The Impact of Side-Scan Sonar Resolution and Acoustic Shadow Phenomenon on the Quality of Sonar Imagery and Data Interpretation Capabilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Underwater Targets Selected for the Research
2.2. Sonar Systems Used for the Research
2.3. Field Survey and Data Acquisition
- side scan sonar layback [m];
- distance between GPS antenna and A-frame [m];
- height of cable block on A-frame above water line [m];
- depth of side-scan sonar [m].
- water depth [m].
- side scan sonar altitude [m].
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SeaBed2030. Available online: https://seabed2030.org/our-mission/ion%20—%20Seabed%202030 (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Wölfl, A.C.; Snaith, H.; Amirebrahimi, S.; Devey, C.W.; Dorschel, B.; Ferrini, V.; Huvenne, V.A.I.; Jakobsson, M.; Jencks, J.; Johnston, G.; et al. Seafloor Mapping—The Challenge of a Truly Global Ocean Bathymetry. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.F.; Sallée, J.-B. Jets and topography: Jet transitions and the impact on transport in the Antarctic circumpolar current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenty, I.; Willis, J.K.; Khazendar, A.; Dinardo, S.; Forsberg, R.; Fukumori, I.; Holland, D.; Jakobsson, M.; Moller, D.; Morison, J.; et al. Oceans melting Greenland: Early results from NASA’S ocean-ice mission in Greenland. Oceanography 2016, 29, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Lubchenco, J.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Novelli, C.; Roberts, C.; Sumaila, U.R. Assessing real progress towards effective ocean protection. Mar. Policy 2018, 91, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHO Publication. Manual on Hydrography, 1st ed.; International Hydrographic Organization: Monte Carlo, Monaco, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, L.A. Frontiers in seafloor mapping and visualization. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2006, 27, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherakis, D.; Vicen-Bueno, R. Sensors to Increase the Security of Underwater Communication Cables: A Review of Underwater Monitoring Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Cui, W.; Chen, C. Review of Underwater Sensing Technologies and Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yu, J.; Huang, Y.; Cui, J.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Ren, K. Automatic tracking method for submarine cables and pipelines of AUV based on side scan sonar. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theberge, A. Appendix: The History of Seafloor Mapping. In Ocean Globe; Breman, J., Ed.; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 237–274. [Google Scholar]
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Brown, C.J. Grand Challenges in Acoustic Remote Sensing: Discoveries to Support a Better Understanding of Our Changing Planet. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 2, 824848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, H.K. Multibeam bathymetric sonar: Sea beam and hydro chart. Mar. Geod. 1980, 4, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, M.F. Introducing an operational multi-beam array sonar. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 1970, 47, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, V.; Allenou, J.P. SeaBeam multibeam echo sounding in Jean Charcot: Description, evaluation and first results. Intern. Hydrog. Rev. 1979, 1, 35–67. [Google Scholar]
- Grządziel, A. Side Scan Sonar—Method of searching for and detecting of underwater objects. Marit. Rev. 2006, 1, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Tang, Y. Side-Scan Sonar and Sub-Bottom Profiler Surveying. In High-Resolution Seafloor Survey and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Blondel, P. Handbook of Sidescan Sonar; Praxis Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-3-540-49886-5. [Google Scholar]
