Landcover Change Amidst Climate Change in the Lake Tana Basin (Ethiopia): Insights from 37 Years of Earth Observation on Landcover–Rainfall Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Landcover Change
2.3. Rainfall Trend
2.4. Potential Soil Erosion
3. Results
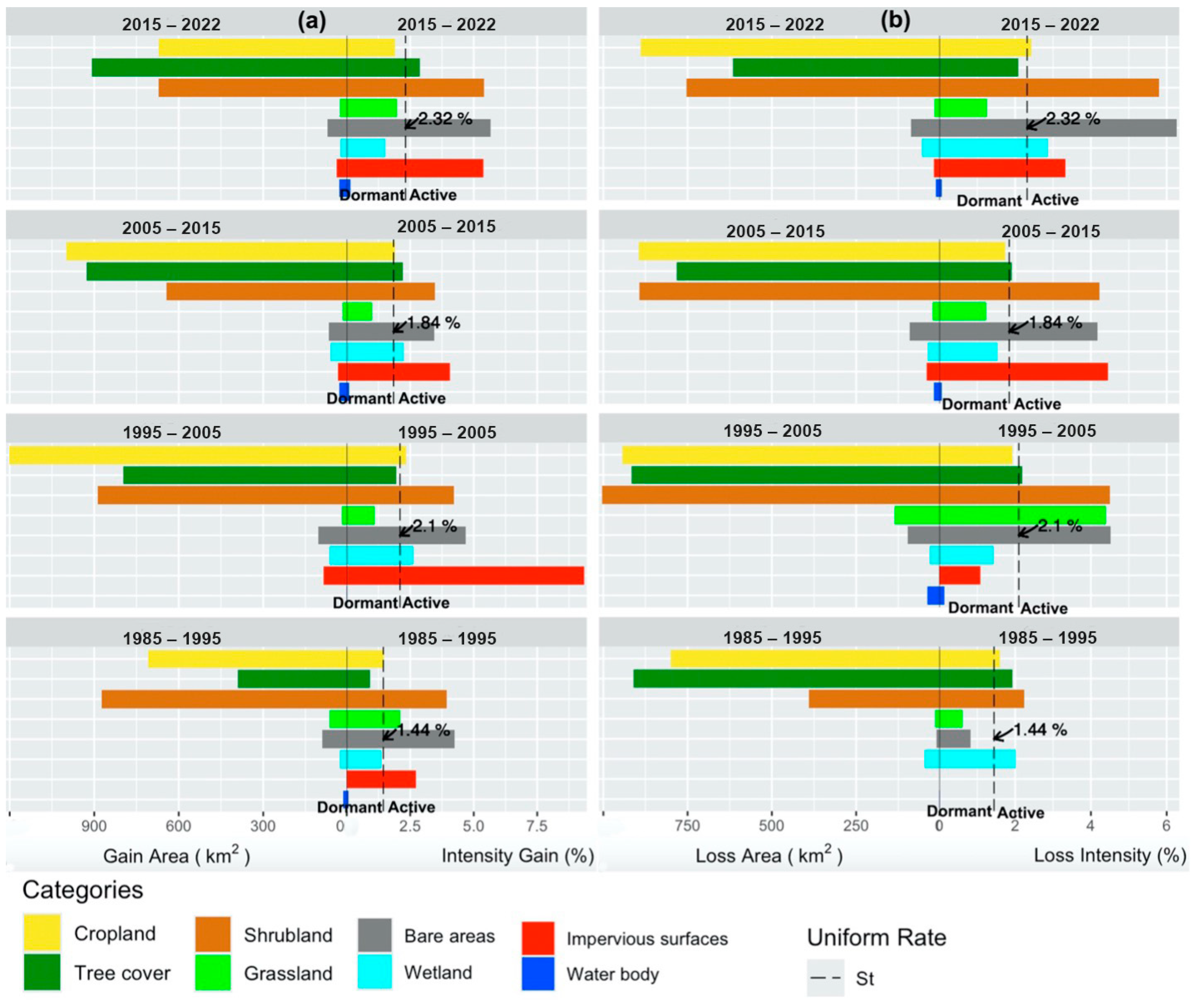
3.1. Landcover Changes
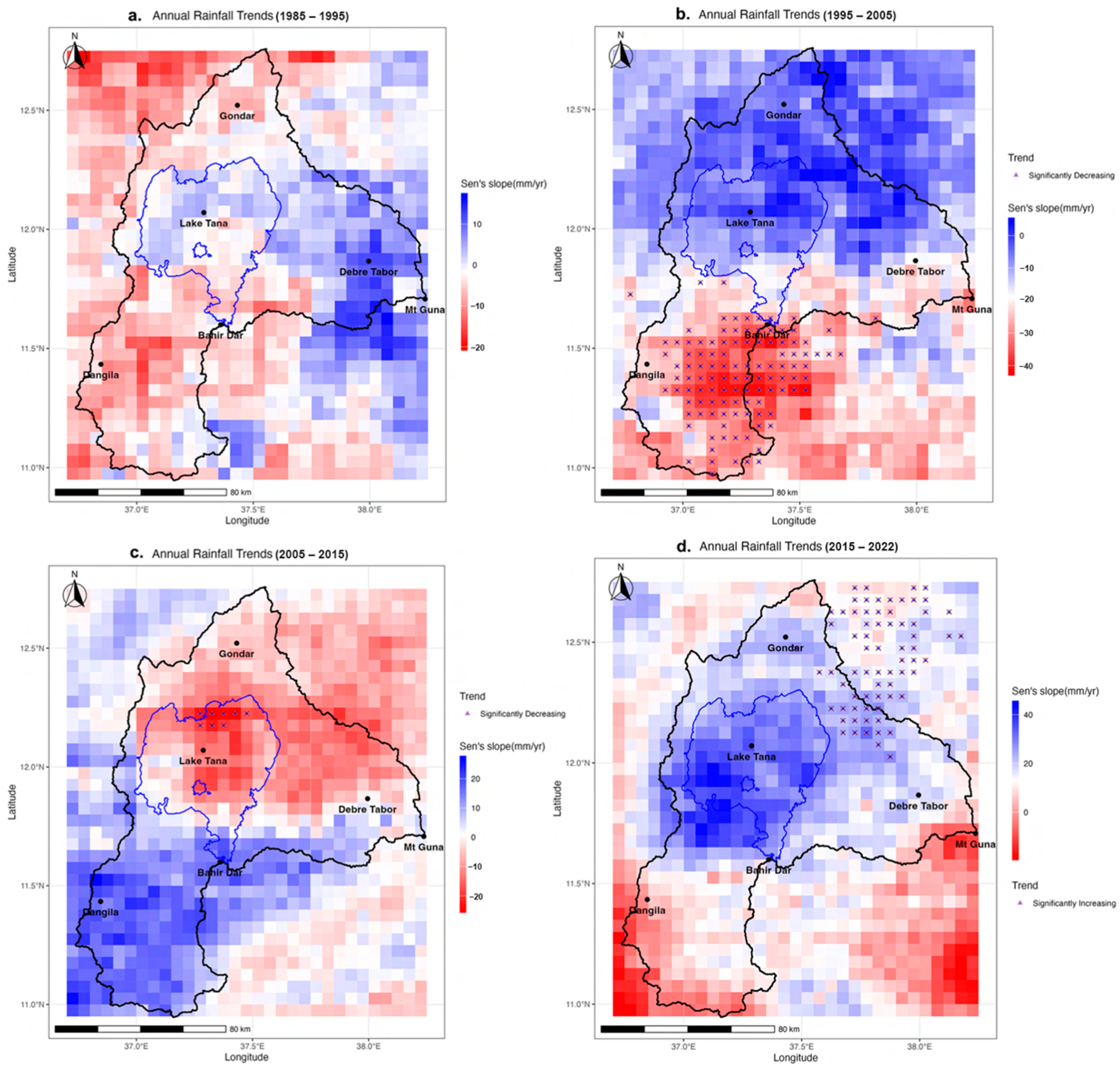
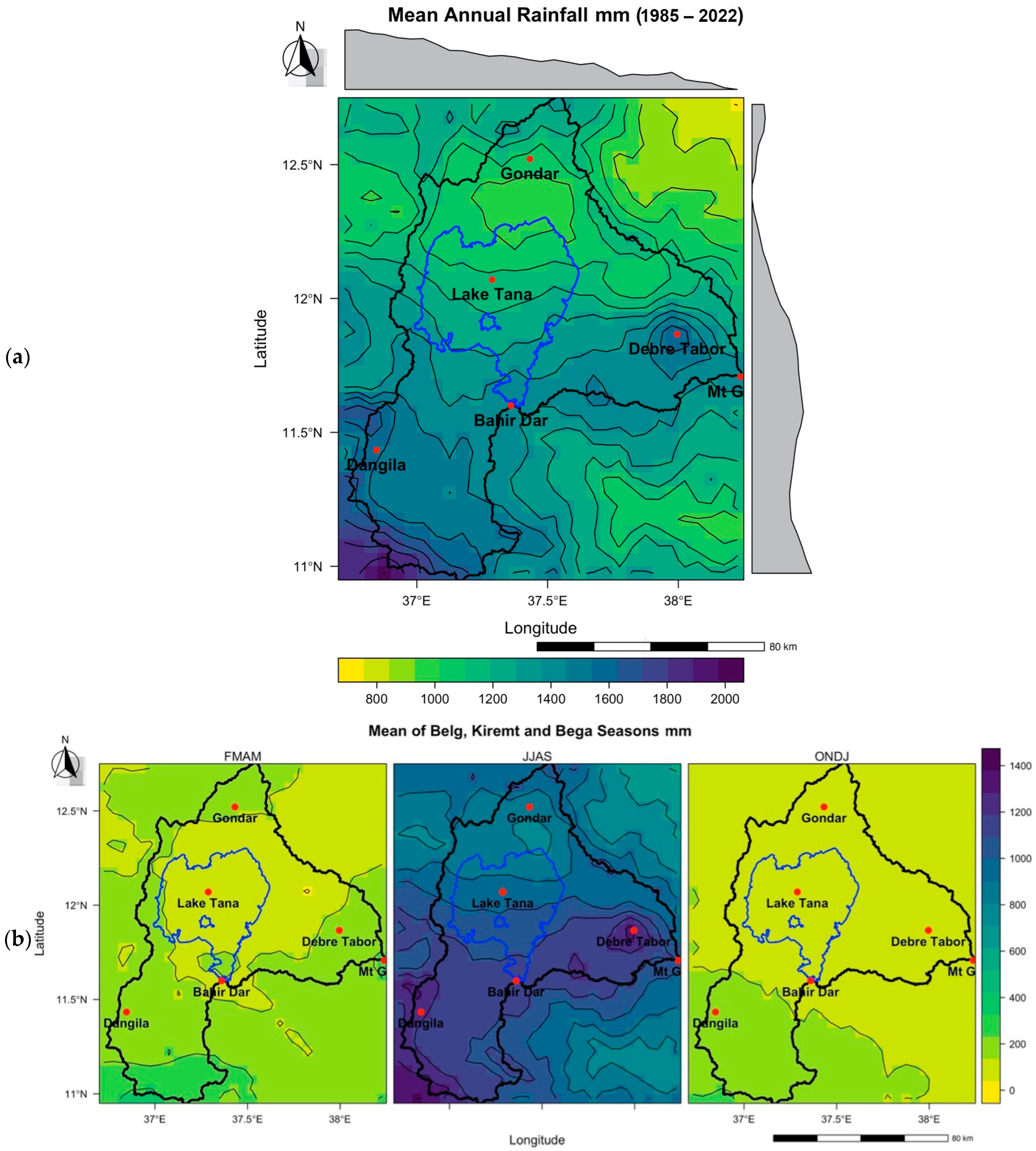
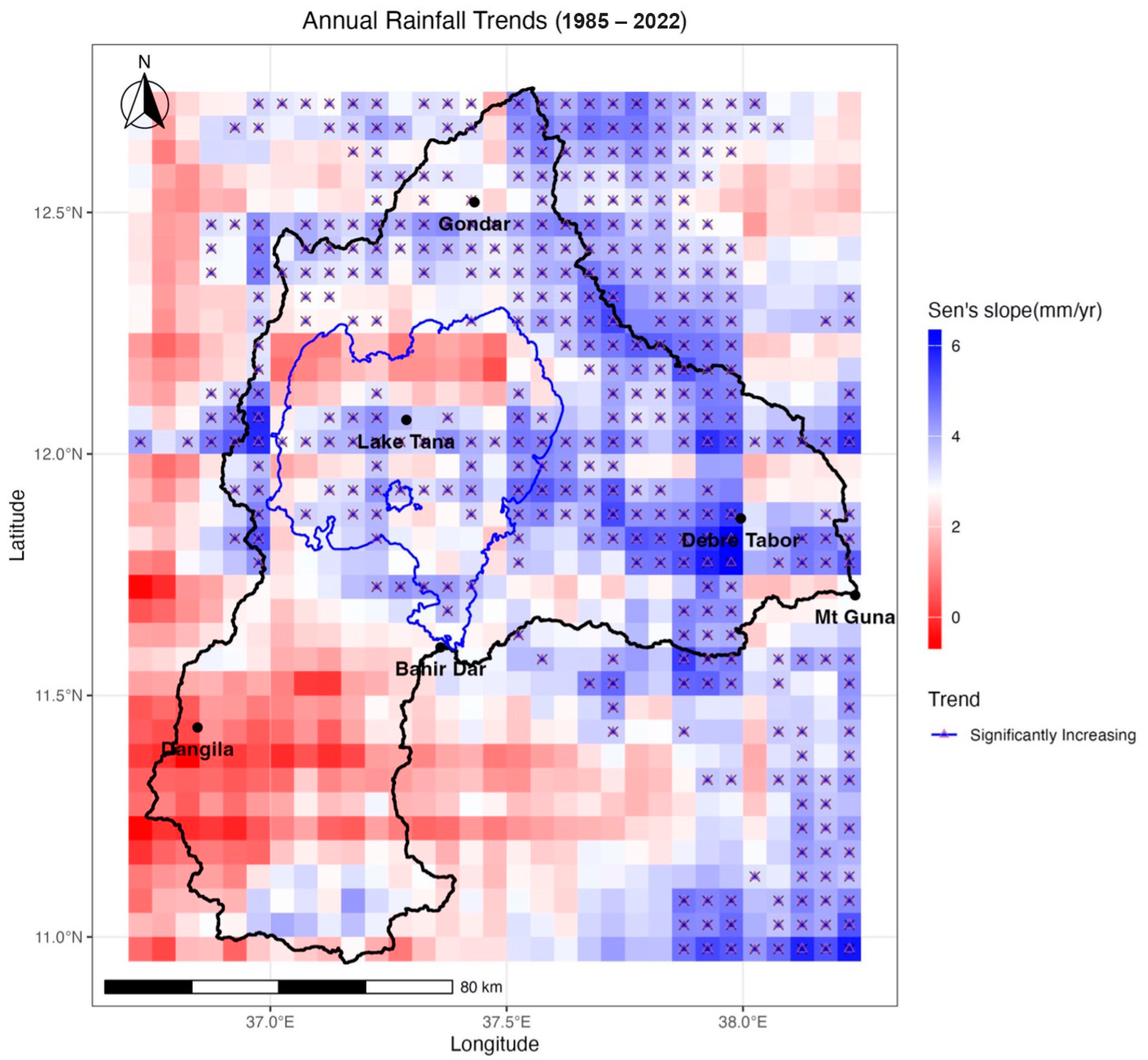
3.2. Rainfall Patterns and Trends
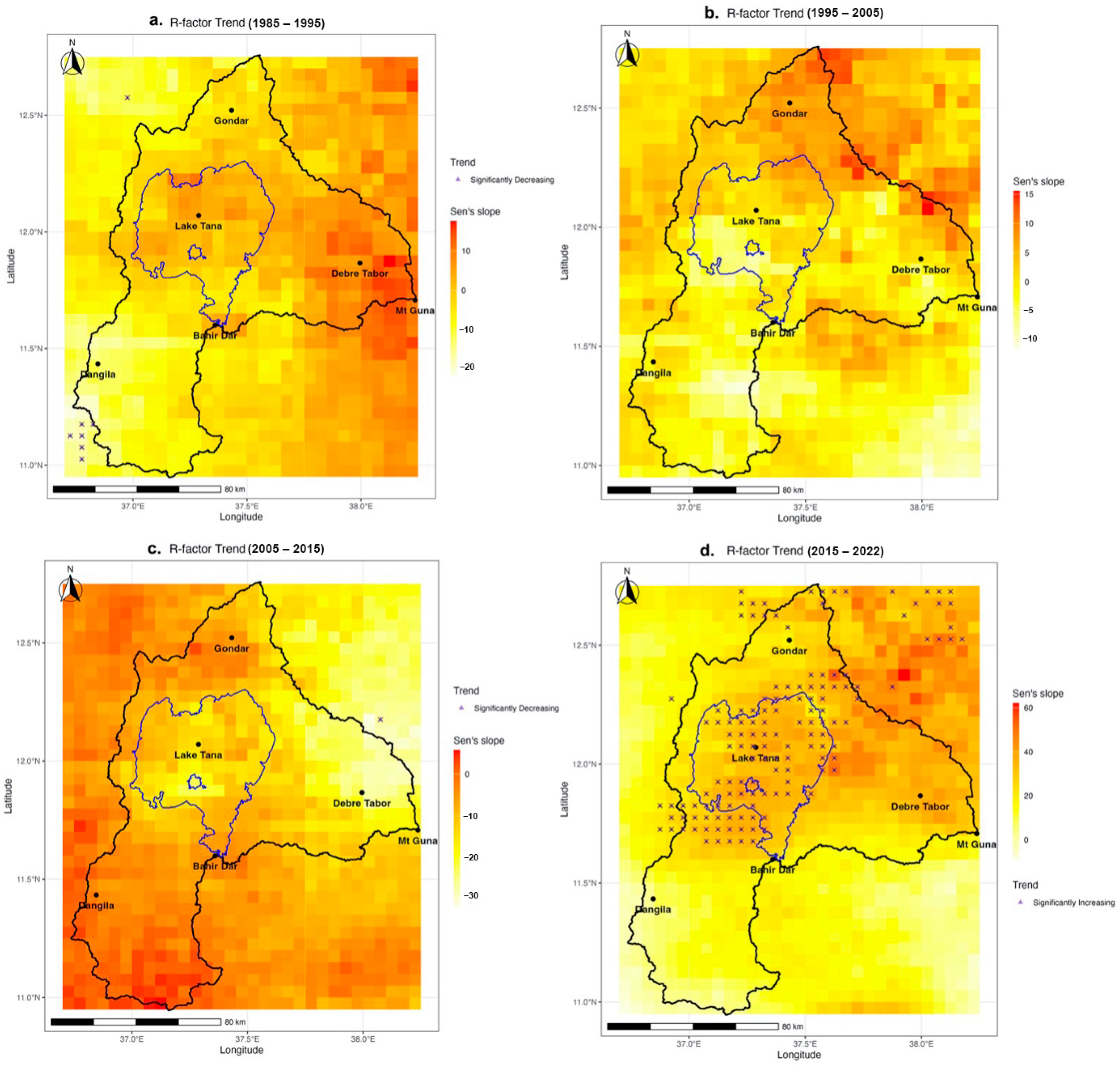
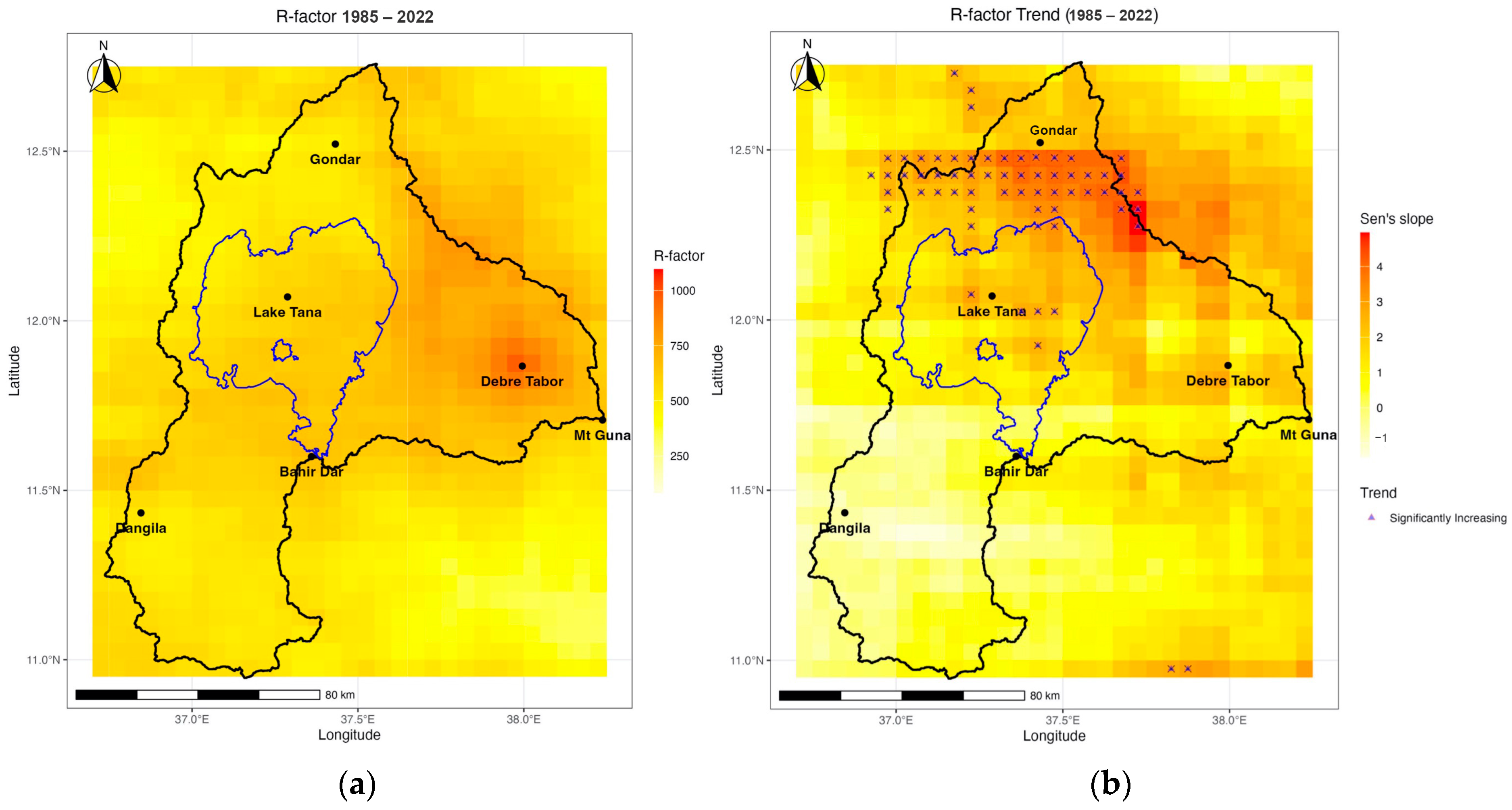
3.3. Rainfall Erosivity
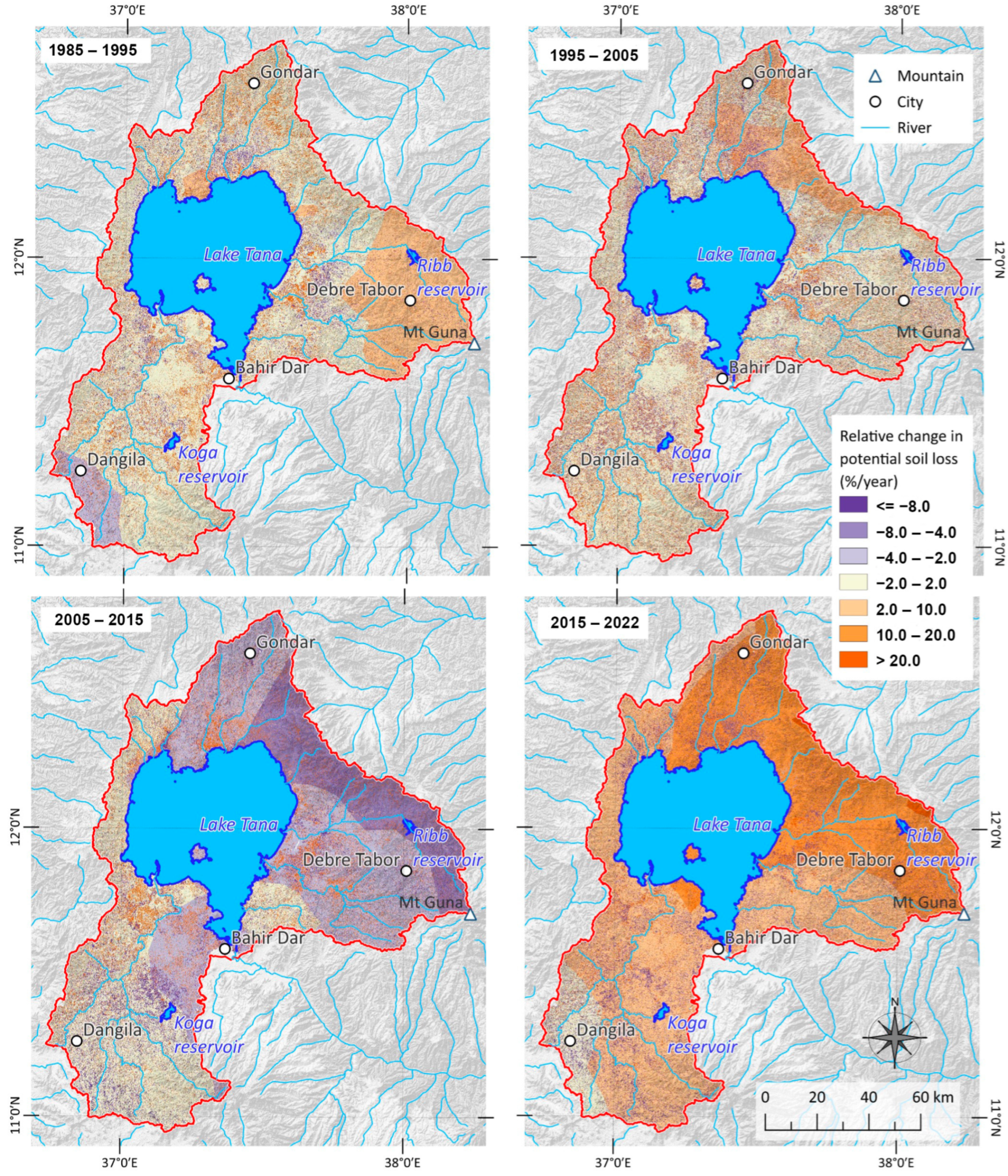
3.4. Interaction Between Changes in Landcover and Rainfall Erosivity
4. Discussion
4.1. Patterns, Drivers, and Implication of LULC Changes
4.2. Implications of Changing Rainfall Patterns and Erosivity
4.3. Effect of the Interactions Between Changes in LULC and Rainfall
4.4. Limitations of Using the RUSLE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Additional Tables and Figures
| Landcover | C-Factor |
|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.15 |
| Tree cover | 0.001 |
| Shrubland | 0.014 |
| Grassland | 0.01 |
| Wetland | 0.05 |
| Bare area | 0.01 |
| Impervious surface | 0.004 |
| Water body | 0.00 |
| Ground Truth Data | Landcover Data | Total | PA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop | Tree | Shrub | Grass | Bare | Wet. | Imp. | Water | (%) | ||
| Year: 2005 | ||||||||||
| Cropland | 78 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 78.0 |
| Tree cover | 13 | 122 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 146 | 83.6 |
| Shrubland | 7 | 13 | 64 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 86 | 74.4 |
| Grassland | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 71.4 |
| Bare areas | 3 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 10.0 |
| Wetland | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 92.9 |
| Impervious surfaces | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 18 | 61.1 |
| Water body | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 100.0 |
| Total | 104 | 149 | 82 | 16 | 4 | 13 | 12 | 4 | 384 | |
| UA (%) | 75.0 | 81.9 | 78.0 | 31.3 | 25.0 | 100.0 | 91.7 | 75.0 | ||
| Overall accuracy: 77.3 Kappa coefficient: 0.69 | ||||||||||
| Year: 2014 | ||||||||||
| Cropland | 157 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 175 | 89.7 |
| Tree cover | 2 | 44 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 89.8 |
| Shrubland | 1 | 8 | 36 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 | 76.6 |
| Grassland | 0 | 4 | 2 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 81.3 |
| Bare areas | 0 | 4 | 2 | 26 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 37 | 13.5 |
