A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bioactive Compounds in Breastmilk
2.1. Antioxidants in Human Milk
2.1.1. Antioxidant Properties of Breastmilk
2.1.2. Antioxidants Present in Breastmilk
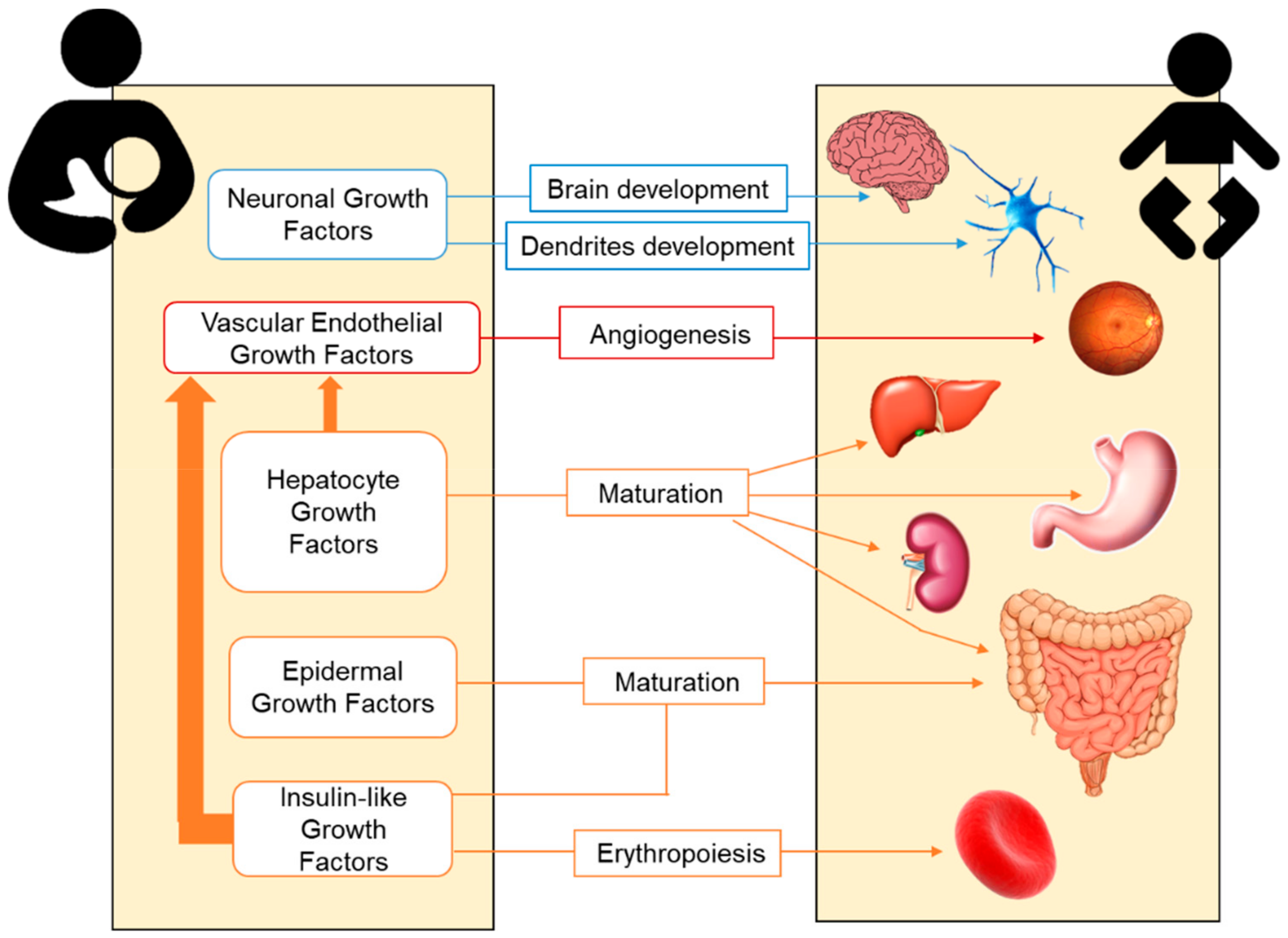
2.2. Growth Factors in Human Milk
2.2.1. Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF)
2.2.2. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
2.2.3. Neuronal Growth Factors
2.2.4. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Superfamily
2.2.5. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
2.2.6. CD14 Protein
2.3. Adipokines in Human Milk
2.3.1. Leptin
2.3.2. Adiponectin
2.3.3. Resistin
2.3.4. Ghrelin
2.3.5. Obestatin
2.3.6. Nesfatin
2.3.7. Apelin
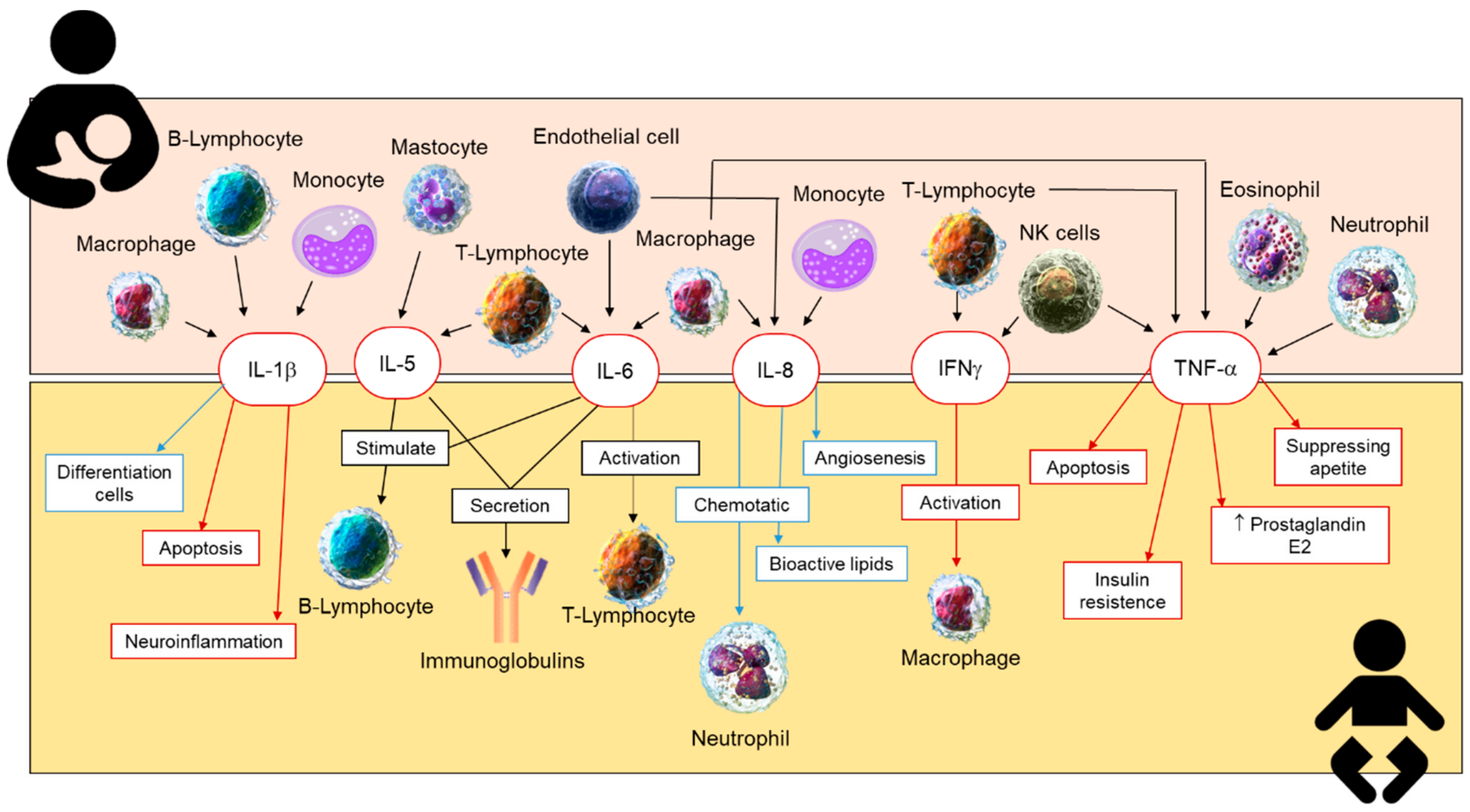
2.4. Cytokines in Human Milk
2.4.1. Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Human Breastmilk
Transforming Growth Factor- β (TGF- β)
2.4.2. Inflammatory Cytokines in Human Breastmilk
3. Human Milk Cells
3.1. Stem Cells in Human Milk
3.2. Leukocytes in Human Milk
4. Human Milk Microbiota
5. Conclusions and Proposal for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guaraldi, F.; Salvatori, G. Effect of Breast and Formula Feeding on Gut Microbiota Shaping in Newborns. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization: Preterm Birth. Available online: https://bit.ly/2RWokG3 (accessed on 23 November 2018).
- Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Chou, D.; Oestergaard, M.; Say, L.; Moller, A.; Kinney, M. Born Too Soon: The Global Epidemiology of 15 Million Preterm Births. Reprod. Health 2013, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, M.S.; Goldenberg, R.L. Global Burden of Prematurity. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 21, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iams, J.D.; Romero, R.; Culhane, J.F.; Goldenberg, R.L. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Interventions to Reduce the Morbidity and Mortality of Preterm Birth. Lancet 2008, 371, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, R.; López Bernal, A. Smoking and Preterm Birth. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-gubory, K. Environmental Pollutants and Lifestyle Factors Induce Oxidative Stress and Poor Prenatal Development. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2014, 29, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón, L.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Boldo, E.; Fernández-Cuenca, R.; Ortiz, C.; Linares, C.; Medrano, M.J.; Galán, I. Smoke-Free Legislation in Spain and Prematurity. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20162068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Oestergaard, M.Z.; Chou, D.; Moller, A.