A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Measures of Efficacy
2.4. Collection of Fecal Samples and 16S rRNA Gene-Based Sequencing for Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Safety Set
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Study Results
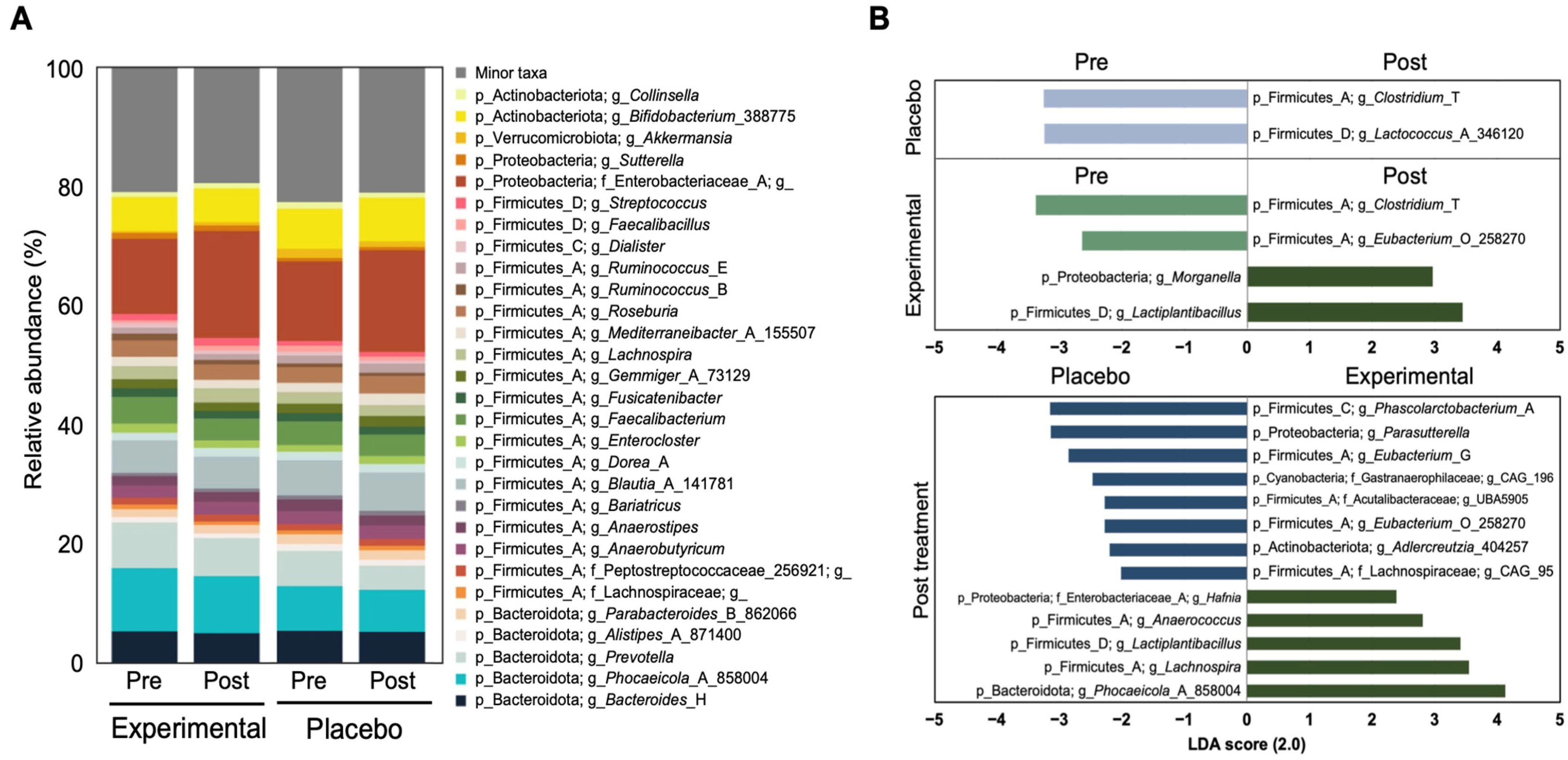
3.2. Fecal Microbiota Analysis
3.3. Safety Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LMT1-48 | Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| DEXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| FTO | Fat mass and obesity-associated gene |
| LEP | Leptin gene |
| KFDA | Korea Food and Drug Administration |
| IP | Investigational product |
| RCT | Double-blind randomized controlled trial |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| CRIS | Clinical Research Information Service |
| AST | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ALT | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| PI | Principal investigator |
| GPAQ | Global Physical Activity Questionnaire |
| EMP | Earth Microbiome Project |
| QIME2 | Quantitative Insights into Microbial Ecology |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| LefSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| LDA score | Linear discriminant analysis effect size analysis |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| α-MSH | α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
References
- Jakubiec, J.; Gmitrzuk, J.; Malinka, Z.; Wiśniewska, K.; Jachymek, A.; Opatowska, M.; Kucharski, T.; Karasiński, M. Obesity in Adults: Causes, Health Consequences, and Treatment Methods. Qual. Sport 2024, 17, 53051. [Google Scholar]
- Sekar, P.K.C.; Veerabathiran, R. Genes linked to obesity-related infertility: Bridging the knowledge gap. Reprod. Dev. Med. 2024, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabathiran, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Kalarani, I.B.; Mohammed, V. A review of genes associated with obesity susceptibility: Findings from association studies. J. Health Sci. Med. Res. 2023, 41, 2023959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-M.; Jung, J.-H.; Yang, Y.S.; Kim, W.; Cho, I.Y.; Lee, Y.-B.; Park, K.-Y.; Nam, G.E.; Han, K. 2023 Obesity Fact Sheet: Prevalence of Obesity and Abdominal Obesity in Adults, Adolescents, and Children in Korea from 2012 to 2021. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 33, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Yang, B.S. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Link of Obesity to Chronic Diseases. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2006, 15, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Vuik, S.; Lerouge, A.; Guillemette, Y.; Feigl, A.; Aldea, A. The Economic Burden of Obesity. OECD 2019; OECD Health Policy Studies, OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, W.; Capasso, A. Diseases and health risks associate d with obesity. Integr. Obes. Diabetes 2018, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Cui, M.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Eftekhar, S.P.; Ala, M. The Pathophysiological Associations Between Obesity, NAFLD, and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Horm. Metab. Res. 2024, 56, 683–696. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Pathophysiological molecular mechanisms of obesity: A link between MAFLD and NASH with cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, C.S. Recent Advances in Anti-Obesity Agents. Korean J. Med. 2018, 93, 501–508. [Google Scholar]