- Barngrover, C.; Althoff, A.; DeGuzman, P.; Kastner, R. A brain–computer interface (BCI) for the detection of mine-like objects in sidescan sonar imagery. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 41, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatan, M.; Daliri, M.R.; Shahri, A.M. Underwater cable detection in the images using edge classification based on texture information. Measurement 2016, 91, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.P. Fast target detection in synthetic aperture sonar imagery: A new algorithm and large-scale performance analysis. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 40, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Adams, J.; Mindell, D.; Foley, B. Imaging underwater for archaeology. J. Field Archaeol. 2000, 27, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.P.; Helferty, M. The geological interpretation of side–scan sonar. Rev. Geophys. 1990, 28, 357–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, T.F.; Stubblefield, W.L.; Swift, D.J.P. Large-scale current lineations on the central New Jersey shelf: Investigations by side-scan sonar. Mar. Geol. 1974, 17, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.A.; Delgado, I. Side-Scan Sonar Imaging of Sediment Bedload. In Encyclopedia of Estuaries; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Kennish, M.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.; Rahman, A.; Kline, R.; Rahman, M. Side scan sonar: A cost-efficient alternative method for measuring seagrass cover in shallow environments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 207, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, P.; Zhu, H. A Local Region-Based Level Set Method With Markov Random Field for Side-Scan Sonar Image Multi-Level Segmentation. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucieer, V.L. Object-oriented classification of sidescan sonar data for mapping benthic marine habitats. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Ruan, F.; Qiao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, X.; Dang, L. Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification Based on Style Transfer and Pre-Trained Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumser, T.K.; Türkay, M. Postmortem changes of human bodies on the Bathyal Sea floor—Two cases of aircraft accidents above the open sea. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, G.; Pinksen, J. Underwater technology used to bring closure to families of drowning victims. J. Ocean Technol. 2010, 5, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, R.; Ruffell, A.; Hughes, D.; Pringle, J. Geophysics and the search of freshwater bodies: A review. Sci. Justice 2010, 50, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes Clarke, J.E.; Mayer, L.A.; Wells, D.E. Shallow-water imaging multibeam sonars: A new tool for investigating seafloor processes in the coastal zone and on the continental shelf. Mar. Geophys. Res. 1996, 18, 607–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergent, G.; Monnier, B.; Clabaut, P.; Gascon, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Valette-Sansevin, A. Innovative method for optimizing Side-Scan Sonar mapping: The blind band unveiled. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 194, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, P.; Murton, B.J. Handbook of Seafloor Sonar ImageryI; John Wiley & Sons Publisher: Chichester, UK, 1997; p. 314. ISBN 0-471-96217-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Chu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J. Active Learning for Recognition of Shipwreck Target in Side-Scan Sonar Image. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gong, Q.; Huang, C.; Zheng, G.; Ma, J. Real-Time Underwater Maritime Object Detection in Side-Scan Sonar Images Based on Transformer-YOLOv5. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jin, S.; Zhao, J.; Huang, C.; Yu, Y. AUV-Based Side-Scan Sonar Real-Time Method for Underwater-Target Detection. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grządziel, A. Side-scan sonar geometry—The key to understanding and interpreting sonar images. Marit. Rev. 2004, 7–8, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fakiris, E.; Papatheodorou, G.; Geraga, M.; Ferentinos, G. An automatic target detection algorithm for swath Sonar backscatter imagery, using image texture and independent component analysis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Meng, J.; Zhao, J. Bottom Detection from Backscatter Data of Conventional Side Scan Sonars through 1D-UNet. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Tian, J.; Liu, J. Underwater Object Classification Method Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution Feature Fusion in Sonar Images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, A.; Amar, A.; Gilboa, A. Mine-Like Objects detection in Side-Scan Sonar images using a shadows-highlights geometrical features space. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailhas, Y.; Petillot, Y.; Capus, C. High-Resolution Sonars: What Resolution Do We Need for Target Recognition? EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2010, 2010, 205095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reed, S.; Petillot, Y.; Bell, J. Automated approach to classification of mine-like objects in sidescan sonar using highlight and shadow information. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2004, 151, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumudham, R.; Rajendran, V. Super resolution enhancement of underwater sonar images. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, D.M.; Zarillo, G.A.; Johnston, S. Recent Developments in the Geomorphic Investigation of Engineered Tidal Inlets. Coast. Eng. J. 2003, 45, 565–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.J.; Healy, C.A.; Parker, K.; Lowers, B. Detecting submerged objects: The application of side scan sonar to forensic contexts. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurton, X. An Introduction to Underwater Acoustics: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Burdic, W.S. Underwater Acoustic System Analysis, 2nd ed.; Peninsula Publishing: Westport, CO, USA, 2003; p. 489. ISBN 978-0932146632. [Google Scholar]
- Mazel, C. Side Scan Sonar Record Interpretation; Klein Associates: Oakland, CA, USA, 1985; p. 146. ISBN 0932146503. [Google Scholar]
- Hac, B. Preliminary Action Plan for the Retrieval Activities on the Franken Shipwreck. Report from the Research Expedition Carried out on the Franken Shipwreck on 23rd–28th April 2018 in the Framework of the Project “Reduction of the Negative Impact of Oil Spills from the Franken Shipwreck” The MARE Foundation, Warsaw. 2018. Available online: https://fundacjamare.pl/file/repository/MARE_report_EN_FRANKEN_1_.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Soroka, M. Polish Navy Ships 1945–1980; Wyd. Morskie: Gdańsk, Poland, 1986; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Gelewski, T.M. Wilhelm Gustloff i General von Steuben Statki Śmierci czy Zbrodnia Wojenna na Morzu? A.E.L. Publishing House: Gdańsk, Poland, 1997; ISBN 83-903896-4-9. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Grządziel, A. Baltic Titanics—History and current state. M/s Goya. Marit. Rev. 2005, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Grooss, P. The Naval War in the Baltic 1939–1945; Naval Institute Press: Barnsley, UK, 2017; p. 416. ISBN 152670000X. [Google Scholar]
