Cell Sorting Using Electrokinetic Deterministic Lateral Displacement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Devices and Experimental Setup
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
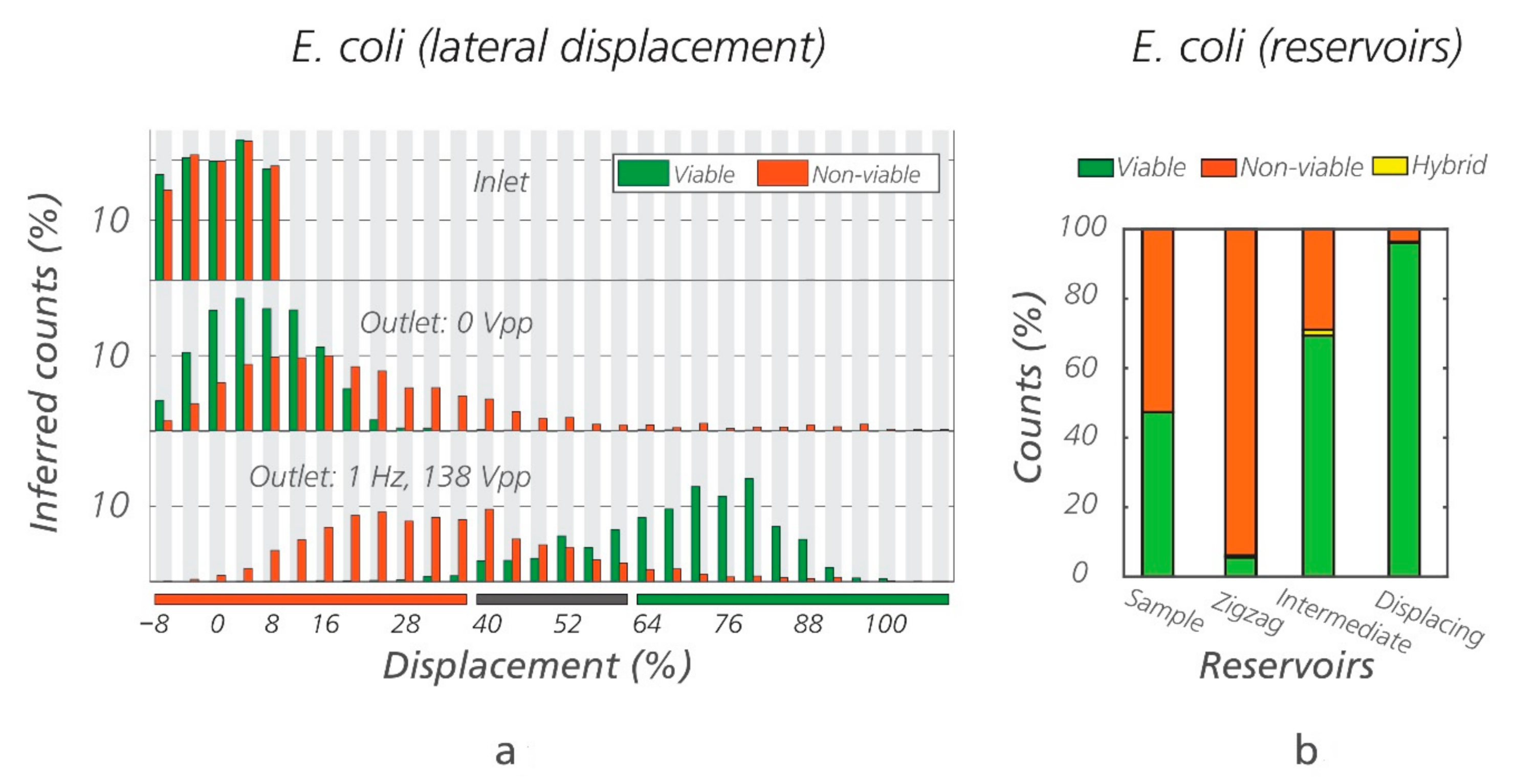
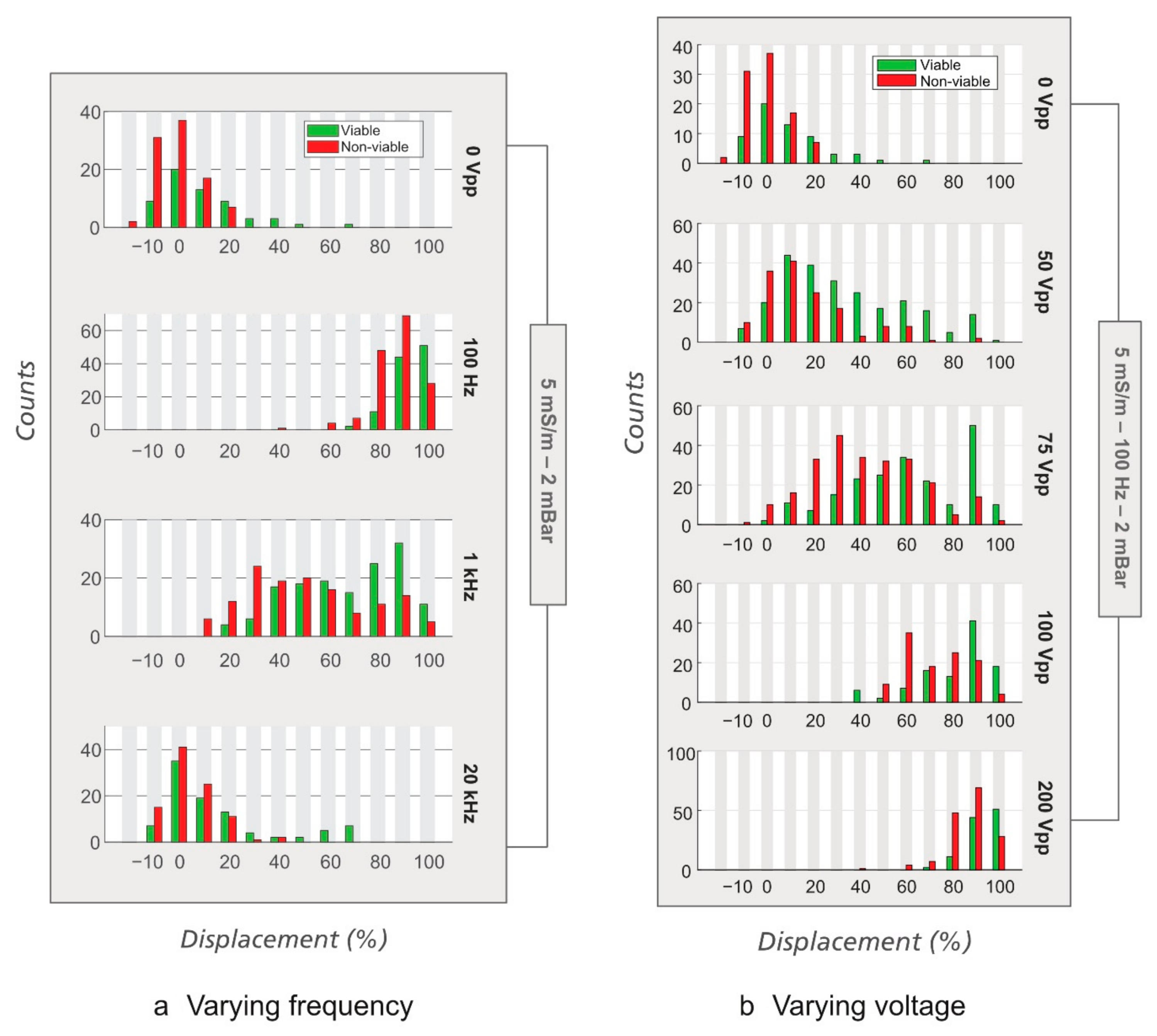
3.1. Sorting of Viable/Non-Viable E. coli
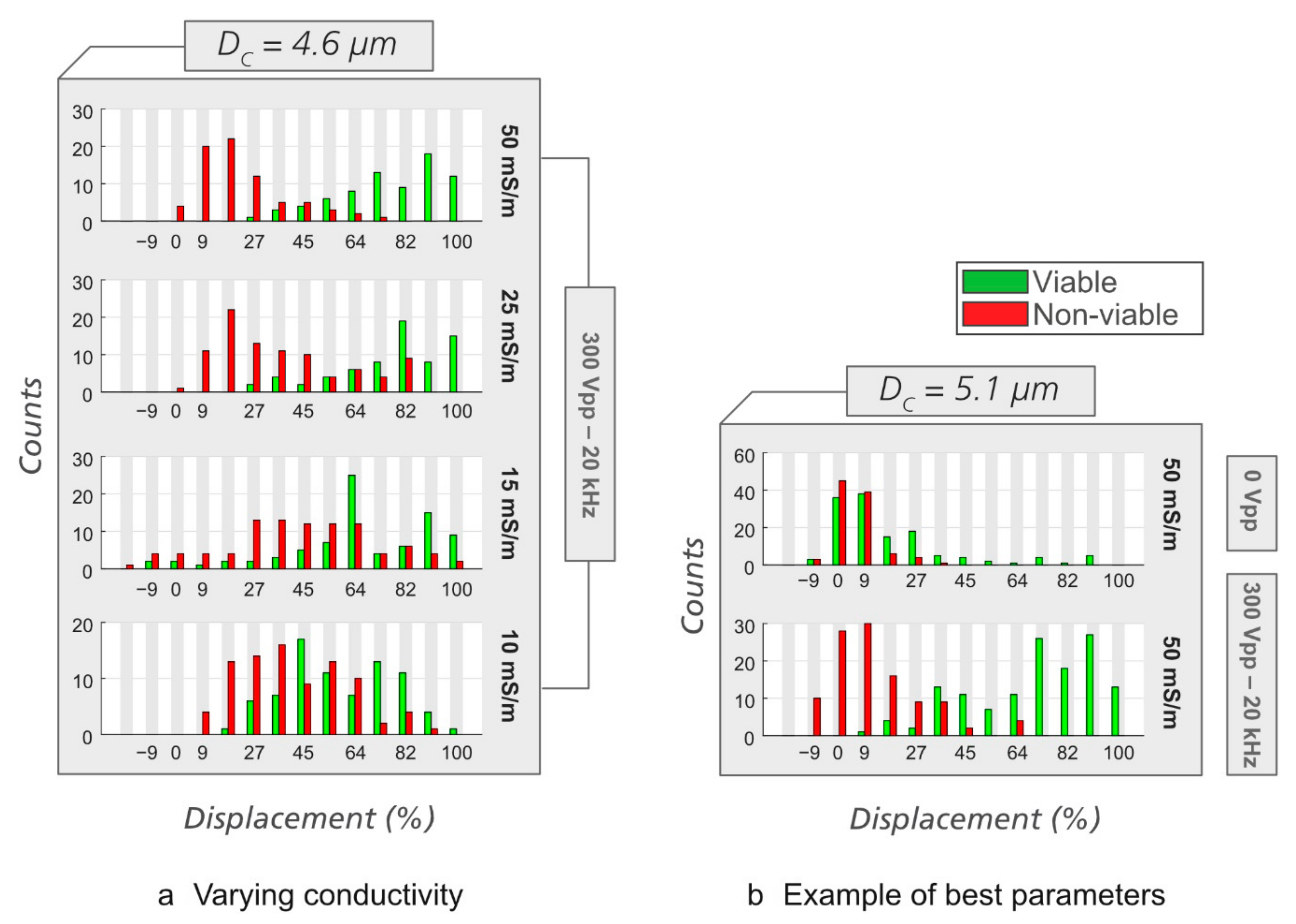
3.2. Sorting of Viable/Non-Viable Yeast Cells
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamada, M.; Nakashima, M.; Seki, M. Pinched Flow Fractionation: Continuous Size Separation of Particles Utilizing a Laminar Flow Profile in a Pinched Microchannel. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5465–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Continuous Particle Separation Through Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, D.; Irimia, D.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18892–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petersson, F.; Åberg, L.; Swärd-Nilsson, A.A.-M.; Laurell, T. Free Flow Acoustophoresis: Microfluidic-Based Mode of Particle and Cell Separation. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5117–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, E.M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J. Mol. Biol. 1975, 98, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, J.P.; Holm, S.H.; Adolfsson, K.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Sorting cells by size, shape and deformability. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beech, J.P.; Ho, B.D.; Garriss, G.; Oliveira, V.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Separation of pathogenic bacteria by chain length. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R. Review Article—Dielectrophoresis: Status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 022811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Cosío, G.; Herrera-López, E.J.; Arellano-Plaza, M.; Mathis, A.G.; Kirchmayr, M.; Amaya-Delgado, L. Application of dielectric spectroscopy to unravel the physiological state of microorganisms: Current state, prospects and limits. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6101–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.A. Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Fields (Cambridge Monographs on Physics); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Hertfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guyot, S.; Gervais, P.; Young, M.; Winckler, P.; Dumont, J.; Davey, H.M. Surviving the heat: Heterogeneity of response inSaccharomyces cerevisiaeprovides insight into thermal damage to the membrane. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillet, F.; Lemonier, S.; Schiavone, M.; Formosa, C.; Martin-Yken, H.; François, J.-M.; Dague, E. Uncovering by Atomic Force Microscopy of an original circular structure at the yeast cell surface in response to heat shock. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.D. Lethal Effects of Heat on Bacterial Physiology and Structure. Sci. Prog. 2003, 86, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrián, G.; Condón, S.; Mañas, P. Physiology of the Inactivation of Vegetative Bacteria by Thermal Treatments: Mode of Action, Influence of Environmental Factors and Inactivation Kinetics. Foods 2017, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pohl, H.A.; Hawk, I. Separation of Living and Dead Cells by Dielectrophoresis. Science 1966, 152, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markx, G.H.; Talary, M.S.; Pethig, R. Separation of viable and non-viable yeast using dielectrophoresis. J. Biotechnol. 