Undernutrition and Intestinal Infections in Children: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Undernutrition in Childhood (Epidemiology, Etiology, General Mechanisms)
4. Intestinal Infections in Children
4.1. Virus
4.2. Bacteria
4.3. Protozoan
4.4. Co-Infections
5. Undernutrition and Environmental Enteropathy: From Epidemiological Studies to Experimental Models
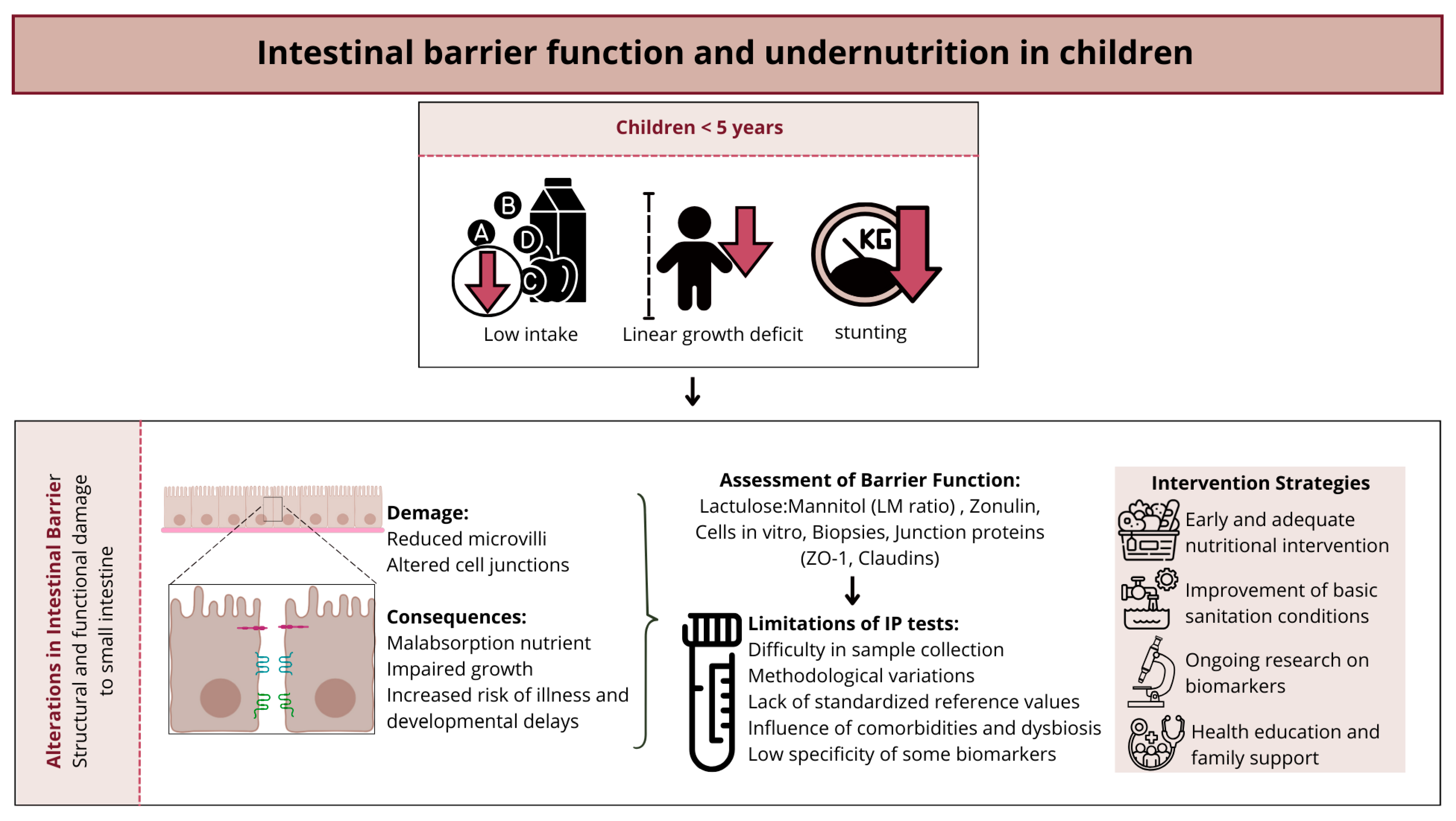
6. Intestinal Barrier Function and Undernutrition in Children
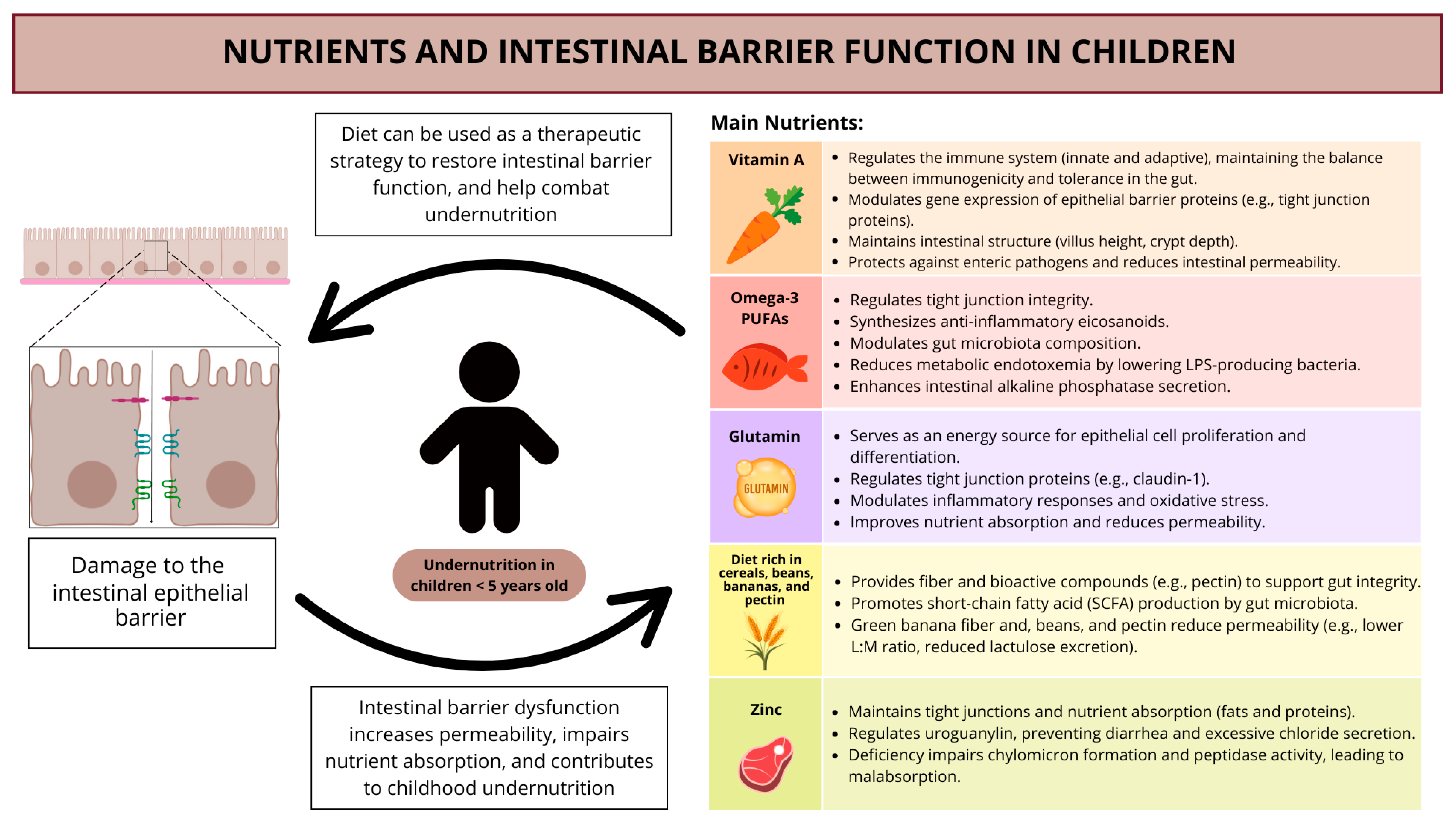
7. Nutrients and Intestinal Barrier Function in Children
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Group Joint Malnutrition Estimates, 2023 Edition. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240025257 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- WHO. Disponível em. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/malnutrition (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Guerrant, R.L.; Oriá, R.B.; Moore, S.R.; Oriá, M.O.; Lima, A.A. Malnutrition as an enteric infectious disease with long-term effects on child development. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpe, P.S.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Environmental enteropathy: Critical implications of a poorly understood condition. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrant, R.L.; Leite, A.M.; Pinkerton, R.; Medeiros, P.H.; Cavalcante, P.A.; DeBoer, M.; Kosek, M.; Duggan, C.; Gewirtz, A.; Kagan, J.C.; et al. Biomarkers of Environmental Enteropathy, Inflammation, Stunting, and Impaired Growth in Children in Northeast Brazil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0158772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owino, V.; Ahmed, T.; Freemark, M.; Kelly, P.; Loy, A.; Manary, M.; Loechl, C. Environmental Enteric Dysfunction and Growth Failure/Stunting in Global Child Health. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20160641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Leptin Regulation of Immune Responses. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Haque, M.A.; Kotloff, K.L.; Nasrin, D.; Hossain, M.J.; Sur, D.; Ahmed, T.; Levine, M.M.; Breiman, R.F.; Faruque, A. Enteric viral pathogens and child growth among under-five children: Findings from South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keusch, G.T.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Denno, D.M.; Duggan, C.; Guerrant, R.L.; Lavery, J.V.; Tarr, P.I.; Ward, H.D.; Black, R.E.; Nataro, J.P.; et al. Implications of acquired environmental enteric dysfunction for growth and stunting in infants and children living in low- and middle-income countries. Food Nutr. Bull. 2013, 34, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denno, D.M.; VanBuskirk, K.; Nelson, Z.C.; Musser, C.A.; Hay Burgess, D.C.; Tarr, P.I. Use of the lactulose to mannitol ratio to evaluate childhood environmental enteric dysfunction: A systematic review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, S213–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael Camilleri, X.; Lyle, B.J.; Madsen, K.L.; Sonnenburg, J.; Verbeke, K.; Wu, G.D. Role for diet in normal gut barrier function: Developing guidance within the framework of food-labeling regulations. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Diarrhoeal Diseases Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific burden of diarrhoeal diseases, their risk factors, and aetiologies, 1990–2021, for 204 countries and territories: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024, 25, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Berkley, J.A.; Bandsma, R.H.J.; Kerac, M.; Trehan, I.; Briend, A. Severe childhood malnutrition. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, G.; Andrews, K.G.; Sudfeld, C.R.; Fink, G.; McCoy, D.C.; Peet, E.; Sania, A.; Smith Fawzi, M.C.; Ezzati, M.; Fawzi, W.W. Risk factors for childhood stunting in 137 developing countries: A comparative risk assessment analysis at global, regional, and country levels. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrant, R.L.; DeBoer, M.D.; Moore, S.R.; Scharf, R.J.; Lima, A.A. The impoverished gut—A triple burden of diarrhoea, stunting and chronic disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, S.; Harris, J.; Nisbett, N.; van den Bold, M. Stories of change in nutrition from Africa and Asia: An introduction to a special series in Food Security. Food Secur. 2021, 13, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- WHO. Child Growth Standards Growth Velocity Based on Weight, Length and Head Circumference Methods and Development. 2009. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44026/9789241547635_eng.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and child malnutrition and overweight in low- and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, S.A.; McCormick, B.J.J.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Lee, G.O.; Seidman, J.C.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T.; Guerrant, R.L.; Petri, W.A.; Rogawski, E.T.; et al. MAL-ED Network Investigators. Enteric dysfunction and other factors associated with attained size at 5 years: MAL-ED birth cohort study findings. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiles, J.M.; Busquets, S.; Lopez-Soriano, F.J. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of cancer cachexia. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.W.; Stephens, J.M. Fat in flames: Influence of cytokines and pattern recognition receptors on adipocyte lipolysis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E205–E213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Nathan, J.A.; Goldberg, A.L. Muscle wasting in disease: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.S.; Schuler, G.; Adams, V. Skeletal muscle wasting in cachexia and sarcopenia: Molecular pathophysiology and impact of exercise training. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, B.M.; Cergole-Novella, M.C.; Dantas, S.T.A.; de Lira, D.R.P.; de Souza, G.F.R.; Fernandes, I.A.; Orsi, H.; Solveira, G.; Rall, V.L.M.; dos Santos, L.F.; et al. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC) isolates obtained from non-diarrheic children carry virulence factor-encoding genes from Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 3551–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Auble, D.; Berkley, J.A.; Black, R.; Ahern, P.P.; Hossain, M.; Hsieh, A.; Ireen, S.; Arabi, M.; Gordon, J.I. An evolving perspective about the origins of childhood undernutrition and nutritional interventions that includes the gut microbiome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1332, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assa, A.; Vong, L.; Pinnell, L.J.; Avitzur, N.; Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Sherman, P.M. Vitamin D deficiency promotes epithelial barrier dysfunction and intestinal inflammation. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, S.; Versloot, C.J.; Voskuijl, W.; van Vliet, S.J.; Di Giovanni, V.; Zhang, L.; Richardson, S.; Bourdon, C.; Netea, M.G.; Berkley, J.A.; et al. Mortality in children with complicated severe acute malnutrition is related to intestinal and systemic inflammation: An observational cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, K.; Berkley, J.A.; Shebbe, M.; Peshu, N.; English, M.; Newton, C.R. Children with severe malnutrition: Can those at highest risk of death be identified with the WHO protocol? PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irena, A.H.; Mwambazi, M.; Mulenga, V. Diarrhea is a major killer of children with severe acute malnutrition admitted to inpatient set-up in Lusaka, Zambia. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbert, A.; Thuo, N.; Karisa, J.; Chesaro, C.; Ohuma, E.; Ignas, J.; Berkley, J.A.; Toromo, C.; Atkinson, S.; Maitland, K. Diarrhoea complicating severe acute malnutrition in Kenyan children: A prospective descriptive study of risk factors and outcome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.L.; Badaloo, A.V.; Chambers, B.; Forrester, T.E.; Wootton, S.A.; Jackson, A.A. Maldigestion and malabsorption of dietary lipid during severe childhood malnutrition. Arch. Dis. Child. 2002, 87, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.H.; Meyer, S.L.; Stehmann, T.A.; Bourdon, C.; Bandsma, R.H.; Voskuijl, W.P. Both Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency and Signs of Pancreatic Inflammation Are Prevalent in Children with Complicated Severe Acute Malnutrition: An Observational Study. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvissberg, M.A.; Dalvi, P.S.; Kerac, M.; Voskuijl, W.; Berkley, J.A.; Priebe, M.G.; Bandsma, R.H. Carbohydrate malabsorption in acutely malnourished children and infants: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olsen, E.M.; Petersen, J.; Skovgaard, A.M.; Weile, B.; Jørgensen, T.; Wright, C.M. Failure to thrive: The prevalence and concurrence of anthropometric criteria in a general infant population. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, Z.; Ee, L.C. Protein energy malnutrition. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 56, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledger, E.; Harawa, P.P.; Daniel, A.I.; Candler, T.; Prentice, A.M.; Bandsma, R.H.J. Dysglycemia in Children with Severe Acute Malnutrition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Pons-Kühnemann, J.; Fechner, A.; Funk, M.; Gromer, S.; Gross, H.J.; Grünert, A.; Schirmer, R.H. Effects of antioxidants on glutathione levels and clinical recovery from the malnutrition syndrome kwashiorkor—A pilot study. Redox Rep. 2005, 10, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, A.G. Malnutrition and the heart. Turk. Pediatr. Ars. 2019, 54, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.T.S.; Parkash, O.; Hashmi, S.A. Malnutrition and liver disease in a developing country. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4985–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, H.; Janssen, M.C.H.; Leij, S.; Wanten, G. Patients With Mitochondrial Disease Have an Inadequate Nutritional Intake. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, B.J.J.; Richard, S.A.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Kang, G.; Lima, A.A.M.; Mduma, E.; Kosek, M.N.; McQuade, E.T.R.; Houpt, E.R.; Bessong, P.; et al. Full breastfeeding protection against common enteric bacteria and viruses: Results from the MAL-ED cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, J.M.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Badr, H.S.; Burnett, E.; Ali, S.A.; Rayamajhi, A.; Satter, S.M.; Eibach, D.; Krumkamp, R.; May, J.; et al. Associations Between Eight Earth Observation-Derived Climate Variables and Enteropathogen Infection: An Independent Participant Data Meta-Analysis. GeoHealth 2022, 6, e2021GH000452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, R.L.; Bolick, D.T.; Swann, J.R. Modeling Enteropathy or Diarrhea with the Top Bacterial and Protozoal Pathogens: Differential Determinants of Outcomes. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Liu, J.; Rogawski, E.T.; Kabir, F.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Siguas, M.; Khan, S.S.; Praharaj, I.; Murei, A.; Nshama, R.; et al. MAL-ED Network Investigators. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to assess the aetiology, burden, and clinical characteristics of diarrhoea in children in low-resource settings: A reanalysis of the MAL-ED cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1309–e1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Babji, S.; Bodhidatta, L.; Gratz, J.; Haque, R.; Havt, A.; McCormick, B.J.; McGrath, M.; Olortegui, M.P.; Samie, A.; et al. Pathogen-specific burdens of community diarrhoea in developing countries: A multisite birth cohort study (MAL-ED). Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e564–e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera-montes, M.; O’ryan, M.; Verstraeten, T. Norovirus and rotavirus disease severity in children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Houpt, E.R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guindo, O.; Sayinzoga-Makombe, N.; McMurry, T.L.; Elwood, S.; Langendorf, C.; Grais, R.F.; et al. Etiology and Incidence of Moderate-to-Severe Diarrhea in Young Children in Niger. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Guo, J.; Wei, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zeng, M. Aetiology of acute diarrhoea in children in Shanghai, 2015–2018. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.A.M.; Oliveira, D.B.; Quetz, J.S.; Havt, A.; Prata, M.M.G.; Lima, I.F.N.; Soares, A.M.; Filho, J.Q.; Lima, N.L.; Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; et al. Etiology and severity of diarrheal diseases in infants at the semiarid region of Brazil: A case-control study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankov, R.C.; Gondim, R.N.D.G.; Prata, M.M.G.; Medeiros, P.H.; Veras, H.N.; Santos, A.K.; Havt, A.; da Silva, M.F.; Fumian, T.M.; Miagostovich, M.P.; et al. Rotavirus A Infections in Community Childhood Diarrhea in the Brazilian Semiarid Region During Post-Vaccination Era. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, e91–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaran, A.; Makvandi, M.; Samarbafzadeh, A.; Neisi, N.; Hoseinzadeh, M.; Rasti, M.; Teymurirad, M.; Teimoori, A.; Varnaseri, M.; Makvandi, K. Study on Rotavirus Infection and Its Genotyping in Children in South West Iran. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2016, 26, e2080. [Google Scholar]
