The Syk Kinase Promotes Mammary Epithelial Integrity and Inhibits Breast Cancer Invasion by Stabilizing the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
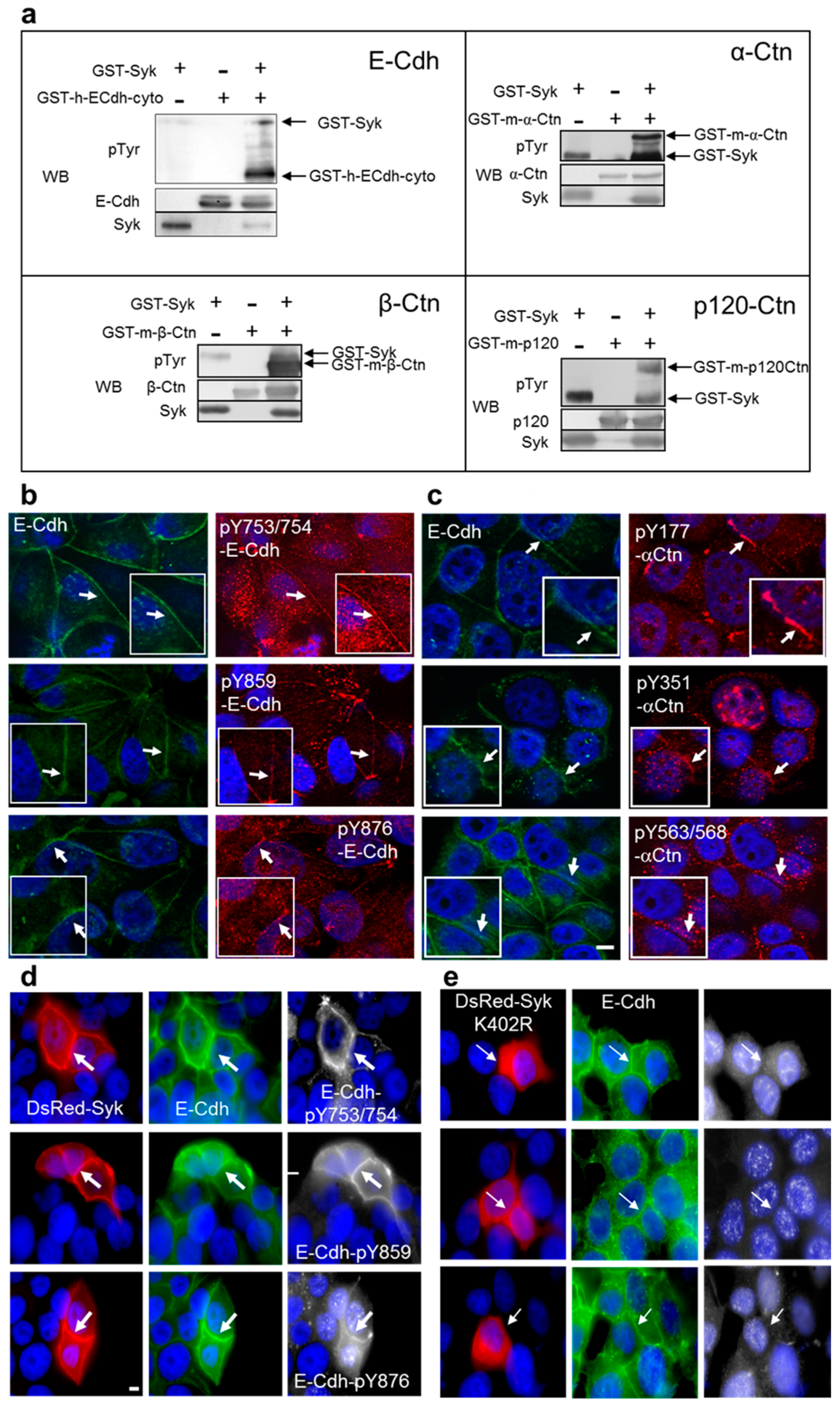
2.1. Syk Phosphorylates the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex on Different Tyrosine Residues
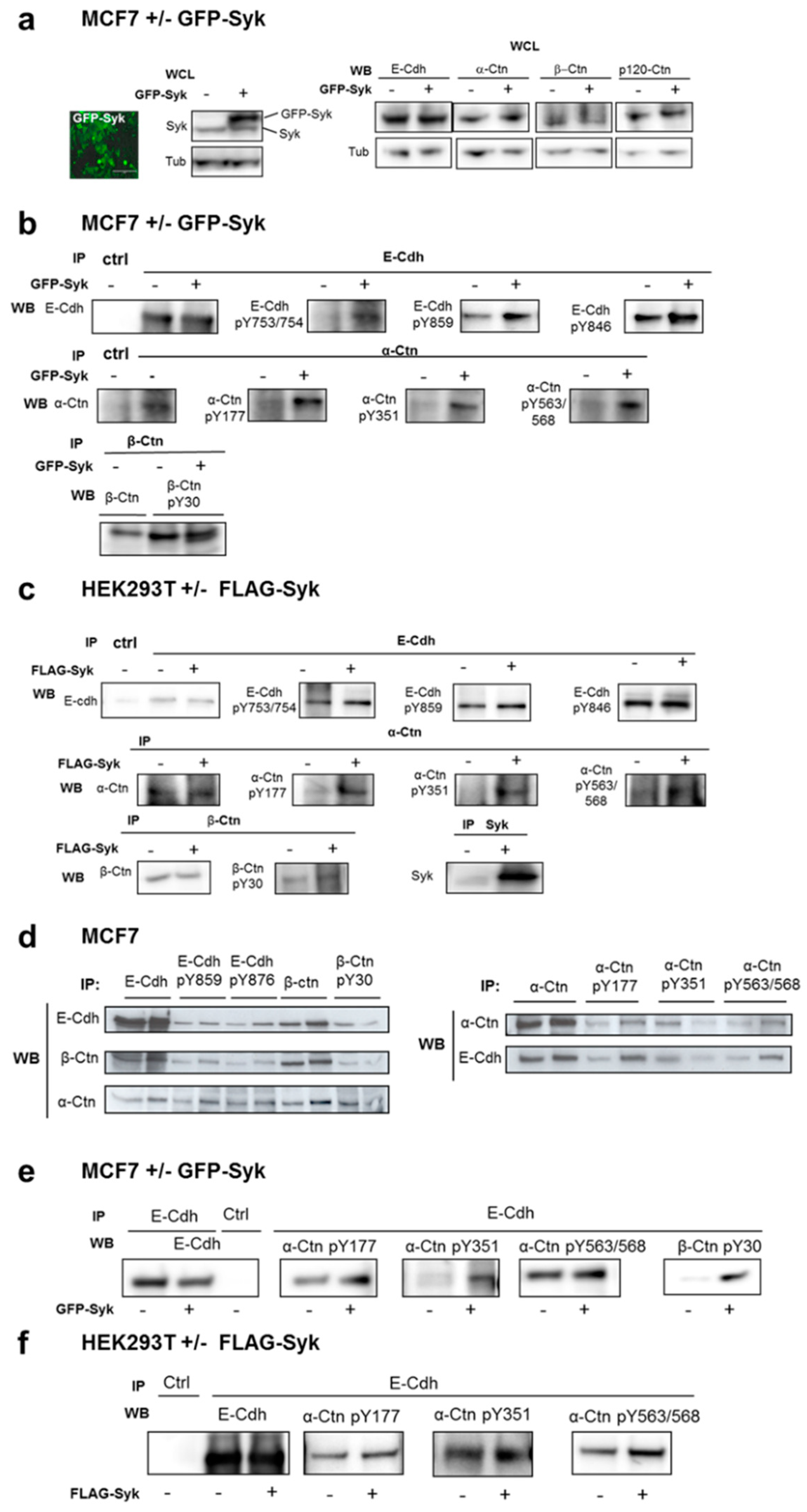
2.2. Exogenous Syk Expression and Oxidative Stress Increase E-Cadherin and Catenin Phosphorylation at Adherens Junctions
2.3. Syk-Mediated Phosphorylation of E-Cadherin Promotes its Interaction with Catenins and Regulates its Internalization in Early Endosomes
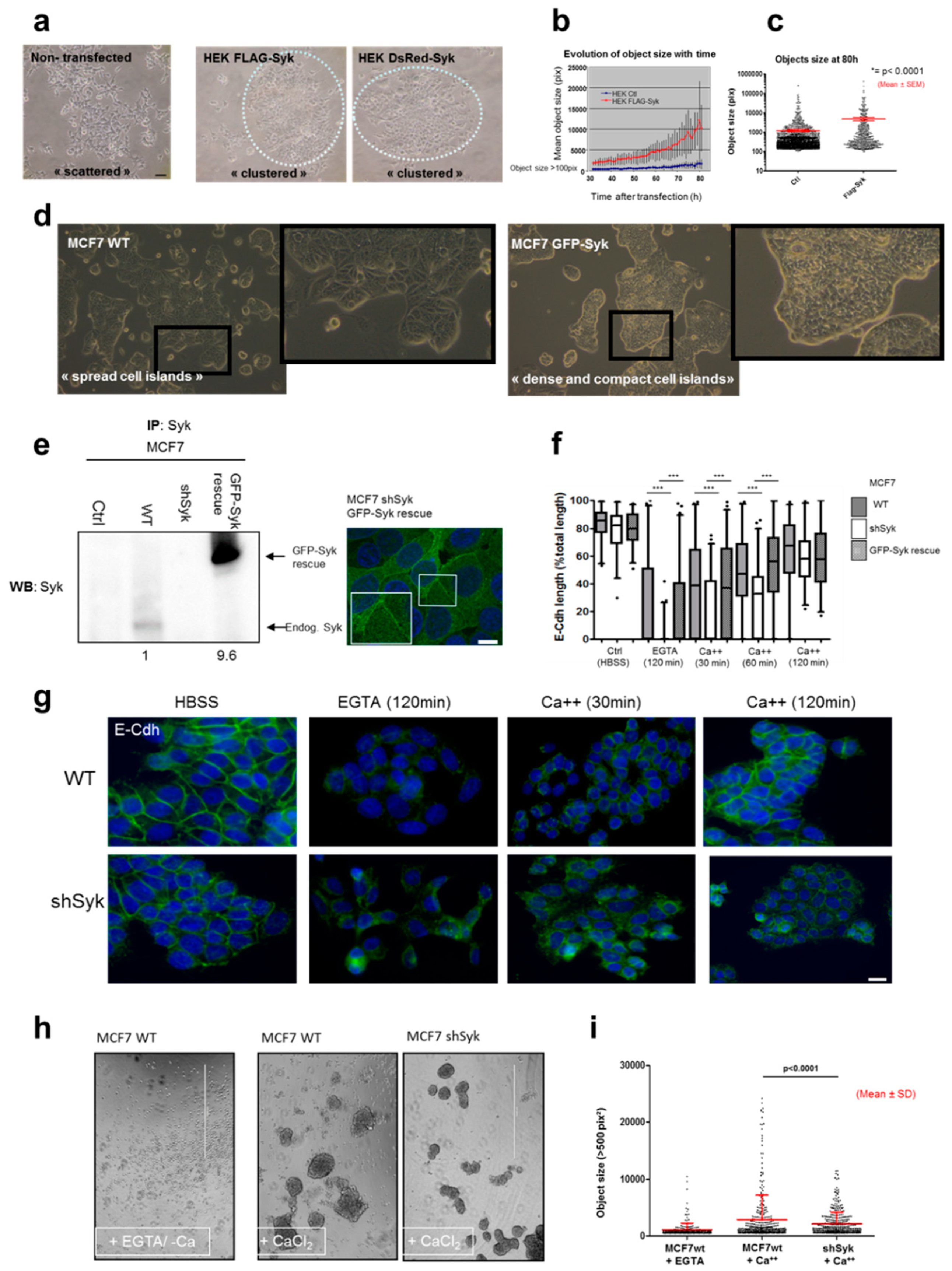
2.4. Syk Positively Affects 2D and 3D Cell Aggregation
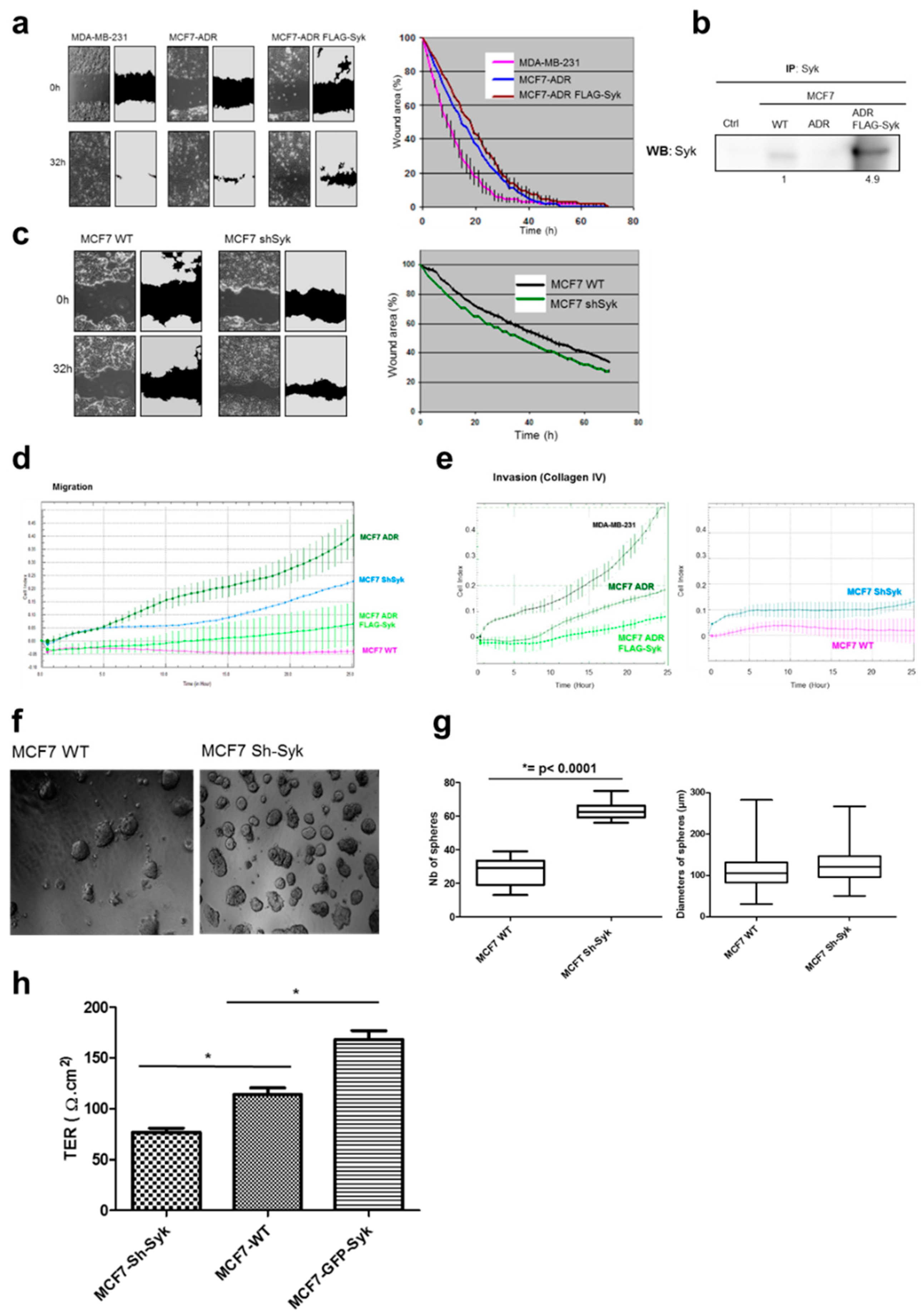
2.5. Syk Negatively Affects Cell Migration, Invasion, and Clonogenicity, and Maintains Epithelial Integrity
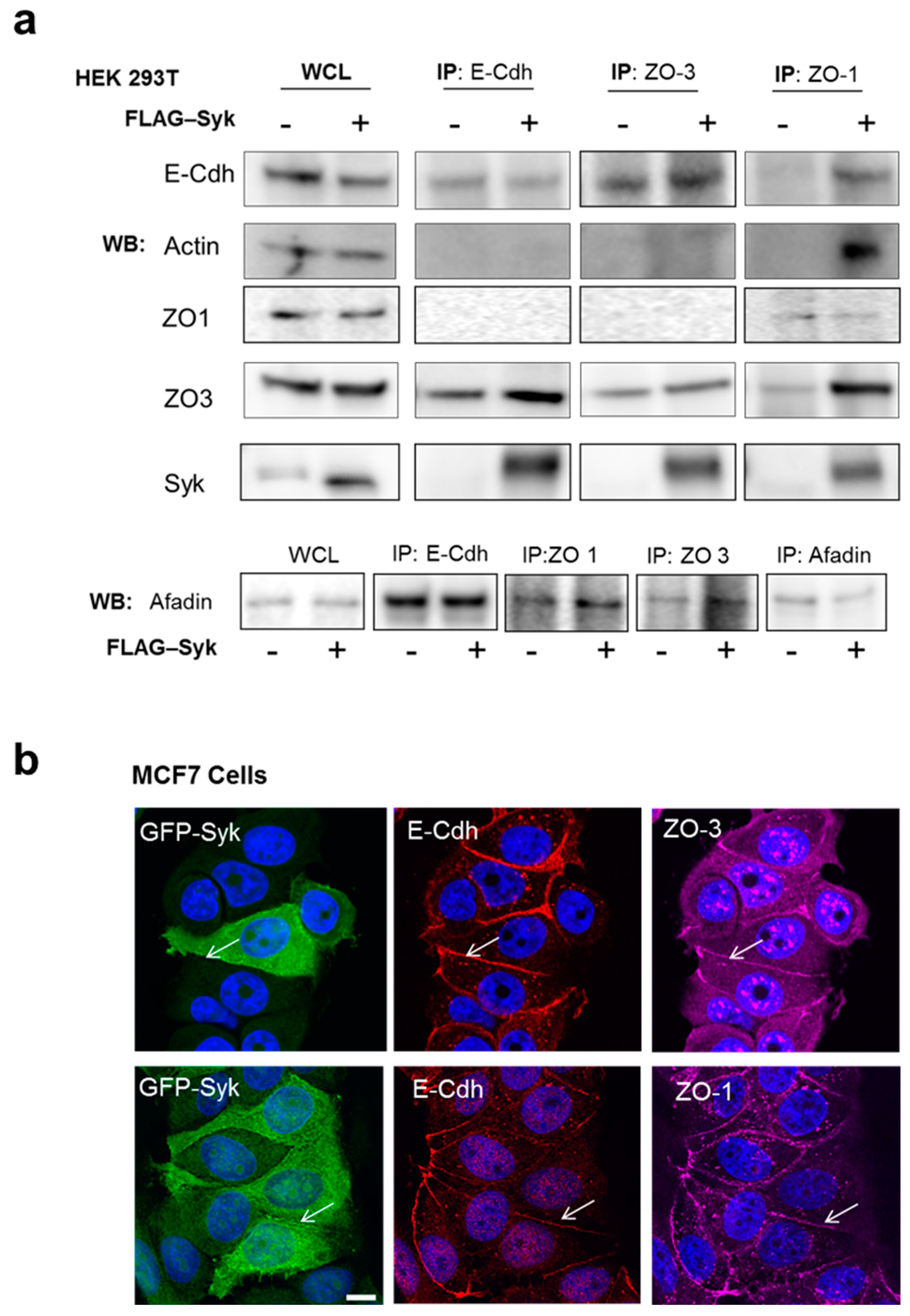
2.6. Enhanced Syk Expression Increases the Interaction between the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex with Zonula Occludens Proteins and the Actin Cytoskeleton
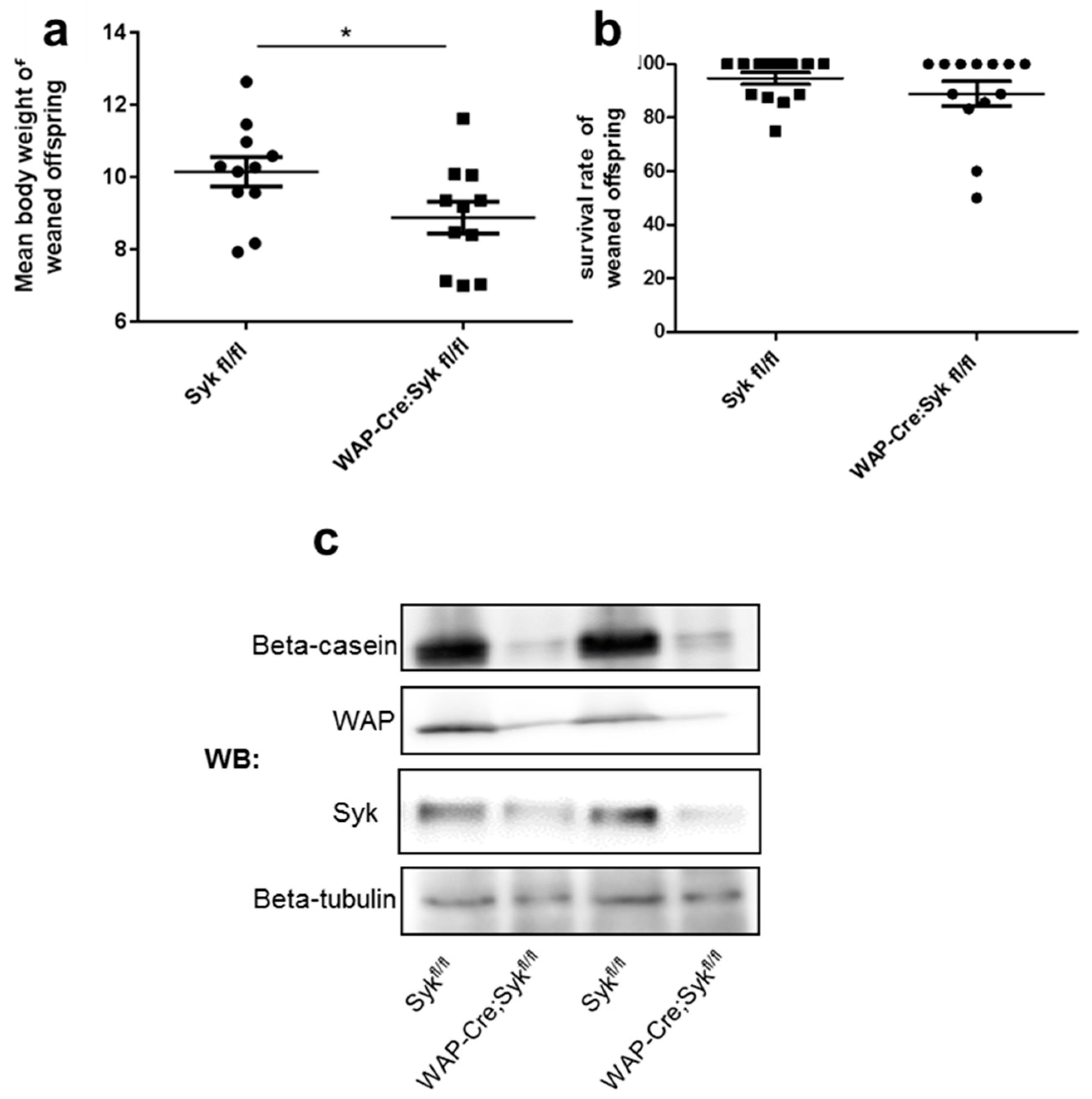
2.7. Syk Loss Affects Alveolar Epithelial Cell Differentiation in Lactating Mammary Glands and Disrupts E-Cadherin Localization at Intercellular Junctions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Plasmids and Transfection
4.3. Antibodies and Reagents
4.4. In Vitro Kinase Assays and Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Immunoprecipitation
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.8. 2D-Cell Aggregation Assays
4.9. Live-Cell Microscopy
4.10. 3D-Cell Aggregation Assays
4.11. Wound Healing Assay
4.12. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays using the xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analysis (RTCA) Technology
4.13. Matrigel Outgrowth Assay
4.14. Transepithelial Resistance (TER) Measurements
4.15. Animal Experiments
4.16. DNA Preparation and PCR Analysis
4.17. Histological Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baum, B.; Georgiou, M. Dynamics of adherens junctions in epithelial establishment, maintenance, and remodeling. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinet, C.; Lecuit, T. Stability and dynamics of cell-cell junctions. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 116, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coopman, P.; Djiane, A. Adherens Junction and E-Cadherin complex regulation by epithelial polarity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Huang, H. Insights into the role of cell-cell junctions in physiology and disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 306, 187–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roy, F.; Berx, G. The cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3756–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.J. Regulation of cell-cell adhesion by the cadherin-catenin complex. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röper, K. Integration of cell-cell adhesion and contractile actomyosin activity during morphogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 112, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, S. Cadherin-actin interactions at adherens junctions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Gao, W.; Chan, J.Y. Transcription regulation of E-cadherin by zinc finger E-box binding homeobox proteins in solid tumors. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 921564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Olmeda, D.; Cano, A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, B.P. Epigenetic regulation of EMT: The Snail story. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beco, S.; Amblard, F.; Coscoy, S. New insights into the regulation of E-cadherin distribution by endocytosis. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 295, 63–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz-Peitz, F.; Zallen, J.A. Junctional trafficking and epithelial morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadwell, C.M.; Su, W.; Kowalczyk, A.P. Cadherin Tales: Regulation of Cadherin Function by Endocytic Membrane Trafficking. Traffic 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecuit, T.; Yap, A.S. E-cadherin junctions as active mechanical integrators in tissue dynamics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, S.S.; Seruca, R.; Gärtner, F.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Gu, J.; Taniguchi, N.; Reis, C.A. Modulation of E-cadherin function and dysfunction by N-glycosylation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.M.; Reynolds, A.B. Tyrosine phosphorylation and cadherin/catenin function. Bioessays 1997, 19, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocchi, C.; Vaman Rao, M.; Zaidel-Bar, R. Regulation of adherens junction dynamics by phosphorylation switches. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 125295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocsai, A.; Ruland, J.; Tybulewicz, V.L. The SYK tyrosine kinase: A crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coopman, P.J.P.; Do, M.T.H.; Barth, M.; Bowden, E.T.; Hayes, A.J.; Basyuk, E.; Blancato, J.K.; Vezza, P.R.; McLeskey, S.W.; Mangeat, P.H.; et al. The Syk tyrosine kinase suppresses malignant growth of human breast cancercells. Nature 2000, 406, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, S.; Inatome, R.; Takano, T.; Yamamura, H. Syk expression and novel function in a wide variety of tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Mendez, R.; Sahin, A.; Dai, J.L. Hypermethylation leads to silencing of the SYK gene in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5558–5561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toyama, T.; Iwase, H.; Yamashita, H.; Hara, Y.; Omoto, Y.; Sugiura, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fujii, Y. Reduced expression of the Syk gene is correlated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2003, 189, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, M.; Soldatenkov, V.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Stoica, G.; Gehan, E.; Rashidi, B.; Singh, B.; Ozdemirli, M.; Mueller, S.C. Progressive Loss of Syk and Abnormal Proliferation in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7346–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coopman, P.J.; Mueller, S.C. The Syk tyrosine kinase: A new negative regulator in tumor growth and progression. Cancer Lett. 2006, 241, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.; Duraisamy, S.; Bradbury, C.M.; Hobbs, C.; Curley, D.P.; Nelson, B.; Bosenberg, M. Epigenetic silencing of novel tumor suppressors in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11187–11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layton, T.; Stalens, C.; Gunderson, F.; Goodison, S.; Silletti, S. Syk tyrosine kinase acts as a pancreatic adenocarcinoma tumor suppressor by regulating cellular growth and invasion. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeller, C.; Thallinger, C.; Pratscher, B.; Bister, M.D.; Schicher, N.; Loewe, R.; Heere-Ress, E.; Roka, F.; Sexl, V.; Pehamberger, H. The non-receptor-associated tyrosine kinase Syk is a regulator of metastatic behavior in human melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisenko, M.O.; Geahlen, R.L. Calling in SYK: SYK’s dual role as a tumor promoter and tumor suppressor in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümmler, C.; Dumitriu, G.; Wickström, M.; Coopman, P.; Valkov, A.; Kogner, P.; Johnsen, J.I.; Moens, U.; Sveinbjörnsson, B. SYK