Multi-Field Characterisation of Material Removal Processes in Ultrasonic Magnetorheological Chemical Compound Polishing of GaN Wafers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Principles
2.2. Experimental Programme
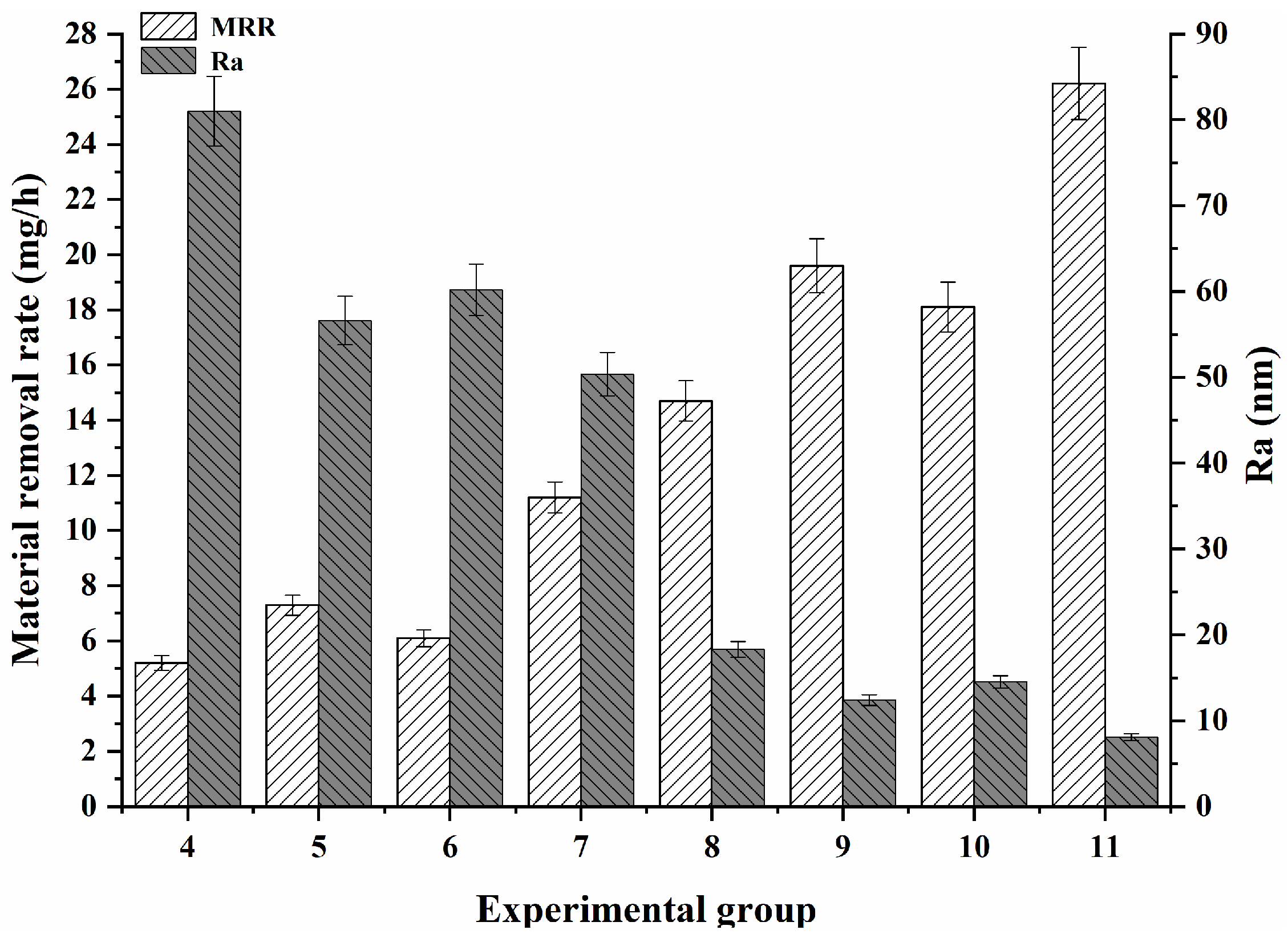
3. Experimental Results
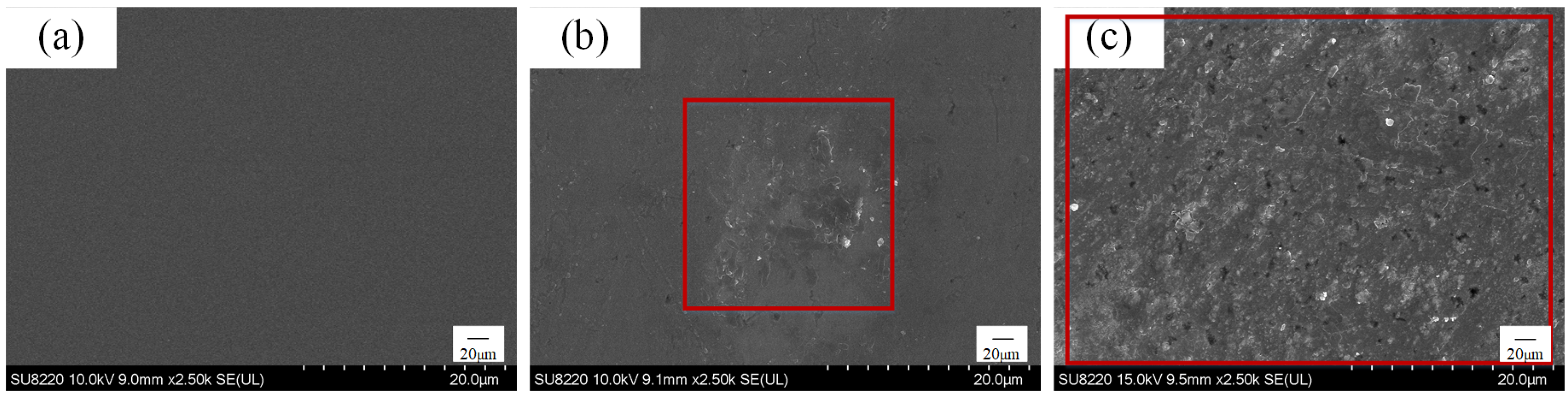
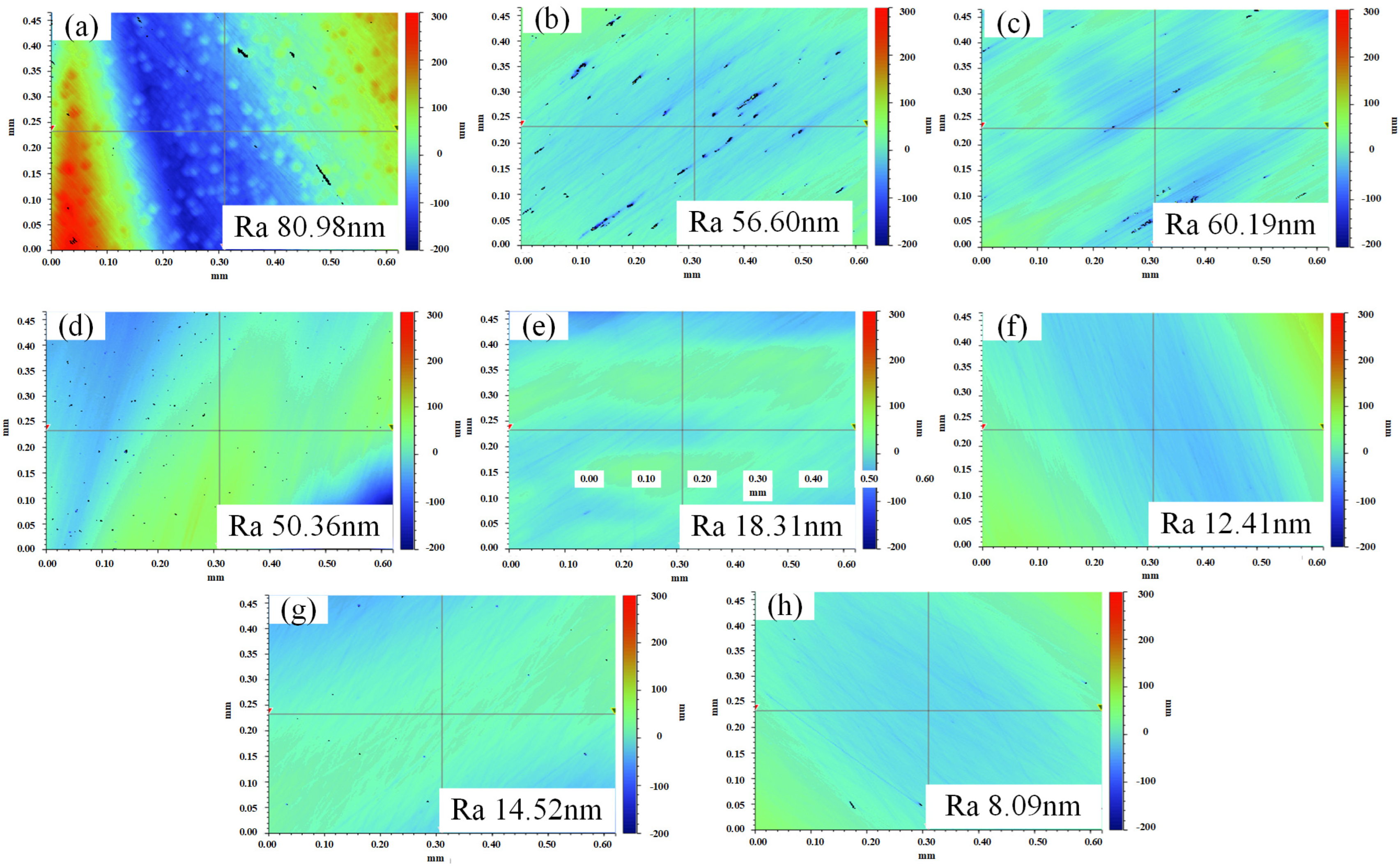
3.1. Reaction Products on the GaN Surfaces
3.2. Effects of the Different Polishing Solution Components on the Polishing Effect of GaN
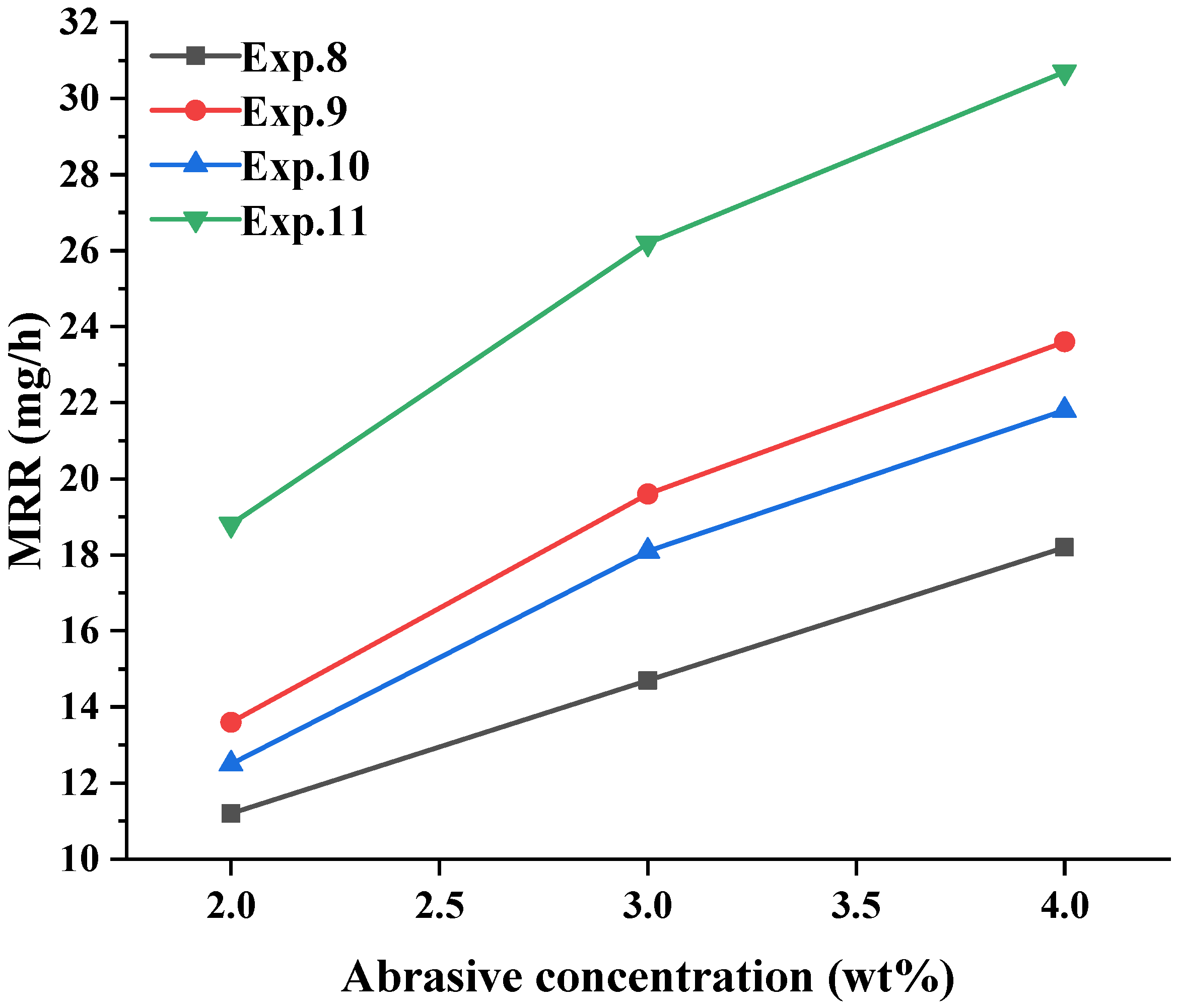
3.3. Effect of the Abrasive Concentration on the GaN Material Removal
3.4. Effects of the Hydrogen Peroxide Concentration on the Polishing Effect of GaN
4. Analysis and Discussion
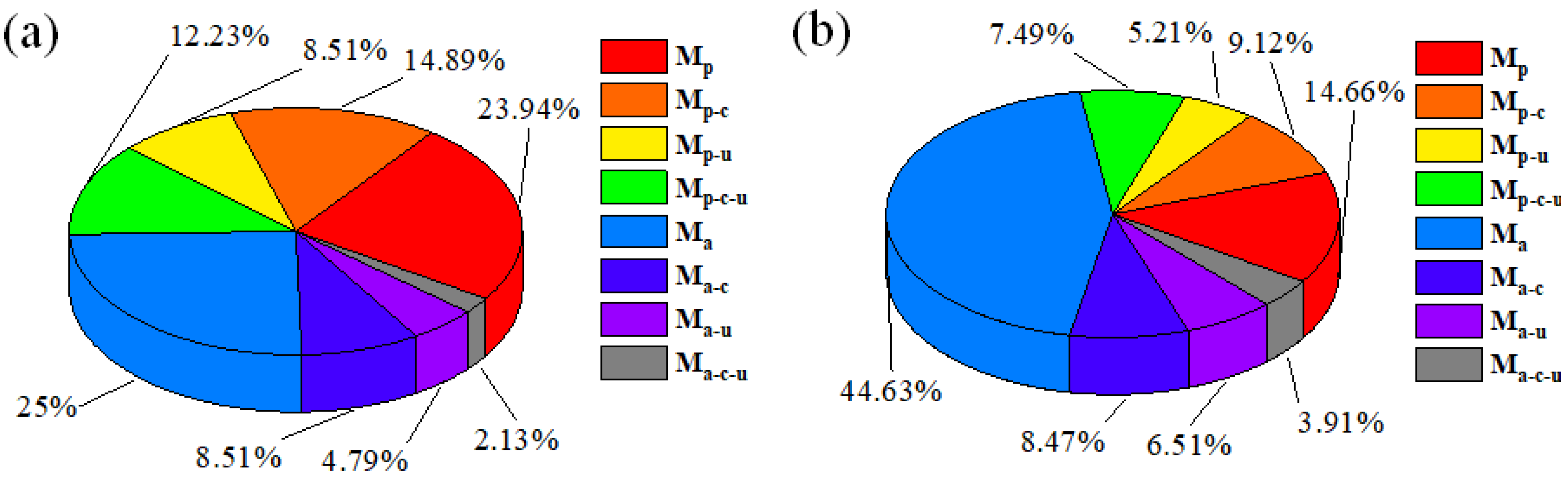
4.1. Material Removal Composition for Compound Polishing
4.2. Analysis of the Role of Factors in Material Removal
4.3. Analysis of the Material Removal Behaviour for Compound Polishing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Edgar, J.H. Substrates for gallium nitride epitaxy. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2002, 37, 61–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.B.; Niu, X.H.; Hou, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, R. Effect and mechanism of oxidant on alkaline chemical mechanical polishing of gallium nitride thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 138, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Deng, H. Highly efficient and damage-free polishing of GaN (0001) by electrochemical etching-enhanced CMP process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 514, 145957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, G.S.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.L.; Zou, C.L.; Zhang, S.A. Investigation on the surface characterization of Ga-faced GaN after chemical-mechanical polishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 338, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xiao, C.; Gao, J.; Li, G.Z.; Wu, H.Q.