- Mboungou, C.L.D.; Mfoutou Mapanguy, C.C.; Mouanga, A.M.; Mikounou Louya, V.; Vouvoungui, J.C.; Ampa, R.; Ntoumi, F. The prevalence of rotavirus infection among Congolese children hospitalized for gastroenteritis. IJID Reg. 2025, 14, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofosu-Appiah, L.H.; Negoro, M.; Amexo, J.X.; Amelor, D.K.; Tonto, P.B.; Laryea, D.O.; Yamasaki, K.; Asiedu-Bekoe, F.; Sugata, K.; Hori, H.; et al. Genetic Analysis of Enteric Viruses in Children with Gastroenteritis in Ghana. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, J.M.; Ahmed, A.M.S.; Soofi, S.B.; Svensen, E.; Haque, R.; Shrestha, J.; Nshama, R.; Bhutta, Z.; Lima, I.F.N.; Samie, A.; et al. Seasonality and within-subject clustering of rotavirus infections in an eight-site birth cohort study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muendo, C.; Laving, A.; Kumar, R.; Osano, B.; Egondi, T.; Njuguna, P. Prevalence of rotavirus infection among children with acute diarrhoea after vaccine introduction in Kenya. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakawesi, J.; Wobudeya, E.; Ndeezi, G.; Mworozi, E. Prevalence and factors associated with rotavirus infection in Uganda. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odimayo, M.S.; Olanrewaju, W.I.; Omilabu, S.A.; Adegboro, B. Prevalence of rotavirus-induced diarrhoea among children under 5 in Ilorin, Nigeria. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2008, 54, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Dreps, S.; González, F.; Bucardo, F. Sapovirus: An emerging cause of childhood diarrhea. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, N.; Groome, M.J.; Murray, T.; Nadan, S.; Netshikweta, R.; Keddy, K.H.; Poonsamy, B.; Moyes, J.; Walaza, S.; Kahn, K.; et al. Sapovirus prevalence in children less than five years of age hospitalised for diarrhoeal disease in South Africa, 2009–2013. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 78, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.; Peñataro Yori, P.; Olortegui, M.P.; Lima, A.A.M.; Ahmed, T.; Mduma, E.R.; George, A.; Samie, A.; Svensen, E.; Lima, I.; et al. The Epidemiology of Sapovirus: Evidence of Protection Following Natural Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondim, R.D.G.; Pankov, R.C.; Prata, M.M.G.; Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Veras, H.N.; Santos, A.K.S.; Magalhães, L.M.C.; Havt, A.; Fumian, T.M.; Miagostovich, M.P.; et al. Genetic Diversity of Norovirus Infections, Co-Infections, and Undernutrition in Children from Brazilian Semiarid Region. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, e117–e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guga, G.; Elwood, S.; Kimathi, C.; Kang, G.; Kosek, M.N.; Lima, A.A.M.; Bessong, P.O.; Samie, A.; Haque, R.; Leite, J.P.; et al. Burden, Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Seasonality of Adenovirus 40/41 Diarrhea in Children in Eight Low-Resource Settings. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olortegui, M.P.; Rouhani, S.; Yori, P.P.; Salas, M.S.; Trigoso, D.R.; Mondal, D.; Bodhidatta, L.; Platts-Mills, J.; Samie, A.; Kabir, F.; et al. Astrovirus Infection and Diarrhea in 8 Countries. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20171326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, R.J.; McQuade, E.T.R.; Svensen, E.; Huggins, A.; Maphula, A.; Bayo, E.; Blacy, L.; Pamplona Ede Souza, P.; Costa, H.; Houpt, E.R.; et al. Early-Life Enteric Pathogen Exposure, Socioeconomic Status, and School-Age Cognitive Outcomes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 109, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Khamrin, P.; Jampanil, N.; Yodmeeklin, A.; Ukarapol, N.; Maneekarn, N.; Kumthip, K. Enterovirus diversity in pediatric acute gastroenteritis in Thailand, 2019–2022. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1414698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, M.G.; Pucciarelli, A.; Serra, F.; Ianiro, G.; Iafusco, M.; Fiorito, F.; Polverino, M.G.; Dimatteo, M.; Monini, M.; Ferrara, D.; et al. Ten viral agents infecting children with gastroenteritis in Southern Italy post-COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski McQuade, E.T.; Scharf, R.J.; Svensen, E.; Huggins, A.; Maphula, A.; Bayo, E.; Blacy, L.; Pamplona, E.S.P.; Costa, H.; Houpt, E.R.; et al. Impact of Shigella infections and inflammation early in life on child growth and school-aged cognitive outcomes: Findings from three birth cohorts over eight years. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, T.L.; Rogawski McQuade, E.T.; Liu, J.; Kang, G.; Kosek, M.N.; Lima, A.A.M.; Bessong, P.O.; Samie, A.; Haque, R.; Mduma, E.R.; et al. Duration of Postdiarrheal Enteric Pathogen Carriage in Young Children in Low-resource Settings. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e806–e814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski McQuade, E.T.; Liu, J.; Mahfuz, M.; Havt, A.; Varghese, T.; Shrestha, J.; Kabir, F.; Peñataro Yori, P.; Samie, A.; Saidi, Q.; et al. Epidemiology of Shigella species and serotypes in children: A retrospective substudy of the MAL-ED observational birth cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 2025. online first. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, H.S.; Colston, J.M.; Nguyen, N.L.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Burnett, E.; Ali, S.A.; Rayamajhi, A.; Satter, S.M.; Van Trang, N.; Eibach, D.; et al. Spatiotemporal variation in risk of Shigella infection in childhood: A global risk mapping and prediction model using individual participant data. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, E373–E384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amour, C.; Gratz, J.; Mduma, E.; Svensen, E.; Rogawski, E.T.; McGrath, M.; Seidman, J.C.; McCormick, B.J.; Shrestha, S.; Samie, A.; et al. Etiology, Risk Factors, and Interactions of Enteric Infections and Malnutrition and the Consequences for Child Health and Development Project (MAL-ED) Network Investigators. Epidemiology and Impact of Campylobacter Infection in Children in 8 Low-Resource Settings: Results From the MAL-ED Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino, F.; Colston, J.M.; Olortegui, M.P.; Peñataro Yori, P.; Mourkas, E.; Pascoe, B.; Lima, A.A.M.; Mason, C.J.; Ahmed, T.; Kang, G.; et al. The epidemiology and impact of persistent Campylobacter infections on childhood growth among children 0–24 months of age in resource-limited settings. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 76, 102841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, N.H.; Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Ribeiro, S.A.; Freitas, T.M.; Santos, A.K.S.; Amaral, M.S.M.G.; Bona, M.D.; Havt, A.; Lima, I.F.N.; Lima, N.L.; et al. Campylobacter jejuni virulence genes and immune-inflammatory biomarkers association with growth impairment in children from Northeastern Brazil. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajuelo, M.J.; Noazin, S.; Cabrera, L.; Toledo, A.; Velagic, M.; Arias, L.; Ochoa, M.; Moulton, L.H.; Saito, M.; Gilman, R.H.; et al. Epidemiology of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and impact on child growth in Lima, Peru. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1332319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazi, M.A.; Alam, M.A.; Fahim, S.M.; Wahid, B.Z.; Khan, S.S.; Islam, M.O.; Hasan, M.M.; Hasan, S.M.T.; Das, S.; Mahfuz, M.; et al. Infection with E. coli Pathotypes and Association with Gut Enteropathy and Nutritional Status in Bangladesh. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 901324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Palit, P.; Haque, M.A.; Mahfuz, M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Ahmed, T. Incidence of genomic subtypes of EPEC and association with inflammation and growth. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, T.J.; Mercado, E.H.; Durand, D.; Rivera, F.P.; Mosquito, S.; Contreras, C.; Riveros, M.; Lluque, A.; Barletta, F.; Prada, A.; et al. Frequency and pathotypes of diarrheagenic E. coli in Peruvian children. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2011, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, E.T.; Guerrant, R.L.; Havt, A.; Lima, I.F.N.; Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Seidman, J.C.; McCormick, B.J.J.; Babji, S.; Hariraju, D.; Bodhidatta, L.; et al. Epidemiology of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli infections and associated outcomes in the MAL-ED birth cohort. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.A.M.; Soares, A.M.; Filho, J.Q.S.; Havt, A.; Lima, I.F.N.; Lima, N.L.; Abreu, C.B.; Junior, F.S.; Mota, R.M.; Pan, W.K.; et al. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Subclinical Infection and Coinfections and Impaired Child Growth in the MAL-ED Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.K.; Duggan, C.; Bhutta, Z.A. Persistent diarrhea in children in developing countries. In Textbook of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Atabati, H.; Kassiri, H.; Shamloo, E.; Akbari, M.; Atamaleki, A.; Sahlabadi, F.; Linh, N.T.T.; Rostami, A.; Fakhri, Y.; Khaneghah, A.M. The association between the lack of safe drinking water and sanitation facilities with intestinal Entamoeba spp. infection risk: A systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Palit, P.; Haque, M.A.; Levine, M.M.; Kotloff, K.L.; Nasrin, D.; Hossain, M.J.; Sur, D.; Ahmed, T.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Symptomatic and asymptomatic enteric protozoan parasitic infection and their association with subsequent growth parameters in under five children in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Ali, I.M.; Sack, R.B.; Farr, B.M.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Amebiasis and mucosal IgA antibody against the Entamoeba histolytica adherence lectin in Bangladeshi children. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, C.A.; Petri, S.E.; Schneider, B.N.; Reichman, D.J.; Jiang, N.; Begum, S.; Watanabe, K.; Jansen, C.S.; Elliott, K.P.; Burgess, S.L.; et al. Role of the gut microbiota of children in diarrhea due to the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, G.L.; Marie, C.; Abhyankar, M.M.; Yoshida, N.; Watanabe, K.; Mentzer, A.J.; Carstensen, T.; Mychaleckyj, J.; Kirkpatrick, B.D.; Rich, S.S.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals genetic link between diarrheaassociated Entamoeba histolytica infection and inflammatory bowel disease. mBio 2018, 9, e01668-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabakaran, M.; Weible, L.J.; Champlain, J.D.; Jiang, R.Y.; Biondi, K.; Weil, A.A.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Ojo, K.K. The Gut-Wrenching Effects of Cryptosporidiosis and Giardiasis in Children. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, S.M.; Angelova, V.V.; DeLeon, H.; Miskovsky, E. What’s eating you? An update on Giardia, the microbiome, and immune responses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcenac, P.; Traoré, A.; Kim, S.; Prentice-Mott, G.; Berendes, D.M.; Powell, H.; Kasumba, I.N.; Nasrin, D.; Jones, J.C.M.; Zaman, S.M.A.; et al. Giardia detection and codetection with other enteric pathogens in young children in the Vaccine Impact on Diarrhea in Africa (VIDA) case-control study: 2015–2018. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76 (Suppl. S1), S106–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, E.; Allain, T.; Siddiq, A.; Sosnowski, O.; Buret, A.G. Giardia spp. and the Gut Microbiota: Dangerous Liaisons. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 618106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siberry, G.K.; Abzug, M.J.; Nachman, S.; Brady, M.T.; Dominguez, K.L.; Handelsman, E.; Mofenson, L.M.; Nesheim, S.; the Panel on Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Exposed and HIV-Infected Children. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-exposed and HIV-infected children: Recommendations from the National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32 (Suppl. S2), i–KK4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donowitz, J.R.; Haque, R.; Kirkpatrick, B.D.; Alam, M.; Lu, M.; Kabir, M.; Kakon, S.H.; Islam, B.Z.; Afreen, S.; Musa, A.; et al. Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth and Environmental Enteropathy in Bangladeshi Children. mBio 2016, 7, e02102-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Rao, P.C.; Blacker, B.F.; Brown, A.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; De Hostos, E.L.; Engmann, C.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Morbidity, mortality, and long-term consequences associated with diarrhoea from Cryptosporidium infection in children younger than 5 years: A meta-analyses study. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e758–e768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, P.W.; Allen, N.; Worthington, P.; George, D.; Compher, C.; the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition; Teitelbaum, D. A.S.P.E.N. clinical guidelines: Support of pediatric patients with intestinal failure at risk of parenteral nutrition–associated liver disease. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpe, P.S.; Valencia, C.; Haque, R.; Mahfuz, M.; McGrath, M.; Houpt, E.; Kosek, M.; McCormick, B.J.J.; Penataro Yori, P.; Babji, S.; et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for cryptosporidiosis in children from 8 low-income sites: Results from the MAL-ED study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qin, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection in children from China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2023, 244, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potgieter, N.; Heine, L.; Ngandu, J.P.K.; Ledwaba, S.E.; Zitha, T.; Mudau, L.S.; Becker, P.; Traore, A.N.; Barnard, T.G. High Burden of Co-Infection with Multiple Enteric Pathogens in Children Suffering with Diarrhoea from Rural and Peri-Urban Communities in South Africa. Pathogens 2023, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.A.; Akhtar, M.; Khan, Z.H.; Islam, M.T.; Firoj, M.G.; Begum, Y.A.; Rahman, S.I.A.; Afrad, M.H.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Chowdhury, F.; et al. Coinfection and clinical impact of ETEC variants and colonization factors: 2017–2022. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 151, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogawski, E.T.; Bartelt, L.A.