| Wetland | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 83.3 |
| Impervious surfaces | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 32 | 93.8 |
| Water body | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 9 | 12 | 75.0 |
| Total | 161 | 75 | 51 | 55 | 5 | 22 | 30 | 9 | 408 | |
| UA (%) | 97.5 | 58.7 | 70.6 | 47.3 | 100.0 | 90.9 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Overall accuracy: 80.2 Kappa coefficient: 0.74 | ||||||||||
| Year: 2022 | ||||||||||
| Cropland | 92 | 17 | 16 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 130 | 70.8 |
| Tree cover | 6 | 147 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 162 | 90.7 |
| Shrubland | 2 | 3 | 33 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 80.5 |
| Grassland | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 80.0 |
| Bare areas | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 12.5 |
| Wetland | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 78.6 |
| Impervious surfaces | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 13 | 84.6 |
| Water body | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 87.5 |
| Total | 105 | 169 | 55 | 16 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 381 | |
| UA (%) | 87.6 | 87.0 | 60.0 | 25.0 | 20.0 | 91.7 | 91.7 | 100.0 | ||
| Overall accuracy: 80.3 Kappa coefficient: 0.72 | ||||||||||

References
- Prăvălie, R.; Nita, I.-A.; Patriche, C.; Niculiță, M.; Birsan, M.-V.; Roșca, B.; Bandoc, G. Global Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and Implications for Land Degradation Neutrality and Climate Stability. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Panagos, P.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Hayas, A.; Foerster, S.; Borrelli, P.; Rossi, M.; Torri, D.; Casalí, J.; Borselli, L.; et al. Measuring, Modelling and Managing Gully Erosion at Large Scales: A State of the Art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshu, G.; Aynalem, S. Problem Overview of the Lake Tana Basin. In Social and Ecological System Dynamics; Stave, K., Goshu, G., Aynalem, S., Eds.; AESS Interdisciplinary Environmental Studies and Sciences Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 9–23. ISBN 978-3-319-45753-6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Nigatu, L.; Beneye, Y.; Abdulahi, A.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D. Mapping the Vegetation of the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia, Using Google Earth Images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Nicholls, R.; Brown, S.; Tebboth, M.; Adger, W.; Ahmad, B.; Biemans, H.; Crick, F.; Lutz, A.; Safra de Campos, R.; et al. The Need for Bottom-up Assessments of Climate Risks and Adaptation in Climate-Sensitive Regions. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, A.; Simane, B.; Hassen, A.; Bantider, A. Variability and Time Series Trend Analysis of Rainfall and Temperature in Northcentral Ethiopia: A Case Study in Woleka Sub-Basin. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2018, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Hülsmann, S.; Bernhofer, C. Regional Climate Projections for Impact Assessment Studies in East Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 044031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, H.; Frankl, A.; Griensven, A.; Poesen, J.; Adgo, E.; Nyssen, J. Identifying Erosion Hotspots in Lake Tana Basin from a Multisite Soil and Water Assessment Tool Validation: Opportunity for Land Managers. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1449–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, G.; Hurni, H. Implications of Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics for Mountain Resource Degradation in the Northwestern Ethiopian Highlands. Mt. Res. Dev. 2001, 21, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, A.J.D.; Annys, S.; Dessie, M.; Nyssen, J.; Dondeyne, S. To What Extent Is Hydrologic Connectivity Taken into Account in Catchment Studies in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia? A Review. Land 2022, 11, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhanu, A.; Masih, I.; van der Zaag, P.; Nyssen, J.; Cai, X. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Hydrology of the Gumara Catchment, Ethiopia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 112, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdaw, F.; Fetahi, T.; Kifle, D. Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics in the Northern Watershed of Lake Tana: Implications for Water Quality. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1426789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikuye, B.G.; Ray, R.L.; Gebeyehu, K.; Teshome, M. Assessing the Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics and Climate Change on Water Resources in Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 4745–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, N.T.; Tsidu, G.M.; Arsiso, B.K. Establishing and Modeling the Causality Relationship of Hydro-Climatic and Land Cover Change Variables with Water Quality over Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Total Environ. Adv. 2024, 10, 200100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, B.; Manjunatha, B.R.; Bhat, H.G. Modeling Projected Impacts of Climate and Land Use/Land Cover Changes on Hydrological Responses in the Lake Tana