The Emerging Role of TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure, Expression, and Mutations
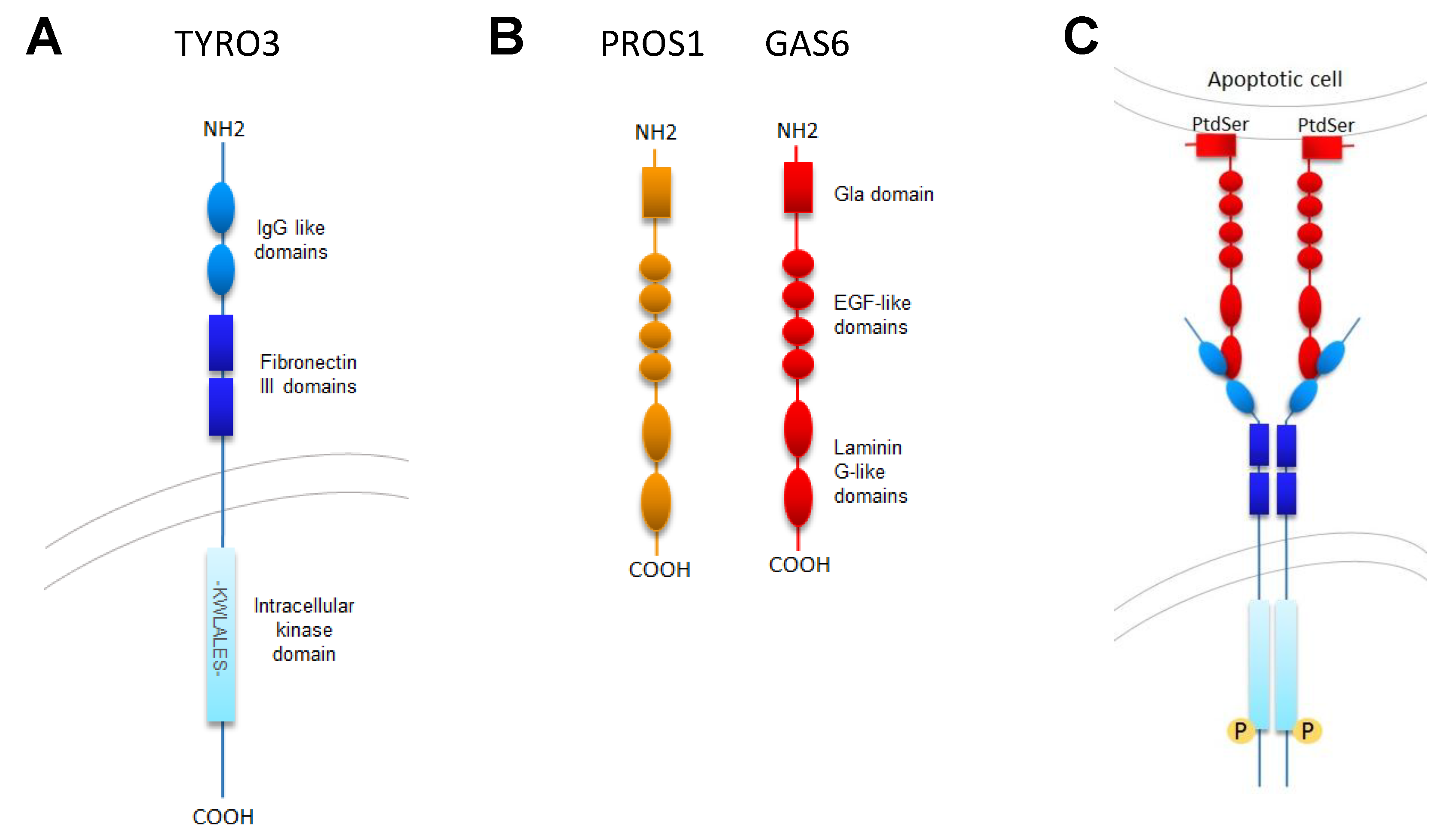
2.1. TYRO3 Structure
2.2. Physiologic TYRO3 Expression
2.3. TYRO3 Expression in Cancer
2.4. Upstream Regulators of TYRO3 Expression
2.5. TYRO3 Mutations in Cancer
3. Activation and Cell Signaling
3.1. TYRO3 Ligands
3.2. TYRO3 Activation
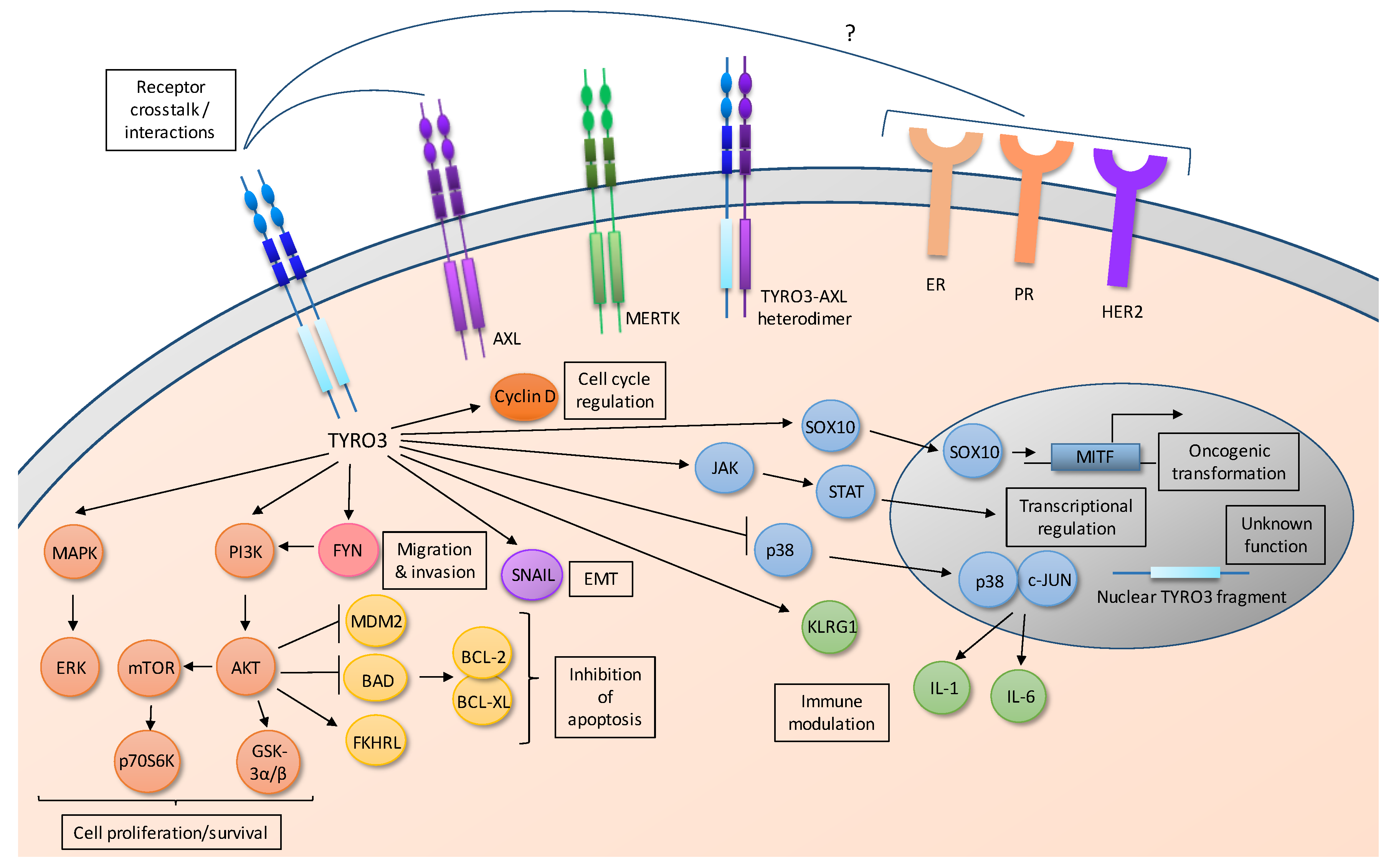
3.3. Downstream Signal Transduction Pathways
3.3.1. TYRO3 Activates the PI3K/AKT Pathway
3.3.2. TYRO3 Activates the SRC-Family Kinase FYN
3.3.3. TYRO3 Activates ERK1/2
3.3.4. TYRO3 Activates the JAK-STAT Pathway
3.3.5. TYRO3 Regulates Expression of MITF
3.4. Nuclear TYRO3
4. Physiologic Functions
4.1. TYRO3 in Thrombosis
4.2. TYRO3 in the Nervous System
4.3. TYRO3 in Osteoclastic Bone Resorption
4.4. TYRO3 in the Immune System
5. Functions in Cancer
5.1. TYRO3 in Tumorigenesis
5.2. TYRO3 in Metastasis
5.3. TYRO3 in Therapeutic Resistance
5.4. TYRO3 in the Tumor Microenvironment
5.5. Prognostic Significance of TYRO3
6. TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target
6.1. Translational Agents Targeting TYRO3
6.2. Potential Side Effects of TYRO3 Inhibition
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Boil. 2013, 5, a009076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.K.; DeRyckere, D.; Davies, K.D.; Earp, H.S. The TAM family: Phosphatidylserine sensing receptor tyrosine kinases gone awry in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, M.R.; Scadden, D.T.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Q.; Goddard, A.; Godowski, P.J. Rse, a novel receptor-type tyrosine kinase with homology to Axl/Ufo, is expressed at high levels in the brain. J. Boil. Chem. 1994, 269, 10720–10728. [Google Scholar]
- Crosier, P.S.; Lewis, P.M.; Hall, L.R.; Vitas, M.R.; Morris, C.M.; Beier, D.R.; Wood, C.R.; Crosier, K.E. Isolation of a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (DTK) from Embryonic Stem Cells: Structure, Genetic Mapping and Analysis of Expression. Growth Factors 2009, 11, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiring, C.; Dahlback, B.; Muller, Y.A. Ligand recognition and homophilic interactions in Tyro3: Structural insights into the Axl/Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinase family. J. Boil. Chem. 2004, 279, 6952–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.M.; Crosier, K.E.; Wood, C.R.; Crosier, P.S. Analysis of the murine Dtk gene identifies conservation of genomic structure within a new receptor tyrosine kinase subfamily. Genomics 1996, 31, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linger, R.M.; Keating, A.K.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: Biologic functions, signaling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2008, 100, 35–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Gore, M.; Zhang, Q.; Camenisch, T.; Boast, S.; Casagranda, F.; Lai, C.; Skinner, M.K.; Klein, R.; Matsushima, G.K.; et al. Tyro-3 family receptors are essential regulators of mammalian spermatogenesis. Nature 1999, 398, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Krodel, M.; Pazos, M.; Lai, C.; Prieto, A.L. Cross-phosphorylation, signaling and proliferative functions of the Tyro3 and Axl receptors in Rat2 cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.; Gore, M.; Lemke, G. Structure, expression, and activity of Tyro 3, a neural adhesion-related receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Nagata, K.; Toshima, J.; Nakano, T.; Arita, H.; Tsuda, H.; Suzuki, K.; Mizuno, K. Stimulation of sky receptor tyrosine kinase by the product of growth arrest-specific gene 6. J. Boil. Chem. 1995, 270, 22681–22684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesecker, L.G.; Giannola, D.M.; Emerson, S.G. Identification of alternative exons, including a novel exon, in the tyrosine kinase receptor gene Etk2/tyro3 that explain differences in 5′ cDNA sequences. Oncogene 1995, 10, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thierry-Mieg, D.; Thierry-Mieg, J. AceView: A comprehensive cDNA-supported gene and transcripts annotation. Genome Boil. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Singh, I.; Bell, R.D.; Deane, R.; Zhong, Z.; Sagare, A.; Winkler, E.A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S controls hypoxic/ischemic blood-brain barrier disruption through the TAM receptor Tyro3 and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor. Blood 2010, 115, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Barrett, T.M.; Zhong, Z.; Fernandez, J.A.; Griffin, J.H.; Freeman, R.S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S blocks the extrinsic apoptotic cascade in tissue plasminogen activator/N-methyl D-aspartate-treated neurons via Tyro3-Akt-FKHRL1 signaling pathway. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Sagare, A.; Fernandez, J.A.; Bell, R.D.; Barrett, T.M.; Griffin, J.H.; Freeman, R.S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S protects neurons from excitotoxic injury by activating the TAM receptor Tyro3-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway through its sex hormone-binding globulin-like region. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15521–15534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, A.; Bliesner, B.; Xu, M.; Nielsen-Preiss, S.; Lemke, G.; Tobet, S.; Wierman, M.E. Axl and Tyro3 modulate female reproduction by influencing gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron survival and migration. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkermann, R.; Aprico, A.; Perera, A.A.; Bujalka, H.; Cole, A.E.; Xiao, J.; Field, J.