TF-REF-RNN: Time-Frequency and Reference Signal Feature Fusion Recurrent Neural Network for Underwater Backscatter Signal Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Source Separation Method
2.2. Underwater Acoustics Signal Separation
3. Problem Description
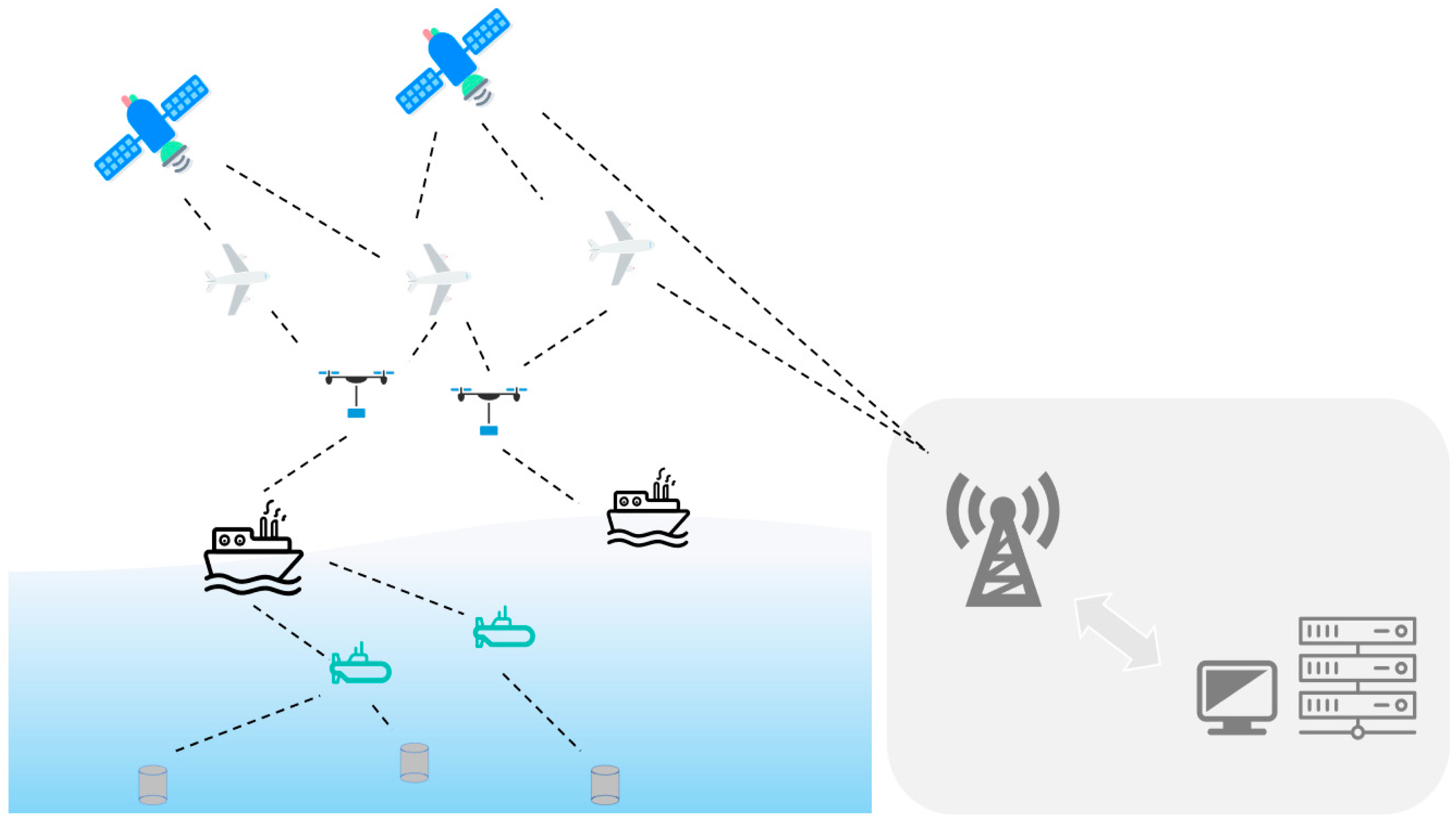
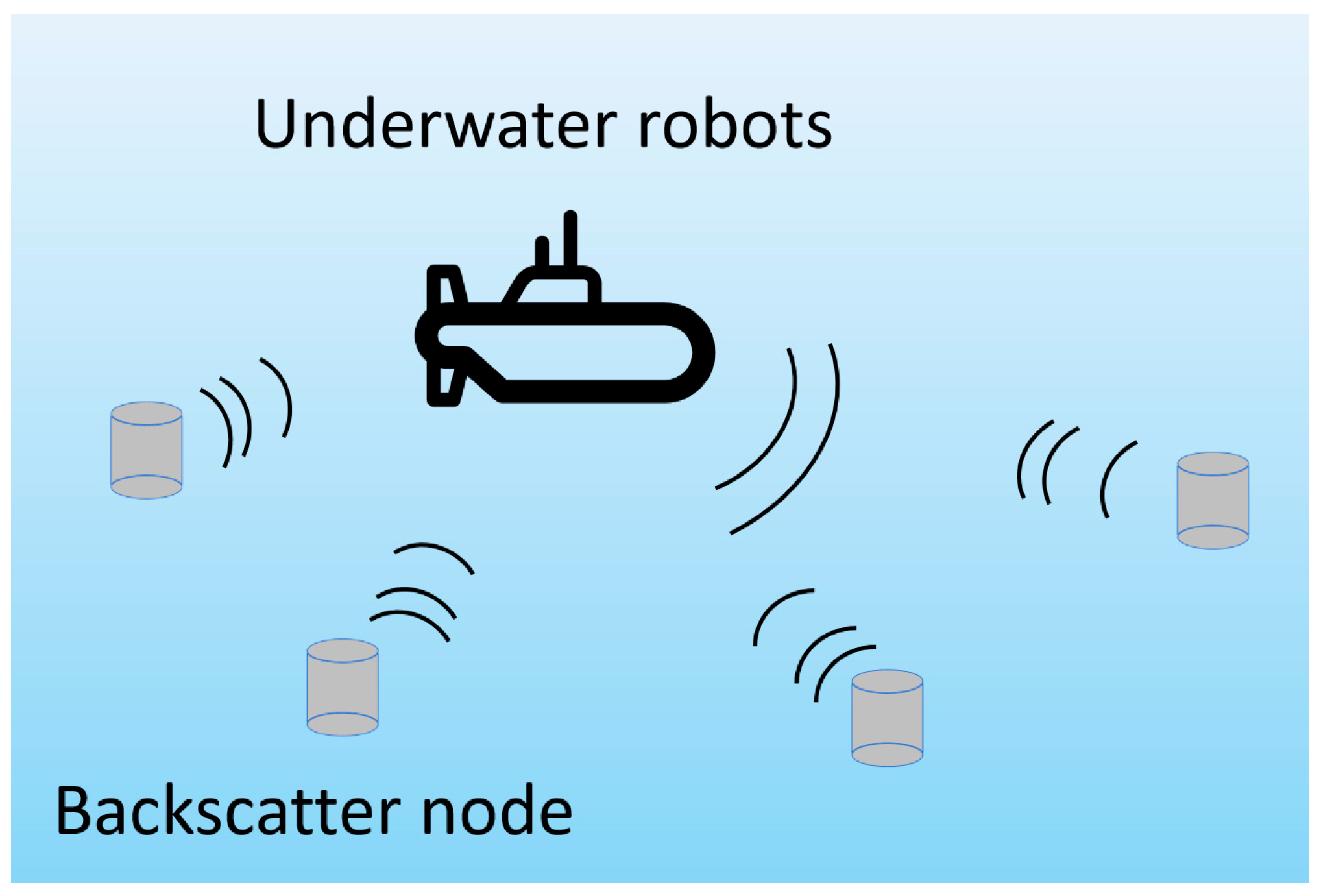
3.1. Underwater Backscatter Mechanism
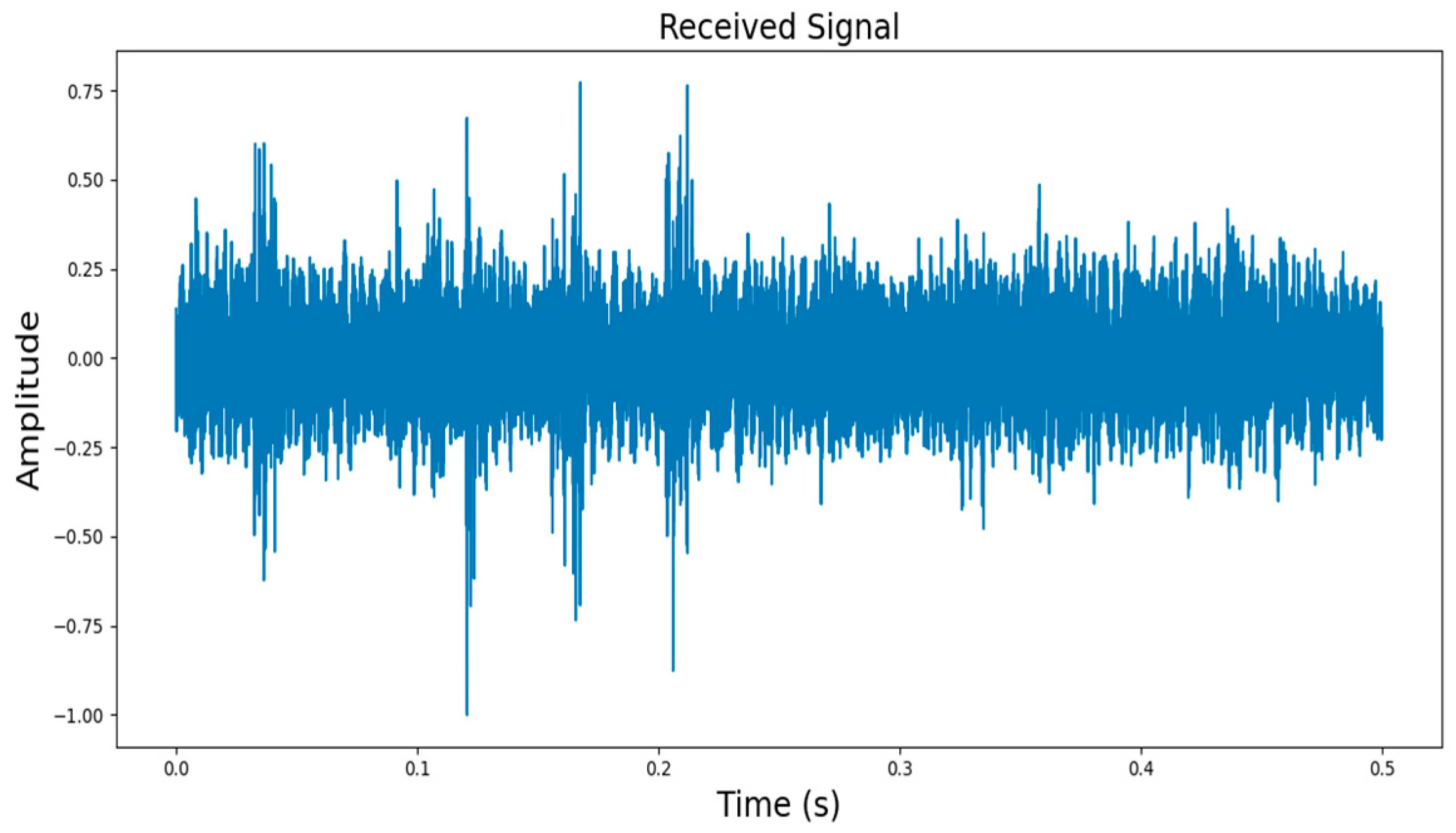
3.2. Description of Underwater Backscatter Signal Separation
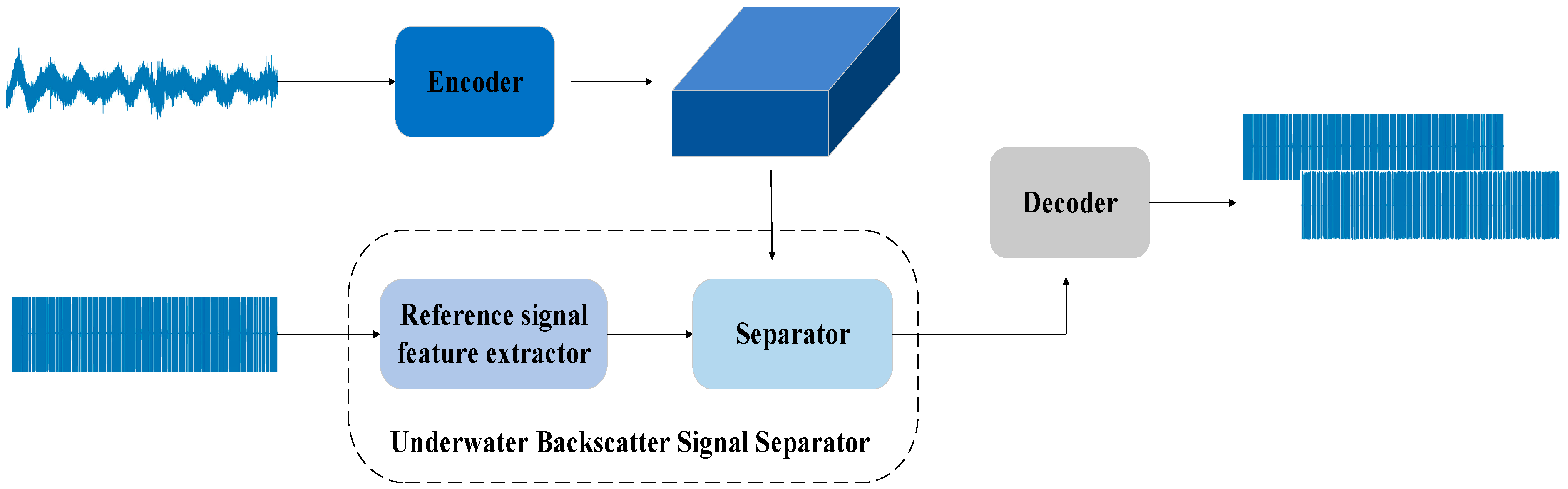
4. Model Construction
4.1. Encoder
4.2. Underwater Backscatter Signal Separator
4.3. Decoder
5. Experimental Procedures
5.1. Simulation Parameter Settings
5.2. Model Configuration
5.3. Experiment Configuration
5.4. Indicators for Model Assessment
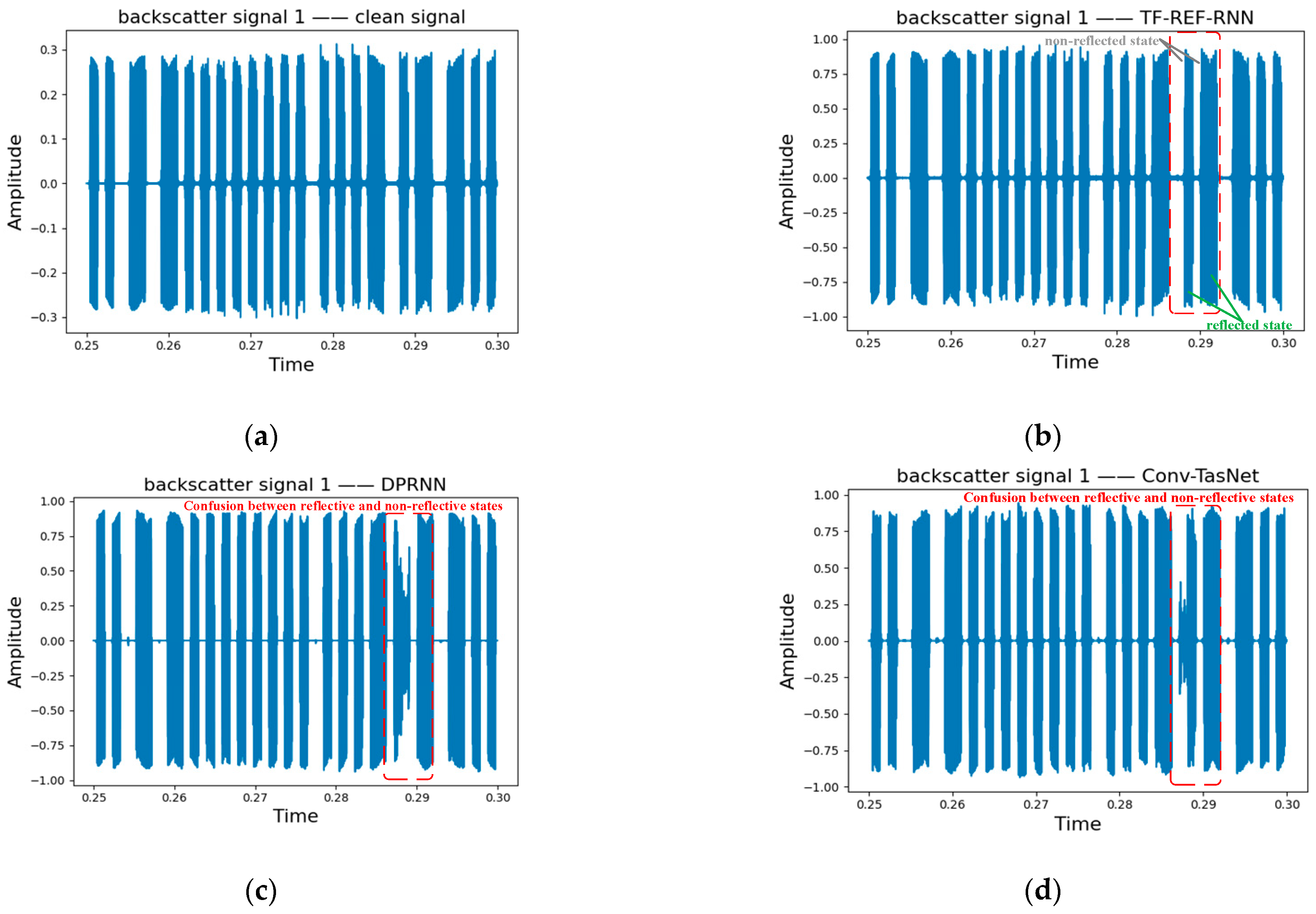
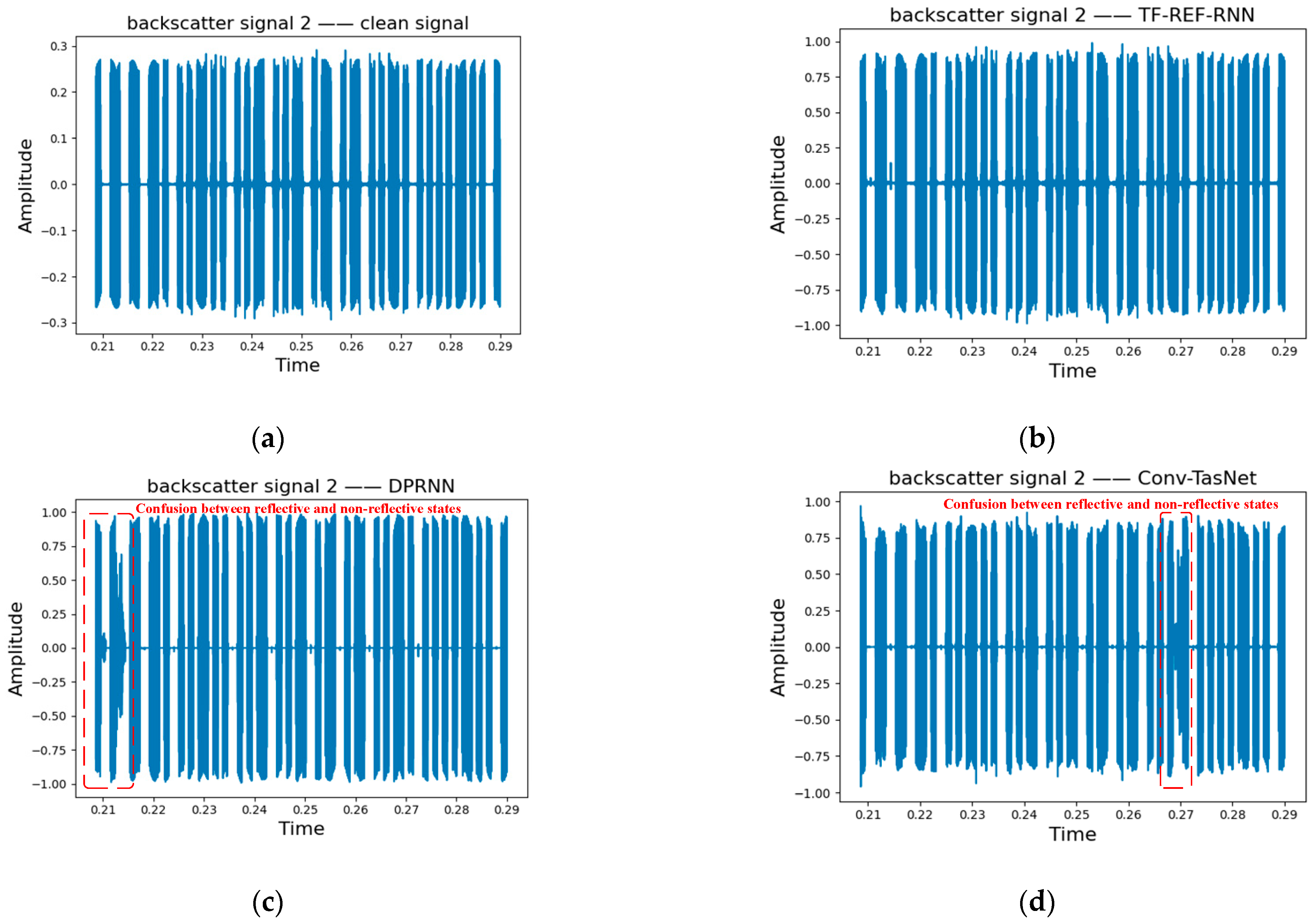
6. Results
6.1. Results on BS-2-Mix
6.2. Ablation Studies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.F.; Jayakody, D.N.K.; Chursin, Y.A.; Affes, S.; Dmitry, S. Recent Advances and Future Directions on Underwater Wireless Communications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 1379–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Localization Algorithm for Underwater Sensor Network: A Review. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13126–13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ullah, I.; Liu, X.; Choi, D. A Review of Underwater Localization Techniques, Algorithms, and Challenges. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 6403161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Peng, M.; Peng, Y.; Feng, M.; Liu, G. Backscatter Communication Meets Practical Battery-Free Internet of Things: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 2021–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yao, C.; Liu, W.; Ye, R.; Juhana, T.; Ai, B. Sensitivity and Distance Based Performance Analysis for Batteryless Tags with Transmit Beamforming and Ambient Backscattering. China Commun. 2022, 19, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galisteo, A.; Varshney, A.; Giustiniano, D. Two to Tango: Hybrid Light and Backscatter Networks for next Billion Devices. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 June 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, G.; Gao, F. Backscatter Technologies and the Future of Internet of Things: Challenges and Opportunities. Intell. Converg. Netw. 2020, 1, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, V.; Parks, A.; Talla, V.; Gollakota, S.; Wetherall, D.; Smith, J.R. Ambient backscatter: Wireless communication out of thin air. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2013, 43, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C. Energy-Efficient Covert Communications for Bistatic Backscatter Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2906–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Galappaththige, D.; Tellambura, C.; Herath, S. Coding Techniques for Backscatter Communications—A Contemporary Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 1020–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shangguan, L.; He, Y.; Jing, N.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y. Saiyan: Design and Implementation of a Low-Power Demodulator for {LoRa} Backscatter Systems. In Proceedings of the 19th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Renton, WA, USA, 4–6 April 2022; pp. 437–451. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.U.; Nguyen, T.N.; Jameel, F.; Jamshed, M.A.; Pervaiz, H.; Javed, M.A.; Jäntti, R. Learning-Based Resource Allocation for Backscatter-Aided Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 19676–19690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrini Li, A.; Carver, C.J.; Shao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Nelakuditi, S. Communication for Underwater Robots: Recent Trends. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2023, 4, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Adib, F. Underwater Backscatter Networking. In Proceedings of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Beijing, China, 19–23 August 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bereketli, A. Interference-free source deployment for coverage in underwater acoustic backscatter networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2022, 15, 1577–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Afzal, S.S.; Akbar, W.; Rodriguez, O.; Mo, F.; Boyle, D.; Adib, F.; Haddadi, H. Towards Battery-Free Machine Learning and Inference in Underwater Environments. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, Tempe, AZ, USA, 9–10 March 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, S.S.; Akbar, W.; Rodriguez, O.; Doumet, M.; Ha, U.; Ghaffarivardavagh, R.; Adib, F. Battery-Free Wireless Imaging of Underwater Environments. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Lin, J.; Wang, G.; He, R.; Wei, X. Sparse Reconstruction Based Channel Estimation for Underwater Piezo-Acoustic Backscatter Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 25–28 April 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, W.; Allam, A.; Adib, F. The Underwater Backscatter Channel: Theory, Link Budget, and Experimental Validation. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Madrid, Spain, 2–6 October 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–15, ISBN 978-1-4503-9990-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffarivardavagh, R.; Afzal, S.S.; Rodriguez, O.; Adib, F. Underwater Backscatter Localization: Toward a Battery-Free Underwater GPS. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks, Virtual, 4–6 November 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Min, M.; Wang, C.; Niyato, D.; Han, Z. Anti-Jamming Colonel Blotto Game for Underwater Acoustic Backscatter Communication. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 10181–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Nie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, F. Weak Underwater Acoustic Target Detection and Enhancement with BM-SEED Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Domínguez, D.; Torres-Guijarro, S.; Cardenal-López, A.; Pena-Gimenez, A. ShipsEar: An underwater vessel noise database. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 113, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, J.R.; Chen, Z.; Le Roux, J.; Watanabe, S. Deep clustering: Discriminative embeddings for segmentation and separation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. Conv-TasNet: Surpassing Ideal Time–Frequency Magnitude Masking for Speech Separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yoshioka, T. Dual-Path RNN: Efficient Long Sequence Modeling for Time-Domain Single-Channel Speech Separation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S. Wave-U-Net: A Multi-Scale Neural Network for End-to-End Audio Source Separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Zeghidour, N.; Grangier, D. Wavesplit: End-to-End Speech Separation by Speaker Clustering. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Proc. 2021, 29, 2840–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subakan, C.; Ravanelli, M.; Cornell, S.; Bronzi, M.; Zhong, J. Attention Is All You Need in Speech Separation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, A.; Ren, K.; Song, J. Underwater Acoustic Source Separation with Deep Bi-LSTM Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP), Shanghai, China, 24 September 2021; pp. 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, K. Separation of Underwater Acoustic Signals Based on C-RNN Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering, Big Data, and Computer Technology (EIBDCT 2022), Sanya, China, 20–22 January 2022; Volume 12256, pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wu, M.; Yu, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, H. Single-Channel Blind Source Separation of Underwater Acoustic Signals Using Improved NMF and FastICA. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1097003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Benezeth, Y. A Deep-Learning Based High-Gain Method for Underwater Acoustic Signal Detection in Intensity Fluctuation Environments. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 211, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhou, M.; Esmaiel, H. Underwater Acoustic Nonlinear Blind Ship Noise Separation Using Recurrent Attention Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhou, H.; Yang, K.; Liu, P.; Du, Y. Study on Weak Sound Signal Separation and Pattern Recognition under Strong Background Noise in Marine Engineering. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2024, 43, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. Deep Attractor Network for Single-Microphone Speaker Separation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, Y.; Roux, J.L.; Chen, Z.; Watanabe, S.; Hershey, J.R. Single-Channel Multi-Speaker Separation Using Deep Clustering. Interspeech 2016, 2016, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.R.; Zhou, S.; Preisig, J.C.; Willett, P. Sparse Channel Estimation for Multicarrier Underwater Acoustic Communication: From Subspace Methods to Compressed Sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1708–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Schmidhuber, J. Framewise Phoneme Classification with Bidirectional LSTM and Other Neural Network Architectures. Neural Netw. 2005, 18, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolbaek, M.; Yu, D.; Tan, Z.-H.; Jensen, J. Multitalker Speech Separation with Utterance-Level Permutation Invariant Training of Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, J.L.; Wisdom, S.; Erdogan, H.; Hershey, J.R. SDR—Half-Baked or Well Done? In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. TaSNet: Time-Domain Audio Separation Network for Real-Time, Single-Channel Speech Separation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 696–700. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Amount of data | 27,000 |
| Working distance (m) | (10, 15) |
| Center frequency (Hz) | 15,000 |
| Sampling frequency (Hz) | 52,734 |
| Signal duration (s) | 0.5 |
| Reflection signal duration (s) | 0.4 |
| Throughput (bit/s) | 1034 |
| Bit length | 414 |
| Encodings | Bi-Phase Space Coding |
| Signal-to-noise ratio (dB) | (−5, 0) |
| Filename | Name | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 85__E__1L | Natural ambient noise sample 1 | 85 s |
| 86__E__2M | Natural ambient noise sample 2 | 99 s |
| 87__E__3H | Natural ambient noise sample 3 | 98 s |
| 88__E__4L | Natural ambient noise sample 4 | 93 s |
| 89__E__5M | Natural ambient noise sample 5 | 93 s |
| 90__E__6H | Natural ambient noise sample 6 | 91 s |
| 91__E__7H_N | Natural ambient noise sample 7 | 34 s |
| 92__E__8H_N | Natural ambient noise sample 8 | 67 s |
| Model | SI-SNRi (dB) | SDRi (dB) |
|---|---|---|
