Pseudo-Spectral Time-Domain Method for Subsurface Imaging with the Lunar Regolith Penetrating Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- Due to the lower spatial sampling density [16], the PSTD-RTM method can save major computational resources such as CPU time and computer memory, which is conducive to finishing the lunar soil collection of the CE-5 lander during the whole exploration.
- (b)
- Combined with the LRPR’s facility, we can estimate the effective imaging subsurface area, which will be meaningful for the shallow geological study of the extraterrestrial planet.
- (c)
- After utilizing the spectral window, we can remove the invalid measured noise in high or low frequencies and improve the imaging visibility to some extent.
- (d)
- Based on the electromagnetic path, direct waves and interface echoes can be eliminated by the path’s propagation time.
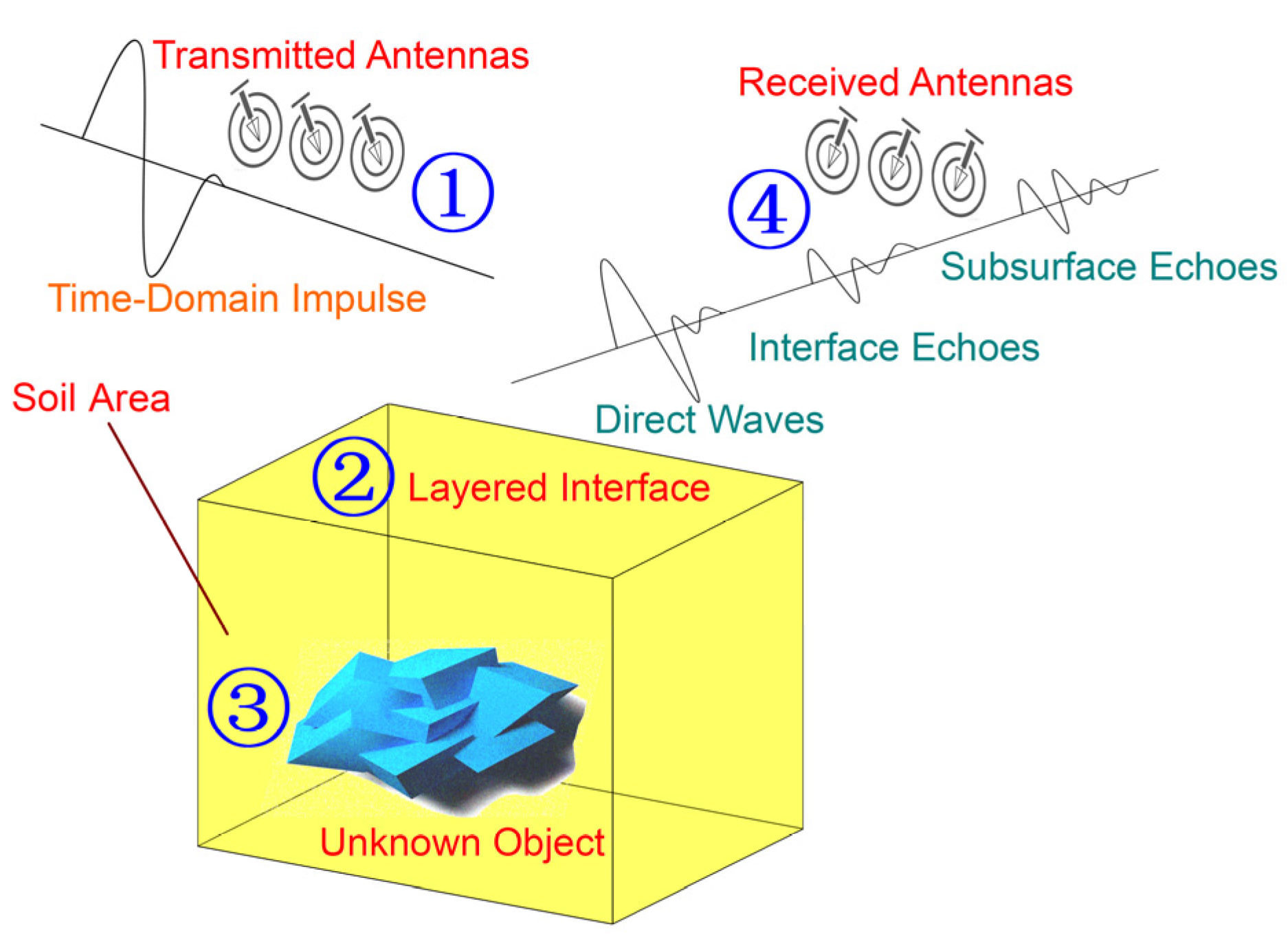
2. Time-Domain Electromagnetic Method and Reverse-Time Migration Method
2.1. Time-Domain Electromagnetic Method
2.2. Collection Process for Measured Data in Layered Area
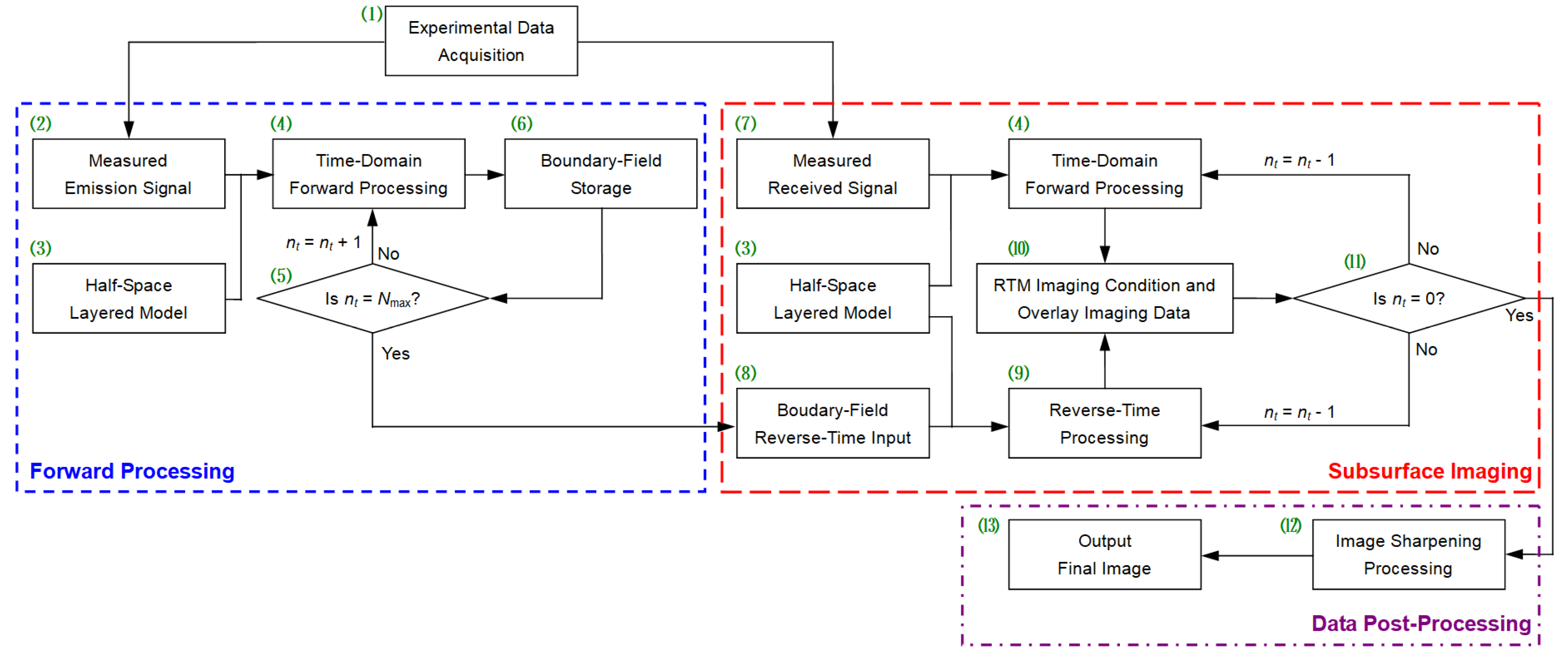
2.3. Procedure Analysis on the RTM Imaging
- (A)
- As reflected in Figure 2, in the blue, short-dashed box marked Forward Processing, the measured emission signal propagates forward into the half-space layered model by using the time-domain electromagnetic algorithm. The time-step boundary fields are prestored for preparing the RTM imaging condition.
