Multi-View Feature Fusion and Rich Information Refinement Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a network designed for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images, named the Multi-View Feature Deep Fusion and Rich Information Refinement Network (MFRNet). MFRNet utilizes MAFF to extract features from Multi-View and uses a Conv-MLP for comprehensive feature fusion. The feature refinement is achieved through EFRM. Our designed encoder can be applied to different depths and types of backbone networks. Additionally, it can address the shortcomings of CNN and Transformer in extracting comprehensive information.
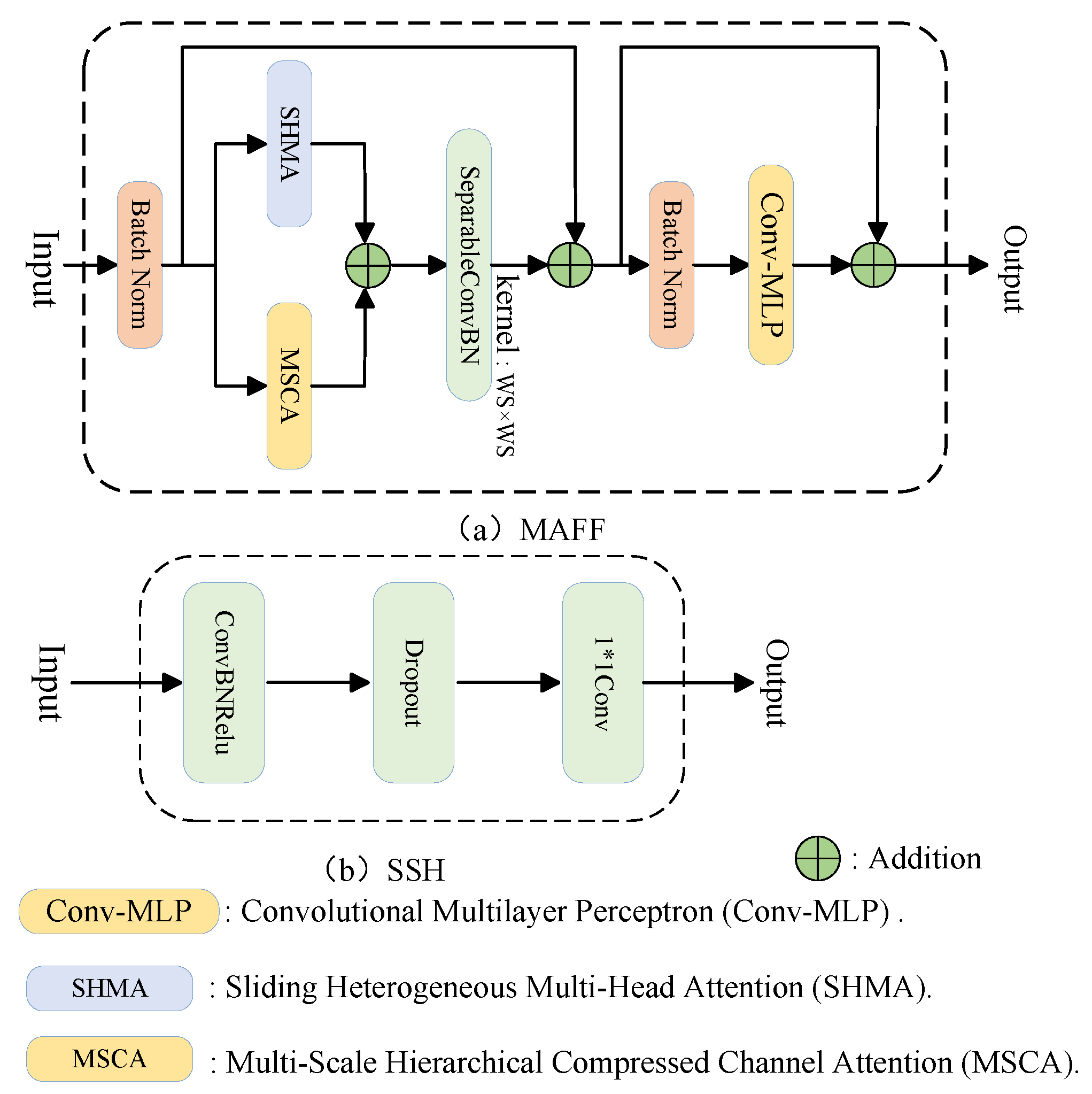
- To extract and fuse features from Multi-View, we introduce MAFF, a Transformer-type module incorporating the MSCA for reliable channel information and the SHMA for extracting local, non-local, and positional information. Finally, we employ a Conv-MLP to scale the features in the channel dimension, achieving the goal of deep feature fusion.
