Abstract
AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) coordinated formation can expand the detection range, improve detection efficiency, and complete complex tasks, which requires each AUV to have the ability to track and locate. A wake detector provides a new technical approach for AUV cooperative formation warfare. Now, most of the existing artificial lateral line detectors are for one-dimensional flow field applications, which are difficult to use for wake detection of AUVs. Therefore, based on the pressure gradient sensing mechanism of the canal neuromasts, we apply Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) technology to develop a lateral line-inspired MEMS wake detector. The sensing mechanism, design, and fabrication are demonstrated in detail. Experimental results show the detector’s sensitivity is 147 mV·(m/s)−1, and the detection threshold is 0.3 m/s. In addition, the vector test results verify it has vector-detecting capacity. This wake detector can serve AUVs wake detection and tracking technology, which will be promising in AUV positioning and coordinated formation.
1. Introduction
With the advancement and maturation of AUV technology, the difficulty and complexity of the tasks it undertakes are also greatly increased. These tasks include large-scale ocean mapping, shipwreck search, seabed exploration, and underwater target detection and identification. AUV collaborative formation technology can effectively expand the detection range, improve detection efficiency, and even complete complex tasks that are difficult to complete with a single AUV [1]. To achieve AUV cooperative formation for combat tasks, each AUV needs to possess sensing, positioning, and tracking of other AUVs.
AUV remote sensing detection technology currently encompasses acoustic, optical, and electromagnetic detection techniques [2]. Acoustic detection has traditionally been the primary method for AUV sensing and positioning. However, sonar detection is greatly influenced by marine ambient noise, and sound waves experience refraction in the ocean’s transition layer, which can adversely affect the performance of active sonar detection. With advancements in AUV silent technology, the role of passive acoustic detection based on hydrophones is becoming increasingly difficult. Optical detectors employ optical imaging technology to detect the underwater environment and sense targets. Nevertheless, the refraction and the dim underwater visual environment seriously impact the sensing and positioning functions of AUVs. Additionally, electromagnetic wave attenuation in the ocean is also severe [3,4]. Consequently, AUV sensing and detection in complex marine environments pose significant challenges.
When the hull is sailing, because of the propulsion system, the wake zone, bubble wake, and turbulent wake generated by the propulsion system exhibit distinct characteristics compared to the surrounding seawater [5]. The two different wake zones can be used as sources of detection. The bubble wake is created by the rotation of the ship’s propellers and can be tracked and located using sound and light methods. This bubble wake tracking and positioning technology is widely employed in torpedo homing [6,7]. However, the bubble wake detection method is not feasible because there is less bubble wake of AUVs in deep water. The turbulent wake can also be used to detect, identify, locate, and track the underwater vehicle. When there is relative motion with seawater, the flow around and vortex inevitably emerge, leaving behind a series of turbulence in the wake. Turbulent wake detection is particularly suitable for homing in underwater unmanned systems.
In nature, when fish move in groups, individual behaviors are elementary. However, when they work together, the entire group exhibits intelligent behavior characteristics in foraging, avoiding obstacles, escaping from natural enemies, and other aspects. The lateral line plays a vital role in communication and perception among fish individuals. With the assistance of the lateral line system, fish can sense and analyze dynamic information such as the flow field and sound field of the external environment [8,9,10]. This system enables them to perform complex behaviors such as feeding, avoiding enemies, reproduction, and navigation [11,12,13,14]. The fish’s lateral line system consists of superficial neuromasts and canal neuromasts, both of which perform their primary functions through ciliary receptors. The superficial nerve column exists on the fish’s surface and is in direct contact with the external flow field, which plays the role of flow sensing. The nerve cilia in the canal neuromasts are concealed within the lateral line canal under the epidermis. They sense the external water flow through the capillary holes on the fish’s epidermis [13]. The low-frequency noise generated by the fish’s movement and various other environmental noises, such as non-biological noise from ocean currents, constitute the noise sources that interfere with the superficial nerve column. The function of the canal in the canal neuromasts is to filter out these noise sources and enhance the fish’s ability to detect targets [15].
Inspired by the fish lateral line perception system, researchers designed various artificial lateral line systems for flow sensing. In 2006, Yang, et al. developed an artificial lateral line sensor based on the hot-wire principle. This sensor, featuring a cantilever beam structure, can sense fluid vibrations [16]. By arranging the hot-wire artificial lateral line sensors in series, they created an artificial lateral line system to sense the weak frequency and amplitude changes in the flow field. In 2014, Kottapallietal, et al. developed a gold piezoresistive unit (MEMS artificial lateral flow sensor) lateral line-inspired MEMS flow sensor. They used this sensor to form biomimetic polymer artificial superficial neuromast micro-sensor arrays for testing the air and water flow, achieving sensitivities of 0.9 mV/(m/s) and 0.022 V/(m/s), respectively [12]. In 2015, Bleckmann, et al. introduced light guide PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) into the MEMS structure. They manufactured an artificial lateral line system based on optical sensing, which can detect a one-dimensional flow field of 185 μm/s in the canal. However, the flow rate of the outflow field of the canal is not tested [15]. In 2017, Jiang, et al. developed an artificial lateral line system with a pressure gradient detection value of about 11 Pa/m at a frequency of 115 Hz [17]. However, most of the artificial lateral line flow detectors studied thus far can only detect one-dimensional flow fields, and it is challenging to observe two-dimensional flow fields.
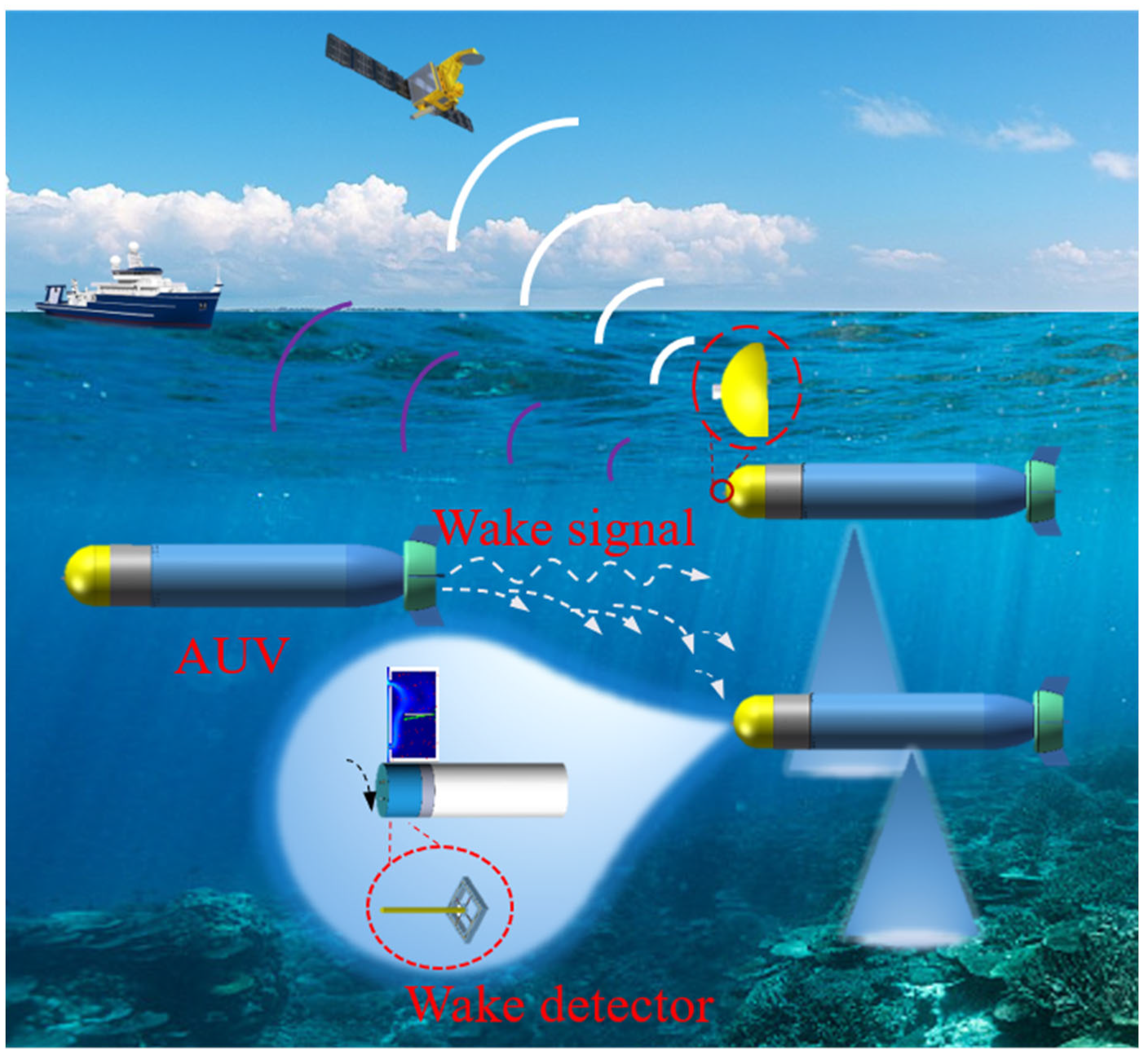
In 2021, Wang, et al. made modifications to the bionic cilia vector hydrophone by packaging it with MEMS turbulence detectors for the purpose of ocean turbulence detection [18,19,20,21,22]. Through indoor water tank experiments and comparison with commercial PNS shear flow detectors, they verified the feasibility of the MEMS turbulence sensor in detecting two-dimensional turbulence signals. However, due to its packaging structure, this turbulence sensor is difficult to apply to AUV wake detection. To address this issue, we propose a wake detector with a bionic package structure for AUVs. This packaging design not only protects the detector from being washed out by high-velocity currents but also avoids underwater foreign objects (silt, etc.) impact. By equipping AUVs with wake detectors, they can navigate in formation and transmit a wider range of detection information to ships and satellites, which is important for ocean exploration, as shown in Figure 1. The red dashed circle is the locally enlarged content and the white arrow indicates the wake signal in the Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Diagram of wake detector applied to AUV coordinated formation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bionic Principle
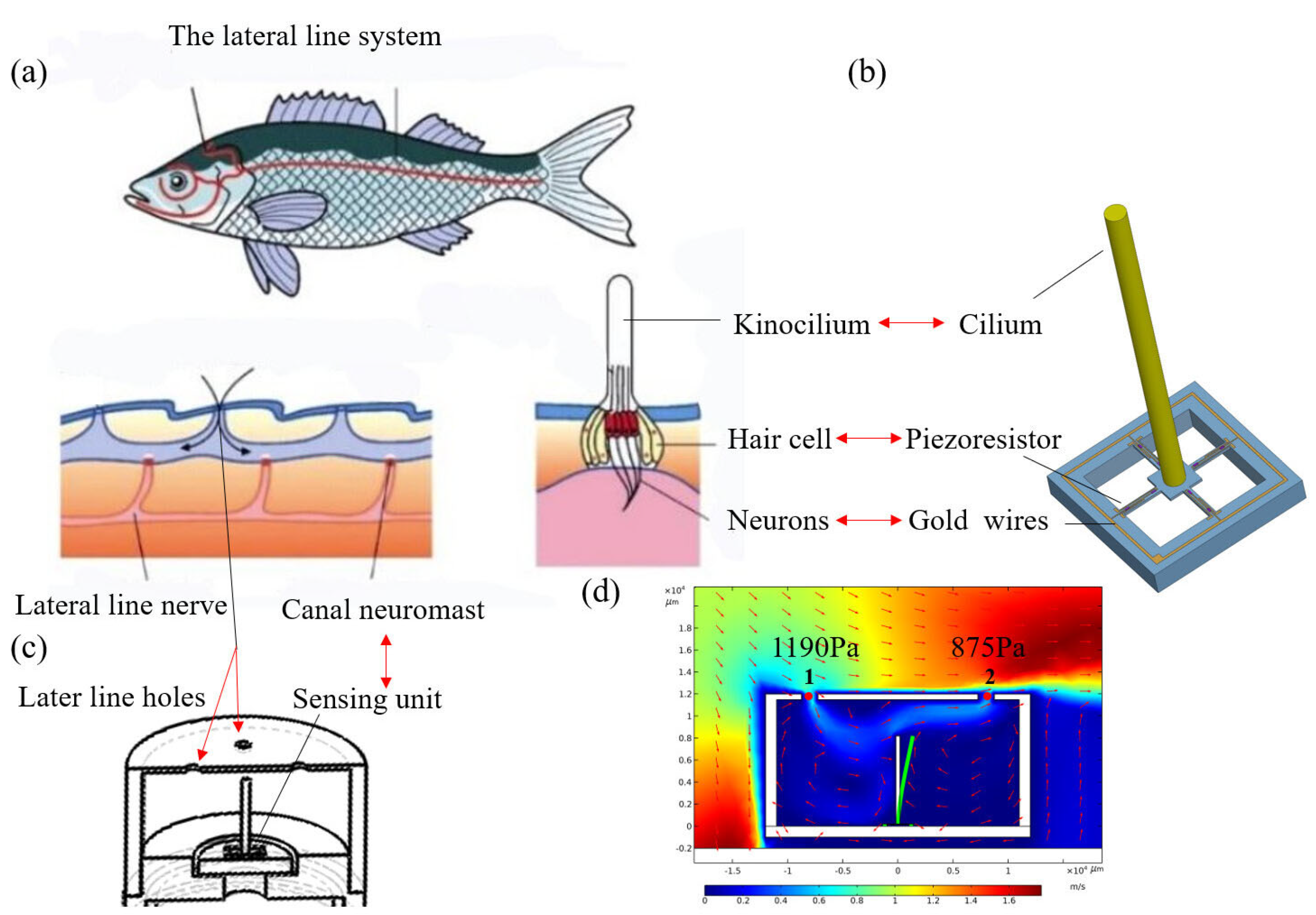
In the lateral line system of fish, the canal neuromasts in the fish’s lateral line play a crucial role. When the fish interacts with the surrounding water flow, the flow velocity and water pressure cause the mucus in the lateral line canal to flow, resulting in the tilting of the cilia. Consequently, the sensory nerves beneath the cilia generate nerve signals that open ion channels in the cell membranes, altering the potential difference between the inside and outside of the cell. This process converts the fluid mechanical information into neural electrical signals, as depicted in Figure 2a [23]. Based on this principle, we have designed a bionic diversion shell and ciliated cross-beam sensitive unit, as shown in Figure 2b,c. The red arrow means imitation, e.g., cilia mimics kinocilium. The bionic MEMS wake detector comprises two main components. The first component is the detector’s core sensitive unit, which emulates the canal neuromasts in the fish’s lateral line system. The second component is the bionic diversion cap, which mimics the structure of the lateral line canal.

