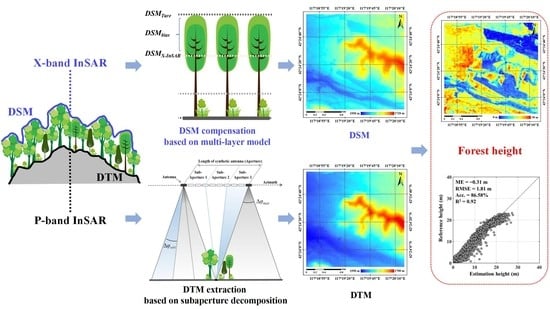
Forest Height Estimation Approach Combining P-Band and X-Band Interferometric SAR Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
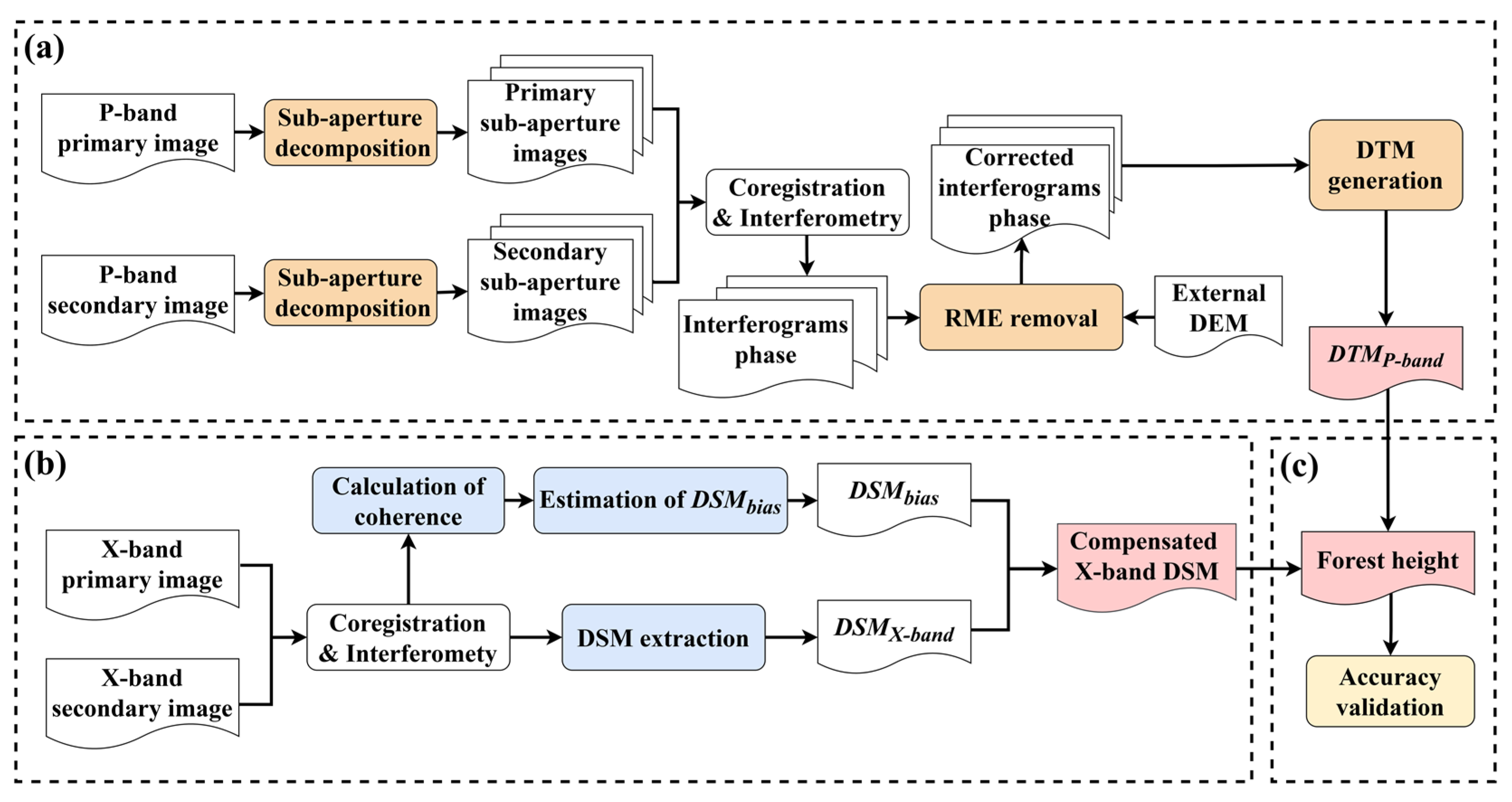
2. Methods
2.1. DTM Extraction Based on P-Band InSAR
2.1.1. Basic Idea of the TF Analysis Approach
2.1.2. Subaperture Decomposition
2.1.3. RME Removal
2.1.4. DTM Generation
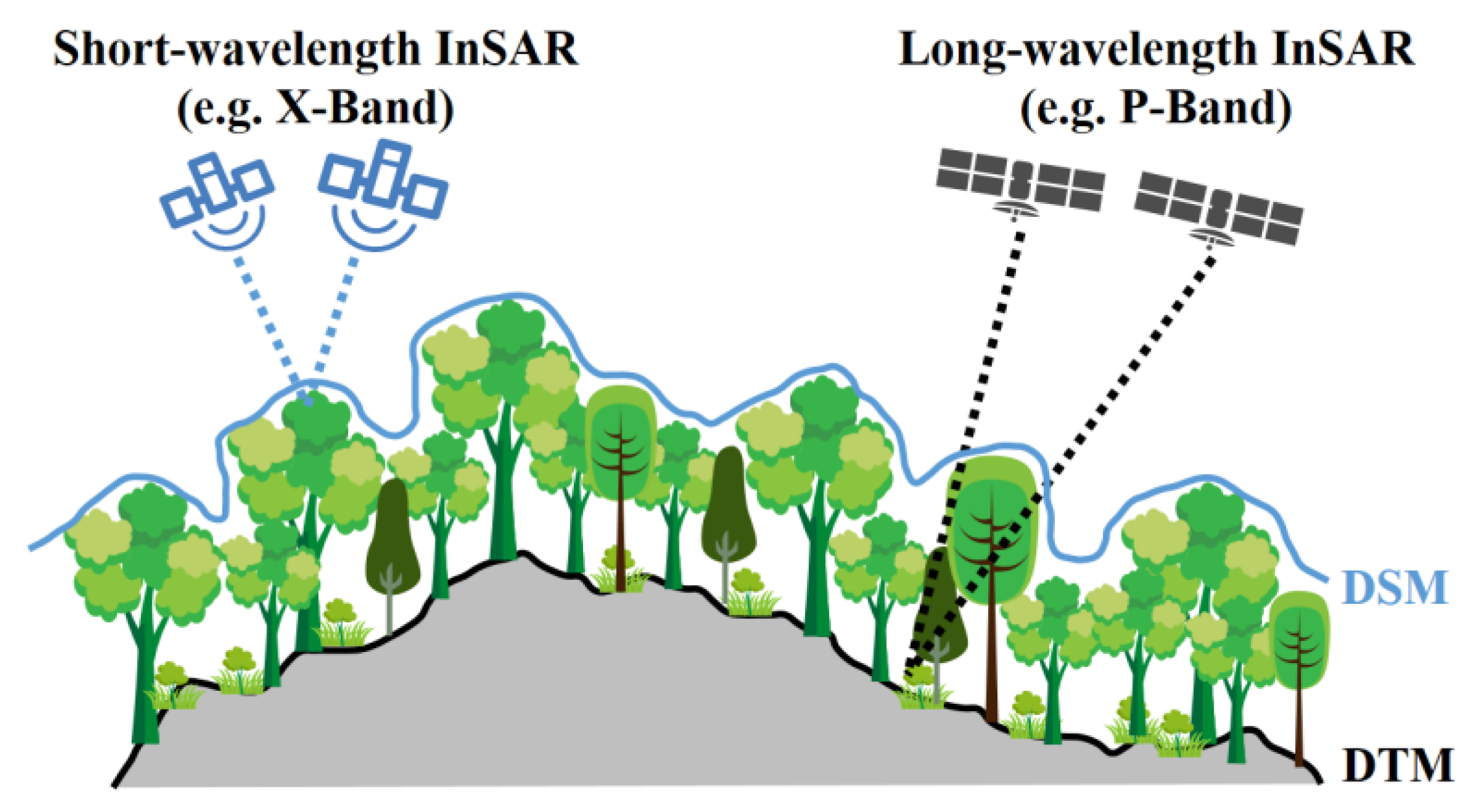
2.2. DSM Extraction and Compensation Based on X-Band InSAR
2.2.1. Bias of DSM Extraction Based on X-Band InSAR
2.2.2. Estimation Method of Bias Based on IDUV
Estimation Model
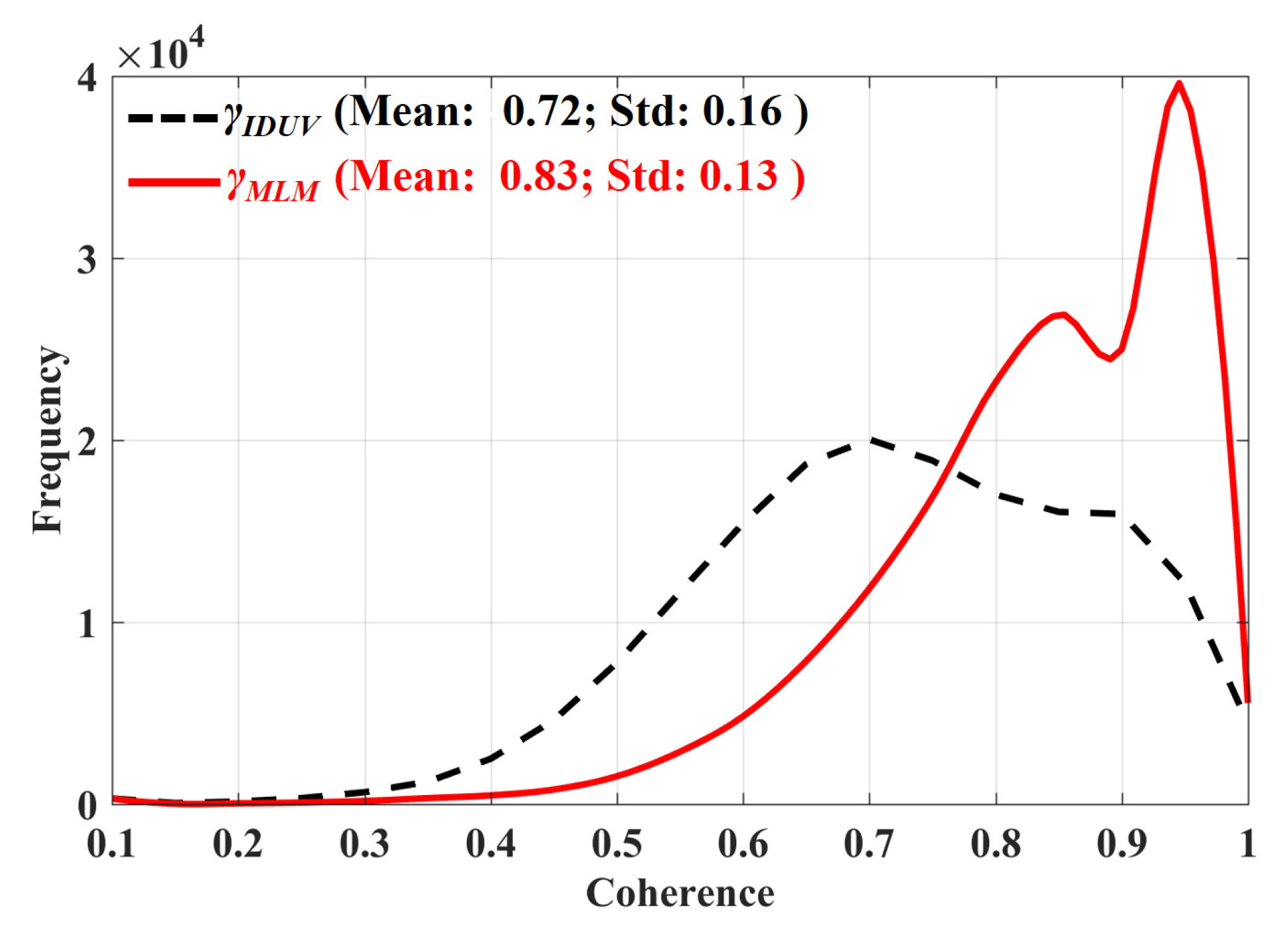
Calculation of Coherence for IDUV
2.2.3. Estimation Method of Bias Based on the MLM
General Estimation Method
Special Case Based on Uniform Distribution
Calculation of Coherence for the MLM
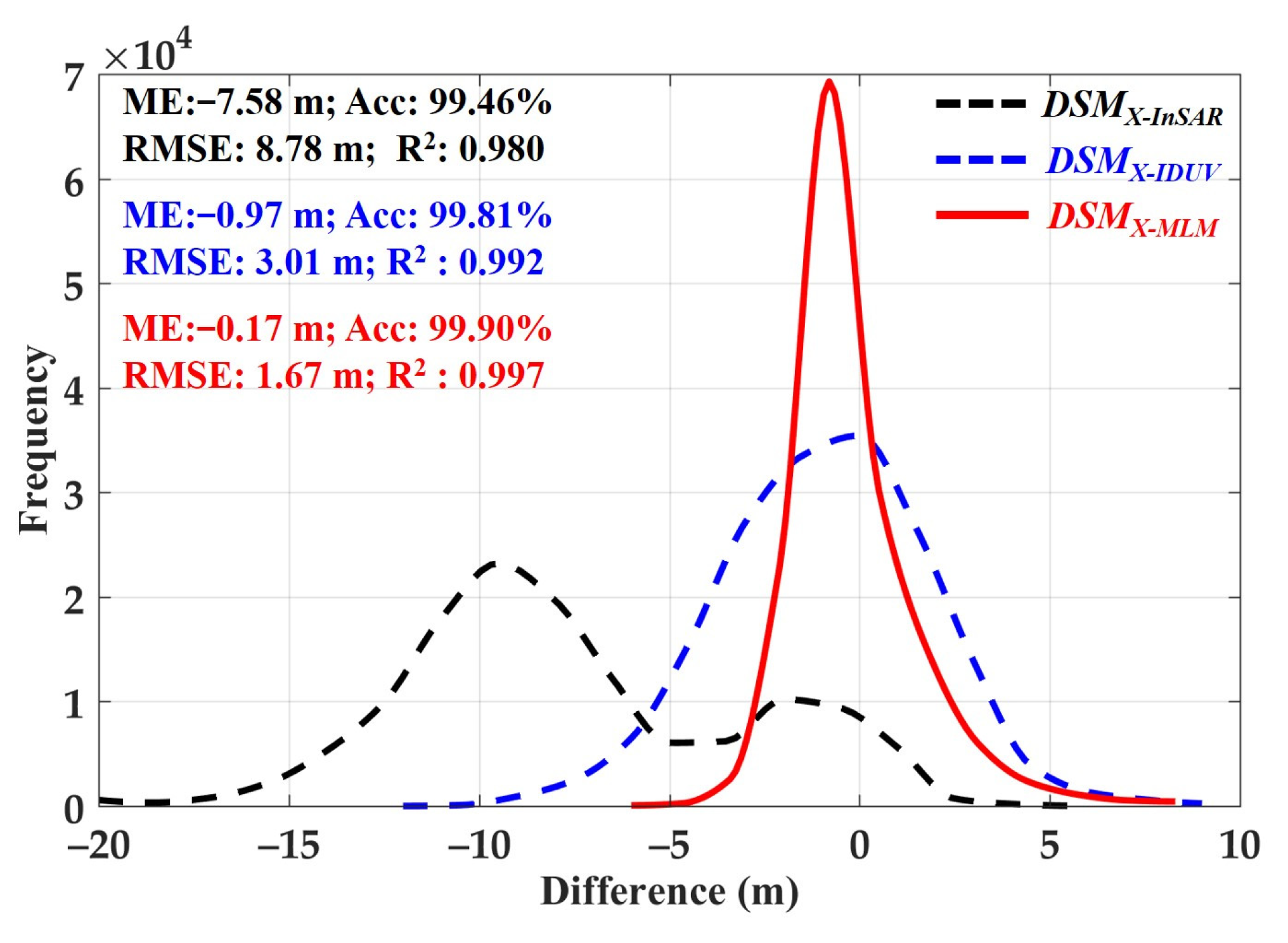
2.3. Accuracy Validation
3. Study Area and Data
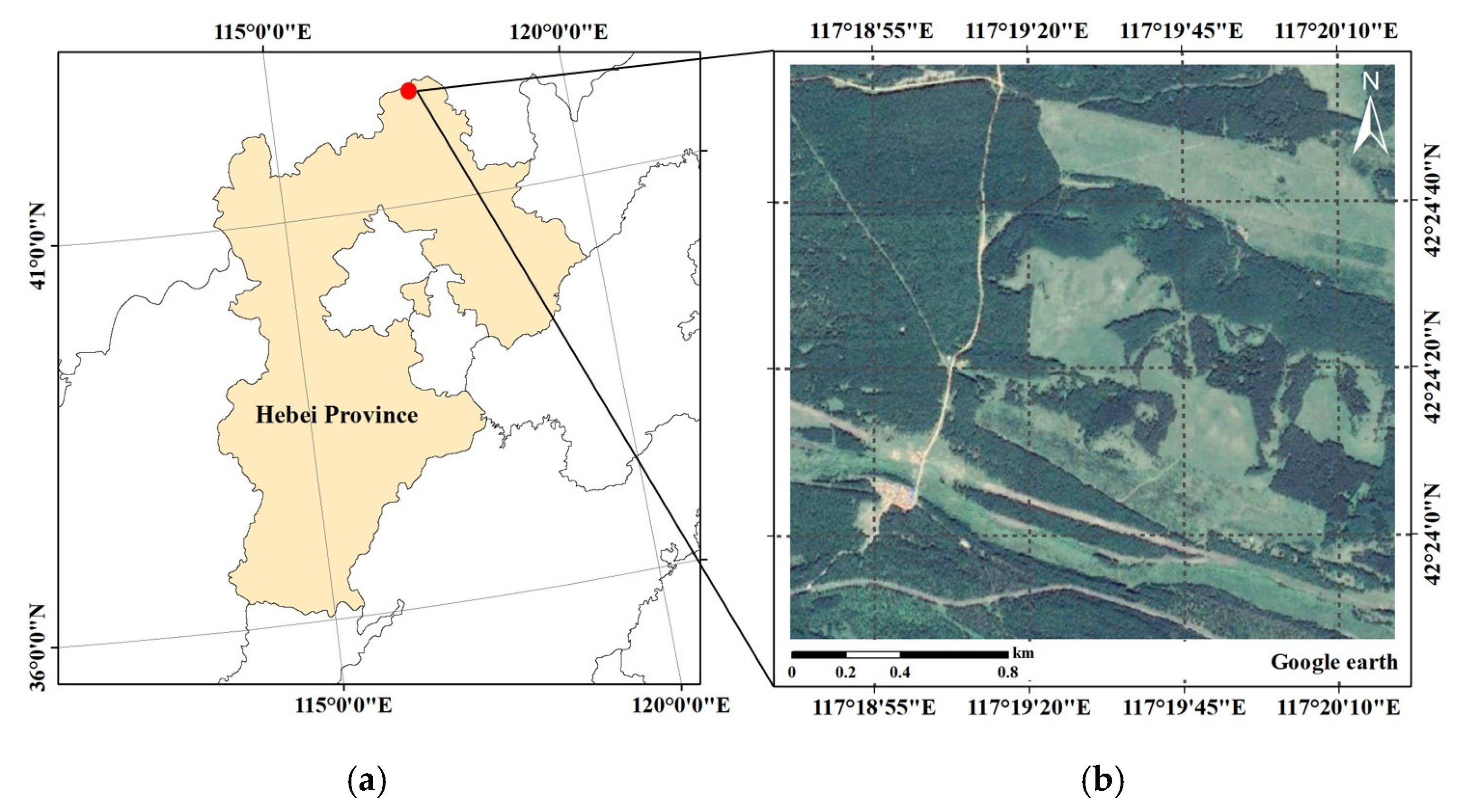
3.1. Study Area
3.2. InSAR Data
3.3. LiDAR Data
4. Data Processing
4.1. DTM Extraction Process
4.2. DSM Extraction and Compensation Process
4.3. Forest Height Estimation and Accuracy Validation
5. Results
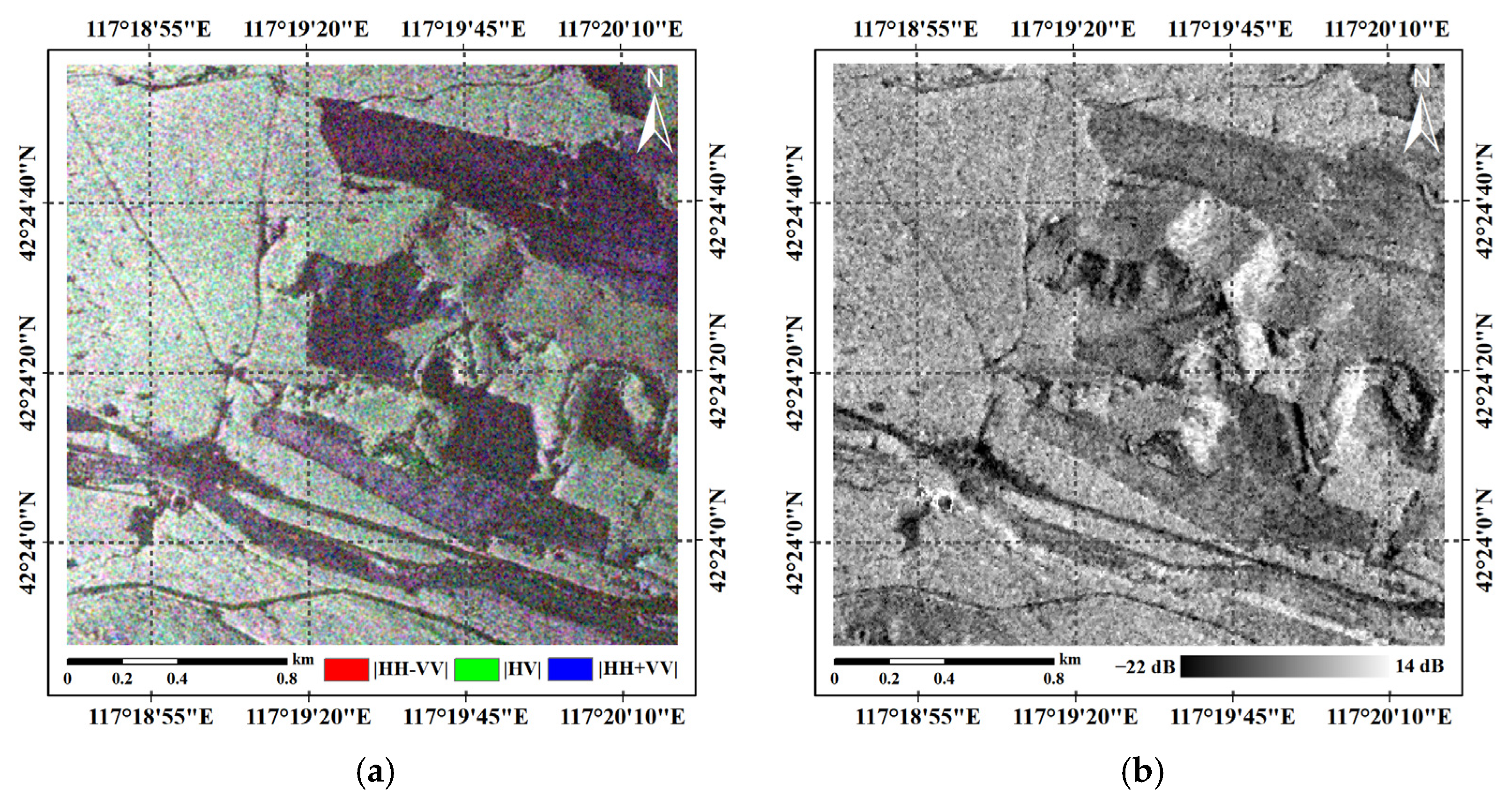
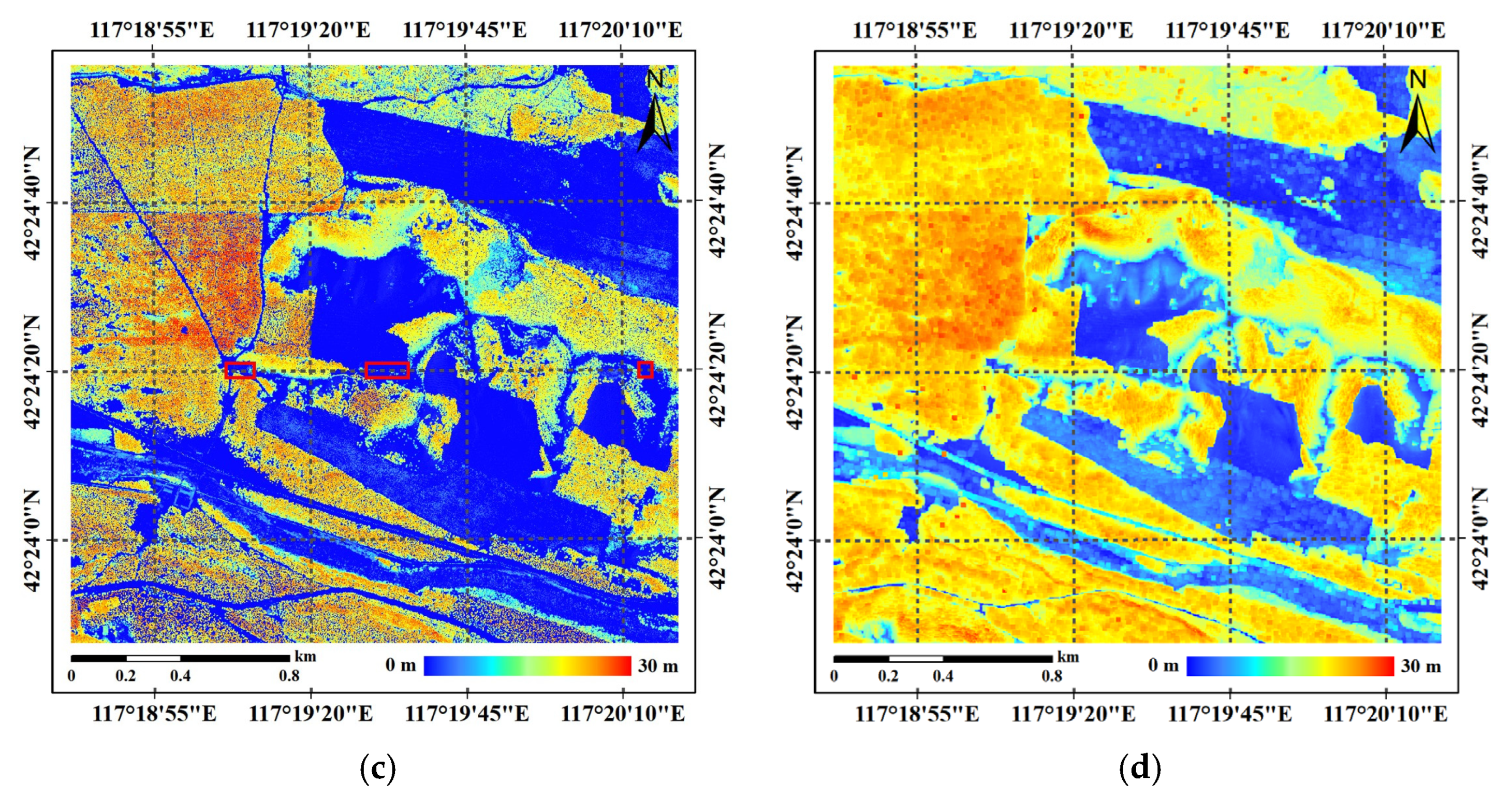
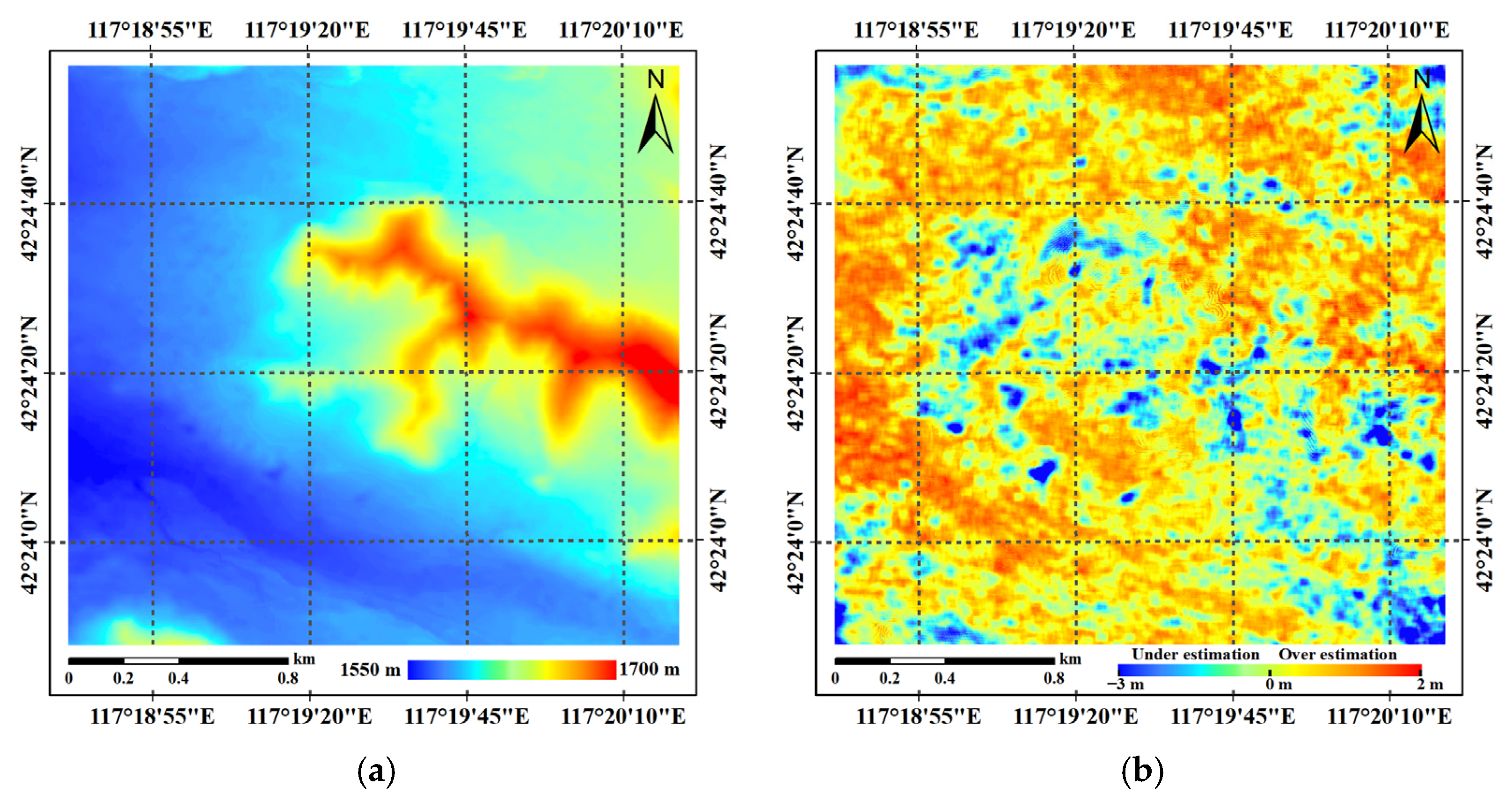
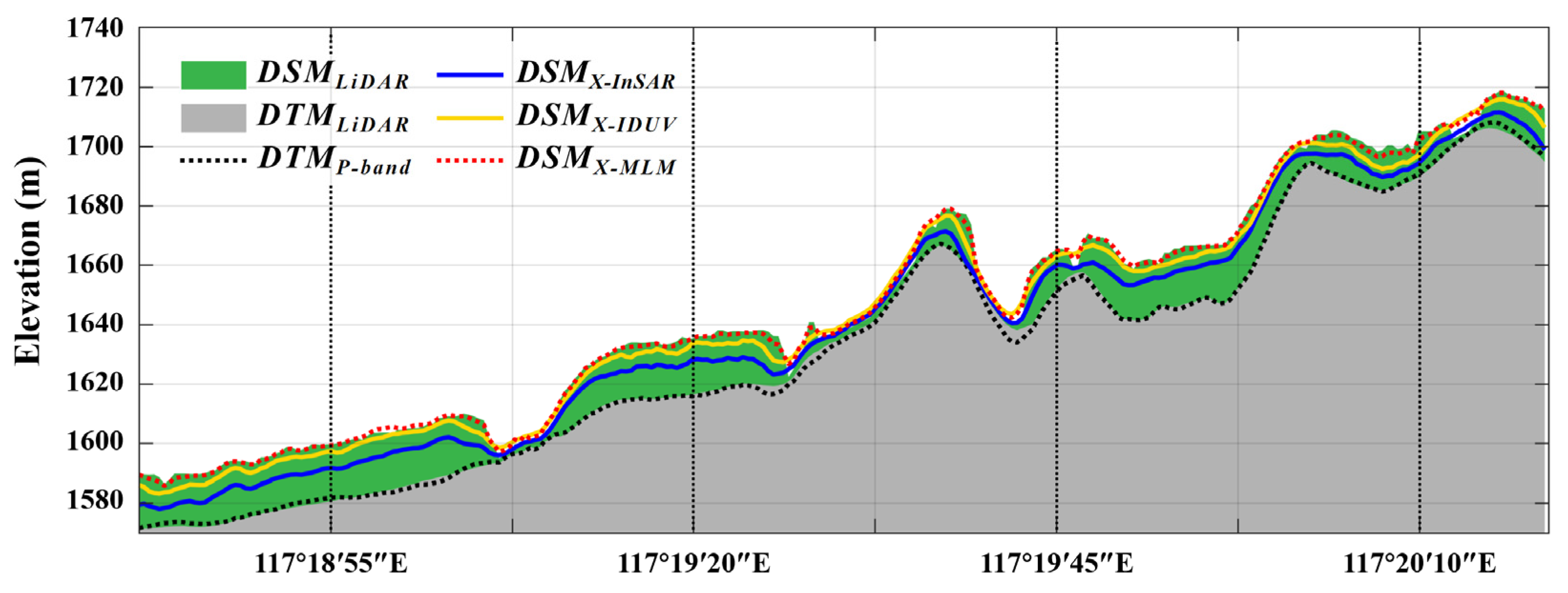
5.1. DTM Extraction from P-Band InSAR Data
5.2. DSM Extraction and Compensation from X-Band InSAR Data
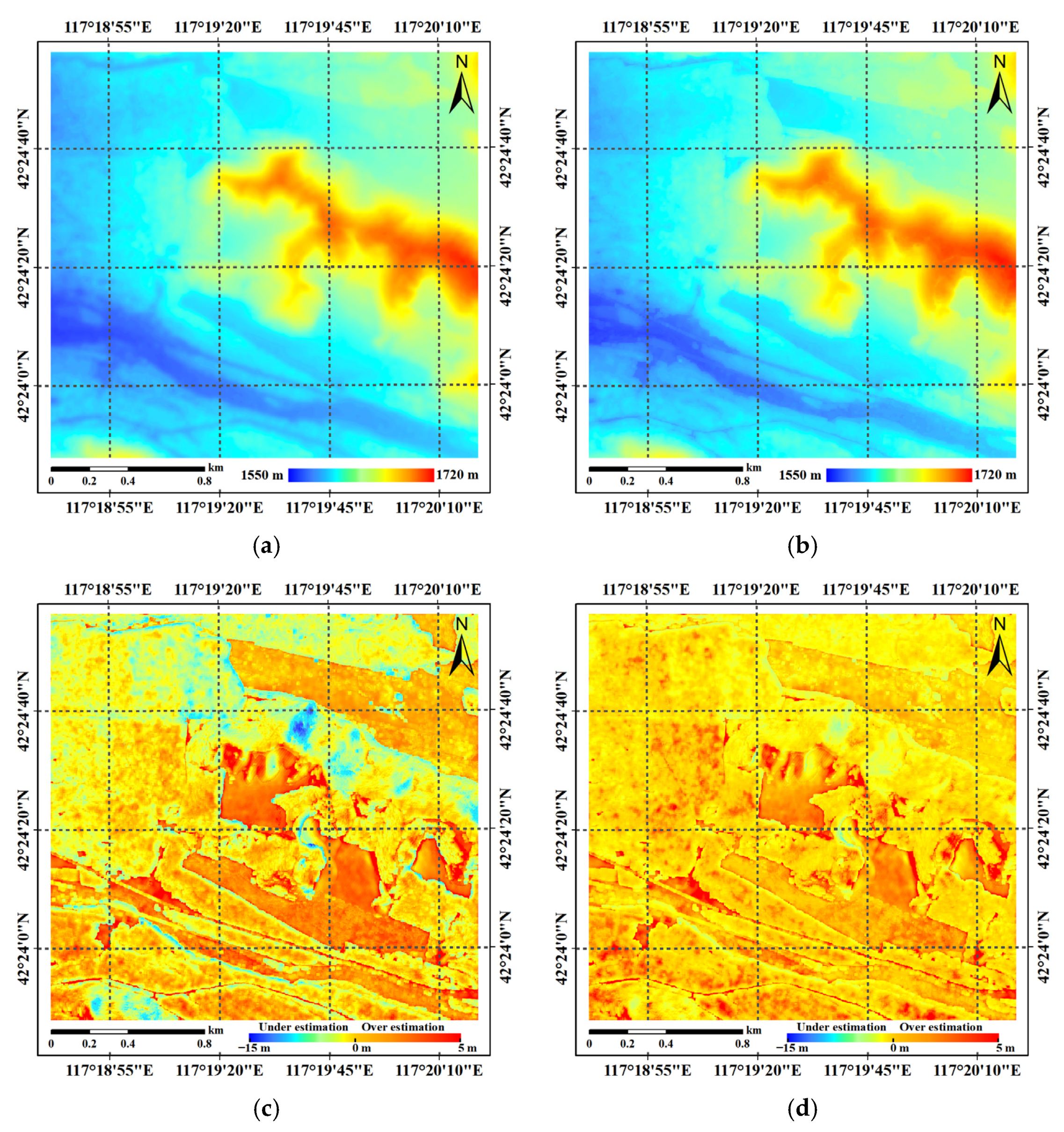
5.2.1. Raw Result of DSM Extraction