1994, 32, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markx, G.H.; Pethig, R. Dielectrophoretic separation of cells: Continuous separation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 45, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Simmons, B.A.; Cummings, E.B.; Fintschenko, Y. Dielectrophoretic Concentration and Separation of Live and Dead Bacteria in an Array of Insulators. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.D.; Beech, J.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabacak, N.M.; Spuhler, P.S.; Fachin, F.; Lim, E.J.; Pai, V.; Ozkumur, E.; Martel, J.M.; Kojic, N.; Smith, C.L.; Chen, P.-I.; et al. Microfluidic, marker-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood samples. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balvin, M.; Sohn, E.; Iracki, T.; Drazer, G.; Frechette, J. Directional Locking and the Role of Irreversible Interactions in Deterministic Hydrodynamics Separations in Microfluidic Devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 078301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, B.H.; Smith, J.T.; Gifford, S.M.; Wang, C.; Brink, M.; Bruce, R.L.; Austin, R.H.; Stolovitzky, G.; Astier, Y. Nanoscale lateral displacement arrays for the separation of exosomes and colloids down to 20 nm. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.A.; Inglis, D.W.; Morton, K.J.; Lawrence, D.A.; Huang, L.R.; Chou, S.Y.; Sturm, J.C.; Austin, R.H. Deterministic hydrodynamics: Taking blood apart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14779–14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Yung, R.; Tai, Y.C.; Kasdan, H. Deterministic lateral displacement MEMS device for continuous blood cell separation. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 30 January–3 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Kamei, D.T.; Ho, C.-M. On-Chip Continuous Blood Cell Subtype Separation by Deterministic Lateral Displacement. In Proceedings of the 2007 2nd IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Bangkok, Thailand, 16–19 January 2007; pp. 932–936. [Google Scholar]