Figure 2.
Biomimetic principles of microstructure. (a) The lateral line system. (b) The sensitive microstructure of the detector. (c) Bionic diversion shell. (d) Pressure gradient simulation.
The bionic principle of the bionic diversion cap is the pressure gradient sensing mechanism of the fish lateral canal. When water flows through the canal, it creates a pressure difference between the two small holes, resulting in the liquid flow from high to low pressure within the canal. Figure 2d depicts the simulation of the pressure gradient principle simulation in the bionic diversion cap. As water flows over the top of the detector, the pressure at point 1 is 1190 Pa, and the pressure at point 2 is 875 Pa. The difference between the two points is 315 Pa. The fluid in the encapsulation cap flows from point 1 to point 2, leading to the deflection of the cilia.
The core of the wake detector primarily consists of cilia and a high-precision four-beam structure, as shown in Figure 2b. The cilia receive wake disturbance signals, and eight varistors are placed on the crossbeam to form the Wheatstone bridge. When water flows, the pressure difference generated by the small holes on both sides causes the liquid within the lateral line encapsulation cap to flow, resulting in the swinging of the cilia. This motion drives the mass block at the bottom of the cilia to deflect, thus driving the deformation of the crossbeam. Consequently, the resistance value of the varistor positioned on the crossbeam changes, causing an imbalance in the Wheatstone bridge, generating the output voltage and thus completing the transition from the wake signal to the electrical signal. The detectors can receive signals in both directions as the two Wheatstone Bridges are vertically aligned.
2.2. Signal Conversion Circuit
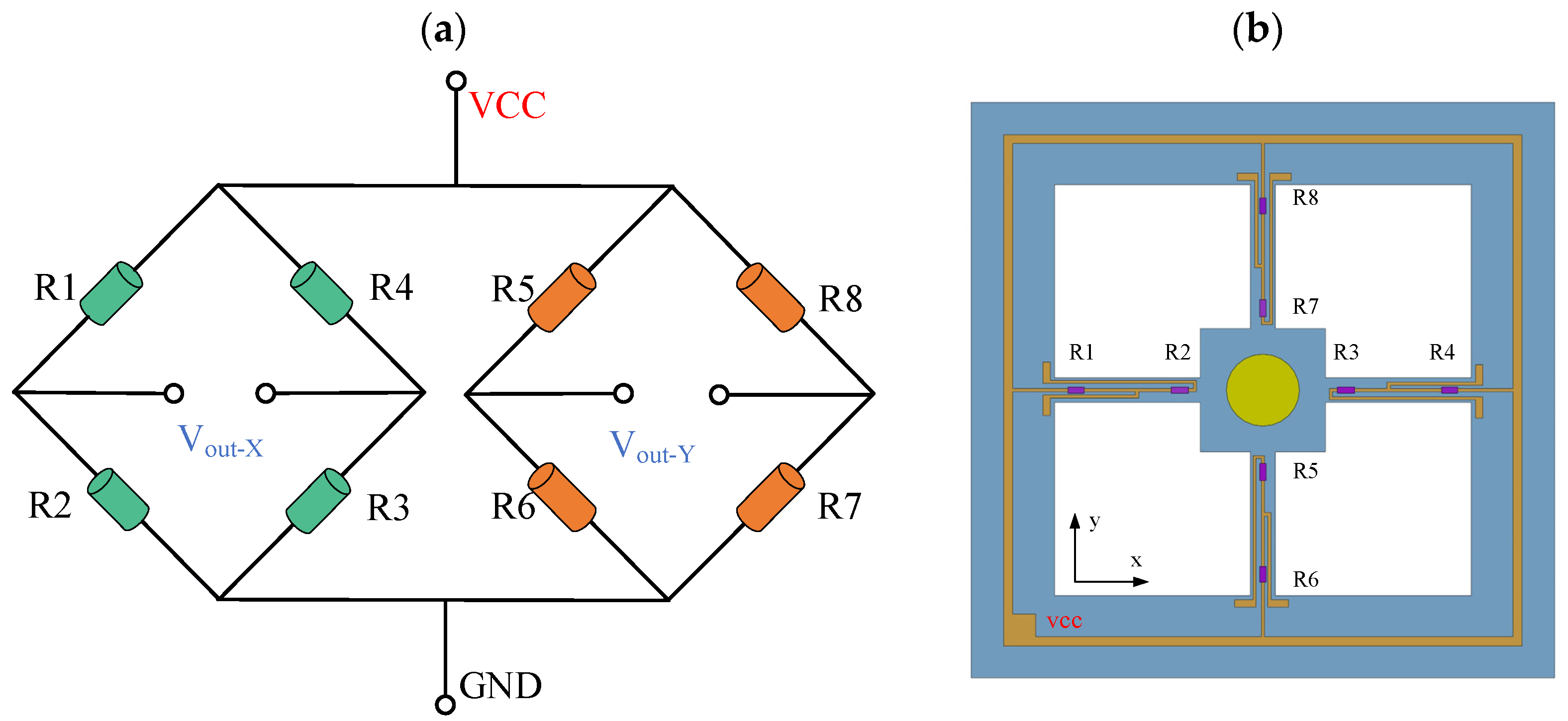
Eight varistors, R1-R8, are fixed on the crossbeam forming two Wheatstone full-bridge circuits, as illustrated in Figure 3b. When the cilium is subjected to the force generated by water movement, it oscillates to one side, driving the mass block at the bottom of the cilium to deflect. At this time, the mass block drives the crossbeam to produce bending. According to the piezoresistive effect, the varistors at each end of the cantilever feel compressive and tensile forces, respectively, so that the two varistors produce opposite changes, a resistance becomes larger, a resistance becomes smaller. The original equilibrium of the Wheatstone bridge is then broken, and the output voltage is generated. By converting the resistance variation of the piezoresistor into a corresponding voltage change across the bridge, the detector converts the wake signal into the output voltage signal.

Figure 3.
Detector circuit. (a) The principle diagram of the detector circuit. (b) The Schematic diagram of resistance arrangement and beam structure.
Due to the identical principles of the two channels, we can take the X channel as an example to analyze the detector’s output. In the absence of a wake signal, the Wheatstone bridge circuit is in balance, and the bridge output is 0. When the wake flows through the cilia, the cilia swing and the Wheatstone bridge loses balance. The output voltage of the X channel, denoted as , can be expressed as follows:
In Equation (1), is the input voltage, and since in the bridge and the cilia is at the center of the crossbeam, , so the above formula can be simplified as follows:
Similarly, Y channel operates based on the same principle. According to the piezoresistive effect, the piezoresistive change is related to the stress on the beam in the following manner:
where is the longitudinal piezoresistive coefficient and is the longitudinal stress of the piezoresistive. From the above equation, it can be seen that the output signal amplitude of the detector is proportional to the stress on the beam. By positioning the piezoresistor in the region of maximum stress on the beam, the sensitivity of the detector can be effectively enhanced.
2.3. Theoretical Analysis of the Detector’s Mechanical Structure
The main properties of the detector include sensitivity and characteristic frequency, and our goal is to enhance the detector’s sensitivity while ensuring it maintains sufficient bandwidth. It is well known that the working bandwidth of the detector is related to the resonant frequency of the detector’s sensitive microstructure. According to previous related studies [24], it can be seen from Equation (4) that the eigenfrequency of the detector microstructure is influenced by the mass m and the elasticity coefficient k.
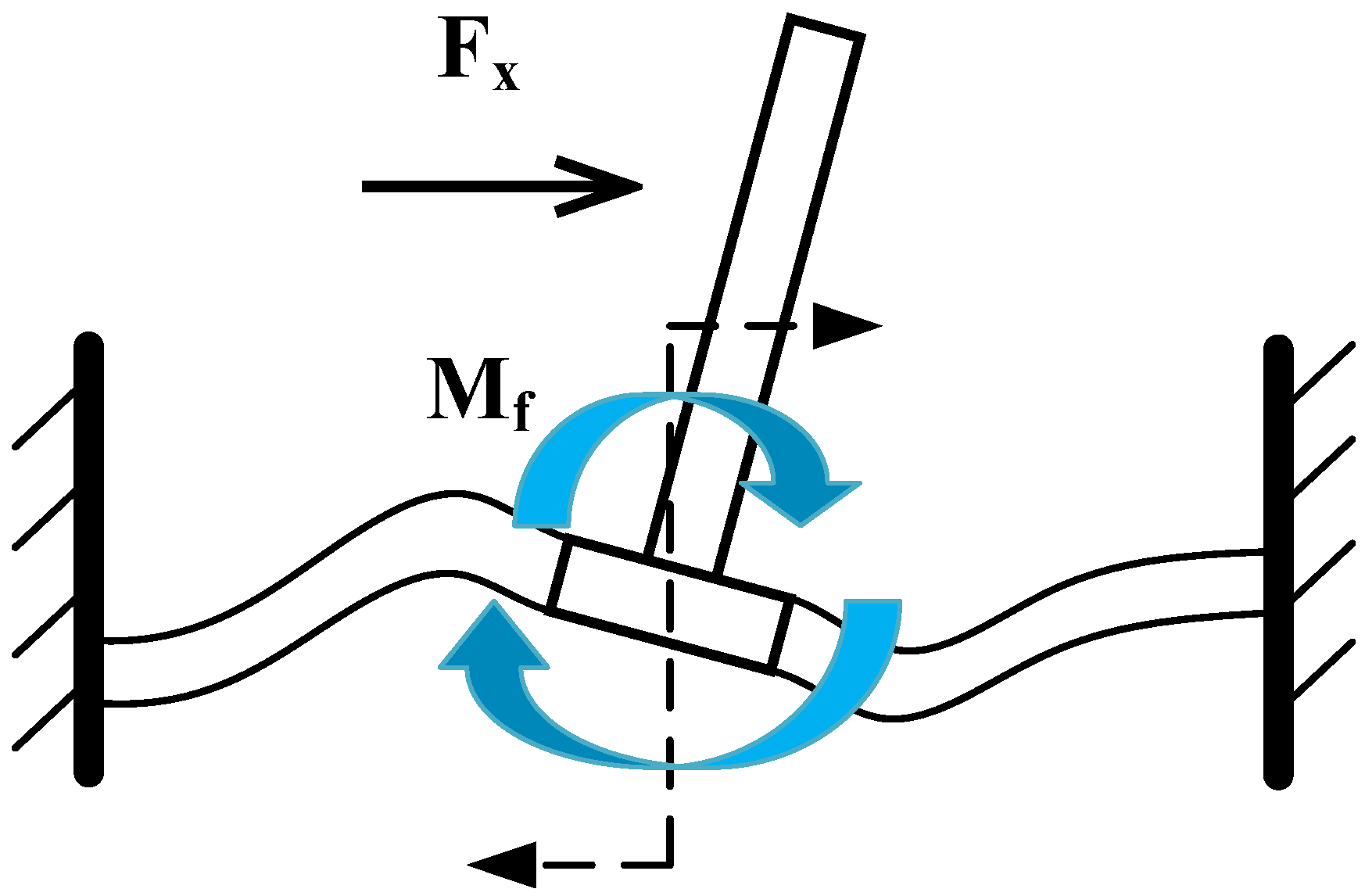
Based on the aforementioned equation, we observe that the resonant frequency of the detector is negatively correlated with the mass and positively correlated with the elasticity coefficient. It can be seen from Equation (3) that the sensitivity characterization of the detector is closely related to the stress on the varistor on the cantilever. As shown in Figure 4, the external pressure signal is transmitted to the crossbeam through the cilium and the central mass block. Then, the moment M at the center of the crossbeam can be calculated through the following formula [25]:

Figure 4.
The diagram for force-bearing analysis on the single-side cantilever beam.
The equation of stress on the cantilever beam is as follows [22]:
In Equations (5) and (6), M is the moment at the central junction of cantilever beams, H is the height of cilium, r is the ciliary radius, p is the pressure on the cilia. X is the length from each point on the beam to the center of the beam, and S is the area of the wake signal received by the cilium. The names of other parameters are presented in Table 1. It can be seen from Equation (6) that the sensitivity of the detector is positively correlated with the height and radius of the cilia.