- Feldens, P. Super Resolution by Deep Learning Improves Boulder Detection in Side Scan Sonar Backscatter Mosaics. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, L.; Shang, C.; Bates, R. Object detection at different resolution in archaeological side-scan sonar images. Eur. Ocean. 2005, 1, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, A. Side-scan Sonar as a tool for seafloor imagery: Examples from the Mediterranean continental margin. In Sonar Systems; Kolev, N., Ed.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeser, A.J.; Litts, T.L.; Tracy, T. Using low-cost side-scan sonar for benthic mapping throughout the lower Flint River, Georgia, USA. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pang, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhu, H. An Image Quality Improvement Method in Side-Scan Sonar Based on Deconvolution. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.C.; Gerg, I.D.; Blanford, T.E. Interpolation Kernels for Synthetic Aperture Sonar Along-Track Motion Estimation. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 45, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewicz, D.; Rowiński, L. Experimental evaluation of high frequency side scan sonar as object search and identification tool. Hydroacoustics 2006, 9, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkerkerk, H.-J.; Theijs, M.J. Handbook of Offshore Surveying. Acquisition Sensors, 2nd ed.; Skilltrade BV: Voorschoten, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Łukaszewicz, D.; Rowiński, L. Possibilities of detection and identification objects located on the sea bottom by means of a simple sidescan sonar. Hydroacoustics 2005, 8, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bowens, A. Underwater Archaeology: The NAS Guide to Principles and Practice; Wiley-Blackwell: West Sussex, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, R.; Dean, M.; Lawrence, M.; Liscoe, S.; Boland, D. Backscatter responses and resolution considerations in archaeological side-scan sonar surveys: A control experiment. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