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.M. Interplay between counter-surface chemistry and mechanical activation in mechanochemical removal of N-faced GaN surface in humid ambient. Tribol. Int. 2021, 159, 107004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Shen, B.; Chen, Z.Z.; Hu, X.D.; Qin, Z.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Wu, J.J.; Yu, T.J.; Kang, X.N.; Fu, X.X.; et al. GaN-based substrates and optoelectronic materials and devices. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 1201–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, H. Present Status and Future Prospect of Widegap Semiconductor High-Power Devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 7565–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, T.; Fujihira, K.; Shiomi, H.; Matsunami, H. High-Voltage 4H-SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes Fabricated on (038) with Closed Micropipes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, T. Polishing of diamond, SiC, GaN based on the oxidation modification of hydroxyl radical: Status, challenges and strategies. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 166, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreejith, P.S.; Ngoi, B.K.A. Material removal mechanisms in precision machining of new materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2001, 41, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, N.; Cheng, J.; Pu, Y. A review on the development of ceria for chemical mechanical polishing. Powder Technol. 2024, 444, 119989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, H.; Takeda, H.; Koyama, K.; Katakura, H.; Sunakawa, K.; Doi, T. Chemical Mechanical Polishing of Gallium Nitride with Colloidal Silica. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, H.; Kim, S.W.; Suzuki, T.; Koyama, K.; Aota, N.; Doi, T.; Yamazaki, T. Surface planarization of GaN-on-sapphire template by chemical mechanical polishing for subsequent GaN homoepitaxy. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, H.; Doi, T.; Takeda, H.; Katakura, H.; Kim, H.; Koyama, K.; Yamazaki, T. Ultraprecision CMP for sapphire, GaN, and SiC for advanced optoelectronics materials. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, G.; Deng, X.; Jiang, C.; Tang, W.; Yin, H.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B. High quality of N-polar GaN film fabricated by layer transfer technology using high selective material removal rate of CMP. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 141, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Liu, S.; Pang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J. Synergistic effect of abrasive friction and glycine on improving chemical mechanical polishing performance of single-crystal GaN substrate. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 21357–21366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M.; Cui, D.; Liu, S. Exploring the mechanism of gallium nitride surface quality enhancement by green organic additives in chemical mechanical polishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670, 160646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, J.; Kubota, A.; Yagi, K.; Sano, Y.; Hara, H.; Arima, K.; Okamoto, T.; Mimura, H.; Yamauchi, K. Chemical planarization of GaN using hydroxyl radicals generated on a catalyst plate in H2O2 solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Pan, G.; Lu, X. Mechanism of GaN CMP based on H2O2 slurry combined with UV light. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Hu, S.; Song, J.; Ji, J.; Song, J. A synergistic polishing technology by mixed abrasives with photocatalysis and fenton reaction. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 166, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Yan, Q. Friction and wear mechanisms for single crystal GaN based on an electro-Fenton enhanced chemical reaction. Wear 2022, 498, 204315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Gu, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Kang, M.; Xi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ye, Q. Surface polishing of CoCrMo alloy by magnetorheological polishing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 475, 130162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yan, Q.; Pan, J.; Luo, K.