Table 1.
Description of microstructure parameter.
Based on the analysis provided in Section 2.2, it is established that the sensitivity of the detector is directly proportional to the stress applied to the beam. Referring to Equations (5) and (6), it becomes evident that the stress on the crossbeam exhibits a positive correlation with the parameters of the cilia. However, it is worth noting that larger cilia parameters result in increased cilia mass. Equation (4) further highlights that a larger mass leads to a smaller resonant frequency. Consequently, based on the above analysis, we observe that the resonant frequency and sensitivity of the detector are contradictory and cannot be simultaneously improved. Therefore, it is necessary to find a suitable parameter to ensure the performance of the detector. In order to address this, we will establish a mathematical model and conduct a parametric scan of the relevant parameters. The cilia material is photosensitive resin, whose density is similar to that of water, which can better pick up the wake vibration signal. In addition, the high Young’s modulus of photosensitive resin can bring higher resonant frequency to the detector and ensure the working bandwidth of the detector.
2.4. Parameterization of Detector’s Sensitive Microstructure
COMSOL is a numerical simulation software. It can optimize detector parameters and find crucial parameters among all of them. COMSOL was used to analyze the stress simulation and modal resonant frequency of the wake detector. In addition, COMSOL was used to simulate the actual application environment of the wake detector and analyze the detector’s performance in the wake environment.
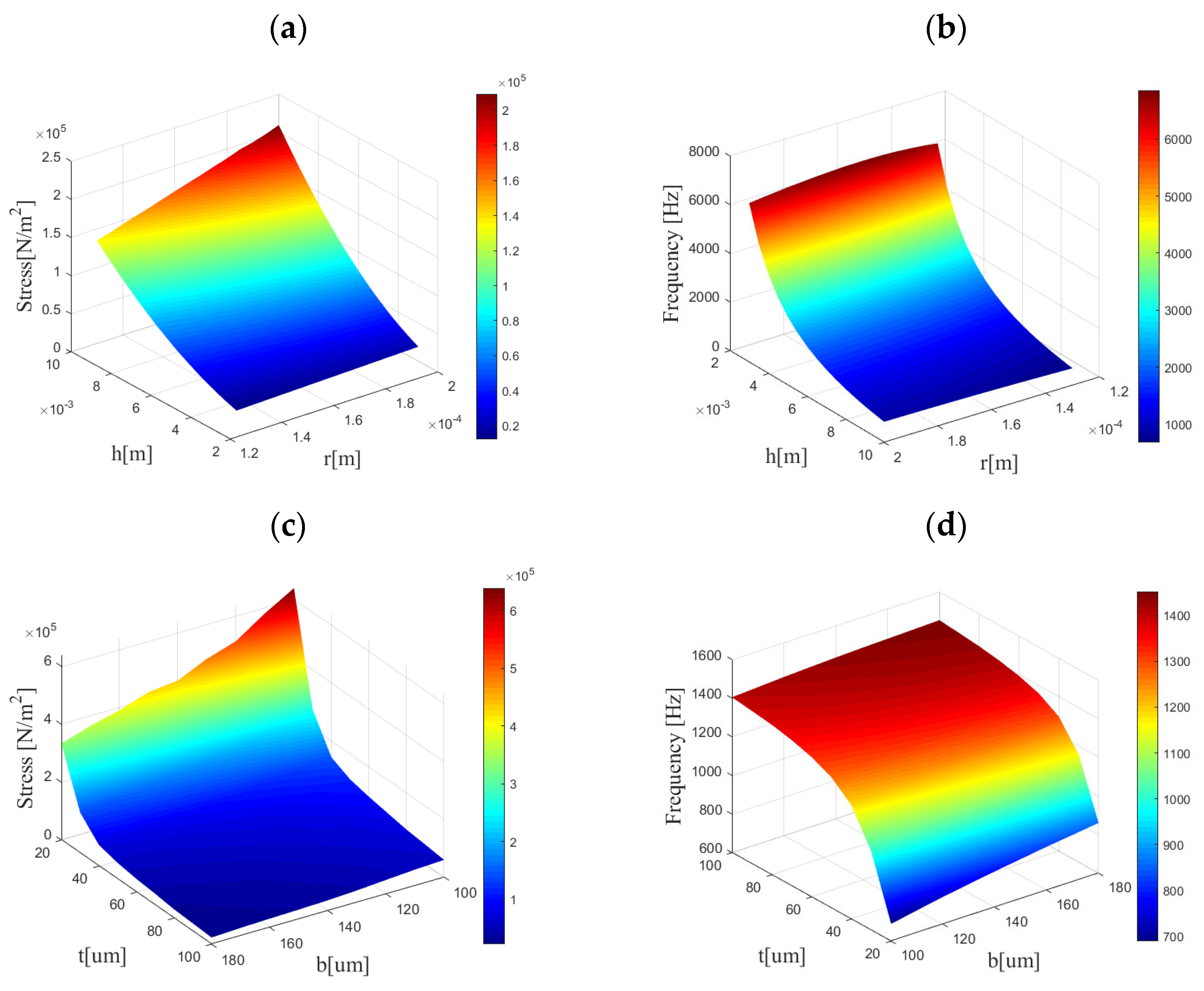
The above analysis makes it easy to find that the sensitivity and resonant frequency of the detector are mainly influenced by the structural dimensions of the cantilever beam and cilia. To obtain the inherent frequencies of the detector microstructure and the maximum stress on the crossbeam, we used the controlled variable method to scan the parameters with COMSOL. The results of the parameter scanning are depicted in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Parameterized scan results of the model. (a) The correlation between max stress on the beam and parameters h, r. (b) The correlation between resonant frequency and parameters h, r. (c) The correlation between max stress on the beam and parameters t, b. (d) The correlation between resonant frequency and parameters t, b.
Upon observing the scanning results, it becomes apparent that the sensitivity of the detector is positively correlated with the cilium height h, negatively correlated with the cilium radius r, and also negatively correlated with both the cantilever beam thickness t and width b. The resonant frequency of the detector is negatively correlated with the cilia height and positively correlated with the cilium radius; it is positively correlated with the thickness and width of the cantilever beam. These simulation results agree with the previous theoretical analysis. We can also find that the sensitivity and resonant frequency are much more influenced by the cilium height and cantilever beam thickness than by the cilium radius and cantilever beam width.
Based on the correlation analysis mentioned above, appropriate structural parameters are selected to enhance the detector sensitivity while ensuring the working bandwidth of the detector. Considering the process fabrication difficulty, we select the following parameters: L = 700 μm, t = 50 μm, b = 120μm, h = 8 mm, and r = 175 μm. Next, we performed eigenfrequency and steady-state simulations for the sensitive microstructures with determined structural parameters.
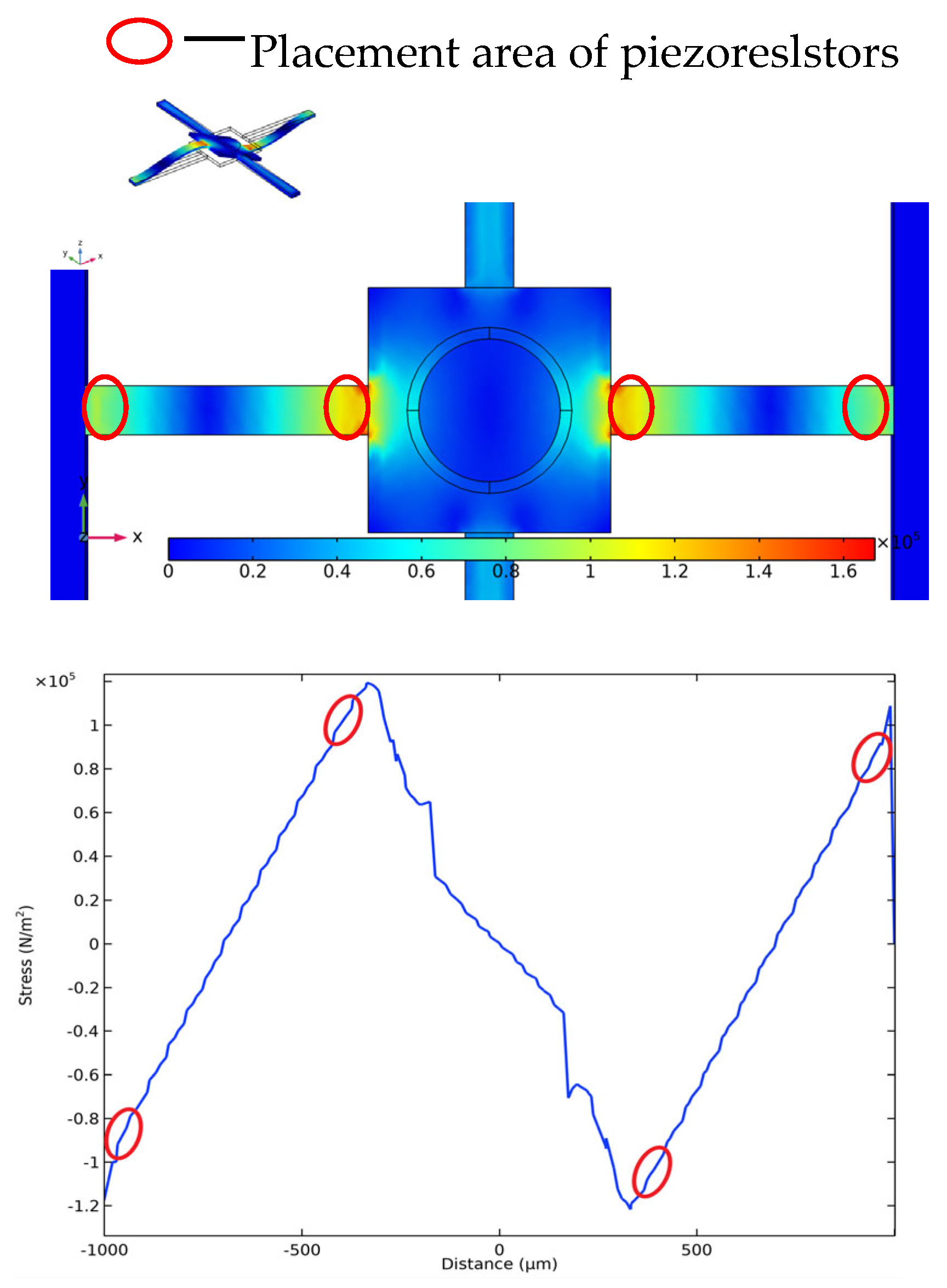
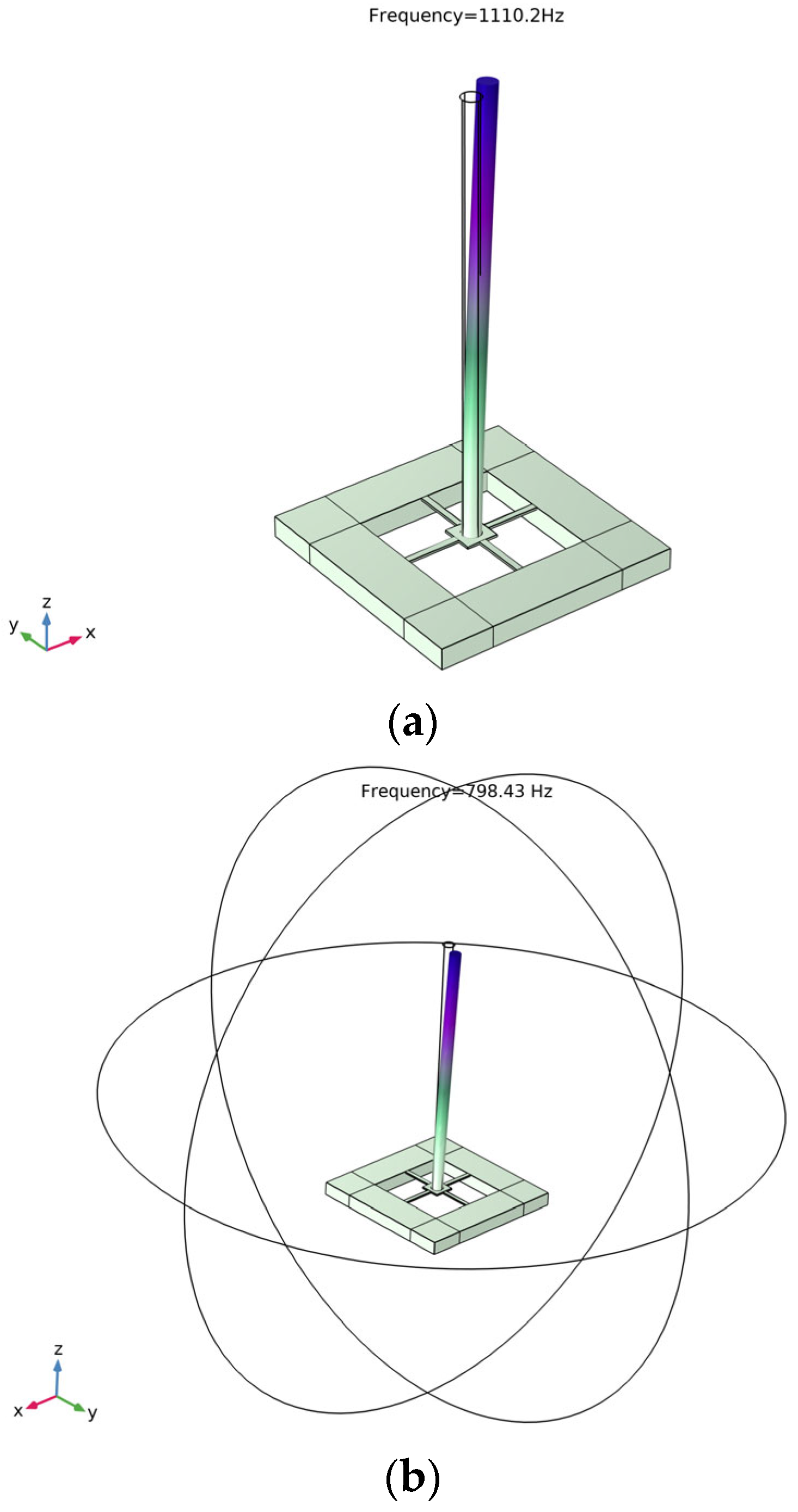
The simulation results are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Figure 6 is the stress distribution diagram in the X direction on the crossbeam. We can see that the largest stress is distributed at both ends of the cantilever. The piezoresistor is arranged in this area to maximize the piezoresistor force and thus improve the sensitivity of the detector. In the resonant frequency simulation, the resonant frequency of the detector microstructure is 1110.2 Hz. Then it was placed in water for wet mode simulation, and the first-order resonant frequency was 798.43 Hz, as shown in Figure 7. The upper bandwidth limit of the wake signal is less than 2/3 of the resonant frequency of the microstructure, which meets the needs of wake detection within 500 Hz [26].

