Factors Associated with (Exclusive) Breastfeeding Duration—Results of the SUKIE-Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Study Design
2.2. Questionnaire
2.3. Participants
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Variables for Breastfeeding Duration
2.4.2. Variables for Exclusive Breastfeeding Duration
2.4.3. Model Subdivisions
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Factors Influencing Total Breastfeeding Duration
3.3. Factors Influencing Exclusive Breastfeeding Duration
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Infant and Young Child Feeding. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and-young-child-feeding (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Horta, B.L.; Loret de Mola, C.; Victora, C.G. Long-term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Sinha, B.; Sankar, M.J.; Taneja, S.; Bhandari, N.; Rollins, N.; Bahl, R.; Martines, J. Breastfeeding and maternal health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO; UNICEF. Global Breastfeeding Scorecard 2021; Protecting Breastfeeding through Bold National Actions during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bagci Bosi, A.T.; Eriksen, K.G.; Sobko, T.; Wijnhoven, T.M.; Breda, J. Breastfeeding practices and policies in WHO European Region Member States. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bürger, B.; Schindler, K.; Tripolt, T.; Stüger, H.P.; Wagner, K.-H.; Weber, A.; Wolf-Spitzer, A. Breastfeeding Prevalence in Austria according to the WHO IYCF Indicators—The SUKIE-Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REVAN; Bruckmüller, M.; Hitthaller, A.; Kiefer, I.; Zwiauer, K. Österreichische Beikostempfehlungen; AGES, BMG & HVB: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni, C.; Braegger, C.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Puntis, J.; Shamir, R. Breast-feeding: A commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFadden, A.; Gavine, A.; Renfrew, M.J.; Wade, A.; Buchanan, P.; Taylor, J.L.; Veitch, E.; Rennie, A.M.; Crowther, S.A.; Neiman, S.; et al. Support for healthy breastfeeding mothers with healthy term babies. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2, CD001141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rollins, N.C.; Bhandari, N.; Hajeebhoy, N.; Horton, S.; Lutter, C.K.; Martines, J.C.; Piwoz, E.G.; Richter, L.M.; Victora, C.G.; Group, T.L.B.S. Why invest, and what it will take to improve breastfeeding practices? Lancet 2016, 387, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.S.; Pundir, P.; Dhyani, V.S.; Krishnan, J.B.; Parsekar, S.S.; D’Souza, S.M.; Ravishankar, N.; Renjith, V. A mixed-methods systematic review on barriers to exclusive breastfeeding. Nutr. Health 2020, 26, 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Indicators for Assessing Infant and Young Child Feeding Practices Part 2 Measurement; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Indicators for Assessing Infant and Young Child Feeding Practices Part 1 Definitions; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Theurich, M.A.; Davanzo, R.; Busck-Rasmussen, M.; Díaz-Gómez, N.M.; Brennan, C.; Kylberg, E.; Bærug, A.; McHugh, L.; Weikert, C.; Abraham, K.; et al. Breastfeeding rates and programs in Europe: A survey of 11 national breastfeeding committees and representatives. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- David, G.; Kleinbaum, M.K. Survival Analysis, 2nd ed.; The text originally published in 1996; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Legal Information System of the Republic of Austria. Mutterschutzgesetz 1979; Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs: Vienna, Austria, 1979. Available online: https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10008464 (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- ONGKG. Baby-Friendly Hospitals in Österreich. Available online: http://www.ongkg.at/baby-friendly/bfh-in-oesterreich.html (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- VSLÖ. Verband der Still- und LaktationsberaterInnen Österreichs IBCLC. Available online: https://www.stillen.at/ (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Österreichisches Hebammengremium. Available online: https://www.hebammen.at/ (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Schmidt, A.E. Austria Country Note. In International Review of Leave Policies and Research 2021; 2021; Available online: http://www.leavenetwork.org/lp_and_r_reports/ (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Nationales Zentrum Frühe Hilfen Österreich. Available online: https://www.fruehehilfen.at/de/Service/English-Information.htm (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- WHO. Guideline: Protecting, Promoting and Supporting Breastfeeding in Facilities Providing Maternity and Newborn Services; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9789241550086. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, E.; Santhakumaran, S.; Gale, C.; Philipps, L.H.; Modi, N.; Hyde, M.J. Breastfeeding after cesarean delivery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of world literature. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Martinez, J.L.; Segura-Pérez, S. Impact of the Baby-friendly Hospital Initiative on breastfeeding and child health outcomes: A systematic review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016, 12, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimi, F.Z.; Sadeghi, R.; Maleki-Saghooni, N.; Khadivzadeh, T. The effect of mother-infant skin to skin contact on success and duration of first breastfeeding: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.R.; Bergman, N.; Anderson, G.C.; Medley, N. Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD003519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.S.; Alexander, D.D.; Krebs, N.F.; Young, B.E.; Cabana, M.D.; Erdmann, P.; Hays, N.P.; Bezold, C.P.; Levin-Sparenberg, E.; Turini, M. Factors associated with breastfeeding initiation and continuation: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatrics 2018, 203, 190–196.e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Implementation Guidance: Protecting, Promoting and Supporting Breastfeeding in Facilities Providing Maternity and Newborn Services: The Revised Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative; World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9241513802. [Google Scholar]
- Fair, F.J.; Morrison, A.; Soltani, H. The impact of Baby Friendly Initiative accreditation: An overview of systematic reviews. Matern. Child Nutr. 2021, 17, e13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, C.C.; Schmied, H.; Dorner, T.E.; Dür, W. The bumpy road to implementing the Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative in Austria: A qualitative study. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2015, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronborg, H.; Væth, M. Validation of the breastfeeding score—A simple screening tool to predict breastfeeding duration. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakya, P.; Kunieda, M.K.; Koyama, M.; Rai, S.S.; Miyaguchi, M.; Dhakal, S.; Sandy, S.; Sunguya, B.F.; Jimba, M. Effectiveness of community-based peer support for mothers to improve their breastfeeding practices: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banderali, G.; Martelli, A.; Landi, M.; Moretti, F.; Betti, F.; Radaelli, G.; Lassandro, C.; Verduci, E. Short and long term health effects of parental tobacco smoking during pregnancy and lactation: A descriptive review. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Primo, C.C.; Ruela, P.B.F.; Brotto, L.D.d.A.; Garcia, T.R.; Lima, E.d.F. Effects of maternal nicotine on breastfeeding infants. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2013, 31, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahlström, A.; Ebersjö, C.; Lundell, B. Nicotine exposure in breastfed infants. Acta Paediatr. 2004, 93, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, B.; Riediger, N.D.; Farrell, S.M.; Uitz, E.; Moghadasian, M.F. Hypothesis: Smoking decreases breast feeding duration by suppressing prolactin secretion. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, T.; Bauer, C.P.; Beyer, K.; Bufe, A.; Friedrichs, F.; Gieler, U.; Gronke, G.; Hamelmann, E.; Hellermann, M.; Kleinheinz, A.; et al. S3-Guideline on allergy prevention: 2014 update: Guideline of the German Society for Allergology and Clinical Immunology (DGAKI) and the German Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine (DGKJ). Allergo J. Int. 2014, 23, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Perinatal Project. European Perinatal Health Report. Core Indicators of the Health and Care of Pregnant Women and Babies in Europe in 2015; Euro-Peristat Project; 2018; Available online: www.europeristat.com (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- Riaz, M.; Lewis, S.; Naughton, F.; Ussher, M. Predictors of smoking cessation during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Addiction 2018, 113, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcksin, R.; Bel, S.; Galjaard, S.; Devlieger, R. Maternal obesity and breastfeeding intention, initiation, intensity and duration: A systematic review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2014, 10, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achike, M.; Akpinar-Elci, M. The role of maternal prepregnancy body mass index in breastfeeding outcomes: A systematic review. Breastfeed. Med. 2021, 16, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, C.D.; McKenzie, S.A.; Devine, C.M.; Thornburg, L.L.; Rasmussen, K.M. Obese women experience multiple challenges with breastfeeding that are either unique or exacerbated by their obesity: Discoveries from a longitudinal, qualitative study. Matern. Child Nutr. 2017, 13, e12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massov, L. Clinically overweight and obese mothers and low rates of breastfeeding: Exploring women′s perspectives. N. Z. Coll. Midwives J. 2015, 51, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarki, M.; Parlesak, A.; Robertson, A. Comparison of national cross-sectional breast-feeding surveys by maternal education in Europe (2006–2016). Public Health Nutr. 2018, 22, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.; França, G.V.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santana, G.S.; Giugliani, E.R.J.; Vieira, T.d.O.; Vieira, G.O. Factors associated with breastfeeding maintenance for 12 months or more: A systematic review. J. Pediatr. 2018, 94, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronborg, H.; Foverskov, E. Multifactorial influence on duration of exclusive breastfeeding; a Danish cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
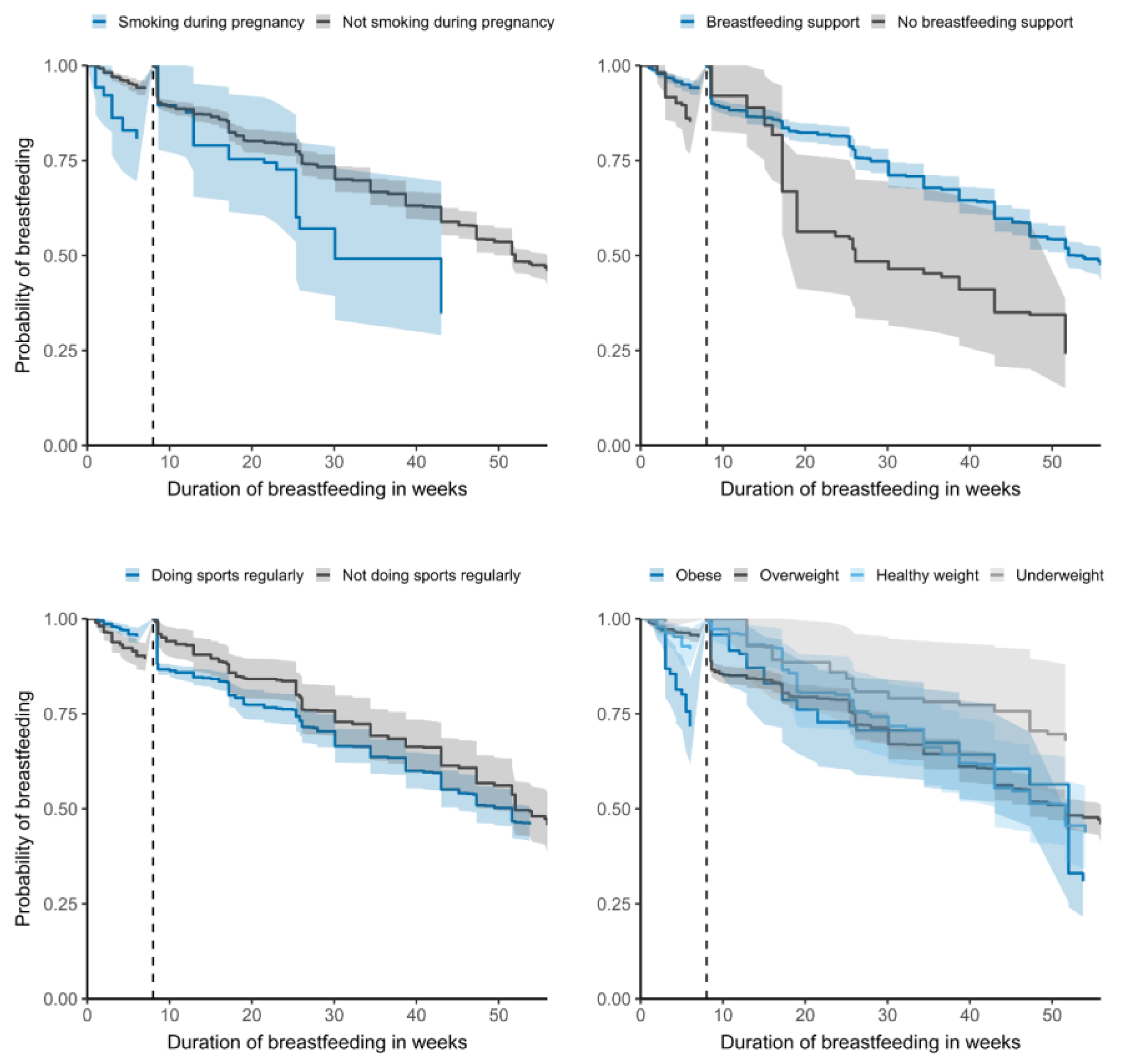

| Ever Breastfed | Any BF at 6 Months | Any BF at 12 Months | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | % | 95% CI | % | 95% CI | |
| Total | 97.5 | 96.5–98.6 | 64.1 | 55.8–72.5 | 40.8 | 31.8–49.7 |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 18–24 | 98.2 | 95.7–100.0 | 56.2 | 47.0–65.5 | 23.5 | 12.6–34.4 |
