Bovine Milk Oligosaccharides with Sialyllactose Improves Cognition in Preterm Pigs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Animal Procedures
2.2. Diets
2.3. Motor Acquisition, Home Cage Activity, Open Field Assessment, and Cognitive Performance
2.4. Tissue Collection
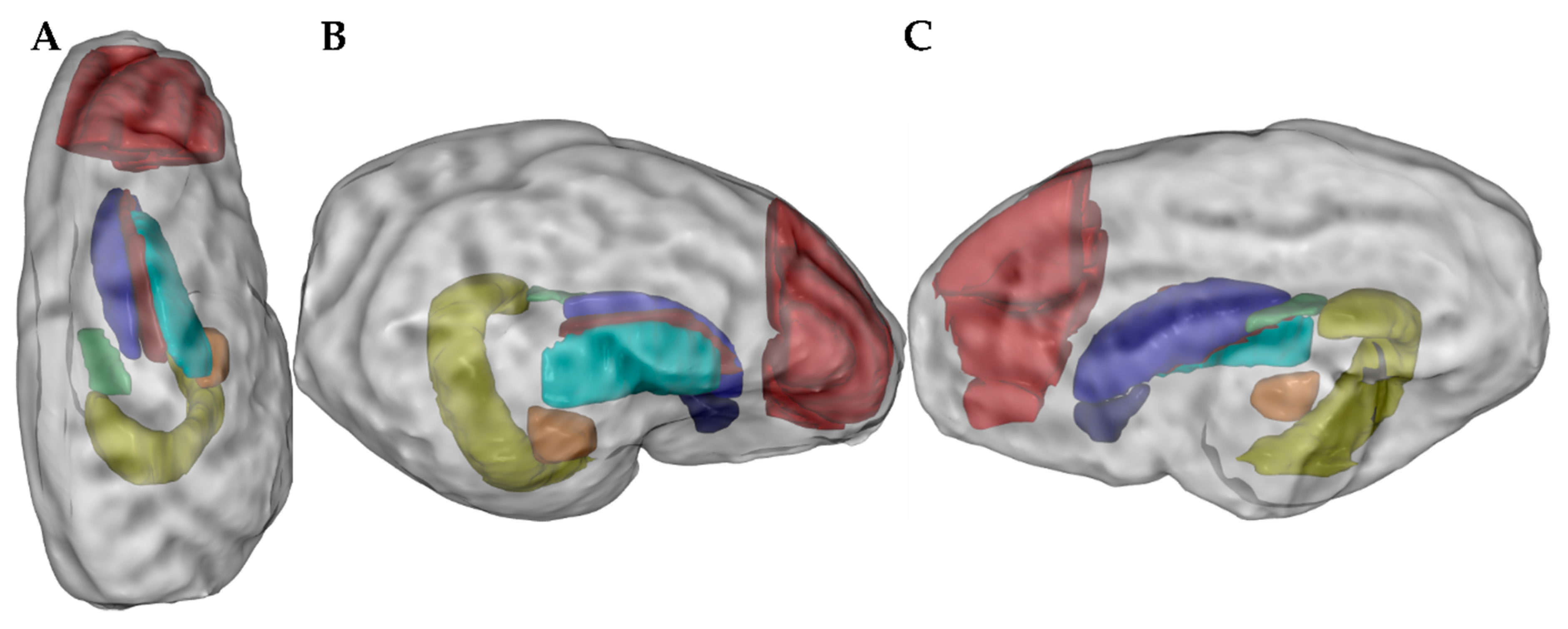
2.5. Ex Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.6. Sialic Acid Measurements
2.7. Hippocampal Gene Expression by qPCR
2.8. In Vitro Oxidative Stress
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcomes and Growth
3.2. Motor Acquisition, Home Cage Activity, Open Field Assessment, and Cognitive Performance
3.3. Brain Weights
3.4. Ex Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3.5. Sialic Acid Levels in Hippocampal Tissue
3.6. Hippocampal Gene Expression
3.7. SAL and Lactose Promote Neuronal Survival In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Oestergaard, M.Z.; Chou, D.; Moller, A.-B.; Narwal, R.; Adler, A.; Vera Garcia, C.; Rohde, S.; Say, L.; et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of preterm birth rates in the year 2010 with time trends since 1990 for selected countries: A systematic analysis and implications. Lancet 2012, 379, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigal, S.; Doyle, L.W. An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood. Lancet 2008, 371, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.E.; Hintz, S.R. Early neurodevelopmental outcomes of extremely preterm infants. Semin. Perinatol. 2016, 40, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaekel, J.; Baumann, N.; Wolke, D. Effects of Gestational Age at Birth on Cognitive Performance: A Function of Cognitive Workload Demands. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, M.; Flannery, D.J.; Schluchter, M.; Cartar, L.; Borawski, E.; Klein, N. Outcomes in Young Adulthood for Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeman, L.D.; Jaekel, J.; Baumann, N.; Bartmann, P.; Wolke, D. Preterm Cognitive Function into Adulthood. Pediatrics 2015, 136, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, A.T.; Cleves, M.A.; Casey, P.H.; Cradock, M.M.; Anand, K.J.S. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2002, 288, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudehope, D.; Fewtrell, M.; Kashyap, S.; Udaeta, E. Nutritional needs of the micropreterm infant. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, S72–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, B.L.; De Mola, C.L.; Victora, C.G. Breastfeeding and Intelligence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Johnstone, B.M.; Remley, D.T. Breast-feeding and cognitive development: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Neuringer, M.; Erdman, J.W.; Kuchan, M.J.; Renner, L.; Johnson, E.E.; Wang, X.; Kroenke, C.D. The effects of breastfeeding versus formula-feeding on cerebral cortex maturation in infant rhesus macaques. Neuroimage 2019, 184, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, W.; Tank, S.; Martin, S.; Shi, R. Human milk and neurodevelopment in children with very low birth weight: A systematic review. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moukarzel, S.; Bode, L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and the Preterm Infant: A Journey in Sickness and in Health. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L. Human milk oligosaccharides: Every baby needs a sugar mama. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B. Sialic Acid Is an Essential Nutrient for Brain Development and Cognition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 177–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Miller, J.B.; McNeil, Y.; McVeagh, P. Sialic acid concentration of brain gangliosides: Variation among eight mammalian species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1998, 119, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Brand-Miller, J.; McVeagh, P.; Petocz, P. Concentration and distribution of sialic acid in human milk and infant formulas. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sosa, S.; Martín, M.-J.; García-Pardo, L.-A.; Hueso, P. Sialyloligosaccharides in Human and Bovine Milk and in Infant Formulas: Variations with the Progression of Lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, T.H.; Brand Miller, J.C.; McNeil, Y.; McVeagh, P. Sialic acid content of infant saliva: Comparison of breast fed with formula fed infants. Arch. Dis. Child. 1997, 77, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Miller, J.B.; Sun, Y.; Ahmad, Z.; McVeagh, P.; Petocz, P. A longitudinal study of salivary sialic acid in preterm infants: Comparison of human milk-fed versus formula-fed infants. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; McVeagh, P.; Petocz, P.; Brand-Miller, J. Brain ganglioside and glycoprotein sialic acid in breastfed compared with formula-fed infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, B.L.G.; Oppenheimer, J.; Winick, M. Effects of essential fatty acid deficiency during late gestation on brain N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolism and behaviour in the progeny. Br. J. Nutr. 1981, 46, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, B.L.G.; Winick, M. A Possible Relationship between Brain N-Acetylneuraminic Acid Content and Behavior. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1979, 161, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.L.G.; Winick, M. Effects of environmental stimulation on brain N-acetylneuraminic acid content and behavior. J. Nutr. 1980, 110, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, B.L.G.; Winick, M. Effects of administration of N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) on brain NANA content and behavior. J. Nutr. 1980, 110, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, F.; Ikeuchi, Y.; Urashima, T.; Fujihara, M.; Ohtsuki, K.; Yanahira, S. Effects of Feeding Sialyllactose and Galactosylated N-Acetylneuraminic Acid on Swimming Learning Ability and Brain Lipid Composition in Adult Rats. J. Appl. Glycosci. 2006, 53, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveros, E.; Vázquez, E.; Barranco, A.; Ramírez, M.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-García, J.; Buck, R.; Rueda, R.; Martín, M. Sialic Acid and Sialylated Oligosaccharide Supplementation during Lactation Improves Learning and Memory in Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikusui, T.; Shimozawa, A.; Kitagawa, A.; Nagasawa, M.; Mogi, K.; Yagi, S.; Shiota, K. N-Acetylmannosamine Improves Object Recognition and Hippocampal Cell Proliferation in Middle-Aged Mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Yu, B.; Karim, M.; Hu, H.; Sun, Y.; McGreevy, P.; Petocz, P.; Held, S.; Brand-Miller, J. Dietary sialic acid supplementation improves learning and memory in piglets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobi, S.K.; Yatsunenko, T.; Li, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Yu, R.K.; Berg, B.M.; Chichlowski, M.; Odle, J. Dietary Isomers of Sialyllactose Increase Ganglioside Sialic Acid Concentrations in the Corpus Callosum and Cerebellum and Modulate the Colonic Microbiota of Formula-Fed Piglets. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangild, P.T.; Thymann, T.; Schmidt, M.; Stoll, B.; Burrin, D.G.; Buddington, R.K. Invited review: The preterm pig as a model in pediatric gastroenterology. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4713–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, A.D.; Sangild, P.T.; Munch, S.L.; van der Beek, E.M.; Renes, I.B.; Van Ginneken, C.; Greisen, G.O.; Thymann, T. Delayed growth, motor function and learning in preterm pigs during early postnatal life. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R481–R492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudd, A.T.; Salcedo, J.; Alexander, L.S.; Johnson, S.K.; Getty, C.M.; Chichlowski, M.; Berg, B.M.; Barile, D.; Dilger, R.N. Porcine Milk Oligosaccharides and Sialic Acid Concentrations Vary Throughout Lactation. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obelitz-Ryom, K.; Rendboe, A.; Nguyen, D.; Rudloff, S.; Brandt, A.; Nielsen, D.; Heckmann, A.; Chichlowski, M.; Sangild, P.; Thymann, T.; et al. Bovine Milk Oligosaccharides with Sialyllactose for Preterm Piglets. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, M.R.P.; Dilger, R.N.; Johnson, R.W. Place and direction learning in a spatial T-maze task by neonatal piglets. Anim. Cogn. 2012, 15, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersen, A.D.; Nguyen, D.N.; Langhorn, L.; Renes, I.B.; van Elburg, R.M.; Hartog, A.; Tims, S.; van de Looij, Y.; Sangild, P.T.; Thymann, T. Synbiotics Combined with Glutamine Stimulate Brain Development and the Immune System in Preterm Pigs. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitz, N.F.; Gibbs, R.B.; Johnson, D.A. Selective lesion of septal cholinergic neurons in rats impairs acquisition of a delayed matching to position T-maze task by delaying the shift from a response to a place strategy. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 77, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veraart, J.; Novikov, D.S.; Christiaens, D.; Ades-Aron, B.; Sijbers, J.; Fieremans, E. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. Neuroimage 2016, 142, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koay, C.G.; Basser, P.J. Analytically exact correction scheme for signal extraction from noisy magnitude MR signals. J. Magn. Reson. 2006, 179, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, E.; Dhital, B.; Kiselev, V.G.; Reisert, M. Gibbs-ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel-shifts. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, S.N.; Kroenke, C.D.; Østergaard, L.; Ackerman, J.J.H.; Yablonskiy, D.A. Modeling dendrite density from magnetic resonance diffusion measurements. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, S.N.; Bjarkam, C.R.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Hansen, B.; Vosegaard, T.; Østergaard, L.; Yablonskiy, D.; Nielsen, N.C.; Vestergaard-Poulsen, P. Neurite density from magnetic resonance diffusion measurements at ultrahigh field: Comparison with light microscopy and electron microscopy. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novikov, D.S.; Fieremans, E.; Jespersen, S.N.; Kiselev, V.G. Quantifying brain microstructure with diffusion MRI: Theory and parameter estimation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.02059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sled, J.G.; Zijdenbos, A.P.; Evans, A.C. A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupé, P.; Yger, P.; Prima, S.; Hellier, P.; Kervrann, C.; Barillot, C. An optimized blockwise nonlocal means denoising filter for 3-D magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonov, V.; Evans, A.C.; Botteron, K.; Almli, C.R.; McKinstry, R.C.; Collins, D.L.; Brain Development Cooperative Group. Unbiased average age-appropriate atlases for pediatric studies. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conrad, M.S.; Sutton, B.P.; Dilger, R.N.; Johnson, R.W. An in vivo three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging-based averaged brain collection of the neonatal piglet (Sus scrofa). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Troy, F.A. LC-MS/MS glycomic analyses of free and conjugated forms of the sialic acids, Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc and KDN in human throat cancers. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Kaalund, S.S.; Skovgaard, K.; Andersen, A.D.; Pakkenberg, B.; Rosenørn, A.; van Elburg, R.M.; Thymann, T.; Greisen, G.O.; Sanglid, P.T. Limited effects of preterm birth and the first enteral nutrition on cerebellum morphology and gene expression in piglets. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pankratova, S.; Gu, B.; Kiryushko, D.; Korshunova, I.; Køhler, L.B.; Rathje, M.; Bock, E.; Berezin, V. A new agonist of the erythropoietin receptor, Epobis, induces neurite outgrowth and promotes neuronal survival. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neiiendam, J.L.; Køhler, L.B.; Christensen, C.; Li, S.; Pedersen, M.V.; Ditlevsen, D.K.; Kornum, M.K.; Kiselyov, V.V.; Berezin, V.; Bock, E. An NCAM-derived FGF-receptor agonist, the FGL-peptide, induces neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival in primary rat neurons. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppa, G.V.; Pierani, P.; Zampini, L.; Carloni, I.; Carlucci, A.; Gabrielli, O. Oligosaccharides in human milk during different phases of lactation. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 1999, 88, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Sugawara, M.; Kawakami, H. Sialic acid in human milk: Composition and functions. Acta Paediatr. Taiwanica 2001, 42, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Brand-Miller, J. The role and potential of sialic acid in human nutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 1351–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, A.; Morley, R.; Cole, T.J. Randomised trial of early diet in preterm babies and later intelligence quotient. BMJ 1998, 317, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, A.; Morley, R.; Isaacs, E. Nutrition and mental development. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, A.T.; Alexander, L.S.; Berding, K.; Waworuntu, R.V.; Berg, B.M.; Donovan, S.M.; Dilger, R.N. Dietary Prebiotics, Milk Fat Globule Membrane, and Lactoferrin Affects Structural Neurodevelopment in the Young Piglet. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, S.; Chichlowski, M.; Berg, B.; Donovan, S.; Dilger, R. Dietary Sialyllactose Does Not Influence Measures of Recognition Memory or Diurnal Activity in the Young Pig. Nutrients 2018, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, J.W.; Dobbing, J. Prenatal and postnatal growth and development of the central nervous system of the pig. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1967, 166, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbing, J.; Sands, J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch. Dis. Child. 