TREM2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Carcinoma through Wnt1/β-catenin and Erk Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
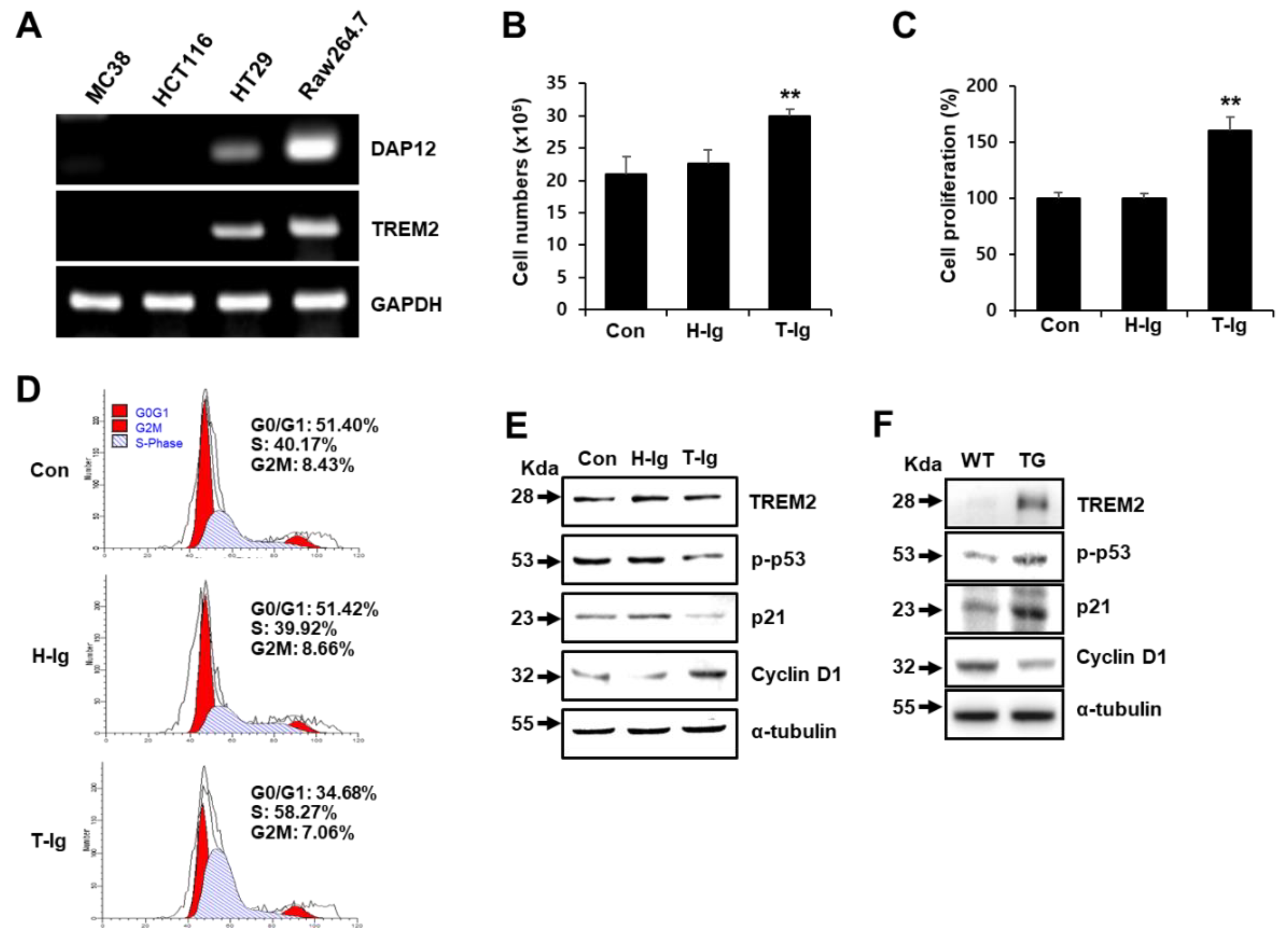
2.1. TREM2 Suppresses the Proliferation of HT29 Colon Cancer Cells by Downregulating Cell Cycle Progression
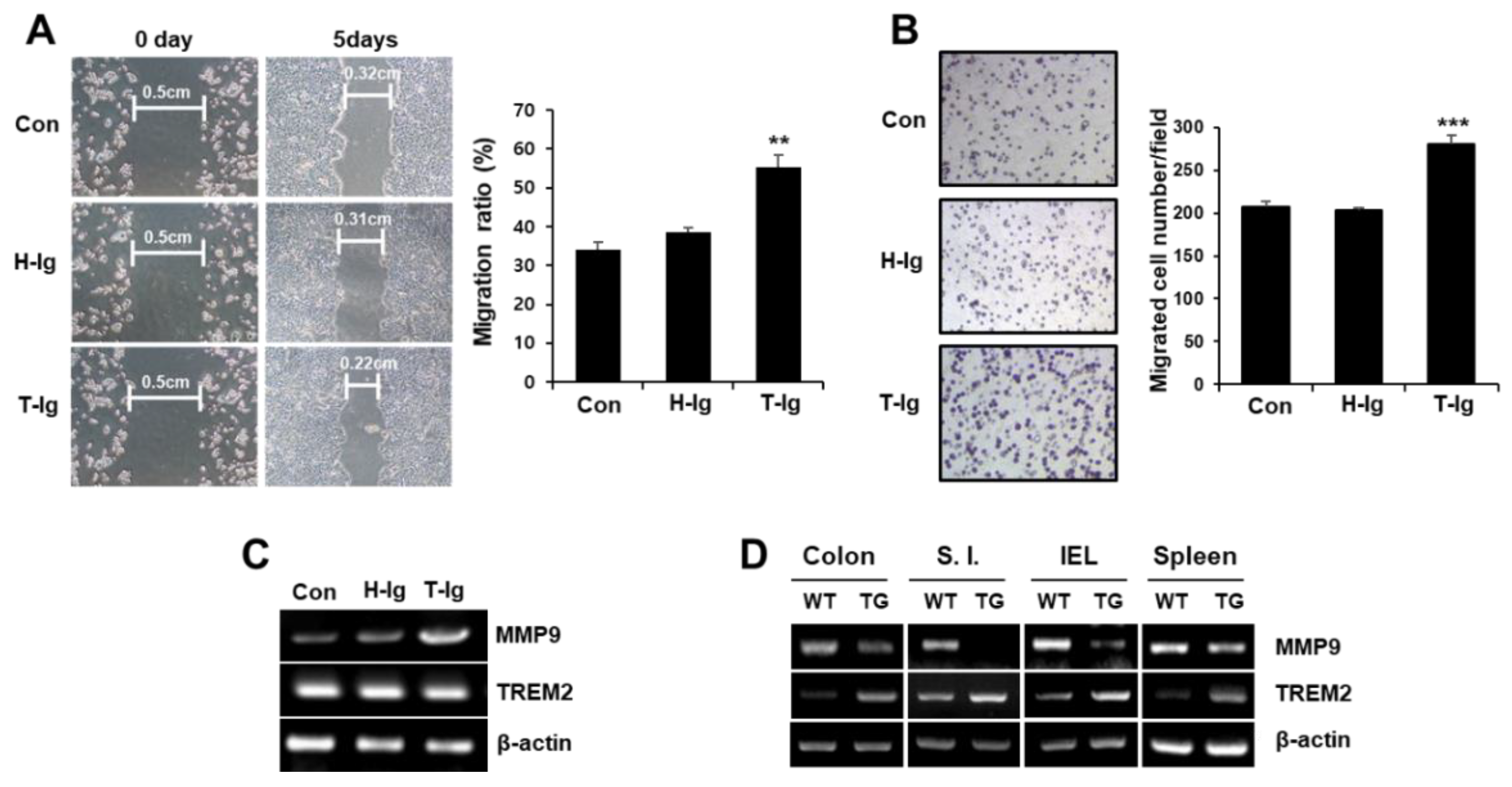
2.2. TREM2 Suppresses the Metastatic Potential of HT29 Colon Cancer Cells
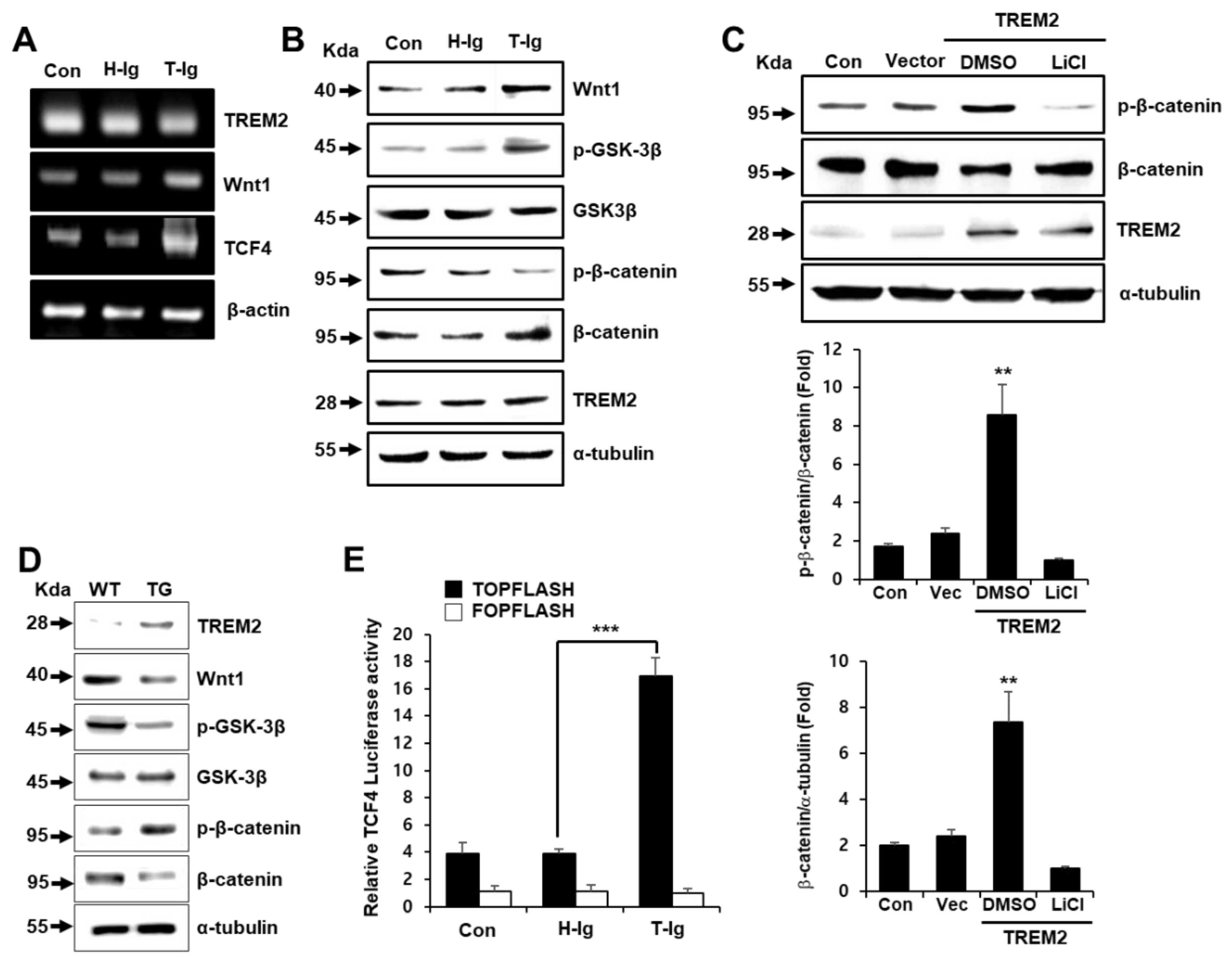
2.3. TREM2 Regulates the Expression of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling-Related Molecules
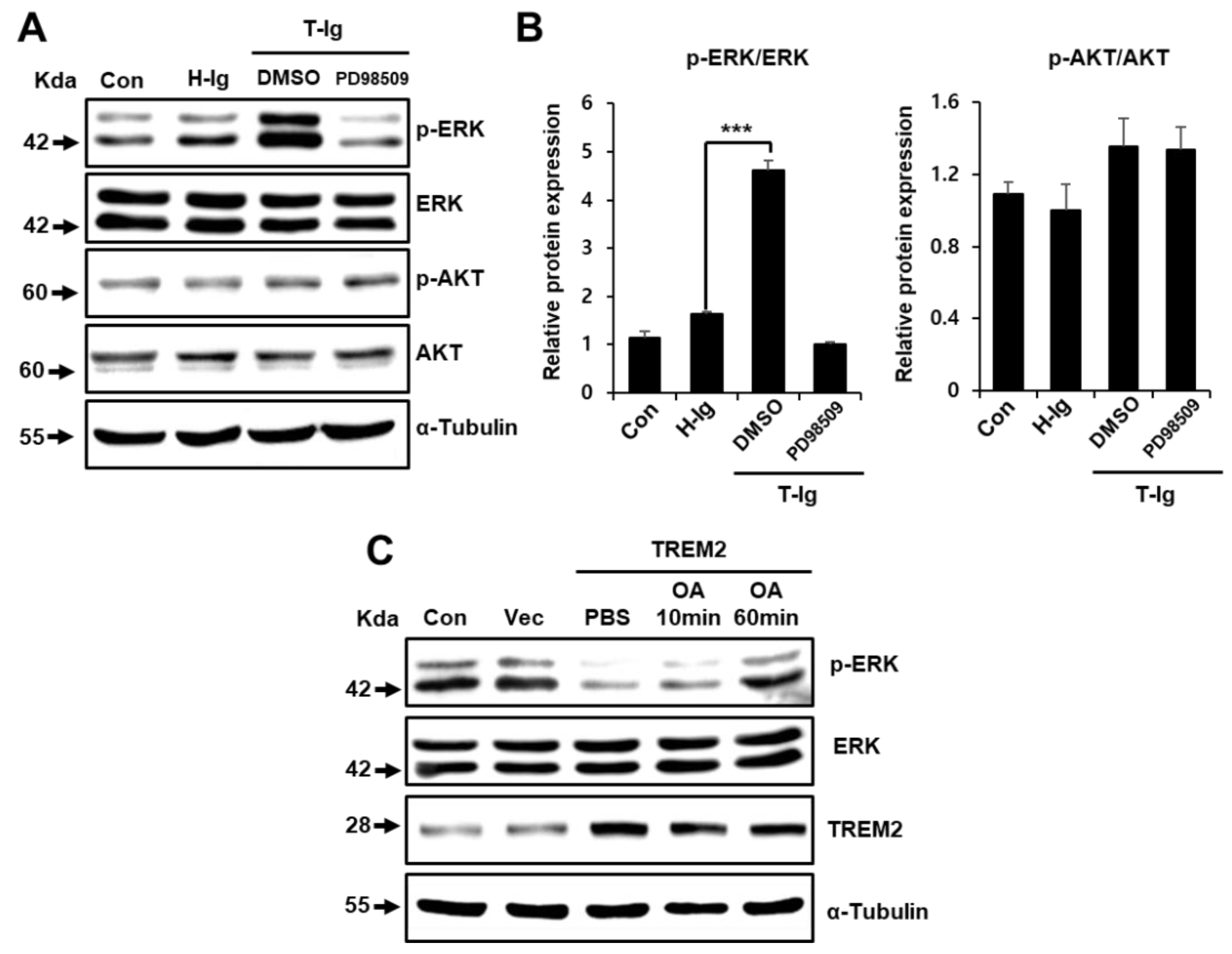
2.4. TREM2 Inhibits the ERK Signaling Pathway
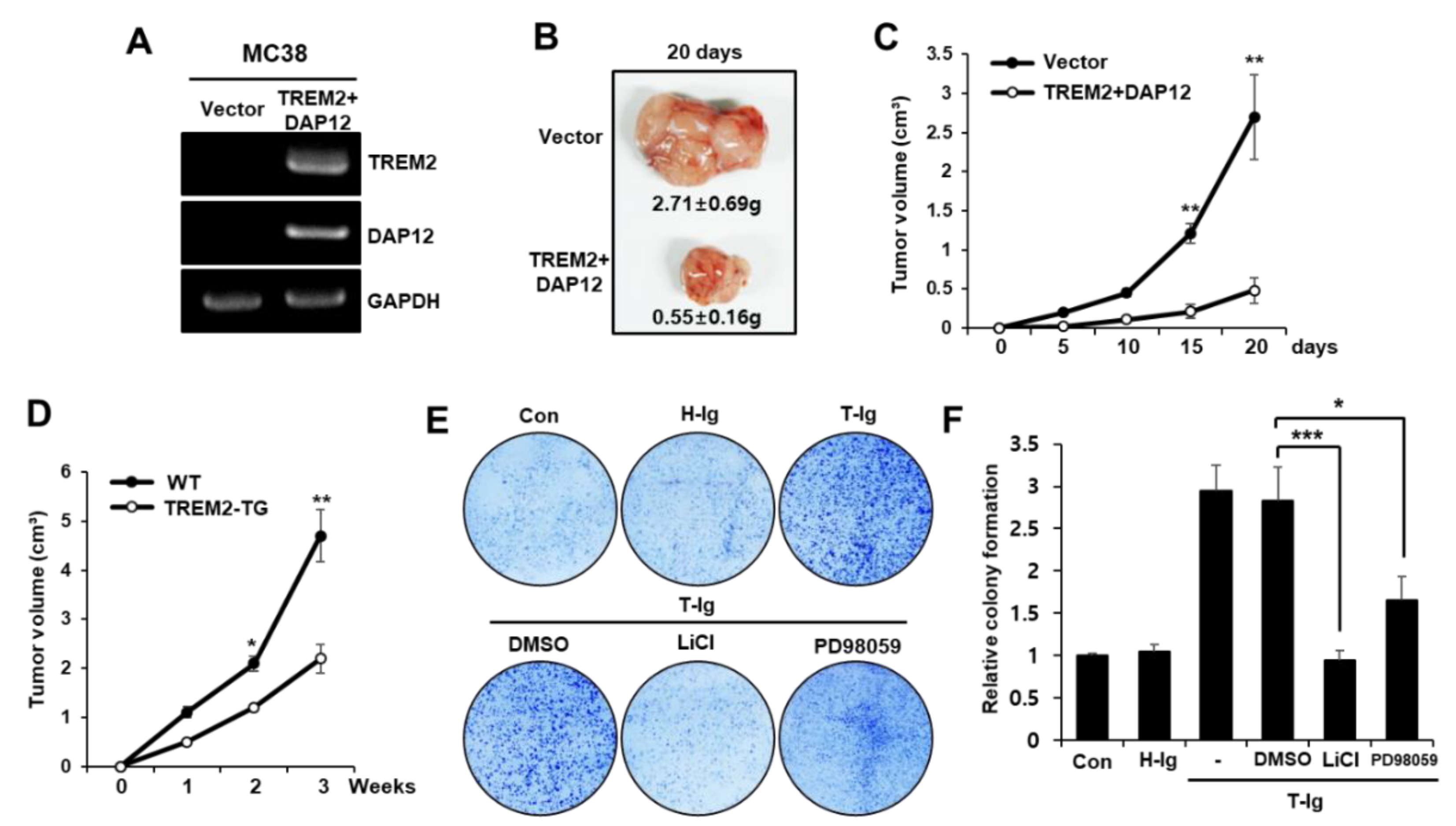
2.5. TREM2 Inhibits the Tumorigenicity of Colon Cancer Cells
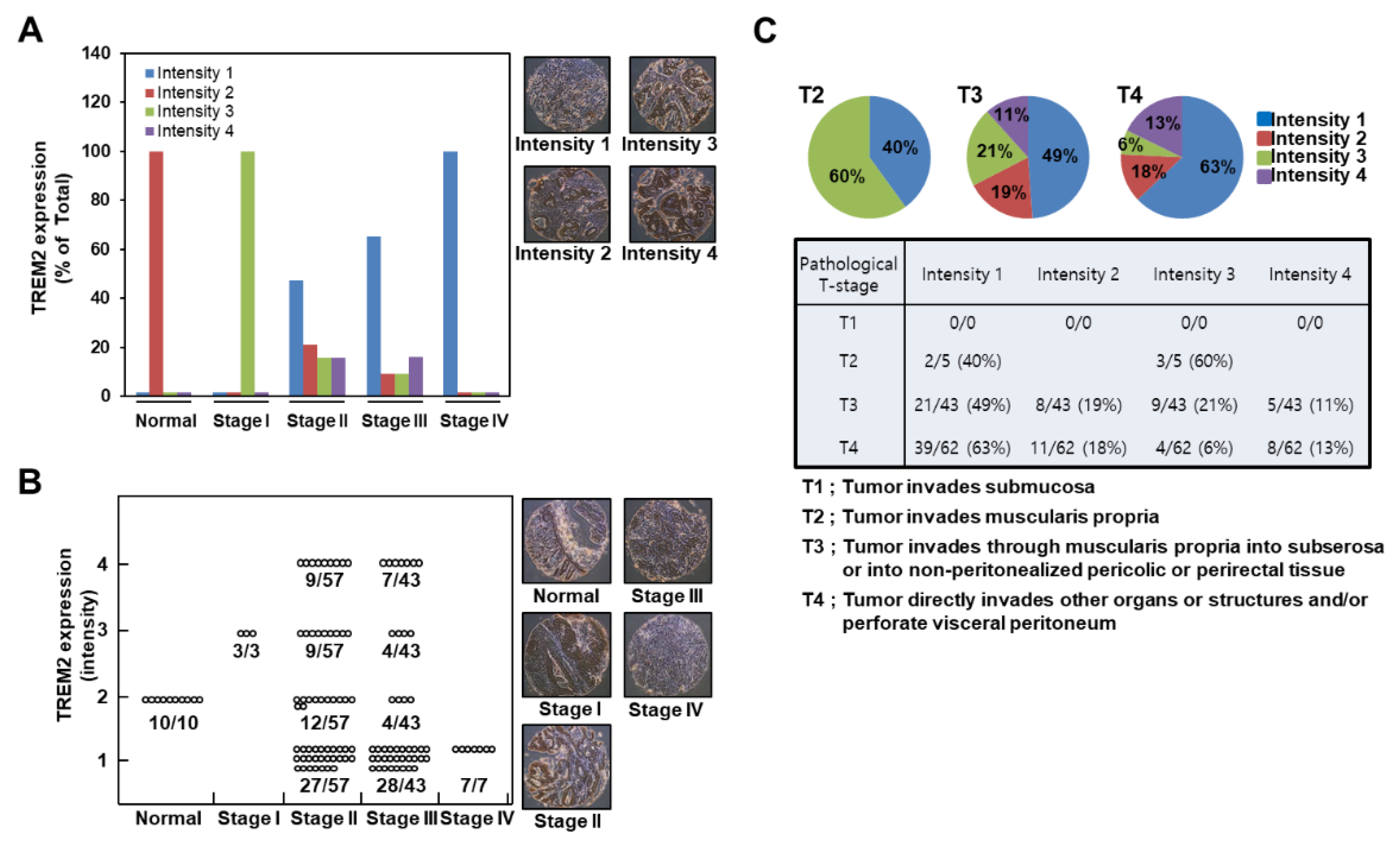
2.6. TREM2 Expression is Downregulated in Highly Proliferative Human Colon Cancers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Tissue Array
4.3. Generation of TREM2-TG Mice
4.4. Cell Lines, Reagents and Antibodies
4.5. Isolation of Primary Colon Cells
4.6. Cell Transfection
4.7. Reverse Transcription-polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Cell Proliferation and Colony Forming Assays
4.10. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.11. Luciferase Reporter Assays
4.12. Scratch Wound-healing Assay
4.13. Matrigel Invasion Assay
4.14. MC38 Cancer Growth in Mice