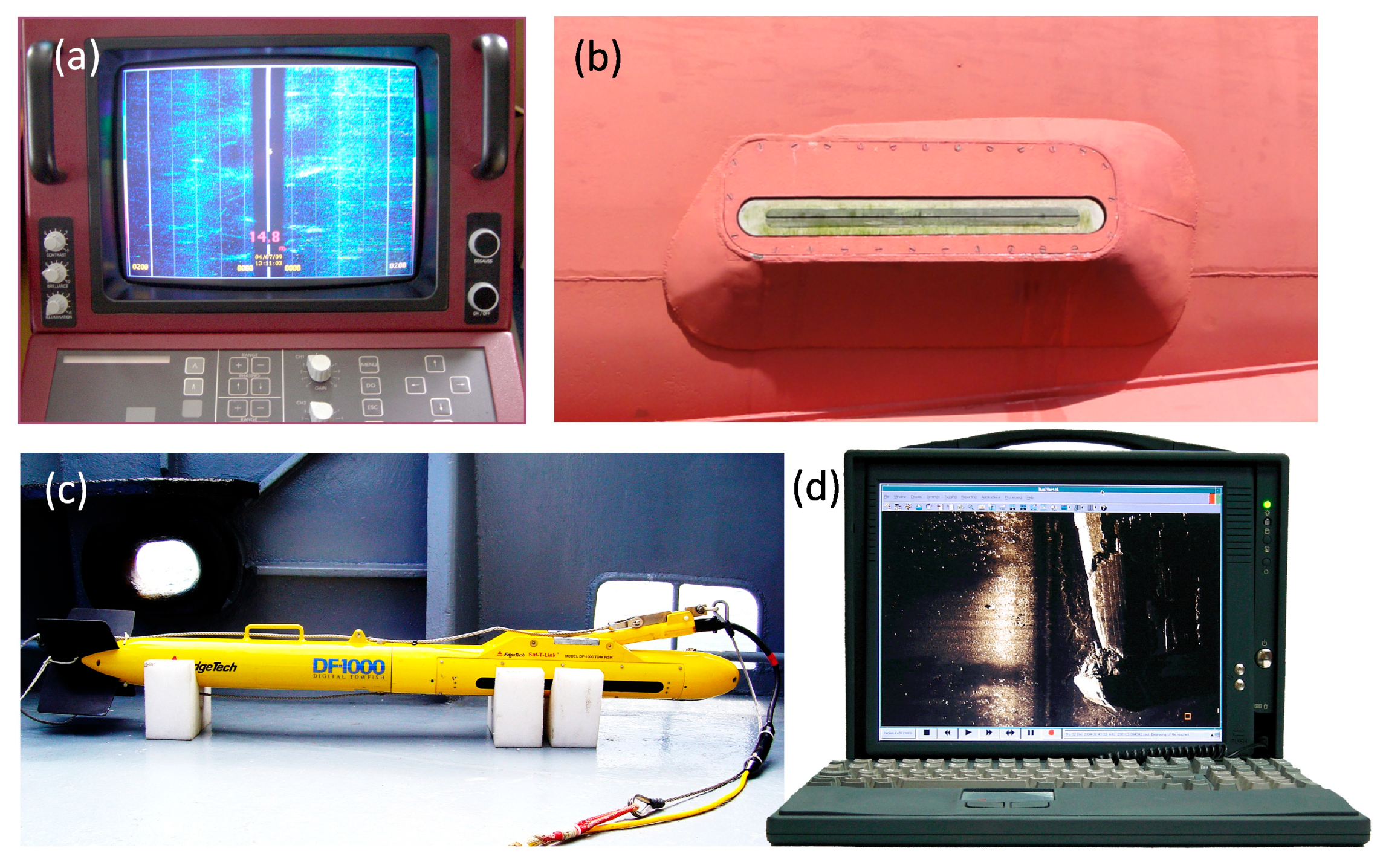

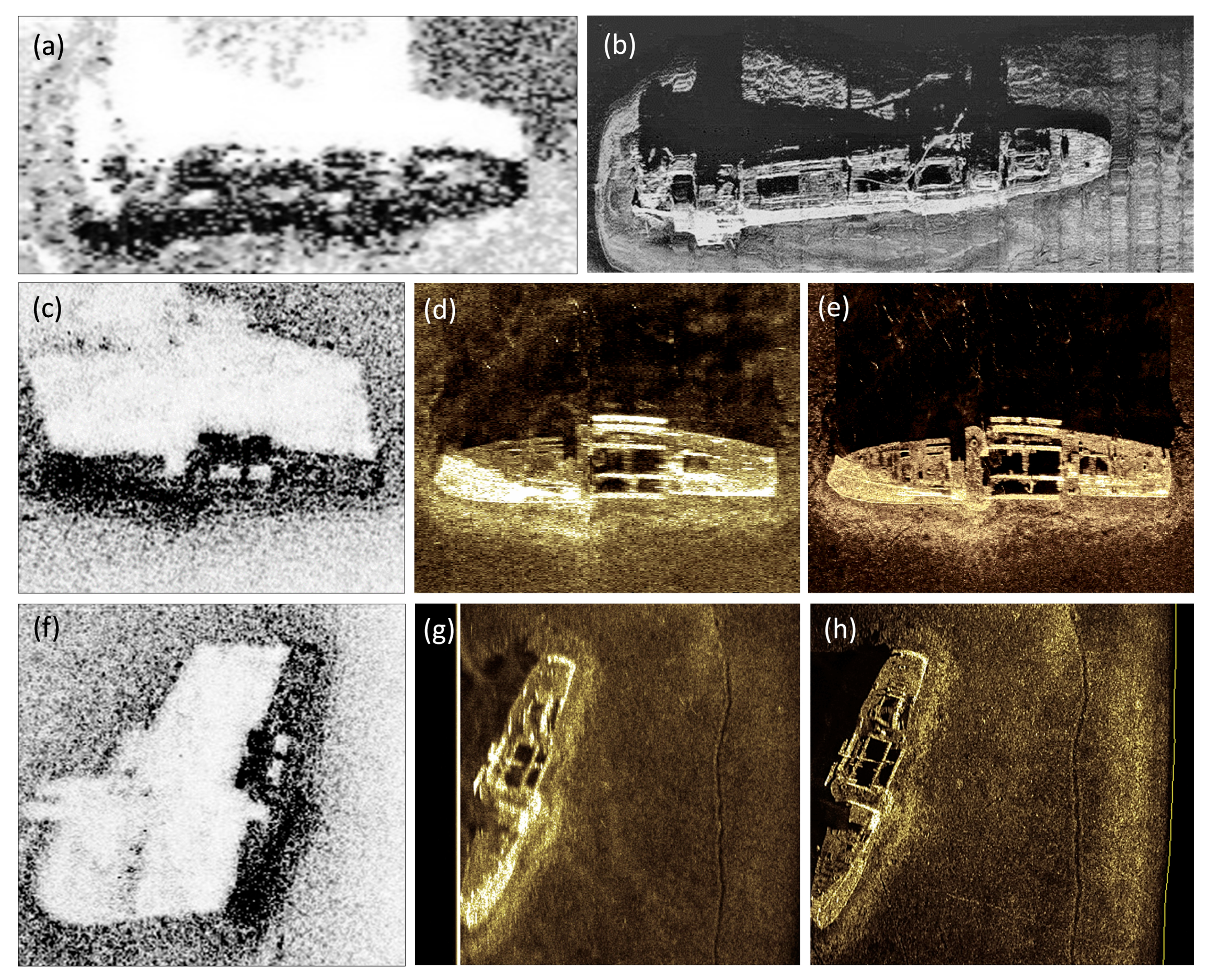


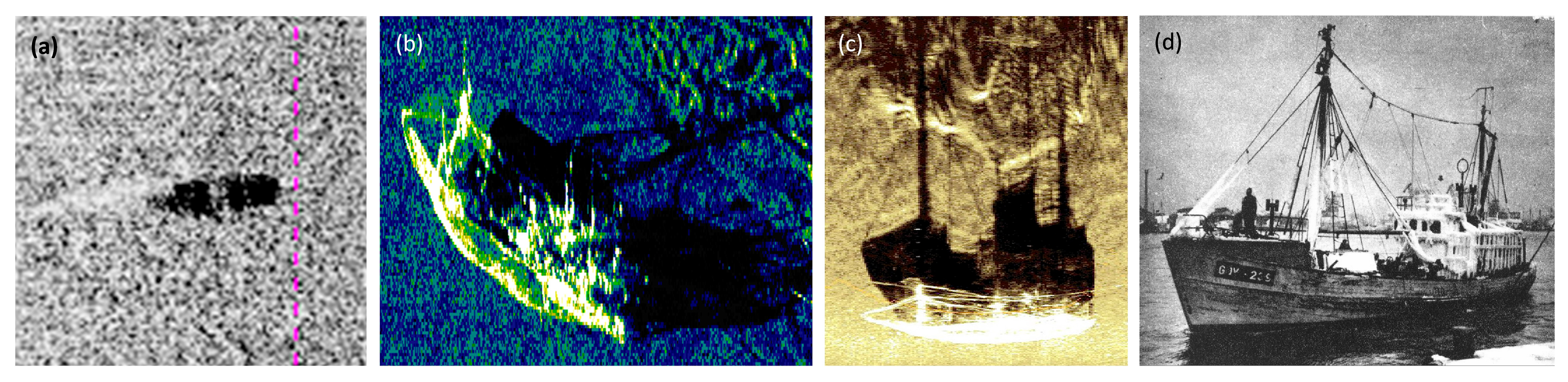
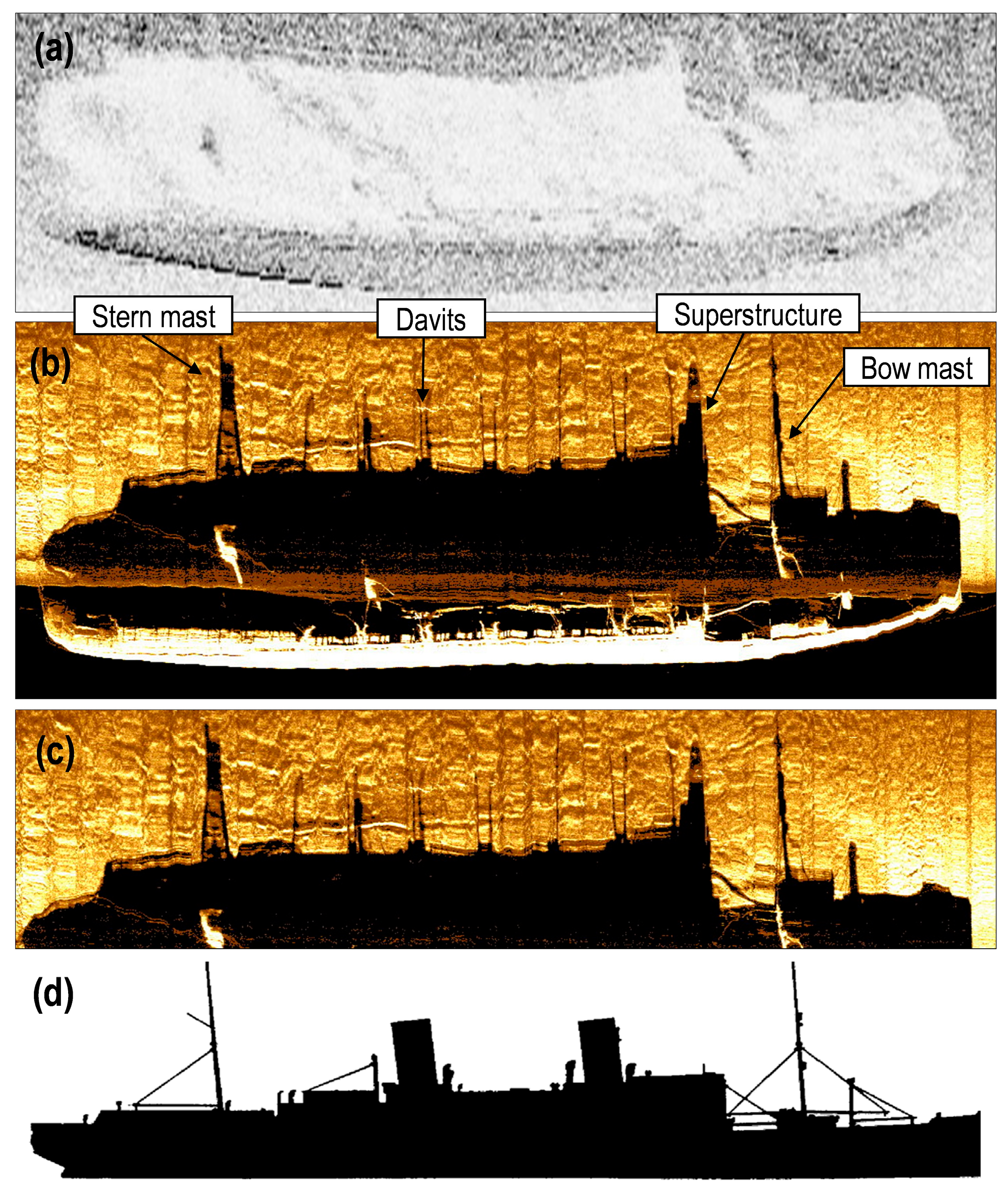
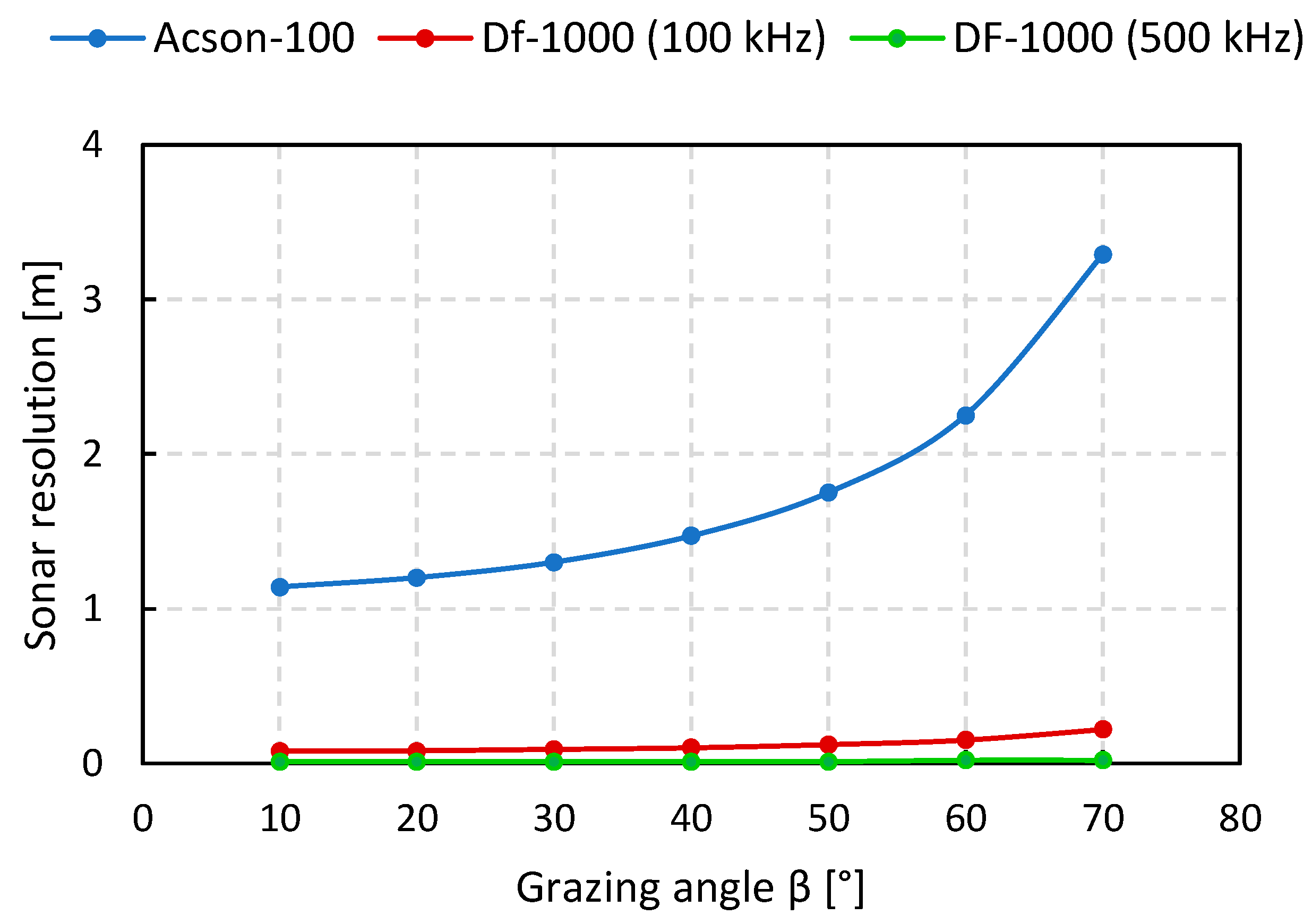
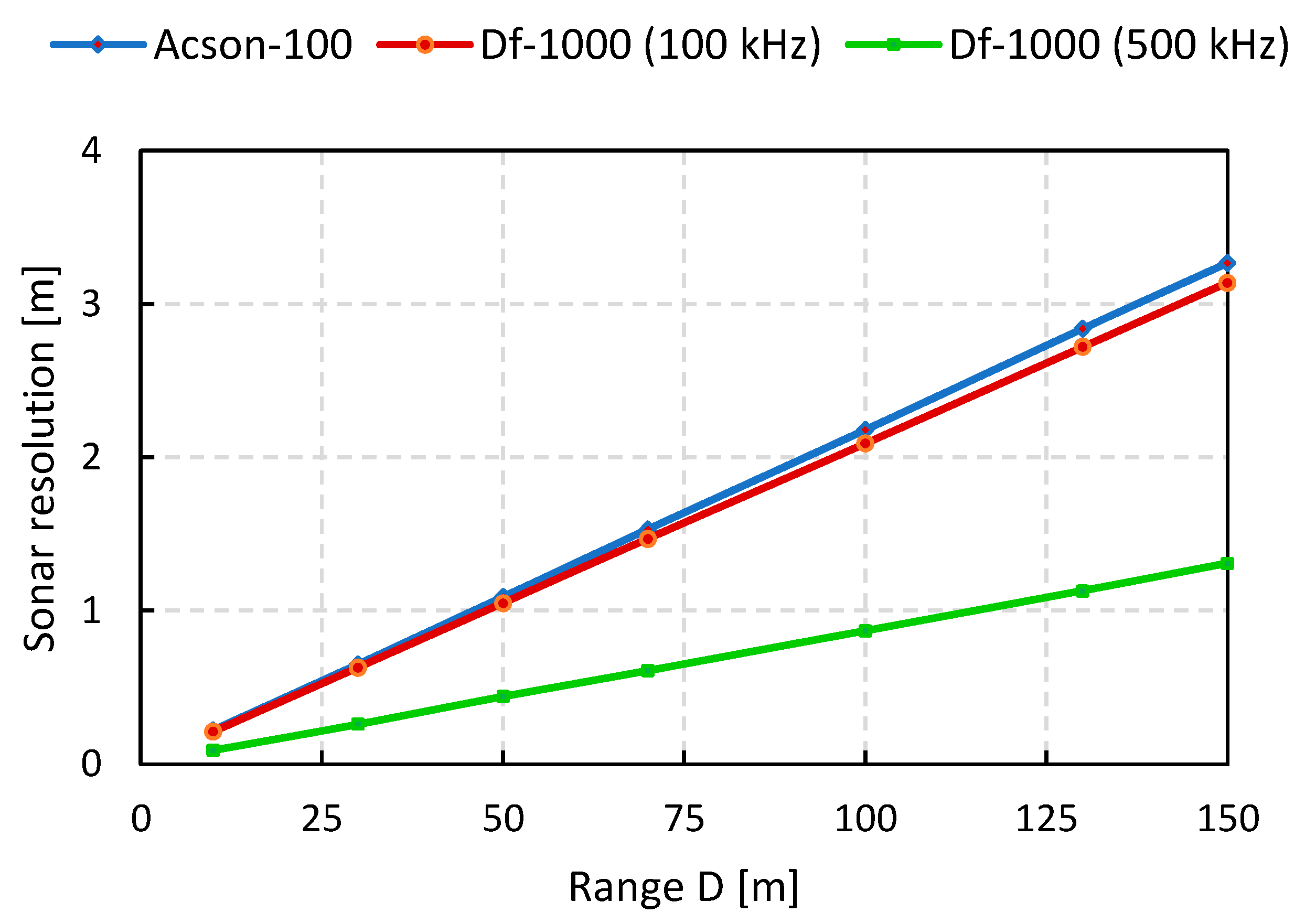
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 100 kHz (standard) |
| 500 kHz (high resolution) | |
| Pulse length | 0.1 ms (100 kHz) |
| 0.01 ms (500 kHz) | |
| Beamwidth (horizontal) | 1.2° (100 kHz) |
| 0.5° (500 kHz) | |
| Beamwidth (vertical) | 50° tilted down 20° |
| A/D resolution | 12 bits/sample |
| Heading | Built-in flux gate compass |
| Tow speed | 12.7 knots maximum |
| Size | 11.4 cm × 158 cm |
| Weight | 30 kg |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 100 kHz |
| Pulse length | 1 ms |
| Beamwidth (horizontal) | 1.25° |
| Beamwidth (vertical) | 75° |
| Acoustic power | 800 W |
| Max depth | 100 m |
| Ranges | 0–500 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grządziel, A. The Impact of Side-Scan Sonar Resolution and Acoustic Shadow Phenomenon on the Quality of Sonar Imagery and Data Interpretation Capabilities. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235599
Grządziel A. The Impact of Side-Scan Sonar Resolution and Acoustic Shadow Phenomenon on the Quality of Sonar Imagery and Data Interpretation Capabilities. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235599
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrządziel, Artur. 2023. "The Impact of Side-Scan Sonar Resolution and Acoustic Shadow Phenomenon on the Quality of Sonar Imagery and Data Interpretation Capabilities" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235599
APA StyleGrządziel, A. (2023). The Impact of Side-Scan Sonar Resolution and Acoustic Shadow Phenomenon on the Quality of Sonar Imagery and Data Interpretation Capabilities. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235599