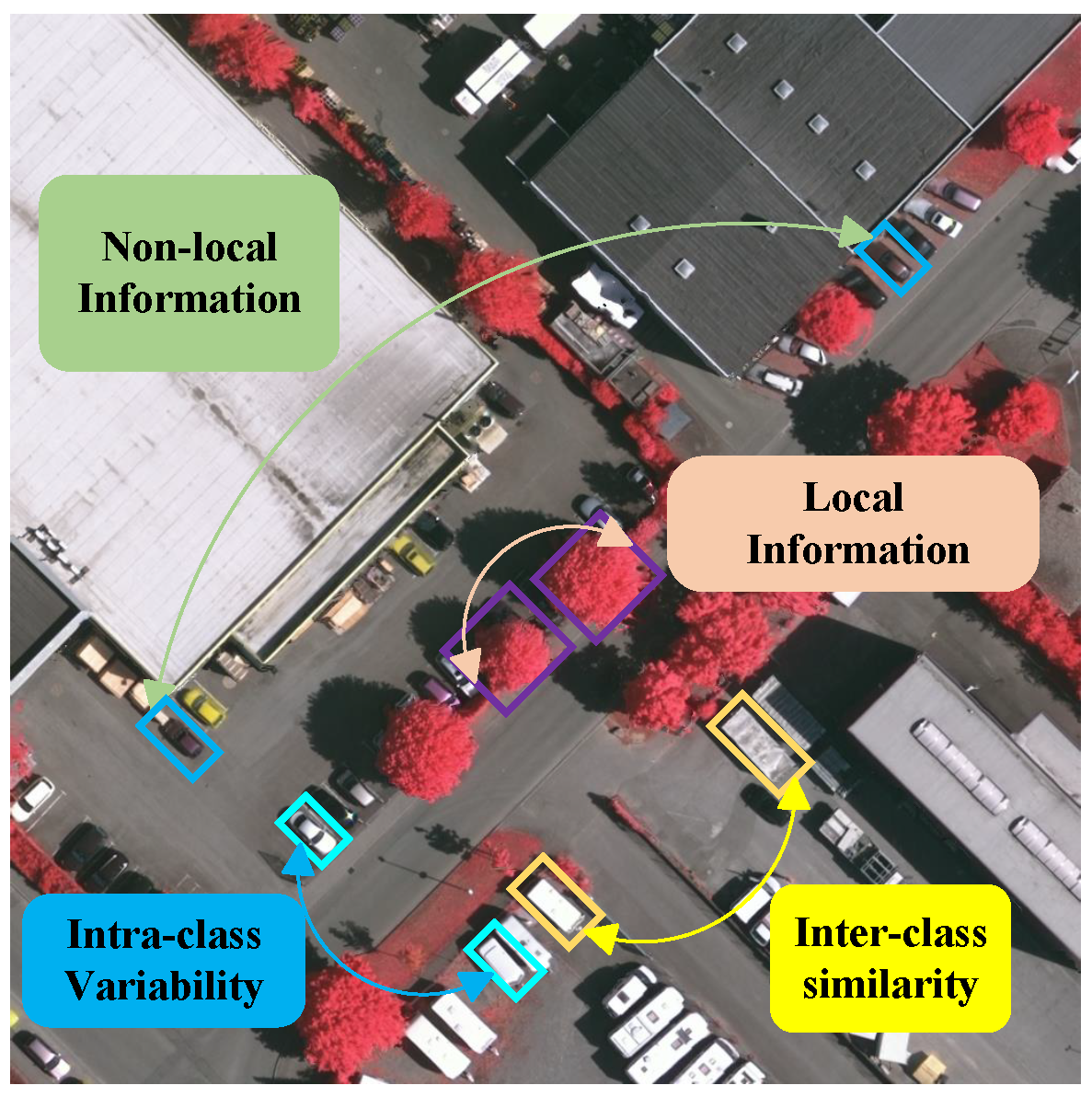
- We creatively introduced EFRM to facilitate the interaction between remote information and local semantic information. By obtaining refinement weights, rich features can be refined, addressing the issue of balanced attention across various categories caused by feature redundancy. This assists the model in focusing on similar categories within the optical remote sensing dataset.
2. Related Work
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Based on CNN
2.1.1. CNN Semantic Segmentation Network
2.1.2. Attention Mechanism in CNN
2.2. Transformer-Based Semantic Segmentation
2.2.1. General Semantic Segmentation
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation
3. Methodology
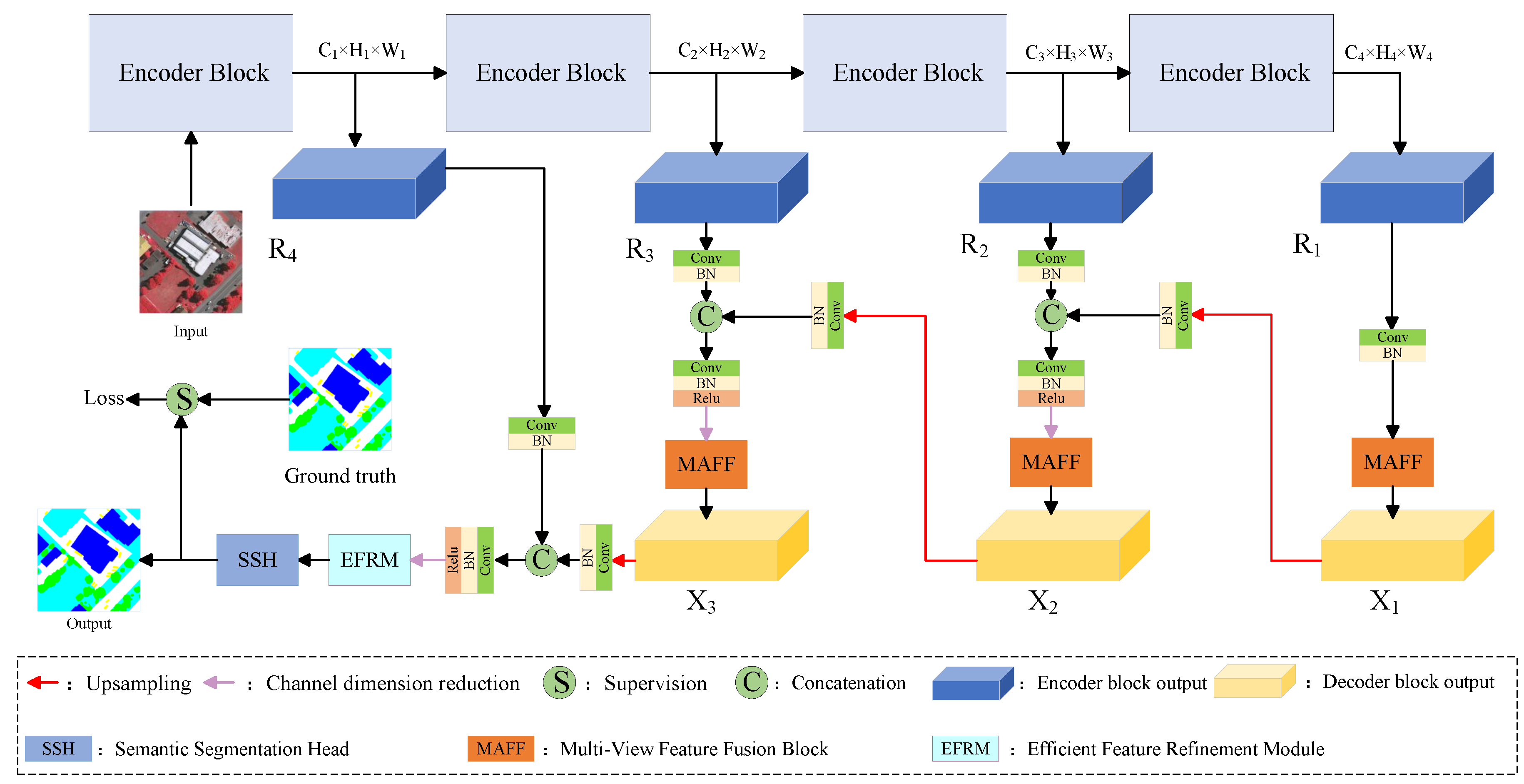
3.1. Overall Architecture of the Model
3.2. Encoder
3.3. Multi-View Feature Fusion Block
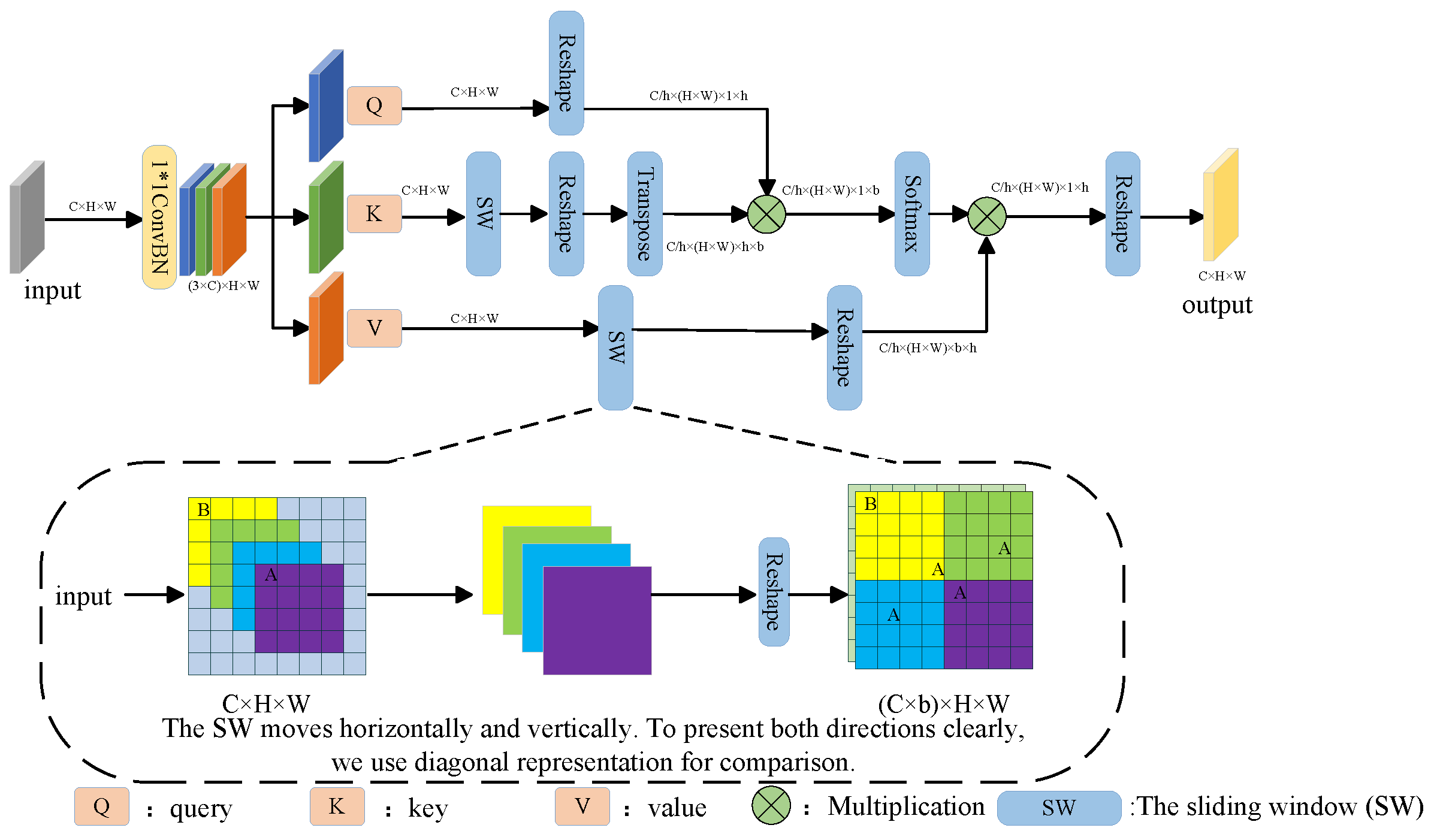
3.3.1. Sliding Heterogeneous Multi-Head Attention
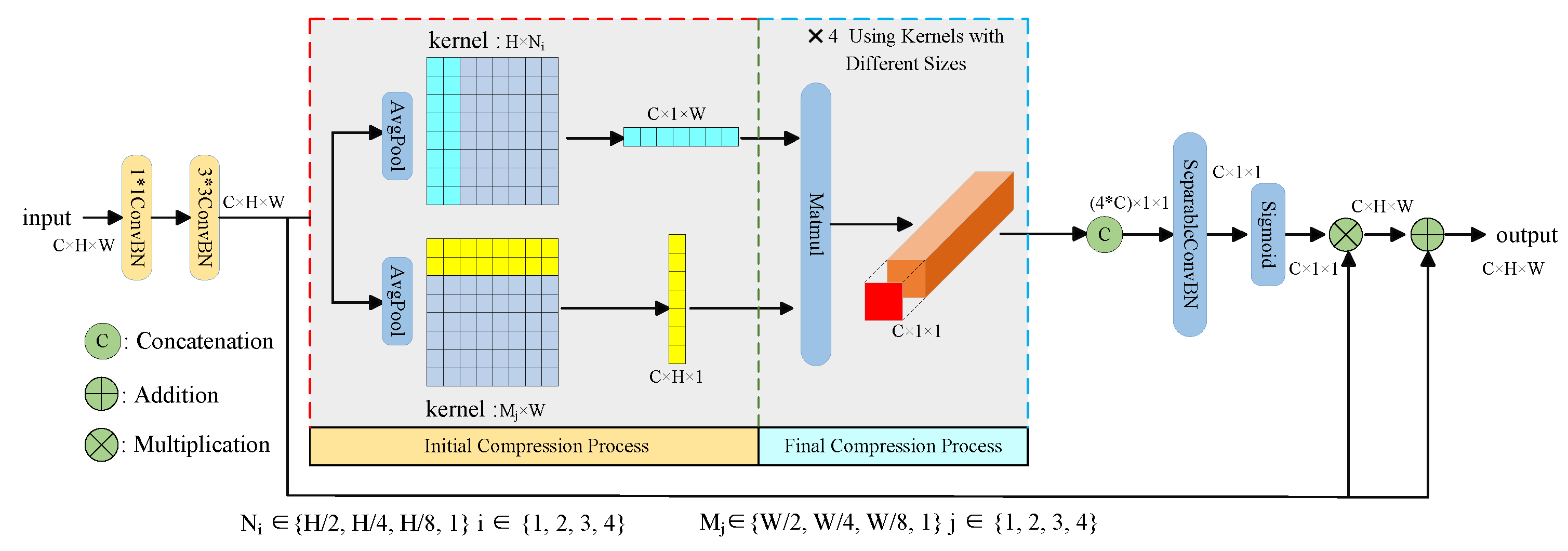
3.3.2. Multi-Scale Hierarchical Compressed Channel Attention
3.4. Efficient Feature Refinement Module
4. Experimental Comparison and Analysis
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. Vaihingen
4.1.2. Potsdam
4.2. Experimental Design
4.2.1. Implementation Details
4.2.2. Loss Function
4.2.3. Validation Metrics
4.3. Ablation Experiment
4.3.1. Ablation Experiment Analysis of the Main Components
4.3.2. Subcomponent Ablation Experiments
4.3.3. Ablation Experiment Analysis of SHMA Window Size
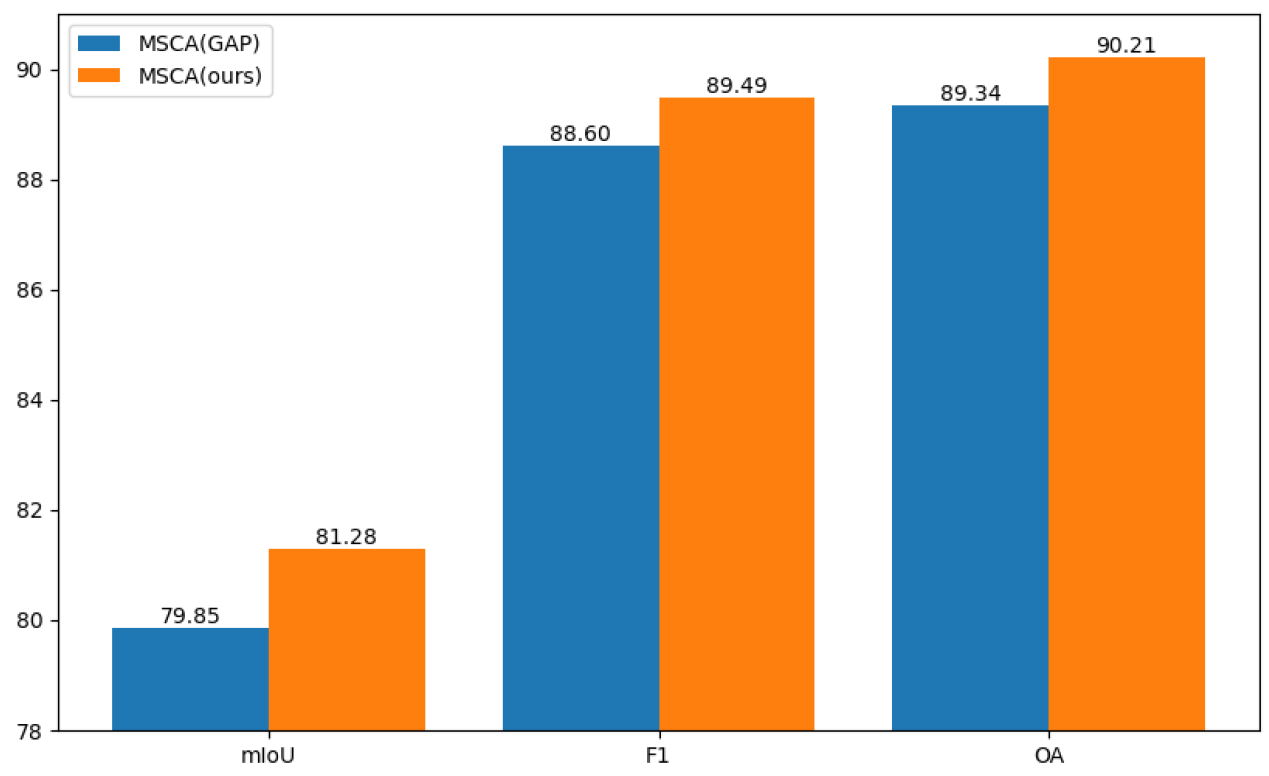
4.3.4. Internal Ablation Experiments on MSCA
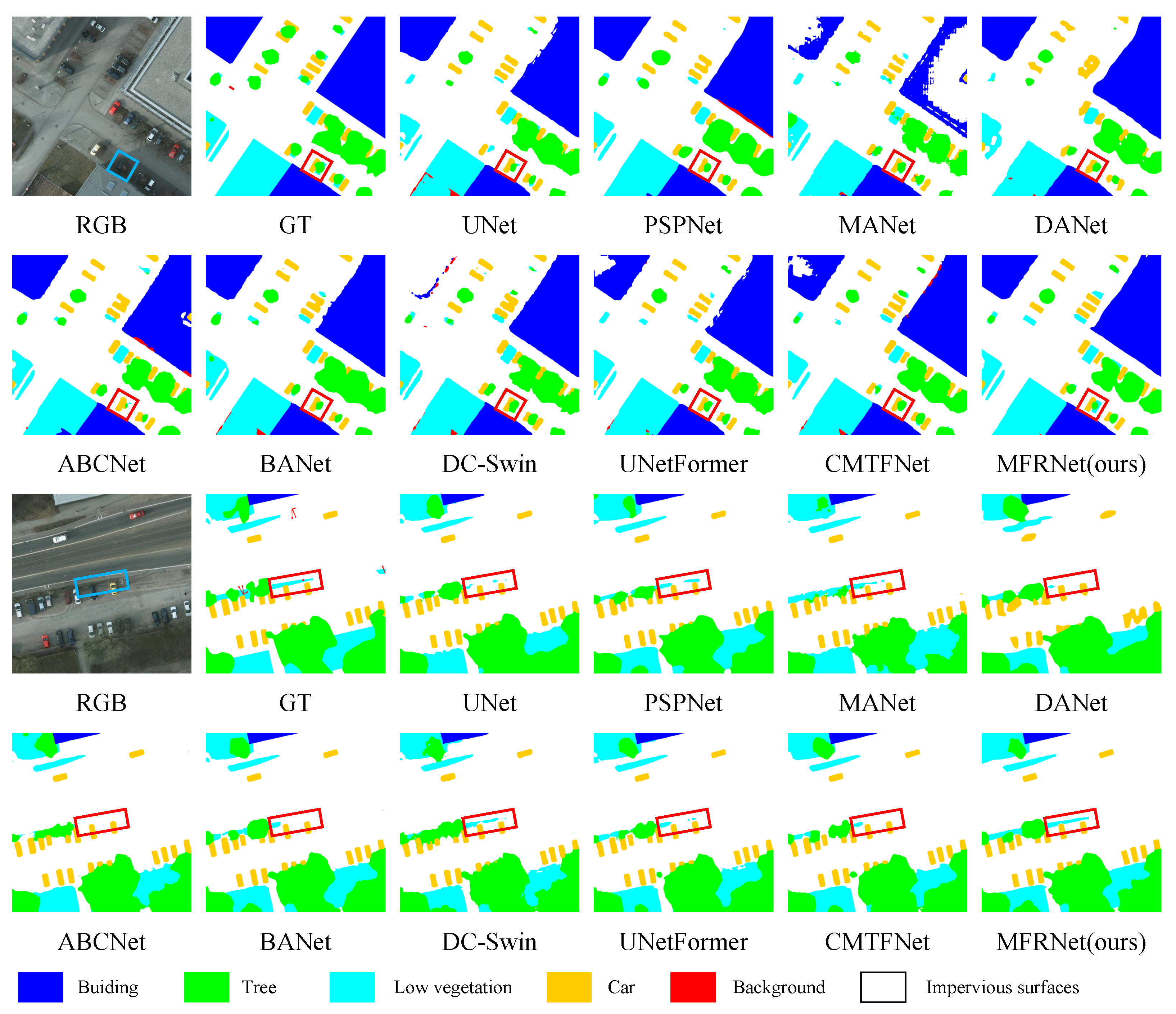
4.4. Comparative Experiments with Advanced Networks
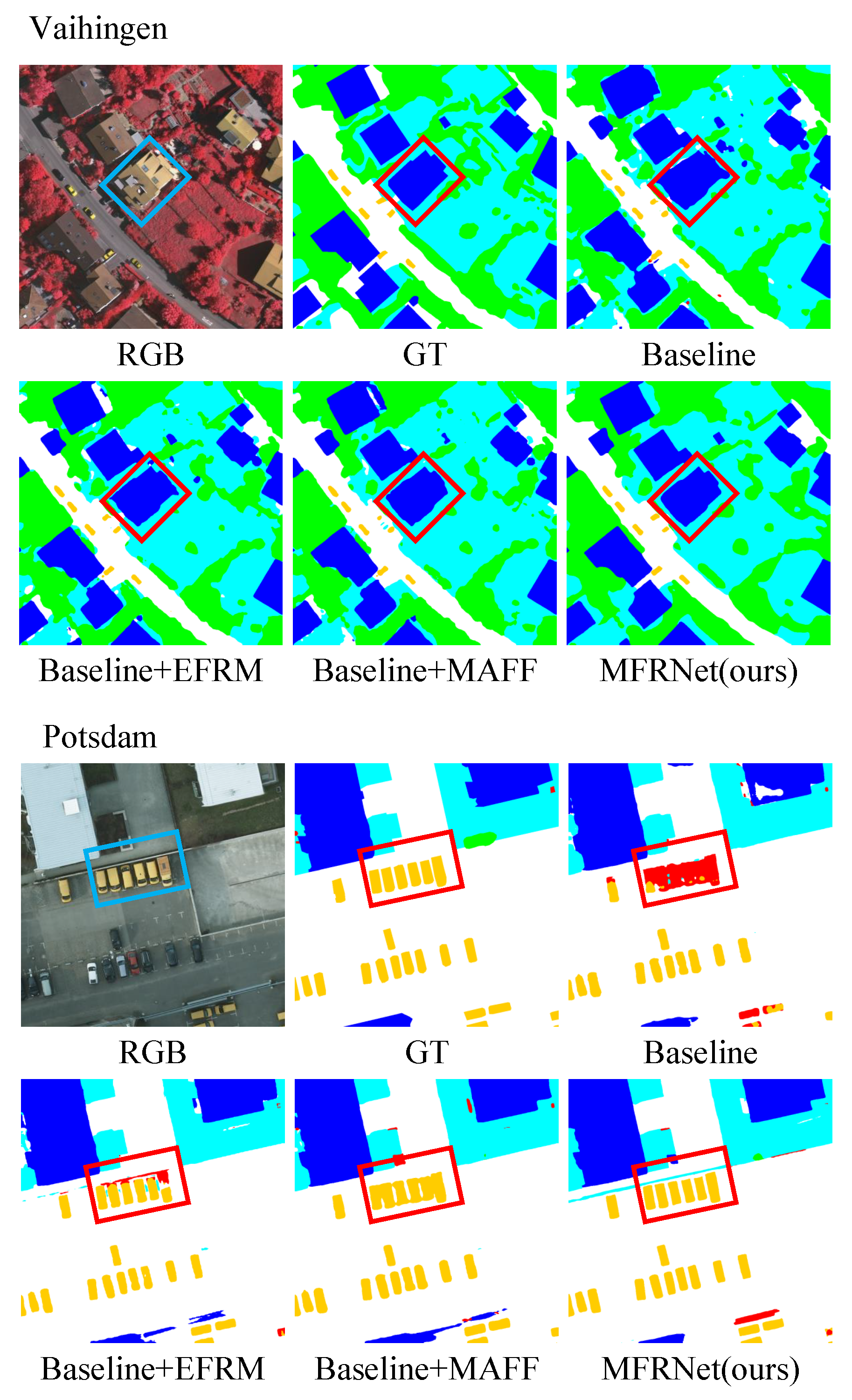
- Our model utilizes a U-shaped structure to obtain features at multiple scales while preserving abundant shape information from the shallow layers of the encoder. The designed MAFF module can extract and fuse diverse feature information. Compared to other models, our model’s features are more comprehensive.