- (B)
- Based on Equations (3) and (4), the reverse-time computation can be obtained below:
- (C)
- For the multiple transmitted antennas, we must repeat steps (A) and (B) and then superpose with all the If (r) to implement the final image on the Data Post-Processing marked inside the purple dot-dashed box.
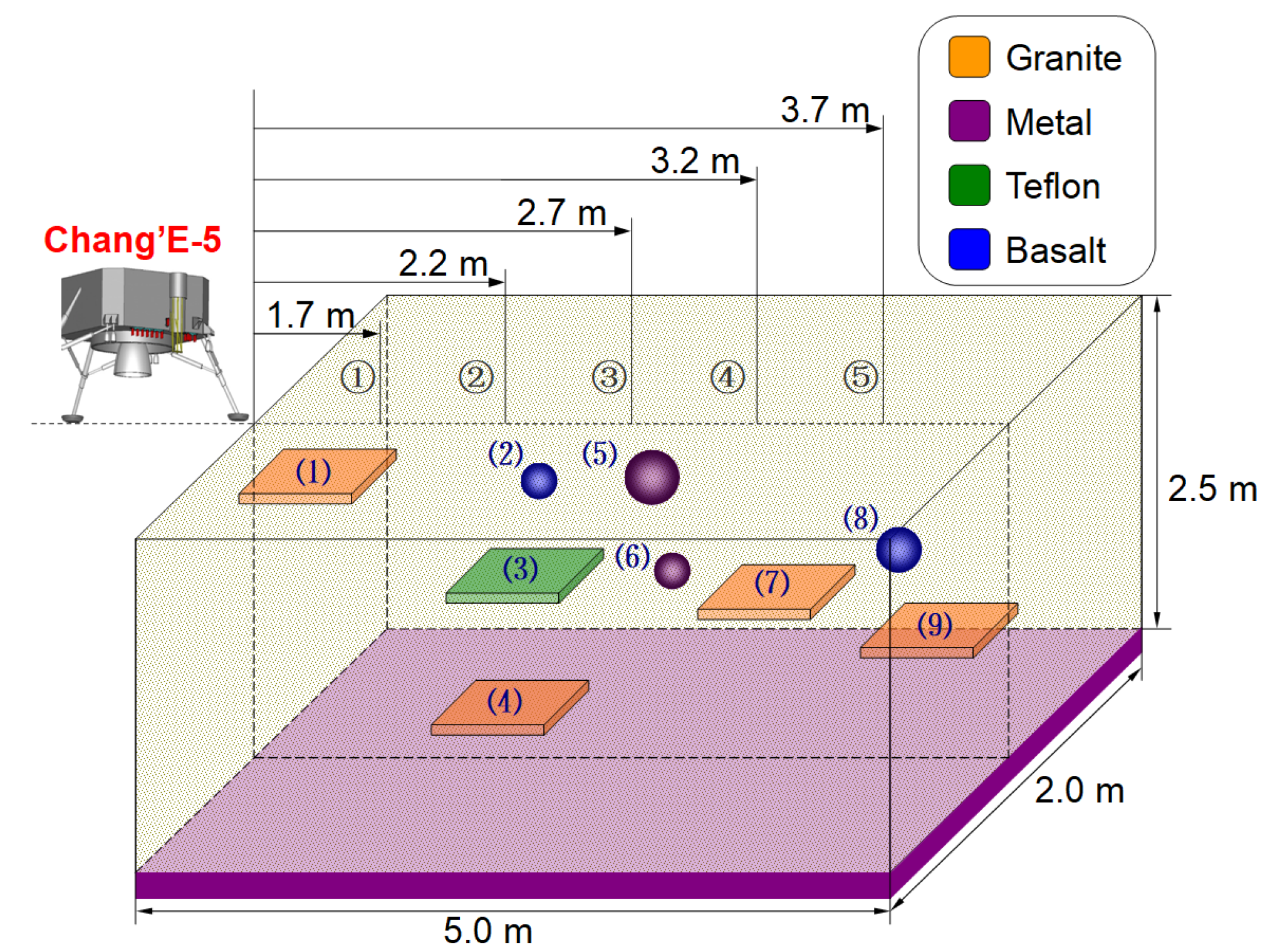
3. Experimental Measurement and Data Analysis for the CE-5 Lander
3.1. The Antenna Layout on the CE-5 Lander
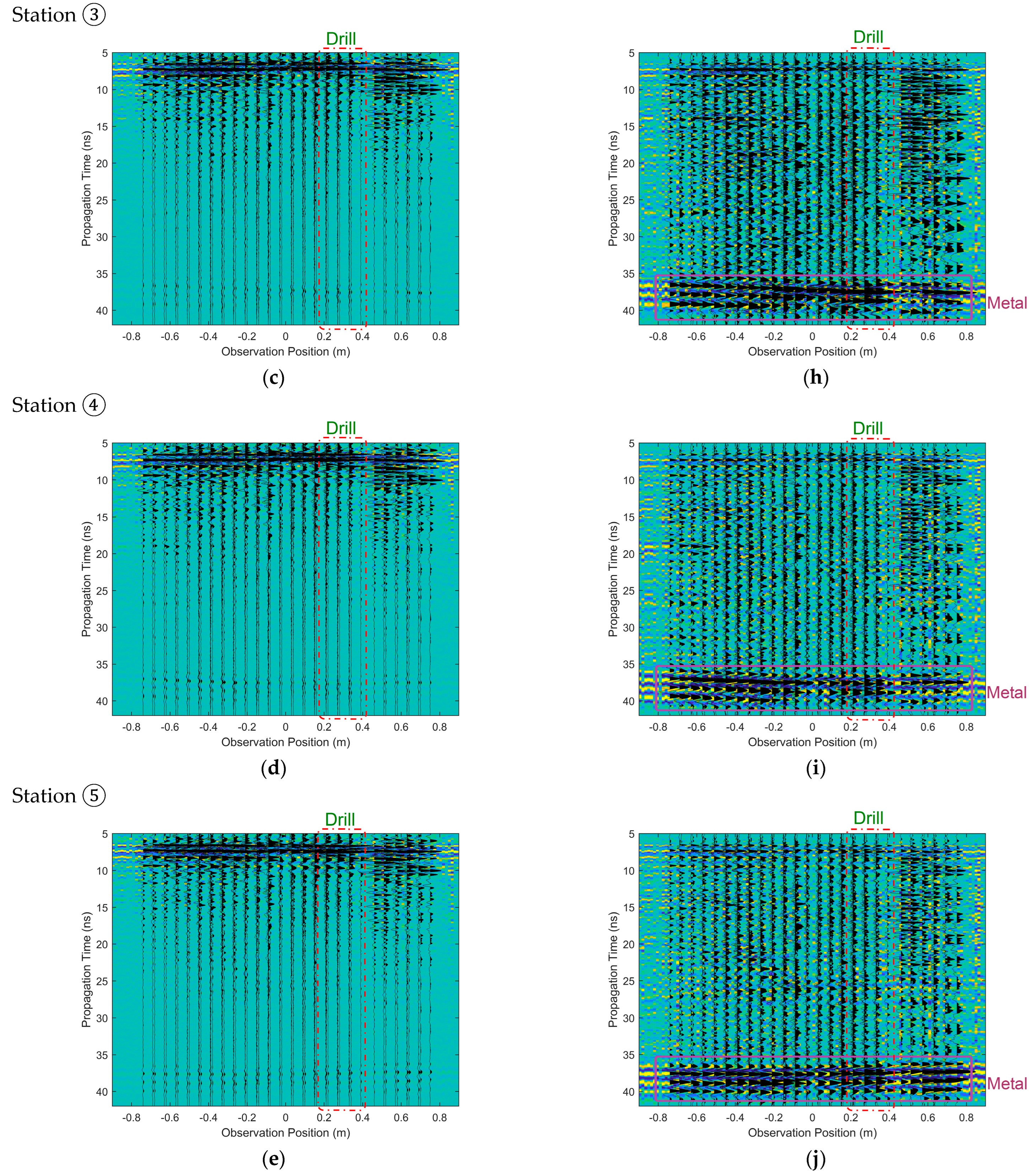
3.2. Measured Data Analysis of the CE-5
3.3. Reasonable Imaging Scope for CE-5 Lander
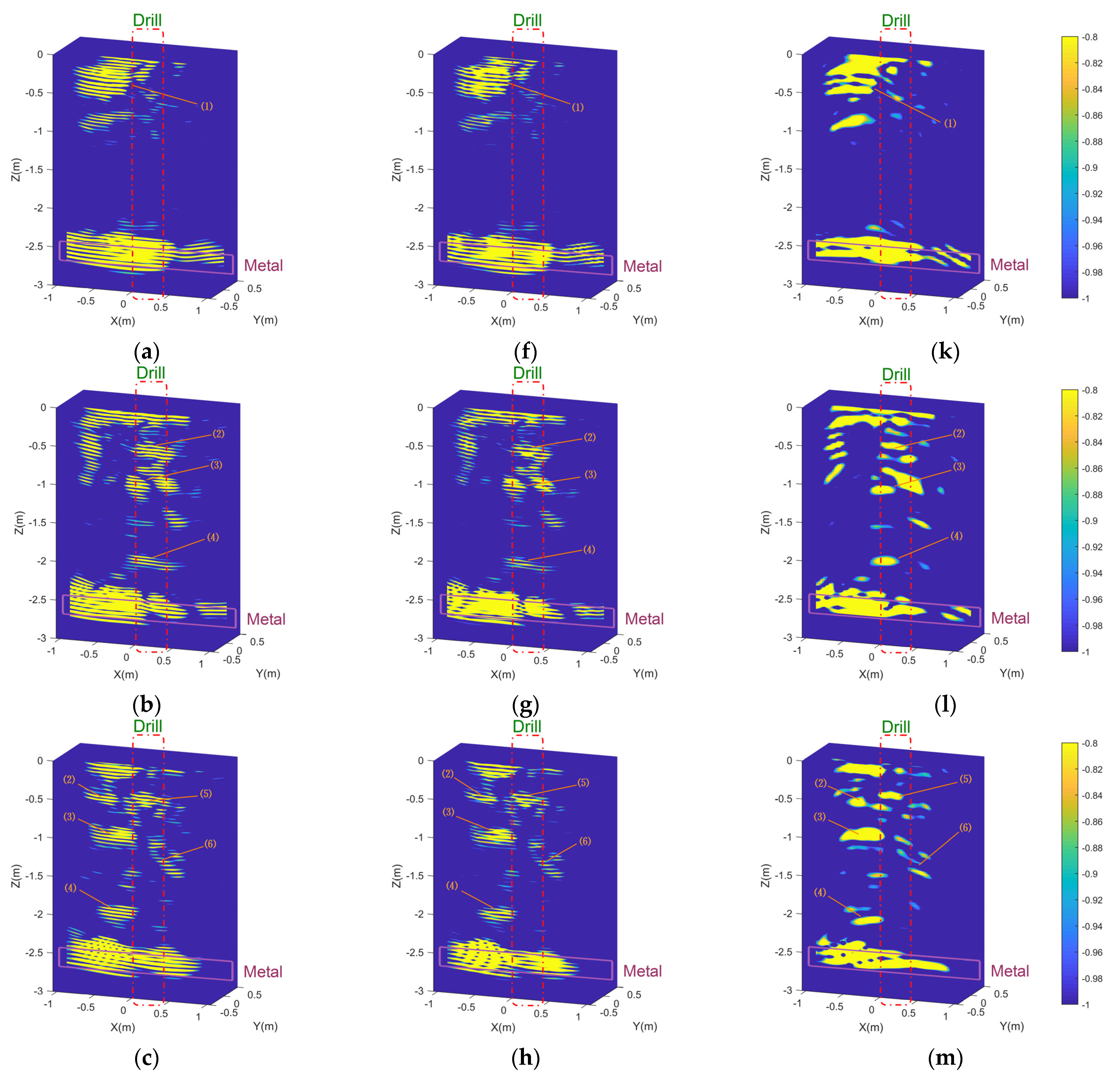
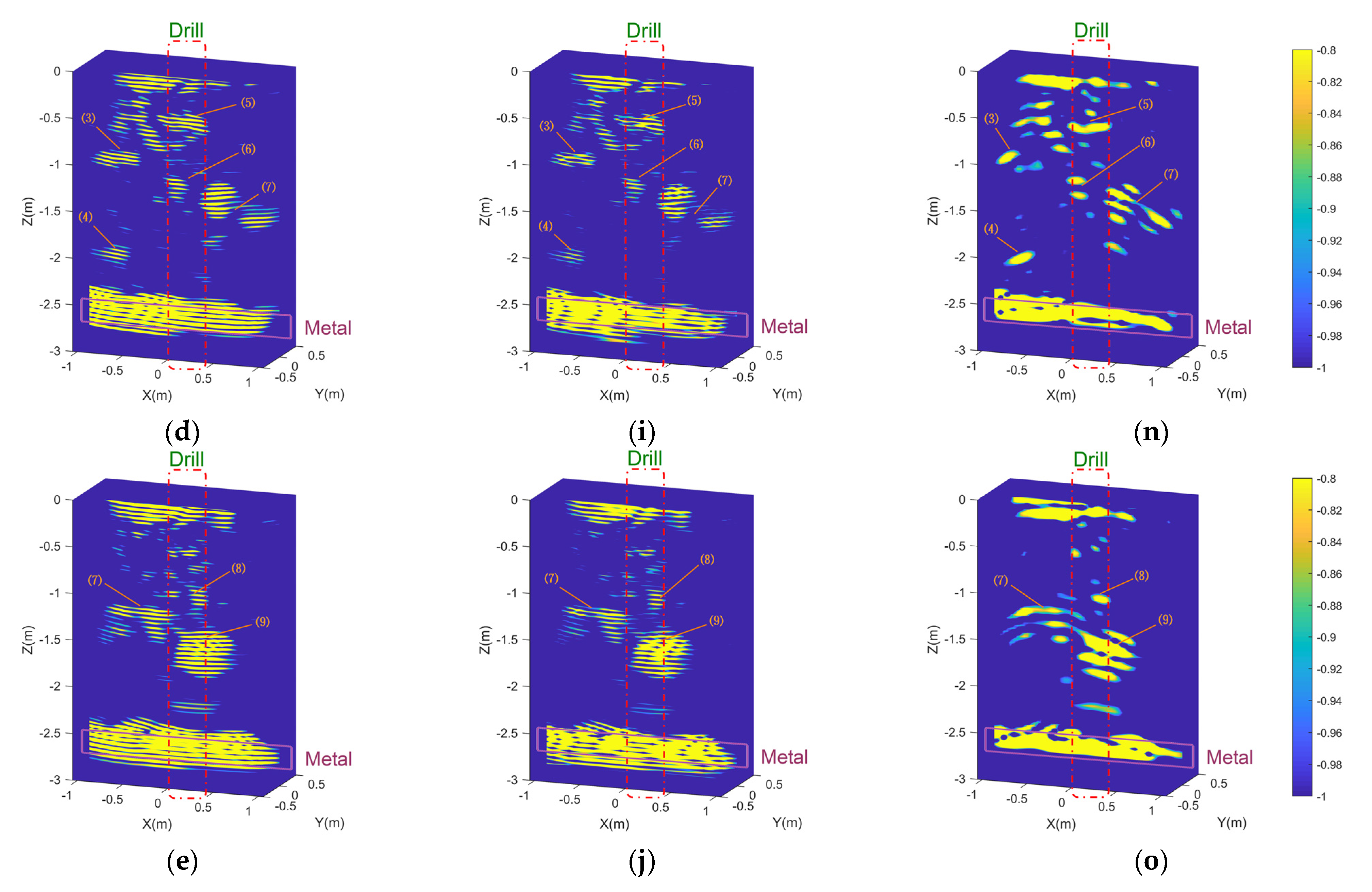
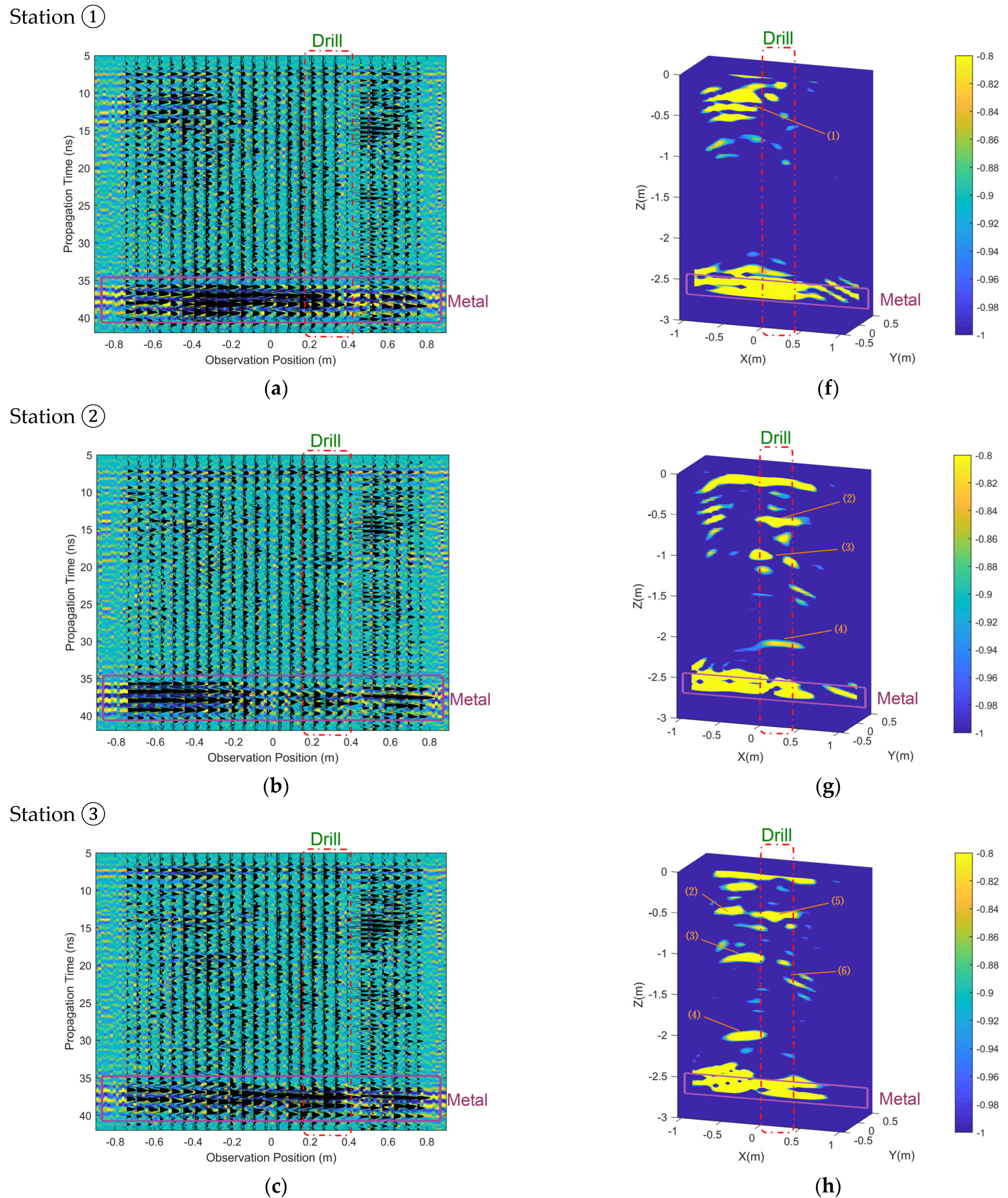
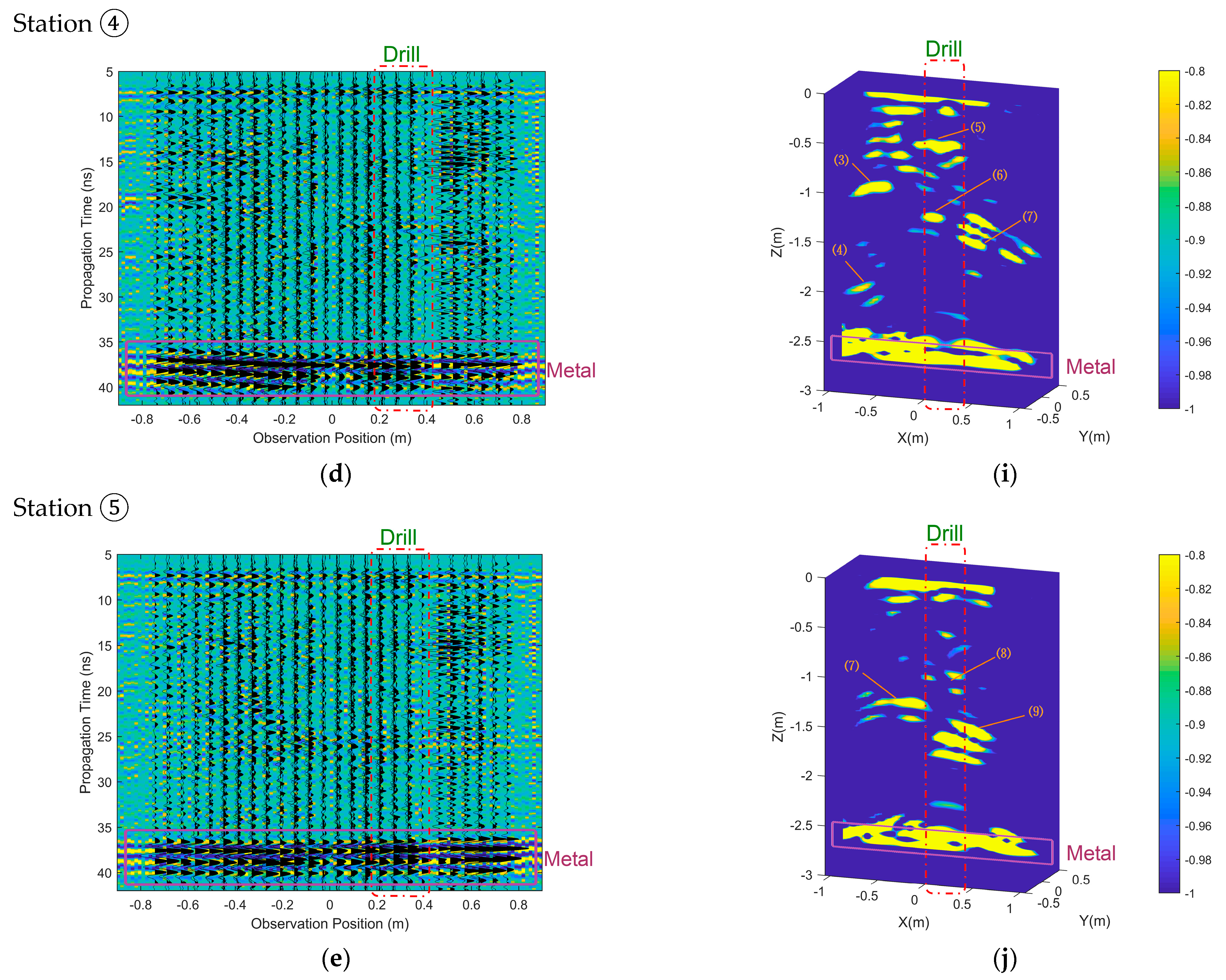
4. Subsurface Imaging for Measured Data from CE-5 Lander
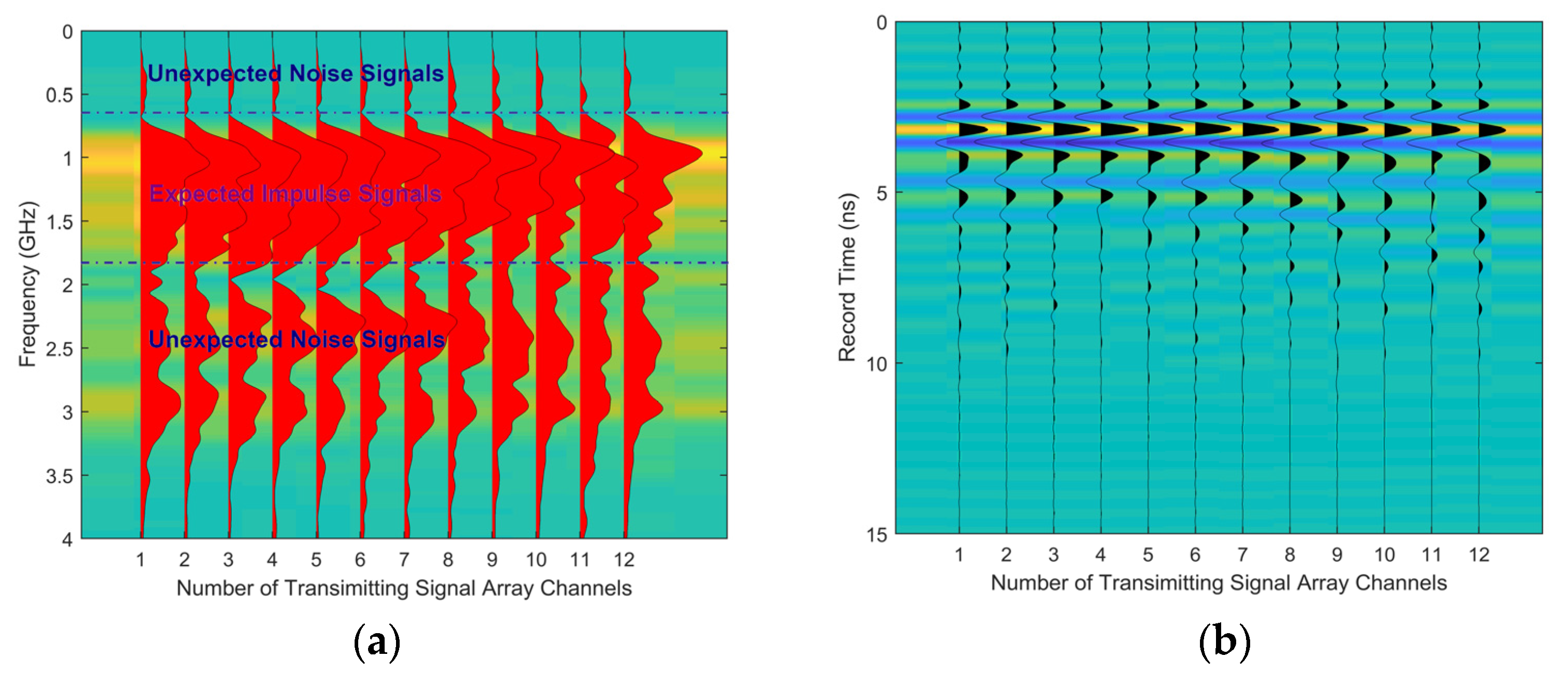
5. Discussions in Frequency-Domain Analysis of Measured Data and Corresponding Imaging