Figure 6.
Stress distribution on the crossbeam.

Figure 7.
Modal simulation of detector structure. (a) Simulation results in the air; (b) simulation results in the water.
2.5. Detector Package Design
According to the pressure difference principle of the fish lateral line canal, the bionic diversion cap is designed, as shown in Figure 8. The cap features four diversion holes that are aligned with the crossbeam and arranged orthogonally. This design enables the enhancement of one-dimensional flow field detection to two-dimensional flow field detection. Furthermore, the presence of this bionic diversion cap can protect the sensitive microstructure from the impact and collision of the current and sediment. In addition, the packaging structure effectively filters out low-frequency marine environmental noise and the low-frequency noise generated by the carrier’s movement [27,28,29].

Figure 8.
The bionic diversion cap of the lateral line canal.
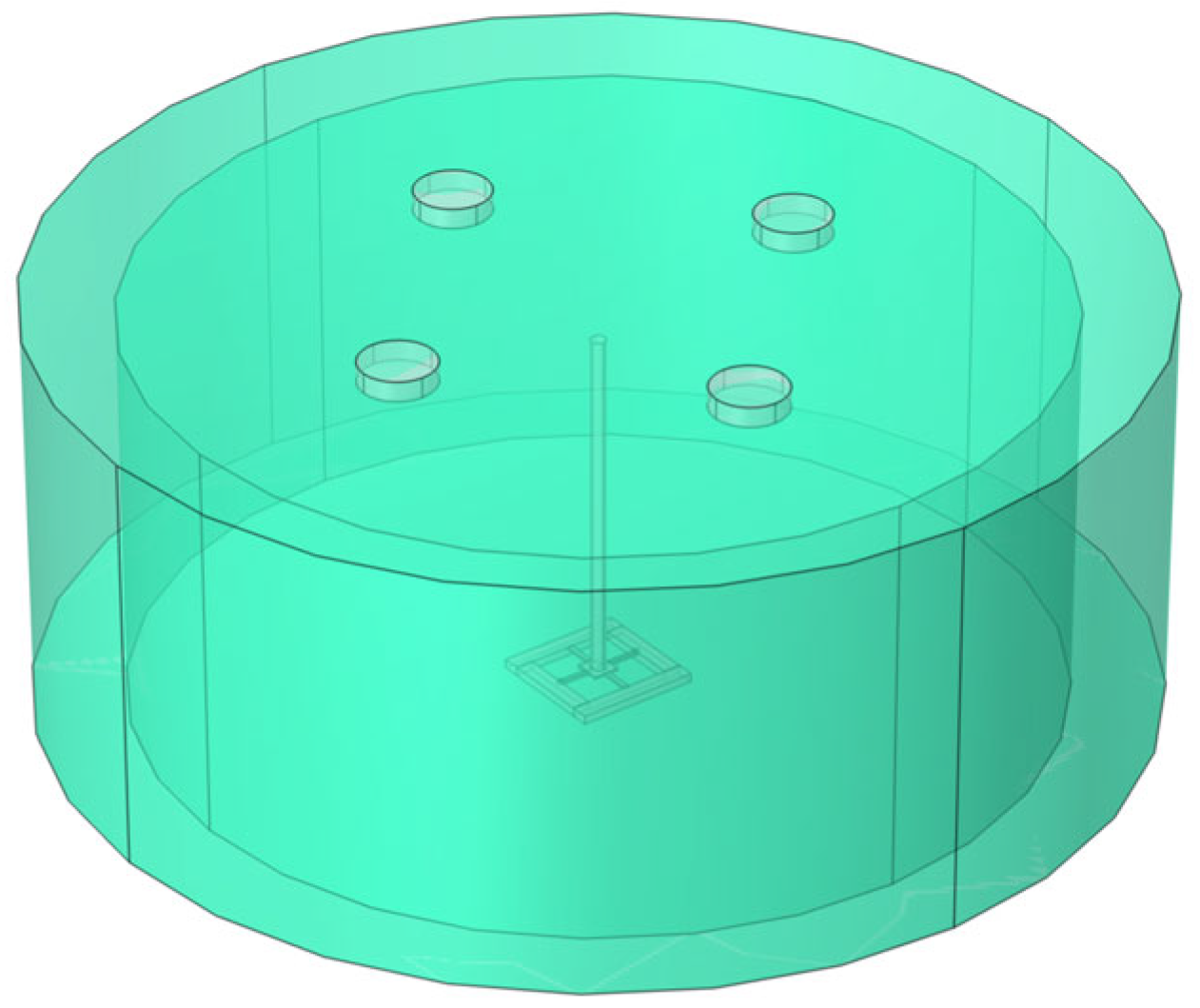
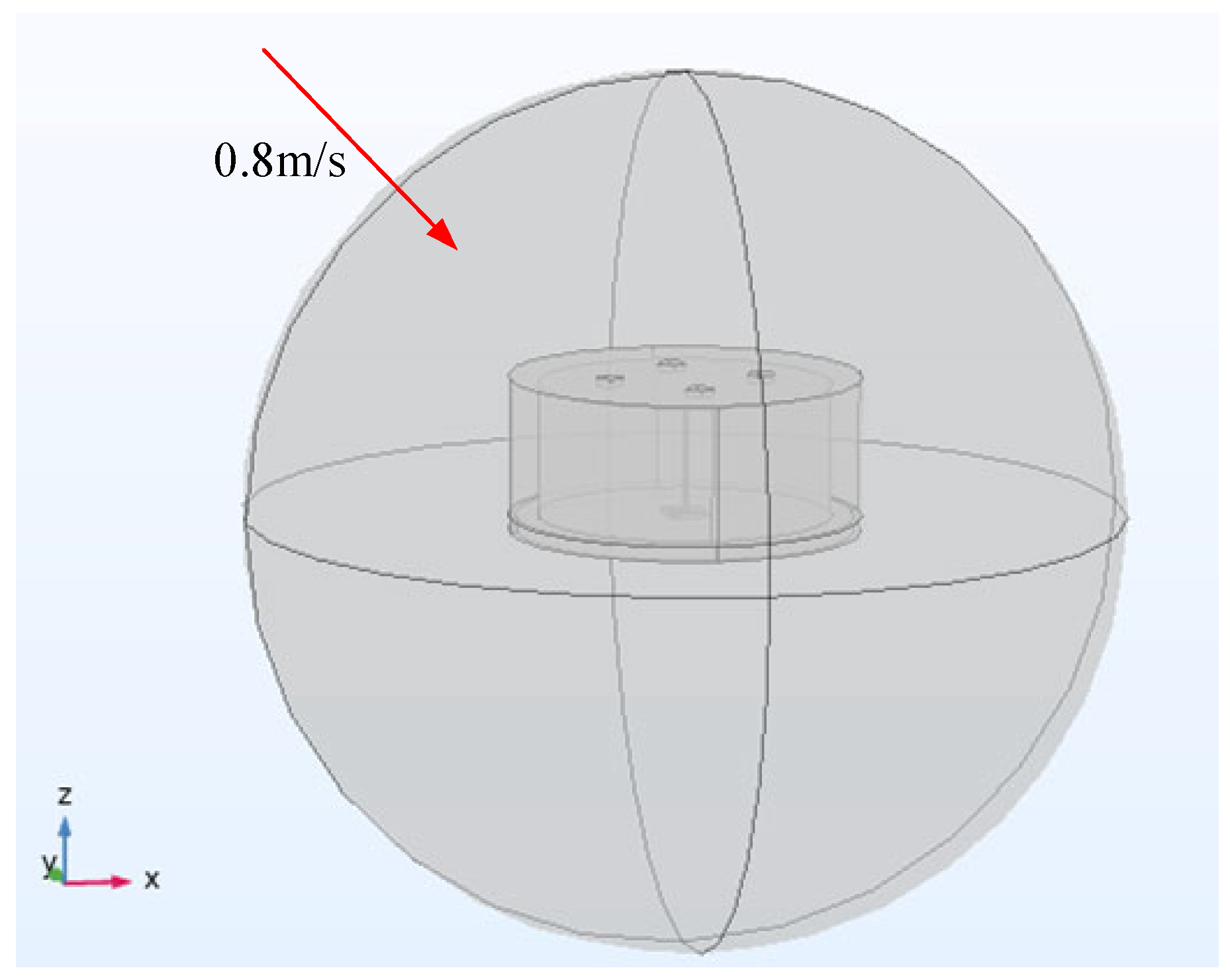
To obtain the optimal size, it is necessary to use the fluid-solid coupling module of COMSOL to construct the corresponding finite element models and conduct a parametric scan of the key parameters that affect the detector’s performance. The primary parameters include the distance s from the diversion hole to the center of the top surface of the hat, the radius n of the diversion hole, and the height m of the diversion hole. Subsequently, the wake detector model is put into the wake environment model with an inlet flow velocity of 0.8 m/s, as shown in Figure 9. In this environment, these parameters are subjected to a parametric scan, and the obtained scanning results are presented below.

Figure 9.
Wake environmental model.
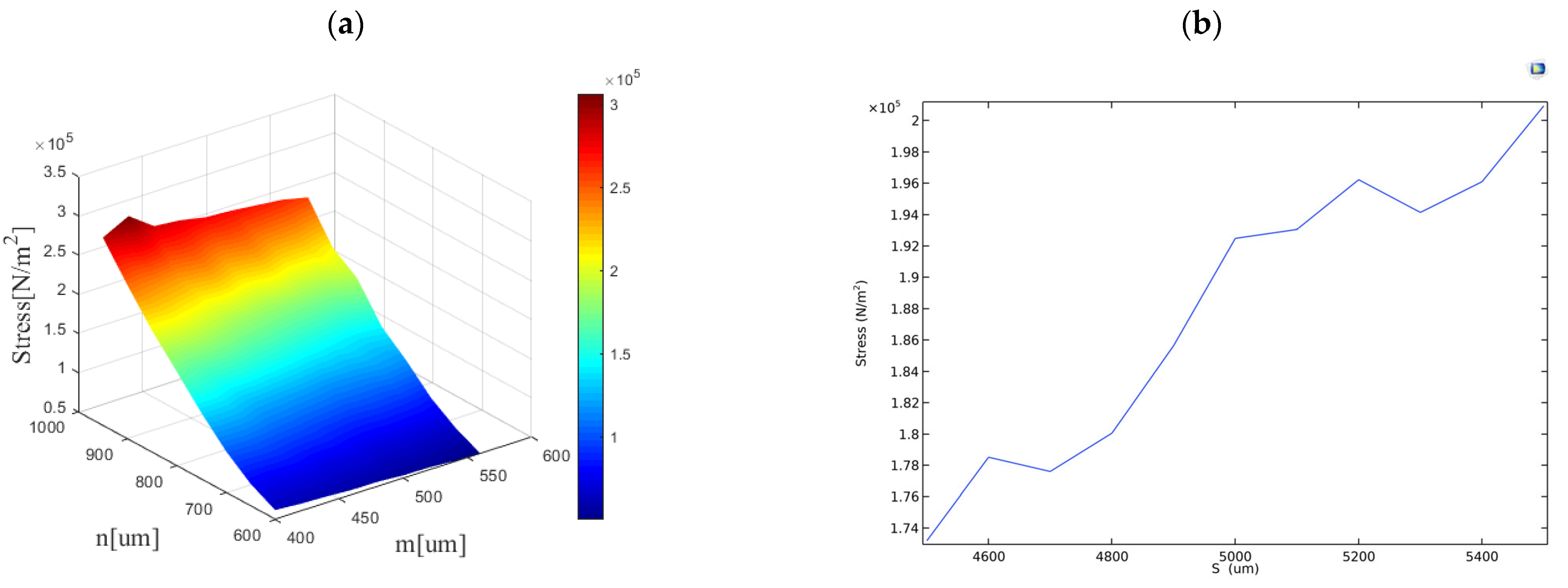
According to the scanning results, as shown in Figure 10, the diversion pore in the bionic diversion cap is also the main factor affecting the detector’s sensitivity. A larger radius of the hole corresponds to higher sensitivity. However, it is crucial to consider the impact of sediment present in seawater, as a larger pore radius does not function better. Here, we choose the radius of the diversion pore as 900 μm. The height of the hole is negatively correlated with the sensitivity of the detector, but the effect is not significant. Considering the accuracy of 3D printing and the hardness of the resin material, we choose m = 500 μm. The distance between the diversion hole and the center is generally positively correlated with sensitivity. Here, we choose the point of maximum stress, s = 5200 μm. Thus, the main parameters of the detector have been determined.