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Seidman, J.C.; Samie, A.; Havt, A.; Babji, S.; Trigoso, D.R.; Qureshi, S.; Shakoor, S.; et al. MAL-ED Network Investigators. Determinants and Impact of Giardia Infection in the First 2 Years of Life in the MAL-ED Birth Cohort. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2017, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt, L.A.; Bolick, D.T.; Guerrant, R.L. Disentangling Microbial Mediators of Malnutrition: Modeling Environmental Enteric Dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 692–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, C.; Das, S.; Coomes, D.; Ahmed, T.; Ali, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Kelly, P.; Mahfuz, M.; Moore, S.R.; Petri, W.A., Jr.; et al. Duodenal transcriptomics demonstrates signatures of tissue inflammation and immune cell infiltration in children with environmental enteric dysfunction across global centers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, S51–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.I.; Murch, S.H.; Elia, M.; Sullivan, P.B.; Sanyang, M.S.; Jobarteh, B.; Lunn, P.G. Chronic T cell-mediated enteropathy in rural west African children: Relationship with nutritional status and small bowel function. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 54, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trehan, I.; Shulman, R.J.; Ou, C.N.; Maleta, K.; Manary, M.J. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of rifaximin, a nonabsorbable antibiotic, in the treatment of tropical enteropathy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.I.; Elia, M.; Lunn, P.G. Growth faltering in rural Gambian infants is associated with impaired small intestinal barrier function, leading to endotoxemia and systemic inflammation. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, A.J.; Manary, M.J.; Stephenson, K.; Agapova, S.; Manary, F.G.; Thakwalakwa, C.; Shulman, R.J.; Manary, M.J. Abnormal gut integrity is associated with reduced linear growth in rural Malawian children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi, S.; Sailer, A.; Roland, J.T.; Haest, X.; Chanez-Paredes, S.D.; Ahmad, K.; Sadiq, K.; Iqbal, N.T.; Ali, S.A.; Turner, J.R. Intestinal Epithelial Digestive, Transport, and Barrier Protein Expression Is Increased in Environmental Enteric Dysfunction. Lab. Investig. 2023, 103, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulger, H.; Arik, M.; Sekeroglu, M.R.; Tarakcioglu, M.; Noyan, T.; Cesur, Y.; Balahoroglu, R. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in Turkish children with protein-energy malnutrition. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Torres, C.; Gonzalez-Martinez, H.; Miliar, A.; Najera, O.; Graniel, J.; Firo, V.; Alvarez, C.; Bonilla, E.; Rodriguez, L. Effect of malnutrition on the expression of cytokines involved in Th1 cell differentiation. Nutrients 2013, 5, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, F.K.; Farmery, S.M.; MacLennan, K.; Sheridan, M.B.; Barclay, G.R.; Guillou, P.J.; Reynolds, J.V. Gut barrier function in malnourished patients. Gut 1998, 42, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; VanBuskirk, K.; Coomes, D.; Mouksassi, S.; Smith, G.; Jamil, Z.; Hossain, M.S.; Syed, S.; Marie, C.; Tarr, P.I.; et al. Histopathology underlying environmental enteric dysfunction in a cohort study of undernourished children in Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Zambia compared with United States children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120 (Suppl. S1), S15–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Manji, K.P.; McDonald, C.M.; Kisenge, R.; Aboud, S.; Sudfeld, C.; Locks, L.; Liu, E.; Fawzi, W.W.; Duggan, C.P. Biomarkers of systemic inflammation and growth in early infancy are associated with stunting in young Tanzanian children. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Iqbal, N.T.; Sadiq, K.; Ma, J.Z.; Akhund, T.; Xin, W.; Moore, S.R.; Liu, E.; Qureshi, S.; Gosselin, K.; et al. Serum anti-flagellin and anti-lipopolysaccharide immunoglobulins as predictors of linear growth faltering in Pakistani infants at risk for environmental enteric dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Willing, B.P.; Vonaesch, P.; Han, J.; Reynolds, L.A.; Arrieta, M.C.; Uhrig, M.; Scholz, R.; Partida, O.; et al. Diet and specific microbial exposure trigger features of environmental enteropathy in a novel murine model. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, I.C.; Medeiros, P.H.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Cavalcante, P.A.; Ribeiro, S.A.; Oliveira, J.S.; Prata, M.M.; Costa, D.V.; Fonseca, S.G.; Guedes, M.M.; et al. Impact of acute undernutrition on growth, ileal morphology and nutrient transport in a murine model. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, e5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, P.M.; Oria, R.B.; Maier, E.A.; Guedes, M.; de Azevedo, O.G.; Wu, D.; Willson, T.; Hogan, S.P.; Lima, A.A.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Alanyl-glutamine promotes intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis in vitro and in a murine model of weanling undernutrition. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G612–G622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt, L.A.; Bolick, D.T.; Kolling, G.L.; Roche, J.K.; Zaenker, E.I.; Lara, A.M.; Noronha, F.J.; Cowardin, C.A.; Moore, J.H.; Turner, J.R.; et al. Cryptosporidium priming is more effective than vaccine for protection against cryptosporidiosis in a murine protein malnutrition model. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bolick, D.T.; Kolling, G.L.; Fu, Z.; Guerrant, R.L. Protein malnutrition impairs intestinal epithelial cell turnover, a potential mechanism of increased cryptosporidiosis in a murine model. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 3542–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, S.; Feenstra, M.; Swain, N.; Cuesta, M.; Bandsma, R.H.J. Starved guts: Morphologic and functional intestinal changes in malnutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Ordiz, M.I.; Stauber, J.; Shaikh, N.; Trehan, I.; Barnell, E.; Head, R.D.; Maleta, K.; Tarr, P.I.; Manary, M.J. Environmental enteric dysfunction includes a broad spectrum of inflammatory responses and epithelial repair processes. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 158–174 e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Bolick, D.T.; Leng, J.; Medlock, G.L.; Kolling, G.L.; Papin, J.A.; Swann, J.R.; Guerrant, R.L. Protein-and zinc-deficient diets modulate the murine microbiome and metabolic phenotype. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.B.; JohnBull, E.A.; Reeves, J.T.; Sevilleja, J.E.; Freire, R.S.; Hoffman, P.S.; Lima, A.A.; Oria, R.B.; Roche, J.K.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Cryptosporidium-malnutrition interactions: Mucosal disruption, cytokines, and TLR signaling in a weaned murine model. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt, L.A.; Bolick, D.T.