- Compared with other models, we include EFRM in the tail to refine the rich features that have just fused shape information by interacting with long-distance information and local semantic information. Preventing redundancy in feature information from leading to category discrimination errors.
- Through comparative and ablation experiments, we can fully confirm that our designed encoder compensates for the shortcomings of feature extraction in CNN and Transformer models. Additionally, it achieves better segmentation results in deeper networks by utilizing feature refinement. This proves that our belief in the necessity of applying multi-view feature extraction and feature refinement in the field of remote sensing image semantic segmentation is correct.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, X.; Shi, J.; Gu, L. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 169, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Tian, Q.; Qu, H. ACTNet: A dual-attention adapter with a CNN-transformer network for the semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Han, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Lithological mapping of geological remote sensing via adversarial semi-supervised segmentation network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 103536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Ren, D.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Lu, F.; Wu, X. MCAFNet: A multiscale channel attention fusion network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sahli, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; He, D.; Yue, A. A hybrid land-use mapping approach based on multi-scale spatial context. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Du, R. TCUNet: A Lightweight Dual-Branch Parallel Network for Sea–Land Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrah, J. Fully Convolutional Networks for Dense Semantic Labelling of High-Resolution Aerial Imagery. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02585. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 10–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Cheng, J. Semantic Segmentation of High Resolution Remote Sensing Image Based on Batch-Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 3856–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Threshold Attention Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4600312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dana, K.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tyagi, A.; Agrawal, A. Context Encoding for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7151–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Feng, Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C. Long-Tailed Effect Study in Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation Based on Graph Kernel Principles. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.; Wang, L.; Li, H. Asymmetric Cross-Attention Hierarchical Network Based on CNN and Transformer for Bitemporal Remote Sensing Images Change Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3245674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Yang, Z. DMAU-Net: An Attention-Based Multiscale Max-Pooling Dense Network for the Semantic Segmentation in VHR Remote-Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; An, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H. Towards Robust LiDAR-Camera Fusion in BEV Space via Mutual Deformable Attention and Temporal Aggregation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 5753–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W. DBCT-Net: A dual branch hybrid CNN-transformer network for remote sensing image fusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 233, 120829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mei, S. Rethinking Transformers for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3302024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yu, X. CMTFNet: CNN and Multiscale Transformer Fusion Network for Remote-Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3314641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. LSRFormer: Efficient Transformer Supply Convolutional Neural Networks With Global Information for Aerial Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 