1973, 48, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mudd, A.; Fleming, S.; Labhart, B.; Chichlowski, M.; Berg, B.; Donovan, S.; Dilger, R. Dietary Sialyllactose Influences Sialic Acid Concentrations in the Prefrontal Cortex and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measures in Corpus Callosum of Young Pigs. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, G.; Boardman, J.P.; Rueckert, D.; Aljabar, P.; Arichi, T.; Merchant, N.; Gousias, I.S.; Edwards, A.D.; Counsell, S.J. The effect of preterm birth on thalamic and cortical development. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Counsell, S.J.; Ball, G.; Pandit, A.; David Edwards, A. Diffusion Imaging in the Developing Brain. In Diffusion MRI; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 283–300. ISBN 9780123964601. [Google Scholar]
- Kroenke, C.D.; Van Essen, D.C.; Inder, T.E.; Rees, S.; Bretthorst, G.L.; Neil, J.J. Microstructural Changes of the Baboon Cerebral Cortex during Gestational Development Reflected in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diffusion Anisotropy. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12506–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroenke, C.D.; Taber, E.N.; Leigland, L.A.; Knutsen, A.K.; Bayly, P.V. Regional patterns of cerebral cortical differentiation determined by diffusion tensor MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 2916–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüppi, P.S.; Maier, S.E.; Peled, S.; Zientara, G.P.; Barnes, P.D.; Jolesz, F.A.; Volpe, J.J. Microstructural Development of Human Newborn Cerebral White Matter Assessed in Vivo by Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Counsell, S.J.; Edwards, A.D.; Chew, A.T.M.; Anjari, M.; Dyet, L.E.; Srinivasan, L.; Boardman, J.P.; Allsop, J.M.; Hajnal, J.V.; Rutherford, M.A.; et al. Specific relations between neurodevelopmental abilities and white matter microstructure in children born preterm. Brain 2008, 131, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Kooij, B.J.M.; de Vries, L.S.; Ball, G.; van Haastert, I.C.; Benders, M.J.N.L.; Groenendaal, F.; Counsell, S.J. Neonatal tract-based spatial statistics findings and outcome in preterm infants. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McJarrow, P.; Schnell, N.; Jumpsen, J.; Clandinin, T. Influence of dietary gangliosides on neonatal brain development. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracun, I.; Rosner, H.; Drnovsek, V.; Vukelic, Z.; Cosovic, C.; Trbojevic-Cepe, M.; Kubat, M. Gangliosides in the human brain development and aging. Neurochem. Int. 1992, 20, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, P.A. The N-acetyl neuraminic-acid content of the milk of various species. J. Dairy Res. 1973, 40, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.M.; Vohr, B.R.; Allan, W.; Schneider, K.C.; Ment, L.R. Evidence for catch-up in cognition and receptive vocabulary among adolescents born very preterm. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moughan, P.J.; Birtles, M.J.; Cranwell, P.D.; Smith, W.C.; Pedraza, M. The piglet as a model animal for studying aspects of digestion and absorption in milk-fed human infants. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1992, 67, 40–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pond, W.G.; Boleman, S.L.; Fiorotto, M.L.; Ho, H.; Knabe, D.A.; Mersmann, H.J.; Savell, J.W.; Su, D.R. Perinatal ontogeny of brain growth in the domestic pig. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 2000, 223, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbing, J.; Sands, J. Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum. Dev. 1979, 3, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöhle, U.; Schauer, R. Metabolism of sialic acids from exogenously administered sialyllactose and mucin in mouse and rat. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1984, 365, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Volumetry (mm3) | PRE-CON | PRE-SAL | TERM-CON | TERM-NAT | ||||