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Kolling, G.L.; Medlock, G.L.; Zaenker, E.I.; Donowitz, J.; Thomas-Beckett, R.V.; Rogala, A.; Carroll, I.M.; et al. Cross-modulation of pathogen-specific pathways enhances malnutrition during enteric co-infection with Giardia lamblia and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, K.R.; Hess, S.Y.; Rouamba, N.; Ouédraogo, Z.P.; Kellogg, M.; Goto, R.; Duggan, C.; Ouédraogo, J.; Brown, K.H. Associations between intestinal mucosal function and changes in plasma zinc concentration following zinc supplementation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, K.R.; Brown, K.H. Estimating the global prevalence of zinc deficiency: Results based on zinc availability in national food supplies and the prevalence of stunting. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, W.; Shawa, T.; Khanam, M.; Jagatiya, P.; Simuyandi, M.; Ndulo, N.; Bevins, C.L.; Sanderson, I.R.; Kelly, P. Intestinal antimicrobial gene expression: Impact of micronutrients in malnourished adults during a randomized trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.; Bolick, D.T.; Roche, J.K.; Noronha, F.; Pinheiro, C.; Kolling, G.L.; Lima, A.; Guerrant, R.L. The micronutrient zinc inhibits EAEC strain 042 adherence, biofilm formation, virulence gene expression, and epithelial cytokine responses benefiting the infected host. Virulence 2013, 4, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QS Medeiros, P.H.; Ledwaba, S.E.; Bolick, D.T.; Giallourou, N.; Yum, L.K.; Costa, D.V.S.; Oria, R.B.; Barry, E.M.; Swann, J.R.; Lima, A.A.M.; et al. A murine model of diarrhea, growth impairment and metabolic disturbances with Shigella flexneri infection and the role of zinc deficiency. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, L.A.; Roche, J.; Kolling, G.; Bolick, D.; Noronha, F.; Naylor, C.; Hoffman, P.; Warren, C.; Singer, S.; Guerrant, R.L. Persistent G lamblia impairs growth in a murine malnutrition model. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2672–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolick, D.T.; Roche, J.K.; Hontecillas, R.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; Nataro, J.P.; Guerrant, R.L. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strain in a novel weaned mouse model: Exacerbation by malnutrition, biofilm as a virulence factor and treatment by nitazoxanide. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62 Pt 6, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.B.; Noronha, F.J.; Roche, J.K.; Sevilleja, J.E.; Warren, C.A.; Oria, R.; Lima, A.; Guerrant, R.L. Novel in vitro and in vivo models and potential new therapeutics to break the vicious cycle of Cryptosporidium infection and malnutrition. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallourou, N.; Arnold, J.; McQuade, E.T.R.; Awoniyi, M.; Becket, R.V.T.; Walsh, K.; Herzog, J.; Gulati, A.S.; Carroll, I.M.; Montgomery, S.; et al. Giardia hinders growth by disrupting nutrient metabolism independent of inflammatory enteropathy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolick, D.T.; Medeiros, P.; Ledwaba, S.E.; Lima, A.A.M.; Nataro, J.P.; Barry, E.M.; Guerrant, R.L. The Critical Role of Zinc in a New Murine Model of Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) Diarrhea. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00183-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolick, D.T.; Kolling, G.L.; Moore, J.H., 2nd; de Oliveira, L.A.; Tung, K.; Philipson, C.; Viladomiu, M.; Hontecillas, R.; BassaganyaRiera, J.; Guerrant, R.L. Zinc deficiency alters host response and pathogen virulence in a mouse model of enteroaggregative escherichia coli- induced diarrhea. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallourou, N.; Medlock, G.L.; Bolick, D.T.; Medeiros, P.H.; Ledwaba, S.E.; Kolling, G.L.; Tung, K.; Guerry, P.; Swann, J.R.; Guerrant, R.L. (2018) A novel mouse model of Campylobacter jejuni enteropathy and diarrhea. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosek, M.N.; MAL-ED Network Investigators. Causal Pathways from Enteropathogens to Environmental Enteropathy: Findings from the MAL-ED Birth Cohort Study. EBioMedicine 2017, 18, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twitchell, E.L.; Tin, C.; Wen, K.; Zhang, H.; Becker-Dreps, S.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Vilchez, S.; Li, G.; Ramesh, A.; Weiss, M.; et al. Modeling human enteric dysbiosis and rotavirus immunity in gnotobiotic pigs. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapesa, J.O.; Maxwell, A.L.; Ryan, E.P. An exposome perspective on environmental enteric dysfunction. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrijheid, M. The exposome: A new paradigm to study the impact of environment on health. Thorax 2014, 69, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijheid, M. Child health and the environment: Where next with birth cohort research? Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 71, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.N.; Soares, A.M.; Filho, J.Q.; Junior, F.S.; Ambikapathi, R.; Rogawski McQuade, E.T.; Guerrant, R.L.; Caulfield, L.E.; Lima, A.A.M.; Maciel, B.L.L. Dietary intake from complementary feeding is associated with intestinal barrier function and environmental enteropathy in Brazilian children from the MAL-ED cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.O.; McCormick, B.J.J.; Seidman, J.C.; Kosek, M.N.; Haque, R.; Paredes Olortegui, M.; Lima, A.A.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Kang, G.; Samie, A.; et al. Infant nutritional status feeding practices enteropathogen exposure socioeconomic status illness are associated with gut barrier function as assessed by the lactulose mannitol test in the MAL-EDbirth cohort. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Makharia, G.K. Techniques of functional and motility test: How to perform and interpret intestinal permeability. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 18, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Musa, M.; Kabir, M.; Iqbal Hossain, M.; Ahmed, E.; Siddique, A.; Rashid, H.; Mahfuz, M.; Mondal, D.; Ahmed, T.; Petri, W.A.; et al. Measurement of intestinal permeability using lactulose and mannitol with conventional five hours and shortened two hours urine collection by two different methods: HPAE-PAD and LC-MSMS. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220397. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, K.; Chew, F.; Torún, B.; MPeerson, J.; HBrown, K. Epidemiology of altered intestinal permeability to lactulose and mannitol in guatemalan infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. 1999, 28, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, A.A.M.; Anstead, G.M.; Zhang, Q.; Figueiredo, Í.L.; Soares, A.M.; Mota, R.M.S.; Lima, N.L.; Guerrant, R.L.; Oriá, R.B. Effects of glutamine alone or in combination with zinc and vitamin A on growth, intestinal barrier function, stress and satiety-related hormones in Brazilian shantytown children. Clinics 2014, 69, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Elburg, R.M.; Uil, J.J.; Kokke, F.T.; Mulder, A.M.; van de Broek, W.G.; Mulder, C.J.; Heymans, H.S. Repeatability of sugar-absorption test, using lactulose and mannitol, for measuring intestinal permeability of sugars. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1995, 20, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.I.; Haque, R.; Mondal, D.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, A.M.S.; Islam, M.M.; Guerrant, R.L.; Petri, W.A.; Ahmed, T. Undernutrition, vitamin A and iron deficiency are associated with impaired intestinal mucosal permeability in young Bangladeshi children assessed by lactulose/mannitol test. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrixson, D.T.; Naskidashvili, N.; Stephenson, K.B.; Laury, M.L.; Koroma, A.S.; Manary, M.J. An Alternative Oat–Containing, Ready-To-Use, Therapeutic Food Does Not Alter Intestinal Permeability or the 16S Ribosomal RNA Fecal Microbiome Configuration Among Children With Severe Malnutrition in Sierra Leone: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 2744–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agapova, S.E.; Stephenson, K.B.; Divala, O.; Kaimila, Y.; Maleta, K.M.; Thakwalakwa, C.; Ordiz, M.I.; Trehan, I.; Manary, M.J. Additional common bean in the diet of Malawian children does not affect linear growth, but reduces intestinal permeability. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, G.H.; Teka, T.; Kumar Saha, S.; Zaman, B.; Majid, N.; Khatun, M.; Wahed, M.A.; Fuchs, G.J. Green Banana and Pectin Improve Small Intestinal Permeability and Reduce Fluid Loss in Bangladeshi Children with Persistent Diarrhea. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, A.; FFetter, W.P.; MWesterbeek, E.A.; van der Vegt, I.M.; Avan der Molen, H.R.; van Elburg, R.M. The Effect of Glutamine-Enriched Enteral Nutrition on Intestinal Permeability in Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 30, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastiadou, S.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Costalos, C.; Skouroliakou, M.; Briana, D.D.; Antsaklis, A.; Roma-Giannikou, E. The impact of oral glutamine supplementation on the intestinal permeability and incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis/septicemia in premature neonates. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, N.C.; Filteau, S.M.; Elson, I.; Tomkins, A.M. Vitamin A supplementation of South African children with severe diarrhea: Optimum timing for improving biochemical and clinical recovery and subsequent vitamin A status. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2000, 19, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.M.; Mondal, P.; Westcott, J.E.; Miller, L.V.; Islam, M.M.; Ahmed, M.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T.; Krebs, N.F. Zinc Absorption from Micronutrient Powders Is Low in Bangladeshi Toddlers at Risk of Environmental Enteric Dysfunction and May Increase Dietary Zinc Requirements. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Nahar, B.; Hamadani, J.D.; Ahmed, T.; Roy, A.K.; Brown, K.H. Intestinal mucosal permeability of severely underweight and nonmalnourished bangladeshi children and effects of nutritional rehabilitation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.E.; Ryan, K.N.; Stephenson, K.B.; Westcott, C.; Thakwalakwa, C.; Maleta, K.; Cheng, J.Y.; Brenna, J.T.; Shulman, R.J.; Trehan, I.; et al. Multiple micronutrient supplementation transiently ameliorates environmental enteropathy in Malawian children aged 12–35 months in a randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Merwe, L.F.; Moore, S.E.; Fulford, A.J.; Halliday, K.E.; Drammeh, S.; Young, S.; Prentice, A.M. Long-chain PUFA supplementation in rural African infants: A randomized controlled trial of effects on gut integrity, growth, and cognitive development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.J. Vitamin A: A key coordinator of host-microbe interactions in the intestine. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Pinto, D.V.; de Almeida, J.Z.; Rêgo, J.M.C.; Rodrigues, F.A.P.; Lima, A.Â.M.; Bolick, D.T.; Guerrant, R.L.; Oriá, R.B. Modulation of intestinal immune and barrier functions by vitamin A: Implications for current understanding of malnutrition and enteric infections in children. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warden, R.A.; Noltorp, R.S.; Francis, J.L.; Dunkley, P.R.; O’loughlin, E.V. Nutrient Requirements and Interactions Vitamin A Deficiency Exacerbates Methotrexate-Induced Jejunal Injury in Rats. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhang, B. The Impact of Zinc and Zinc Homeostasis on the Intestinal Mucosal Barrier and Intestinal Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, E.; Balsiger, L.M.; Maurizi, V.; Rinninella, E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Giostra, N.; Santori, P.; Abenavoli, L.; Rasetti, C. Zinc and gut microbiota in health and gastrointestinal disease under the COVID-19 suggestion. BioFactors 2022, 48, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Samak, G. Role of glutamine in protection of intestinal epithelial tight junctions. J. Epithel. Biol. Pharmacol. 2012, 5, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Achamrah, N.; Dechelotte, P.; Coeffier, M. Glutamine and the regulation of intestinal permeability: From bench to bedside. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of omega-3 fatty acids on the gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkin, L.A.; Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and the intestinal epithelium—A review. Foods 2020, 9, 199. [Google Scholar]


| Study/Setting | Population | Major Pathogens | Association with Severity/Outcomes | Relevant Observations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEMS—Global Enteric Multicenter Study (Africa and Asia) | 9439 children <5 years old | Rotavirus, Cryptosporidium, ETEC (ST), Shigella, typical EPEC | Moderate to severe diarrhea; Mortality in <2 years | ETEC (ST) and typical EPEC linked to deaths in children < 11 months; Cryptosporidium associated with deaths between 12–23 months | [67] |
| MAL-ED (8 low-income countries: Bangladesh, Brazil, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Peru, South Africa, Tanzania) | 1715 children <2 years, 6625 surveillance samples | Shigella, sapovirus, rotavirus, adenovirus 40/41, ETEC, norovirus, astrovirus, Campylobacter jejuni or C. coli, Cryptosporidium, typical EPEC, EAEC | Campylobacter, EAEC, astrovirus, and Giardia associated with severe infections and growth failure; Giardia related to persistent infection in the first 6 months of age and growth failure | Viral infections more frequent than bacterial/parasitic in first 2 years; EAEC was more prevalent (94.8%) even without causing diarrhea; Campylobacter related to markers of intestinal and systemic inflammation and severe intestinal damage; sapovirus more prevalent in places with anti-rotavirus vaccination, and high probability of co-infection | [44,60,72,79,92,99] |
