Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway on Susceptibility to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables
2.3. Genetic Variables
2.3.1. DNA Isolation
2.3.2. Detection of Gene Polymorphisms and Quality Control
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Genotype Distribution
3.3. Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Risk of NSCLC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN: Cancer Tomorrow. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/bars?mode=population&bar_mode=stacked&cancers=15&populations=905_908_724&types=1 (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, C.; Cañadas-Garre, M.; Alnatsha, A.; Villar, E.; Delgado, J.R.; Calleja-Hernández, M.; Faus-Dáder, M.J. Impact of DNA repair, folate and glutathione gene polymorphisms on risk of non small cell lung cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Parra-Cuentas, E.; Wistuba, I.I. Diagnosis and Molecular Classification of Lung Cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2016, 170, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Jing, H.; Wei, Q.; Wei, G.; Heng, Z. Associations of the risk of lung cancer with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and dietary vitamin D intake: A dose-response PRISMA meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudeen, S.; Shah, I.; Al Menhali, A. A Narrative Role of Vitamin D and Its Receptor: With Current Evidence on the Gastric Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R.; Marcocci, C.; Carmeliet, G.; Bikle, D.; White, J.H.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lips, P.; Munns, C.F.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Giustina, A.; et al. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1109–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N. Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.M.; Shin, E.A. Exploring vitamin D metabolism and function in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda Lancheros, L.E.; Pérez Ramírez, C.; Sánchez Martín, A.; Gálvez Navas, J.M.; Martínez Martínez, F.; Ramírez Tortosa, M.d.C.; Jiménez Morales, A. Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Metabolic Pathway of Vitamin D and Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maj, E.; Trynda, J.; Maj, B.; Gębura, K.; Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Chodyński, M.; Kutner, A.; Wietrzyk, J. Differential response of lung cancer cell lines to vitamin D derivatives depending on EGFR, KRAS, p53 mutation status and VDR polymorphism. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 193, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, N.; Chu, X.M.; Xuan, Y.P.; Ren, D.Q.; Wang, Y.; Ma, K.; Gao, H.J.; Jiao, W.J. Associations between abnormal vitamin D metabolism pathway function and non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7538–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Rojo, P.; Pérez Ramírez, C.; Gálvez Navas, J.M.; Pineda Lancheros, L.E.; Rojo Tolosa, S.; Ramírez Tortosa, M.D.C.; Jiménez Morales, A. Vitamin D-Related Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Risk Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ballesteros, A.I.; Meza-Meza, M.R.; Vizmanos-Lamotte, B.; Parra-Rojas, I.; de la Cruz-Mosso, U. Association of Vitamin D Metabolism Gene Polymorphisms with Autoimmunity: Evidence in Population Genetic Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Gao, S.; Yu, H.; Qian, B. Genetic Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Pathway and Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Survival. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, I.; Onen, H.I.; Yurdakul, A.S.; Konac, E.; Ozturk, C.; Varol, A.; Ekmekci, A. Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene and risk of lung cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, BR232–BR242. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y. Association of vitamin D receptor gene Apa1 and Taq1 polymorphisms with susceptibility to lung squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hebei Med. Univ. 2017, 37, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Kaabachi, W.; Kaabachi, S.; Rafrafi, A.; Amor, A.B.; Tizaoui, K.; Haj Sassi, F.; Hamzaoui, K. Association of vitamin D receptor FokI and ApaI polymorphisms with lung cancer risk in Tunisian population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 6545–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Jia, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Zang, A. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and genetic susceptibility of nonsmall cell lung cancer. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 16, 905–908. [Google Scholar]
- Çiçek, H.; Güleken, N.; Öztuzcu, S.; Sevinç, A. Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and related biochemical parameters in various cancer species. Turk. J. Biochem. 2017, 42, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromowski, T.; Gapska, P.; Scott, R.J.; Kąklewski, K.; Marciniak, W.; Durda, K.; Lener, M.; Górski, B.; Cybulski, C.; Sukiennicki, G.; et al. Serum 25(OH)D concentration, common variants of the VDR gene and lung cancer occurrence. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, K. Vitamin D-Related Gene Polymorphisms, Plasma 25-Hydroxy-Vitamin D, Cigarette Smoke and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Chen, G.; Pan, D.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Meng, J.; Chen, X. Clinical value of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in lung cancer screening. Chin. J. Prim. Med. Pharm. 2018, 21, 2320–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Su, G.; Ling, Z.; Wei, S.; Guangxi, L. Clinical study effection of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism on the susceptibility of lung squamous cell carcinoma, and chemotherapy curative. Chronic Pathematol. J. 2014, 15, 349–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Xu, F.; Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Yu, H.; Qian, B. Genetic polymorphisms in the vitamin D pathway in relation to lung cancer risk and survival. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.-Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.-K.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Tan, W. The Association Between VDR and GC Polymorphisms and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2020, 24, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, P.; Liao, Y.; Gu, X.; Hu, F.; Chen, B. The association study between CYP24A1 gene polymorphisms and risk of liver, lung and gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, A.; He, R.; Dang, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Shi, P.; Bu, X.; Gao, D.; Zhang, N.; et al. Gene polymorphism of cytochrome P450 significantly affects lung cancer susceptibility. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4892–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Li, X.; Quan, X.; Xia, L.; Fang, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, B. Polymorphism in CYP24A1 Is Associated with Lung Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study in Chinese Female Nonsmokers. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa Mangado, E.; Madoz-Gúrpide, A.; Vicente Muelas, N. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la dependencia de alcohol. Med. Y Segur. Del Trab. 2009, 55, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, J.J.; Falbe, K. A step-by-step guide to propensity score matching in R. Pract. Assess Res. Eval. 2014, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 4.0.2; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, X.; Guinó, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; Abecasis, G.R. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heist, R.S.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Neuberg, D.; Su, L.; Asomaning, K.; Hollis, B.W.; Lynch, T.J.; Wain, J.C.; et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D, VDR polymorphisms, and survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5596–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Heist, R.S.; Liu, G.; Neuberg, D.S.; Asomaning, K.; Su, L.; Wain, J.C.; Lynch, T.J.; Giovannucci, E.; Christiani, D.C. Polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, Z.B.; Xu, L.; Shu, Y.Q.; Pan, S.Y.; Dai, J.C.; Jin, G.F.; Ma, H.X.; Shen, H.B. Plasma Vitamin D Levels And Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphisms Are Associated with Survival of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 23, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Morikawa, T.; Odaka, M.; Nakada, T.; Kamiya, N.; Yamashita, M.; Yabe, M.; Inagaki, T.; Asano, H.; Mori, S.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation and Survival of Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4089–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. Vitamin D in the Context of Evolution. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochel, N. Vitamin D and Its Receptor from a Structural Perspective. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, C. Vitamin D and Its Target Genes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, N.; Yang, T.; Shi, P.; He, R.; Chen, M. Association between Polymorphisms of Vitamin D Receptor and Lung Cancer Susceptibility: Evidence from an Updated Meta-analysis. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latacz, M.; Snarska, J.; Kostyra, E.; Fiedorowicz, E.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Grzybowski, R.; Cieślińska, A. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1-Alpha-Hydroxylase (CYP27B1) Gene: The Risk of Malignant Tumors and Other Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczek, M.; Strzelczyk, J.K.; Biernacki, K.; Salatino, S.; Osadnik, T.; Ostrowska, Z. New Variants of the Cytochrome P450 2R1 (CYP2R1) Gene in Individuals with Severe Vitamin D-Activating Enzyme 25(OH)D Deficiency. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, R.F. New perspectives on the vitamin D binding protein. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2012, 30, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozmus, D.; Płomiński, J.; Augustyn, K.; Cieślińska, A. rs7041 and rs4588 Polymorphisms in Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene (VDBP) and the Risk of Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