| 25–29 | 96.8 | 94.6–99.0 | 56.8 | 38.9–74.7 | 35.5 | 17.2–53.8 |
| 30–34 | 97.4 | 95.6–99.2 | 64.1 | 46.8–81.4 | 41.3 | 23.3–59.2 |
| 35–39 | 98.1 | 96.4–99.9 | 80.3 | 75.4–85.2 | 56.0 | 50.1–61.8 |
| >40 | 100.0 | 93.6–100.0 | 81.9 | 70.0–93.8 | 61.2 | 46.4–76.0 |
| Country of birth | ||||||
| Austria | 97.2 | 95.9–98.5 | 60.0 | 50.9–69.1 | 35.7 | 26.4–44.9 |
| other country | 98.5 | 97.2–99.7 | 78.6 | 71.0–86.3 | 57.4 | 45.3–69.4 |
| Education level | ||||||
| low | 94.9 | 89.2–100.0 | 50.7 | 31.5–69.9 | 26.0 | 10.4–41.6 |
| middle | 97.6 | 96.5–98.7 | 60.2 | 49.0–71.3 | 40.0 | 27.9–52.2 |
| high | 99.0 | 98.2–99.9 | 83.7 | 80.3–87.0 | 49.3 | 44.7–53.9 |
| EBF | Not EBF | Not BF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 95% CI | % | 95% CI | % | 95% CI | |
| Total | 30.5 | 28.0–33.1 | 46.9 | 41.1–52.6 | 22.6 | 17.0–28.3 |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 18–24 | 16.0 | 8.3–23.7 | 47.9 | 39.1–56.7 | 36.1 | 26.7–45.6 |
| 25–29 | 27.6 | 22.9–32.3 | 40.5 | 23.1–58.0 | 31.9 | 14.5–49.2 |
| 30–34 | 35.4 | 31.3–39.4 | 49.5 | 45.5–53.6 | 15.1 | 11.6–18.6 |
| 35–39 | 35.4 | 29.5–41.3 | 52.5 | 46.8–58.2 | 12.1 | 8.0–16.2 |
| >40 | 44.5 | 30.2–58.8 | 42.7 | 28.0–57.4 | 12.8 | 1.8–23.7 |
| Country of birth | ||||||
| Austria | 32.1 | 28.5–35.7 | 43.5 | 39.4–47.6 | 24.4 | 18.7–30.1 |
| other country | 25.0 | 16.8–33.1 | 58.5 | 47.2–69.8 | 16.5 | 10.1–22.9 |
| Education level | ||||||
| low | 35.1 | 17.9–52.2 | 32.4 | 16.1–48.7 | 32.5 | 15.9–49.2 |
| middle | 24.3 | 21.5–27.0 | 50.8 | 43.2–58.4 | 24.9 | 17.4–32.5 |
| high | 51.9 | 47.4–56.3 | 37.9 | 33.6–42.2 | 10.2 | 7.6–12.9 |
| Infant Age in Completed Weeks | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–8 | 9–52 | |||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Mother not born in Austria | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mother born in Austria | 0.94 | 0.48–1.82 | 0.85 | 1.23 | 0.92–1.65 | 0.17 |
| Mother not working before pregnancy | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mother working before pregnancy | 1.42 | 0.63–3.24 | 0.40 | 1.17 | 0.85–1.62 | 0.34 |
| Mother not smoking during pregnancy | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mother smoking during pregnancy | 1.87 | 0.85–4.11 | 0.12 | 1.81 | 1.15–2.87 | 0.01 |
| Vaginal delivery | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Caesarean section | 1.57 | 0.91–2.71 | 0.11 | 1.20 | 0.94–1.53 | 0.15 |
| No breastfeeding support | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Breastfeeding support | 0.40 | 0.21–0.75 | <0.01 | 0.54 | 0.37–0.78 | <0.01 |
| Mother not practising sports regularly | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mother practising sports regularly | 0.67 | 0.40–1.12 | 0.13 | 1.27 | 1.02–1.57 | 0.03 |
| Mother not breastfed as infant | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mother breastfed as infant | 0.62 | 0.37–1.02 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.71–1.10 | 0.26 |
| Infant sex: girl | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Infant sex: boy | 0.87 | 0.52–1.44 | 0.59 | 0.86 | 0.70–1.05 | 0.13 |
| BMI mother: healthy weight | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| BMI mother: underweight | 0.29 | 0.04–2.15 | 0.23 | 0.73 | 0.45–1.16 | 0.18 |
| BMI mother: overweight | 0.90 | 0.45–1.80 | 0.77 | 0.98 | 0.76–1.27 | 0.89 |
| BMI mother: obese | 3.17 | 1.69–5.93 | <0.01 | 1.35 | 0.89–2.06 | 0.16 |
| Infant Age in Completed Weeks | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Week of Age | 2–8 Weeks of Age | 9–17 Weeks of Age | |||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Mother not born in Austria | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mother born in Austria | 1.11 | 0.79–1.56 | 0.55 | 0.72 | 0.39–1.31 | 0.28 | 0.79 | 0.48–1.30 | 0.36 |
