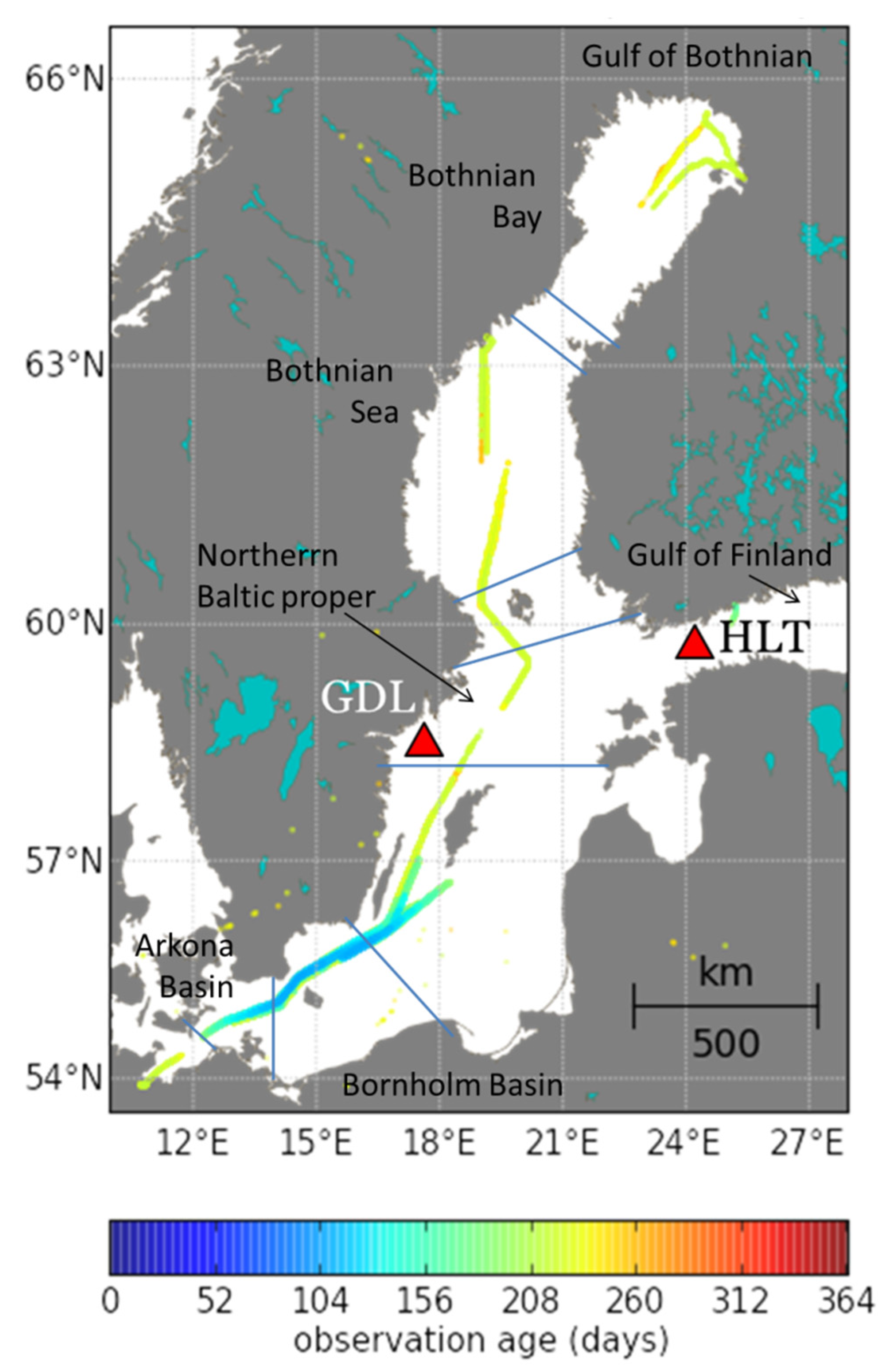
2.1. In Situ Radiometric Data
2.2. OLCI-A, VIIRS and MODIS-Aqua Processors
2.3. Match-Up Procedure and Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donlon, C.; Berruti, B.; Buongiorno, A.; Ferreira, M.H.; Femenias, P.; Frerick, J.; Goryl, P.; Klein, U.; Laur, H.; Mavrocordatos, C.; et al. The global monitoring for environment and security (GMES) sentinel-3 mission. Remote Sens.Environ. 2012, 120, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Talone, M.; Voss, K.J.; Johnson, C.B. Impact of spectral resolution of in situ ocean color radiometric data in satellite matchups analyses. Opt. Express 2017, 25, A798–A812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Pardo, S.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Nencioli, F.; Dessailly, D.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Casal, T.; Donlon, C. Performance of ocean colour algorithms for Sentinel-3 OLCI, MODIS-Aqua and VIIRS in open-ocean waters of the Atlantic. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, F.; Hunt, B.P.V.; Jacoby, D.; Costa, M. Performance of OLCI Sentinel-3A satellite in the Northeast Pacific coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jamet, C.; Zhu, J.H.; Han, B.; Li, T.J.; Yang, A.N.; Guo, K.; Jia, D. Error budget in the validation of radiometric products derived from OLCI around the China Sea from open Ocean to Coastal Waters Compared with MODIS and VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mograne, M.A.; Jamet, C.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Meriaux, X.; Cauvin, A. Evaluation of five atmospheric correction algorithms over French optically-complex waters for the Sentinel-3A OLCI Ocean Color Sensor. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.F. A Regional Assessment of OLCI Data Products. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renosh, P.R.; Doxaran, D.; Keukelaere, L.D.; Gossn, J.I. Evaluation of atmospheric correction algorithms for sentinel-2-MSI and sentinel-3-OLCI in highly turbid estuarine waters. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leppäranta, M.; Myrberg, K. Physical Oceanography of the Baltic Sea; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Omstedt, A.; Elken, J.; Lehmann, A.; Piechura, J. Knowledge of the Baltic Sea physics gained during the BALTEX and related programmes. Prog. Oceanogr. 2004, 63, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Bradtke, K.M.; Krężel, A. Comparison of satellite chlorophyll a algorithms for the Baltic Sea. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ylöstalo, P.; Seppälä, J.; Kaitala, S.; Maunula, P.; Simis, S. Loadings of dissolved organic matter and nutrients from the Neva River into the Gulf of Finland–Biogeochemical composition and spatial distribution within the salinity gradient. Marine Chem. 2016, 186, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products. In Technical Report: Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group; Wang, M. (Ed.) International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010; Volume 10, Available online: https://www.ioccg.org/reports/report10.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Koponen, S.; Attila, J.; Pulliainen, J.; Kallio, K.; Pyhälahti, T.; Lindfors, A.; Rasmus, K.; Hallikainen, M. A case study of airborne and satellite remote sensing of a spring bloom event in the Gulf of Finland. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, H.; Neumann, A.; Walzel, T.; Hetscher, M.; Siegel, H. Application of multispectral interpretation algorithm to remote sensing data over the Baltic Sea. In Proceedings of the Ocean Optics XIII, Halifax, NS, Canada, 6 February 1997; Volume 2963, pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W. A current review of empirical procedures of remote sensing in inland and near coastal transitional waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alimonte, D.; Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.