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Binder, M.D. The TAM receptor Tyro3 regulates myelination in the central nervous system. Glia 2017, 65, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, W.; Xian, N.; Wu, B. Inhibition of TYRO3/Akt signaling participates in hypoxic injury in hippocampal neurons. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Torii, T.; Takada, S.; Ohno, N.; Saitoh, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ito, A.; Ogata, T.; Terada, N.; Tanoue, A.; et al. Involvement of the Tyro3 receptor and its intracellular partner Fyn signaling in Schwann cell myelination. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 3489–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.Y.; Carrera Silva, E.A.; De Kouchkovsky, D.; Joannas, L.D.; Hao, L.; Hu, D.; Huntsman, S.; Eng, C.; Licona-Limon, P.; Weinstein, J.S.; et al. The TAM family receptor tyrosine kinase TYRO3 is a negative regulator of type 2 immunity. Science 2016, 352, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Lemke, G. Homeostatic regulation of the immune system by receptor tyrosine kinases of the Tyro 3 family. Science 2001, 293, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraux, A.; Lu, Q.; Fernandez, N.; Riou, S.; Di Santo, J.P.; Raulet, D.H.; Lemke, G.; Roth, C. Natural killer cell differentiation driven by Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinases. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.M.; Camenisch, T.D.; Lemke, G.; Earp, H.S.; Matsushima, G.K. Macrophages and Dendritic Cells Use Different Axl/Mertk/Tyro3 Receptors in Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5635–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.K.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, H.Z.; Wu, H.; Tang, H.M.; Xiong, W.P.; Ma, J.; Ge, Y.H.; Lu, Q.X.; et al. The role of Tyro 3 subfamily receptors in the regulation of hemostasis and megakaryocytopoiesis. Haematol.-Hematol. J. 2007, 92, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Burnier, L.; Flores, N.; Savi, P.; DeMol, M.; Schaeffer, P.; Herbert, J.-M.; Lemke, G.; Goff, S.P.; Matsushima, G.K.; et al. Role of Gas6 receptors in platelet signaling during thrombus stabilization and implications for antithrombotic therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosemans, J.M.; Van Kruchten, R.; Olieslagers, S.; Schurgers, L.J.; Verheyen, F.K.; Munnix, I.C.; Waltenberger, J.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Carmeliet, P.; et al. Potentiating role of Gas6 and Tyro3, Axl and Mer (TAM) receptors in human and murine platelet activation and thrombus stabilization. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, W.R.; Baxi, S.M.; Schroeder, R.; Peng, Y.W.; Leadley, R.J.; Peterson, J.T.; Perrin, L.A. Gas6 receptors Axl, Sky and Mer enhance platelet activation and regulate thrombotic responses. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, M.; Hakeda, Y.; Chikazu, D.; Ogasawara, T.; Takato, T.; Kumegawa, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kawaguchi, H. Mechanism of stimulation of osteoclastic bone resorption through Gas6/Tyro 3, a receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, in mouse osteoclasts. J. Boil. Chem. 2001, 276, 7376–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.S.; Hakeda, Y.; Takakura, N.; Kameda, T.; Hamaguchi, I.; Miyamoto, T.; Kakudo, S.; Nakano, T.; Kumegawa, M.; Suda, T. Tyro 3 receptor tyrosine kinase and its ligand, Gas6, stimulate the function of osteoclasts. Stem Cells 1998, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishina, Y.; Mukouyama, Y.; Yanagisawa, M.; Watanabe, T.; Nakano, T.; Nomura, K.; Arita, H.; Nishimune, Y.; et al. A receptor tyrosine kinase, Sky, and its ligand Gas 6 are expressed in gonads and support primordial germ cell growth or survival in culture. Dev. Biol. 1996, 180, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Koyanagi, M.; Maeda, T.; Feldman, A.M.; Makino, N. Upregulation of anticoagulant proteins, protein S and tissue factor pathway inhibitor, in the mouse myocardium with cardio-specific TNF-α overexpression. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H2352–H2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, S.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Matuyama, T.; Gotoh, K. Role of Tyro3, Axl, and Mer Receptors and Their Ligands (Gas6, and Protein S) in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer Ther. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sather, S.; Kenyon, K.D.; Lefkowitz, J.B.; Liang, X.; Varnum, B.C.; Henson, P.M.; Graham, D.K. A soluble form of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells and platelet aggregation. Blood 2007, 109, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.W.; Hou, P.C.; Wu, H.C.; Chang, Y.L.; Lin, S.C.; Lin, S.C.; Lin, B.W.; Lee, J.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Sun, H.S.; et al. Targeting TYRO3 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases drug sensitivity in colon cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5872–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Valls, A.F.; Yerbes, R.; von Richter, S.; Kahlert, C.; Loges, S.; Weitz, J.; Schneider, M.; Ruiz de Almodovar, C.; Ulrich, A.; et al. TAM receptors Tyro3 and Mer as novel targets in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56355–56370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekyalongo, R.C.; Mukohara, T.; Funakoshi, Y.; Tomioka, H.; Kataoka, Y.; Shimono, Y.; Chayahara, N.; Toyoda, M.; Kiyota, N.; Minami, H. TYRO3 as a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasikara, C.; Kumar, S.; Kimani, S.; Tsou, W.I.; Geng, K.; Davra, V.; Sriram, G.; Devoe, C.; Nguyen, K.N.; Antes, A.; et al. Phosphatidylserine Sensing by TAM Receptors