Figure 10.
Scanning results of stress. The influence of (a) n and m on stress; (b) s on stress.
We performed finite element simulation analysis in COMSOL and placed the sensitive microstructure in the bionic diversion cap to form the detector model. The material parameters used in the simulation model are the actual values in the detector manufacturing process. Then, the constructed detector model was placed within the wake simulation environment for further analysis. This enabled us to obtain the flow field distribution around and inside the detector, as well as the displacement stress distribution of the crossbeam.
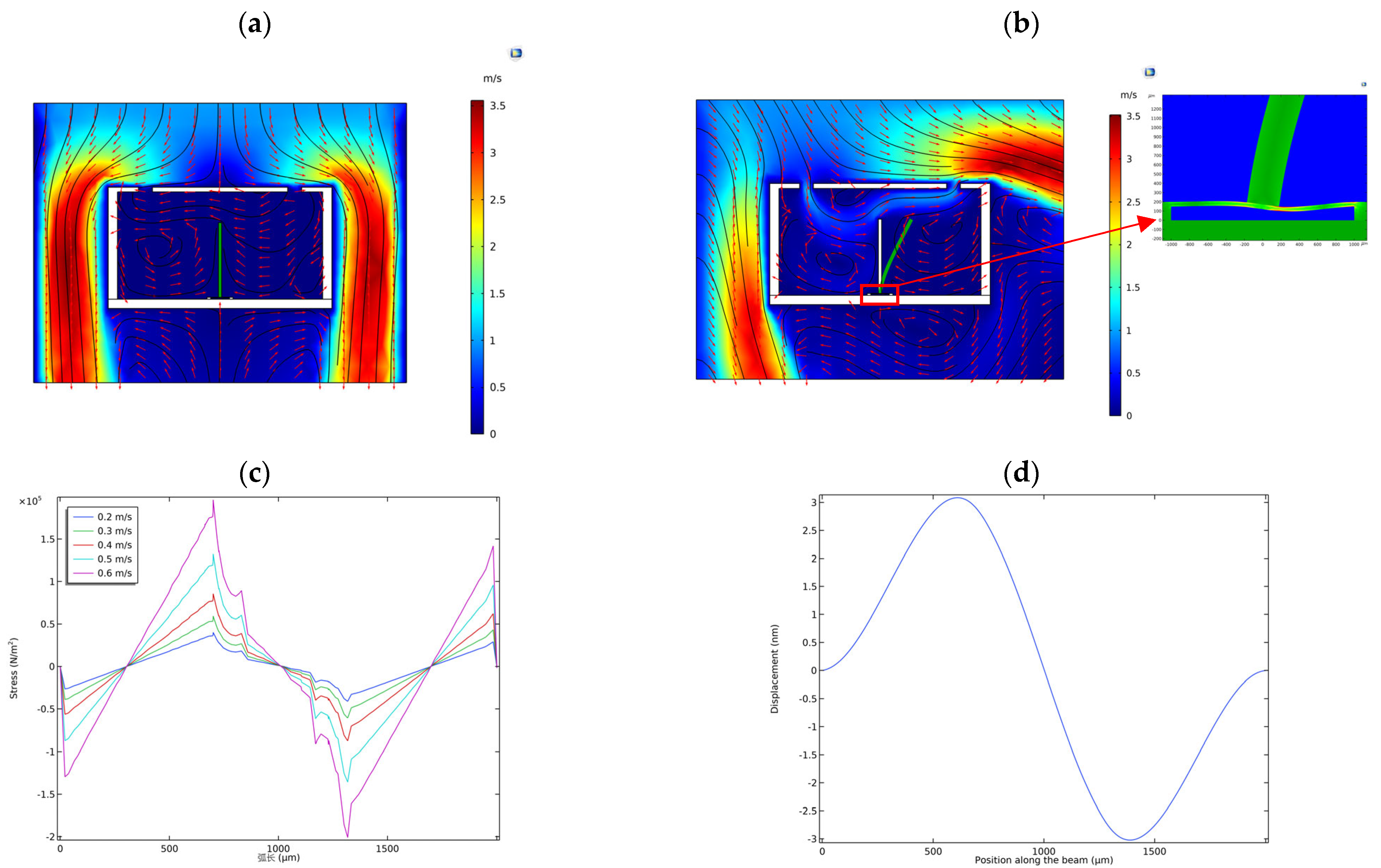
The wake detector’s axis aligns parallel to the axis of the AUV carrier. When the AUV moves forward straightly, or the wake comes straight along the axis of the AUV, there is neither a pressure difference between the diversion pore of the wake detector nor obvious flow in the chamber. As a result, the output voltage of the detector is approximately zero, as shown in Figure 11a. However, when the wake comes along the direction deviated from the axis of the wake detector, the cilium would vibrate, and there would be a corresponding output signal, as shown in Figure 11b. In addition, the bionic diversion cap mimicking the lateral line canal can also filter out the low-frequency marine environmental noise and the noise generated by the movement of the carrier [12]. Figure 11c shows the stress distribution on crossbeams at different flow rates, and Figure 11d demonstrates the displacement curve on the crossbeams corresponding to Figure 11b.

Figure 11.
Results of the finite element analysis. (a) The flow velocity distribution around and inside the encapsulation cap when vx = 0 m/s; (b) Velocity distribution around and inside the encapsulation cap and displacement of the cilium crossbeam when vx = 0.5 m/s; (c) Stress distribution curves on crossbeams at different flow rates; (d) Displacement curve in (b).
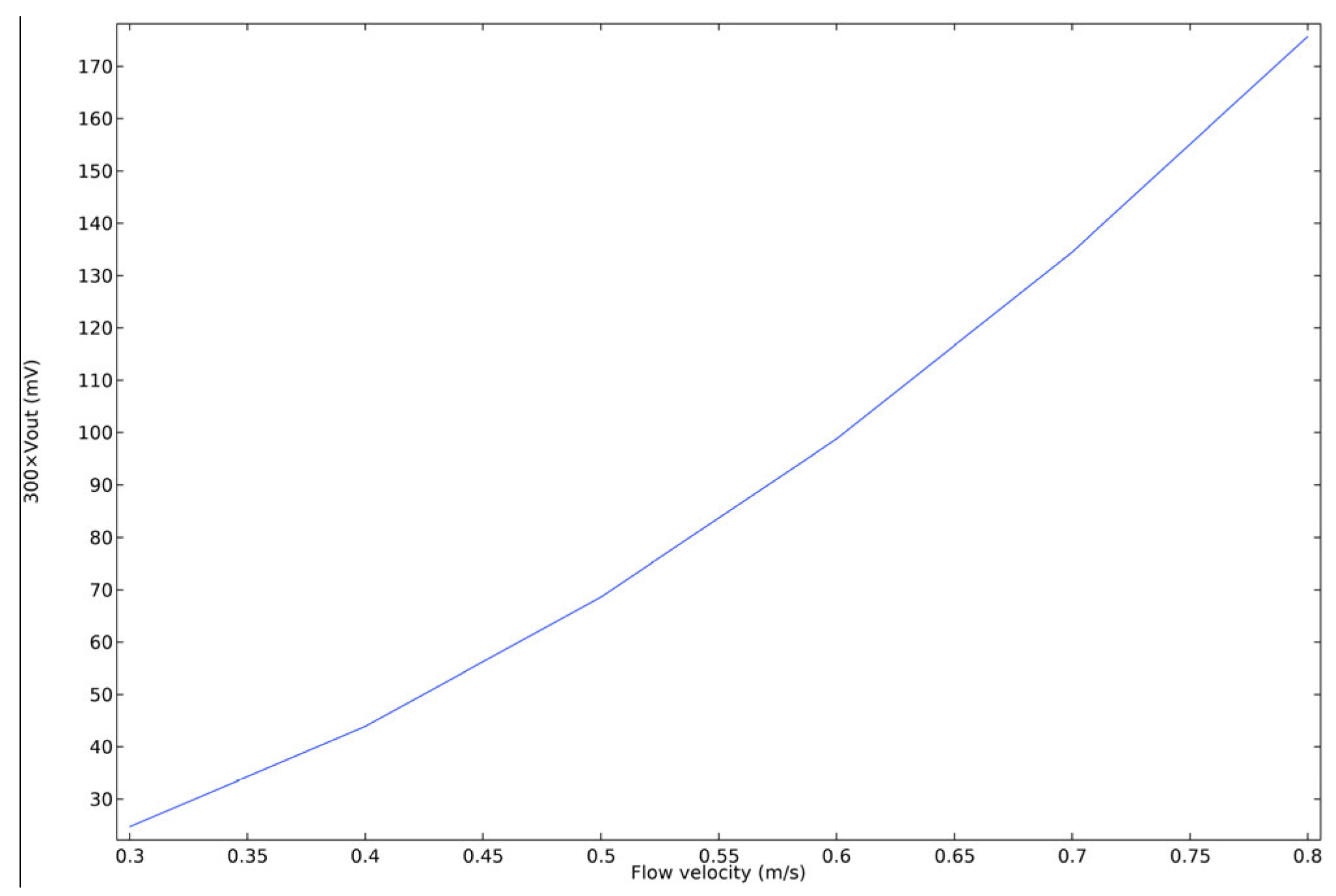
After all parameters are determined, the output voltage of the detector is simulated. According to the simulation calculation of Formulas (2) and (3), the output sensitivity curve of the detector after 300 times amplification is shown in Figure 12. The sensitivity of the wake detector obtained by simulation is 300 mV·(m/s)−1.

Figure 12.
Simulation curve of wake detector output sensitivity after 300 times magnification.
2.6. Process Preparation
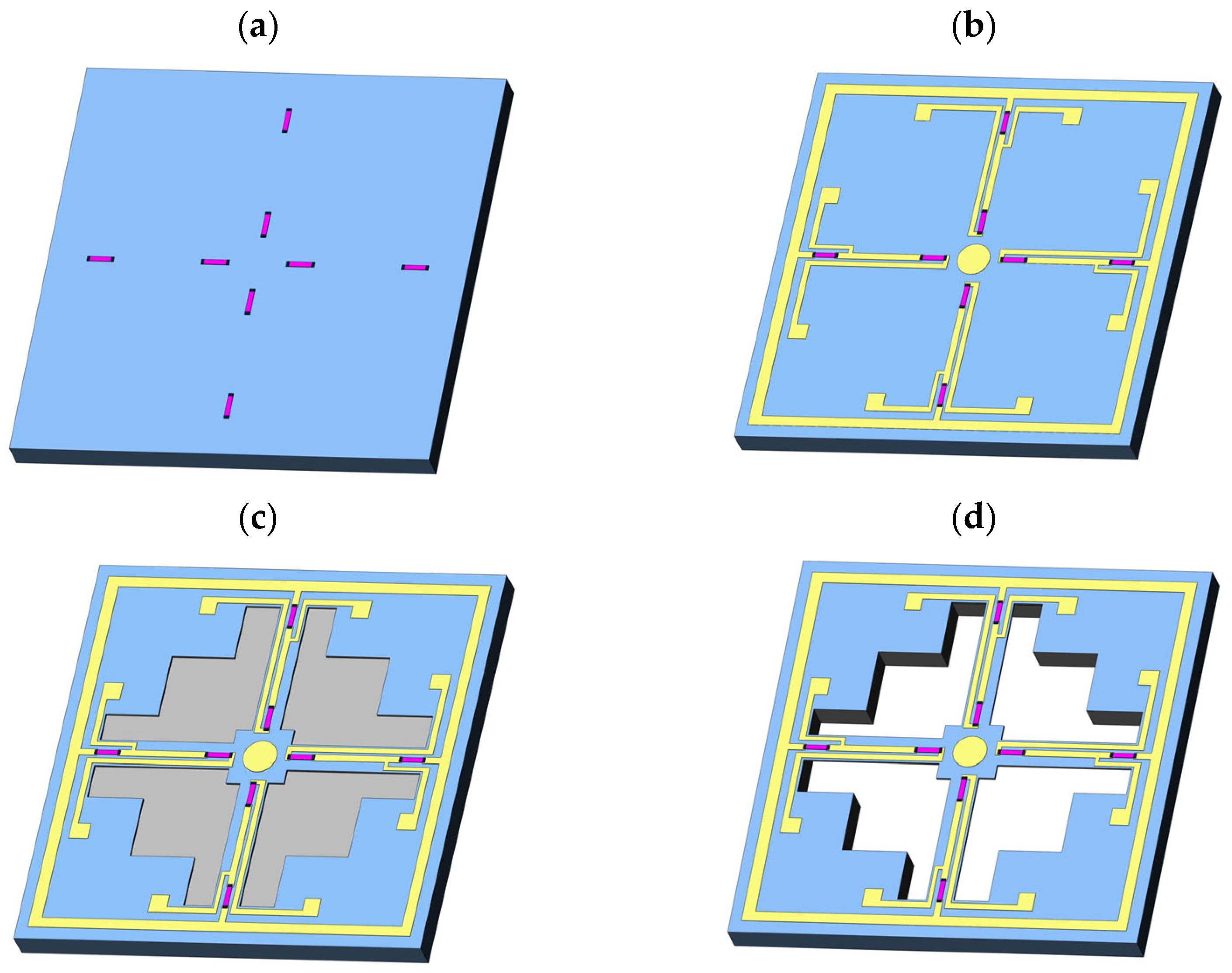
The first step was to form piezoresistive and heavily doped regions, as shown in Figure 13a. The prepared SOI sheets were standard cleaned, and the wafers were pretreated with (HMDS) to enhance the adhesion between SOI and photoresist. The silicon wafer was coated with a photoresist and exposed by a lithographer to form a piezoresistive mask. The piezoresistive region was then subjected to ion implantation (boron ions) to form a varistor, which was then de-gelled. After lithography, a heavily doped region mask was formed to expose the silicon at both ends of the piezoresistive region. Finally, both ends of the silicon were injected with concentrated boron ions.