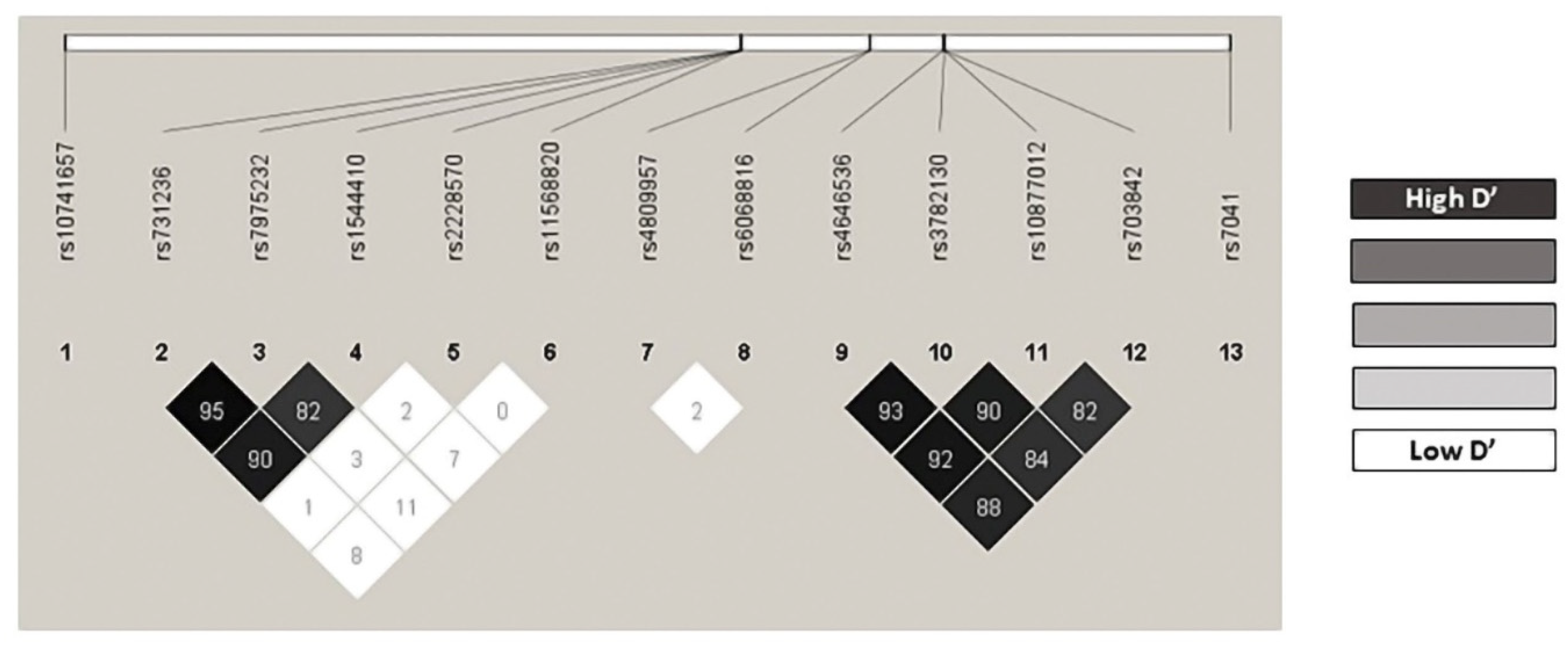
| Gene | Location, SNP | dbSNP ID | Assay ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| VDR (12q13.11) | Exon 8, G > A | rs1544410 (BsmI) | AN324M4 * |
| Exon 1, G > A | rs11568820 (Cdx-2) | C___2880808_10 | |
| Exon 2, C > T | rs2228570 (FokI) | C__12060045_20 | |
| Exon 8, C > A | rs7975232 (ApaI) | C__28977635_10 | |
| Exon 9, T > C | rs731236 (TaqI) | C___2404008_10 | |
| CYP27B1 (12q14.1) | Intron 6, T > C | rs4646536 | C__25623453_10 |
| Promoter 5′, G>A/G>C | rs3782130 | ANGZRHH * | |
| 5′ UTR, A > G 3′ UTR, A > G | rs10877012 rs703842 | C__26237740_10 ANH6J3F * | |
| CYP24A1 (20q13.2) | Exon 6, G > A | rs6068816 | C__25620091_20 |
| 3′ UTR, G > C | rs4809957 | C___3120981_20 | |
| GC (4q13.3) | Exon 11, T > G | rs7041 | C___3133594_30 |
| CYP2R1 (11p15.2) | 5′ UTR, A > G | rs10741657 | C___2958430_10 |
| Cases | Controls | χ2 | p-Value | Reference | OR | CI95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | n (%) | N | n (%) | ||||||
| Gender | 204 | 408 | |||||||
| Female | 54 (26.5) | 129 (31.6) | 1.7189 | 0.1898 | |||||
| Male | 150 (73.5) | 279 (68.4) | |||||||
| Age | 204 | 61.1 ± 10.7 | 408 | 64 (52,75) | 0.1030 * | ||||
| Tobacco consumption | 204 | 396 | |||||||
| Current-smokers | 96 (47.96) | 68 (17.2) | 81.179 | <0.001 | Non-smokers | 8.88 | 5.42–14.9 | ||
| Former-smokers | 81 (39.71) | 150 (37.9) | 3.43 | 2.14–5.63 | |||||
| Non-smokers | 27 (13.24) | 178 (44.9) | 1 | ||||||
| Alcohol consumption | 168 | 369 | |||||||
| Current-drinkers | 34 (20.24) | 104 (28.2) | 3.9433 | 0.1392 | |||||
| Former-drinkers | 6 (3.57) | 14 (3.8) | |||||||
| Non-drinkers | 128 (76.2) | 251 (60.0) | |||||||
| Family history of cancer | 204 | 408 | |||||||
| Yes | 101 (49.5) | 26 (6.37) | 160.35 | <0.001 | No | 15.2 | 9.55–25.2 | ||
| No | 103 (50.5) | 382 (93.6) | |||||||
| Previous lung disease | 204 | 408 | |||||||
| Yes | 70 (34.3) | 142 (34.8) | 0.0144 | 0.9044 | |||||
| No | 134 (65.7) | 266 (65.2) | |||||||
| Histology | 198 | ||||||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 125 (63.1) | ||||||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 73 (36.87) | ||||||||
| Tumor stage | 202 | ||||||||
| I, II or IIIA | 64 (31.7) | ||||||||
| IIIB or IV | 138 (68.3) | ||||||||
| Models | Genotype | Cases [n (%)] | Controls [n (%)] | p-Value a | Adjusted p-Value b | OR c | CI95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotypic | GG | 71 (34.8) | 126 (31.2) | 0.00278 | 0.0361 | 1 | |
| AG | 108 (52.9) | 181 (44.8) | 1.058 | 0.72–1.54 | |||
| AA | 25 (12.3) | 97 (24.0) | 0.457 | 0.26–0.76 | |||
| Dominant | A | 133 (65.2) | 278 (68.8) | 0.3684 | 1 | ||
| GG | 71 (34.8) | 126 (31.2) | |||||
| Recessive | AA | 25 (12.3) | 97 (24.0) | 0.00063 | 0.0082 | 0.442 | 0.26–0.70 |
| G | 179 (87.7) | 307 (76.0) | |||||
| Allelic | A | 158 (38.7) | 375 (46.4) | 0.01076 | 0.1399 | ||
| G | 250 (61.3) | 433 (53.6) | |||||