Regulates AKT-Dependent Chemoresistance and PD-L1 Expression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, I.C.; Roy, S.; Yaswen, P.; Stampfer, M.R.; Varmus, H.E. Mouse mammary tumors express elevated levels of RNA encoding the murine homology of SKY, a putative receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Boil. Chem. 1995, 270, 6872–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, P.B.; Chen, R.; Gong, C.; Yuan, L.; Jasper, J.S.; Ding, Y.; Markowitz, G.J.; Yang, P.; Xu, X.; McDonnell, D.P.; et al. Distinct Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Subsets Mediate Anti-HER2 Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. J. Boil. Chem. 2017, 292, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmel, A.; Rohner, I.; Ramaswamy, A.; Heidtmann, H.H.; Seitz, R.; Kraus, M.; Schuermann, M. Synthesis and secretion of the anticoagulant protein S and coexpression of the Tyro3 receptor in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer 1999, 86, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.; Petti, F.; Sujka-Kwok, I.; Mercado, P.; Bean, J.; Monaghan, M.; Seymour, S.L.; Argast, G.M.; Epstein, D.M.; Haley, J.D. A systems view of epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling states. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linger, R.M.; Cohen, R.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Sather, S.; Migdall-Wilson, J.; Middleton, D.H.; Lu, X.; Baron, A.E.; Franklin, W.A.; Merrick, D.T.; et al. Mer or Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition promotes apoptosis, blocks growth and enhances chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Wong, W.; Chua, S.C.; Wee, H.L.; Lim, S.G.; Chua, B.T.; Ho, H.K. Overexpression of Tyro3 and its implications on hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, T.D.; Ganda, C.; Brown, R.M.; Beveridge, D.J.; Richardson, K.L.; Chaturvedi, V.; Candy, P.; Epis, M.; Wintle, L.; Kalinowski, F.; et al. A microRNA-7/growth arrest specific 6/TYRO3 axis regulates the growth and invasiveness of sorafenib-resistant cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilla, E.; Guarino, V.; Visciano, C.; Liotti, F.; Svelto, M.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Franco, R.; Melillo, R.M. Activation of TYRO3/AXL tyrosine kinase receptors in thyroid cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1792–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wurdak, H.; Wang, Y.; Galkin, A.; Tao, H.; Li, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Yan, F.; Tu, B.P.; Miraglia, L.; et al. A genomic screen identifies TYRO3 as a MITF regulator in melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17025–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarest, S.J.; Gardner, J.; Vendel, M.C.; Ailor, E.; Szak, S.; Huang, F.; Doern, A.; Tan, X.; Yang, W.; Grueneberg, D.A.; et al. Evaluation of Tyro3 expression, Gas6-mediated Akt phosphorylation, and the impact of anti-Tyro3 antibodies in melanoma cell lines. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3102–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easty, D.J.; Ganz, S.E.; Farr, C.J.; Lai, C.; Herlyn, M.; Bennett, D.C. Novel and known protein tyrosine kinases and their abnormal expression in human melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easty, D.J.; Gray, S.G.; O’Byrne, K.J.; O’Donnell, D.; Bennett, D.C. Receptor tyrosine kinases and their activation in melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2011, 24, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tworkoski, K.; Singhal, G.; Szpakowski, S.; Zito, C.I.; Bacchiocchi, A.; Muthusamy, V.; Bosenberg, M.; Krauthammer, M.; Halaban, R.; Stern, D.F. Phosphoproteomic screen identifies potential therapeutic targets in melanoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensi, M.; Catani, M.; Castellano, G.; Nicolini, G.; Alciato, F.; Tragni, G.; De Santis, G.; Bersani, I.; Avanzi, G.; Tomassetti, A.; et al. Human cutaneous melanomas lacking MITF and melanocyte differentiation antigens express a functional Axl receptor kinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammoun, S.; Cunliffe, C.H.; Allen, J.C.; Chiriboga, L.; Giancotti, F.G.; Zagzag, D.; Hanemann, C.O.; Karajannis, M.A. ErbB/HER receptor activation and preclinical efficacy of lapatinib in vestibular schwannoma. Neuro-Oncol. 2010, 12, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammoun, S.; Provenzano, L.; Zhou, L.; Barczyk, M.; Evans, K.; Hilton, D.A.; Hafizi, S.; Hanemann, C.O. Axl/Gas6/NFkappaB signalling in schwannoma pathological proliferation, adhesion and survival. Oncogene 2014, 33, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, C. Metformin targets Axl and Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinases to inhibit cell proliferation and overcome chemoresistance in ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C. Overexpression of Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinase leads to the acquisition of taxol resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, Y.A.; Jo, S.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, C. Inhibition of IL-6/STAT3 axis and targeting Axl and Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinases by apigenin circumvent taxol resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, F.H.; van Rijswijk, A.; Teubel, W.; van Weerden, W.M.; Reneman, S.; van den Bemd, G.J.; Roobol, M.J.; Bangma, C.H.; Staal, F.J.; Jenster, G. Profiling of antibody production against xenograft-released proteins by protein microarrays discovers prostate cancer markers. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taichman, R.S.; Patel, L.R.; Bedenis, R.; Wang, J.; Weidner, S.; Schumann, T.; Yumoto, K.; Berry, J.E.; Shiozawa, Y.; Pienta, K.J. GAS6 receptor status is associated with dormancy and bone metastatic tumor formation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Barbosa, C.; Lesluyes, T.; Loarer, F.L.; Chibon, F.; Treilleux, I.; Coindre, J.M.; Meeus, P.; Brahmi, M.; Bally, O.; Ray-Coquard, I.; et al. Expression and role of TYRO3 and AXL as potential therapeutical targets in leiomyosarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayadi, H.; Pissaloux, D.; Alberti, L.; Tabone-Eglinger, S.; Ranchere, D.; Decouvelaere, A.V.; Tabone, E.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Caux, C.; Fayette, J.; et al. Autocrine role for Gas6 with Tyro3 and Axl in leiomyosarcomas. Target Oncol. 2013, 8, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, T.; Ohashi, K.; Akashi, T.; Johnson, J.D.; Hirokawa, K. Overexpression of protein tyrosine kinases in human esophageal cancer. Pathobiol. J. Immunopathol. Mol. Cell. Boil. 1997, 65, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.S.; Fujimoto, J.; Tamaya, T. Coexpression of growth arrest-specific gene 6 and receptor tyrosine kinases Axl and Sky in human uterine endometrial cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2003, 14, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, J.; Couderc, G.; Tarte, K.; Jourdan, M.; Requirand, G.; Delteil, M.C.; Rossi, J.F.; Mechti, N.; Klein, B. Identifying intercellular signaling genes expressed in malignant plasma cells by using complementary DNA arrays. Blood 2001, 98, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosier, P.S.; Hall, L.R.; Vitas, M.R.; Lewis, P.M.; Crosier, K.E. Identification of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase expressed in acute myeloid leukemic blasts. Leuk. Lymphoma 1995, 18, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, Y.; Pedersen, E.A.; Taichman, R.S. GAS6/Mer axis regulates the homing and survival of the E2A/PBX1-positive B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the bone marrow niche. Exp. Hematol. 2010, 38, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eryildiz, F.; Tyner, J. Abstract 1265: Dysregulated tyrosine kinase Tyro3 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Boysen, J.; Nelson, M.; Secreto, C.; Warner, S.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Lesnick, C.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Kay, N.E.; Ghosh, A.K. Targeted Axl Inhibition Primes Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B Cells to Apoptosis and Shows Synergistic/Additive Effects in Combination with BTK Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, F.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q. NGF-induced Tyro3 and Axl function as survival factors for differentiating PC12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, S.; Bebb, G. The CXCR4/SDF-1 chemokine receptor axis: A new target therapeutic for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, A.; Qian, W. MicroRNA-7 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via TYRO3 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein B kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway suppression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshagiri, S.; Stawiski, E.W.; Durinck, S.; Modrusan, Z.; Storm, E.E.; Conboy, C.B.; Chaudhuri, S.; Guan, Y.; Janakiraman, V.; Jaiswal, B.S.; et al. Recurrent R-spondin fusions in colon cancer. Nature 2012, 488, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Getz, G.; Wheeler, D.A.; Mardis, E.R.; McLellan, M.D.; Cibulskis, K.; Sougnez, C.; Greulich, H.; Muzny, D.M.; Morgan, M.B.; et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2008, 455, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, N.; Van Allen, E.M.; Treacy, D.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Rosenberg, M.; Goetz, E.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, C.; Smith, R.; Cahill, D.P.; Stephens, P.; Stevens, C.; Teague, J.; Greenman, C.; Edkins, S.; Bignell, G.; Davies, H.; et al. A hypermutation phenotype and somatic MSH6 mutations in recurrent human malignant gliomas after alkylator chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3987–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loriaux, M.M.; Levine, R.L.; Tyner, J.W.; Frohling, S.; Scholl, C.; Stoffregen, E.P.; Wernig, G.; Erickson, H.; Eide, C.A.; Berger, R.; et al. High-throughput sequence analysis of the tyrosine kinome in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 4788–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Yonescu, R.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Klimstra, D.S.; Maitra, A.; Eshleman, J.R.; Herman, J.G.; Poh, W.; Pelosof, L.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing of pancreatic neoplasms with acinar differentiation. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauthammer, M.; Kong, Y.; Ha, B.H.; Evans, P.; Bacchiocchi, A.; McCusker, J.P.; Cheng, E.; Davis, M.J.; Goh, G.; Choi, M.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic RAC1 mutations in melanoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, C.A.; Bottomly, D.; Savage, S.L.; White, L.; Wilmot, B.; Reister Schultz, A.M.; Uchida, K.A.; Agarwal, A.; Traer, E.; Beppu, L.; et al. Characterization of the Genomic Landscape of BCR-ABL1 Kinase-Independent Mechanisms of Resistance to ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 1119. [Google Scholar]