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, L. China’s touch on the Moon. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Rising Start: Science is reaping the benefits of China’s investment in space. Nature 2017, 547, 395–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hand, E. China blasts off on lunar exploration. Nature 2007, 450, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakdawalla, E. China lands on the Moon. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Jolliff, B.L.; Wang, A.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Xiao, L.; et al. Correlated compositional and mineralogical investigations at the Chang’E-3 landing site. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Zuo, W.; Zeng, X.; Xu, R.; Tan, X.; et al. Chang’E-4 initial spectroscopic identification of lunar far-side mantle-derived materials. Nature 2019, 569, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, X.; Yan, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Y.; Zeng, X.; Chen, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Descent trajectory reconstruction and landing site positioning of Change’E-4 on the lunar side. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvi, S.; Cinti, F.R.; Colini, L.; D’addezio, G.; Doumaz, F.; Pettinelli, E. Investigation of the active Celano-L’Aquila fault system, Abruzzi (central Apennines, Italy) with combined ground-penetrating radar and palaeoseismic trenching. Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 155, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strange, A.D.; Ralston, J.C.; Chandran, V. Near-surface interface detection for coal mining applications using bispectral features and GPR. Subsurf. Sens. Technol. Appl. 2005, 6, 125–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettinelli, E.; Barone, P.M.; Di Matteo, A.; Mattei, E.; Lauro, S.E. Mapping the undiscovered ruins of pompeii (naples, Italy) using ground penetrating radar. Archaeometry 2012, 54, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.; Pajewski, L. Civil Engineering Applications of Ground Penetrating Radar; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.H. Reverse time migration using the pseudospectral time-domain algorithm. J. Comput. Acoust. 2016, 24, 1650005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhuang, M.