Figure 13.
General fabrication of the sensitive unit. (a) Making piezoresistive and heavily doped regions. (b) Sputtering and graphing the metal leads. (c) Forming the crossbeam. (d) Releasing the crossbeam structure.
The second step was to sputter and graphic the metal leads as shown in Figure 13b. Firstly, a layer of 300 nm aluminum metal was sputtered on the surface of the device layer by a magnetron sputtering machine. Then the lead mask was formed by photoresist lithography on the aluminum film. The photolithographic wafer was corroded in an aluminum etching solution to form metal leads. After corrosion and complete annealing in a vacuum annealing furnace, an ohmic contact is formed.
The third step was reactive ion etching (RIE) to form a crossbeam as shown in Figure 13c. The photoresist was used to create a crossbeam pattern. Then RIE machine was used to etch the device layer and the buried oxygen layer, forming a crossbeam structure.
The final step was back-deep silicon etching (DRIE) as shown in Figure 13a. The photoresist was used on the back of the wafer for lithography and formation of the back cavity pattern. A deep silicon etching machine was used to etch the silicon on the substrate to release the crossbeam structure.
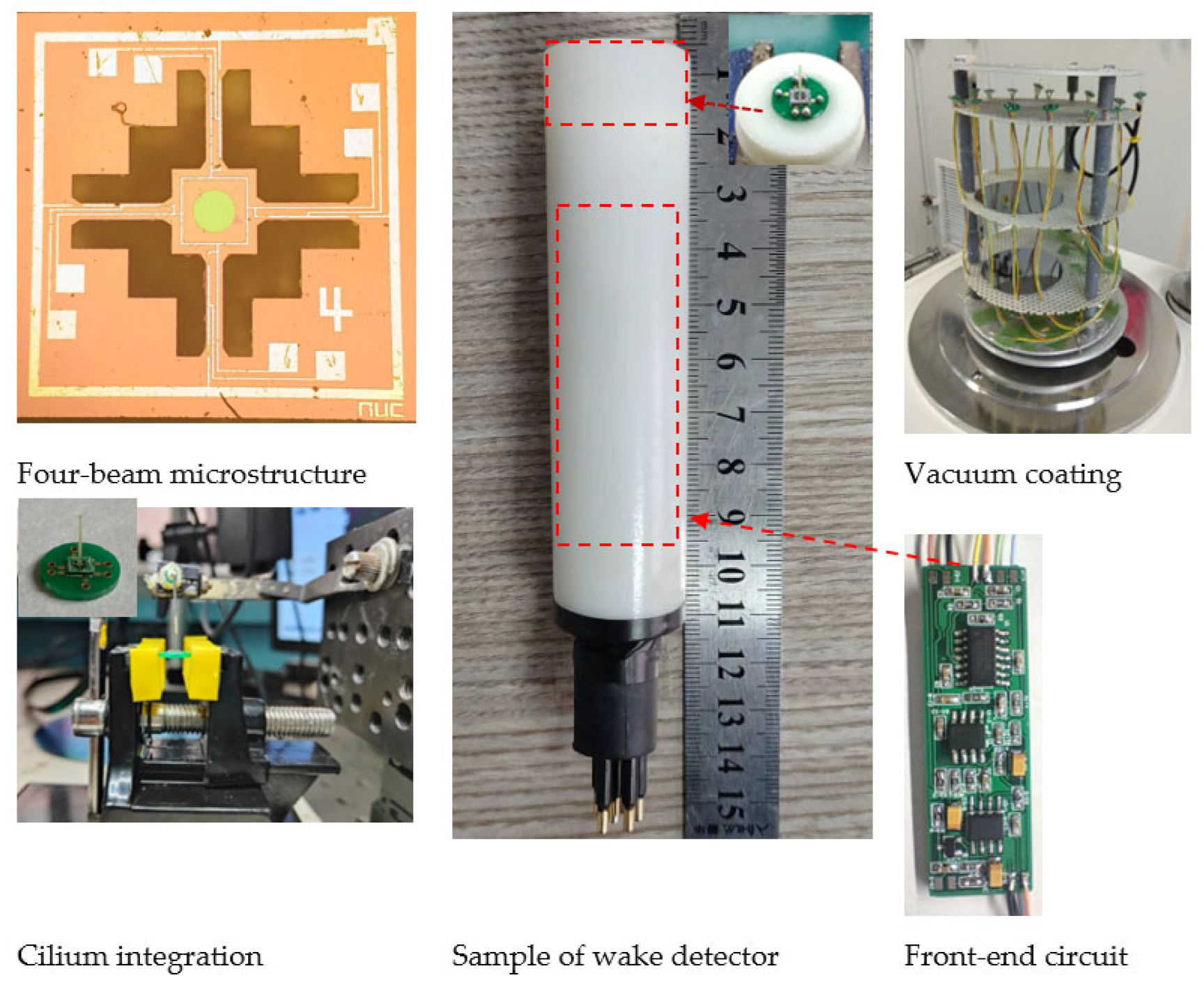
2.7. Detector Integration and Packaging
We glued the detector chip prepared by the process to the receiving circuit board and bonded the two with gold wire. The 3D-printed columnar cilia were then glued to the center of the crossbeam using UV glue. They were then fed into the chemical vapor deposition system to deposit a layer of 6μm thick parylene, thus achieving an insulation and waterproofing effect [30]. In addition, it can strengthen the bond between the chip and the cilia. Figure 14 shows the packaging process and structure of the detector. Since the wake detector produces a weak signal, we have incorporated a pre-amplification circuit that amplifies the output by a factor of 300. At the same time, the circuit can filter out noise signals above 500 Hz.

Figure 14.
The encapsulation of the wake detector.
3. Results
3.1. Detector Sensitivity Test
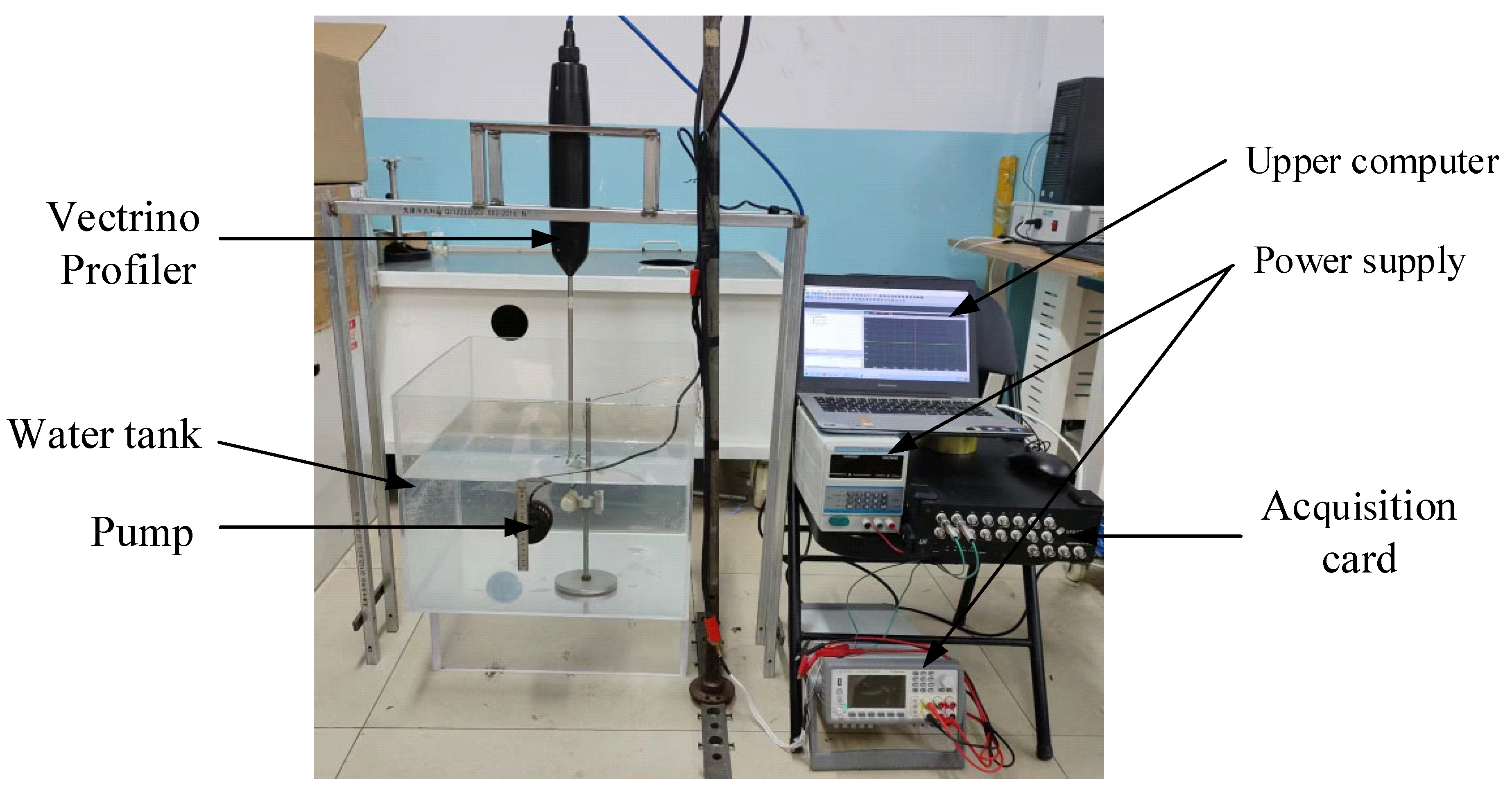
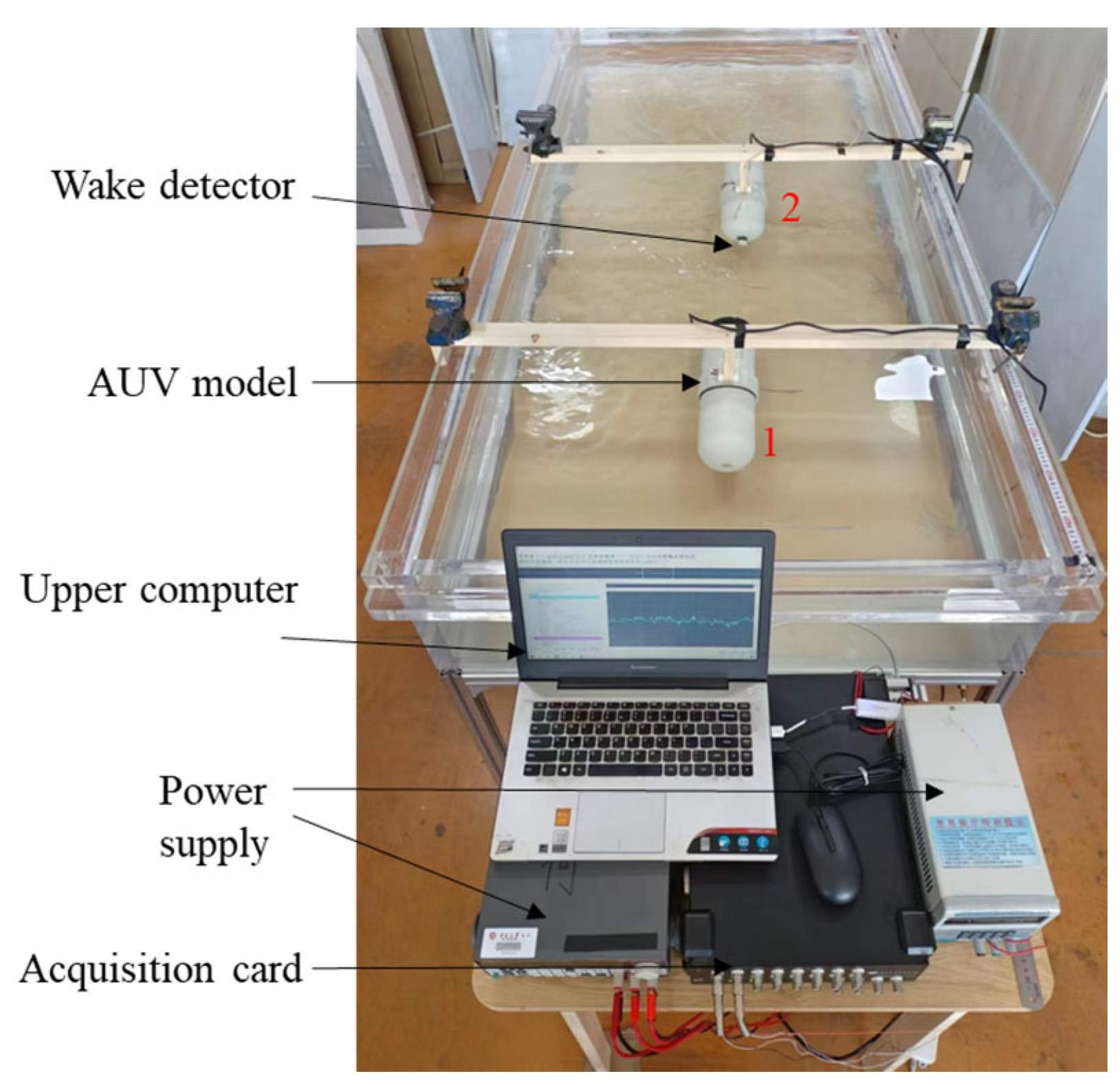
To determine the most critical performance of detector sensitivity, we have designed a calibration system for detector sensitivity measurement. The measuring system mainly includes a water tank, flow pump, Vectrino Profiler, NI acquisition card, fixed steel frame, upper computer, power supply, and so on. Figure 15 shows the platform photo.