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. Mechanism and experimental study of photoelectro-Fenton composite magnetorheological polishing. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 41962–41969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nie, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Effect mechanism of multi-phase coupling on particle behaviors in magnetorheological foam plane finishing process. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 109, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Al-amin, M.; Grøndahl, L.; Lu, M.; Cheung, C.F.; Huang, H. MD simulation of chemically enhanced polishing of 6H-SiC in aqueous H2O2. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 107, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. A unique insight into the atomic-scale removal on 6H-SiC. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 143, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Kang, R. Atomistic mechanisms of chemical mechanical polishing of diamond (100) in aqueous H2O2/pure H2O: Molecular dynamics simulations using reactive force field (ReaxFF). Comp. Mater. Sci. 2019, 157, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Lei, J.; Mo, M.M.Q.; Li, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.P.; Hu, Y.C.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.T. Impacts of ultrasound-assisted Fenton degradation and alkaline de-esterification on structural properties and biological effects of pectic polysaccharides from Tartary buckwheat leaves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 106, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; He, C.S.; Zhou, P.; Lai, B. Mechanical agitation and ultrasound constructed in situ Fenton system: The role of atomic hydrogen for Fe(III) reduction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 340, 126859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savun-Hekimoğlu, B. A review on sonochemistry and its environmental applications. Acoustics 2020, 2, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, W.; Fu, Y.; Jian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, D.; He, J. Surface oxidation properties of GaN wafers in chemical magnetorheological polishing process by ultrasonic action. Precis. Eng. 2025, 94, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhong, M.; Xu, W. Macro and micro-nano machining mechanism for ultrasonic vibration assisted chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 640, 158343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Ji, A.; Bi, E.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Lin, W. Investigation on roller-type ultrasonic assisted magnetorheological finishing for biomedical small and complex surface of titanium alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Kato, M.; Otsu, H. Effect of oxidation-reduction potential on an electrochemical Fenton-type process. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lu, J.; Pan, J.; Yan, Q. Material removal process of single-crystal SiC in chemical-magnetorheological compound finishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Lu, J.; Zeng, S.; Yan, Q.; Pan, J. Processing properties for the Si-face of the 4H-SiC substrates using the magnetically-controlled abrasive solidification orientation–solid-phase Fenton reaction for the fabrication of the lapping–polishing plate. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 120, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Oxidant (H2O2) | Catalyst (Fe3O4) | Magnetic Oarticle (CIP) | Abrasive | Ultrasonic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 2 wt% | - | - | + |
| 2 | 3 wt% | 2 wt% | - | - | - |
| 3 | 3 wt% | 2 wt% | - | - | + |
| 4 | - | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | - | - |
| 5 | 3 wt% (1 wt%, 5 wt%) | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | - | - |
| 6 | - | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | - | + |
| 7 | 3 wt% (1 wt%, 5 wt%) | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | - | + |
| 8 | - | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | 3 wt% (2 wt%, 4 wt%) | - |
| 9 | 3 wt% (1 wt%, 5 wt%) | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | 3 wt% (2 wt%, 4 wt%) | - |
| 10 | - | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | 3 wt% (2 wt%, 4 wt%) | + |
| 11 | 3 wt% (1 wt%, 5 wt%) | 2 wt% | 12 wt% | 3 wt% (2 wt%, 4 wt%) | + |
| Exp. 1 | Exp. 2 | Exp. 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elt. | Mass Norm. | Atom | Elt. | Mass Norm. | Atom | Elt. | Mass Norm. | Atom |
| O | 0.04% | 0.02% | O | 4.51% | 13.61% | O | 8.37% | 23.26% |
| N | 16.29% | 49.22% | N | 7.28% | 25.17% | N | 7.04% | 22.45% |
| Ga | 83.67% | 50.76% | Ga | 88.21% | 61.22% | Ga | 84.59% | 54.19% |
| Total | 100% | 100% | Total | 100% | 100% | Total | 100% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, H.; Chen, W.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Mo, L.; Wen, Q.; Liu, D.; He, J. Multi-Field Characterisation of Material Removal Processes in Ultrasonic Magnetorheological Chemical Compound Polishing of GaN Wafers. Micromachines 2025, 16, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050502
Liang H, Chen W, Fu Y, Zhou W, Mo L, Wen Q, Liu D, He J. Multi-Field Characterisation of Material Removal Processes in Ultrasonic Magnetorheological Chemical Compound Polishing of GaN Wafers. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050502
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Huazhuo, Wenjie Chen, Youzhi Fu, Wenjie Zhou, Ling Mo, Qi Wen, Dawei Liu, and Junfeng He. 2025. "Multi-Field Characterisation of Material Removal Processes in Ultrasonic Magnetorheological Chemical Compound Polishing of GaN Wafers" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050502
APA StyleLiang, H., Chen, W., Fu, Y., Zhou, W., Mo, L., Wen, Q., Liu, D., & He, J. (2025). Multi-Field Characterisation of Material Removal Processes in Ultrasonic Magnetorheological Chemical Compound Polishing of GaN Wafers. Micromachines, 16(5), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050502