- Stitt, T.N.; Conn, G.; Gore, M.; Lai, C.; Bruno, J.; Radziejewski, C.; Mattsson, K.; Fisher, J.; Gies, D.R.; Jones, P.F.; et al. The anticoagulation factor protein S and its relative, Gas6, are ligands for the Tyro 3/Axl family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 1995, 80, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godowski, P.J.; Mark, M.R.; Chen, J.A.; Sadick, M.D.; Raab, H.; Hammond, R.G. Reevaluation of the Roles of Protein-S and Gas6 as Ligands for the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Rse/Tyro-3. Cell 1995, 82, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, L.; Li, L.; Darden, T.; Monroe, D.M.; Pedersen, L.G. Prediction of solution structures of the Ca2+-bound gamma-carboxyglutamic acid domains of protein S and homolog growth arrest specific protein 6: Use of the particle mesh Ewald method. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, W.I.; Nguyen, K.Q.; Calarese, D.A.; Garforth, S.J.; Antes, A.L.; Smirnov, S.V.; Almo, S.C.; Birge, R.B.; Kotenko, S.V. Receptor tyrosine kinases, TYRO3, AXL, and MER, demonstrate distinct patterns and complex regulation of ligand-induced activation. J. Boil. Chem. 2014, 289, 25750–25763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadahiro, H.; Kang, K.D.; Gibson, J.T.; Minata, M.; Yu, H.; Shi, J.; Chhipa, R.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Simoni, Y.; et al. Activation of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase AXL Regulates the Immune Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3002–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, L.; Negrier, C.; Boukerche, H. Protein S: A multifunctional anticoagulant vitamin K-dependent protein at the crossroads of coagulation, inflammation, angiogenesis, and cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2013, 88, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davra, V.; Kimani, S.G.; Calianese, D.; Birge, R.B. Ligand Activation of TAM Family Receptors-Implications for Tumor Biology and Therapeutic Response. Cancers 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meer, J.H.; van der Poll, T.; van’t Veer, C. TAM receptors, Gas6, and protein S: Roles in inflammation and hemostasis. Blood 2014, 123, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caberoy, N.B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W. Tubby and tubby-like protein 1 are new MerTK ligands for phagocytosis. Embo J. 2010, 29, 3898–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caberoy, N.B.; Alvarado, G.; Bigcas, J.L.; Li, W. Galectin-3 is a new MerTK-specific eat-me signal. J. Cell Physiol. 2012, 227, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vouri, M.; An, Q.; Pilkington, G.; Hafizi, S. Hetero-interaction amongst Tyro3 and Axl receptor tyrosine kinases diversifies cancer signaling. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 69, S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, W.; Wu, S.; Lu, L.; Xu, M.; Dai, W. Transforming activity of receptor tyrosine kinase tyro3 is mediated, at least in part, by the PI3 kinase-signaling pathway. Blood 2000, 95, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toshima, J.; Ohashi, K.; Iwashita, S.; Mizuno, K. Autophosphorylation activity and association with Src family kinase of Sky receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 209, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taichman, R.; Merida, I.; Torigoe, T.; Gaulton, G.N.; Reed, J.C. Evidence That Protein-Tyrosine Kinase P56-Lck Regulates the Activity of Phosphatidylinositol-3′-Kinase in Interleukin-2-Dependent T-Cells. J. Boil. Chem. 1993, 268, 20031–20036. [Google Scholar]
- Susa, M.; Rohner, D.; Bichsel, S. Differences in binding of PI 3-kinase to the src-homology domains 2 and 3 of p56 lck and p59 fyn tyrosine kinases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 220, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linger, R.M.; Keating, A.K.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. Taking aim at Mer and Axl receptor tyrosine kinases as novel therapeutic targets in solid tumors. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 1073–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Musa, N.L.; Li, J.; Liu, P.T.; Pestell, R.G.; Hershenson, M.B. Catalytic activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases induces cyclin D1 expression in primary tracheal myocytes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 18, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, P.K.; Komaravelli, N.; Singh, N.; Sharma, P. Interplay between MEK-ERK signaling, cyclin D1, and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulates cell cycle reentry and apoptosis of neurons. Mol. Boil. Cell 2012, 23, 3722–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, J.N.; LAllemain, G.; Brunet, A.; Muller, R.; Pouyssegur, J. Cyclin D1 expression is regulated positively by the p42/p44(MAPK) and negatively by the p38/HOG(MAPK) pathway. J. Boil. Chem. 1996, 271, 20608–20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.D.; Raben, D.M.; Phillips, P.J.; Baldassare, J.J. Sustained activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) is required for the continued expression of cyclin D1 in G1 phase. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafizi, S.; Gustafsson, A.; Stenhoff, J.; Dahlback, B. The Ran binding protein RanBPM interacts with Axl and Sky receptor tyrosine kinases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Boil. 2005, 37, 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, L.M.; Maitland, M.E.R.; McTavish, C.J.; Schild-Poulter, C. Cell signalling pathway regulation by RanBPM: Molecular insights and disease implications. Open Boil. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Y.; Fisher, D.E. Melanocyte biology and skin pigmentation. Nature 2007, 445, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Rosen, K.M.; Corfas, G. Biological function of nuclear receptor tyrosine kinase action. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Boil. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.J. Functional Characterization of nuclear TYRO3 in colorectal cancer. AACR 2018 Proc. 2018, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenneti, L.; Lipton, S.A. Involvement of activated caspase-3-like proteases in N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced apoptosis in cerebrocortical neurons. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, A.M.; Keating, A.K. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: Expression, disease and oncogenesis in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 2014, 1542, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Yu, J.; Mui, R.K.; Niibori, R.; Taufique, H.B.; Aslam, R.; Semple, J.W.; Cordes, S.P. The tyrosine kinase receptor Tyro3 enhances lifespan and neuropeptide Y (Npy) neuron survival in the mouse anorexia (anx) mutation. Dis. Model Mech. 2017, 10, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, B.F.G.; Pirko, I.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Pathology of Multiple Sclerosis: Where Do We Stand? Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2013, 19, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, A.; Xu, M.; Bliesner, B.; Liu, Z.; Richards, J.; Tobet, S.; Wierman, M.E. Hypothalamic but not pituitary or ovarian defects underlie the reproductive abnormalities in Axl/Tyro3 null mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 339, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdle, A.; Marecic, O.; Tevlin, R.; Walmsley, G.G.; Chan, C.K.; Longaker, M.T.; Wan, D.C. The role and regulation of osteoclasts in normal bone homeostasis and in response to injury. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Zhao, Y.; Derer, A.; Braun, T.; Engelke, K.; Neumann, E.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Liu, Y.; Zwerina, J.; Schett, G. Deletion of the receptor tyrosine kinase Tyro3 inhibits synovial hyperplasia and bone damage in arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyasu, S.; Moro, K. Type 2 innate immune responses and the natural helper cell. Immunology 2011, 132, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Carrera-Silva, E.A.; Bosurgi, L.; Ghosh, S. TAM receptor signaling in immune homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S.; Hanayama, R.; Kawane, K. Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell 2010, 140, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polvi, A.; Armstrong, E.; Lai, C.; Lemke, G.; Huebner, K.; Spritz, R.A.; Guida, L.C.; Nicholls, R.D.; Alitalo, K. The human TYRO3 gene and pseudogene are located in chromosome 15q14-q25. Gene 1993, 134, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Mizuno, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T.; Nakamura, T. Cloning of the cDNA for a novel receptor tyrosine kinase, Sky, predominantly expressed in brain. Oncogene 1994, 9, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Pan, H.; Hassanain, H.; Gupta, S.L.; Murphy, M.J., Jr. Molecular cloning of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase, tif, highly expressed in human ovary and testis. Oncogene 1994, 9, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Sakamaki, T.; Pestell, R.G. Minireview: Cyclin D1: Normal and abnormal functions. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5439–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chai, K.; Ying, X.; Zhou, B.P. The Role of Snail in EMT and Tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.K.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: Cancer as a paradigm. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Ben-Batalla, I.; Schultze, A.; Loges, S. Macrophage-tumor crosstalk: Role of TAMR tyrosine kinase receptors and of their ligands. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 1391–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loges, S.; Schmidt, T.; Tjwa, M.; van Geyte, K.; Lievens, D.; Lutgens, E.; Vanhoutte, D.; Borgel, D.; Plaisance, S.; Hoylaerts, M.; et al. Malignant cells fuel tumor growth by educating infiltrating leukocytes to produce the mitogen Gas6. Blood 2010, 115, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubil, E.; Caskey, L.; Holtzhausen, A.; Hunter, D.; Story, C.; Earp, H.S. Tumor-secreted Pros1 inhibits macrophage M1 polarization to reduce antitumor immune response. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2356–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, D.S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, P.; Jin, S.J.; Jiang, G.Q. The prognostic correlation of AFP level at diagnosis with pathological grade, progression, and survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, G.M.; An, Y.; Cai, Z.W.; Chen, X.T.; Clark, C.; Cornelius, L.A.; Dai, J.; Gullo-Brown, J.; Gupta, A.; Henley, B.; et al. Discovery of N-(4-(2-amino-3-chloropyridin-4-yloxy)-3-fluorophenyl)-4-ethoxy-1-(4-fluorophenyl )-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide (BMS-777607), a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of the Met kinase superfamily. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remsing Rix, L.L.; Rix, U.; Colinge, J.; Hantschel, O.; Bennett, K.L.; Stranzl, T.; Muller, A.; Baumgartner, C.; Valent, P.; Augustin, M.; et al. Global target profile of the kinase inhibitor bosutinib in primary chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 2009, 23, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Knyazev, P.G.; Cheburkin, Y.V.; Sharma, K.; Knyazev, Y.P.; Orfi, L.; Szabadkai, I.; Daub, H.; Keri, G.; Ullrich, A. AXL is a potential target for therapeutic intervention in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.I.; Hunt, J.P.; Herrgard, S.; Ciceri, P.; Wodicka, L.M.; Pallares, G.; Hocker, M.; Treiber, D.K.; Zarrinkar, P.P. Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Finerty, P., Jr.; Walker, J.R.; Butler-Cole, C.; Vedadi, M.; Schapira, M.; Parker, S.A.; Turk, B.E.; Thompson, D.A.; Dhe-Paganon, S. Structural insights into the inhibited states of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Struct. Boil. 2009, 165, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Greger, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, Y.; Greshock, J.; Annan, R.; Halsey, W.; Sathe, G.M.; Martin, A.M.; Gilmer, T.M. Novel mechanism of lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast tumor cells: Activation of AXL. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6871–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolino, M.; Choidas, A.; Wallner, S.; Pranjic, B.; Uribesalgo, I.; Loeser, S.; Jamieson, A.M.; Langdon, W.Y.; Ikeda, F.; Fededa, J.P.; et al. The E3 ligase Cbl-b and TAM receptors regulate cancer metastasis via natural killer cells. Nature 2014, 507, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.B.; Peek, V.L.; Ajamie, R.; Buchanan, S.G.; Graff, J.R.; Heidler, S.A.; Hui, Y.H.; Huss, K.L.; Konicek, B.W.; Manro, J.R.; et al. LY2801653 is an orally bioavailable multi-kinase inhibitor with potent activity against MET, MST1R, and other oncoproteins, and displays anti-tumor activities in mouse xenograft models. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minson, K.A.; Smith, C.C.; DeRyckere, D.; Libbrecht, C.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Lasater, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, G.D.; Stashko, M.A.; Zhang, W.; et al. The MERTK/FLT3 inhibitor MRX-2843 overcomes resistance-conferring FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; DeRyckere, D.; Hunter, D.; Liu, J.; Stashko, M.A.; Minson, K.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Lee, M.; Glaros, T.G.; Newton, D.L.; et al. UNC2025, a potent and orally bioavailable MER/FLT3 dual inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7031–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruvolo, P.; Ma, H.; Ruvolo, V.; Zhang, X.; Mu, H.; Schober, W.; Hernandez, I.; Gallardo, M.; Khoury, J.; Cortes, J.; et al. Anexelekto/MER tyrosine kinase inhibitor ONO-7475 arrests growth and kills FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3-internal tandem duplication mutant acute myeloid leukemia cells by diverse mechanisms. Haematologica 2017, 102, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, E.; Tindall, E.; Franovic, A.; Schairer, A.E.; Uryu, S.; Oh, J.; Falk, M.D.; Martin, E.; Yokoyama, Y.; Li, G.G.; et al. 65—RXDX-106 Is an orally-available, potent and selective TAM/MET inhibitor demonstrating preclinical efficacy in MET-dependent human malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 69, S28–S29. [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan, P.P.; Ivy, K.S.; Musi, E.; de Stanchina, E.; Schwartz, G.K. Significant blockade of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases by MGCD516 (Sitravatinib), a novel small molecule inhibitor, shows potent anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of sarcoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4093–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Simpson, C.; Deryckere, D.; Van Deusen, A.; Miley, M.J.; Kireev, D.; Norris-Drouin, J.; Sather, S.; Hunter, D.; et al. Discovery of Novel Small Molecule Mer Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph, S.; Deryckere, D.; Schlegel, J.; Frazer, J.K.; Batchelor, L.A.; Trakhimets, A.Y.; Sather, S.; Hunter, D.M.; Cummings, C.T.; Liu, J.; et al. UNC569, a novel small-molecule mer inhibitor with efficacy against acute lymphoblastic leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, J.; Sambade, M.J.; Sather, S.; Moschos, S.J.; Tan, A.C.; Winges, A.; DeRyckere, D.; Carson, C.C.; Trembath, D.G.; Tentler, J.J.; et al. MERTK receptor tyrosine kinase is a therapeutic target in melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Stashko, M.A.; Deryckere, D.; Cummings, C.T.; Hunter, D.; Yang, C.; Jayakody, C.N.; Cheng, N.; Simpson, C.; et al. UNC1062, a new and potent Mer inhibitor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Zhang, W.; Menachof, K.K.; Hill, A.A.; Rinella, S.; Kirkpatrick, G.; Page, L.S.; Stashko, M.A.; Jordan, C.T.; Wei, Q.; et al. Efficacy of a Mer and Flt3 tyrosine kinase small molecule inhibitor, UNC1666, in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6722–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Stashko, M.A.; Nichols, J.; Miley, M.J.; Norris-Drouin, J.; Chen, Z.; Machius, M.; DeRyckere, D.; et al. Design and Synthesis of Novel Macrocyclic Mer Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.A.; Hoffman, J.K.; Ciske, F.L.; Kohrt, J.T.; Baxi, S.M.; Peng, Y.W.; Zhong, M.; Catana, C.; Ohren, J.; Perrin, L.A.; et al. Optimization of highly selective 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-5-carboxamide inhibitors of Sky kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.A.; Hoffman, J.K.; Ciske, F.L.; Kaufman, M.D.; Kohrt, J.T.; Quin, J., 3rd; Sheehan, D.J.; Delaney, A.; Baxi, S.M.; Catana, C.; et al. Highly selective 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-5-carboxamide inhibitors of Sky kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.A.; Kohrt, J.T.; Filipski, K.J.; Kaufman, M.; Sheehan, D.; Edmunds, J.E.; Delaney, A.; Wang, Y.; Bourbonais, F.; Lee, D.Y.; et al. Novel and selective spiroindoline-based inhibitors of Sky kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Stashko, M.A.; DeRyckere, D.; Vasileiadi, E.; Parker, R.E.; Hunter, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Highly Selective MERTK Inhibitors Achieved by a Single Methyl Group. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10242–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer | Expression | Functional Roles | Reference(s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Lines | Patient Samples | Cell Proliferation and/or Survival | Anchorage-Independent Colony Formation | Xenograft Model | Migration and/or Invasion | EMT | Metastasis | Drug Resistance | Unfavorable Prognosis | ||