Inhibition Potentiates the Effect of Chemotherapeutic Drugs on Neuroblastoma Cells in Vitro. Cancers 2019, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Colbert, R.A. Healing the Syk through kinase inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larive, R.M.; Urbach, S.; Poncet, J.; Jouin, P.; Mascré, G.; Sahuquet, A.; Mangeat, P.H.; Coopman, P.J.; Bettache, N. Phosphoproteomic analysis of Syk kinase signaling in human cancer cells reveals its role in cell-cell adhesion. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nelson, W.J.; Dickinson, D.J.; Weis, W.I. Roles of cadherins and catenins in cell-cell adhesion and epithelial cell polarity. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 116, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shrikhande, U.; Alicie, B.M.; Zhou, Q.; Geahlen, R.L. Role of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk in regulating cell-cell adhesion and motility in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Krause, G.; Scheffner, M.; Zechner, D.; Leddy, H.E.; Behrens, J.; Sommer, T.; Birchmeier, W. Hakai, a c-Cbl-like protein, ubiquitinates and induces endocytosis of the E-cadherin complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartsock, A.; Nelson, W.J. Competitive regulation of E-cadherin juxtamembrane domain degradation by p120-catenin binding and Hakai-mediated ubiquitination. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedra, J.; Miravet, S.; Castaño, J.; Pálmer, H.G.; Heisterkamp, N.; García de Herreros, A.; Duñach, M. p120 Catenin-associated Fer and Fyn tyrosine kinases regulate beta-catenin Tyr-142 phosphorylation and beta-catenin-alpha-catenin Interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Náger, M.; Visa, A.; Sallán, M.C.; Coopman, P.J.; Cantí, C.; Herreros, J. Phosphorylated Tyr142 β-catenin localizes to centrosomes and is regulated by Syk. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3632–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Oh, I.H.; McCrea, P.D. Phosphorylation and isoform use in p120-catenin during development and tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Das, J.K.; Kumar, N. Janus kinase 3 regulates adherens junctions and epithelial mesenchymal transition through β-catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16406–16419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Sada, K.; Yamamura, H. Role of protein-tyrosine kinase syk in oxidative stress signaling in B cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2002, 4, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, E.C.; Kajita, M.; Wadlow, A.; Tobiansky, L.; Niessen, C.; Ariga, H.; Daniel, J.; Fujita, Y. A role for the cleaved cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin in the nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12691–12700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, R.; Serra, S.; Asa, S.L. Loss of membrane localization and aberrant nuclear E-cadherin expression correlates with invasion in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, M.S.; Gill, A.J.; Conaglen, J.V.; Clarkson, A.; Cook, R.J.; Little, N.S.; Robinson, B.G.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; McDonald, K.L. Nuclear accumulation of E-cadherin correlates with loss of cytoplasmic membrane staining and invasion in pituitary adenomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Chow, S.Y.; Yusoff, P.; Seetharaman, J.; Ng, C.; Sinniah, S.; Koh, X.W.; Asgar, N.F.; Li, D.; Yim, D.; et al. Structure of a novel phosphotyrosine-binding domain in Hakai that targets E-cadherin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.L.; Kim, A.C.; Hens, J.R. The role and function of cadherins in the mammary gland. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.; Mee, P.J.; Costello, P.S.; Williams, O.; Price, A.A.; Duddy, L.P.; Furlong, M.T.; Geahlen, R.L.; Tybulewicz, V.L. Perinatal lethality and blocked B-cell development in mice lacking the tyrosine kinase Syk. Nature 1995, 378, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.M.; Rowley, B.; Pao, W.; Hayday, A.; Bolen, J.B.; Pawson, T. Syk tyrosine kinase required for mouse viability and B-cell development. Nature 1995, 378, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.U.; Wall, R.J.; St-Onge, L.; Gruss, P.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Garrett, L.; Li, M.; Furth, P.A.; Hennighausen, L. Cre-mediated gene deletion in the mammary gland. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4323–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennighausen, L.; Robinson, G.W. Information networks in the mammary gland. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.N.; Schwesinger, C.; Ye, J.; Denker, B.M.; Nigam, S.K. Reassembly of the tight junction after oxidative stress depends on tyrosine kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22048–22055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsube, T.; Tsuji, H.; Onoda, M. Nitric oxide attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced barrier disruption and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in monolayers of intestinal epithelial cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntaka, S.R.; Samak, G.; Seth, A.; LaRusso, N.F.; Rao, R. Epidermal growth factor protects the apical junctional complexes from hydrogen peroxide in bile duct epithelium. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1396–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sung, Y.M.; Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Mueller, D.; Sentissi, K.; Johnson, P.; Urbach, E.; Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, F.; Johnson, M.D.; Mueller, S.C. Tumor suppressor function of Syk in human MCF10A in vitro and normal mouse mammary epithelium in vivo. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jaumouillé, V.; Farkash, Y.; Jaqaman, K.; Das, R.; Lowell, C.A.; Grinstein, S. Actin cytoskeleton reorganization by Syk regulates Fcγ receptor responsiveness by increasing its lateral mobility and clustering. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahian, F.; Guerriero, A.; Sebzda, E.; Lu, M.M.; Zhou, R.; Mocsai, A.; Myers, E.E.; Huang, B.; Jackson, D.G.; Ferrari, V.A.; et al. Regulation of blood and lymphatic vascular separation by signaling proteins SLP-76 and Syk. Science 2003, 299, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, M.D. Key stages in mammary gland development: The cues that regulate ductal branching morphogenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, H.; Hinck, L. Mammary gland development. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussadia, O.; Kutsch, S.; Hierholzer, A.; Delmas, V.; Kemler, R. E-cadherin is a survival factor for the lactating mouse mammary gland. Mech. Dev. 2002, 115, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejmek, J.; Leandersson, K.; Manjer, J.; Bjartell, A.; Emdin, S.O.; Vogel, W.F.; Landberg, G.; Andersson, T. Expression and Signaling Activity of Wnt-5a/Discoidin Domain Receptor-1 and Syk Plays Distinct but Decisive Roles in Breast Cancer Patient Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 520–528. [Google Scholar]
- Blancato, J.; Graves, A.; Rashidi, B.; Moroni, M.; Tchobe, L.; Ozdemirli, M.; Kallakury, B.; Makambi, K.H.; Marian, C.; Mueller, S.C. SYK allelic loss and the role of Syk-regulated genes in breast cancer survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Khanna, N.; Wu, J.; Godri Pollitt, K.; Evans, G.J.; Chow, C.W.; Scott, J.A. Syk mediates airway contractility independent of leukocyte function. Allergy 2015, 70, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotra, V.P.; He, S.; van der Horst, G.; Nijhoff, S.; de Bont, H.; Lekkerkerker, A.; Janssen, R.; Jenster, G.; van Leenders, G.J.; Hoogland, A.M.; et al. SYK is a candidate kinase target for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Dong, S.; Zhang, P.; Xu, N.; Yan, H.