Figure 15.
The photo of the detector test platform.
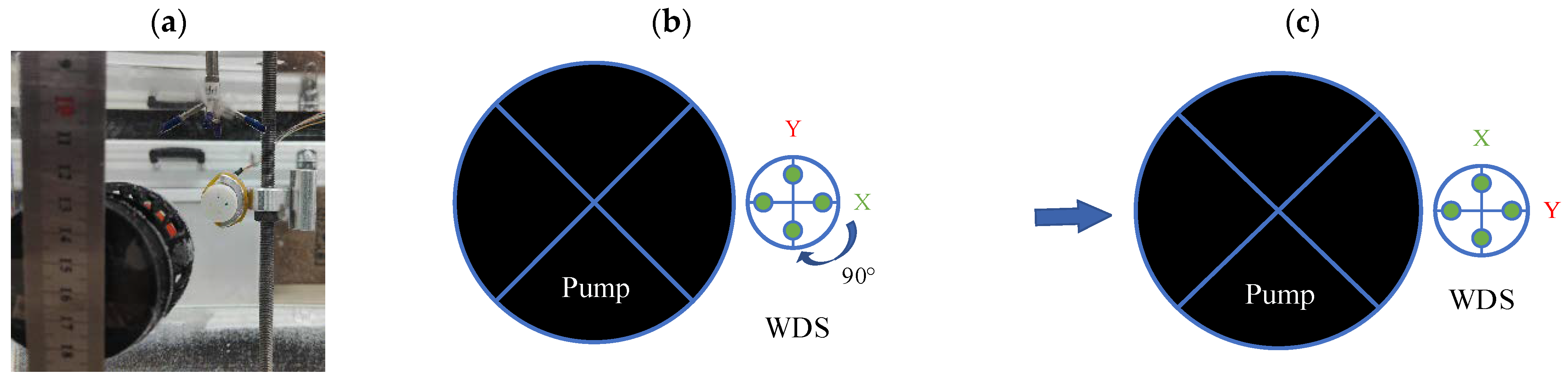
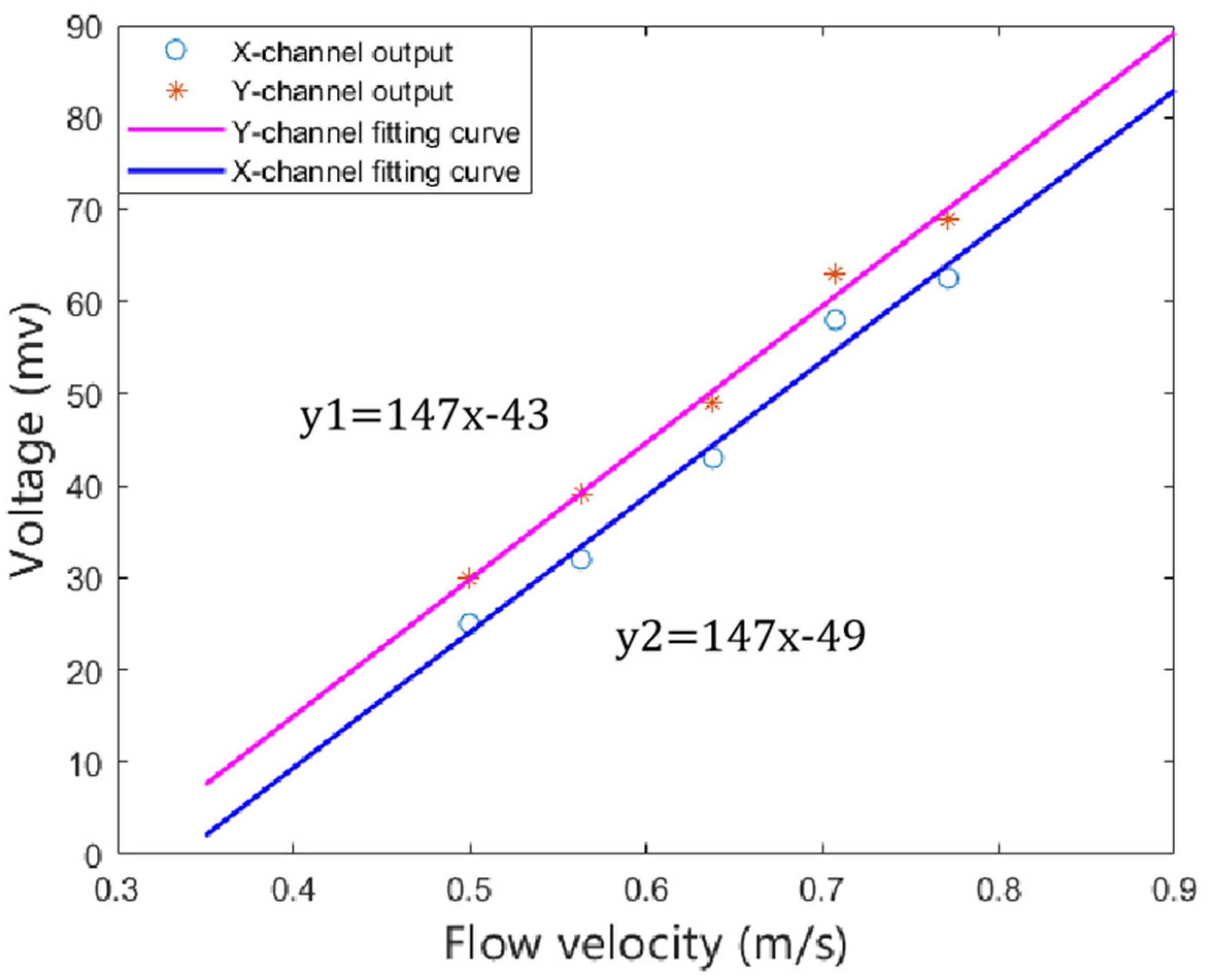
In the experiment, we used the flow generator pump to generate the wake flow and used the Vectrino Profiler to measure the different flow rates at the fixed point (where the detector is located). The position of the detector and the flow-generating pump is shown in Figure 16. Firstly, the output of the X channel was measured, and then the output of the Y channel was measured by rotating the detector 90°. The detector probe was situated 5 cm away from the pump. The NI acquisition card was used to collect the output voltage signal of the detector. We repeated the test at different flow rates and calculated the root-mean-square value of the collected data. The fitting curve was obtained, as shown in Figure 17. It can be seen from Figure 17 that the output voltage of the detector has a linear relation with the flow velocity. The sensitivity of the two channels is highly consistent, with a sensitivity of 147 mV·(m/s)−1 and a detection threshold of 0.3 m/s. Due to the test equipment and packaging, the actual sensitivity of the detector is only half of the simulated result.

Figure 16.
Diagram of detector position. (a) Detector position diagram during testing. (b) Detector position diagram when measuring X channel signal. (c) Detector position diagram when measuring Y channel signal.

Figure 17.
The fitting curve detector sensitivity.
In order to showcase the superiority of the wake detector, we conducted tests using the same experimental method to evaluate the PNS and turbulence sensors. The results of these tests are presented in Table 2. Comparing the wake detector with PNS and artificial lateral flow sensors, the wake detector has superior sensitivity and 2D vector properties. Because the cilia of the turbulence sensor are directly exposed to water and directly disturbed by water flow, its sensitivity is higher than that of the wake detector. However, the disadvantage of the turbulence sensor is that it cannot be directly loaded on the AUV.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of different detectors.
Additionally, in order to show the working efficiency of the detector, we tested the effective value of the output voltage of the detector without external excitation is 2 mV. The effective value of the output voltage of the detector at the minimum flow velocity is 32 mV. The SNR (signal-noise-ratio) of the detector is calculated as: .
3.2. Experiment for Vector Property of Detector
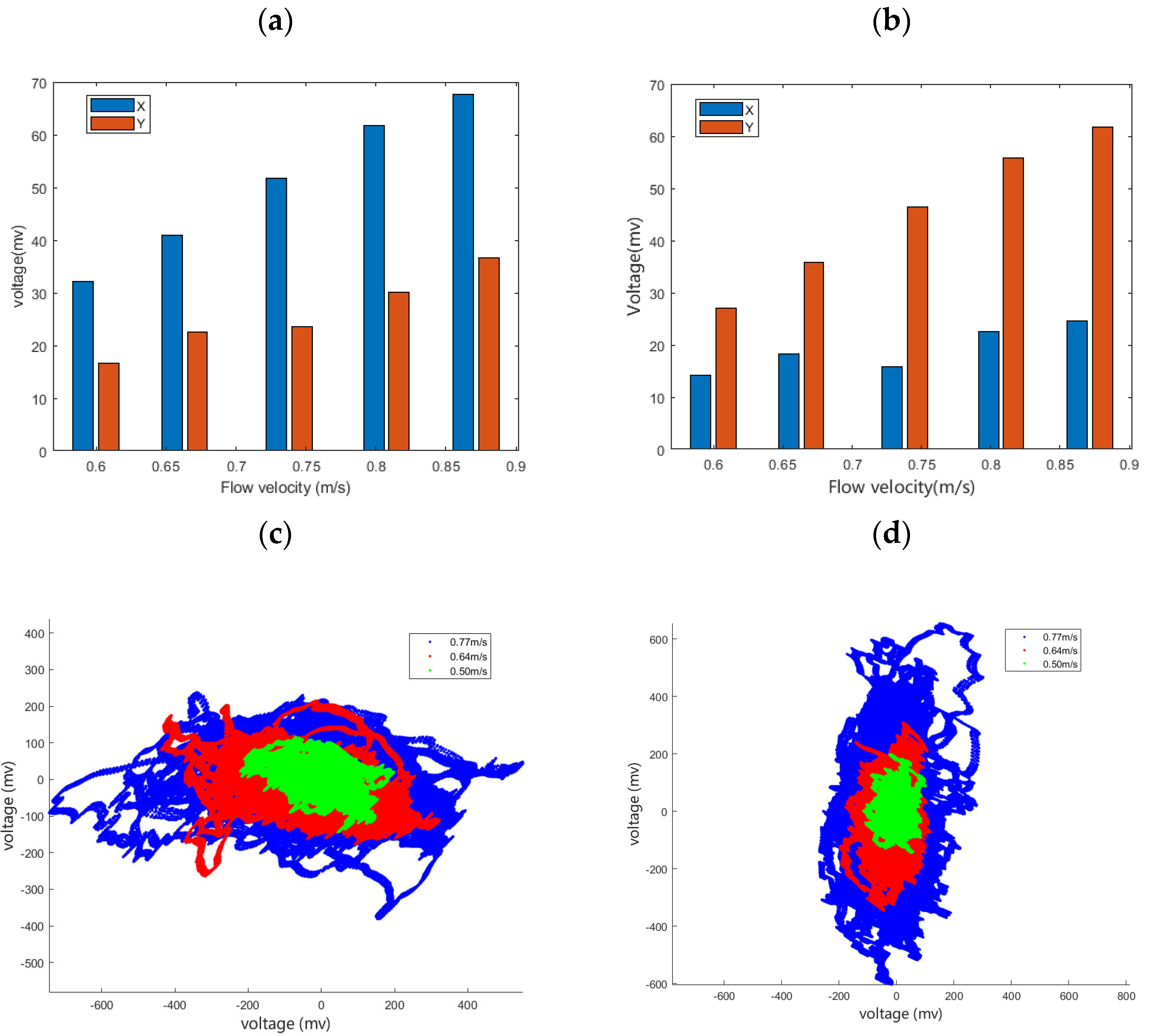
The vector test process is the same as the sensitivity test process. In this process, the detector is first placed in the position shown in Figure 16b, and the two output voltage signals of the detector at different flow rates are collected. From the principle of differential pressure detection, the output of the X-way of the detector should be larger than the output of the Y-way when placed in this way. The previous experiment was repeated by rotating the wake detector by 90°. Figure 18a,b show the results of the root-mean-square calculation of the experimental data. The histograms compare the output of the X-way and Y-way of the wake detection, visually showing the difference in the horizontal and vertical wake signals. Figure 18c,d show the voltage distribution points of the wake signal collected by the wake detector in the two experiments, respectively. These points represent the actual trajectory of the cilia. In Figure 18a, the strength of the wake flow received by the cilium in the lateral direction is greater than that received in the vertical direction. When the detector is rotated by 90°, we can see that the voltage point map in Figure 18d is also rotated by 90° compared to Figure 18c. This result further verifies the vector performance of the wake detector and its feasibility for wake detection.