- Alsuhibani, A.; Alrasheed, M.; Gari, M.; Hincapie, A.L.; Guo, J.J. Descriptive analysis of reported adverse events associated with anti-obesity medications using FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) databases 2013–2020. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2022, 44, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Krentz, A.; Fujioka, K.; Hompesch, M. Evolution of pharmacological obesity treatments: Focus on adverse side-effect profiles. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohn, J.-E.; Seol, M.-K.; Bae, E.-Y.; Cho, Y.-J.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, B.-O. The potential probiotic and functional health effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional korean fermented foods. J. Life Sci. 2020, 30, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Jeon, G. The inhibitory effect of lactobacillus sakei kbl isolated from kimchi on the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 2611–2615. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Bok, M.K.; Son, K.; Lee, M.; Park, H.; Yang, J.; Lim, H. Bifidobacterium lactis IDCC 4301 (B. lactis Fit™) supplementation effects on body fat, serum triglyceride, and adipokine ratio in obese women: A randomized clinical trial. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8448–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shin, J.; Kim, M.-j.; Bae, S.; Lee, N.D.; Yoo, B. Efficacy and Safety of WCFA19 (Weissella confusa WIKIM51) in Reducing Body Fat in Overweight and Obese Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G.; et al. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Dong, H.J.; Jeong, H.U.; Jung, H.H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, T.H. Antiobesity effects of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 accompanied by inhibition of Enterobacter cloacae in the intestine of diet-induced obese mice. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 560–566. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.J.; Dong, H.J.; Jeong, H.U.; Ryu, D.W.; Song, S.M.; Kim, Y.R.; Jung, H.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.-H. Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 exerts anti-obesity effect in high-fat diet-induced obese mice by regulating expression of lipogenic genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 869. [Google Scholar]