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.H. Reverse time migration of elastic waves using the pseudospectral time-domain method. J. Theor. Comput. Acoust. 2018, 26, 1750033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Long, Z.; Tian, B.; Han, F.; Fang, G.; Liu, Q.H. Two-Dimensional Reverse-Time Migration Applied to GPR With a 3-D-to-2-D Data Conversion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4313–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschen, J.C.; Plumb, G.R. A matched-filter-based reverse-time migration algorithm for ground-penetrating radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Feng, N.; Zhuang, M.; Feng, X.; Fang, G.; Liu, Q.H. A 3-D High-Order Reverse-Time Migration Method for High-Resolution Subsurface Imaging with a Multistation Ultra-Wideband Radar System. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, K.S. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problem involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1966, 17, 585–589. [Google Scholar]
- Taflove, A.; Hagness, S.C. Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yin, W.Y. Development of a novel FDTD (2,4)-compatible conformal scheme for electromagnetic computations of complex curved PEC objects. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Large-scale simulations of electromagnetic and acoustic measurements using the pseudospectral time-domain (PSTD) algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 917–926. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Fan, G.X. Simulations of GPR in dispersive media using a frequency-dependent PSTD algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Fa, W.; Zhu, M.H.; Liu, T.; Plescia, J.B. Regolith stratigraphy at the Chang’E-3 landing site as seen by lunar penetrating radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10179–10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Blewett, D.T.; Cloutis, E.A.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J. Submicroscopic metallic iron in lunar soils estimated from the in situ spectra of the Chang’E-3 mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
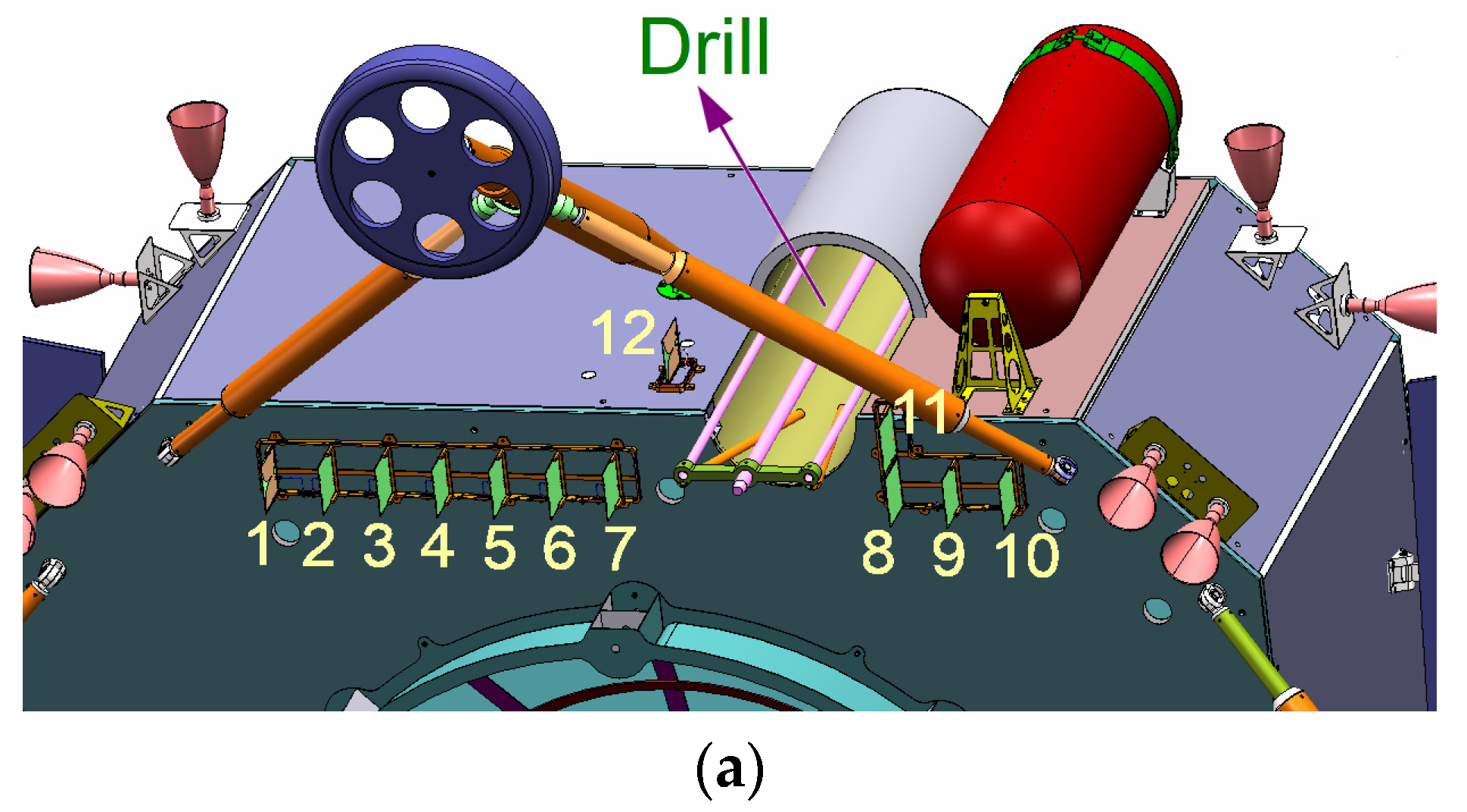
