Small Intestinal Bacterial and Fungal Overgrowth: Health Implications and Management Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
2.1. Prevalence and Pathophysiology of SIBO
2.2. Methods Used to Diagnose SIBO
2.3. Mechanisms Linking SIBO to Diseases
3. Small Intestinal Fungal Overgrowth
3.1. Prevalence and Pathophysiology of SIFO
3.2. Methods Used to Diagnose SIFO
3.3. Mechanisms Linking SIFO to Diseases
4. Treatment and Management Strategies for SIBO and SIFO
5. Future Directions in SIBO and SIFO Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, K.; Bukavina, L.; Ghannoum, M. Symbiosis and Dysbiosis of the Human Mycobiome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The human microbiome: At the interface of health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorathia, S.J.; Chippa, V.; Rivas, J.M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546634/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Yersin, S.; Vonaesch, P. Small intestinal microbiota: From taxonomic composition to metabolism. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, M.; Adamson, E. Total Gut Balance: Fix Your Microbiome Fast for Complete Digestive Wellness; The Countryman Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum, M.; Smith, C.; Adamson, E.; Isham, N.; Salem, I.; Retuerto, M. Effect of Mycobiome diet on Gut Fungal and Bacterial Communities of Healthy Adults. J. Prob. Health 2020, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukowicz, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Levine, G.M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A comprehensive review. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 3, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bohm, M.; Shin, A.; Teagarden, S.; Xu, H.; Gupta, A.; Siwiec, R.; Nelson, D.; Wo, J.M. Risk Factors Associated with Upper Aerodigestive Tract or Coliform Bacterial Overgrowth of the Small Intestine in Symptomatic Patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Cukrowska, B. How to Recognize and Treat Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.S.; Gao, X.; Bohm, M.; Lin, H.; Gupta, A.; Nelson, D.E.; Toh, E.; Teagarden, S.; Siwiec, R.; Dong, Q.; et al. Characterization of Proximal Small Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Suspected Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z. Overview of Malabsorption. Available online: https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/malabsorption-syndromes/overview-of-malabsorption (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Rao, S.S.C.; Rehman, A.; Yu, S.; Andino, N.M. Brain fogginess, gas and bloating: A link between SIBO, probiotics and metabolic acidosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, M.; Chung, S.; Chitti, L.; Tran, C.; Kritas, S.; Butler, R.; Cummins, A. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth is a common cause of chronic diarrhea. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 19, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, R.L.; Steiner, T.S.; Lima, A.A.M.; Bobak, D.A. How Intestinal Bacteria Cause Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, S331–S337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beam, A.; Clinger, E.; Hao, L. Effect of Diet and Dietary Components on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterfreund, G.L.; Vandivier, L.E.; Sinha, R.; Marozsan, A.J.; Olson, W.C.; Zhu, J.; Bushman, F.D. Succession in the gut microbiome following antibiotic and antibody therapies for Clostridium difficile. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Shukla, R.; Ghoshal, U. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Bridge between Functional Organic Dichotomy. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denison, H.; Wallerstedt, S. Bacterial overgrowth after high-dose corticosteroid treatment. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1989, 24, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseda, D.; Ricciotti, E. NSAID-Gut Microbiota Interactions. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Lai, S.; Lee, A.; He, X.; Chen, S. Meta-analysis: Proton pump inhibitors moderately increase the risk of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.K.; Chan, W.W. Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Spannenburg, L.; Thite, P.; Morrison, M.; Fairlie, T.; Koloski, N.; Kashyap, P.C.; Pimentel, M.; Rezaie, A.; Gores, G.J.; et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in chronic liver disease: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies. EClinicalMedicine 2025, 80, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Werlang, M.E.; Watthanasuntorn, K.; Panjawatanan, P.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Gomez, V.; Lukens, F.J.; Ungprasert, P. Obesity and Risk of Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kim, J.J.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Dai, N. Prevalence and predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Spiegel, B.M.R.; Talley, N.J.; Moayyedi, P. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Morrison, M.; Burger, D.; Martin, N.; Rich, J.; Jones, M.; Koloski, N.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Holtmann, G.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaghenda, F.K.; Hong, J.; Shao, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhu, X. The Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB): A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2024, 34, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurusamy, S.R.; Shah, A.; Talley, N.J.; Koloski, N.; Jones, M.P.; Walker, M.M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Functional Dyspepsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2021, 116, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ran, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, S.; Jia, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Association of gut microbiota with lactose intolerance and coeliac disease: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1395801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Su, B.-B.; Xu, S.-P. Helicobacter pylori infection and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.C.; Day, L.W.; Somsouk, M.; Sewell, J.L. Meta-analysis: Antibiotic therapy for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Mekelburg, S.; Tafesh, Z.; Coburn, E.; Weg, R.; Malik, N.; Webb, C.; Hammad, H.; Scherl, E.; Bosworth, B.P. Testing and Treating Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Reduces Symptoms in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Feng, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z.; Tao, H.; Li, L.; Xuan, J.; Wang, F. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is associated with clinical relapse in patients with quiescent Crohn’s disease: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Brignolo, P.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Reggiani, S.; Sguazzini, C.; Smedile, A.; Pellicano, R.; Resegotti, A.; Astegiano, M.; et al. Glucose breath test and Crohn’s disease: Diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and evaluation of therapeutic response. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlesak, A.; Klein, B.; Schecher, K.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C. Prevalence of small bowel bacterial overgrowth and its association with nutrition intake in nonhospitalized older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.J.; Potts, L.F.; Malhotra, R.; Mountford, R. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in subjects living in residential care homes. Age Ageing 1999, 28, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, A.; Milani, C.; López, P.; Cuervo, A.; Arboleya, S.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; González, S.; Suárez, A.; Gueimonde, M.; et al. Intestinal dysbiosis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. mBio 2014, 5, e01548-01514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisroe, K.; Baron, M.; Frech, T.; Nikpour, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2020, 5, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robey, B.S.; Peery, A.F.; Dellon, E.S. Small Bowel Diverticulosis and Jejunal Perforation in Marfan Syndrome. ACG Case Rep. J. 2018, 5, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Barbera, L.; Macaluso, F.; Fasano, S.; Grasso, G.; Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G. Microbiome Changes in Connective Tissue Diseases and Vasculitis: Focus on Metabolism and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Talley, N.J.; Jones, M.; Kendall, B.J.; Koloski, N.; Walker, M.M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, T.; Kagami, H.; Kinomoto, H.; Ito, A.; Kondo, T.; Shimaoka, K. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth and rice malabsorption in healthy and physically disabled older adults. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet 2003, 16, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, I.; Maslennikov, R.; Poluektova, E.; Vasilieva, E.; Zharikov, Y.; Suslov, A.; Letyagina, Y.; Kozlov, E.; Levshina, A.; Ivashkin, V. Epidemiology of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 3400–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.H.; Pimentel, M. Gastrointestinal bacterial overgrowth: Pathogenesis and clinical significance. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2013, 4, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, R.J.; Chey, W.D. Breath testing for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: Maximizing test accuracy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bures, J.; Cyrany, J.; Kohoutova, D.; Förstl, M.; Rejchrt, S.; Kvetina, J.; Vorisek, V.; Kopacova, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Rezaie, A. Pros and Cons of Breath Testing for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Intestinal Methanogen Overgrowth. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 19, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Losurdo, G.; Leandro, G.; Ierardi, E.; Perri, F.; Barone, M.; Principi, M.; Leo, A.D. Breath Tests for the Non-invasive Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Sakamaki, A.; Takahashi, K.; Naruse, T.; Sato, C.; Kawata, Y.; Tominaga, K.; Abe, H.; Sato, H.; Tsuchiya, A.; et al. Hydrogen-producing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is associated with hepatic encephalopathy and liver function. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, A.; Shah, A.; Jones, M.P.; Koloski, N.; Talley, N.J.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G. Methane positive small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1933313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Millan, M.J.; Leite, G.; Wang, J.; Morales, W.; Parodi, G.; Pimentel, M.L.; Barlow, G.M.; Mathur, R.; Rezaie, A.; Sanchez, M.; et al. Methanogens and Hydrogen Sulfide Producing Bacteria Guide Distinct Gut Microbe Profiles and Irritable Bowel Syndrome Subtypes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.F.; Yu, T.C.; Hong, J.; Fang, J.Y. Emerging Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide in Inflammatory and Neoplastic Colonic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, E.; Kadac-Czapska, K.; Grembecka, M. The importance of food quality, gut motility, and microbiome in SIBO development and treatment. Nutrition 2024, 124, 112464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorens, J.; Froehlich, F.; Schwizer, W.; Saraga, E.; Bille, J.; Gyr, K.; Duroux, P.; Nicolet, M.; Pignatelli, B.; Blum, A.L.; et al. Bacterial overgrowth during treatment with omeprazole compared with cimetidine: A prospective randomised double blind study. Gut 1996, 39, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.F.; Padam, P.; Ruban, A. Aetiology, diagnosis and management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.K.; Tan, M.W. Bacterial biofilms in the human body: Prevalence and impacts on health and disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1237164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, J.R.; Kowdley, K.V.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Sepe, T.; Golner, B.; Perrone, G.; Russell, R.M. Bacterial overgrowth without clinical malabsorption in elderly hypochlorhydric subjects. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E.; Skar, V.; Høverstad, T.; Melby, K. Fasting hypochlorhydria with gram positive gastric flora is highly prevalent in healthy old people. Gut 1992, 33, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iivonen, M.K.; Ahola, T.O.; Matikainen, M.J. Bacterial overgrowth, intestinal transit, and nutrition after total gastrectomy. Comparison of a jejunal pouch with Roux-en-Y reconstruction in a prospective random study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 33, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.; Manzar, H.S. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in older people. Rev. Clin. Gerontol. 2015, 25, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, M.; Lynch, M.; Mullins, E.; O′Moore, R.R.; Walsh, J.B.; Keane, C.T.; Coakley, D. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth--an incidental finding? J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1994, 42, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, X.Q. The prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging 2022, 14, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.H.; Mu, B.; Pan, D.; Shi, Y.N.; Yuan, J.H.; Guan, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.Y.; Guo, L. Association between small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and beta-cell function of type 2 diabetes. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520937866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszak, M.; Górna, I.; Woźniak, D.; Przysławski, J.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. Association between Gut Dysbiosis and the Occurrence of SIBO, LIBO, SIFO and IMO. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, E.; Pyleris, E.; Pimentel, M.; Triantafyllou, K.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth Can Form an Indigenous Proinflammatory Environment in the Duodenum: A Prospective Study. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, A.P.B.; Fisberg, M.; de Morais, M.B. Intestinal permeability and small intestine bacterial overgrowth in excess weight adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Yu, Z.; Meng, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Ren, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in obesity and its related diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 212, 115546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belei, O.; Olariu, L.; Dobrescu, A.; Marcovici, T.; Marginean, O. The relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth among overweight and obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, P.M.; Näslund, E.; Edholm, T.; Schmidt, P.T.; Kristensen, J.; Theodorsson, E.; Holst, J.J.; Efendic, S. GLP-1 suppresses gastrointestinal motility and inhibits the migrating motor complex in healthy subjects and patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Sato, T.; Fujita, H.; Kawatani, M.; Yamada, Y. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonist on changes in the gut bacterium and the underlying mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carris, N.W.; Wallace, S.; DuCoin, C.G.; Mhaskar, R.; Stern, M.; Bunnell, B. Discontinuing semaglutide after weight loss: Strategy for weight maintenance and a possible new side effect. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2024, 102, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, R.; Sridharan, M.; Sullivan, M.; Doran, A.; Frye, J. S792 Weighting on Methane: Weight Loss Medications Associated with Increased Incidence of SIBO. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2024, 119, S546–S547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xu, L.; Tian, Z. Association between small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and toll-like receptor 4 in patients with pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglio, A.E.V.; Grillo, T.G.; De Oliveira, E.C.S.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Gut microbiota, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, X.; Zeng, M.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, J.; He, P.; Sun, J.; Xie, Q.; Chang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. The Role of Fecal Fusobacterium nucleatum and pks(+) Escherichia coli as Early Diagnostic Markers of Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 1171239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulamir, A.S.; Hafidh, R.R.; Abu Bakar, F. The association of Streptococcus bovis/gallolyticus with colorectal tumors: The nature and the underlying mechanisms of its etiological role. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmerich, S.; Djouder, N.; Schöller, M.; Klein, J.P. Production of cytokines by monocytes, epithelial and endothelial cells activated by Streptococcus bovis. Cytokine 2000, 12, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cao, B.; Tian, Q. The effect of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.D.; Van Domselaar, G.; Bernstein, C.N. The Gut Microbiota in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Sessarego, M.; Greco, A.; Bazzica, M.; Filaci, G.; Setti, M.; Savarino, E.; Indiveri, F.; Savarino, V.; Ghio, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients suffering from scleroderma: Clinical effectiveness of its eradication. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Paolino, S.; Greco, A.; Drago, F.; Mansi, C.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A.; Savarino, V. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in rosacea: Clinical effectiveness of its eradication. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B. Rosacea in Crohn’s Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhabale, A.; Nagpure, S. Types of Psoriasis and Their Effects on the Immune System. Cureus 2022, 14, e29536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojetti, V.; De Simone, C.; Aguilar Sanchez, J.; Capizzi, R.; Migneco, A.; Guerriero, C.; Cazzato, A.; Gasbarrini, G.; Amerio, P.; Gasbarrini, A. Malabsorption in psoriatic patients: Cause or consequence? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Indemini, E.; Savarino, V.; Parodi, A. Psoriasis and small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Cordara, V.; Paudice, M.; Herzum, A.; Parodi, A. Oral psoriasis and SIBO: Is there a link? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, e368–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.C.; Tan, G.; Abdulla, H.; Yu, S.; Larion, S.; Leelasinjaroen, P. Does colectomy predispose to small intestinal bacterial (SIBO) and fungal overgrowth (SIFO)? Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, A.; Rao, S.S. Small intestinal fungal overgrowth. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagatwala, J.; Rao, S.S.C. Small intestinal bacterial and fungal overgrowth. In Clinical and Basic Neurogastroenterology and Motility; Rao, S.S.C., Lee, Y.Y., Ghoshal, U.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambrigde, MA, USA, 2020; Chapter 24; pp. 343–358. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, C.; Coss Adame, E.; Attaluri, A.; Valestin, J.; Rao, S.S. Dysmotility and proton pump inhibitor use are independent risk factors for small intestinal bacterial and/or fungal overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, J.; Sonnenborn, U. Yeasts in the gut: From commensals to infectious agents. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2009, 106, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santelmann, H.; Howard, J.M. Yeast metabolic products, yeast antigens and yeasts as possible triggers for irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 17, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retuerto, M.; Al-Shakhshir, H.; Herrada, J.; McCormick, T.S.; Ghannoum, M.A. Analysis of Gut Bacterial and Fungal Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Their Non-Autistic Siblings. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, G.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Hager, C.; Chandra, J.; Retuerto, M.A.; Neut, C.; Vermeire, S.; Clemente, J.; Colombel, J.F.; et al. Bacteriome and Mycobiome Interactions Underscore Microbial Dysbiosis in Familial Crohn’s Disease. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hube, B. From commensal to pathogen: Stage- and tissue-specific gene expression of Candida albicans. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, V.H.; Wang, Y.; Bandara, H.; Mayer, M.P.A.; Samaranayake, L.P. Probiotic lactobacilli inhibit early stages of Candida albicans biofilm development by reducing their growth, cell adhesion, and filamentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6415–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Mullin, G.E. A Wasting Syndrome and Malnutrition Caused by Small Intestine Fungal Overgrowth: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Integr. Med. A Clin. J. 2017, 16, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum, M. Mycobiome, Candida, and the Science of Biofilms. Presented at Standard Process Wholistic Matters, Palmyra, WI, USA, April 2024. Available online: https://mdpi-res.com/data/mdpi_references_guide_v9.