- Crovesy, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Ferreira, D.; Rosado, E.; Soares-Mota, M. Effect of Lactobacillus on body weight and body fat in overweight subjects: A systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, N.; Yamashita, T.; Osone, T.; Hosooka, T.; Shinohara, M.; Kitahama, S.; Sasaki, K.; Sasaki, D.; Yoneshiro, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Bacteroides spp. promotes branched-chain amino acid catabolism in brown fat and inhibits obesity. iScience 2021, 24, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, R.; Lucas, N.; Dominique, M.; Azhar, S.; Deroissart, C.; Le Solliec, M.A.; Rondeaux, J.; Nobis, S.; Guerin, C.; Leon, F.; et al. Commensal Hafnia alvei strain reduces food intake and fat mass in obese mice-a new potential probiotic for appetite and body weight management. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; DiBaise, J.K.; Zuccolo, A.; Kudrna, D.; Braidotti, M.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Crowell, M.D.; Wing, R.; Rittmann, B.E.; et al. Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennoune, N.; Chan, P.; Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Chabane, Y.N.; Akkermann, K.; Jarv, A.; Ouelaa, W.; Takagi, K.; Ghouzali, I.; et al. Bacterial ClpB heat-shock protein, an antigen-mimetic of the anorexigenic peptide alpha-MSH, at the origin of eating disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lopez, M.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Tindall, B.J.; Gronow, S.; Woyke, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Hahnke, R.L.; Goker, M. Analysis of 1000 Type-Strain Genomes Improves Taxonomic Classification of Bacteroidetes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Feng, X.; Xin, F.; An, R.; Huang, H.; Mao, L.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, X.; et al. B. vulgatus ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity through modulating intestinal serotonin synthesis and lipid absorption in mice. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2423040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislawski, M.A.; Dabelea, D.; Wagner, B.D.; Sontag, M.K.; Lozupone, C.A.; Eggesbo, M. Pre-pregnancy weight, gestational weight gain, and the gut microbiota of mothers and their infants. Microbiome 2017, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Martoni, C.J.; Tamber, S.; Parent, M.; Prakash, S. Evaluation of safety and tolerance of microencapsulated Lactobacillus reuteri NCIMB 30242 in a yogurt formulation: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.J.; Yu, J.G.; Lee, I.A.; Liu, M.J.; Shen, Y.F.; Sharma, S.P.; Jamal, M.A.; Yoo, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.T. Intestinal removal of free fatty acids from hosts by Lactobacilli for the treatment of obesity. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ejtahed, H.-S.; Angoorani, P.; Soroush, A.-R.; Atlasi, R.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Larijani, B. Probiotics supplementation for the obesity management; A systematic review of animal studies and clinical trials. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 228–242. [Google Scholar]