-B.; Narwal, R.; Adler, A.; Garcia, C.V.; Rohde, S.; Say, L.; et al. National, Regional, and Worldwide Estimates of Preterm Birth Rates in the Year 2010 with Time Trends since 1990 for Selected Countries: A Systematic Analysis and Implications. Lancet 2012, 379, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanler, R.J.; Shulman, R.J.; Lau, C. Feeding Strategies for Premature Infants: Beneficial Outcomes of Feeding Fortified Human Milk Versus Preterm Formula. Pediatrics 1999, 103, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzen-Derr, J.; Poindexter, B.; Wrage, L.; Morrow, A.L.; Stoll, B.; Donovan, E.F. Role of Human Milk in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants’ Risk of Necrotizing Enterocolitis or Death. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maayan-Metzger, A.; Avivi, S.; Schushan-Eisen, I.; Kuint, J. Human Milk Versus Formula Feeding Among Preterm Infants: Short-Term Outcomes. Am. J. Perinatol. 2012, 29, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiterer, F.; Scheuchenegger, A.; Resch, B.; Maurer-Fellbaum, A.; Avian, A.; Urlesberger, B. Outcomes of Very Preterm Infants with and without BPD Followed to Preschool Age. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, E.B.; Fischl, B.R.; Quinn, B.T.; Chong, W.K.; Gadian, D.G.; Lucas, A. Impact of Breast Milk on Intelligence Quotient, Brain Size, and White Matter Development. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parkinson, J.R.C.; Hyde, M.J.; Gale, C.; Santhakumaran, S.; Modi, N. Preterm Birth and the Metabolic Syndrome in Adult Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1240–e1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapillonne, A.; Griffin, I.J. Feeding Preterm Infants Today for Later Metabolic and Cardiovascular Outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howson, C.P.; Kinney, M.V.; Mcdougall, L.; Lawn, J.E. Born Too Soon: Preterm Birth Matters. Reprod. Health 2013, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Castañeda, P.C.; Gaxiola-Robles, R.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Defensas Antioxidantes En Leche Materna En Relación Al Número De Gestas Y A La Edad De Las Madres. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Castañeda, P.C.; García-González, A.; Bencomo-Alvarez, A.E.; Barros-Nuñez, P.; Gaxiola-Robles, R.; Celina Méndez-Rodríguez, L.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Micronutrient Content and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Human Breast Milk. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 51, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human Milk Composition: Nutrients and Bioactive Factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization: Exclusive Breastfeeding. Available online: https://bit.ly/2FaaEkE (accessed on 23 November 2018).