5.2.2. DSM Compensation Result
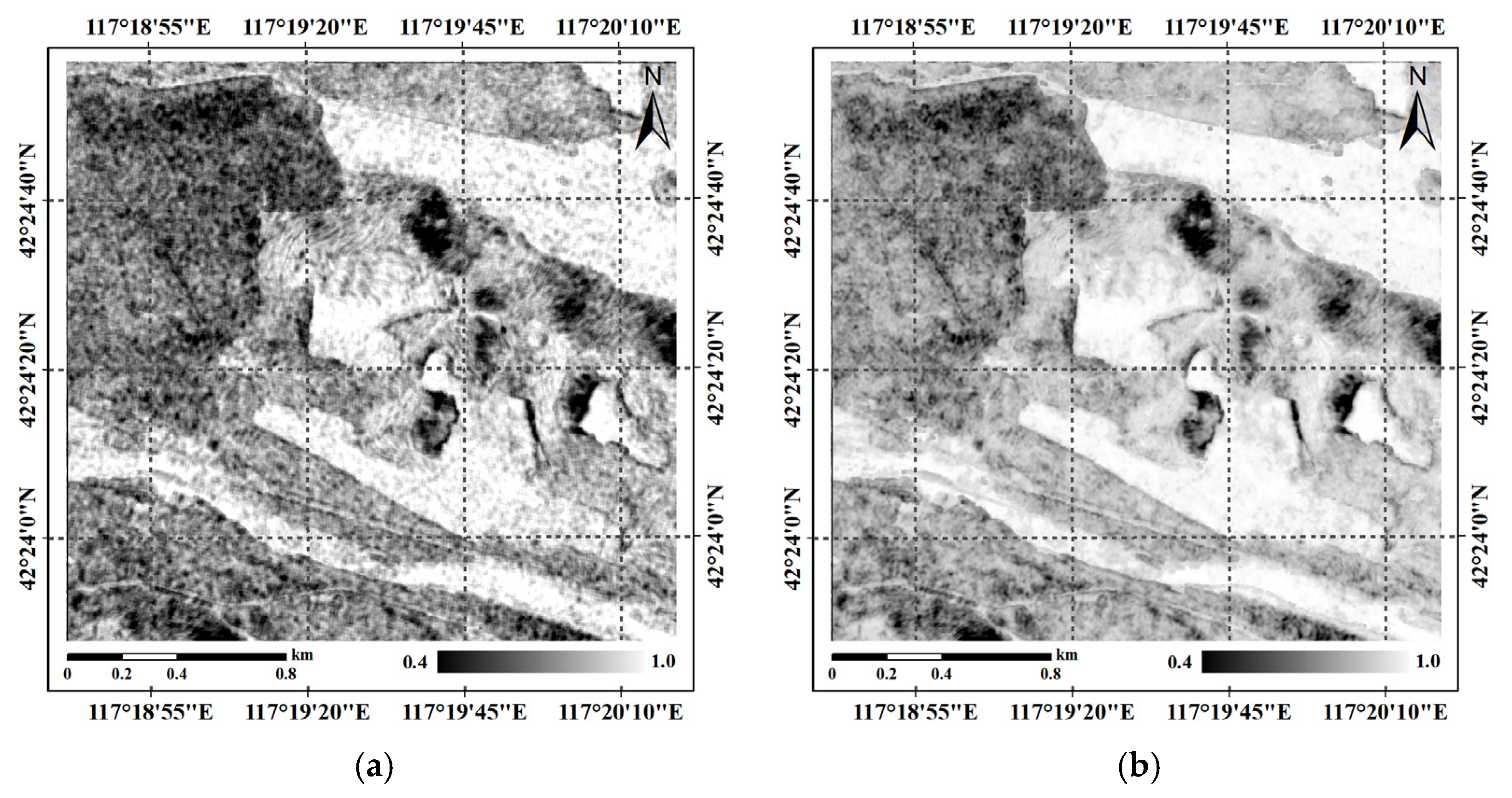
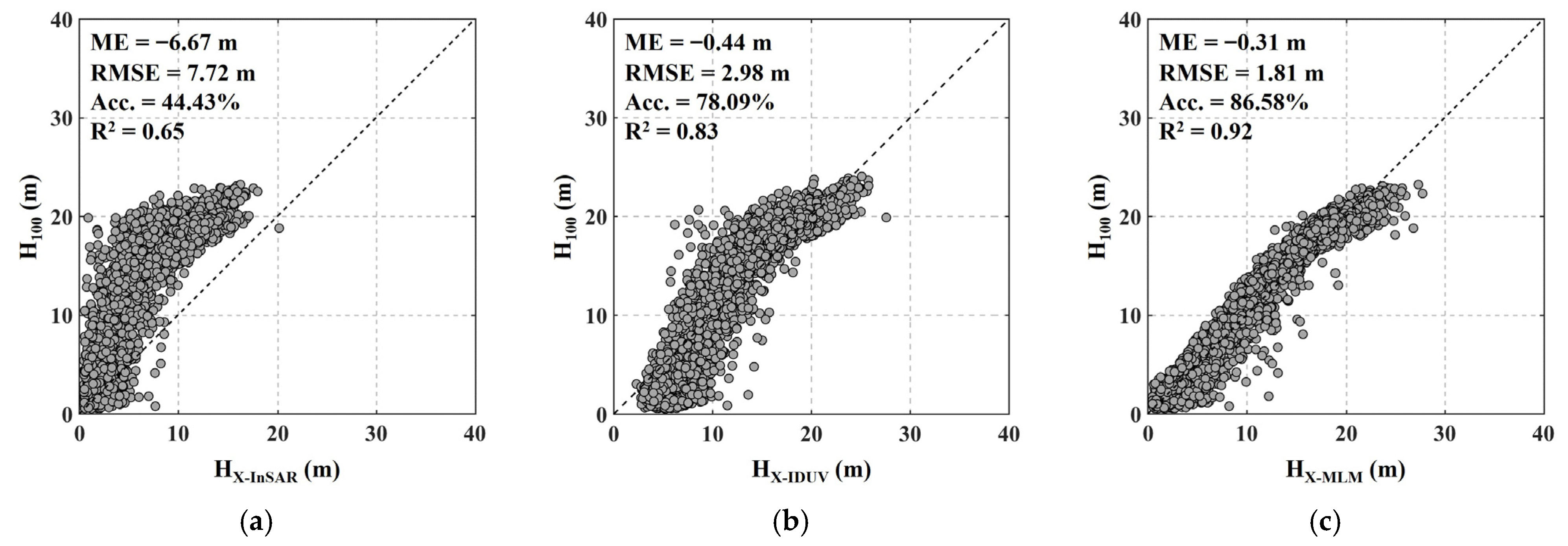
5.3. Estimation Results of Forest Height
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GCOS. The Global Observing System for Climate: Implementation Needs; Global Climate Observing System: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, J.O.; Bax, T.; Siqueira, P.; Swenson, J.J.; Hensley, S. A comparison of lidar, radar, and field measurements of canopy height in pine and hardwood forests of southeastern North America. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Saarela, S.; Armston, J.; Ståhl, G.; Dubayah, R. Forest biomass estimation over three distinct forest types using TanDEM-X InSAR data and simulated GEDI lidar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldini, S.; Rocca, F. Multibaseline polarimetric SAR tomography of a boreal forest at P-and L-bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S. Polarisation: Applications in Remote Sensing; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aulinger, T.; Mette, T.; Papathanassion, K.; Hajnsek, I.; Heurich, M.; Krzystek, P. Validation of heights from interferometric SAR and LIDAR over the temperate forest site “Nationalpark Bayerischer Wald”. In Proceedings of the POLinSAR 2005 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 17–21 January 2005; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, H.