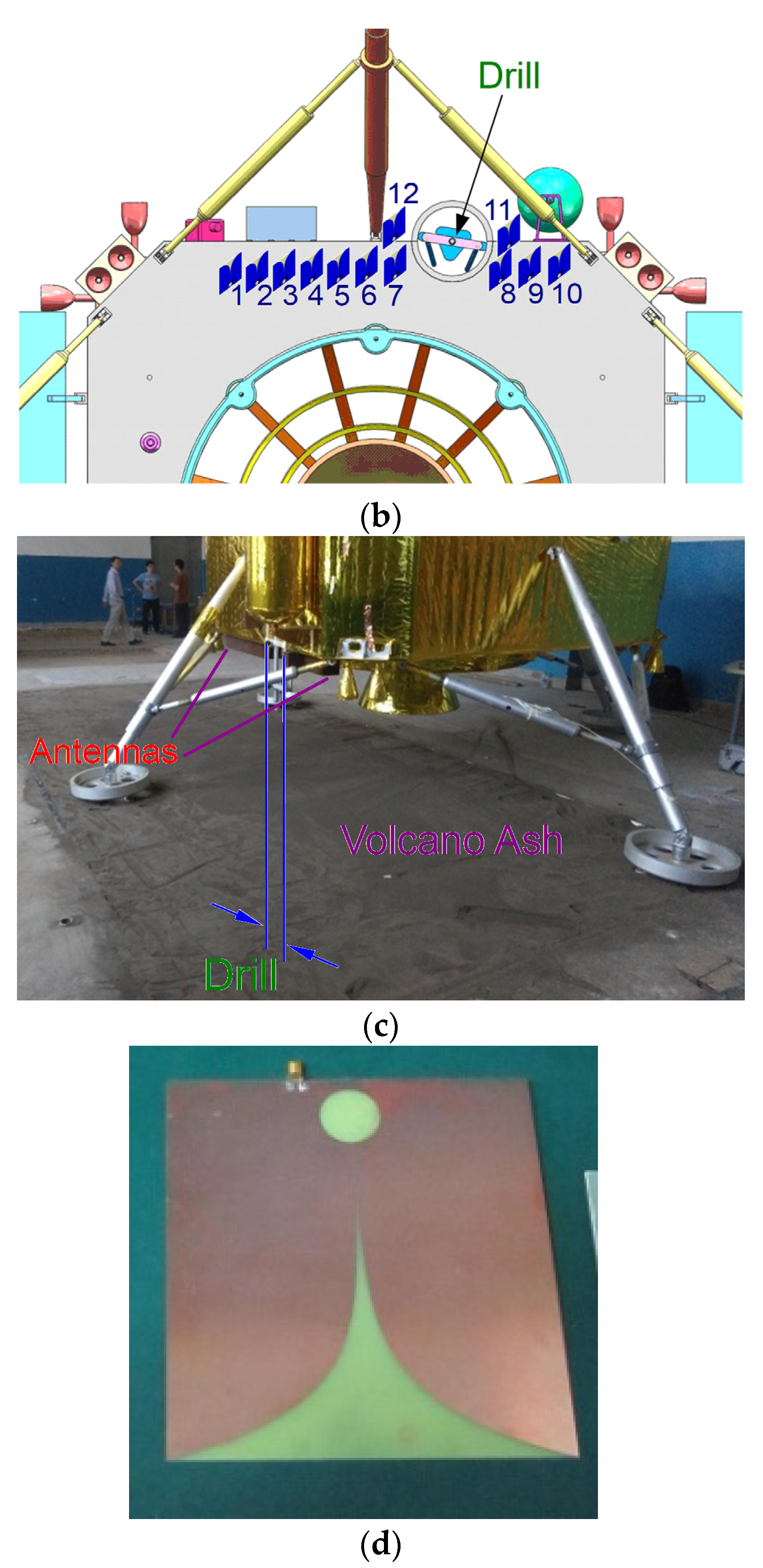
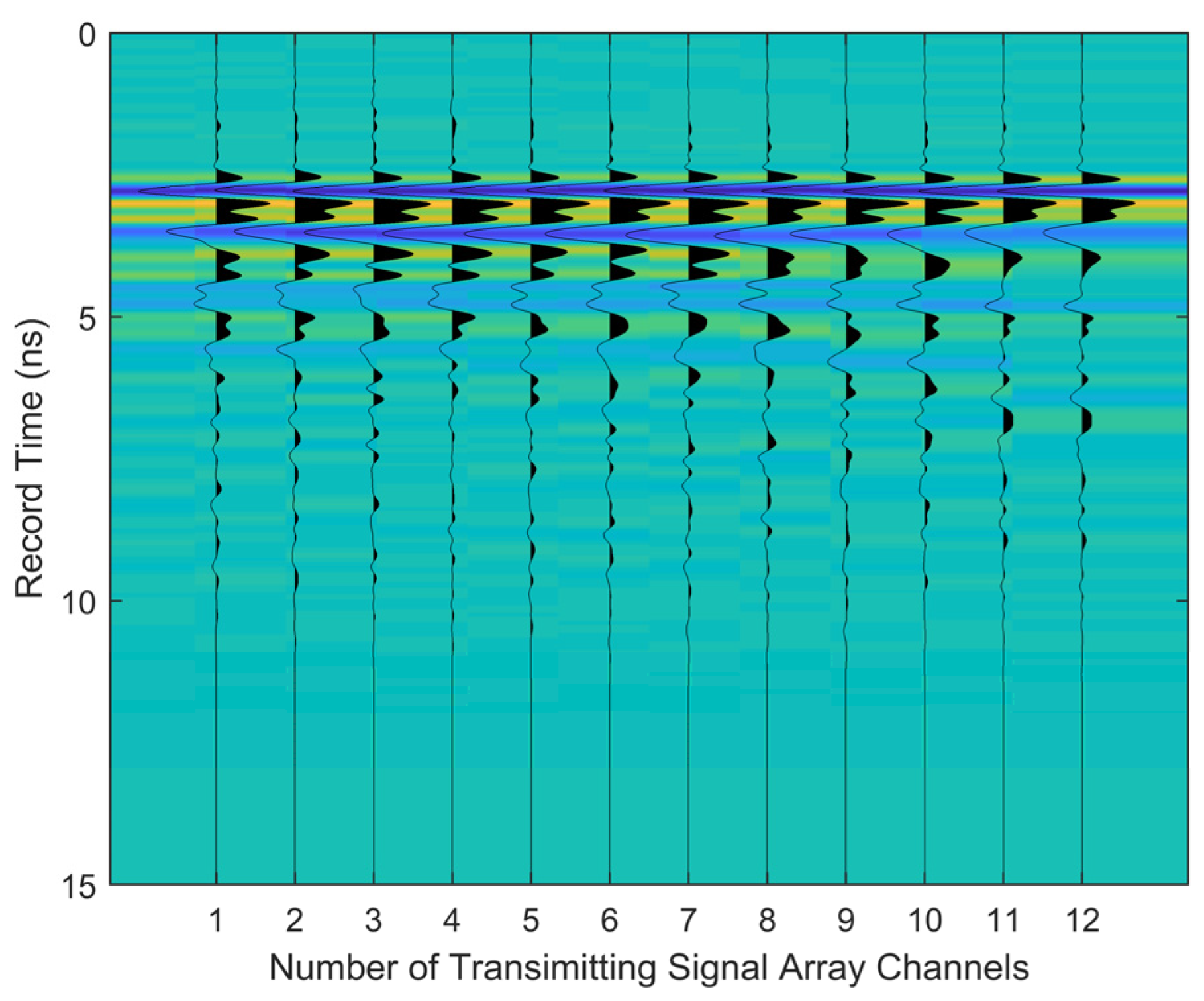
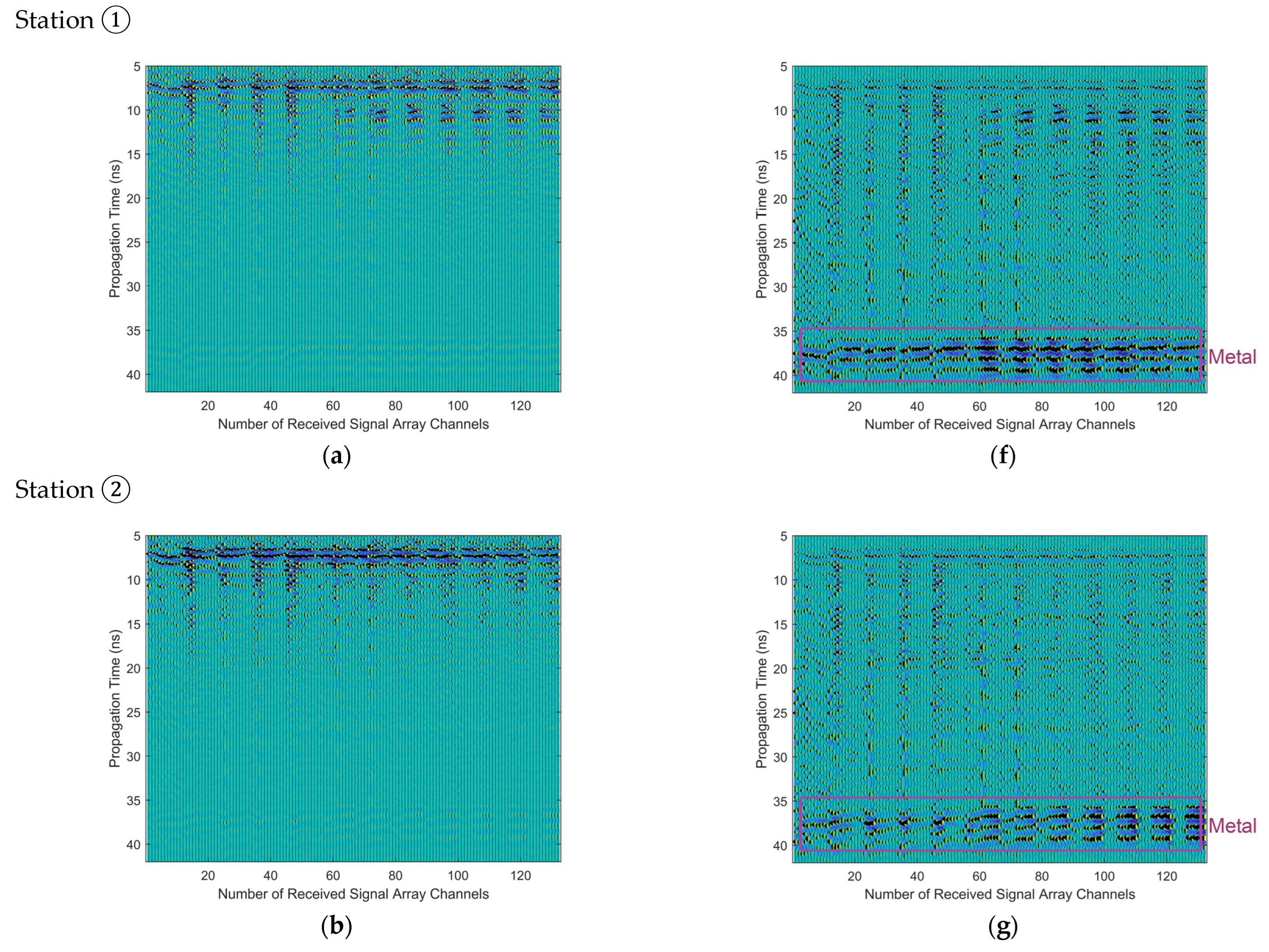
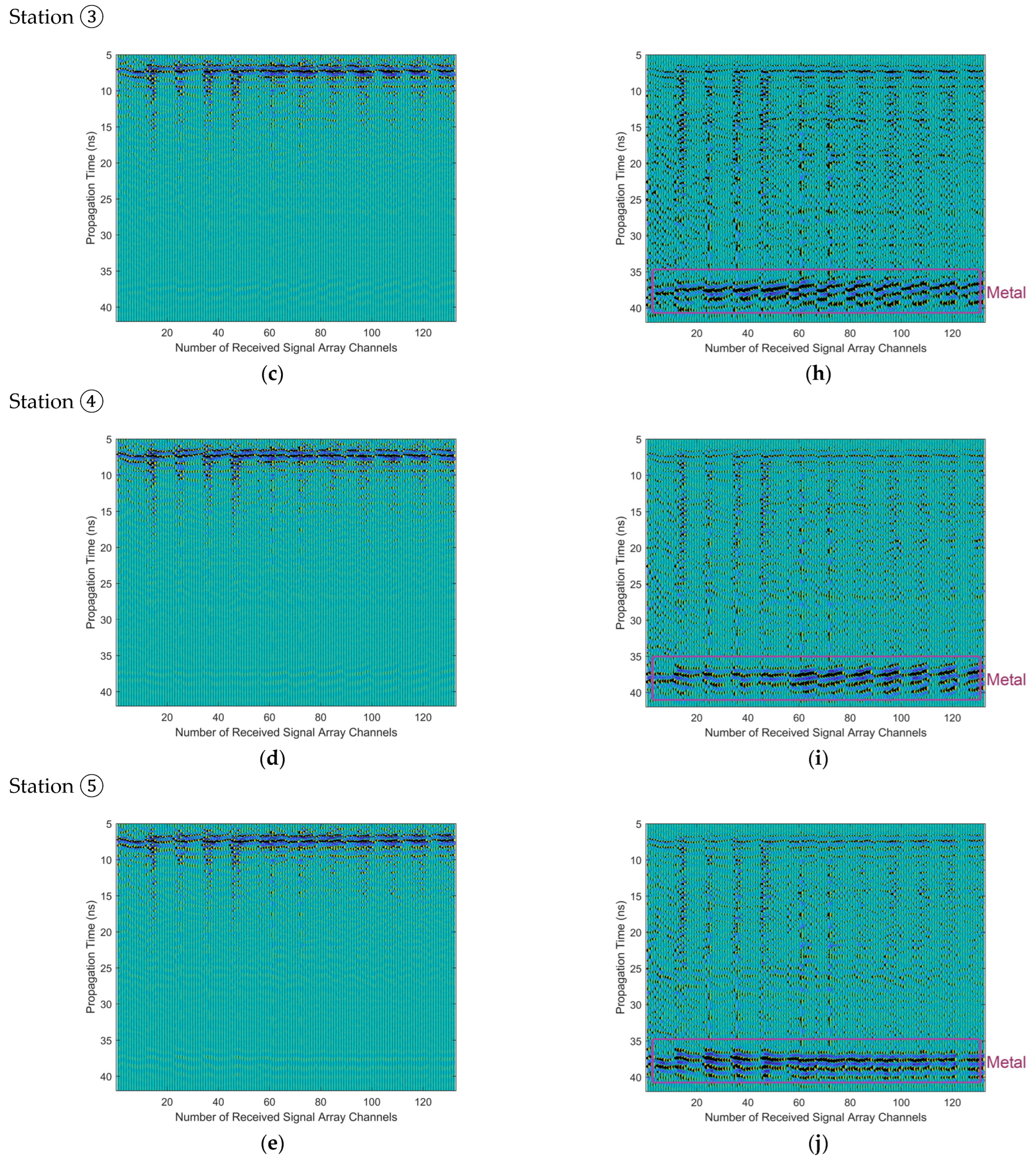


| Antenna No. | Coordinates (m) | Antenna No. | Coordinates (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (−0.80, 0.00, 0.95) | 7 | (−0.08, 0.00, 0.95) |
| 2 | (−0.68, 0.00, 0.95) | 8 | (0.52, 0.00, 0.95) |
| 3 | (−0.56, 0.00, 0.95) | 9 | (0.64, 0.00, 0.95) |
| 4 | (−0.44, 0.00, 0.95) | 10 | (0.76, 0.00, 0.95) |
| 5 | (−0.32, 0.00, 0.95) | 11 | (0.52, 0.12, 0.95) |
| 6 | (−0.20, 0.00, 0.95) | 12 | (−0.02, 0.18, 1.13) |
| Object No. | Buried Depth (m) | Object No. | Buried Depth (m) | Object No. | Buried Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.30 | 4 | 2.00 | 7 | 1.25 |
| 2 | 0.50 | 5 | 0.50 | 8 | 1.00 |
| 3 | 1.00 | 6 | 1.10 | 9 | 1.50 |
| Time-Domain Method | Spatial-Sampling Density (PPW) | Grid Scale (m) | Grid Number (Nx, Ny, Nz) | Memory (GB) | CPU Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-FDTD | 15 | 1.00 × 10−2 | (300, 201, 480) | 16.033 | 445.4802 |
| HO-FDTD | 9 | 1.67 × 10−2 | (181, 121, 288) | 4.708 | 93.8403 |
| PSTD | 4 | 3.77 × 10−2 | (81, 55, 129) | 1.012 | 4.3852 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Feng, N.; Xie, G.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z. Pseudo-Spectral Time-Domain Method for Subsurface Imaging with the Lunar Regolith Penetrating Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122791
Zhang Y, Feng N, Xie G, Yang L, Huang Z. Pseudo-Spectral Time-Domain Method for Subsurface Imaging with the Lunar Regolith Penetrating Radar. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122791
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuxian, Naixing Feng, Guoda Xie, Lixia Yang, and Zhixiang Huang. 2022. "Pseudo-Spectral Time-Domain Method for Subsurface Imaging with the Lunar Regolith Penetrating Radar" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122791
APA StyleZhang, Y., Feng, N., Xie, G., Yang, L., & Huang, Z. (2022). Pseudo-Spectral Time-Domain Method for Subsurface Imaging with the Lunar Regolith Penetrating Radar. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122791