- World Health Organization: Infant and Young Child Feeding. Available online: https://bit.ly/2VyOnRL (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singhal, A.; Sadaf Farooqi, I.; O’Rahilly, S.; Cole, T.J.; Fewtrell, M.; Lucas, A. Early Nutrition and Leptin Concentrations in Later Life. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessen, R.; Kavanagh, K. Practice Paper of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Abstract: Promoting and Supporting Breastfeeding. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, S.; Yigit, A.A.; Cinar, M.; Atmaca, N.; Onaran, Y. Oxidant and Antioxidant Status of Human Breast Milk During Lactation Period. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Cole, T.J.; Lucas, A. Early Nutrition in Preterm Infants and Later Blood Pressure: Two Cohorts after Randomised Trials. Lancet 2001, 357, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, J.; Sánchez, C.L.; Bravo, R.; Sánchez, J.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Rivero, M.; Barriga, C. Analysis of the Antioxidant Activity in Human Milk, Day Vs. Night. Cell Membr. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 1, 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- De Vicente, B. 1 De Cada 5 Bebés no Recibe Leche Materna En Los Países Ricos. Available online: https://bit.ly/2RiYzeR (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- Heiman, H.; Schanler, R.J. Nutrición Enteral En Prematuros: El Rol De La Leche Humana. Rev. Enferm. 2007, 12, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, C.; Lyden, E.; Furtado, J.; Van Ormer, M.; Anderson-Berry, A. A Comparison of Nutritional Antioxidant Content in Breast Milk, Donor Milk, and Infant Formulas. Nutrients 2016, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Petrova, A. Is Variation in Total Antioxidant Capacity of Human Milk Associated with Levels of Bio-Active Proteins? J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Benetti, S.; Liguori, S.A.; Sorrenti, M.; Montezemolo, L.C. Di Advances on Human Milk Hormones and Protection Against Obesity. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2013, 59, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Garwolińska, D.; Namieśnik, J.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Hewelt-Belka, W. Chemistry of Human Breast Milk—A Comprehensive Review of the Composition and Role of Milk Metabolites in Child Development. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11881–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutinati, M.; Pantaleo, M.; Roncetti, M.; Piccinno, M.; Rizzo, A.; Sciorsci, R.L. Oxidative Stress in Neonatology: A Review. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2014, 49, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilinska, M.; Borszewska-Kornacka, M.K.; Niemiec, T.; Jakiel, G. Oxidative Stress and Total Antioxidant Status in Term Newborns and Their Mothers. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceti, A.; Beghetti, I.; Martini, S.; Faldella, G.; Corvaglia, L. Oxidative Stress and Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Opportunities for Intervention, and Role of Human Milk. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thibeault, D.W. The Precarious Antioxidant Defenses of the Preterm Infant. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, P.; Jaleel, C.A.; Salem, M.A.; Nabi, G.; Sharma, S. Roles of Enzymatic and Nonenzymatic Antioxidants in Plants During Abiotic Stress. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010, 30, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friel, J.K.; Martin, S.M.; Langdon, M.; Herzberg, G.R.; Buettner, G.R. Milk from Mothers of Both Premature and Full-Term Infants Provides Better Antioxidant Protection than Does Infant Formula. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 51, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Velasco, I.; Garcia-Escobar, E.; Garcia-Serrano, S.; Rodríguez-Pacheco, F.; Linares, F.; Ruiz De Adana, M.S.; Rubio-Martin, E.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Cobos-Bravo, J.F.; et al. Does Dietary Iodine Regulate Oxidative Stress and Adiponectin Levels in Human Breast Milk? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledo, A.; Arduini, A.; Asensi, M.A.; Sastre, J.; Escrig, R.; Brugada, M.; Aguar, M.; Saenz, P.; Vento, M. Human Milk Enhances Antioxidant Defenses Against Hydroxyl Radical Aggression in Preterm Infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friel, J.K.; Diehl-Jones, B.; Cockell, K.A.; Chiu, A.; Rabanni, R.; Davies, S.S.; Jackson Roberts, L. Evidence of Oxidative Stress in Relation to Feeding Type During Early Life in Premature Infants. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quiles, J.L.; Ochoa, J.J.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M.C.; Linde, J.; Bompadre, S.; Battino, M.; Narbona, E.; Maldonado, J.; Mataix, J. Coenzyme Q Concentration and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Human Milk at Different Stages of Lactation in Mothers of Preterm and Full-Term Infants. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarban, A.; Taheri, F.; Chahkandi, T.; Sharifzadeh, G.; Khorashadizadeh, M. Antioxidant and Radical Scavenging Activity of Human Colostrum, Transitional and Mature Milk. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ankrah, N.A.; Appiah-Opong, R.; Dzokoto, C. Human Breastmilk Storage and the Glutathione Content. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2000, 46, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Aguilar, M.T.; De La Torre, M.J.L.; Borja-Herrero, C.; Lasarte-Velillas, J.J.; Martorell-Juan, L. Antioxidant Properties of Human Milk. J. Pediatr. Biochem. 2013, 3, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht, K.; Goelz, R. Postnatal Cytomegalovirus Infection through Human Milk in Preterm Infants. Clin. Perinatol 2016, 44, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.A.; Baquero-Artiago, F. Review and Guidelines on the Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Post-Natal Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Pediatr (Barc) 2011, 74, 52.e1–52.e13. [Google Scholar]