| Nucleus accumbens | 36.8 ± 4.9 | 38.8 ± 6.1 | 41.2 ± 2.8 | 43.5 ± 5.0 | ||||
| Caudate nucleus | 189 ± 14 | 196 ± 17 | 213 ± 14 | 231 ± 16 | ||||
| Lentiform nucleus | 203 ± 21 | 196 ± 22 | 217 ± 13 | 234 ± 15 | ||||
| Fornix | 16.8 ± 3.0 | 16.7 ± 2.6 | 19.3 ± 2.6 | 19.2 ± 2.8 | ||||
| Amygdala | 53.8 ± 7.6 | 54.8 ± 7.8 | 56.9 ± 6.4 | 64.6 ± 7.0 | ||||
| Prefrontal cortex | 1050 ± 104 | 1043 ± 92 | 1109 ± 78 | 1280 ± 72 | ∆∆∆ | |||
| Internal capsule | 92.8 ± 11.5 | 95.2 ± 10.5 | 100.8 ± 6.4 | 110.7 ± 5.9 | ||||
| Extra-neurite diffusivity (µm2/ms) | ||||||||
| Nucleus accumbens | 0.352 ± 0.026 | 0.353 ± 0.025 | 0.328 ± 0.020 | 0.356 ± 0.015 | ∆∆ | |||
| Caudate nucleus | 0.358 ± 0.018 | 0.357 ± 0.026 | 0.331 ± 0.013 | § | 0.369 ± 0.020 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Lentiform nucleus | 0.362 ± 0.032 | 0.358 ± 0.028 | 0.326 ± 0.009 | § | 0.372 ± 0.013 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Fornix | 0.441 ± 0.148 | 0.432 ± 0.110 | 0.658 ± 0.503 | 0.409 ± 0.109 | ||||
| Amygdala | 0.373 ± 0.043 | 0.362 ± 0.038 | 0.346 ± 0.014 | 0.381 ± 0.014 | ∆∆∆ | |||
| Prefrontal cortex | 0.363 ± 0.026 | 0.366 ± 0.023 | 0.340 ± 0.005 | § | 0.367 ± 0.013 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Internal capsule | 0.306 ± 0.043 | 0.304 ± 0.028 | 0.274 ± 0.013 | § | 0.313 ± 0.021 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Intra-neurite diffusivity (µm2/ms) | ||||||||
| Nucleus accumbens | 2.08 ± 0.36 | 2.08 ± 0.47 | 1.63 ± 0.23 | § | 2.06 ± 0.22 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Caudate nucleus | 1.90 ± 0.13 | 1.85 ± 0.31 | 1.58 ± 0.13 | § | 1.82 ± 0.19 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Lentiform nucleus | 1.82 ± 0.23 | 1.77 ± 0.26 | 1.52 ± 0.10 | 1.74 ± 0.12 | ∆∆∆ | |||
| Fornix | 2.00 ± 0.27 | 1.92 ± 0.17 | 1.93 ± 0.40 | 2.10 ± 0.47 | ||||
| Amygdala | 2.25 ± 0.33 | 2.22 ± 0.43 | 1.87 ± 0.19 | § | 2.28 ± 0.23 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Prefrontal cortex | 2.57 ± 0.18 | 2.55 ± 0.39 | 2.16 ± 0.09 | §§§ | 2.44 ± 0.13 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Internal capsule | 1.39 ± 0.09 | 1.36 ± 0.15 | 1.20 ± 0.07 | § | 1.33 ± 0.09 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Neurite density | ||||||||
| Nucleus accumbens | 0.273 ± 0.036 | 0.279 ± 0.044 | 0.321 ± 0.022 | §§§ | 0.286 ± 0.041 | ∆ | ||
| Caudate nucleus | 0.293 ± 0.029 | 0.286 ± 0.038 | 0.343 ± 0.018 | §§ | 0.297 ± 0.030 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Lentiform nucleus | 0.291 ± 0.036 | 0.265 ± 0.026 | 0.331 ± 0.029 | 0.296 ± 0.025 | ∆∆ | |||
| Fornix | 0.641 ± 0.050 | 0.640 ± 0.065 | 0.601 ± 0.119 | 0.651 ± 0.055 | ||||
| Amygdala | 0.293 ± 0.053 | 0.262 ± 0.051 | 0.310 ± 0.024 | 0.282 ± 0.026 | ∆ | |||
| Prefrontal cortex | 0.287 ± 0.038 | 0.350 ± 0.232 | 0.336 ± 0.020 | § | 0.295 ± 0.015 | ∆∆∆ | ||
| Internal capsule | 0.499 ± 0.035 | 0.486 ± 0.033 | 0.549 ± 0.038 | § | 0.518 ± 0.049 |
| PRE-CON | PRE-SAL | TERM-CON | TERM-NAT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein-bound Neu5Gc | 0.099 ± 0.018 | € | 0.085 ± 0.023 | 0.129 ± 0.033 | 0.162 ± 0.019 | ∆ | ||