3366709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Sun, S.; Hu, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, W. DeepUNet: A Deep Fully Convolutional Network for Pixel-Level Sea-Land Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampffmeyer, M.; Salberg, A.B.; Jenssen, R. Semantic Segmentation of Small Objects and Modeling of Uncertainty in Urban Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiao, L.; Yang, J.; Wei, Z. CNN-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network With Pixel- and Superpixel-Level Feature Fusion for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8657–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6230–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.M.; Feng, J. Strip Pooling: Rethinking Spatial Pooling for Scene Parsing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4002–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Su, J.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. Multiattention Network for Semantic Segmentation of Fine-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3093977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. ABCNet: Attentive bilateral contextual network for efficient semantic segmentation of Fine-Resolution remotely sensed imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 181, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Álvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.15203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lau, R. BiFormer: Vision Transformer with Bi-Level Routing Attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 10323–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Duan, C.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Fang, S. A Novel Transformer Based Semantic Segmentation Scheme for Fine-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 3143368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Geng, J.; Jiang, W. MMT: Mixed-Mask Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3289408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, L.; Huang, G.; Du, D.; Wang, X. Attention-Guided Unified Network for Panoptic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7019–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.; El-Nouby, A.; Touvron, H.; Stock, P.; Joulin, A.; Jégou, H.; Douze, M. LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet’s Clothing for Faster Inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12239–12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Zheng, S. A2-FPN for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remotely sensed images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 1131–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Che, R.; Hong, T.; Ma, M.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhang, W. SACANet: Scene-aware class attention network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Multimedia Expo. (ICME), Brisbane, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; pp. 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ma, M.; Hu, C.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhang, W. Log-Can: Local-Global Class-Aware Network For Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




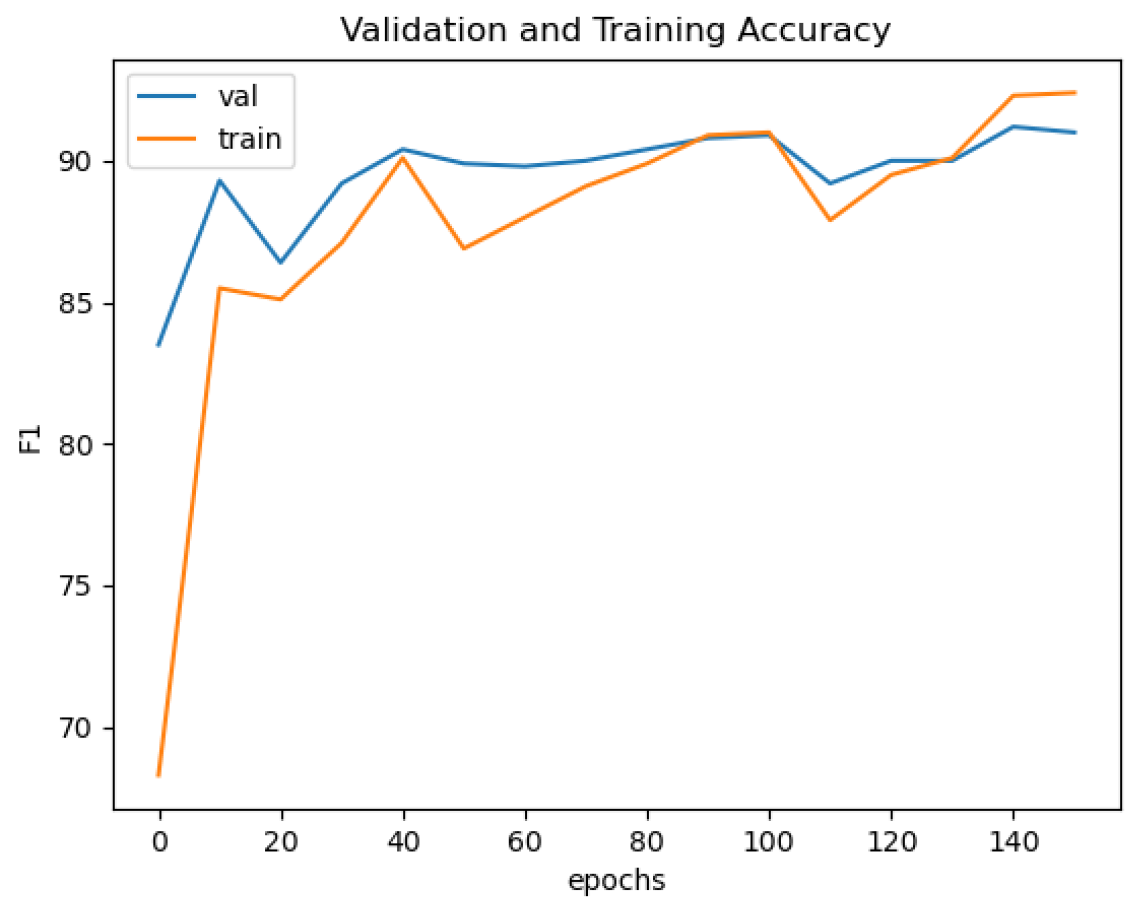
| Models | Component | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | F1 | mIoU | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFRNet-R | Baseline (ResNet18) | 13.02 | 131.22 | 87.84 | 78.69 | 89.09 |
| Baseline + EFRM | 13.22 | 138.32 | 89.73 | 81.68 | 90.59 | |
| Baseline + MAFF | 18.25 | 160.38 | 90.46 | 82.85 | 91.03 | |
| MFRNet | 18.47 | 167.48 | 91.45 | 84.51 | 91.97 | |
| MFRNet-S | Baseline (Swin-S) | 45.91 | 68.95 | 85.06 | 75.18 | 89.75 |
| Baseline + EFRM | 49.53 | 70.61 | 89.88 | 81.86 | 90.41 | |
| Baseline + MAFF | 54.46 | 76.27 | 91.10 | 82.77 | 91.42 | |
| MFRNet | 54.46 | 77.94 | 92.14 | 85.66 | 92.64 |
| Component | SHMA | MSCA | EFRM | F1 | mIoU | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 87.84 | 78.69 | 89.09 | |||
| Baseline + MAFF (SHMA) | √ | 89.79 | 81.29 | 90.31 | ||
| Baseline + MAFF (MSCA) | √ | 89.49 | 81.28 | 90.21 | ||
| Baseline + EFRM | √ | 89.73 | 81.68 | 90.59 | ||
| Baseline + MAFF (SHMA + MSCA) | √ | √ | 90.46 | 82.85 | 91.03 | |