| Monthly net household income >€2500 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| ≤€2500 | 1.05 | 0.76–1.44 | 0.79 | 1.86 | 1.06–3.25 | 0.03 | 1.71 | 1.06–2.75 | 0.03 |
| Mother not working before pregnancy | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mother working before pregnancy | 1.02 | 0.66–1.59 | 0.93 | 1.19 | 0.54–2.59 | 0.67 | 1.68 | 0.85–3.32 | 0.14 |
| Mother not smoking during pregnancy | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mother smoking during pregnancy | 1.07 | 0.64–1.80 | 0.80 | 0.43 | 0.10–1.83 | 0.25 | 1.92 | 0.87–4.21 | 0.11 |
| Delivery not in BFH | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Delivery in BFH | 0.59 | 0.40–0.89 | 0.01 | 0.83 | 0.42–1.63 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 0.44–1.42 | 0.44 |
| No breastfeeding support | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Breastfeeding support | 0.99 | 0.65–1.50 | 0.95 | 0.31 | 0.16–0.59 | <0.01 | 0.35 | 0.19–0.67 | <0.01 |
| Mother not practising sports regularly | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mother practising sports regularly | 0.79 | 0.61–1.02 | 0.07 | 0.61 | 0.37–1.01 | 0.05 | 0.94 | 0.63–1.42 | 0.78 |
| Mother not breastfed as infant | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mother breastfed as infant | 0.88 | 0.68–1.14 | 0.34 | 0.73 | 0.43–1.21 | 0.22 | 1.03 | 0.66–1.60 | 0.92 |
| Not first birth | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| First birth | 2.02 | 1.53–2.67 | <0.01 | 1.02 | 0.60–1.73 | 0.95 | 1.02 | 0.66–1.58 | 0.93 |
| Vaginal birth | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Caesarean section | 1.38 | 1.04–1.83 | 0.03 | 1.61 | 0.93–2.79 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 0.36–1.16 | 0.15 |
| Infant sex: girl | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Infant sex: boy | 1.05 | 0.82–1.34 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.41–1.10 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 0.65–1.45 | 0.88 |
| BMI mother: healthy weight | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| BMI mother: underweight | 0.72 | 0.40–1.31 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.02–1.12 | 0.06 | 1.37 | 0.69–2.71 | 0.37 |
| BMI mother: overweight | 1.20 | 0.88–1.63 | 0.26 | 1.19 | 0.65–2.17 | 0.57 | 1.41 | 0.87–2.27 | 0.16 |
| BMI mother: obese | 1.67 | 1.11–2.51 | 0.01 | 2.34 | 1.03–5.31 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.35–2.89 | 0.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bürger, B.; Schindler, K.; Tripolt, T.; Griesbacher, A.; Stüger, H.P.; Wagner, K.-H.; Weber, A.; Wolf-Spitzer, A. Factors Associated with (Exclusive) Breastfeeding Duration—Results of the SUKIE-Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091704
Bürger B, Schindler K, Tripolt T, Griesbacher A, Stüger HP, Wagner K-H, Weber A, Wolf-Spitzer A. Factors Associated with (Exclusive) Breastfeeding Duration—Results of the SUKIE-Study. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091704
Chicago/Turabian StyleBürger, Bernadette, Karin Schindler, Tanja Tripolt, Antonia Griesbacher, Hans Peter Stüger, Karl-Heinz Wagner, Adelheid Weber, and Alexandra Wolf-Spitzer. 2022. "Factors Associated with (Exclusive) Breastfeeding Duration—Results of the SUKIE-Study" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091704
APA StyleBürger, B., Schindler, K., Tripolt, T., Griesbacher, A., Stüger, H. P., Wagner, K.-H., Weber, A., & Wolf-Spitzer, A. (2022). Factors Associated with (Exclusive) Breastfeeding Duration—Results of the SUKIE-Study. Nutrients, 14(9), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091704