- Mederle, A.L.; Dima, M.; Stoicescu, E.R.; Căpăstraru, B.F.; Levai, C.M.; Hațegan, O.A.; Maghiari, A.L. Impact of Gut Microbiome Interventions on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2024, 14, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalowo, O.E.; Adegoye, G.A.; Obuotor, T.M. Microbial-based bioactive compounds to alleviate inflammation in obesity. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 1810–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilstra, D.; Younes, J.A.; Brummer, R.J.; Kleerebezem, M. Perspective: Fundamental limitations of the randomized controlled trial method in nutritional research: The example of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 561–571. [Google Scholar]

| LMT1-48 (n = 53) | Placebo (n = 53) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Male) | 21 (39.6) | 18 (34.0) | 0.546 |
| Age | 44.6 ± 12.9 | 40.7 ± 10.2 | 0.084 |
| Height (cm) | 166.3 ± 8.3 | 166.7 ± 9.3 | 0.780 |
| Weight (kg) | 75.5 ± 8.2 | 75.3 ± 9.6 | 0.762 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 1.3 | 27.0 ± 1.3 | 0.303 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 126.0 ± 13.4 | 117.9 ± 12.2 | 0.002 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 75.3 ± 9.9 | 71.8 ± 11.6 | 0.043 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 86.7 ± 8.3 | 85.8 ± 9.2 | 0.205 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 208.8 ± 34.6 | 198.4 ± 30.5 | 0.104 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 136.9 ± 136.8 | 111.1 ± 57.4 | 0.825 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.6 ± 15.0 | 52.1 ± 9.3 | 0.546 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 126.3 ± 29.4 | 125.0 ± 25.2 | 0.796 |
| AST (IU/L) | 27.4 ± 12.4 | 24.3 ± 7.2 | 0.181 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 27.8 ± 17.9 | 26.9 ± 20.1 | 0.612 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.75 ± 0.18 | 0.74 ± 0.13 | 0.918 |
| Arm circumference (cm) | 30.9 ± 2.3 | 30.3 ± 1.9 | 0.140 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 57.4 ± 4.5 | 57.4 ± 3.5 | 0.960 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 103.9 ± 3.8 | 104.4 ± 4.4 | 0.539 |
| Waist/hip ratio | 0.90 ± 0.06 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.497 |
| Smoking status | 0.340 | ||
| Never smoker | 38 (71.7) | 43 (81.1) | |
| Ex-smoker | 6 (11.3) | 2 (3.8) | |
| Current smoker | 9 (17.0) | 8 (15.1) | |
| Alcohol intake | 31 (58.5) | 32 (60.4) | 0.843 |
| Physical activity (MET value, h/week) | 64.31 ± 67.84 | 53.10 ± 40.89 | 0.528 |
| Body fat mass (kg) | 30.0± 4.4 | 29.0 ± 4.4 | 0.286 |
| Body fat percentage (%) | 40.9 ± 6.8 | 39.7 ± 5.8 | 0.211 |
| Lean mass (kg) | 41.9 ± 8.5 | 42.5 ± 8.2 | 0.464 |
| Visceral fat area (cm2) | 129.7 ± 43.8 | 112.2 ± 34.5 | 0.043 |
| Subcutaneous fat area (cm2) | 236.8 ± 57.0 | 243.8 ± 57.2 | 0.533 |
| Total abdominal fat area (cm2) | 366.5 ± 66.0 | 356.0 ± 70.6 | 0.433 |
| Group | Baseline | Week 6 | p-Value † | p-Value ‡ | Week 12 | p-Value † | p-Value ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | LMT1-48 | 75.5 ± 8.2 | 74.6 ± 8.4 | <0.001 | 0.249 | 74.1 ± 8.2 | <0.001 | 0.453 |
| Placebo | 75.3 ± 9.6 | 74.8 ± 9.8 | 0.021 | 74.2 ± 9.9 | <0.001 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | LMT1-48 | 27.3 ± 1.3 | 26.9 ± 1.4 | <0.001 | 0.186 | 26.7 ± 1.3 | <0.001 | 0.421 |
| Placebo | 27.0 ± 1.3 | 26.8 ± 1.5 | 0.016 | 26.6 ± 1.6 | <0.001 | |||