| Baseline + MAFF (SHMA) + EFRM | √ | √ | 90.81 | 83.25 | 91.43 | |
| Baseline + MAFF (MSCA) + EFRM | √ | √ | 90.86 | 83.84 | 91.47 | |
| Baseline + MAFF (SHMA + MSCA) + EFRM | √ | √ | √ | 91.45 | 84.51 | 91.97 |
| Method | Backbone | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | Imp.Surf. | Building | Lowveg. | Tree | Car | F1 | mIoU | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet [8] | ResNet18 | 22.61 | 71.26 | 91.11 | 95.25 | 81.11 | 88.21 | 83.48 | 87.84 | 78.69 | 89.09 |
| PSPNet [26] | ResNet18 | 12.66 | 40.10 | 91.91 | 95.25 | 80.92 | 86.70 | 79.47 | 86.85 | 77.28 | 89.21 |
| DANet [38] | ResNet18 | 12.09 | 36.92 | 90.17 | 94.74 | 81.12 | 86.90 | 66.77 | 83.94 | 73.46 | 88.59 |
| BANet [39] | ResT-Lite | 12.14 | 49.09 | 93.05 | 96.41 | 82.49 | 88.99 | 91.03 | 90.49 | 82.93 | 90.94 |
| ABCNet [30] | ResNet18 | 14.06 | 18.72 | 88.20 | 91.17 | 78.19 | 86.05 | 68.80 | 82.48 | 70.96 | 86.62 |
| UNetFormer [34] | ResNet18 | 11.14 | 10.94 | 93.13 | 96.42 | 83.86 | 89.60 | 88.97 | 90.40 | 82.57 | 91.26 |
| DC-Swin [35] | Swin-S | 63.80 | 258.13 | 93.36 | 96.54 | 84.74 | 89.92 | 86.17 | 90.15 | 82.36 | 91.58 |
| MANet [29] | ResNet18 | 11.43 | 82.96 | 89.89 | 93.23 | 79.45 | 86.04 | 72.11 | 84.14 | 73.35 | 87.61 |
| -FPN [40] | ResNet18 | 22.77 | 158.84 | 92.69 | 96.15 | 83.64 | 89.38 | 88.81 | 90.13 | 82.31 | 90.89 |
| SACANet [41] | HRNet-v2 | 28.81 | 210.65 | 92.04 | 95.84 | 84.89 | 91.00 | 86.32 | 90.02 | 82.09 | 91.00 |
| LOG-CAN [42] | ResNet50 | 29.48 | 184.7 | 91.13 | 94.78 | 84.57 | 89.45 | 81.14 | 88.21 | 79.25 | 90.07 |
| CMTFNet [20] | ResNet50 | 28.68 | 122.07 | 92.13 | 95.22 | 83.16 | 89.23 | 85.59 | 89.07 | 80.57 | 90.37 |
| MFRNet-R (ours) | ResNet18 | 18.47 | 167.48 | 93.72 | 97.11 | 84.78 | 90.19 | 91.46 | 91.45 | 84.51 | 91.97 |
| MFRNet-S (ours) | Swin-S | 54.46 | 77.94 | 94.43 | 97.31 | 85.94 | 90.90 | 92.15 | 92.14 | 85.66 | 92.64 |
| Method | Backbone | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | Imp.Surf. | Building | Lowveg. | Tree | Car | F1 | mIoU | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet [8] | ResNet18 | 22.61 | 71.26 | 90.42 | 94.41 | 83.51 | 85.69 | 94.35 | 89.68 | 81.58 | 87.69 |
