Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MiRNA Localization in the Genomic Regions with SCNAs in Cancers
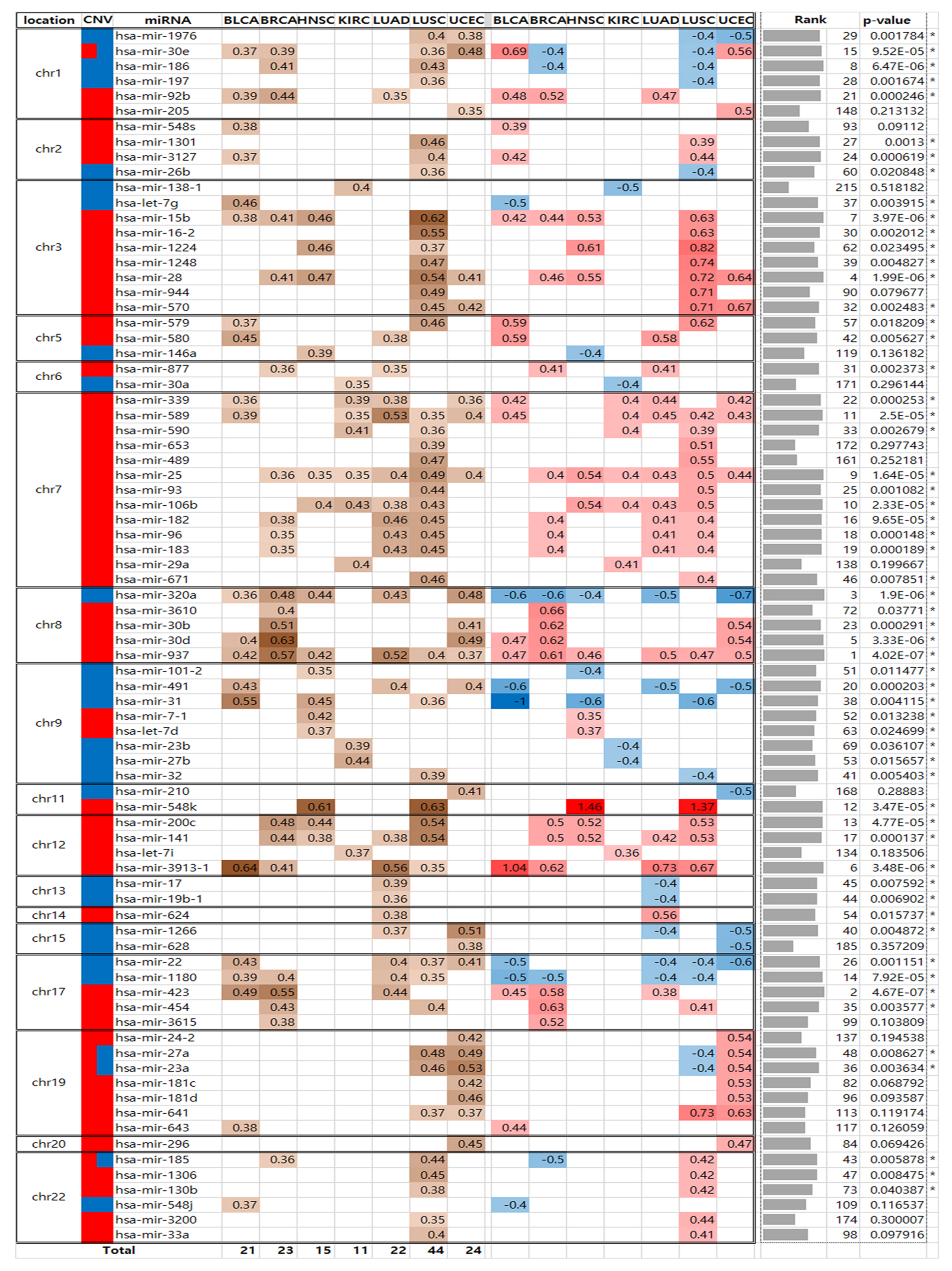
2.2. Identification of miRNAs Associated with SCNAs
2.3. Comparison between Pan-Cancer SCNA Regions and the SCNA-miRNA Regions
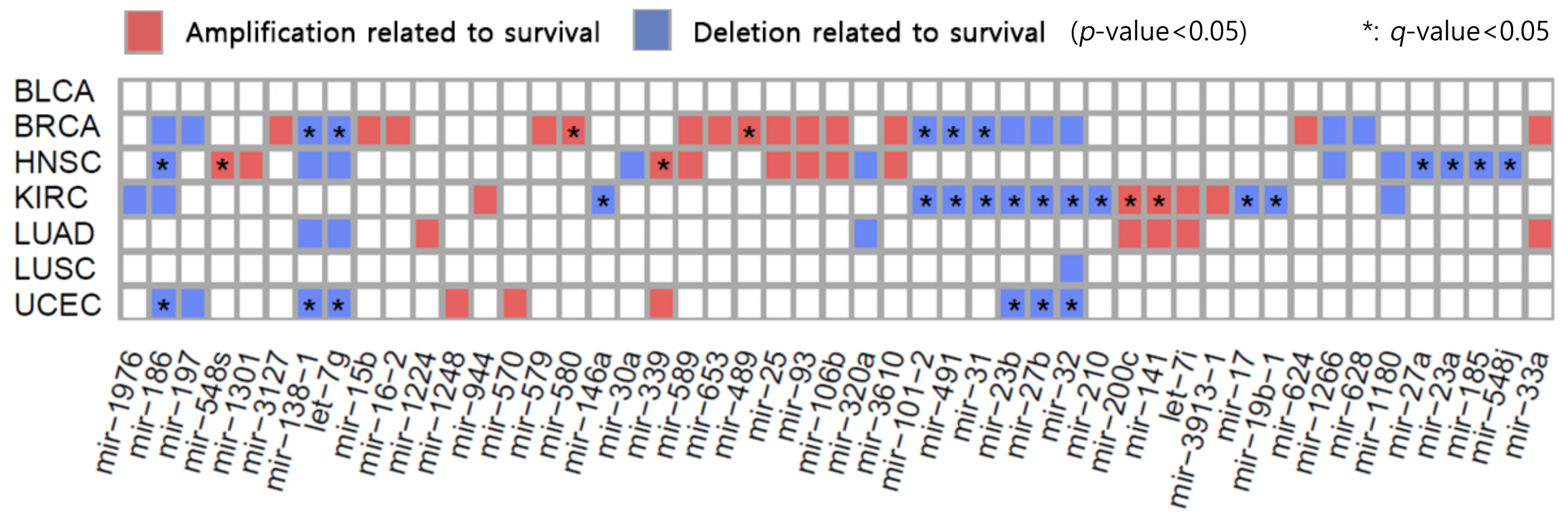
2.4. Association between SCNA-miRNA and Survival of Cancer Patients
2.5. miR-589 as a New Potential Cancer Biomarker
2.6. Investigation of miRNAs Commonly Associated with SCNAs Across Seven Cancer Types
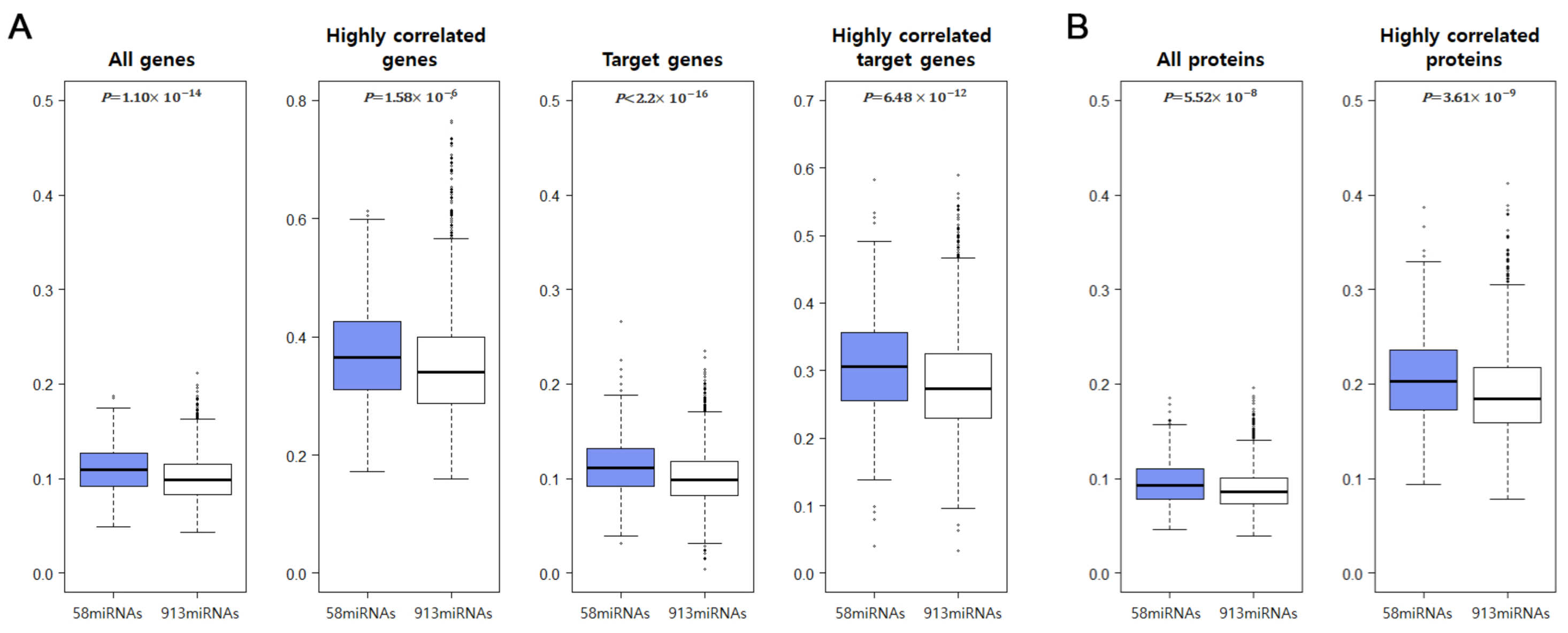
2.7. CC-SCNA-miRNA Effects on mRNA and Protein Expression Levels
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Data Pre-Processing
4.3. Identifying SCNA-Associated miRNAs
4.4. Identification of miRNAs Commonly Associated with SCNAs Across Seven Cancer Types
4.5. miRNA Effects on mRNAs and Proteins
4.6. Survival Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLCA | Urothelial bladder carcinoma |
| BRCA | Breast invasive carcinoma |
| CC-SCNA-miRNAs | SCNA-miRNAs common for all cancers |
| SCNA-miRNAs | Copy number variable miRNAs |
| CRV | Common rank value |
| FRA | Fragile sites |
| HNSC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| KIRC | Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| PCCs | Pearson correlation coeffients |
| SCNAs | Somatic copy number alterations |
| TCGA | The cancer genome atlas |
| UCEC | Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma |
References
- Djuranovic, S.; Nahvi, A.; Green, R. miRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing by Translational Repression Followed by mRNA Deadenylation and Decay. Science 2012, 336, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebert, M.S.; Sharp, P.A. Roles for MicroRNAs in Conferring Robustness to Biological Processes. Cell 2012, 149, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.; Mendell, J. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.P.; Rajapakshe, K.; Hartig, S.M.; Reva, B.; McLellan, M.D.; Kandoth, C.; Ding, L.; Zack, T.I.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Wheeler, D.A.; et al. Identification of a pan-cancer oncogenic microRNA superfamily anchored by a central core seed motif. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zack, T.I.; Schumacher, S.E.; Carter, S.L.; Cherniack, A.D.; Saksena, G.; Tabak, B.; Lawrence, M.S.; Zhang, C.; Wala, J.; Mermel, C.H.; et al. Pan-cancer patterns of somatic copy number alteration. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Kong, S.W.; Park, P.J. Integrative analysis reveals the direct and indirect interactions between DNA copy number aberrations and gene expression changes. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amgalan, B.; Lee, H. DEOD: Uncovering dominant effects of cancer-driver genes based on a partial covariance selection method. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, Z.; Patil, V.; Thinagararjan, S.; Rao, S.A.; Hegde, A.S.; Arivazhagan, A.; Santosh, V.; Somasundaram, K. Impact of somatic copy number alterations on the glioblastoma miRNome: miR-4484 is a genomically deleted tumour suppressor. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 927–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamilzhalagan, S.; Rathinam, D.; Ganesan, K. Amplified 7q21-22 gene MCM7 and its intronic miR-25 suppress COL1A2 associated genes to sustain intestinal gastric cancer features. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 1590–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, R.; Wang, S.; Fang, Z. Amplification and up-regulation of MIR30D was associated with disease progression of cervical squamous cell carcinomas. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubak, K.; Lewandowska, M.A.; Klonowska, K.; Roszkowski, K.; Kowalewski, J.; Figlerowicz, M.; Kozlowski, P. High copy number variation of cancer-related microRNA genes and frequent amplification of DICER1 and DROSHA in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, N.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, F.; Xu, Y. An integrated approach to reveal miRNAs’ impacts on the functional consequence of copy number alterations in cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y. Novel Candidate Key Drivers in the Integrative Network of Genes, MicroRNAs, Methylations, and Copy Number Variations in Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 358125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, C.W.; Howell, V.M.; Hahn, M.A.; Marsh, D.J. Genomic alterations as mediators of miRNA dysregulation in ovarian cancer. Genes Chromosome Cancer 2014, 54, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veigaard, C.; Kjeldsen, E. Exploring the genome-wide relation between copy number status and microRNA expression. Genomics 2014, 104, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilting, S.M.