| Additive | - | - | - | 0.01217 | 0.1582 |
| Genotypic | Dominant | Recessive | Additive | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA vs. GG | AG vs. GG | A vs. GG | AA vs. G | A vs. G | |||||||||||
| p-Value | OR | CI95% | p-Value | OR | CI95% | p-Value | OR | CI95% | p-Value | OR | CI95% | p-Value | OR | CI95% | |
| Tobacco consumption | |||||||||||||||
| Current smokers | <0.001 | 6.11 | 3.51–10.8 | <0.001 | 6.11 | 3.51–10.8 | <0.001 | 5.91 | 3.40–10.4 | <0.001 | 6.10 | 3.50–10.8 | <0.001 | 5.96 | 3.43–10.5 |
| Former smokers | 0.0003 | 2.64 | 1.57–4.55 | 0.0003 | 2.64 | 1.57–4.55 | 0.0004 | 2.58 | 1.53–4.43 | 0.0003 | 2.64 | 1.56–4.54 | 0.0003 | 2.59 | 1.54–4.46 |
| Family history of cancer | |||||||||||||||
| Yes | <0.001 | 10.9 | 6.67–18.4 | <0.001 | 10.9 | 6.67–18.4 | <0.001 | 11.3 | 6.90–18.9 | <0.001 | 10.9 | 6.68–18.4 | <0.001 | 11.1 | 6.81–18.8 |
| rs1544410 | 0.0377 | 0.51 | 0.27–0.95 | 0.7786 | 1.06 | 0.67–1.70 | 0.5478 | 0.87 | 0.56–1.36 | 0.0140 | 0.49 | 0.27–0.85 | 0.0752 | 0.76 | 0.57–1.02 |
| rs1544410 | rs7975232 | rs731236 | rs4646536 | rs703842 | rs3782130 | rs10877012 | Freq | OR (CI95%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G | C | T | A | T | G | G | 0.3283 | 1.00 | --- |
| 2 | A | A | C | A | T | G | G | 0.2364 | 0.63 (0.44–0.91) | 0.015 |
| 3 | A | A | C | G | C | C | T | 0.1053 | 1.00 (0.65–1.53) | 0.99 |
| 4 | G | A | T | A | T | G | G | 0.082 | 0.95 (0.58–1.53) | 0.82 |
| 5 | G | C | T | G | C | C | T | 0.0661 | 0.90 (0.48–1.65) | 0.72 |
| 6 | A | C | T | A | T | G | G | 0.0241 | 0.00 (−Inf–Inf) | 1 |
| 7 | G | A | T | G | C | C | T | 0.019 | 0.40 (0.09–1.84) | 0.24 |
| 8 | A | A | T | A | T | G | G | 0.0136 | 1.26 (0.27–5.88) | 0.77 |
| 9 | G | A | C | A | T | G | G | 0.0133 | 0.11 (0.01–0.94) | 0.044 |
| 10 | G | C | T | G | T | C | T | 0.011 | 0.00 (−Inf–Inf) | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pineda Lancheros, L.E.; Rojo Tolosa, S.; Gálvez Navas, J.M.; Martínez Martínez, F.; Sánchez Martín, A.; Jiménez Morales, A.; Pérez Ramírez, C. Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway on Susceptibility to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214668
Pineda Lancheros LE, Rojo Tolosa S, Gálvez Navas JM, Martínez Martínez F, Sánchez Martín A, Jiménez Morales A, Pérez Ramírez C. Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway on Susceptibility to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nutrients. 2022; 14(21):4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214668
Chicago/Turabian StylePineda Lancheros, Laura Elena, Susana Rojo Tolosa, José María Gálvez Navas, Fernando Martínez Martínez, Almudena Sánchez Martín, Alberto Jiménez Morales, and Cristina Pérez Ramírez. 2022. "Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway on Susceptibility to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Nutrients 14, no. 21: 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214668
APA StylePineda Lancheros, L. E., Rojo Tolosa, S., Gálvez Navas, J. M., Martínez Martínez, F., Sánchez Martín, A., Jiménez Morales, A., & Pérez Ramírez, C. (2022). Effect of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway on Susceptibility to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nutrients, 14(21), 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214668