-F.; Canuti, E.; Kajiyama, T. Performance and applicability of bio-optical algorithms in different European seas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.F.; Mélin, F.; D’Alimonte, D.; Kaitala, S. Validation of satellite ocean color primary products at optically complex coastal sites: Northern Adriatic Sea, Northern Baltic Proper and Gulf of Finland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2574–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Brockmann, C.; Moore, G. Using MERIS full resolution data to monitor coastal waters–a case study from Himmerfjarden, a fjord-like bay in the north western Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2284–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.-F. Assessment of satellite ocean color products at a coastal site. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darecki, M.; Stramski, D. An evaluation of MODIS and SeaWiFS bio-optical algorithms in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 326–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohde, T.; Sturm, B.; Siegel, H. Derivation of SeaWiFS vicarious calibration coefficients using in situ measurements in Case 2 water of the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Abaunza, J.M.; Kratzer, S.; Brockmann, C. Evaluation of MERIS products from Baltic Sea coastal waters rich in CDOM. Ocean Sci. 2014, 10, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attilla, J.; Koponen, S.; Kallio, K.; Lindfors, A.; Kaitala, S.; Ylöstalo, P. MERIS Case II water processor comparison on coastal sites of the northern Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikas, K.; Ansko, I.; Vabson, V.; Ansper, A.; Kangro, K.; Uudeberg, K.; Ligi, M. Consistency of radiometric satellite data over lakes and coastal waters with local field measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratzer, S.; Plowey, M. Integrating mooring and ship-based data for improved validation of OLCI chlorophyll-a products in the Baltic Sea. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Géoinf. 2021, 94, 102212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.-F. Comparison of SeaWiFS, MODIS and MERIS radiometric products at a coastal site. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L06617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.-F.; Holben, B.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.; D’Alimonte, D.; Vandemark, D.; Feng, H.; Schuster, G.; et al. AERONET-OC: A network for the validation of ocean color primary products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Holben, B.N.; Talone, M.; D’Alimonte, D.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.M.; Sorokin, M.G. Advances in the ocean colour component of the Aerosol Robotic network (AERONET). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 725–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Simis, S.G.; Tilstone, G.H. Radiometric validation of atmospheric correction for MERIS in the Baltic Sea based on continuous observations from ships and AERONET-OC. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simis, S.; Qin, P.; Attila, J.; Kervinen, M.; Kallio, K.; Koponen, S.; Väkevä, S.; Pardo, S.; Tilstone, G. Baltic sea shipborne hyperspectral reflectance data from 2016 (1.0). Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, S.G.H.; Olsson, J. Unattended processing of shipborne hyperspectral reflectance measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of atmospheric correction algorithms for the sentinel-2A multispectral imager over coastal and inland waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, S.B.; Lazin, G.; Zibordi, G.; McLean, S. An evaluation of above-and inwater methods for determining water-leaving radiances. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 486–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D. OLCI Level 2 Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Atmospheric corrections over Case 1 waters (“Clear Waters Atmospheric Corrections” or “CWAC”). European Space Agency, Report No. S3-L2-SD-03-C07-LOV-ATBD. 2010. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/documents/247904/0/OLCI_L2_ATBD_Ocean_Colour_Products_Case-1_Waters.pdf/4e1c1cd4-697e-4491-b574-777a791b5141 (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Wang, M.H.; Shi, W. Cloud masking for ocean color data processing in the coastal regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3105–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramska, M.; Petelski, T. Observations of oceanic whitecaps in the north polar waters of the Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2003, 108, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frouin, R.; Schwindling, M.; Deschamps, P.-Y. Spectral reflectance of sea foam in the visible and near-infrared: In situ measurements and remote sensing implications. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 1996, 101, 14361–14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brockmann, C.; Doerffer, R.; Peters, M.; Kerstin, S.; Embacher, S.; Ruescas, A. Evolution of the C2R-CC neural network for Sentinel 1 and 3 for the retrieval of ocean colour products in normal and extreme optically complex waters. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; Volume 740, p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Aznay, O.; Santer, R. MERIS atmospheric correction over coastal waters: Validation of the MERIS aerosol models using AERONET. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4663–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoble, J.; Herman, M.; Deuzé, J.L.; Lafrance, B.; Santer, R.; Tanré, D. A successive order of scattering code for solving the vector equation of transfer in the earth’s atmosphere with aerosols. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2007, 107, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-3 Mission Performance Centre. Report. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/home (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Steinmetz, F.; Ramon, D. Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI consistent ocean colour products using POLYMER. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Open and Coastal Ocean and Inland Waters, Honolulu, HI, USA, 30 October 2018; Frouin, R.J., Murakami, H., Eds.; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Pardo, S.; van Dongen-Vogels, V.; Boss, E.S. Underway spectrophotometry along the Atlantic Meridional Transect reveals high performance in satellite chlorophyll retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Sathyendranath, S.; Muller, D.; Brockrnann, C.; Deschamps, P.Y.; Devred, E.; Doerffer, R.; Fomferra, N.; Franz, B.; Grant, M.; et al. The Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative: III. A round-robin comparison on in-water bio-optical algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, D.; Krasemann, H.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Brockmann, C.; Deschamps, P.Y.; Doerffer, R.; Fomferra, N.; Franz, B.A.; Grant, M.G.; Groom, S.B.; et al. The Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative: II. Spatial and temporal homogeneity of satellite data retrieval due to systematic effects in atmospheric correction processors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClain, C.R. A decade of satellite ocean color observations. Annu. Rev. Marine Sci. 2009, 1, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, T.S.; Campbell, J.W.; Feng, H. Characterizing the uncertainties in spectral remote sensing reflectance for SeaWiFS and MODIS-Aqua based on global in situ matchup data sets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurin, D.A.; Dierssen, H.M. Advantages and limitations of ocean color remote sensing in CDOM-dominated, mineral-rich coastal and estuarine waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 125, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Mélin, F.; Berthon, J.F.; Canuti, E. Assessment of MERIS ocean color data products for European seas. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlund, T.; Håkansson, B.; Land, P. Aerosol optical depth over the Baltic Sea derived from AERONET and SeaWiFS measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, S.G.H.; YloÈstalo, P.; Kallio, K.Y.; Spilling, K.; Kutser, T. Contrasting seasonality in optical-biogeochemical properties of the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P. Seasonal variability of yellow substance absorption in the surface layer of the Baltic Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 1999, 104, 30047–30058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J.; McClain, C.R. Sensor-independent approach to the vicarious calibration of satellite ocean color radiometry. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 5068–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthon, J.-F.; Zibordi, G. Optically black waters in the northern Baltic Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, L09605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Frouin, R.; Ramon, D.; Steinmetz, F. On the adequacy of representing water reflectance by semi-analytical models in ocean color remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Vecchio, R.; Subramaniam, A. Influence of the Amazon river on the surface optical properties of thewestern tropical North Atlantic ocean. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2004, 109, C11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, A.R.; Gonnelli, M.; Hansell, D.A.; Santinelli, C. Black Sea dissolved organic matter dynamics: Insights from optical analyses. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1425–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-Z.; Zhang, H.-H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.-P. Seasonal variation in chromophoric dissolved organic matter and relationships among fluorescent components, absorption coefficients and dissolved organic carbon in the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. J. Marine Syst. 2018, 180, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrulik, D.; Kratzer, S. Evaluation of sentinel-3A OLCI products derived using the case-2 regional coast colour processor over the Baltic sea. Sensors 2019, 19, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Mallor-Hoya, S.; Gohin, F.; Bel Couto, A.; Sa, C.; Gloela, P.; Cristina, S.; Airs, R.; Icely, J.; Zuhlke, M.; et al. Which ccean colour algorithm for MERIS in NW european coastal waters? Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdun, A.; Rozwadowska, A.; Kratzer, S. Seasonal variability in the optical properties of Baltic aerosols. Oceanologia 2011, 53, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Estimation of near-infrared water-leaving reflectance for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 7521–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Wang, M.; Maritorena, S.; Robinson, W. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery: The black pixel assumption. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3582–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R. Atmospheric correction of ocean color imagery in the earth observing system era. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17081–17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyens, C.; Jamet, C.; Schroeder, T. Evaluation of four atmospheric correction algorithms for MODIS-Aqua imagery over contrasted coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G.; Carlund, T.; Holben, B.N.; Stefan, S. Validation of SeaWiFS and MODIS Aqua/Terra aerosol products in coastal regions of European marginal seas. Oceanologia 2013, 55, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, W.; Gatebe, C.K.; Jamet, C.; Zibordi, G.; Schroeder, T.; Stamnes, K. Atmospheric correction over coastal waters using multilayer neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 218–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Ruddick, K.; Ansko, I.; Moore, G.; Kratzer, S.; Icely, J.; Reinart, A. In situ determination of the remote sensing reflectance: An intercomparison. Ocean Sci. 2012, 8, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilstone, G.