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Verlaat, W.; Jaspers, A.V.; Van De Wiel, M.A.; Van Wieringen, W.N.; Meijer, G.A.; Kenter, G.G.; Yi, Y.; Sage, C.; et al. Altered microRNA expression associated with chromosomal changes contributes to cervical carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, N.; Greshock, J.; Megraw, M.S.; Giannakakis, A.; Liang, S.; Naylor, T.L.; Barchetti, A.; Ward, M.R.; et al. microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9136–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamy, P.; Andersen, C.L.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Tørring, N.; Ørntoft, T.; Wiuf, C. Are microRNAs located in genomic regions associated with cancer? Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder carcinoma. Nature 2014, 507, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2013, 499, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature 2013, 497, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature 2012, 490, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Saini, H.K.; van Dongen, S.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D154–D158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Helman, E.; McKenna, A.; Shen, H.; Zack, T.; Laird, P.W.; Onofrio, R.C.; Winckler, W.; Weir, B.A.; et al. Absolute quantification of somatic DNA alterations in human cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Fan, X.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.S. Accurity: Accurate tumor purity and ploidy inference from tumor-normal WGS data by jointly modelling somatic copy number alterations and heterozygous germline single-nucleotide-variants. Bioinformatics 2018, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, S.A.; Beare, D.; Boutselakis, H.; Bamford, S.; Bindal, N.; Tate, J.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.; Dawson, E.; Ponting, L.; et al. COSMIC: Somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D777–D783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakakis, A.; Sandaltzopoulos, R.; Greshock, J.; Liang, S.; Huang, J.; Hasegawa, K.; Li, C.; O’Brien-Jenkins, A.; Katsaros, D.; Weber, B.L.; et al. miR-210 links hypoxia with cell cycle regulation and is deleted in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, G.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, L.; Yu, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y. microRNA-423-3p promotes tumor progression via modulation of AdipoR2 in laryngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.