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | OX | OX | + | [45] | |||||||
| OX | [33] | ||||||||||
| + | OX | + | + | + * | + | [46] | |||||
| Colorectal cancer | + | OX | + | + | + | + | [36] | ||||
| + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [35] | ||
| OX | + | + | [72] | ||||||||
| Esophageal Cancer | + | OX | [63] | ||||||||
| Melanoma | + | [50] | |||||||||
| + | OX | + | + | + | + | [48] | |||||
| + | [51] | ||||||||||
| + | [52] | ||||||||||
| + | [53] | ||||||||||
| + | OX | + | [49] | ||||||||
| Thyroid Cancer | Ectopic | + | [47] | ||||||||
| Lung cancer | + | [41] | |||||||||
| + | + | [44] | |||||||||
| + | [43] | ||||||||||
| + | [42] | ||||||||||
| Prostate cancer | OX | OX | [59] | ||||||||
| + | + | [60] | |||||||||
| Breast cancer | OX | [39] | |||||||||
| + | + | [37] | |||||||||
| + | + | + | [38] | ||||||||
| + | + # | + | [40] | ||||||||
| Ovarian Cancer | + | + | + | [57] | |||||||
| + | + | [56] | |||||||||
| + | + | [58] | |||||||||
| Endometrial Cancer | + | [64] | |||||||||
| Leiomyosarcoma | OX | [62] | |||||||||
| + | + | + | + | [61] | |||||||
| Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma | + | [61] | |||||||||
| Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma | + | [61] | |||||||||
| Synovial Sarcoma | + | [61] | |||||||||
| Schwanomma | + | [54] | |||||||||
| OX | [55] | ||||||||||
| Multiple Myeloma | + | [65] | |||||||||
| AML | + | + | [66] | ||||||||
| + | [67] | ||||||||||
| + | + | [68] | |||||||||
| ALL (B-cell & T-cell) | Ectopic | [66] | |||||||||
| + | [67] | ||||||||||
| CML | + | [66] | |||||||||
| CLL | OX | [69] | |||||||||
| Compound | Primary Target | TYRO3 Activity | MERTK Activity | AXL Activity | Other Targets | Development Phase | Indications | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMS-777607/ASLAN002 | MET | IC50 = 4.3 nM | IC50 = 14 nM | IC50 = 1.1 nM | RON, AURKB, FLT3 | Phase I | Advanced solid tumors | [127] |
| Bosutinib (SKI-606, PF-5208763) | SRC, ABL | Kd = 61 nM | Kd = 110 nM | Kd = 52 nM | LYN, HCK, TEC, STE20K, CAMK2G | Approved | Breast cancer, glioblastoma, Ph+ CML | [128,129,130] |
| C52 | IC50 = 96 nM | IC50 = 110 nM | IC50 = 140 nM | [131] | ||||
| Foretinib | MET, VEGFR2 | Kd = 2 nM | Kd = 0.3 nM | Kd = 0.1 nM | RON, PDGFRβ, KIT, FLT3, TIE2 | Breast cancer, NSCLC | [130,132] | |
| LDC1267 | TYRO3, MERTK, AXL | IC50 = 8 nM | IC50 < 5 nM | IC50 = 29 nM | MET, AURKB, LCK | Preclinical | Metastatic melanoma | [133] |
| LY2801653 | MET | IC50 = 28 nM * | IC50 = 0.8 nM | ND | MST1R, FLT3, TEK, ROS, DDR1/2 | Phase I | Advanced cancer | [134] |
| MRX-2843 | MERTK, FLT3 | IC50 = 17 nM | IC50 = 1.3 nM | IC50 = 15 nM | TRKA, LOK | Phase I | Advanced solid tumors | [135,136] |
| ONO-7475 (ONO-9330547) | FLT3, TYRO3, MERTK, AXL | IC50 = 1.9 nM | IC50 = 0.4 nM | IC50 = 2.2 nM | Phase I | Acute leukemia | [137] | |
| RXDX-106 (CEP-40783) | TYRO3, MERTK, AXL, MET | IC50 = 19 nM | IC50 = 29 nM | IC50 = 7 nM | Phase I | Advanced solid tumors | [138] | |
| Pfizer Compound 19 | TYRO3 | IC50 = 10 nM | ND | ND | Thrombosis | [146] | ||
| Pfizer Compound 21 | TYRO3 | IC50 = 0.7 nM | ND | ND | MERTK | Thrombosis | [146] | |
| Pfizer Compound 32 | TYRO3 | IC50 = 70 nM | ND | ND | MERTK | Thrombosis | [147] | |
| Sitravatinib (MGCD516) | TYRO3, MERTK, AXL, VEGFR, PDGFR, KIT | IC50 < 1 nM | IC50 < 1 nM | IC50 < 1 nM | MET, RET | Phase I/II | Urethlial carcinoma, liposarcoma, advanced cancer, NSCLC | [139] |
| UNC569 | MERTK | IC50 = 48 nM | IC50 = 2.9 nM | IC50 = 37 nM | FLT3, MAPKAPK2, RET | ALL | [140,141] | |
| UNC1062 | MERTK | IC50 = 60 nM | IC50 = 1.1 nM | IC50 = 85 nM | FLT3 | Metastatic melanoma | [142,143] | |
| UNC1666 | MERTK, FLT3 | IC50 = 29 nM | IC50 = 0.55 nM | IC50 = 37 nM | TRKA, TRKB, TRKC | AML | [144] | |
| UNC2025 | MERTK, FLT3 | IC50 = 18 nM | IC50 = 0.7 nM | IC50 = 7.5 nM | TRKA, TRKC | Preclinical | ALL, AML | [136] |
| UNC3133 | MERTK | IC50 = 57 nM | IC50 = 8 nM | IC50 = 22 nM | FGFR1, ITK, KDR, PDGRα, TRKA, AURKA, p70S6K | [145] | ||
| UNC Compound 5 | TYRO3 | IC50 = 6.7 nM | IC50 = 19 nM | IC50 = 206 nM | MERTK | [149] | ||
| Vandetinib | VEGFR2, VEGFR3, EGFR | Kd = 93 nM | Kd = 1400 nM | Kd = 250 nM | RET | Approved | Thyroid cancer, NSCLC | [130] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smart, S.K.; Vasileiadi, E.; Wang, X.; DeRyckere, D.; Graham, D.K. The Emerging Role of TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120474
Smart SK, Vasileiadi E, Wang X, DeRyckere D, Graham DK. The Emerging Role of TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers. 2018; 10(12):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120474
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmart, Sherri K., Eleana Vasileiadi, Xiaodong Wang, Deborah DeRyckere, and Douglas K. Graham. 2018. "The Emerging Role of TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer" Cancers 10, no. 12: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120474
APA StyleSmart, S. K., Vasileiadi, E., Wang, X., DeRyckere, D., & Graham, D. K. (2018). The Emerging Role of TYRO3 as a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers, 10(12), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120474