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Ghannoum, M. Microbial Biofilms; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tomičić, Z.; Zupan, J.; Matos, T.; Raspor, P. Probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii (nom. nud.) modulates adhesive properties of Candida glabrata. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, M.; Nobile, C.J. Candida albicans biofilms: Development, regulation, and molecular mechanisms. Microbes. Infect. 2016, 18, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, J.; McCormick, T.S.; Imamura, Y.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Ghannoum, M.A. Interaction of Candida albicans with adherent human peripheral blood mononuclear cells increases C. albicans biofilm formation and results in differential expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2612–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangl, I.; Pap, I.J.; Aspöck, C.; Schüller, C. The role of Lactobacillus species in the control of Candida via biotrophic interactions. Microb. Cell 2019, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, A.; Murzyn, A.; Dyjankiewicz, A.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Dziadkowiec, D. The antagonistic effect of Saccharomyces boulardii on Candida albicans filamentation, adhesion and biofilm formation. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009, 9, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.P.; Cowley, E.S.; Nobile, C.J.; Hartooni, N.; Newman, D.K.; Johnson, A.D. Anaerobic Bacteria Grow within Candida albicans Biofilms and Induce Biofilm Formation in Suspension Cultures. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2411–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, M.A. Potential role of phospholipases in virulence and fungal pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, R.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M. Role and relevance of mast cells in fungal infections. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, N.; Tani, K.; Enomoto, U.; Nakai, K.; Watanabe, S. The skin fungus-induced Th1- and Th2-related cytokine, chemokine and prostaglandin E2 production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Santos, N.; Gaffen, S.L. Th17 cells in immunity to Candida albicans. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemniak-Wojtowicz, D.; Kucharska, A.M.; Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, A.; Majcher, A.; Pyrżak, B. Changes of Peripheral Th17 Cells Subset in Overweight and Obese Children After Body Weight Reduction. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 917402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, S.; Paltser, G.; Chan, Y.; Tsui, H.; Engleman, E.; Winer, D.; Dosch, H.M. Obesity predisposes to Th17 bias. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnuaimi, A.D.; Ramdzan, A.N.; Wiesenfeld, D.; O′Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Kolev, S.D.; Reynolds, E.C.; McCullough, M.J. Candida virulence and ethanol-derived acetaldehyde production in oral cancer and non-cancer subjects. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Kong, C.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Qu, X.; Qin, N.; Qin, H. Dysbiosis signature of mycobiota in colon polyp and colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, O.O.; Nakatsu, G.; Dai, R.Z.; Wu, W.K.K.; Wong, S.H.; Ng, S.C.; Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Yu, J. Enteric fungal microbiota dysbiosis and ecological alterations in colorectal cancer. Gut 2019, 68, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Liu, Z. The research progress in the interaction between Candida albicans and cancers. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 988734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, L.; Scarpignato, C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Rifaximin is effective and safe for the treatment of small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X. Efficacy of rifaximin in treating with small intestine bacterial overgrowth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Zocco, M.A.; D’Aversa, F.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Eubiotic properties of rifaximin: Disruption of the traditional concepts in gut microbiota modulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, E.C.; Gabrielli, M.; Scarpellini, E.; Lupascu, A.; Novi, M.; Sottili, S.; Vitale, G.; Cesario, V.; Serricchio, M.; Cammarota, G.; et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth recurrence after antibiotic therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Saad, R.J.; Long, M.D.; Rao, S.S.C. ACG Clinical Guideline: Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahan, S.; Melli, L.C.F.; Mello, C.S.; Rodrigues, M.S.C.; Bezerra Filho, H.; de Morais, M.B. Effectiveness of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and metronidazole in the treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children living in a slum. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.M.; Murray, J.A.; Pimentel, M. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achufusi, T.G.O.; Sharma, A.; Zamora, E.A.; Manocha, D. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Comprehensive Review of Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment Methods. Cureus 2020, 12, e8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Cuevas, L.; Belloch, L.; Martín-Carbonell, V.; Nicolás, A.; Alexandra, I.; Sanchis, L.; Ynfante, M.; Colmenares, M.; Mora, M.; Liebana, A.R.; et al. Do Herbal Supplements and Probiotics Complement Antibiotics and Diet in the Management of SIBO? A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Xing, H.; Chen, D.; Wei, Y. Clinical efficacy of fecal microbiota transplantation for patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinic study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, F.; Frey, S.; Iannelli, A. Surgical Management of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 4677–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Siwiec, R.M.; Wo, J.M. Diagnosis and management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, J.; Ford, A.C.; Yuan, Y.; Chey, W.D.; Lacy, B.E.; Saito, Y.A.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Moayyedi, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Evaluating the Efficacy of a Gluten-Free Diet and a Low FODMAPs Diet in Treating Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; Reed, D.E.; Schneider, T.; Dang, F.; Keshteli, A.H.; De Palma, G.; Madsen, K.; Bercik, P.; Vanner, S. FODMAPs alter symptoms and the metabolome of patients with IBS: A randomised controlled trial. Gut 2017, 66, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.J.; Staudacher, H.M.; Ford, A.C. Efficacy of a low FODMAP diet in irritable bowel syndrome: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut 2022, 71, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.R.F.; Ramos, M.R.Z.; de Oliveira Carlos, L.; da Cruz, M.R.R.; Taconeli, C.A.; Filho, A.J.B.; Nassif, L.S.; Schieferdecker, M.E.M.; Campos, A.C.L. Effects of Probiotics Supplementation on Gastrointestinal Symptoms and SIBO after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Collinot, G.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.O.; Martínez-Bencomo, M.A.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Jara, L.J.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Montes-Cortes, D.H.; Medina, G.; Cruz-Domínguez, M.P. Effectiveness of Saccharomyces boulardii and Metronidazole for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventogiannis, K.; Gkolfakis, P.; Spithakis, G.; Tsatali, A.; Pistiki, A.; Sioulas, A.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Triantafyllou, K. Effect of a Preparation of Four Probiotics on Symptoms of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Association with Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Qu, C.; Wang, B.; Liang, S.; Zeng, B. Probiotics for Preventing and Treating Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Current Evidence. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; McCormick, T.S.; Retuerto, M.; Bebek, G.; Cousineau, S.; Hartman, L.; Barth, C.; Schrom, K. Evaluation of Microbiome Alterations Following Consumption of BIOHM, a Novel Probiotic. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Microbiome Project Consortium. A framework for human microbiome research. Nature 2012, 486, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heniedy, A.M.; Mahdy, D.M.; Abo Elenien, W.I.; Mourad, S.; El-Kadi, R.A. Postbiotics as a health-promoting technique: A review article on scientific and commercial interest. Process Biochem. 2024, 144, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.F.; Murphy, E.F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Lucey, A.J.; Humphreys, M.; Hogan, A.; Hayes, P.; O’Reilly, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; Wood-Martin, R.; et al. Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut 2014, 63, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Pither, J.; Baumeister, P.; Little, J.P.; Gill, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmadi-Vand, Z.; Marsden, K.R.; Gibson, D.L. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
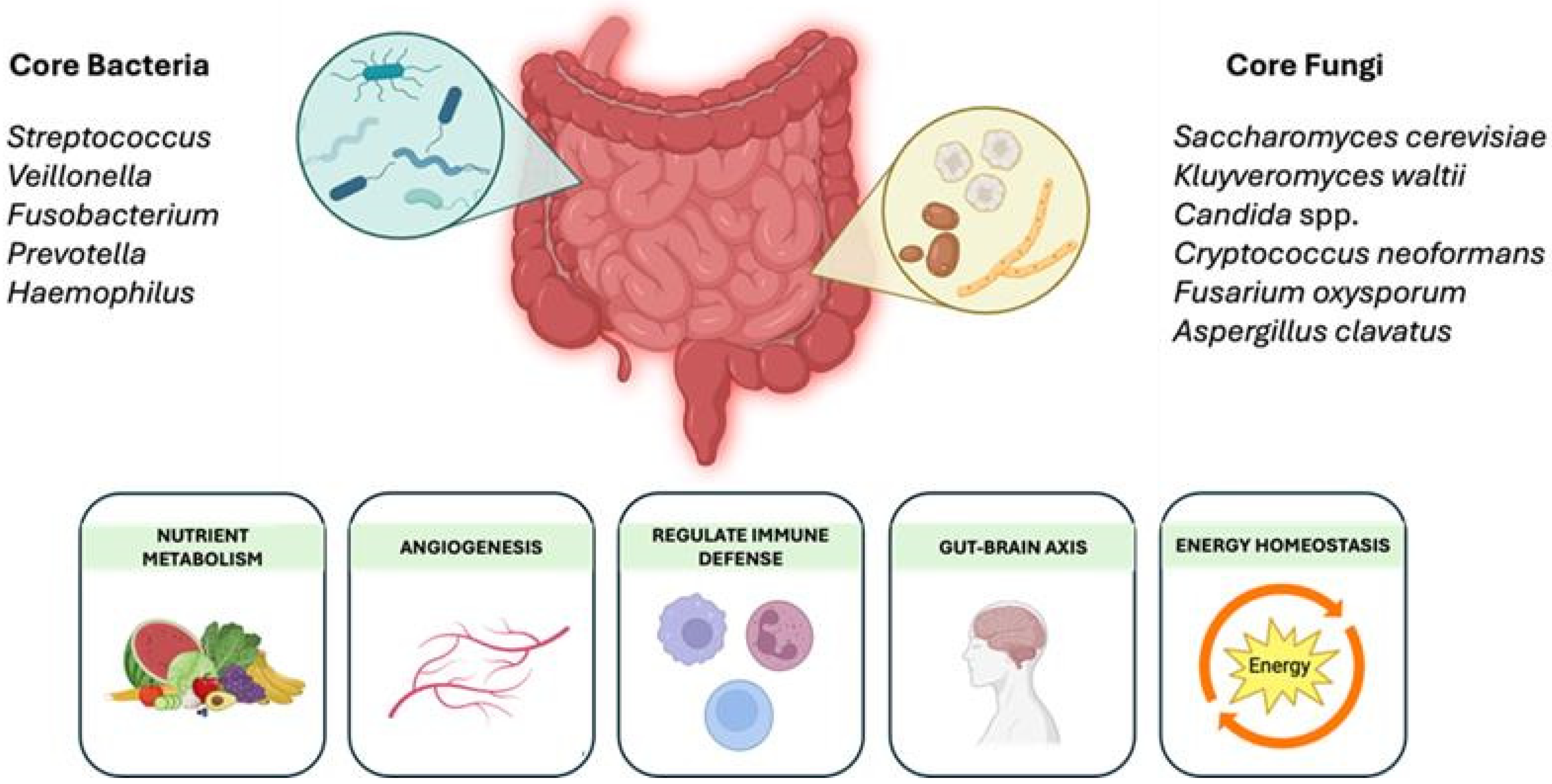

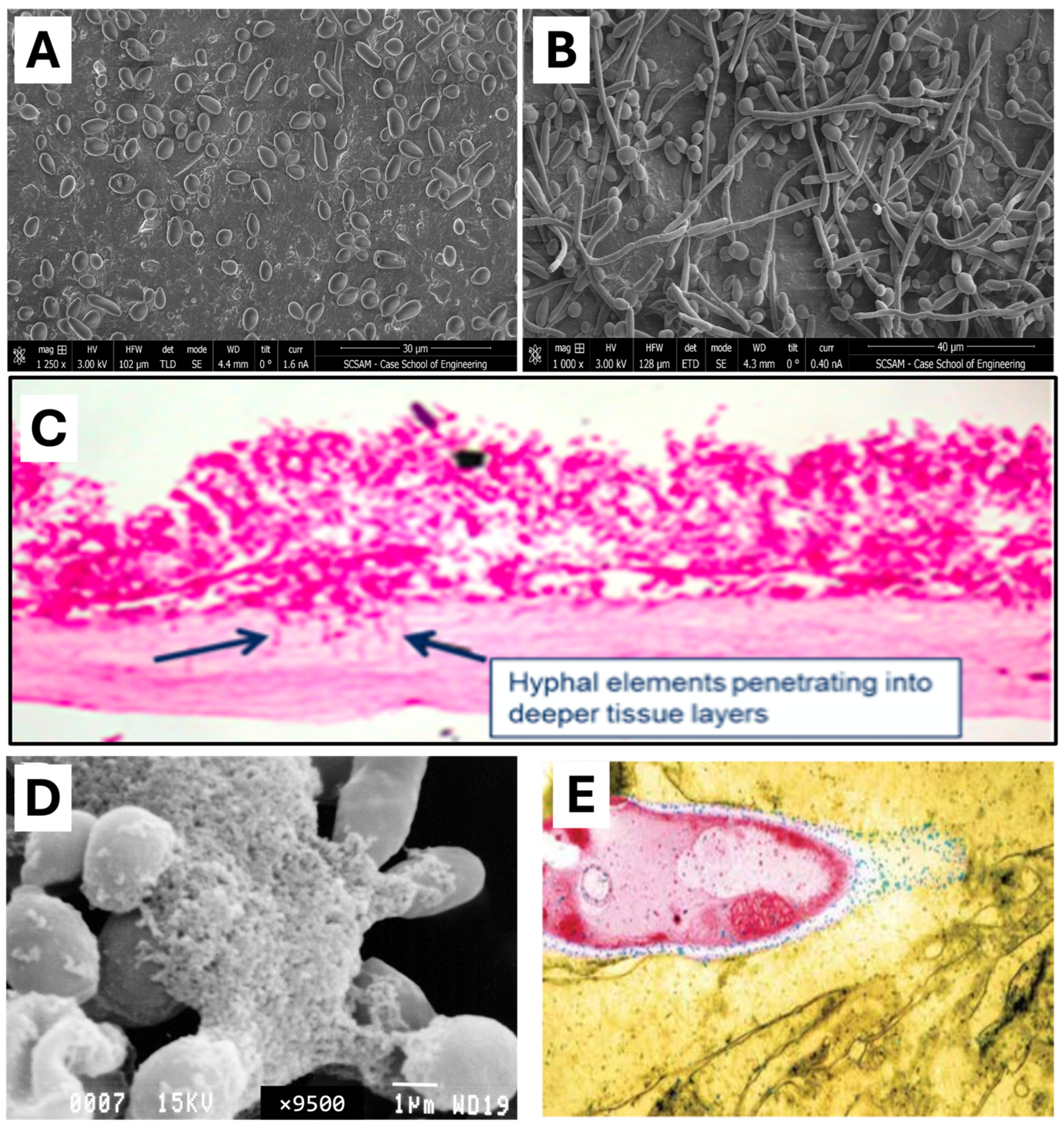
| Features | Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) | Small Intestinal Fungal Overgrowth (SIFO) |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Overgrowth of bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Klebsiella, Streptococcus) | Overgrowth of fungi (mainly Candida species) |
| Risk Factors | Hypochlorhydria (e.g., PPI use) Impaired motility Anatomical abnormalities Aging | Antifungal or steroid use immunosuppression Diabetes, cancer, or malnutrition |
| Prevalence | Higher in patients with IBS, IBD, liver disease, obesity, elderly; exact prevalence unclear | Under-recognized; up to 34% of SIBO patients may have coexisting SIFO |
| Pathogenesis | Bacterial overgrowth leads to nutrient malabsorption, bile salt de-conjugation, gas production, leaky gut | Fungal overgrowth disrupts epithelial integrity, forms biofilms, and causes virulence enzymes |
| Symptoms | Bloating, diarrhea, constipation (depending on gas type), flatulence, malabsorption | Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, indigestion, gas; often mimics other GI disorders |
| Diagnostic Methods | Gold standard: jejunal aspirate (>105 CFUs/mL) Breath tests (hydrogen, methane) | Gold standard: fungal culture from small intestinal aspirate Clinical suspicion |
| Antimicrobial Therapy | Rifaximin, TMP-SMX + Metronidazole | Fluconazole, Nystatin, Amphotericin B |
| Dietary Approaches | Low FODMAP diet (≤6 weeks), mycobiome diet [5,6] | Mycobiome diet |
| Probiotics | Mixed results; strain-specific | Saccharomyces boulardii may help |
| Herbal/Botanical Agents | Ginger, garlic (allicin), turmeric, oregano, etc. | Same as SIBO |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Stress reduction, sleep, exercise | Same as SIBO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soliman, N.; Kruithoff, C.; San Valentin, E.M.; Gamal, A.; McCormick, T.S.; Ghannoum, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial and Fungal Overgrowth: Health Implications and Management Perspectives. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081365
Soliman N, Kruithoff C, San Valentin EM, Gamal A, McCormick TS, Ghannoum M. Small Intestinal Bacterial and Fungal Overgrowth: Health Implications and Management Perspectives. Nutrients. 2025; 17(8):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081365
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoliman, Natalie, Caroline Kruithoff, Erin Marie San Valentin, Ahmed Gamal, Thomas S. McCormick, and Mahmoud Ghannoum. 2025. "Small Intestinal Bacterial and Fungal Overgrowth: Health Implications and Management Perspectives" Nutrients 17, no. 8: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081365
APA StyleSoliman, N., Kruithoff, C., San Valentin, E. M., Gamal, A., McCormick, T. S., & Ghannoum, M. (2025). Small Intestinal Bacterial and Fungal Overgrowth: Health Implications and Management Perspectives. Nutrients, 17(8), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081365







