Epoch-Wise Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Receiver DCB under High and Low Solar Activity Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. MCCL for Receiver DCB Variation and Ionosphere Parameter Estimation
2.2. Isolation of Initial RCB from MCCL-Derived Ionosphere Parameters
3. Results and Analysis
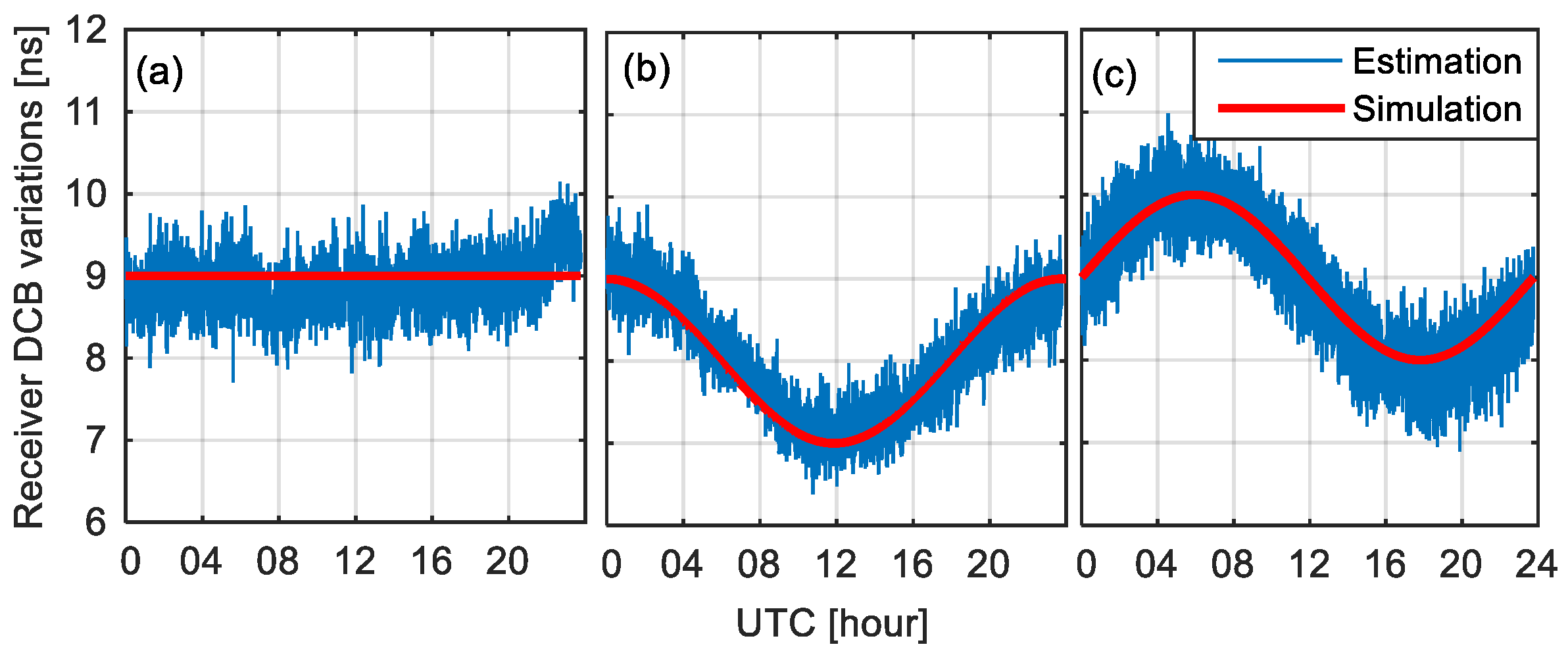
3.1. Validation of Epoch-Wise Receiver DCB Estimates Based on Simulated and Experimental Data
3.2. Statistical Results for the Intraday Stability of Receiver DCBs at IGS Stations
3.3. Intraday Variation Characteristics of Epoch-Wise Receiver DCBs
3.4. Factors Affecting the Intraday Variability of Receiver DCBs
3.5. Effects of Intraday Variations in Receiver DCBs on STEC Observables
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.; Sanz, J. New approaches in global ionospheric determination using ground GPS data. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 1999, 61, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrud, L.; Jovancevic, A.; Brown, A.; Wilson, D.; Ganguly, S. Ionospheric measurement with GPS: Receiver techniques and methods. Radio Sci. 2008, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Rosen, I.G.; Tsurutani, B.T.; Verkhoglyadova, O.P.; Meng, X.; Mannucci, A.J. Statistical characterization of ionosphere anomalies and their relationship to space weather events. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2016, 6, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jakowski, N.; Heise, S.; Wehrenpfennig, A.; Schlüter, S.; Reimer, R. GPS/GLONASS-based TEC measurements as a contributor for space weather forecast. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Mei, D. Ionospheric TEC disturbances over China during the strong geomagnetic storm in September 2017. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2529–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.; Ding, F.; Kiryushkin, V.; Astafyeva, E.; Jin, S.; Sankov, V. TEC response to the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in comparison with other strong earthquakes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3601–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Liu, A.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, K. Regional ionospheric TEC modeling based on a two-layer spherical harmonic approximation for real-time single-frequency PPP. J. Geodesy 2019, 93, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, J.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Sanz, J.; Ramos-Bosch, P.; Aragon-Angel, A.; Orus, R.; Ochieng, W.; Feng, S.; Jofre, M.; Coutinho, P. Enhanced precise point positioning for GNSS users. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4213–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.; Odijk, D. A novel un-differenced PPP-RTK concept. J. Navig. 2011, 64, S180–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, P.; Zha, J.; Liu, T. Integer-estimable FDMA model as an enabler of GLONASS PPP-RTK. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Hou, P. Ionosphere-weighted undifferenced and uncombined PPP-RTK: Theoretical models and experimental results. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, P.; Zha, J.; Liu, T. PPP–RTK functional models formulated with undifferenced and uncombined GNSS observations. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Three methods to retrieve slant total electron content measurements from ground-based GPS receivers and performance assessment. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, C. Single-frequency precise point positioning (PPP) for retrieving ionospheric TEC from BDS B1 data. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Pengfei, C.; Jinzhong, B.; Hanjiang, W.; Hua, W. Calibration of regional ionospheric delay with uncombined precise point positioning and accuracy assessment. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 121, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Ou, J. A generalized trigonometric series function model for determining ionospheric delay. Prog. Nat. Sci.-Mater. Int. 2004, 14, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Hernandez-Pajares, M.; Huo, X. SHPTS: Towards a new method for generating precise global ionospheric TEC map based on spherical harmonic and generalized trigonometric series functions. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciraolo, L.; Azpilicueta, F.; Brunini, C.; Meza, A.; Radicella, S.M. Calibration errors on experimental slant total electron content (TEC) determined with GPS. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, Y.V.; Mylnikova, A.; Kunitsyn, V.; Padokhin, A. Influence of GPS/GLONASS differential code biases on the determination accuracy of the absolute total electron content in the ionosphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 2015, 55, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC maps: A reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardón, E.; Zarraoa, N. Estimation of total electron content using GPS data: How stable are the differential satellite and receiver instrumental biases? Radio Sci. 1997, 32, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Shi, L.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, Z. Accuracy analysis of the GPS instrumental bias estimated from observations in middle and low latitudes. In Annales Geophysicae; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Coster, A.; Williams, J.; Weatherwax, A.; Rideout, W.; Herne, D. Accuracy of GPS total electron content: GPS receiver bias temperature dependence. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y. Estimation and analysis of the short-term variations of multi-GNSS receiver differential code biases using global ionosphere maps. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tan, B. Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshin, M. A new algorithm for single receiver DCB estimation using IGS TEC maps. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Shi, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, Z. The variation of the estimated GPS instrumental bias and its possible connection with ionospheric variability. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2014, 57, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.; Miguel Juan, J.; Rovira-Garcia, A.; González-Casado, G. GPS differential code biases determination: Methodology and analysis. Gps Solut. 2017, 21, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P. Zero-baseline Analysis of GPS/BeiDou/Galileo Between-Receiver Differential Code Biases (BR-DCBs): Time-wise Retrieval and Preliminary Characterization. J. Inst. Navig. 2016, 63, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ammar, M.; Aquino, M.; Vadakke Veettil, S.; Andreotti, M. Estimation and analysis of multi-GNSS differential code biases using a hardware signal simulator. Gps Solut. 