| Arm circumference | LMT1-48 | 30.9 ± 2.3 | 30.8 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | 0.497 | 30.7 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | 0.342 |
| Placebo | 30.3 ± 1.9 | 30.2 ± 1.9 | 0.135 | 30.1 ± 1.8 | 0.023 | |||
| Waist circumference | LMT1-48 | 94.5 ± 4.6 | 93.8 ± 4.6 | <0.001 | 0.318 | 93.5 ± 4.5 | <0.001 | 0.452 |
| Placebo | 94.2 ± 5.9 | 93.8 ± 5.9 | 0.015 | 93.3 ± 6.2 | <0.001 | |||
| Hip circumference | LMT1-48 | 103.9 ± 3.8 | 103.5 ± 3.6 | 0.002 | 0.173 | 103.3 ± 3.5 | <0.001 | 0.548 |
| Placebo | 104.4 ± 4.4 | 104.2 ± 4.3 | 0.208 | 104 ± 4.2 | 0.034 | |||
| Calorie intake (kcal) | LMT1-48 | 1637.8 ± 407.4 | 1355.4 ± 380.4 | <0.001 | 0.294 | 1304.5 ± 426.8 | <0.001 | 0.139 |
| Placebo | 1639.4 ± 405.0 | 1309.1 ± 389.7 | <0.001 | 1223.5 ± 386.1 | <0.001 | |||
| Physical activity (MET, hr/week) | LMT1-48 | 64.31 ± 67.84 | 67.09 ± 51.55 | 0.789 | 0.705 | 65.82 ± 39.19 | 0.880 | 0.654 |
| Placebo | 53.1 ± 40.89 | 58.43 ± 48.01 | 0.391 | 62.79 ± 47.46 | 0.173 |
| Group | Baseline | Week 12 | p-Value † | p-Value ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fat mass (kg) | LMT1-48 | 30.0 ± 4.4 | 28.3 ± 4.1 | <0.001 | 0.009 |
| Placebo | 29.0 ± 4.4 | 28.3 ± 4.3 | 0.020 | ||
| Body fat percentage (%) | LMT1-48 | 40.9 ± 6.8 | 39.4 ± 6.3 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| Placebo | 39.7 ± 5.8 | 39.3 ± 5.8 | 0.229 | ||
| Lean mass (kg) | LMT1-48 | 41.9 ± 8.5 | 42.1 ± 8.1 | 0.388 | 0.026 |
| Placebo | 42.5 ± 8.2 | 42.2 ± 8.4 | 0.061 | ||
| Visceral fat area (cm2) | LMT1-48 | 129.7 ± 43.8 | 120.9 ± 43.7 | <0.001 | 0.368 |
| Placebo | 112.2 ± 34.5 | 107.0 ± 33.4 | 0.017 | ||
| Subcutaneous fat area (cm2) | LMT1-48 | 236.8 ± 57.0 | 222.2 ± 61.8 | <0.001 | 0.185 |
| Placebo | 243.8 ± 57.2 | 236.2 ± 64.7 | 0.055 | ||
| Total abdominal fat area (cm2) | LMT1-48 | 366.5 ± 66.0 | 343.1 ± 73.3 | <0.001 | 0.116 |
| Placebo | 356.0 ± 70.6 | 343.2 ± 81.2 | 0.012 | ||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | LMT1-48 | 86.7 ± 8.3 | 86.3 ± 8.5 | 0.354 | 0.116 |
| Placebo | 85.8 ± 9.2 | 86.1 ± 9.7 | 0.146 | ||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | LMT1-48 | 208.8 ± 34.6 | 205.8 ± 31.8 | 0.417 | 0.249 |
| Placebo | 198.4 ± 30.5 | 191.9 ± 30.9 | 0.028 | ||
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | LMT1-48 | 136.9 ± 136.8 | 105.6 ± 68.2 | 0.048 | 0.995 |
| Placebo | 111.1 ± 57.4 | 94.3 ± 51.1 | 0.006 | ||
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | LMT1-48 | 55.6 ± 15.0 | 55.3 ± 14.1 | 0.764 | 0.660 |
| Placebo | 52.1 ± 9.3 | 51.3 ± 8.9 | 0.280 | ||
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | LMT1-48 | 126.3 ± 29.4 | 128.9 ± 28.2 | 0.429 | 0.114 |
| Placebo | 125.0 ± 25.2 | 122.4 ± 25.6 | 0.307 | ||
| Free fatty acid (μmol/L c) | LMT1-48 | 587.6 ± 315.0 | 596.2 ± 212.8 | 0.830 | 0.471 |
| Placebo | 545.1 ± 219.6 | 624.3 ± 298.6 | 0.051 | ||
| Adiponectin (μg/mL) | LMT1-48 | 4.08 ± 0.84 | 4.85 ± 0.56 | <0.001 | 0.540 |
| Placebo | 4.11 ± 0.81 | 4.87 ± 0.52 | <0.001 |
| Body Fat Mass | Group | Baseline | Week 12 | p-Value † | p-Value ‡ |
| Head (kg) | LMT1-48 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.501 | 0.259 |
| Placebo | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0.037 | ||