-D.; Liu, T.-Q.; Wang, G.-B.; Zhang, C.-L.; Liu, H.-X. MicroRNA-570 promotes lung carcinoma proliferation through targeting tumor suppressor KLF9. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 2829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almog, N.; Ma, L.; Schwager, C.; Brinkmann, B.G.; Beheshti, A.; Vajkoczy, P.; Folkman, J.; Hlatky, L.; Abdollahi, A. Consensus Micro RNAs Governing the Switch of Dormant Tumors to the Fast-Growing Angiogenic Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, G. miR-937 contributes to the lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting INPP4B. Life Sci. 2016, 155, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.M.; Orosco, R.K.; Shen, J.P.; Egloff, A.M.; Carter, H.; Hofree, M.; Choueiri, M.; Coffey, C.S.; Lippman, S.M.; Neil, D.; et al. Multi-tiered genomic analysis of head and neck cancer ties TP53 mutation to 3p loss. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ling, B.; Wang, G.-X.; Long, G.; Qiu, J.-H.; Hu, Z.-L. Tumor suppressor miR-22 suppresses lung cancer cell progression through post-transcriptional regulation of ErbB3. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, C.; Tu, J.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Cui, Q. HMDD v2.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1070–D1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Granberg, K.J.; Wang, Q.; Moore, L.M.; Ji, P.; Gumin, J.; Sulman, E.P.; Calin, G.A.; Haapasalo, H.; et al. Two mature products of MIR-491 coordinate to suppress key cancer hallmarks in glioblastoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajbhandari, R.; McFarland, B.C.; Patel, A.; Gerigk, M.; Gray, G.K.; Fehling, S.C.; Bredel, M.; Berbari, N.F.; Kim, H.; Marks, M.P.; et al. Loss of tumor suppressive microRNA-31 enhances TRADD/NF-κB signaling in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creighton, C.J.; Fountain, M.D.; Yu, Z.; Nagaraja, A.K.; Zhu, H.; Khan, M.; Olokpa, E.; Zariff, A.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Matzuk, M.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Uncovers a p53-Associated Role for MicroRNA-31 in Inhibiting the Proliferation of Serous Ovarian Carcinomas and Other Cancers. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vrba, L.; Jensen, T.J.; Garbe, J.C.; Heimark, R.L.; Cress, A.E.; Dickinson, S.; Stampfer, M.R.; Futscher, B.W. Role for DNA Methylation in the Regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 Expression in Normal and Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejero, R.; Navarro, A.; Campayo, M.; Viñolas, N.; Marrades, R.M.; Cordeiro, A.; Ruíz-Martínez, M.; Santasusagna, S.; Molins, L.; Ramirez, J.; et al. miR-141 and miR-200c as Markers of Overall Survival in Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.G.; Zhu, W.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.N.; Zhou, S.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Zeng, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augoff, K.; McCue, B.; Plow, E.F.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, B.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhuo, H. Down-regulation of miR-31 expression in gastric cancer tissues and its clinical significance. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, Y.; You, W.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhou, C.Y.; Li, H. miR-491-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting JMJD2B in ERα-positive breast cancer. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 812–821. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Li, K.; Pan, M.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H. miR-589 promotes gastric cancer aggressiveness by a LIFR-PI3K/AKT-c-Jun regulatory feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, A.; Silber, J.; Harinath, G.; Huse, J.T.; Schultz, N.; Sander, C. Analysis of microRNA-target interactions across diverse cancer types. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, D.; Lee, H. Prioritizing cancer-related microRNAs by integrating microRNA and mRNA datasets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.A. Combining Independent Tests of Significance. J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 1948, 2, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.D.; Lin, F.M.; Wu, W.Y.; Liang, C.; Huang, W.C.; Chan, W.L.; Tsai, W.; Chen, G.; Lee, C.J.; Chiu, C.M.; et al. miRTarBase: A database curates experimentally validated microRNA–target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D163–D169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Chr. | Genomic Location | Cytoband | miRNA | State | Cancer-Related Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr1 | 26554542-26554593 | 1p36.11 | hsa-mir-1976 | Deleted | ARID1A **, SDHB *** |
| 40754355-40754446 | 1p34.2 | hsa-mir-30e | Amplified | MYCL *** | |
| 71067631-71067716 | 1p31.1 | hsa-mir-186 | Deleted | ||