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Hieronymi, M.; Ruddick, K.; Beck, M.; Ligi, M.; Costa, M.; D’Alimonte, D.; Vellucci, V.; Vansteenwegen, D.; et al. Field intercomparison of radiometer measurements for ocean colour validation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinski, S.; Verstraete, M.; Peterson, T.C.; Richter, C.; Simmons, A.; Zemp, M. The Concept of Essential Climate Variables in Support of Climate Research, Applications, and Policy. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GCOS. Systematic Observation Requirements from Satellite-Based Data Products for Climate 2011 Update. In Supplemental Details to the Satellite-Based Component of the “Implementation Plan for the Global Observing System for Climate in Support of the UNFCCC”; Technical Report; World Meteorological Organisation (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Brockmann, C.; Brotas, V.; Calton, B.; Chuprin, A.; Cipollini, P.; Couto, A.B.; Dingle, J.; Doerffer, R.; et al. An Ocean-Colour Time Series for Use in Climate Studies: The Experience of the Ocean-Colour Climate Change Initiative (OC-CCI). Sensors 2019, 19, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brando, V.E.; Sammartino, M.; Colella, S.; Bracaglia, M.; Di Cicco, A.; D’Alimonte, D.; Kajiyama, T.; Kaitala, S.; Attila, J. Phytoplankton bloom dynamics in the Baltic sea using a consistently reprocessed time series of multi-sensor reflectance and novel chlorophyll-a retrievals. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Vantrepotte, V.; Chuprin, A.; Grant, M.; Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S. Assessing the fitness-for-purpose of satellite multi-mission ocean color climate data records: A protocol applied to OC-CCI chlorophyll-a data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Processor | Flags Implemented |
|---|---|
| OLCI pb 2.23–2.29 | CLOUD, CLOUD_AMBIGUOUS, CLOUD_MARGIN, INVALID, COSMETIC, SATURATED, SUSPECT, HISOLZEN, HIGHGLINT, SNOW_ICE, AC_FAIL, WHITECAPS, NOT_ABSO_D, ANNOT_MIXR1, ANNOT_TAU06, RWNEG_O2, RWNEG_O3, RWNEG_O4, RWNEG_O5, RWNEG_O6, RWNEG_O7, RWNEG_O8 |
| OLCI pb OL_L2.003.00 | CLOUD, CLOUD_AMBIGUOUS, CLOUD_MARGIN, INVALID, COSMETIC, SATURATED, SUSPECT, HISOLZEN, HIGHGLINT, SNOW_ICE, AC_FAIL, WHITECAPS, ADJAC, RWNEG_O2, RWNEG_O3, RWNEG_O4, RWNEG_O5, RWNEG_O6, RWNEG_O7, RWNEG_O8. |
| OLCI POLYMER v4.13 | Processor flags: INVALID, NEGATIVE_BB, OUT_OF_BOUNDS, EXCEPTION, THICK_AEROSOLS, HIGH_AIR_MASS, IDEPIX Pixel classification flags: IDEPIX_INVALID, IDEPIX_CLOUD, IDEPIX_CLOUD_AMBIGUOUS, IDEPIX_CLOUD_SURE, IDEPIX_CLOUD_BUFFER, IDEPIX_CLOUD_SHADOW, IDEPIX_SNOW_ICE, IDEPIX_BRIGHT, IDEPIX_WHITE |
| OLCI C2R-CC vSnap8 | Processor flags: CLOUD_RISK, RHOW_OOS, RTOSA_OOS, RTOSA_OOR, RHOW_OOR Quality flags: BRIGHT, STRAYLIGHT_RISK, INVALID, COSMETIC, SUN_GLINT_RISK, DUBIOUS, LAND |
| MODIS-Aqua/Suomi-VIIRS | ATMFAIL, LAND, HIGLINT, HILT, HISATZEN, STRAYLIGHT, CLDICE, COCCOLITH, HISOLZEN, LOWLW, CHLFAIL, NAVWARN, MAXAERITER, ATMWARN, NAVFAIL |
| Statistical Quantities | OLCI-A | pb 2.23–2.29 | N = 208 TOT | N = 5 GDL | N = 4 HLT | N = 199 Ferry |
| 412 nm | 443 nm | 490 nm | 560 nm | 665 nm | 709 nm | |
| S | 4.182 | 1.841 | 0.83 | 0.663 | 0.75 | 0.788 |
| I | −0.007 | −0.003 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | 0 | −0.0001 |
| r | 0.29 | 0.4 | 0.58 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.55 |
| Ψ | 0.0015 | 0.0011 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 |
| δ | −0.001 | −0.0009 | −0.0004 | 0 | −0.0002 | −0.0002 |
| Δ | 0.0009 | 0.0007 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| RPD | 90.64 | 55.13 | 24.14 | 17.33 | 33.48 | 32.23 |
| Statistical Quantities | OLCI-A | OL_L2M.003 | N = 208 TOT | N = 5 GDL | N = 4 HLT | N = 199 Ferry |