| Trunk (kg) | LMT1-48 | 15.4 ± 2.2 | 14.4 ± 2.2 | <0.001 | 0.013 |
| Placebo | 14.8 ± 2.6 | 14.4 ± 2.5 | 0.001 | ||
| Android (kg) | LMT1-48 | 2.6 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | 0.041 |
| Placebo | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.4 ± 0.6 | 0.015 | ||
| Gynoid (kg) | LMT1-48 | 4.8 ± 1.0 | 4.6 ± 0.9 | <0.001 | 0.011 |
| Placebo | 4.7 ± 1.0 | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 0.030 | ||
| Rt. arm (kg) | LMT1-48 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 0.012 | 0.098 |
| Placebo | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.806 | ||
| Lt. arm (kg) | LMT1-48 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.032 | 0.152 |
| Placebo | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.835 | ||
| Rt. leg (kg) | LMT1-48 | 4.8 ± 1.2 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| Placebo | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | 0.007 | ||
| Lt. leg (kg) | LMT1-48 | 4.8 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| Placebo | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 1.0 | 0.122 | ||
| Body Fat Percentage | Group | Baseline | Week 12 | p-Value † | p-Value ‡ |
| Head (%) | LMT1-48 | 26.5 ± 0.4 | 26.5 ± 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.370 |
| Placebo | 26.3 ± 0.4 | 26.4 ± 0.5 | 0.177 | ||
| Trunk (%) | LMT1-48 | 42.3 ± 6.1 | 40.5 ± 5.9 | <0.001 | 0.011 |
| Placebo | 40.9 ± 5.4 | 40.5 ± 5.4 | 0.289 | ||
| Android (%) | LMT1-48 | 45.4 ± 5.7 | 43.4 ± 5.3 | <0.001 | 0.028 |
| Placebo | 44.1 ± 5.3 | 43.5 ± 5.2 | 0.073 | ||
| Gynoid (%) | LMT1-48 | 41.5 ± 7.9 | 39.8 ± 7.1 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| Placebo | 40.5 ± 7.1 | 40.1 ± 7.0 | 0.159 | ||
| Rt. arm (%) | LMT1-48 | 46.0 ± 10.9 | 44.8 ± 10.2 | 0.001 | 0.026 |
| Placebo | 45.6 ± 9.2 | 45.5 ± 9.1 | 0.770 | ||
| Lt. arm (%) | LMT1-48 | 44.9 ± 10.5 | 43.7 ± 10.0 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| Placebo | 43.4 ± 8.4 | 43.8 ± 8.9 | 0.301 | ||
| Rt. leg (%) | LMT1-48 | 40.4 ± 8.9 | 38.8 ± 7.8 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| Placebo | 39.1 ± 7.8 | 38.5 ± 7.8 | 0.067 | ||
| Lt. leg (%) | LMT1-48 | 39.5 ± 8.5 | 37.9 ± 8.0 | <0.001 | 0.003 |
| Placebo | 38.7 ± 7.8 | 38.2 ± 7.6 | 0.081 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-B.; Yoo, B.; Baeg, C.; Yun, J.; Ryu, D.-w.; Kim, G.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.H. A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071191
Lee S-B, Yoo B, Baeg C, Yun J, Ryu D-w, Kim G, Kim S, Shin H, Lee JH. A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071191
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sung-Bum, Byungwook Yoo, Chaemin Baeg, Jiae Yun, Dong-wook Ryu, Gyungcheon Kim, Seongok Kim, Hakdong Shin, and Ju Hee Lee. 2025. "A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071191
APA StyleLee, S.-B., Yoo, B., Baeg, C., Yun, J., Ryu, D.-w., Kim, G., Kim, S., Shin, H., & Lee, J. H. (2025). A 12-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 on Body Fat Loss. Nutrients, 17(7), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071191