- Păduraru, L.; Dimitriu, D.C.; Avasiloaiei, A.L.; Moscalu, M.; Zonda, G.I.; Stamatin, M. Total Antioxidant Status in Fresh and Stored Human Milk from Mothers of Term and Preterm Neonates. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, A.M.; Rai, K.; Hegde, A.M. Total Antioxidant Concentrations of Breastmilk-An Eye-Opener to the Negligent. J. Heal. Popul. Nutr. 2011, 29, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.; Woodside, J. Antioxidants in Health and Disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.M.; Basak, A. Human Catalase: Looking for Complete Identity. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R. Tissue-Specific Functions of Individual Glutathione Peroxidases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groussard, C.; Rannou-Bekono, F.; Machefer, G.; Chevanne, M.; Vincent, S.; Sergent, O.; Cillard, J.; Gratas-Delamarche, A. Changes in Blood Lipid Peroxidation Markers and Antioxidants after a Single Sprint Anaerobic Exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 89, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, D.; Miranda, M.; Muriach, M.; Almansa, I.; Jareno, E.; Romero, F.J. Antioxidant Capacity of Human Milk: Effect of Thermal Conditions for the Pasteurization. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballatori, N.; Krance, S.M.; Notenboom, S.; Shi, S.; Tieu, K.; Hammond, C.L. Glutathione Dysregulation and the Etiology and Progression of Human Diseases. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free Radicals and Antioxidants in Normal Physiological Functions and Human Disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebmann, P.M.; Wölfler, A.; Felsner, P.; Holfer, D.; Schauenstein, K. Melatonin and the Immune System. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1997, 112, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J. Antioxidant Actions of Melatonin. Adv. Pharmacol. 1996, 38, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kennaway, D.J.; Wright, H. Melatonin and Circadian Rhythms. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blask, D.E.; Sauer, L.A.; Dauchy, R.T. Melatonin as a Chronobiotic/Anticancer Agent: Cellular, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Their Implications for Circadian-Based Cancer Therapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Reiter, R.J. Pharmacological Actions of Melatonin in Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin-Immune System Relationships. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Cabrera, J.; D’Arpa, D.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Ramos, S. The Oxidant/Antioxidant Network: Role of Melatonin. Biol. Signals Recept. 1999, 8, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X. What Constitutes a Physiological Concentration of Melatonin? J. Pineal Res. 2003, 34, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Hardeland, R.; Manchester, L.C.; Poeggeler, B.; Lopez-Burillo, S.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Reiter, R.J. Mechanistic and Comparative Studies of Melatonin and Classic Antioxidants in Terms of Their Interactions with the ABTS Cation Radical. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 34, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Collin, F. Melatonin: Action as Antioxidant and Potential Applications in Human Disease and Aging. Toxicology 2010, 278, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, M.; Biran, V.; Baud, O. Melatonin and the Newborn Brain. Early Hum. Dev. 2016, 102, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melatonin. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed); National Library of Medicine (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006.
- Shelby, R.D.; Cromeens, B.; Rager, T.M.; Besner, G.E. Influence of Growth Factors on the Development of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Clin. Perinatol. 2019, 46, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.M.; Pane, C.A. Human Breast Milk: Current Concepts of Immunology and Infectious Diseases. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2007, 37, 7–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loui, A.; Eilers, E.; Strauss, E.; Pohl-Schickinger, A.; Obladen, M.; Koehne, P. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Soluble VEGF Receptor 1 (sFlt-1) Levels in Early and Mature Human Milk from Mothers of Preterm versus Term Infants. J. Hum. Lact. 2012, 28, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, C.; Ichiba, H.; Saito, M.; Shintaku, H.; Yamano, T.; Kusuda, S. Trophic Effect of Multiple Growth Factors in Amniotic Fluid or Human Milk on Cultured Human Fetal Small Intestinal Cells. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 34, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munblit, D.; Abrol, P.; Sheth, S.; Chow, L.Y.; Khaleva, E.; Asmanov, A.; Lauriola, S.; Padovani, E.M.; Comberiati, P.; Boner, A.L.; et al. Levels of Growth Factors and Iga in the Colostrum of Women from Burundi and Italy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi, H.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte Growth Factor: From Diagnosis to Clinical Applications. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 327, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobata, R.; Tsukahara, H.; Ohshima, Y.; Ohta, N.; Tokuriki, S.; Tamura, S.; Mayumi, M. High Levels of Growth Factors in Human Breast Milk. Early Hum. Dev. 2008, 84, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.-K.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Gho, Y.S.; Oh, G.T.; Kwon, Y.-G. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Suppresses Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Expression of Endothelial ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 by Inhibiting the Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.L.; Taylor, S.N.; Johnson, D. Host factors in amniotic fluid and breast milk that contribute to gut maturation. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 34, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Chao, J.C.-J. Effect of human milk and epidermal growth factor on growth of human intestinal Caco-2 cells. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 34, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, A.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Otabor, I.; Olson, J.K.; Besner, G.E. Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factor promotes intestinal anastomotic healing. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 171, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, K.E.; Walker, W.A. Immunologic factors in human milk and disease prevention in the preterm infant. Curr. Pediatr. Rep. Online 2013, 1, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, B.; Fituch, C.C.; Williams, C.S.; Hurst, N.M.; Schanler, R.J. Increased Epidermal Growth Factor Levels in Human Milk of Mothers with Extremely Premature Infants. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 54, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellote, C.; Casillas, R.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Castell, M.; Moretones, M.G.; López-Sabater, M.C.; Franch, A. Premature Delivery Influences the Immunological Composition of Colostrum and Transitional and Mature Human Milk. J. Nutr. 2011, 110, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesmans, W.; Gomes, P.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J.; Vanden Berghe, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor amplifies neurotransmitter responses and promotes synaptic communication in the enteric nervous system. Gut 2008, 57, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Babers, G.M.; El Rehany, M.A. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Sera of Breastfed Epileptic Infants and in Breastmilk of Their Mothers. Breastfeed. Med. 2015, 10, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Xia, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, K. S100b protein, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in human milk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.W.; Baumrucker, C.R. Colostral and milk insulin-like growth factors and related substances: Mammary gland and neonatal (intestinal and systemic) targets. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2002, 23, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, S.R.; Blum, W.F.; Gunn, A.J. Temporal changes in insulin-like growth factors I and II and in insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1, 2, and 3 in human milk. Horm. Res. 2008, 69, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgurtas, T.; Aydin, I.; Turan, O.; Koc, E.; Hirfanoglu, I.M.; Acikel, C.H.; Akyol, M.; Erbil, M.K. Vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, insulin-like growth factor-I and platelet-derived growth factor levels in human milk of mothers with term and preterm neonates. Cytokine 2010, 50, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmlinger, M.W.; Hochhaus, F.; Loui, A.; Frommer, K.W.; Obladen, M.; Ranke, M.B. Insulin-like growth factors and binding proteins in early milk from mothers of preterm and term infants. Horm. Res. 2007, 68, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhartova, N.; Matasova, K.; Lasabova, Z.; Javorka, K.; Calkovska, A. Impact of early aggressive nutrition on retinal development in premature infants. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, S215–S226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Ohsaki, A.; Oh-I, S.; Okada, S.; Mori, M. A new anorexigenic protein, nesfatin-1. Peptides 2009, 30, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapping, R.I.; Tobias, P.S. Soluble CD14-Mediated Cellular Responses to Lipopolysaccharide. Chem. Immunol. 2000, 74, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulevitch, R.J.; Tobias, P.S. Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms of Cell Stimulation by Bacterial Endotoxin. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1995, 13, 437–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munblit, D.; Peroni, D.G.; Boix-Amorós, A.; Hsu, P.S.; Land, B.V.; Gay, M.C.L.; Kolotilina, A.; Skevaki, C.; Boyle, R.J.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Human Milk and Allergic Diseases: An Unsolved Puzzle. Nutrients 2017, 9, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodayar-Pardo, P.; Mira-Pascual, L.; Collado, M.C.; Martínez-Costa, C. Impact of lactation stage, gestational age and mode of delivery on breast milk microbiota. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliomäki, M.; Ouwehand, A.; Arvilommi, H.; Kero, P.; Isolauri, E. Transforming growth factor-β in breast milk: A potential regulator of atopic disease at an early age. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, F.; Papacci, P.; Costa, S.; Giannantonio, C.; Cota, F.; Vento, G.; Romagnoli, C. Effect of early expressed human milk on insulin-like growth factor 1 and short-term outcomes in preterm infants. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saso, A.; Blyuss, O.; Munblit, D.; Faal, A.; Moore, S.E.; Doare, K. Le Breast Milk Cytokines and Early Growth in Gambian Infants. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 6, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Lupica, M.M. Adipokines in breast milk and preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catli, G.; Anik, A.; Tuhan, H.Ü.; Kume, T.; Bober, E.; Abaci, A. The relation of leptin and soluble leptin receptor levels with metabolic and clinical parameters in obese and healthy children. Peptides 2014, 56, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, N.; Yura, S.; Itoh, H.; Kakui, K.; Takemura, M.; Nuamah, M.A.; Ogawa, Y.; Masuzaki, H.; Nakao, K.; Fujii, S. Possible role of placental leptin in pregnancy: A review. Endocrine 2002, 19, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.; Fissore, M.; Oggero, R. Breast Milk Hormones and Their Protective Effect on Obesity. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2009, 2009, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith-Kirwin, S.; O’Connor, D.; De Johnston, J.; Lancey, E.; Hassink, S.; Funanage, V. Leptin expression in human mammary epithelial cells and breast milk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabiell, X.; Piñeiro, V.; Tomé, M.A.; Peinó, R.; Diéguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Presence of leptin in colostrum and/or breast milk from lactating mothers: A potential role in the regulation of neonatal food intake. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Rong, S.S.; Sun, X.; Ding, G.; Wan, W.; Zou, L.; Wu, S.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Associations of breast milk adiponectin, leptin, insulin and ghrelin with maternal characteristics and early infant growth: A longitudinal study. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilers, E.; Ziska, T.; Harder, T.; Plagemann, A.; Obladen, M.; Loui, A. Leptin determination in colostrum and early human milk from mothers of preterm and term infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseknecht, K.L.; McGuire, M.K.; Portocarrero, C.P.; McGuire, M.A.; Beerman, K. Leptin is present in human milk and is related to maternal plasma leptin concentration and adiposity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 240, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miralles, O.; Sánchez, J.; Palou, A.; Picó, C. A physiological role of breast milk leptin in body weight control in developing infants. Obesity 2006, 14, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uçar, B.; Kırel, B.; Bör, Ö.; Κılıç, F.S.; Doğruel, Ν.; Durmuş Aydoğdu, S.; Tekin, N. Breast Milk Leptin Concentrations in Initial and Terminal Milk Samples: Relationships to Maternal and Infant Plasma Leptin Concentrations, Adiposity, Serum Glucose, Insulin, Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 13, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Fields, D.; Demerath, E.W. Relationship of insulin, glucose, leptin, IL-6 and TNF-α in human Breast-Milk with Infant Growth and Body Composition. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resto, M.; O’Connor, D.; Leef, K.; Funanage, V.; Spear, M.; Locke, R. Leptin Levels in Preterm Human Breast Milk and Infant Formula. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, N.O.; Anal, O.; Dundar, B.; Ozkan, H.; Cahskan, S.; Büyükgebiz, A. Longitudinal Investigation of the Relationship between Breast Milk Leptin Levels and Growth in Breast-fed Infants. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 18, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.W.; Lind, M.V.; Larnkjær, A.; Due, A.P.; Blom, I.C.; Wells, J.; Lai, C.T.; Mølgaard, C.; Geddes, D.T.; Michaelsen, K.F. Excessive weight gain followed by catch-down in exclusively breastfed infants: An exploratory study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, N.; Yano, W.; Kubota, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Itoh, S.; Kumagai, H.; Kozono, H.; Takamoto, I.; Okamoto, S.; Shiuchi, T.; et al. Adiponectin Stimulates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in the Hypothalamus and Increases Food Intake. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, N.; Takahashi, M.; Funahashi, T.; Kihara, S.; Nishizawa, H.; Kishida, K.; Nagaretani, H.; Matsuda, M.; Komuro, R.; Ouchi, N.; et al. PPARγ Ligands Increase Expression and Plasma Concentrations of Adiponectin, an Adipose-Derived Protein. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luoto, R.; Laitinen, K.; Nermes, M.; Isolauri, E. Impact of maternal probiotic-supplemented dietary counseling during pregnancy on colostrum adiponectin concentration: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.J.; Woo, J.G.; Geraghty, S.R.; Altaye, M.; Davidson, B.S.; Banach, W.; Dolan, L.M.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Morrow, A.L. Adiponectin is present in human milk and is associated with maternal factors. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, W.; Morrow, A.; Peng, Y. Variation of maternal milk adiponectin and its correlation with infant growth. Chin. J. Pediatr. 2011, 49, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Dündar, N.O.; Dündar, B.; Cesur, G.; Yilmaz, N.; Sütu, R.; Özgüner, F. Ghrelin and adiponectin levels in colostrum, cord blood and maternal serum. Pediatr. Int. 2010, 52, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozarda, Y.; Gunes, Y.; Tuncer, G.O. The concentration of adiponectin in breast milk is related to maternal hormonal and inflammatory status during 6 months of lactation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyermann, M.; Brenner, H.; Rothenbacher, D. Adipokines in Human Milk and Risk of Overweight in Early Childhood. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburg, D.S.; Woo, J.G.; Morrow, A.L. Characteristics and Potential Functions of Human Milk Adiponectin. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, S1–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Sorrenti, M.; Benetti, S.; Lupica, M.M.; Liguori, S.A.; Oggero, R. Resistin and leptin in breast milk and infants in early life. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcol, Y.O.; Hizli, Z.B.; Eroz, E. Resistin is present in human breast milk and it correlates with maternal hormonal status and serum level of C-reactive protein. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briana, D.D.; Boutsikou, M.; Baka, S.; Gourgiotis, D.; Marmarinos, A.; Hassiakos, D.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A. Perinatal Changes of Plasma Resistin Concentrations in Pregnancies with Normal and Restricted Fetal Growth. Neonatology 2008, 93, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Lee, C.H.; Lam, C.W.K.; Chan, I.H.S.; Wong, E.; Fok, T.F. Ghrelin in preterm and term newborns: Relation to anthropometry, leptin and insulin. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Lely, A.J.; Tschöp, M.; Heiman, M.L.; Ghigo, E. Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 426–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Ozkan, Y.; Erman, F.; Gurates, B.; Kilic, N.; Colak, R.; Gundogan, T.; Catak, Z.; Bozkurt, M.; Akin, O.; et al. Presence of obestatin in breast milk: Relationship among obestatin, ghrelin, and leptin in lactating women. Nutrition 2008, 24, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, S.; Ozkan, Y.; Kumru, S. Ghrelin is present in human colostrum, transitional and mature milk. Peptides 2006, 27, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kierson, J.; Dimatteo, D.; Locke, R.; MacKley, A.; Spear, M. Ghrelin and cholecystokinin in term and preterm human breast milk. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2006, 95, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Geckil, H.; Karatas, F.; Donder, E.; Kumru, S.; Kavak, E.C.; Colak, R.; Ozkan, Y.; Sahin, I. Milk and blood ghrelin level in diabetics. Nutrition 2007, 23, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesur, G.; Ozguner, F.; Yilmaz, N.; Dundar, B. The relationship between ghrelin and adiponectin levels in breast milk and infant serum and growth of infants during early postnatal life. J. Physiol. Sci. 2012, 62, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Petrucci, E.; Lupica, M.M.; Nanni, G.E.; Oggero, R. Assay of ghrelin concentration in infant formulas and breast milk. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, I.; Walpole, C.; Amorim, L.; Josh, P.; Herington, A.; Chopin, L. The expanding roles of the ghrelin-gene derived peptide obestatin in health and disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osakia, A.; Shimizu, H.; Ishizuka, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Mori, M.; Inoue, S. Enhanced expression of nesfatin/nucleobindin-2 in white adipose tissue of ventromedial hypothalamus-lesioned rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 521, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S. The presence of the peptides apelin, ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in the human breast milk, and the lowering of their levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 2010, 31, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesmin, C.; Fenaille, F.; Becher, F.; Tabet, J.C.; Ezan, E. Identification and characterization of apelin peptides in bovine colostrum and milk by liquid chromatography-Mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5222–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castan-Laurell, I.; Dray, C.; Attané, C.; Duparc, T.; Knauf, C.; Valet, P. Apelin, diabetes, and obesity. Endocrine 2011, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcilar, R.; Turgut, S.; Caner, V.; Akcilar, A.; Ayada, C.; Elmas, L.; Özcan, T.O. The effects of apelin treatment on a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Adv. Med. Sci. 2015, 60, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen, M.V.; Purhonen, A.K.; Miettinen, P.; Pääkkönen, M.; Pirinen, E.; Alhava, E.; Åkerman, K.; Herzig, K.H. Apelin, orexin-A and leptin plasma levels in morbid obesity and effect of gastric banding. Regul. Pept. 2005, 130, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Qin, Y.J.; Mo, J.R.; Wang, N.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, Q. Central apelin-13 inhibits food intake via the CRF receptor in mice. Peptides 2012, 33, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Karmaus, W.; Davis, S.; Gangur, V. Immune markers in breast milk and fetal and maternal body fluids: A systematic review of perinatal concentrations. J. Hum. Lact. 2011, 27, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.A.E.; de Oliveira, G.G.; Oda, J.M.M.; Ono, M.A.; Guembarovski, R.L. Cytokines in Human Breast Milk: Immunological Significance for Newborns. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni, D.G.; Pescollderungg, L.; Piacentini, G.L.; Rigotti, E.; Maselli, M.; Watschinger, K.; Piazza, M.; Pigozzi, R.; Boner, A.L. Immune regulatory cytokines in the milk of lactating women from farming and urban environments. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajani, P.S.; Seppo, A.E.; Järvinen, K.M. Immunologically Active Components in Human Milk and Development of Atopic Disease, With Emphasis on Food Allergy, in the Pediatric Population. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, A.; Tunc, T.; Erdem, G.; Yerebasmaz, N.; Tas, A.; Beken, S.; Basbozkurt, G.; Saldir, M.; Zenciroglu, A.; Yaman, H.; et al. Interleukin-8 and its receptors in human milk from mothers of full-term and premature infants. Breastfeed. Med. 2016, 11, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall, R.; Prentice, A.M.; Ngom, P.T. Interleukin 7 from maternal milk crosses the intestinal barrier and modulates T-cell development in offspring. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, A.; Lu, W.; Lacson, A.; Barleycorn, A.A.; Nolan, S.; Christensen, R.D.; Calhoun, D.A. Effects of Interleukin-8 on the Developing Human Intestine. Cytokine 2002, 20, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Petrova, A. Very Preterm Gestation and Breastmilk Cytokine Content During the First Month of Lactation. Breastfeed. Med. 2011, 6, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, A.E.; Chuang, S.L.; Hayes, P.; Fell, J.M.E. Evolution of in vitro cow’s milk protein-specific inflammatory and regulatory cytokine responses in preterm infants with necrotising enterocolitis. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branton, M.H.; Kopp, J.B. TGF-beta and fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet-Hughes, A.; Duc, N.; Serrant, P.; Vidal, K.; Schiffrin, E. Bioactive molecules in milk and their role in health and disease: The role of transforming growth factor-β. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, Y.; Campos-Alberto, E.; Yamaide, F.; Nakano, T.; Ohnisi, H.; Kawamoto, M.; Kawamoto, N.; Matsui, E.; Kondo, N.; Kohno, Y.; et al. TGF-β Concentration in Breast Milk is Associated with the Development of Eczema in Infants. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, S.R.; Walker, W.A. Immune factors in breast milk and the development of atopic disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogier, E.W.; Frantz, A.L.; Bruno, M.E.C.; Wedlund, L.; Cohen, D.A.; Stromberg, A.J.; Kaetzel, C.S. Secretory antibodies in breast milk promote long-term intestinal homeostasis by regulating the gut microbiota and host gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3074–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reed, J.R.; Schwertfeger, K.L. Immune cell location and function during post-natal mammary gland development. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2010, 15, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustundag, B.; Yilmaz, E.; Dogan, Y.; Akarsu, S.; Canatan, H.; Halifeoglu, I.; Cikim, G.; Denizmen Aygun, A. Levels of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α) and trace elements (Zn, Cu) in breast milk from mothers of preterm and term infants. Med. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, J.S.; Bryan, D.L.; James, M.J.; Gibson, R.A. Cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β1, and TGF-β2) and prostaglandin E2in human milk during the first three months postpartum. Pediatr. Res. 1999, 46, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrdý, J.; Novotná, O.; Kocourková, I.; Prokešová, L. Cytokine expression in the colostral cells of healthy and allergic mothers. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2012, 57, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbaǧci, A.B.; Çekmen, M.B.; Balat, Ö.; Balat, A.; Aksoy, F.; Tarakçioǧlu, M. Persistency of high proinflammatory cytokine levels from colostrum to mature milk in preeclampsia. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Ramírez, N.; Boyd, K.; Zhang, H.; Gangur, V.; Goetzl, L.; Karmaus, W. Maternal serum but not breast milk IL-5, IL-6, and IL-13 immune markers are associated with scratching among infants. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patki, S.; Kadam, S.; Chandra, V.; Bhonde, R. Human breast milk is a rich source of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Hum. Cell 2010, 23, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molès, J.P.; Tuaillon, E.; Kankasa, C.; Bedin, A.S.; Nagot, N.; Marchant, A.; McDermid, J.M.; Van de Perre, P. Breastmilk cell trafficking induces microchimerism-mediated immune system maturation in the infant. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacho, N.T.; Lawrence, R.M. Innate immunity and breast milk. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, K.-M.; Soumalainen, H. Leucocytes in human milk and lymphocyte subsets in cow ’s milk-allergic infants. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 13, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vass, R.A.; Kemeny, A.; Dergez, T.; Ertl, T.; Reglodi, D.; Jungling, A.; Tamas, A. Distribution of bioactive factors in human milk samples. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2019, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bendiks, M.; Kopp, M.V. The relationship between advances in understanding the microbiome and the maturing hygiene hypothesis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, P.F.; Dore, J.; Leclerc, M.; Levenez, F.; Benyacoub, J.; Serrant, P.; Segura-Roggero, I.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Donnet-Hughes, A. Bacterial Imprinting of the Neonatal Immune System: Lessons from Maternal Cells? Pediatrics 2007, 119, e724–e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcguire, M.K.; Mcguire, M.A. Human Milk: Mother Nature’s Prototypical Probiotic Food? Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix-Amorós, A.; Collado, M.C.; Mira, A. Relationship between milk microbiota, bacterial load, macronutrients, and human cells during lactation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönlund, M.; Gueimonde, M.; Laitinen, K.; Kociubinski, G.; Gronroos, T.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Maternal breast-milk and intestinal bifidobacteria guide the compositional development of the bifidobacterium microbiota in infants at risk of allergic disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, V.; Maldonado-Barragán, A.; Moles, L.; Rodriguez-Baños, M.; Del Campo, R.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, E. Sharing of Bacterial Strains Between Breast Milk and Infant Feces. J. Hum. Lact. 2012, 28, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueimonde, M.; Sakata, S.; Kalliomäki, M.; Isolauri, E.; Benno, Y.; Salminen, S. Effect of maternal consumption of Lactobacillus GG on transfer and establishment of fecal bifidobacterial microbiota in neonates. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 42, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthow, C.; Wickens, K.; Stanley, T.; Mitchell, E.A.; Maude, R.; Abels, P.; Purdie, G.; Murphy, R.; Stone, P.; Kang, J.; et al. The Probiotics in Pregnancy Study (PiP Study): Rationale and design of a double-blind randomised controlled trial to improve maternal health during pregnancy and prevent infant eczema and allergy. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2016, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, M.A.; Gaerlan, S.; De Leoz, M.L.A.; Dimapasoc, L.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Lemay, D.G.; German, J.B.; Mills, D.A.; Lebrilla, C.B. Human milk oligosaccharides in premature infants: Absorption, excretion, and influence on the intestinal microbiota. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antioxidant Compounds | Preterm Infants | Term Infants | Formula Feeding | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preterm | Term | |||
| α-carotene | 7.7 | 3.6 | 0.51 | 1.40 |
| β-carotene | 49.1 | 13.7 | 71.1 | 63.9 |
| Lycopene | 66.1 | 11.9 | 1.5 | 5.8 |
| Retinol | 401.6 | 185.8 | 3086.2 | 911.8 |
| α-tocopherol | 5880.8 | 1381.9 | 20,109.1 | 13,360.2 |
| γ-tocopherol | 1207.1 | 622.8 | 6787.1 | 6561.6 |
| Antioxidant | Activity | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Superoxide dismutase | Eliminates superoxide anion | 2.01–6.26 nmol/min/mL |
| Catalase | Eliminates hydrogen peroxide | 1.84–26.1 nmol/min/mL |
| Glutathione peroxidase | Eliminates hydrogen peroxide | 6.6–17.7 mM/min/L |
| Glutathione | Regeneration of other antioxidants | 10.4–43.1 nmol/mg of protein |
| Melatonin | Free radical scavenger, antioxidant expression | <10–23 ng/L |
| Growth factors | Main Tissue Synthesized | Range (μg/mL) | Main Neonatal Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epidermal-GF | Submandibular salivary gland | 24–37 | Intestinal mucosa maturation and healing, nutrient absorption, protein synthesis |
| Neuronal-GF | Cerebral cortex and hippocampus | 2.8–934 | Nervous system maturation, learning, and memory |
| Insulin-like-GF | Placenta and digestive system | 5–35 | Retinal vascularization, brain maturation |
| Vascular Endothelial-GF | 505–650 | Angiogenesis |
| Adipokines | Tissue Synthesized | Range (ng/mL) | Preterm Infants | Main Neonatal Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leptin | White adipose Placenta Mammary | 0.2–10.1 | ↑/? | Anorexigenic T-lymphocyte responses |
| Adiponectin | Adipocytes | 4.2–87.9 | ≈/? | Orexigenic Regulation of lipid/glucose metabolism Improvement of insulin sensitivity Anti-inflammatory actions |
| Resistin | Immune cells Epithelial cells | 0.2–1.8 | ↑/? | Regulation of glucose homeostasis Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation Inflammatory response |
| Ghrelin | Stomach Pituitary Other | 0.07–6 | ? | Orexigenic Gastric motility and secretion Adipogenesis Anti-inflammatory actions |
| Obestatin | Stomach Small intestine | 0.4–1.3 | ? | Anorexigenic Body weight regulation |
| Nesfatin | Neurons Pancreas Other | 0.008–0.01 | ? | Anorexigenic Production of body fat |
| Apelin | Heart Lung Other | 43–81 | ? | Regulation of cardiovascular system Fluid homeostasis Angiogenesis Regulation of insulin secretion |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gila-Diaz, A.; Arribas, S.M.; Algara, A.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; López de Pablo, Á.L.; Sáenz de Pipaón, M.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D. A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061307
Gila-Diaz A, Arribas SM, Algara A, Martín-Cabrejas MA, López de Pablo ÁL, Sáenz de Pipaón M, Ramiro-Cortijo D. A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061307
Chicago/Turabian StyleGila-Diaz, Andrea, Silvia M. Arribas, Alba Algara, María A. Martín-Cabrejas, Ángel Luis López de Pablo, Miguel Sáenz de Pipaón, and David Ramiro-Cortijo. 2019. "A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity" Nutrients 11, no. 6: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061307
APA StyleGila-Diaz, A., Arribas, S. M., Algara, A., Martín-Cabrejas, M. A., López de Pablo, Á. L., Sáenz de Pipaón, M., & Ramiro-Cortijo, D. (2019). A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity. Nutrients, 11(6), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061307