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klesney-Tait, J.; Turnbull, I.R.; Colonna, M. The TREM receptor family and signal integration. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, I.R.; Colonna, M. Activating and inhibitory functions of DAP12. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N.; Hurlstone, A.; Musisi, H.; Miles, A.; Bienz, M.; Clevers, H. The chromatin remodelling factor Brg-1 interacts with beta-catenin to promote target gene activation. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4935–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, R.; Watson, S.R.; Lanier, L.L. DAP12: an adapter protein with dual functionality. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 214, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillon, J.M. Monocyte TREM-1 membrane expression in non-infectious inflammation. Crit. Care 2009, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibot, S.; Massin, F.; Marcou, M.; Taylor, V.; Stidwill, R.; Wilson, P.; Singer, M.; Bellingan, G. TREM-1 promotes survival during septic shock in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamerman, J.A.; Jarjoura, J.R.; Humphrey, M.B.; Nakamura, M.C.; Seaman, W.E.; Lanier, L.L. Cutting edge: inhibition of TLR and FcR responses in macrophages by triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM)-2 and DAP12. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2051–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, C.D.; Sautkulis, L.N.; Danielson, P.E.; Cooper, J.; Hasel, K.W.; Hilbush, B.S.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Carson, M.J. Heterogeneous expression of the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 on adult murine microglia. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchon, A.; Dietrich, J.; Colonna, M. Cutting edge: inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4991–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.H.; Seaman, W.E.; Daws, M.R. Characterization of TREM-3, an activating receptor on mouse macrophages: definition of a family of single Ig domain receptors on mouse chromosome 17. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Taylor, P.R. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Rochford, C.D.; Neumann, H. Clearance of apoptotic neurons without inflammation by microglial triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchon, A.; Hernandez-Munain, C.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. A DAP12-mediated pathway regulates expression of CC chemokine receptor 7 and maturation of human dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paloneva, J.; Mandelin, J.; Kiialainen, A.; Bohling, T.; Prudlo, J.; Hakola, P.; Haltia, M.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Peltonen, L. DAP12/TREM2 deficiency results in impaired osteoclast differentiation and osteoporotic features. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Laskin, J.D.; Gordon, M.K.; Laskin, D.L. Regulation of TREM expression in hepatic macrophages and endothelial cells during acute endotoxemia. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2008, 84, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, R.H.; van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2003, 1653, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.; Jerchow, B.A.; Wurtele, M.; Grimm, J.; Asbrand, C.; Wirtz, R.; Kühl, M.; Wedlich, D.; Birchmeier, W. Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with beta-catenin, APC, and GSK3beta. Science 1998, 280, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Sparks, A.B.; Rago, C.; Hermeking, H.; Zawel, L.; da Costa, L.T.; Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science 1998, 281, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.S.; Kim, S.E.; Jeon, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, K.Y. Both ERK and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways are involved in Wnt3a-induced proliferation. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Xia, W.; Liu, J.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, D.F.; Xia, J.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Erk associates with and primes GSK-3beta for its inactivation resulting in upregulation of beta-catenin. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Han, L.; Bellido, T.; Manolagas, S.C.; Kousteni, S. Wnt proteins prevent apoptosis of both uncommitted osteoblast progenitors and differentiated osteoblasts by beta-catenin-dependent and -independent signaling cascades involving Src/ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 41342–41351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottinger, E.; Besnardeau, L.; Lepage, T. A Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway is required for development of the sea urchin embryo micromere lineage through phosphorylation of the transcription factor Ets. Development 2004, 131, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, D.N.; Cooper, M.D.; Potter, J.L.; Roberts, M.H.; Cheng, H.; Jarvis, G.A. TREM-2 binds to lipooligosaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and is expressed on reproductive tract epithelial cells. Mucosal. Immunol. 2008, 1, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Chung, H.J.; Min, H.Y.; Park, E.J.; Lee, M.A.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.K. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates the antitumor activity of magnolol in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carragher, L.A.; Snell, K.R.; Giblett, S.M.; Aldridge, V.S.; Patel, B.; Cook, S.J.; Winton, D.J.; Marais, R.; Pritchard, C.A. V600EBraf induces gastrointestinal crypt senescence and promotes tumour progression through enhanced CpG methylation of p16INK4a. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, L.F.; Wasmer, M.H.; Rau, T.T.; Krebs, P. Cytokine-Induced Modulation of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markman, J.L.; Shiao, S.L. Impact of the immune system and immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest Oncol. 2015, 6, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.C.; Kim, N.; Kadono, Y.; Rho, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lorenzo, J.; Choi, Y. Osteoimmunology: interplay between the immune system and bone metabolism. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, M.B.; Daws, M.R.; Spusta, S.C.; Niemi, E.C.; Torchia, J.A.; Lanier, L.L.; Seaman, W.E.; Nakamura, M.C. TREM2, a DAP12-associated receptor, regulates osteoclast differentiation and function. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Saqcena, M.; Foster, D.A. Synthetic lethality in KRas-driven cancer cells created by glutamine deprivation. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 807–808. [Google Scholar]
- Went, P.; Vasei, M.; Bubendorf, L.; Terracciano, L.; Tornillo, L.; Riede, U.; Kononen, J.; Simon, R.; Sauter, G.; Baeuerle, P.A. Frequent high-level expression of the immunotherapeutic target Ep-CAM in colon, stomach, prostate and lung cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Wang, X.W. Activation of hepatic stem cell marker EpCAM by Wnt-beta-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10831–10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetsu, O.; McCormick, F. Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 1999, 398, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, S.E.; Ward-Hartstonge, K.A.; Taylor, E.S.; Kemp, R.A. Immune cell interplay in colorectal cancer prognosis. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 7, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Caro, G.; Marchesi, F.; Laghi, L.; Grizzi, F. Immune cells: plastic players along colorectal cancer progression. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.C.; Varner, J.A. Myeloid cells in the tumor microenvironment: modulation of tumor angiogenesis and tumor inflammation. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 201026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W.; Kotwaliwale, A.; Vass, K.; Janosch, P. The role of Raf kinases in malignant transformation. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2002, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downward, J. Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Yi, J.W.; Kim, E.M.; Yoon, I.J.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Ji, K.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Jang, J.H.; Oh, S.S.; et al. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) promotes adipogenesis and diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2015, 64, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Mun, B.R.; Lee, S.J.; Joh, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Ji, K.Y.; Choi, H.R.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, E.M.; Jang, J.H.; et al. TREM2 promotes Abeta phagocytosis by upregulating C/EBPalpha-dependent CD36 expression in microglia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-M.; Kim, E.-M.; Ji, K.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Yee, S.-M.; Woo, S.-M.; Yi, J.-W.; Yun, C.-H.; Choi, H.; Kang, H.-S. TREM2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Carcinoma through Wnt1/β-catenin and Erk Signaling. Cancers 2019, 11, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091315
Kim S-M, Kim E-M, Ji K-Y, Lee H-Y, Yee S-M, Woo S-M, Yi J-W, Yun C-H, Choi H, Kang H-S. TREM2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Carcinoma through Wnt1/β-catenin and Erk Signaling. Cancers. 2019; 11(9):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091315
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Su-Man, Eun-Mi Kim, Kon-Young Ji, Hwa-Youn Lee, Su-Min Yee, Su-Min Woo, Ja-Woon Yi, Chul-Ho Yun, Harim Choi, and Hyung-Sik Kang. 2019. "TREM2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Carcinoma through Wnt1/β-catenin and Erk Signaling" Cancers 11, no. 9: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091315
APA StyleKim, S.-M., Kim, E.-M., Ji, K.-Y., Lee, H.-Y., Yee, S.-M., Woo, S.-M., Yi, J.-W., Yun, C.-H., Choi, H., & Kang, H.-S. (2019). TREM2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Carcinoma through Wnt1/β-catenin and Erk Signaling. Cancers, 11(9), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091315




