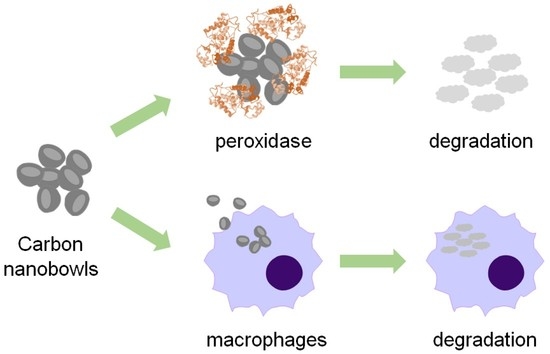
Enzymatic and Cellular Degradation of Carbon-Based Biconcave Nanodisks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Enzymatic Degradation of CBBNs in the Presence of HRP and H2O2
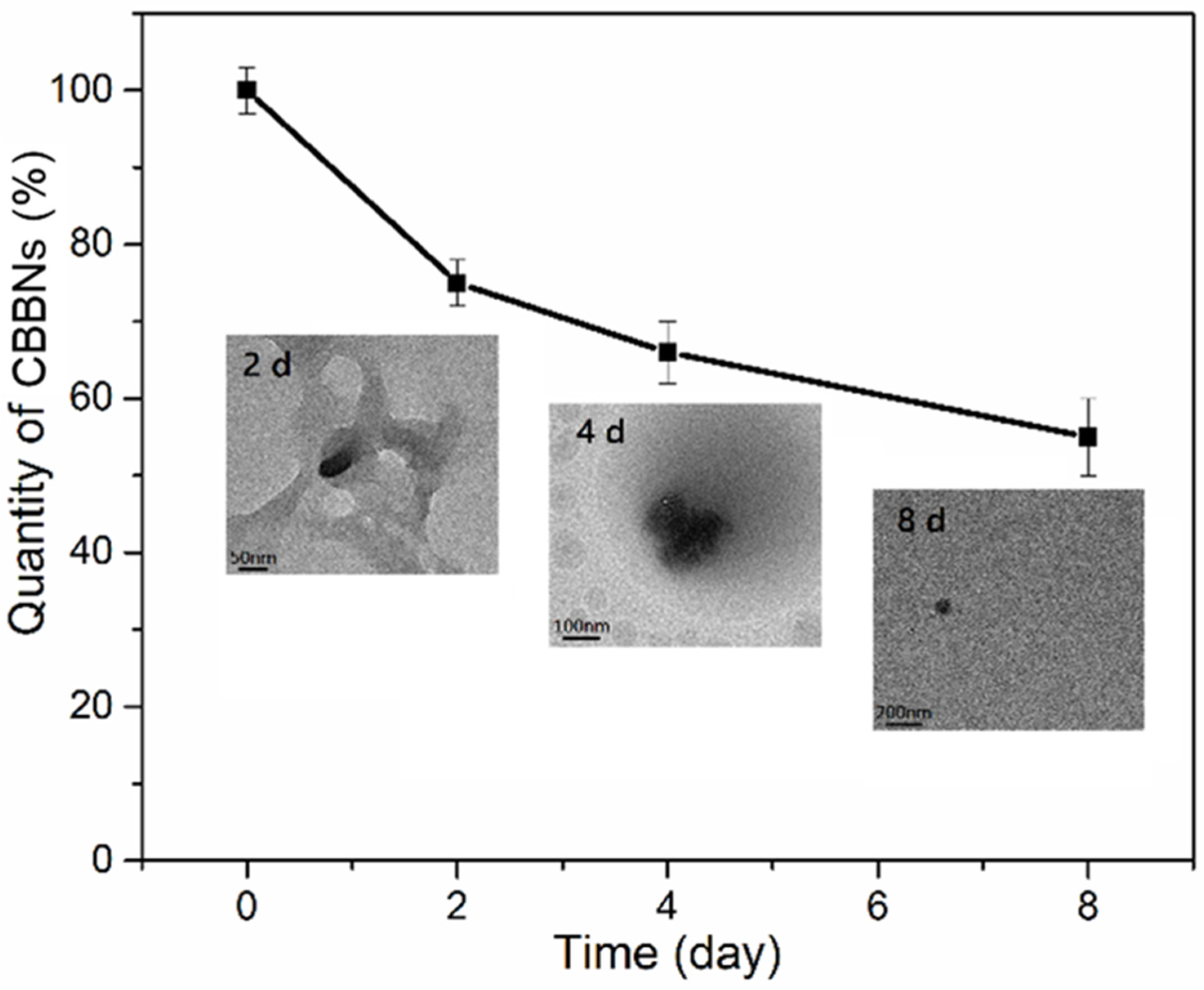
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
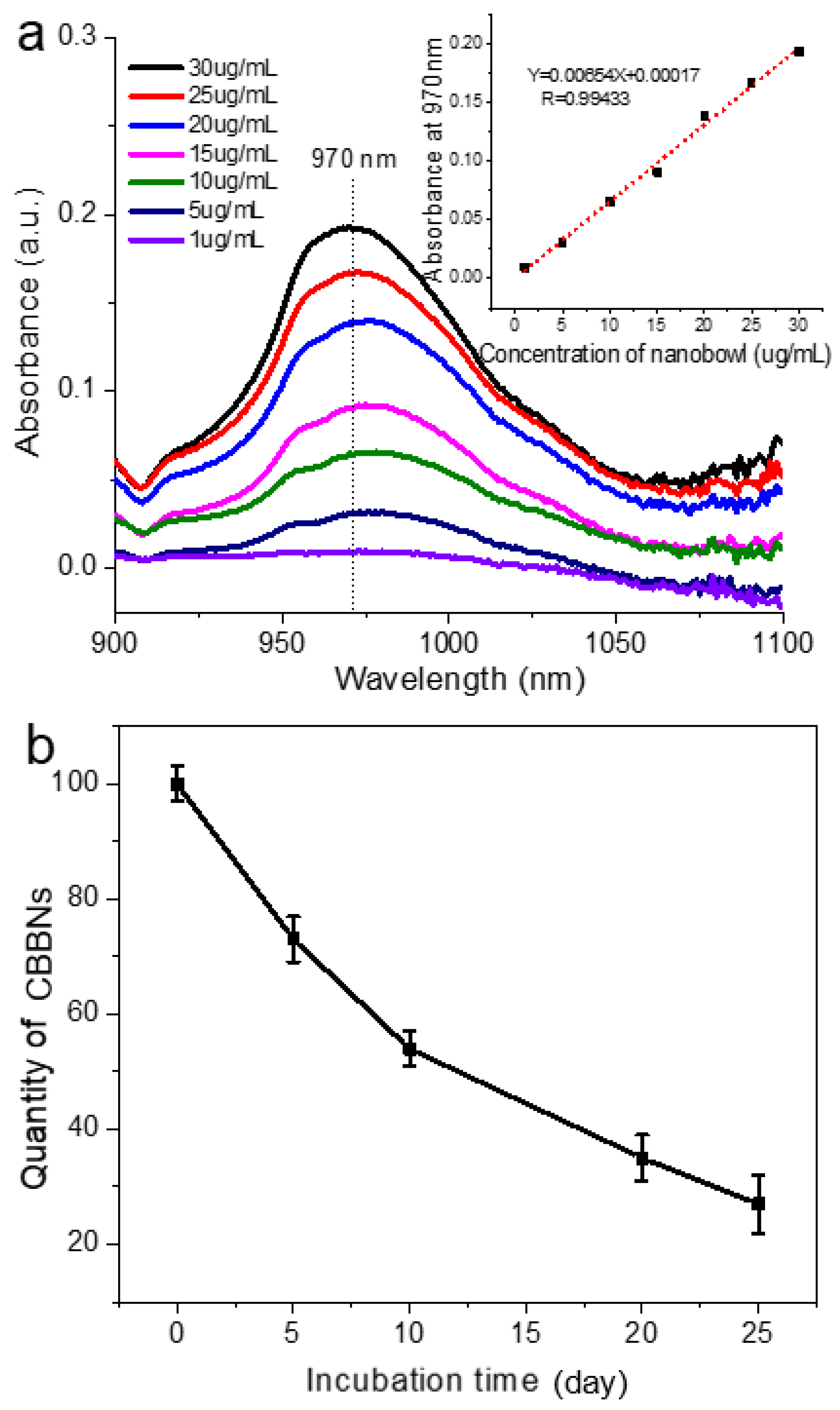
2.4. Near-Infrared (IR) Absorption Spectroscopy
2.5. Cellular Degradation of CBBNs in Macrophages
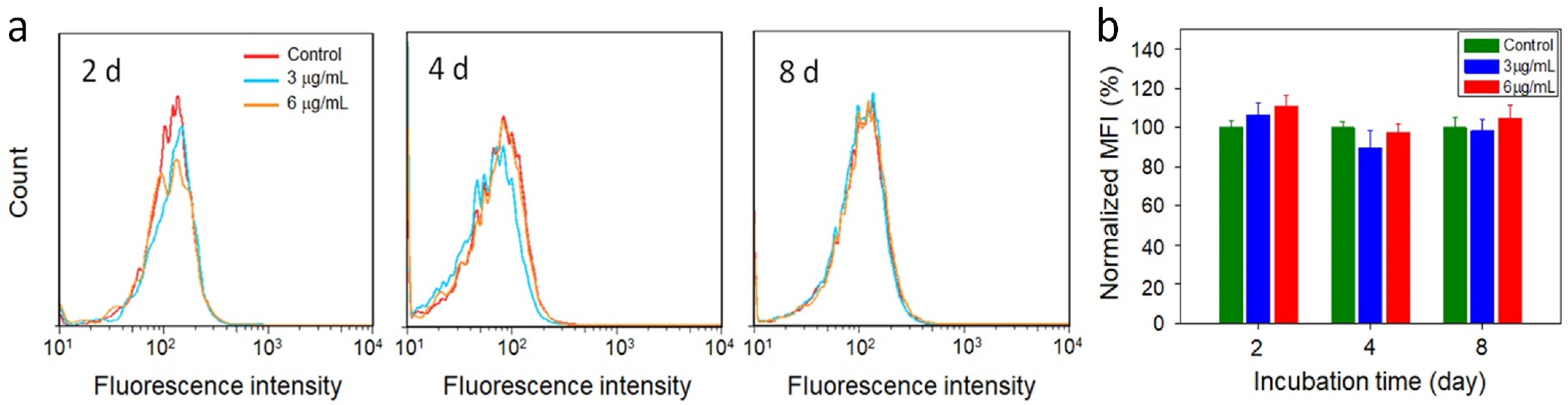
2.6. Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection
2.7. Cell Viability
3. Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K.; Prato, M. Making carbon nanotubes biocompatible and biodegradable. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotchey, G.P.; Zhao, Y.; Kagan, V.E.; Star, A. Peroxidase-mediated biodegradation of carbon nanotubes in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, N.; Haniu, H.; Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Hara, K.; Takanashi, S.; Shimizu, M.; Narita, N.; Okamoto, M.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Safe Clinical Use of Carbon Nanotubes as Innovative Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpell, C.J.; Kostarelos, K.; Davis, B.G. Can Carbon Nanotubes Deliver on Their Promise in Biology? Harnessing Unique Properties for Unparalleled Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, J.; Kong, X.; Hyeon, T.; Ling, D. Dynamic nanoparticle assemblies for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.; Guerrero, A.; Hassan-Lopez, N.; Morales, J.O.; Bollo, S.; Corvalan, A.; Quest, A.F.; Kogan, M.J. Organic and inorganic nanoparticles for prevention and diagnosis of gastric cáncer. Curr. Pharm. Design 2015, 21, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, B.R.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanomaterials for in vivo imaging. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, I.I.; Kapralov, A.A.; Michael, Z.P.; Burkert, S.C.; Shurin, M.R.; Star, A.; Shvedova, A.A.; Kagan, V.E. Enzymatic oxidative biodegradation of nanoparticles: Mechanisms, significance and applications. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2016, 299, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Mukherjee, S.P.; Gallud, A.; Burkert, S.C.; Bistarelli, S.; Bellucci, S.; Bottini, M.; Star, A.; Fadeel, B. Biological interactions of carbon-based nanomaterials: From coronation to degradation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunzmann, A.; Andersson, B.; Thurnherr, T.; Krug, H.; Scheynius, A.; Fadeel, B. Toxicology of engineered nanomaterials: Focus on biocompatibility, biodistribution and biodegradation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.L.; Kichambare, P.D.; Vlasova, I.I.; Kapralov, A.A.; Konduru, N.; Kagan, V.E.; Star, A. Biodegradation of single-walled carbon nanotubes through enzymatic catalysis. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.L.; Kotchey, G.P.; Chen, Y.; Yanamala, N.V.K.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Kagan, V.E.; Star, A. Mechanistic investigations of horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed degradation of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Allen, B.L.; Star, A. Enzymatic degradation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 9536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andón, F.T.; Kapralov, A.A.; Yanamala, N.; Feng, W.; Baygan, A.; Chambers, B.J.; Hultenby, K.; Ye, F.; Toprak, M.S.; Brandner, B.D.; et al. Biodegradation of single-walled carbon nanotubes by eosinophil peroxidase. Small 2013, 9, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, V.E.; Konduru, N.V.; Star, A.; Shvedova, A.A. Carbon nanotubes degraded by neutrophil myeloperoxidase induce less pulmonary inflammation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Pei, R.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanomaterials: Single-wall nanotube, multi-wall nanotube, and fullerene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Davis, C.; Cai, W.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Dai, H. Circulation and long-term fate of functionalized, biocompatible single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice probed by Raman spectroscopy. PNAS 2008, 105, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sureshbabu, A.R.; Kurapati, R.; Russier, J.