| 412 nm | 443 nm | 490 nm | 560 nm | 665 nm | 709 nm | |
| S | 12.984 | 4.402 | 0.883 | 0.524 | 0.42 | 0.374 |
| I | −0.02 | −0.008 | −0.0004 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.00002 |
| r | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.45 |
| Ψ | 0.0015 | 0.0012 | 0.001 | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 |
| δ | −0.0009 | −0.0008 | -0.0007 | −0.0003 | −0.0004 | −0.0004 |
| Δ | 0.0012 | 0.0009 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| RPD | 91.66 | 59.63 | 35.36 | 19.51 | 46.52 | 56.82 |
| Statistical Quantities | OLCI-A | C2R-CC | N = 208 TOT | N = 5 GDL | N = 4 HLT | N = 199 Ferry |
| 412 nm | 443 nm | 490 nm | 560 nm | 665 nm | 709 nm | |
| S | 1.923 | 2.353 | 2.103 | 1.295 | 0.918 | 0.741 |
| I | −0.0007 | −0.002 | −0.002 | −0.00002 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| r | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.6 |
| Ψ | 0.0012 | 0.0015 | 0.0018 | 0.0013 | 0.0003 | 0.0002 |
| δ | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0 |
| Δ | 0.0007 | 0.0008 | 0.0009 | 0.0008 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| RPD | 80.33 | 75.31 | 66.52 | 37 | 29.96 | −0.71 |
| Statistical Quantities | OLCI-A | POLYMER | N = 208 TOT | N = 5 GDL | N = 4 HLT | N = 199 Ferry |
| 412 nm | 443 nm | 490 nm | 560 nm | 665 nm | 709 nm | |
| S | 0.356 | 0.262 | 0.338 | 0.464 | 0.46 | 0.601 |
| I | 0.0008 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.0004 | −0.00003 |
| r | 0.59 | 0.54 | 0.6 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.38 |
| Ψ | 0.0006 | 0.0005 | 0.0007 | 0.0007 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 |
| δ | −0.0004 | −0.0002 | −0.0004 | −0.0001 | −0.0001 | −0.0003 |
| Δ | 0.0004 | 0.0005 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| RPD | 30.06 | 22.53 | 21.17 | 17.57 | 25.87 | 26.95 |
| Statistical Quantities | VIIRS | N = 475 TOT | N = 14 GDL | N = 32 HLT | N = 429 Ferry |
| 412 nm | 443 nm | 486 nm | 560 nm | 671 nm | |
| S | 0.871 | 0.692 | 0.6 | 0.623 | 0.564 |
| I | −0.0005 | 0.00008 | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | 0.00006 |
| r | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.88 |
| Ψ | 0.0011 | 0.0009 | 0.001 | 0.0012 | 0.0005 |
| δ | −0.0008 | −0.0006 | −0.0008 | −0.0009 | −0.0004 |
| Δ | 0.0008 | 0.0006 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 | 0.0003 |
| RPD | 66.81 | 34.94 | 28.86 | 22.19 | 38.36 |
| Statistical Quantities | MODIS-A | N = 177 TOT | N = 16 GDL | N = 39 HLT | N = 122 Ferry |
| 412 nm | 443 nm | 488 nm | 560 nm | 667 nm | |
| S | 6.968 | 1.871 | 0.493 | 0.918 | 1.076 |
| I | −0.006 | −0.001 | 0.0007 | −0.0002 | −0.0003 |
| r | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.4 | 0.77 | 0.91 |
| Ψ | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 0.0002 |
| δ | 0 | −0.0001 | −0.0002 | −0.0004 | −0.0002 |
| Δ | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 |
| RPD | 83.76 | 34.14 | 22.55 | 16.87 | 32.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tilstone, G.H.; Pardo, S.; Simis, S.G.H.; Qin, P.; Selmes, N.; Dessailly, D.; Kwiatkowska, E. Consistency between Satellite Ocean Colour Products under High Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010089
Tilstone GH, Pardo S, Simis SGH, Qin P, Selmes N, Dessailly D, Kwiatkowska E. Consistency between Satellite Ocean Colour Products under High Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010089
Chicago/Turabian StyleTilstone, Gavin H., Silvia Pardo, Stefan G. H. Simis, Ping Qin, Nick Selmes, David Dessailly, and Ewa Kwiatkowska. 2022. "Consistency between Satellite Ocean Colour Products under High Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption in the Baltic Sea" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010089
APA StyleTilstone, G. H., Pardo, S., Simis, S. G. H., Qin, P., Selmes, N., Dessailly, D., & Kwiatkowska, E. (2022). Consistency between Satellite Ocean Colour Products under High Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010089