| TasNet [42] | 14.85 | 10.98 |
| Conv-TasNet [25] | 25.24 | 16.55 |
| DPRNN [26] | 25.73 | 17.02 |
| TF-REF-RNN | 28.55 | 19.51 |
| Model | SI-SNRi (dB) | SDRi (dB) |
|---|---|---|
| DPRNN | 25.73 | 17.02 |
| Encoder with STFT branch | 27.6 | 18.56 |
| Underwater backscatter separator | 28.55 | 19.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Gong, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, H.; Tan, J. TF-REF-RNN: Time-Frequency and Reference Signal Feature Fusion Recurrent Neural Network for Underwater Backscatter Signal Separation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193635
Liu J, Gong S, Zhang T, Zhao Z, Dong H, Tan J. TF-REF-RNN: Time-Frequency and Reference Signal Feature Fusion Recurrent Neural Network for Underwater Backscatter Signal Separation. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(19):3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193635
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jun, Shenghua Gong, Tong Zhang, Zhenxiang Zhao, Hao Dong, and Jie Tan. 2024. "TF-REF-RNN: Time-Frequency and Reference Signal Feature Fusion Recurrent Neural Network for Underwater Backscatter Signal Separation" Remote Sensing 16, no. 19: 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193635
APA StyleLiu, J., Gong, S., Zhang, T., Zhao, Z., Dong, H., & Tan, J. (2024). TF-REF-RNN: Time-Frequency and Reference Signal Feature Fusion Recurrent Neural Network for Underwater Backscatter Signal Separation. Remote Sensing, 16(19), 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193635