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Bartolini, I.; Meneghetti, M.; Kostarelos, K.; Bianco, A. Degradation-by-design: Surface modification with functional substrates that enhance the enzymatic degradation of carbon nanotubes. Biomaterials 2015, 72, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modugno, G.; Ksar, F.; Battigelli, A.; Russier, J.; Lonchambon, P.; da Silva, E.E.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Soula, B.; Galibert, A.-M.; Pinault, M.; et al. A comparative study on the enzymatic biodegradability of covalently functionalized double-and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2016, 100, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, M.; Bussy, C.; Iijima, S.; Kostarelos, K.; Yudasaka, M. Biodegradation of carbon nanohorns in macrophage cells. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgrabli, D.; Dachraoui, W.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Liu, X.J.; Begin, D.; Begin-Colin, S.; Bianco, A.; Gazeau, F.; Alloyeau, D. Carbon nanotube degradation in macrophages: Live nanoscale monitoring and understanding of biological pathway. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussy, C.; Hadad, C.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. Intracellular degradation of chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes using a long-term primary microglial culture model. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, M.; Morimoto, T.; Tajima, N.; Ichiraku, K.; Fujita, K.; Iijima, S.; Yudasaka, M.; Okazakia, T. Size-dependent cell uptake of carbon nanotubes by macrophages: A comparative and quantitative study. Carbon 2018, 127, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, M.; Nakajima, H.; Yudasaka, M.; Iijima, S.; Okazaki, T. Time-dependent degradation of carbon nanotubes correlates with decreased reactive oxygen species generation in macrophages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Biodegradation of carbon nanotubes by macrophages. Front. Mater. 2019, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, A.H.; Landon, P.B.; Emerson, C.D.; Zhang, C.; Anzenberg, P.; Akkiraju, S.; La, R. Synthesis of nano-bowls with a Janus template. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, L.; Qiao, S.Z. A mesoporous organosilica nano-bowl with high DNA loading capacity–a potential gene delivery carrier. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17446–17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, P.; An, Z. Carbon nanobowls supported ultrafine palladium nanocrystals: A highly active electrocatalyst for the formic acid oxidation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ma, Y.-Q. Computer simulation of the translocation of nanoparticles with different shapes across a lipid bilayer. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.E.A.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. PNAS 2008, 105, 11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Wang, H.; Gu, X.; Stephen, Z.R.; Yen, C.; Chang, F.C.; Dayringer, C.J.; Zhang, M. Biconcave Carbon Nanodisks for Enhanced Drug Accumulation and Chemo-Photothermal Tumor Therapy. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 8, e1801505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/TS23034; 2021 Nanotechnologies―Method to Estimate Cellular Uptake of Carbon Nanomaterials by Using Optical Absorption Measurement. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Tahara, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M.; Iijima, S.; Yudasaka, M. Lysosomal membrane destabilization induced by high accumulation of single-walled carbon nanohorns in murine macrophage RAW 264.7. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2762–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Z.; Mu, Q.; Wang, H.; Lin, G.; Zhang, M. Enzymatic and Cellular Degradation of Carbon-Based Biconcave Nanodisks. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071144
Wei Z, Mu Q, Wang H, Lin G, Zhang M. Enzymatic and Cellular Degradation of Carbon-Based Biconcave Nanodisks. Micromachines. 2022; 13(7):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071144
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Zhiyong, Qingxin Mu, Hui Wang, Guanyou Lin, and Miqin Zhang. 2022. "Enzymatic and Cellular Degradation of Carbon-Based Biconcave Nanodisks" Micromachines 13, no. 7: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071144
APA StyleWei, Z., Mu, Q., Wang, H., Lin, G., & Zhang, M. (2022). Enzymatic and Cellular Degradation of Carbon-Based Biconcave Nanodisks. Micromachines, 13(7), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071144