Basin, Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkwasa, A.; Chawanda, C.J.; Van Griensven, A. Regionalization of the SWAT+ Model for Projecting Climate Change Impacts on Sediment Yield: An Application in the Nile Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, L.; Frankl, A.; Poesen, J.; Admasu, T.; Dessie, M.; Adgo, E.; Deckers, J.; Nyssen, J. Geomorphology of the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. J. Maps 2013, 9, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, M.G.; Tsegaye, E.A.; Tolossa, A.R.; Nyssen, J.; Frankl, A.; Ranst, E.V.; Dondeyne, S. Soil-Forming Factors of High-Elevation Mountains along the East African Rift Valley: The Case of the Mount Guna Volcano, Ethiopia. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, M.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Adgo, E.; Deckers, J.; Poesen, J.; Nyssen, J. Water Balance of a Lake with Floodplain Buffering: Lake Tana, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.G.; Rayner, D.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B.; Srinivasan, R. Impact of Climate Change on the Hydroclimatology of Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 2010WR009248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth Resources Observation And Science (EROS) Center. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global Land-Cover Product with Fine Classification System at 30 m Using Time-Series Landsat Imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2753–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. Thematic and Positional Accuracy Assess- Ment of Digital Remotely Sensed Data. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual Forest Inventory and Analysis Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 3–6 October 2005; McRoberts, R.E., Reams, G.A., McWilliams, H., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Portland, ME, USA, 2007; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.M.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J.W. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, UYA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-471-15227-9. [Google Scholar]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G. Intensity Analysis to Unify Measurements of Size and Stationarity of Land Changes by Interval, Category, and Transition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Gao, Y.; Giner, N.M.; Kohyama, T.; Osaki, M.; Hirose, K. Design and Interpretation of Intensity Analysis Illustrated by Land Change in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land 2013, 2, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exavier, R.; Zeilhofer, P. OpenLand: Software for Quantitative Analysis and Visualization of Land Use and Cover Change. R J. 2021, 12, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2023. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations—A New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayehu, G.T.; Tadesse, T.; Gessesse, B.; Dinku, T. Validation of New Satellite Rainfall Products over the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, J.E.; Sung, H.S.; Konecky, B.L.; Palace, M.W.; Salerno, J.; Hartter, J. Rainfall Characteristics and Trends—And the Role of Congo Westerlies—In the Western Uganda Transition Zone of Equatorial Africa From 1983 to 2017. JGR Atmos. 2019, 124, 10712–10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Maidment, R.; Tadesse, T.; Gadain, H.; Ceccato, P. Validation of the CHIRPS Satellite Rainfall Estimates over Eastern of Africa: Validation of the CHIRPS Satellite Rainfall Estimates. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Phinney, B.; Cavadias, G. The Influence of Autocorrelation on the Ability to Detect Trend in Hydrological Series. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1807–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronaugh, D.A. Werner Package “Zyp” 2015. Available online: http://cran.nexr.com/web/packages/zyp/zyp.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A Rank-Invariant Method of Linear and Polynomial Regression Analysis. In Henri Theil’s Contributions to Economics and Econometrics: Econometric Theory and Methodology; Raj, B., Koerts, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 345–381. ISBN 978-94-011-2546-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 537.
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-16-048938-9.
- Arnoldus, H. Methodology Used to Determine the Maximum Potential Average Annual Soil Loss Due to Sheet and Rill Erosion in Morocco. FAO Soils Bull. 1977, 34, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Freimund, J.R. Using Monthly Precipitation Data to Estimate the R-Factor in the Revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Sterk, G.; de Jong, S.M. Satellite-Based Estimation of Rainfall Erosivity for Africa. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Yasuda, H.; Shimizu, K.; Haregeweyn, N.; Kawai, T.; Sultan, D.; Ebabu, K.; Belay, A.S. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Trends of Rainfall and Erosivity in the Eastern Africa Region. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4555–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W. Modeling the Hydrological Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Changes in the Andassa Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, A.J.D.; Dondeyne, S.; Lemma, H.; Nyssen, J.; Annys, S.; Frankl, A. Recent Dynamics in Sediment Connectivity in the Ethiopian Highlands. Reg. Environ. Change 2024, 24, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerihun, M.; Mohammedyasin, M.S.; Sewnet, D.; Adem, A.A.; Lakew, M. Assessment of Soil Erosion Using RUSLE, GIS and Remote Sensing in NW Ethiopia. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 12, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, S.; Gärdenäs, A.; Bewket, W.; Seibert, J.; Ilstedt, U.; Bishop, K. The Long-Term Hydrology of East Africa’s Water Tower: Statistical Change Detection in the Watersheds of the Abbay Basin. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, N.; Birhane, E.; Tilahun, M.; Schauer, M.; Gebremedhin, M.A.; Gebremariam, F.T.; Gidey, T.; Newete, S.W. Revitalizing Ethiopia’s Highland Soil Degradation: A Comprehensive Review on Land Degradation and Effective Management Interventions. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddese, G. Land Degradation: A Challenge to Ethiopia. Environ. Manag. 2001, 27, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, M. An Opinion Note on Population Growth and Land Degradation in Ethiopia. Reg. Environ. Change 2024, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanza, A.K.; Dondeyne, S.; Kimaro, D.N.; Kafiriti, E.; Poesen, J.; Deckers, J.A. Effectiveness of Soil Conservation Measures in Two Contrasting Landscape Units of South Eastern Tanzania. Z. Geomorphol. 2013, 57, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimore, M.; Tiffen, M. Population Growth and a Sustainable Environment. The Machakos Story. Environment 1994, 10–20, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Haile, M.; Moeyersons, J.; Deckers, J.; Hurni, H. Effects of Land Use and Land Cover on Sheet and Rill Erosion Rates in the Tigray Highlands, Ethiopia. Z. Geomorphol. 2009, 53, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, Z.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Nohmi, M.; Tsubo, M.; Aklog, D.; Meshesha, D.T.; Abele, S. Factors Affecting Small-Scale Farmers’ Land Allocation and Tree Density Decisions in an Acacia Decurrens-Based Taungya System in Fagita Lekoma District, North-Western Ethiopia. Small-Scale For. 2017, 16, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshager Abeje, M.; Tsunekawa, A.; Adgo, E.; Haregeweyn, N.; Nigussie, Z.; Ayalew, Z.; Elias, A.; Molla, D.; Berihun, D. Exploring Drivers of Livelihood Diversification and Its Effect on Adoption of Sustainable Land Management Practices in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulti, D.T.; Abebe, B.G. Analyzing the Impacts of Urbanization on Runoff Characteristics in Adama City, Ethiopia. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisa, M.B.; Dejene, I.N.; Gemeda, D.O. Integration of Geospatial Technologies with Multiple Regression Model for Urban Land Use Land Cover Change Analysis and Its Impact on Land Surface Temperature in Jimma City, Southwestern Ethiopia. Appl. Geomat. 2022, 14, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssewankambo, G.; Kabenge, I.; Nakawuka, P.; Wanyama, J.; Zziwa, A.; Bamutaze, Y.; Gwapedza, D.; Palmer, C.T.; Tanner, J.; Mantel, S.; et al. Assessing Soil Erosion Risk in a Peri-Urban Catchment of the Lake Victoria Basin. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 1633–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD; Policy Studies Institute (Eds.) Rural Development Strategy Review of Ethiopia: Reaping the Benefits of Urbanisation; OECD Development Pathways; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 978-92-64-52648-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lenaerts, L.; Breusers, M.; Dondeyne, S.; Bauer, H.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J. ‘This Pasture Is Ours since Ancient Times’: An Ethnographic Analysis of the Reduction in Conflicts along the Post-1991 Afar-Tigray Regional Boundary. J. Mod. Afr. Stud. 2014, 52, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Hülsmann, S.; Bernhofer, C. Long-Term Trends in Rainfall and Temperature Using High-Resolution Climate Datasets in East Africa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudoshava, M.; Wainwright, C.; Hirons, L.; Endris, H.S.; Segele, Z.T.; Woolnough, S.; Atheru, Z.; Artan, G. Atmospheric and Oceanic Conditions Associated with Early and Late Onset for Eastern Africa Short Rains. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 6562–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, T.; Gebrechorkos, S.; Radeny, M.; Solomon, D. Climate Risk Profile for East Africa; International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI): Nairobi, Kenya, 2024; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Tsunekawa, A.; Poesen, J.; Tsubo, M.; Meshesha, D.T.; Fenta, A.A.; Nyssen, J.; Adgo, E. Comprehensive Assessment of Soil Erosion Risk for Better Land Use Planning in River Basins: Case Study of the Upper Blue Nile River. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutebuka, J.; De Taeye, S.; Kagabo, D.; Verdoodt, A. Calibration and Validation of Rainfall Erosivity Estimators for Application in Rwanda. CATENA 2020, 190, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, T.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, L. GLC_FCS30D: The First Global 30 m Land-Cover Dynamics Monitoring Product with a Fine Classification System for the Period from 1985 to 2022 Generated Using Dense-Time-Series Landsat Imagery and the Continuous Change-Detection Method. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 1353–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaye, H.; Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Lemma, H.; Meshesha, D.T.; Wassie, A.; Adgo, E.; Fentie, D.; Frankl, A. Event-based Run-off and Sediment Yield Dynamics and Controls in the Subhumid Headwaters of the Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, S.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tsunekawa, A.; Ayana, M.; Mulualem, T.; Wubet, A. Effects of Soil Bund Spacing on Runoff, Soil Loss, and Soil Water Content in the Lake Tana Basin of Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M. Erosion Risk Assessment for Prioritization of Conservation Measures in Geleda Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Landcover | Producers’ Accuracy (%) | Users’ Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2014 | 2022 | 2005 | 2014 | 2022 | |
| Cropland | 78.0 | 89.7 | 70.8 | 75.0 | 97.5 | 87.6 |
| Tree cover | 83.6 | 89.8 | 90.7 | 81.9 | 58.7 | 87.0 |
| Shrubland | 74.4 | 76.6 | 80.5 | 78.1 | 70.6 | 60.0 |
| Grassland | 71.4 | 81.3 | 80.0 | 31.3 | 47.3 | 25.0 |
| Bare areas | 10.0 | 13.5 | 12.5 | 25.0 | 100.0 | 20.0 |
| Wetland | 92.9 | 83.3 | 78.6 | 100.0 | 90.9 | 91.7 |
| Impervious surfaces | 61.1 | 93.8 | 84.6 | 91.7 | 100.0 | 91.8 |
| Water body | 100.0 | 75.0 | 87.5 | 75.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fofang, S.T.; Mukama, E.B.; Adem, A.A.; Dondeyne, S. Landcover Change Amidst Climate Change in the Lake Tana Basin (Ethiopia): Insights from 37 Years of Earth Observation on Landcover–Rainfall Interactions. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17050747
Fofang ST, Mukama EB, Adem AA, Dondeyne S. Landcover Change Amidst Climate Change in the Lake Tana Basin (Ethiopia): Insights from 37 Years of Earth Observation on Landcover–Rainfall Interactions. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(5):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17050747
Chicago/Turabian StyleFofang, Sullivan Tsay, Erasto Benedict Mukama, Anwar Assefa Adem, and Stefaan Dondeyne. 2025. "Landcover Change Amidst Climate Change in the Lake Tana Basin (Ethiopia): Insights from 37 Years of Earth Observation on Landcover–Rainfall Interactions" Remote Sensing 17, no. 5: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17050747
APA StyleFofang, S. T., Mukama, E. B., Adem, A. A., & Dondeyne, S. (2025). Landcover Change Amidst Climate Change in the Lake Tana Basin (Ethiopia): Insights from 37 Years of Earth Observation on Landcover–Rainfall Interactions. Remote Sensing, 17(5), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17050747