2018, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. A modified carrier-to-code leveling method for retrieving ionospheric observables and detecting short-term temporal variability of receiver differential code biases. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teunissen, P. Zero Order Design: Generalized Inverses, Adjustment, the Datum Problem and S-Transformations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.S.; Yuan, Y.B.; Li, H.; Ou, J.K.; Huo, X.L. Two-step method for the determination of the differential code biases of COMPASS satellites. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.C.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Characterization of multi-GNSS between-receiver differential code biases using zero and short baselines. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]












| Receiver Name | Receiver Type | Antenna Type | Location | Observation Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLFT | JPS LEGACY | JPSREGANT_DD_E | 51.98°E, 4.39°N | 2010, day 172 |
| DLF4 | SEPT POLARX2 | LEIAT504 | ||
| DLF5 | SEPT POLARX2 | LEIAT504 | ||
| ALGO | AOA BENCHMARK ACT | AOAD/M_T | 78.07°W, 45.95°N | 2017, day 07 |
| ALG2 | TPS NET-G3A | NOV750.R4 | ||
| ALG3 | TPS NETG3 | TPSCR.G3 |
| Station | 2014 | 2017 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receiver Type | Antenna Type | Receiver Type | Antenna Type | |
| CHIL | TPS NET-G3A | TPSCR.G3 | TPS NET-G3A | TPSCR.G3 |
| COYQ | TRIMBLE NETRS | ASH700936D_M | TRIMBLE NETRS | ASH700936D_M |
| ZECK | JAVAD TRE_G3TH | JAVRINGANT_DM | JAVAD TRE_G3TH | JAVRINGANT_DM |
| POVE | TRIMBLE NETR5 | TRM29659.00 | TRIMBLE NETRS | ASH701945B_M |
| COCO | TRIMBLE NETR8 | AOAD/M_T | SEPT POLARXS | AOAD/M_T |
| SFER | TRIMBLE NETRS | TRM29659.00 | LEICA GR25 | LEIAR20 |
| PRDS | TPS NET-G3A | AOAD/M_T | JAVAD TRE_G3TH | AOAD/M_T |
| PALV | JPS EGGDT | ASH700936D_M | JAVAD TRE_G3TH | ASH700936D_M |
| YAR2 | ASHTECH UZ-12 | AOAD/M_T | SEPT POLARX4TR | AOAD/M_T |
| Time | Firmware Version | Temperature Span (°C) | PCC | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 January 2017 | 4.02.386 | 22.9~44.2 | −0.914 | −0.11 |
| 31 January 2017 | 4.10.598 | 21.6~42.6 | −0.927 | −0.16 |
| 17 June 2017 | 4.11.606 | 2.5~24.7 | −0.791 | −0.092 |
| 29 June 2017 | 4.11.606 | 1.7~17.5 | −0.693 | −0.078 |
| 21 May 2018 | 4.11.606 | 2.3~22.5 | −0.52 | −0.036 |
| 22 May 2018 | 4.20.232 | 7.3~22.92 | −0.65 | −0.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Xia, L.; Lin, H.; Li, Q. Epoch-Wise Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Receiver DCB under High and Low Solar Activity Conditions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082190
Zhang X, Xia L, Lin H, Li Q. Epoch-Wise Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Receiver DCB under High and Low Solar Activity Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(8):2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiao, Linyuan Xia, Hong Lin, and Qianxia Li. 2023. "Epoch-Wise Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Receiver DCB under High and Low Solar Activity Conditions" Remote Sensing 15, no. 8: 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082190
APA StyleZhang, X., Xia, L., Lin, H., & Li, Q. (2023). Epoch-Wise Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Receiver DCB under High and Low Solar Activity Conditions. Remote Sensing, 15(8), 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15082190