-E.; McGaughey, R.; Reutebuch, S.; Schreudera, G.; Agee, J.; Mercer, B. Estimating canopy fuel parameters in a Pacific Northwest conifer forest using multifrequency polarimetric IFSAR. Image 2004, 900, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.; Neeff, T.; Dutra, L.; Araujo, L.; Gama, F.; Elmiro, M. Tropical forest biomass mapping from dual frequency SAR interferometry (X and P-Bands). ISPRS Int. Soc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Tech. Comm. VII 2004, 35, 1682–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Shiroma, G.H.X.; de Macedo, K.A.C.; Wimmer, C.; Moreira, J.R.; Fernandes, D. The dual-band PolInSAR method for forest parametrization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzter, H.; Rowland, C.S.; Saich, P. Forest canopy height and carbon estimation at Monks Wood National Nature Reserve, UK, using dual-wavelength SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamvasis, K.; Karathanassi, V. Forest canopy height estimation using double-frequency repeat pass interferometry. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2015), Paphos, Cyprus, 16–19 March 2015; pp. 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kugler, F.; Schulze, D.; Hajnsek, I.; Pretzsch, H.; Papathanassiou, K.P. TanDEM-X Pol-InSAR performance for forest height estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6404–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, C. A review of underlying topography estimation over forest areas by InSAR: Theory, advances, challenges and perspectives. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rignot, E. Dual-frequency interferometric SAR observations of a tropical rain-forest. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercer, B.; Zhang, Q.; Schwaebisch, M.; Denbina, M.; Cloude, S. Forest height and ground topography at L-band from an experimental single-pass airborne Pol-InSAR system. In Proceedings of the POLinSAR 2009, Frascati, Italy, 26–31 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; He, B.; van Dijk, A.I.; Bai, X.; Quan, X. The impacts of spatial baseline on forest canopy height model and digital terrain model retrieval using P-band PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Champion, I. Forest height inversion using high-resolution P-band Pol-InSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3544–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, R. Underlying topography estimation over forest areas using high-resolution P-band single-baseline PolInSAR data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Siqueira, P.R. Vertical structure of vegetated land surfaces from interferometric and polarimetric radar. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Guo, Q. A practical method for SRTM DEM correction over vegetated mountain areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlund, M.; Baron, D.; Magdon, P.; Erasmi, S. Canopy penetration depth estimation with TanDEM-X and its compensation in temperate forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 147, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Guo, Z.; Sun, G.; Chi, H. Investigation of forest height retrieval using SRTM-DEM and ASTER-GDEM. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 2111–2114. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G.; Guo, Z.; He, Y. The penetration depth derived from the synthesis of ALOS/PALSAR InSAR data and ASTER GDEM for the mapping of forest biomass. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7303–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solberg, S.; May, J.; Bogren, W.; Breidenbach, J.; Torp, T.; Gizachew, B. Interferometric SAR DEMs for forest change in Uganda 2000–2012. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dall, J. InSAR elevation bias caused by penetration into uniform volumes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Zan, F.; Krieger, G.; López-Dekker, P. On some spectral properties of TanDEM-X interferograms over forested areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soja, M.J.; Ulander, L.M. Two-level forest model inversion of interferometric TanDEM-X data. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2014, 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 3–5 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y. A New Approach for Forest Height Inversion Using X-Band Single-Pass InSAR Coherence Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soja, M.J.; Persson, H.; Ulander, L.M. Estimation of forest height and canopy density from a single InSAR correlation coefficient. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soja, M.J.; Persson, H.J.; Ulander, L.M. Detection of forest change and robust estimation of forest height from two-level model inversion of multi-temporal, single-pass InSAR data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 3886–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Treuhaft, R.; Gonçalves, F. Automated estimation of forest height and underlying topography over a Brazilian tropical forest with single-baseline single-polarization TanDEM-X SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Pine forest height inversion using single-pass X-band PolInSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 46, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A.; Pottier, E. Scene characterization using sub-aperture polarimetric interferometric SAR data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 702–704. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Datcu, M. SAR target analysis based on multiple-sublook decomposition: A visual exploration approach. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A. Real-time synthetic aperture radar(SAR) processing with a new subaperture approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. Generation of Digital Elevation Models through Spaceborne SAR Interferometry; University of Zurich: Zurich, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, J.A. Remote Sensing with Imaging Radar; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ju, H.; Lu, H.; Jia, W.; Si, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, L. LiCHy: The CAF’s LiDAR, CCD and hyperspectral integrated airborne observation system. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jia, W.; Si, L.; Yan, G.; Shi, J. The comprehensive airborne remote sensing experiment in Saihanba forest farm. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 25, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y. Improved filtering parameter determination for the Goldstein radar interferogram filter. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. JOSA A 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieger, G.; Moreira, A.; Fiedler, H.; Hajnsek, I.; Werner, M.; Younis, M.; Zink, M. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3317–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minh, D.H.T.; Le Toan, T.; Rocca, F.; Tebaldini, S.; Villard, L.; Réjou-Méchain, M.; Phillips, O.L.; Feldpausch, T.R.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.; Scipal, K. SAR tomography for the retrieval of forest biomass and height: Cross-validation at two tropical forest sites in French Guiana. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Tong, Q.; Xu, L.; Ji, P.; Dong, F.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Xie, C. The P-band SAR Satellite: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 26–29 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]