- Loutherback, K.; D’Silva, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, A.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Deterministic separation of cancer cells from blood at 10 mL/min. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 042107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, F.; Du, J.; Shu, W.; Feng, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y. Rapid isolation of cancer cells using microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement structure. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S.H.; Beech, J.P.; Barrett, M.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Separation of parasites from human blood using deterministic lateral displacement. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S.H.; Beech, J.P.; Barrett, M.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Simplifying microfluidic separation devices towards field-detection of blood parasites. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.A. Microfluidic Separation of Blood Components through Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Ph.D. Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zeming, K.K.; Thakor, N.V.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.-H. Real-time modulated nanoparticle separation with an ultra-large dynamic range. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, J.P.; Jönsson, P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Tipping the balance of deterministic lateral displacement devices using dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Lithography. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1998, 37, 550–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, V.; García-Sánchez, P.; Honrado, C.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. AC electrokinetic biased deterministic lateral displacement for tunable particle separation. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
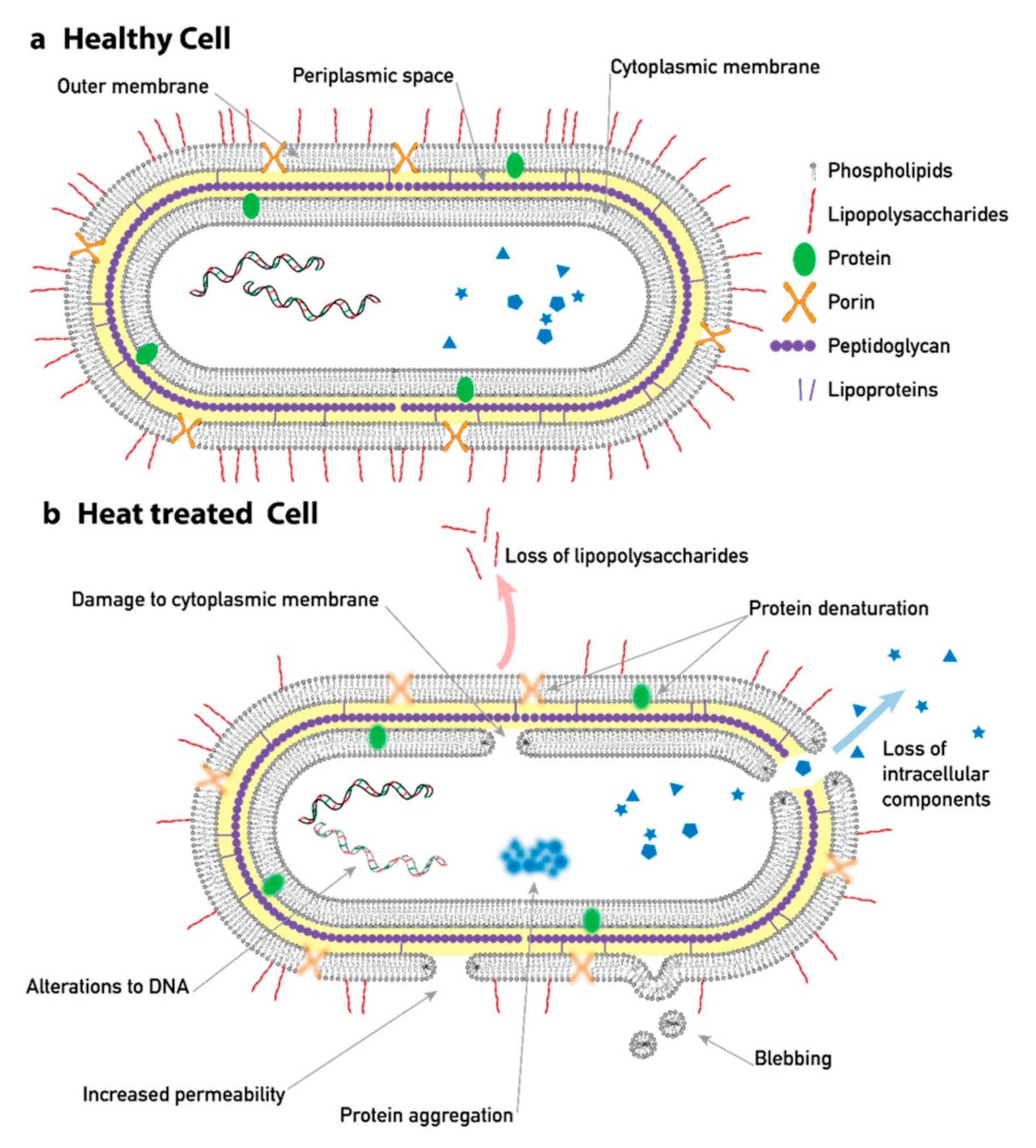

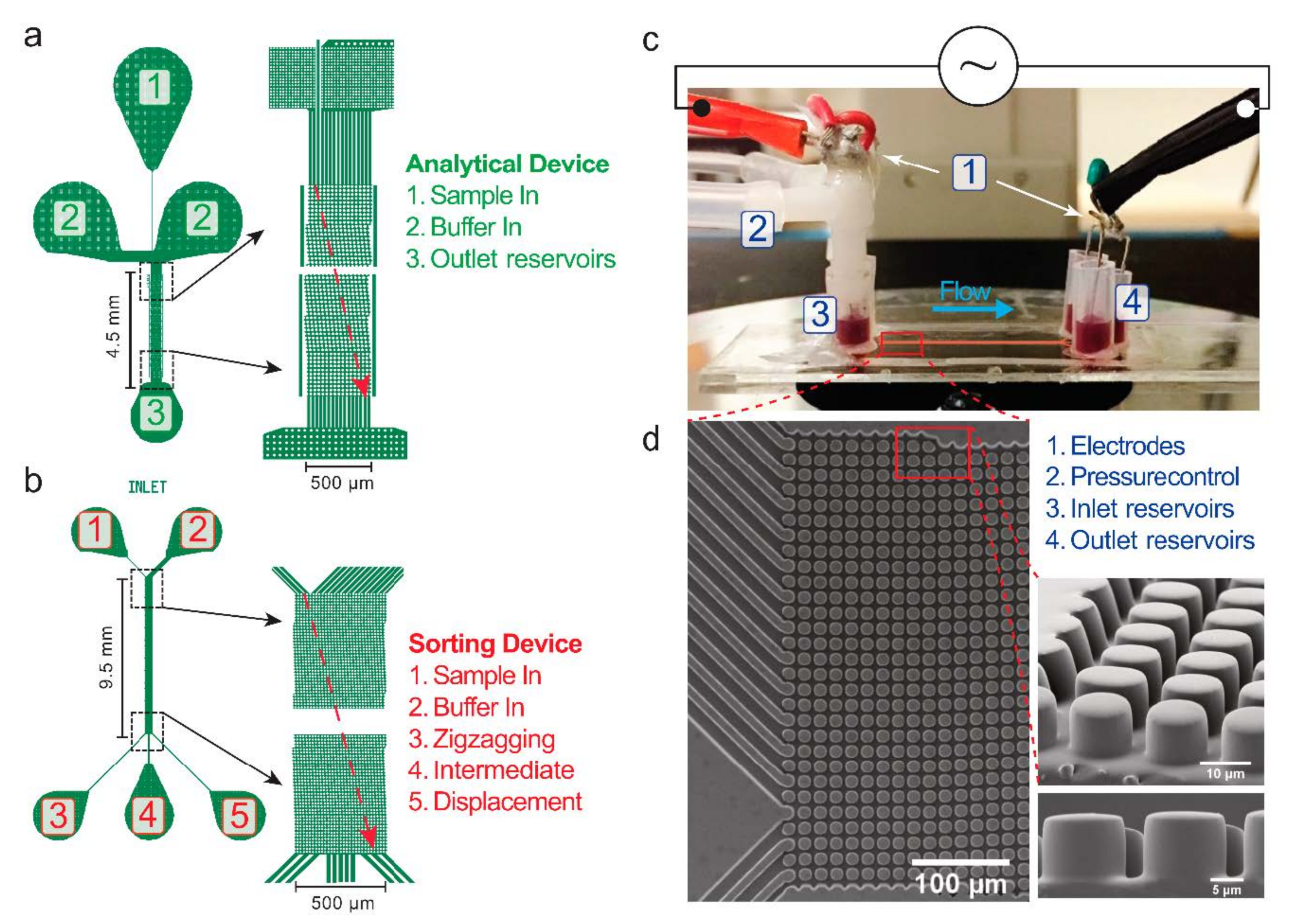
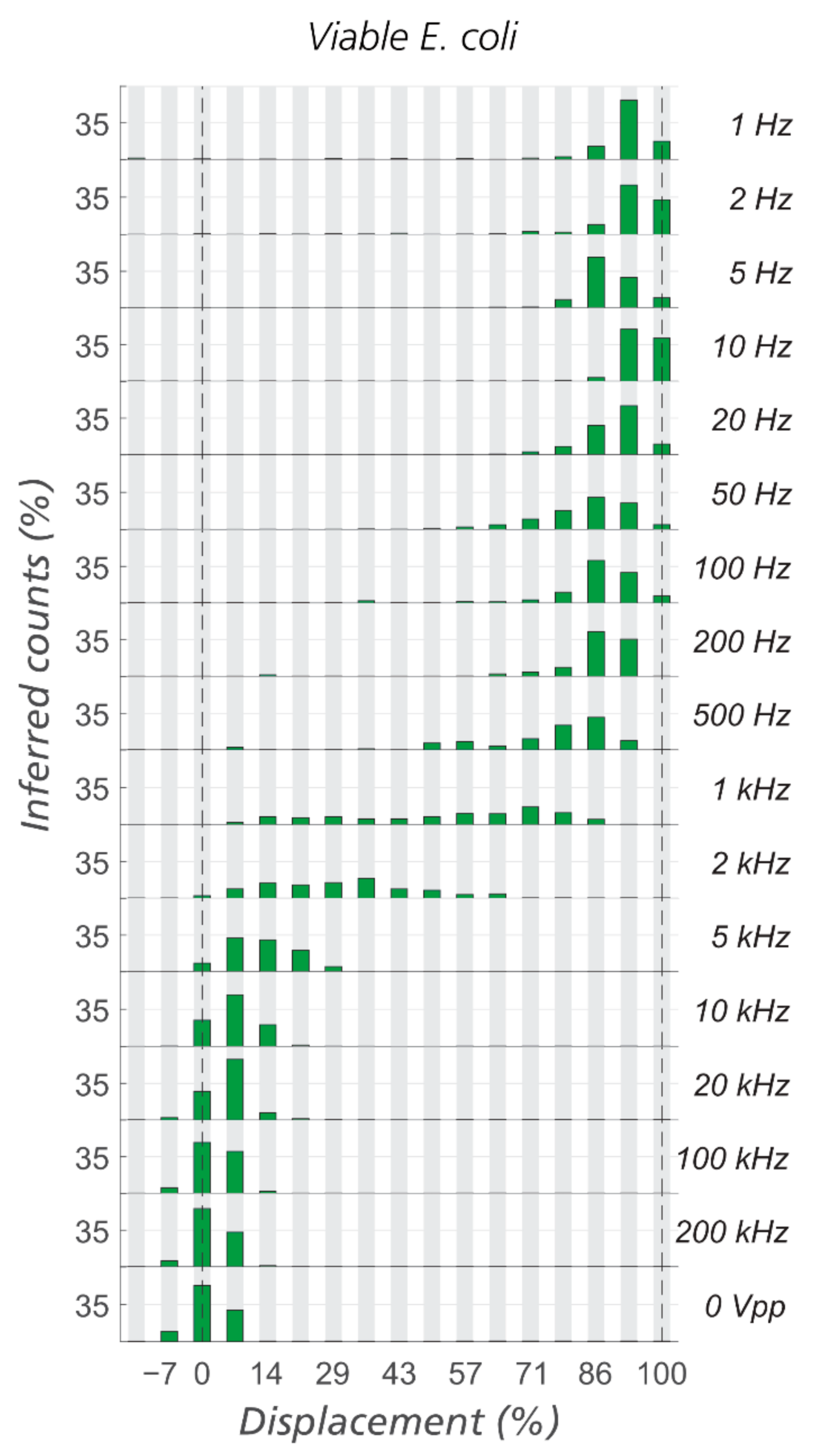
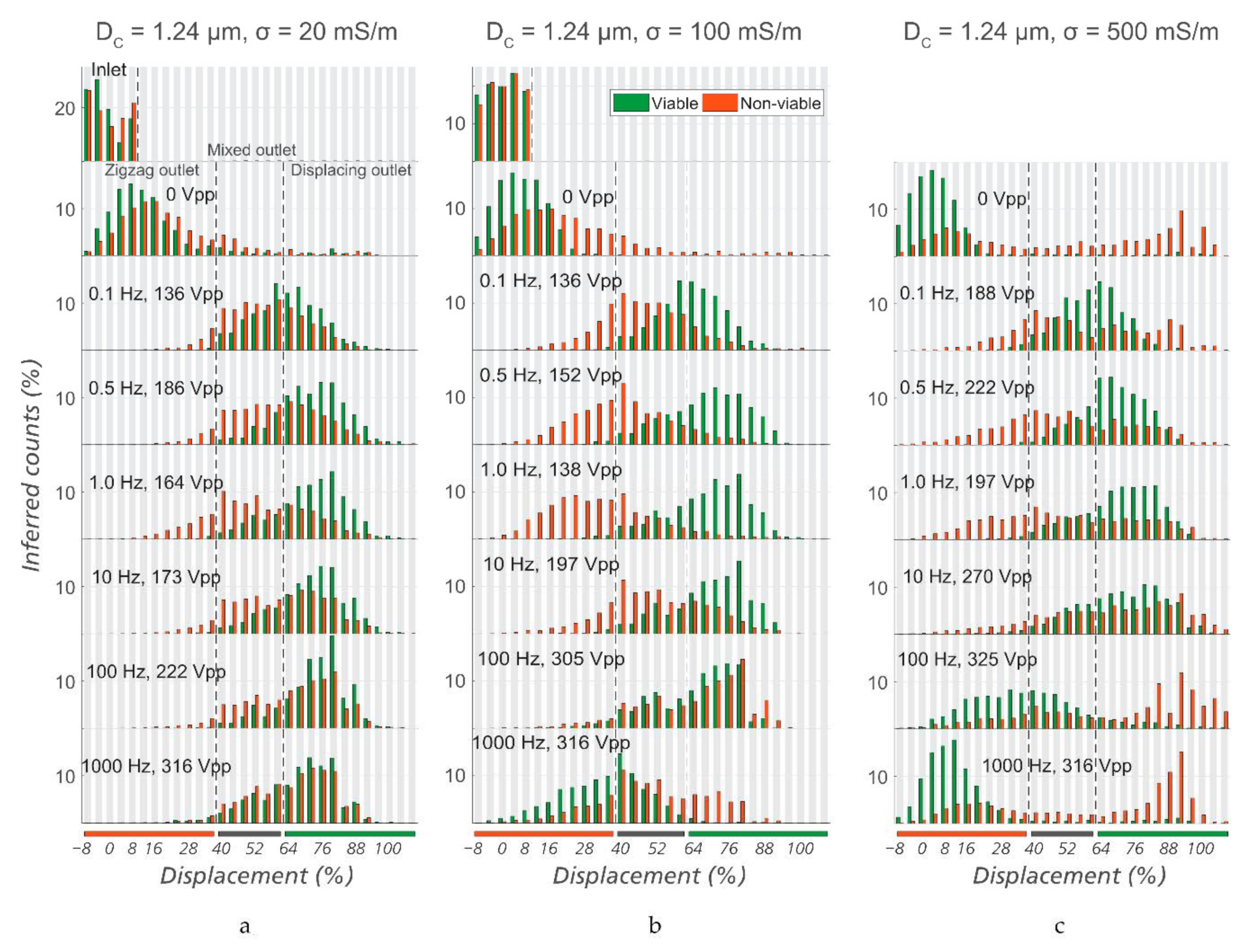
| Device Name | Gap (µm) | N | DC (µm) | Deflection, θ | Cell Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical device #1 | 4 | 10 | 1.9 | 5.71° | E. coli |
| Analytical device #2 | 10 | 10 | 4.6 | 5.71° | Yeast |
| Analytical device #3 | 11 | 10 | 5.1 | 5.71° | Yeast |
| Analytical device #4 | 12 | 10 | 5.6 | 5.71° | Yeast |
| Device Name | Gap (µm) | N | DC (µm) | Channel Length (mm) | Deflection θ | Deflection (µm) | Deflection/Channel Width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorting device #1 | 4 | 23 | 1.24 | 9.5 | 2.49° | 400 | 86% |
| Sorting device #2 | 3 | 50 | 0.64 | 22.9 | 1.15° | 450 | 86% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, B.D.; Beech, J.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Cell Sorting Using Electrokinetic Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Micromachines 2021, 12, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010030
Ho BD, Beech JP, Tegenfeldt JO. Cell Sorting Using Electrokinetic Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Micromachines. 2021; 12(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Bao D., Jason P. Beech, and Jonas O. Tegenfeldt. 2021. "Cell Sorting Using Electrokinetic Deterministic Lateral Displacement" Micromachines 12, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010030
APA StyleHo, B. D., Beech, J. P., & Tegenfeldt, J. O. (2021). Cell Sorting Using Electrokinetic Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Micromachines, 12(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010030