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q. The relationship between methylation of the Syk gene in the promoter region and the genesis of lung cancer. Clin. Lab. 2010, 56, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Sun, Q.; Hao, Y.; Cong, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. Syk is low-expressed in non-small-cell lung cancer and inversely correlates with patient’s survival. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Greninger, P.; Rhodes, D.; Koopman, L.; Violette, S.; Bardeesy, N.; Settleman, J. A gene expression signature associated with “K-Ras addiction” reveals regulators of EMT and tumor cell survival. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.K.; Berchuck, J.E.; Ross, K.N.; Kakoza, R.M.; Clauser, K.; Schinzel, A.C.; Ross, L.; Galinsky, I.; Davis, T.N.; Silver, S.J.; et al. Proteomic and genetic approaches identify Syk as an AML target. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puissant, A.; Fenouille, N.; Alexe, G.; Pikman, Y.; Bassil, C.F.; Mehta, S.; Du, J.; Kazi, J.U.; Luciano, F.; Rönnstrand, L.; et al. SYK is a critical regulator of FLT3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, D.; Di Liberto, M.; Martin, P.; Huang, X.; Sharman, J.; Blecua, P.; Mathew, S.; Vijay, P.; Eng, K.; Ali, S.; et al. Cell-cycle reprogramming for PI3K inhibition overrides a relapse-specific C481S BTK mutation revealed by longitudinal functional genomics in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cárcer, G. The Mitotic Cancer Target Polo-Like Kinase 1: Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor? Genes 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargier, G.; Favard, C.; Parmeggiani, A.; Sahuquet, A.; Merezegue, F.; Morel, A.; Denis, M.; Molinari, N.; Mangeat, P.H.; Coopman, P.J.; et al. Centrosomal targeting of Syk kinase is controlled by its catalytic activity and depends on microtubules and the dynein motor. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyss, D.; Montcourrier, P.; Vidal, B.; Anguille, C.; Mérezègue, F.; Sahuquet, A.; Mangeat, P.H.; Coopman, P.J. The Syk Tyrosine Kinase Localizes to the Centrosomes and Negatively Affects Mitotic Progression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10872–10880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, K.C.; Khromykh, T.; Christy, P.; Le, T.L.; Gottardi, C.J.; Yap, A.S.; Stow, J.L.; Teasdale, R.D. A dileucine motif targets E-cadherin to the basolateral cell surface in Madin-Darby canine kidney and LLC-PK1 epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22565–22572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendeville, A.; Rayne, F.; Bonhoure, A.; Bettache, N.; Montcourrier, P.; Beaumelle, B. HIV-1 Tat enters T cells using coated pits before translocating from acidified endosomes and eliciting biological responses. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larive, R.M.; Abad, A.; Cardaba, C.M.; Hernández, T.; Cañamero, M.; de Álava, E.; Santos, E.; Alarcón, B.; Bustelo, X.R. The Ras-like protein R-Ras2/TC21 is important for proper mammary gland development. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kassouf, T.; Larive, R.M.; Morel, A.; Urbach, S.; Bettache, N.; Marcial Medina, M.C.; Mèrezègue, F.; Freiss, G.; Peter, M.; Boissière-Michot, F.; et al. The Syk Kinase Promotes Mammary Epithelial Integrity and Inhibits Breast Cancer Invasion by Stabilizing the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex. Cancers 2019, 11, 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121974
Kassouf T, Larive RM, Morel A, Urbach S, Bettache N, Marcial Medina MC, Mèrezègue F, Freiss G, Peter M, Boissière-Michot F, et al. The Syk Kinase Promotes Mammary Epithelial Integrity and Inhibits Breast Cancer Invasion by Stabilizing the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121974
Chicago/Turabian StyleKassouf, Toufic, Romain Maxime Larive, Anne Morel, Serge Urbach, Nadir Bettache, Ma Cleofas Marcial Medina, Fabrice Mèrezègue, Gilles Freiss, Marion Peter, Florence Boissière-Michot, and et al. 2019. "The Syk Kinase Promotes Mammary Epithelial Integrity and Inhibits Breast Cancer Invasion by Stabilizing the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121974
APA StyleKassouf, T., Larive, R. M., Morel, A., Urbach, S., Bettache, N., Marcial Medina, M. C., Mèrezègue, F., Freiss, G., Peter, M., Boissière-Michot, F., Solassol, J., Montcourrier, P., & Coopman, P. (2019). The Syk Kinase Promotes Mammary Epithelial Integrity and Inhibits Breast Cancer Invasion by Stabilizing the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex. Cancers, 11(12), 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121974