| Evaluation Index | Symbol | Formula | Ideal Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Error | ME | 0 | |
| Root Mean Square Error | RMSE | 0 | |
| Accuracy | Acc. | 100% | |
| Coefficient of Determination | R2 | 1 |
| Parameters | P-Band | X-Band |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 0.45 GHz | 9.65 GHz |
| Polarization | HH/HV/VH/VV | HH |
| Center Incidence Angle | 63° | 43° |
| Spatial baseline | 60.25 m | 332.77 m |
| HoA (mean) | 81 m | 44 m |
| SLC Resolution (a × r) | 1.45 m × 1.50 m | 2.21 m × 1.36 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, K.; Zhao, L.; Chen, E.; Li, K.; Liu, D.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y. Forest Height Estimation Approach Combining P-Band and X-Band Interferometric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133070
Xu K, Zhao L, Chen E, Li K, Liu D, Li T, Li Z, Fan Y. Forest Height Estimation Approach Combining P-Band and X-Band Interferometric SAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133070
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Kunpeng, Lei Zhao, Erxue Chen, Kun Li, Dacheng Liu, Tao Li, Zengyuan Li, and Yaxiong Fan. 2022. "Forest Height Estimation Approach Combining P-Band and X-Band Interferometric SAR Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133070
APA StyleXu, K., Zhao, L., Chen, E., Li, K., Liu, D., Li, T., Li, Z., & Fan, Y. (2022). Forest Height Estimation Approach Combining P-Band and X-Band Interferometric SAR Data. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133070