| Total protein-bound sialic acid | 2.33 ± 0.28 | 2.25 ± 0.35 | 2.59 ± 0.48 | 2.61 ± 0.45 | ||||
| Ganglioside-bound Neu5Gc | 5.63 ± 1.69 | 5.64 ± 2.42 | 4.23 ± 0.68 | 8.18 ± 4.34 | ∆ | |||
| Total ganglioside-bound sialic acid | 146 ± 19 | 159 ± 43 | 122 ± 9 | §§§ | 201 ± 90 | ∆∆ |
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Fold Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NTRK2 (2) | Neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 2 | −1.594 | <0.05 |
| DLG4 (1) | Discs, large homolog 4 | 1.326 | <0.05 |
| NCAM1 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | 1.135 | <0.05 |
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Fold Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCS1 (1) | Neuronal calcium sensor 1 | 1.871 | <0.01 |
| NSC1 (2) | 3.063 | <0.001 | |
| ST3GAL3 | ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 2 | 2.625 | <0.001 |
| CAMK2A (1) | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha | 2.055 | <0.001 |
| CAMK2A (2) | 2.441 | <0.001 | |
| DCX | Doublecortin | 2.469 | <0.001 |
| NEFH | Neurofilament heavy chain | 2.039 | <0.001 |
| GRIA4 (1) | Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 4 | 1.944 | <0.001 |
| CREB1 (1) | cAMP-responsive element binding protein 1 | 1.678 | <0.001 |
| CREB1 (2) | 1.788 | <0.001 | |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A | 1.752 | <0.001 |
| SLC2A3/GLUT3 | Solute carrier family 2 member 3 | 1.643 | <0.05 |
| FGF2 (2) | Fibroblast growth factor 2 | 1.636 | <0.001 |
| NCAM2 (1) | Neural cell adhesion molecule 2 | 1.619 | <0.001 |
| NCAM2 (2) | 1.631 | <0.001 | |
| NTRK2 (1) | Neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 2 | 1.574 | <0.001 |
| NTRK2 (2) | 1.476 | <0.001 | |
| SYNPO | Synaptopodin | 1.494 | <0.01 |
| BDNF (1) | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor | −1.410 | <0.05 |
| B4GALNT1 | Beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 1 | 1.381 | <0.01 |
| OCLN | Occludin | 1.368 | <0.01 |
| DLG4 (2) | Discs, large homolog 4 | 1.352 | <0.05 |
| NCAM1 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | 1.218 | <0.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obelitz-Ryom, K.; Bering, S.B.; Overgaard, S.H.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Ringgaard, S.; Olesen, J.L.; Skovgaard, K.; Pankratova, S.; Wang, B.; Brunse, A.; et al. Bovine Milk Oligosaccharides with Sialyllactose Improves Cognition in Preterm Pigs. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061335
Obelitz-Ryom K, Bering SB, Overgaard SH, Eskildsen SF, Ringgaard S, Olesen JL, Skovgaard K, Pankratova S, Wang B, Brunse A, et al. Bovine Milk Oligosaccharides with Sialyllactose Improves Cognition in Preterm Pigs. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061335
Chicago/Turabian StyleObelitz-Ryom, Karina, Stine Brandt Bering, Silja Hvid Overgaard, Simon Fristed Eskildsen, Steffen Ringgaard, Jonas Lynge Olesen, Kerstin Skovgaard, Stanislava Pankratova, Bing Wang, Anders Brunse, and et al. 2019. "Bovine Milk Oligosaccharides with Sialyllactose Improves Cognition in Preterm Pigs" Nutrients 11, no. 6: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061335
APA StyleObelitz-Ryom, K., Bering, S. B., Overgaard, S. H., Eskildsen, S. F., Ringgaard, S., Olesen, J. L., Skovgaard, K., Pankratova, S., Wang, B., Brunse, A., Heckmann, A. B., Rydal, M. P., Sangild, P. T., & Thymann, T. (2019). Bovine Milk Oligosaccharides with Sialyllactose Improves Cognition in Preterm Pigs. Nutrients, 11(6), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061335