Figure 18.
(a,b) Histogram of the output signal of the detector in vector property test; (c,d) distribution diagram of vector property test points.
3.3. Detection Range Experiment
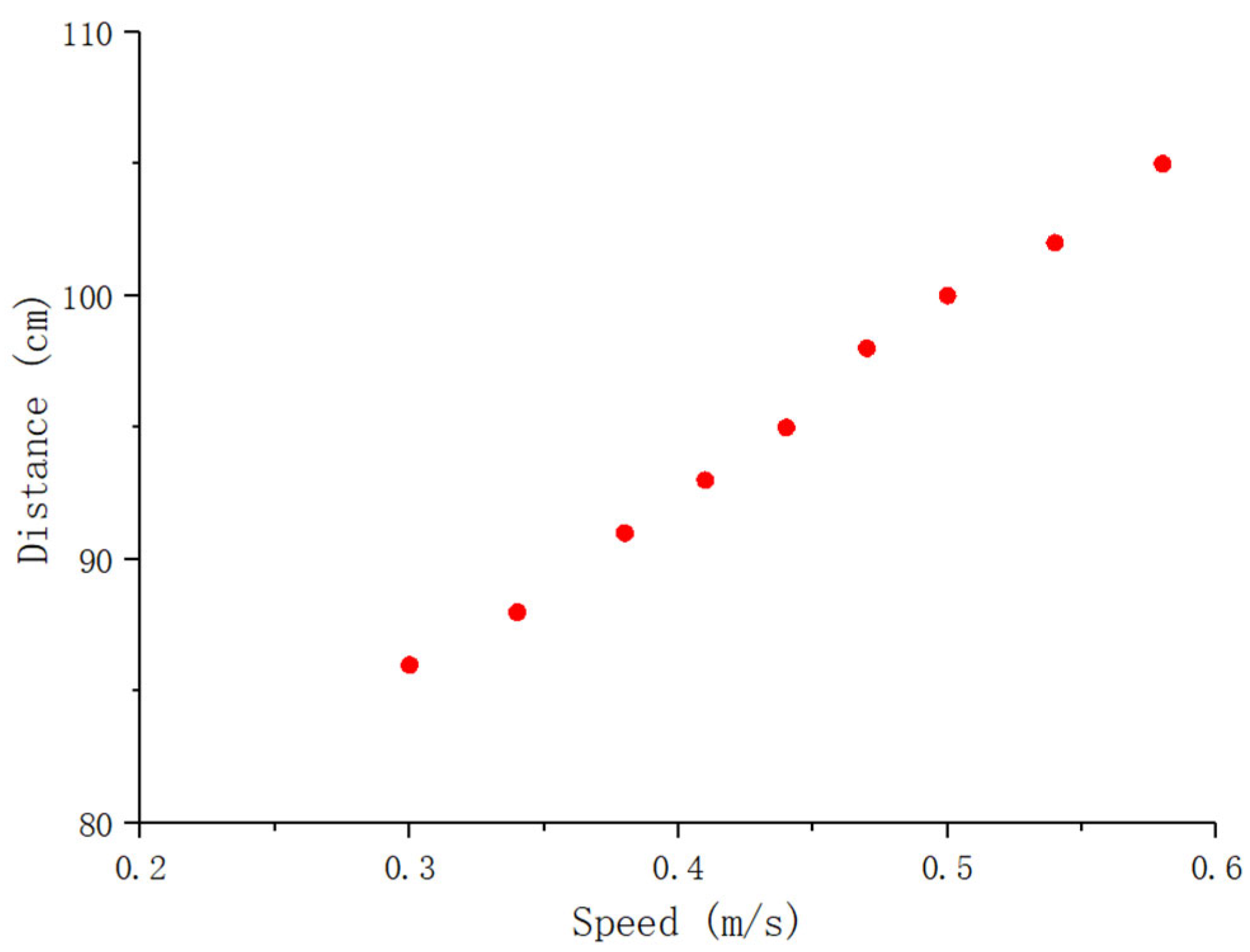
We designed two AUV models with the wake detector installed on AUV-2. Before commencing the experiment, we measured the specific speed of the nine-speed gears of AUV-1. At the beginning of the experiment, the AUV-1 was fixed at the position shown in Figure 19. The AUV-1 was set to the first gear, and then the head of AUV-2 was placed at the end of the wake area to collect the wake signal using an acquisition card. If the signal was successfully collected, AUV-2 was moved back by 1 cm until the wake signal could not be collected. In this case, the previous position was considered as the detectable range of the AUV wake signal. If the wake signal cannot be collected, AUV-2 was moved forward by 1 cm until the wake signal was successfully collected. This position was then identified as the detectable range of the AUV wake signal. Then, the gear of AUV-1 was adjusted to the second gear. Based on the detection range of the AUV wake signal at the first gear speed, the detectable range of the AUV wake signal at the second gear speed was measured. Finally, the detectable range of the AUV wake signal at the remaining seven gear speeds was repeatedly tested. Figure 20 shows the scatter diagram of the wake signal detection range of the AUV at different speeds.

Figure 19.
The photo of the detector test platform.

Figure 20.
Detection range scatter of the detector at different AUV speeds.
4. Discussion
In the discussion, several key points are addressed. Firstly, it is noted that the axis of the wake detector and the AUV carrier are parallel. When the AUV moves straight ahead or when the wake flows directly along the AUV axis, there is no pressure difference between the diversion pores of the wake detector, resulting in an output voltage close to zero (Figure 11a). Secondly, when the wake flows in a direction deviating from the axis of the wake detector, the cilium vibrates, generating a corresponding output signal (Figure 11b). This case can be further divided into two scenarios. When the wake detector is aligned along the X direction of the wake, with the AUVs propeller as the axis (Figure 16b), the output voltage of the wake detector is shown in Figure 18c. Similarly, when the wake detector is aligned along the Y direction of the wake, the ground output voltage of the wake detector is shown in Figure 18d.
Finally, it should be pointed out that the wake detector is a novel concept introduced for the first time, and its stability, sensitivity, and threshold need further improvement. Future work will focus on enhancing the overall performance of the detector by refining the packaging and experimental methods. The emergence of a wake detector provides a new solution for AUV collaborative detection technology, which holds strategic and military significance for ocean exploration and operations.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study draws inspiration from the fish lateral line system and combines it with a turbulence sensor to design the MEMS wake detector. This paper introduces the wake detector’s principle, design, simulation, manufacturing process, and experimental characterization results. The lateral line structure of the wake detector not only maintains the vector performance of the turbulence sensor but also enables wake detection during AUV movement. The canal structure not only acted as a package to the detector protecting the cilium and crossbeam but also acted as a high-pass filter. Through COMSOL finite element simulation, the correlation between the detector’s sensitive microstructure, resonant frequency, and stress on the beam is analyzed, and the dimensions of the diversion cap structure are determined. Additionally, the detector’s performance in a wake flow environment is simulated. In the sensitivity calibration experiment, the wake detector exhibits a sensitivity of 147 mV·(m/s)−1, with a lower detection threshold of 0.3 m/s. The feasibility of the detector to detect a two-dimensional wake flow field is confirmed through vector experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.W. and H.Y.; methodology, R.W.; software, G.L.; validation, Q.Q., X.K. and S.W.; formal analysis, Q.Q. and X.K.; investigation, R.W. and H.Y.; resources, C.H. and Q.Q.; data curation, Q.Q., X.K. and S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Q.; writing—review and editing, R.W. and Q.Q.; visualization, X.K. and L.J.; supervision, G.Z. and W.Z.; project administration, Y.Y. and J.C.; funding acquisition, W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 52275578, 61927807), the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302123027, 20210302124203), National key research and development program (2020YFC0122102) and by Shanxi “1331 Project” Key Subject Construction (1331KSC).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hongzhou, C.H.A.I.; Zhenqiang, D.U.; Minzhi, X.; Ziru, H. The research status and development trend of UUVs cooperative localization technology. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2022, 10, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, M.; Dosso, E.; Barclay, R. Modeling AUV localization error in a long baseline acoustic positioning system. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 43, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, D.; Miller, A.; Farrell, J.A. Underwater inertial navigation with long base line transceivers: A near-real-time approach. IEEE Conf. Decis. Control 2013, 2, 5042–5047. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, B.; Deng, Z.; Fu, M.; Ling, Y. An acoustic communication time delays compensation method for master-slave AUV cooperative navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, G.; Bianco, P. Wake Studies and Simulations for Underwater Struggle; UDT Europe: Rostock, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; He, C.; Chen, C.Y. Defense Technologies Against Wake Homing Torpedo. Torpedo Technol. 2007, 15, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, J. Simulation and Optimization of Homing Strategy for Acoustic Wake Homing Torpedo. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2012, 24, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A.T.; Kaldenbach, F.; Rüter, A.; Bleckmann, H. What We Can Learn from Artificial Lateral Line sensor Arrays. In HAWKINSA Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life Ii; Poppera, N., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Dagamseh, A.; Wiegerink, R.; Lammerink, T.; Krijnen, G. Imaging dipole flow sources using an artificial lateral-line system made of biomimetic hair flow sensors. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Bleckmann, H. Determination of object position, vortex shedding frequency and flow velocity using artificial lateral line canals. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 2276–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Asadnia, M.; Miao, J.; Triantafyllou, M. Soft polymer membrane micro-sensor arrays inspired by the mechanodetectory lateral line on the blind cavefish. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottapalli, A.G.P.; Asadnia, M.; Miao, J.; Triantafyllou, M. Touch at a distance sensing: Lateral-line inspired MEMS flow sensors. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2014, 9, 046011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, G. Fish Lateral Line Inspired Flow sensors and Flow-aided Control: A Review. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 264–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Nguyen, N.; Chen, N.; Lockwood, M.; Tucker, C.; Hu, H.; Bleckmann, H.; Liu, C.; Jones, D.L. Artificial lateral line with biomimetic neuromasts to emulate fish sensing. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2010, 5, 016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Klein, A.; Bleckmann, H.; Liu, C. Artificial lateral line canal for hydrodynamic detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 023701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Engel, J.; Pandya, S.; Chen, N.; Tucker, C.; Coombs, S.; Jones, D.L.; Liu, C. Distant touch hydrodynamic imaging with an artificial lateral line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18891–18895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhang, D. Development of a Flexible Artificial Lateral Line Canal System for Hydrodynamic Pressure Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Peng, J.; Wu, B.; Xue, X.; Zang, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Vector High-Resolution Marine Turbulence sensor Based on a MEMS Bionic Cilium-Shaped Structure. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8741–8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, H. Design, fabrication, and preliminary characterization of a novel MEMS bionic vector hydrophone. Microelectron. J. 2007, 38, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qiao, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, J.; Xue, C.; Zhang, G. Modeling and characterization of a micromachined artificial hair cell vector hydrophone. Microsyst. Technol. 2008, 14, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, G.-J.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.-J.; Xue, C.-Y.; Yang, S.-E.; Zhang, W.-D. A bionic fish cilia median-low frequency three-dimensional piezoresistive MEMS vector hydrophone. Nano-Micro Lett. 2014, 6, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Qiao, Q.; Yang, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Song, D.; Jia, L.; Cui, J.; et al. High-Sensitivity MEMS Shear Probe for Autonomous Profiling Observation of Marine Turbulence. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, S.; Bleckmann, H.; Fay, R.R.; Popper, A.N. (Eds.) The Lateral Line System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.D.; Guan, L.G.; Zhang, G.J.; Xue, C.Y.; Zhang, K.R.; Wang, J.P. Research of DOA Estimation Based on Single MEMS Vector Hydrophone. Sensors 2009, 9, 6823–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, G.; Du, J.; Zhao, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J. ‘Lollipop-shaped’ high-sensitivity Microelectromechanical Systems vector hydrophone based on Parylene encapsulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 044501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shen, W.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Li, N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, G.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W. Design and implementation of a jellyfish otolith-inspired MEMS vector hydrophone for low-frequency detection. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, J.; Hanke, W.; Mogdans, J.; Bleckmann, H. Hydrodynamic stimuli and the fish lateral line. Nature 2000, 408, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.; Coombs, S.; Halstead, M. Biology of the mechanosensory lateral line in fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1995, 5, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Munz, H.; Bleckmann, H. The significance of lateral line canal morphology on the trunk of the marine teleost Xiphister atropurpureus (Stichaeidae). J. Comp. Physiol. A 2013, 199, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Bai, B.; Guo, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Xue, C.; et al. Wide-frequency-bandwidth whisker-inspired MEMS vector hydrophone encapsulated with parylene. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 07LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).