| chr3 | 195699401-195699497 | 3q29 | hsa-mir-570 | Amplified | TFRC *** |
| chr5 | 36147892-36147988 | 5p13.2 | hsa-mir-580 | Amplified | IL7R, LIFR * |
| 160485352-160485450 | 5q34 | hsa-mir-146a | Deleted | EBF1 **, FGFR4 **, FLT4 *, ITK ***, NPM1 *, TLX3, NSD1, RANBP17 **, PWWP2A *** | |
| chr8 | 116874728-116874800 | 8q23.3 | hsa-mir-3610 | Amplified | |
| 143812957-143813042 | 8q24.3 | hsa-mir-937 | Amplified | NDRG1 ***, RECQL4 *** | |
| chr9 | 4850297-4850375 | 9p24.1 | hsa-mir-101-2 | Deleted | NFIB *** |
| 20716105-20716188 | 9p21.3 | hsa-mir-491 | Deleted | CDKN2A** | |
| 21512115-21512185 | hsa-mir-31 | Deleted | |||
| chr11 | 568089-568198 | 11p15.5 | hsa-mir-210 | Deleted | HRAS *, CARS * |
| 70283955-70284070 | 11q13.3 | hsa-mir-548k | Amplified | CCND1 | |
| chr12 | 69584722-69584823 | 12q15 | hsa-mir-3913-1 | Amplified | MDM2 ***, HMGA2 **, PTRRB |
| chr17 | 1713903-1713987 | 17p13.3 | hsa-mir-22 | Deleted | YWHAE *** |
| 30117079-30117172 | 17q12 | hsa-mir-423 | Amplified | ERBB2 *, CDL12, NF1 **, RARA | |
| 74748613-74748699 | 17q25.3 | hsa-mir-3615 | Amplified | RNF213* | |
| chr19 | 13836287-13836359 | 19p13.12 | hsa-mir-24-2 | Amplified | BRD4 ***, LYL1 *** |
| 13836440-13836517 | hsa-mir-27a | Amplified | |||
| 13836587-13836659 | hsa-mir-23a | Amplified | |||
| 13874699-13874808 | hsa-mir-181c | Amplified | |||
| 13874875-13875011 | hsa-mir-181d | Amplified | |||
| chr20 | 58817615-58817694 | 20q13.33 | hsa-mir-296 | Amplified | |
| chr22 | 20033139-20033220 | 22q11.21 | hsa-mir-185 | Amplified | BCR ***, SEPT5 **, MAPK1, LZTR1 ***, CLTCL1 *** |
| 20086058-20086142 | hsa-mir-1306 | Amplified | |||
| 21653304-21653385 | 22q11.22 | hsa-mir-130b | Amplified |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soh, J.; Cho, H.; Choi, C.-H.; Lee, H. Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120475
Soh J, Cho H, Choi C-H, Lee H. Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Cancer. Cancers. 2018; 10(12):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120475
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoh, Jihee, Hyejin Cho, Chan-Hun Choi, and Hyunju Lee. 2018. "Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Cancer" Cancers 10, no. 12: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120475
APA StyleSoh, J., Cho, H., Choi, C.-H., & Lee, H. (2018). Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Cancer. Cancers, 10(12), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120475