| Rotasiil vaccine clinical trial (Niger) | Children <2 years, 1729 episodes | Shigella, Cryptosporidium, rotavirus, ST-ETEC | Cryptosporidium leading cause of severe diarrhea and hospitalization | 60.5% of severe shigellosis cases occurred between 12–23 months | [47] |
| Study in Shanghai (2015–2018) | 2692 children with acute diarrhea | Rotavirus (16%), Norovirus (15.5%), NTS (10.3%), EPEC (6.5%), EAEC (6.2%) | Predominance of viral infections; NTS was the most frequently isolated bacterium | Bacterial diagnosis was by culture, possibly underestimating fastidious pathogens | [48] |
| Brazilian semiarid cross-sectional study | 1200 children 2–36 months from six cites | Norovirus GII, Adenovirus, typical EPEC, ETEC LT and ST, rotavirus, STEC, EAEC, and Giardia | Norovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus, STEC, Giardia spp. and EAEC were predictive pathogens for diarrhea | Norovirus linked to poor anthropometric outcomes, co-infection (EAEC and Shigella), and respiratory symptoms; EAEC was associated with high diarrhea severity score, and co-infection with rotavirus | [49,50,61] |
| Peru birth cohort | 345 children 0–24 months | ETEC | High burden in neonates and increased infections with age | High recurrence of ST-ETEC infections linked to stunting and wasting post-diarrhea | [75] |
| Bangladesh child study | 1050 stunted and at risk of stunting children | ETEC, EPEC, EAEC, Shigella/EIEC, STEC | Growth faltering and inflammation | EAEC and ETEC influences gut health; EPEC is associated with linear growth and underweight | [76] |
| Bangladesh surveillance study | Children <5 years | ETEC | Common co-infection in diarrheal cases | High prevalence of ETEC co-infections with rotavirus in children | [98] |
| Co-infection studies (Sub-Saharan Africa and MAL-ED) | Children with diarrhea | No single etiology | 59% of samples had co-infections; most with 2 (53%) to 3 (22%) pathogens | Co-infection increases risk of persistent diarrhea, although persistence and severity were not assessed | [97] |
| Co-infection studies (Sub-Saharan Africa and MAL-ED) | Children without diarrhea | EAEC + Campylobacter, ETEC (LT), Cryptosporidium, atypical EPEC | Co-infections associated with increased intestinal inflammation and low weight/height and weight/age | Campylobacter was the pathogen most correlated with EAEC; co-infections with EAEC increase intestinal inflammation and reduce weight/height or age | [80] |
| Category | Population/Model | Finding | Evidence | Observations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etiology | MAL-ED cohort | Enteric infections (Norovirus, Campylobacter, LT-ETEC, Shigella, EAEC and co-pathogens) | Associated with growth retardation | Samples with and without diarrhea | [9,44,80] |
| Children 9 to 15 months, MAL-ED cohort | Low-fiber diet | Increased EE scores | In children during complementary feeding | [140] | |
| Children aged 6–23 months in Burkina Faso and <5 years in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia | Zinc deficiency | Stunted children with EE | — | [123,124] | |
| Intestinal changes | Upper GI tract of 90 two-year-old children, Bangladesh birth cohort | Quantitative anomaly (>105 CFU/mL) in small intestine | Associated with growth deficits and intestinal inflammation | Changes are independent of recent or frequent diarrhea; no increased intestinal permeability or systemic inflammation | [92] |
| Duodenal biopsy transcriptome (3 EE/malnutrition cohorts) | ↑ IL-17, ↑ JAK-STAT, ↑ cytokine receptors, ↓ detox/antioxidant capacity | Immune dysfunction and reduced detox capacity | Consistent across study sites | [26] | |
| Small intestine biopsies, children 0.5–3 years, The Gambia | Villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia | Common in EE | Compared to children from privileged settings (Europe, Brazil) | [102] | |
| Clinical studies with children aged 2–16 months | Increased permeability, tight junction alterations | Intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction | Permeability linked to reduced linear growth and ↑ claudin-4 | [103,106] | |
| Children 0.5–5 years (Gambia, Mexico, Turkey), malnourished elderly | ↑ B and T cells, ↑ IFN-γ, ↓ IL-10 | Intestinal/systemic immune dysregulation | Lamina propria and blood | [102,107,108,109] | |
| Biomarkers | Serum and stool | ↑ A1AT, ↑ Reg-1, ↑ zonulin, ↑ L:M, ↑ LPS, ↑ MPO, ↑ LCN-2, ↑ CRP, ↓ IGF-1 | Associated with intestinal inflammation/dysfunction | Not always mutually correlated | [5,100,111,112] |
| Animal models | Protein-deficient mice/piglets | ↑ L:M, ↓ villus height, ↑ MPO, ↑ LCN-2, ↑ TLR2/TLR4, ↓ intraepithelial/lamina propria lymphocytes | Intestinal barrier dysfunction, inflammation, villous atrophy, ↓ CD4+ T cells | No crypt hyperplasia; differs from EE | [113,114,115,116,120,121,122,140] |
| Zinc-deficient mice | Impaired Paneth cell function | Only partial EE signs with infection | Alone, does not impact growth or gut morphology | [125] | |
| Mice on protein/energy/zinc-deficient diets | ↓ Villus height, ↑ crypt depth, ↑ permeability, ↓ growth | EE features with chronic injury | No clear histological damage; no assessment of inflammation/bacterial translocation | [31] | |
| Deficient mice/piglets + infections (EAEC, ETEC, Campylobacter, etc.) | ↑ Weight loss, ↑ villus height, ↑ crypt depth (Cryptosporidium), ↑ permeability (E. coli/Giardia), ↑ inflammation (EAEC, Campylobacter) | Greater inflammation and gut damage | Partially mimic EE; usually no crypt hyperplasia; models need microbiota depletion | [113,115,122,128,129,130,131,132,133,134] | |
| Gnotobiotic piglets with EE child microbiota | ↑ Rotavirus diarrhea | Does not fully reproduce EE; no histological changes | Worsens rotavirus diarrhea | [136] | |
| Other contributing factors | Various studies | Environmental toxins (exposome) | Contribute to EE pathogenesis | May explain limits of animal models | [137,138,139] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, M.C.d.C.; Ribeiro, S.A.; de Sousa, L.S.; Lima, A.Â.M.; Maciel, B.L.L. Undernutrition and Intestinal Infections in Children: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091479
Carvalho MCdC, Ribeiro SA, de Sousa LS, Lima AÂM, Maciel BLL. Undernutrition and Intestinal Infections in Children: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(9):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091479
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Maria Clara da Cruz, Samilly Albuquerque Ribeiro, Lélia Sales de Sousa, Aldo Ângelo Moreira Lima, and Bruna Leal Lima Maciel. 2025. "Undernutrition and Intestinal Infections in Children: A Narrative Review" Nutrients 17, no. 9: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091479
APA StyleCarvalho, M. C. d. C., Ribeiro, S. A., de Sousa, L. S., Lima, A. Â. M., & Maciel, B. L. L. (2025). Undernutrition and Intestinal Infections in Children: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 17(9), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091479