| PSPNet [26] | ResNet18 | 12.66 | 40.10 | 90.64 | 94.64 | 84.38 | 85.85 | 94.08 | 89.92 | 81.95 | 88.25 |
| DANet [38] | ResNet18 | 12.09 | 36.92 | 91.06 | 95.22 | 86.09 | 87.97 | 86.00 | 89.27 | 80.80 | 89.34 |
| BANet [39] | ResT-Lite | 12.14 | 49.09 | 92.68 | 96.24 | 87.06 | 88.79 | 95.68 | 92.09 | 85.56 | 90.67 |
| ABCNet [30] | ResNet18 | 14.06 | 18.72 | 90.36 | 93.34 | 84.05 | 84.98 | 93.73 | 89.29 | 80.90 | 87.64 |
| UNetFormer [34] | ResNet18 | 11.14 | 10.94 | 92.07 | 95.86 | 86.74 | 88.05 | 95.21 | 91.59 | 84.69 | 90.03 |
| DC-Swin [35] | Swin-S | 63.80 | 258.13 | 93.03 | 96.42 | 87.78 | 88.67 | 95.85 | 92.35 | 85.99 | 90.95 |
| MANet [29] | ResNet18 | 11.43 | 82.96 | 86.73 | 89.37 | 80.60 | 81.01 | 91.22 | 85.91 | 75.36 | 83.75 |
| -FPN [40] | ResNet18 | 22.77 | 158.84 | 92.59 | 96.08 | 87.06 | 88.54 | 95.86 | 92.03 | 85.45 | 90.54 |
| SACANet [41] | HRNet-v2 | 28.81 | 210.65 | 92.92 | 96.03 | 88.13 | 88.97 | 96.65 | 92.54 | 86.31 | 90.98 |
| LOG-CAN [42] | ResNet50 | 29.48 | 184.70 | 91.91 | 96.60 | 86.07 | 88.17 | 95.00 | 91.55 | 84.66 | 90.17 |
| CMTFNet [20] | ResNet50 | 28.68 | 122.07 | 92.69 | 95.87 | 87.54 | 88.14 | 95.50 | 91.95 | 85.30 | 90.57 |
| MFRNet-R (ours) | ResNet18 | 18.47 | 167.48 | 93.12 | 96.67 | 87.68 | 89.05 | 96.44 | 92.59 | 86.43 | 91.12 |
| MFRNet-S (ours) | Swin-S | 54.46 | 77.94 | 94.73 | 97.30 | 88.71 | 90.03 | 96.95 | 93.55 | 88.08 | 92.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Cheng, S.; Du, A. Multi-View Feature Fusion and Rich Information Refinement Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173184
Liu J, Cheng S, Du A. Multi-View Feature Fusion and Rich Information Refinement Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173184
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiang, Shuli Cheng, and Anyu Du. 2024. "Multi-View Feature Fusion and Rich Information Refinement Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173184
APA StyleLiu, J., Cheng, S., & Du, A. (2024). Multi-View Feature Fusion and Rich Information Refinement Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173184






