Baseline MRI-Radiomics Can Predict Overall Survival in Non-Endemic EBV-Related Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients Characteristics
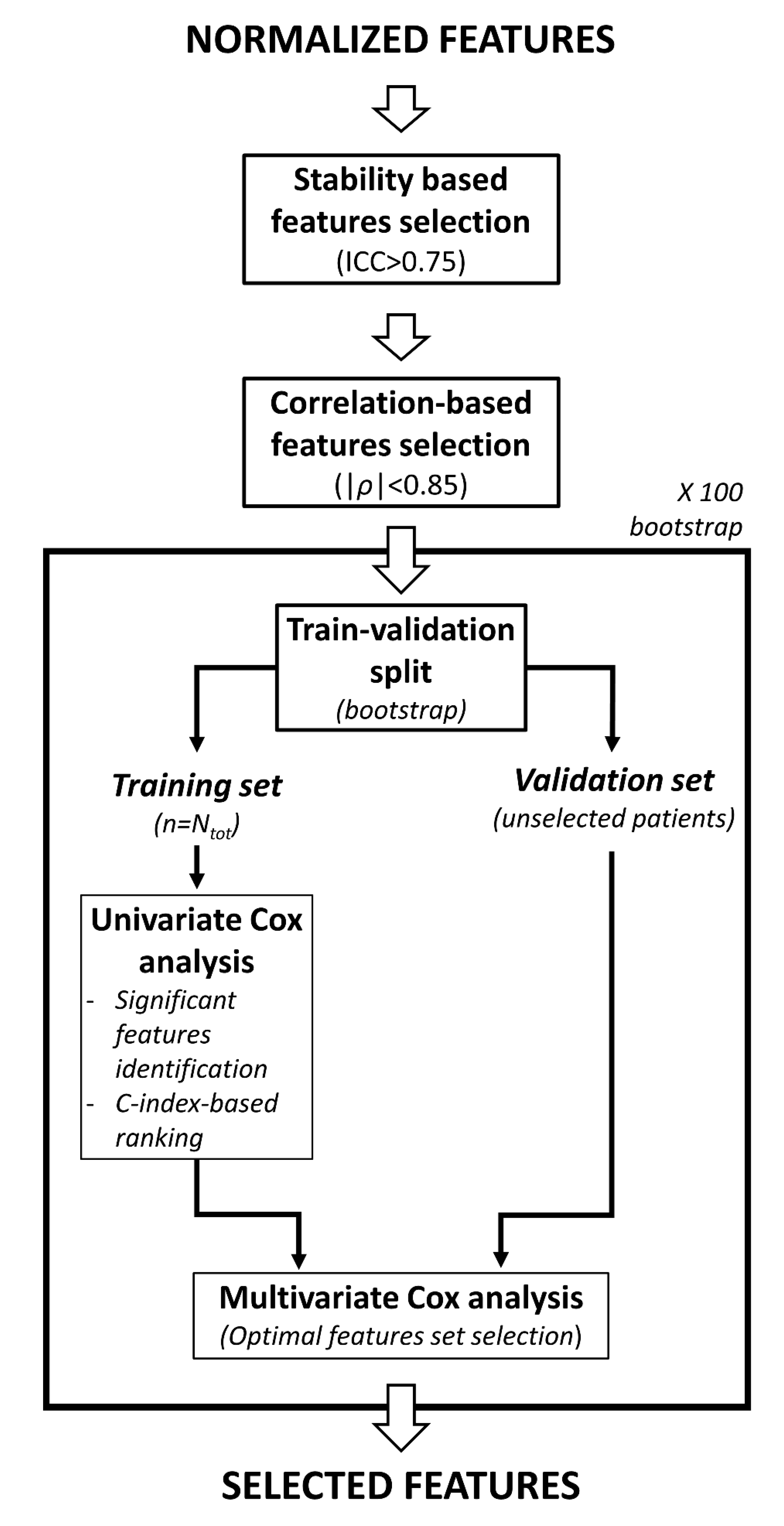
2.2. Features Selection and Survival Models Training
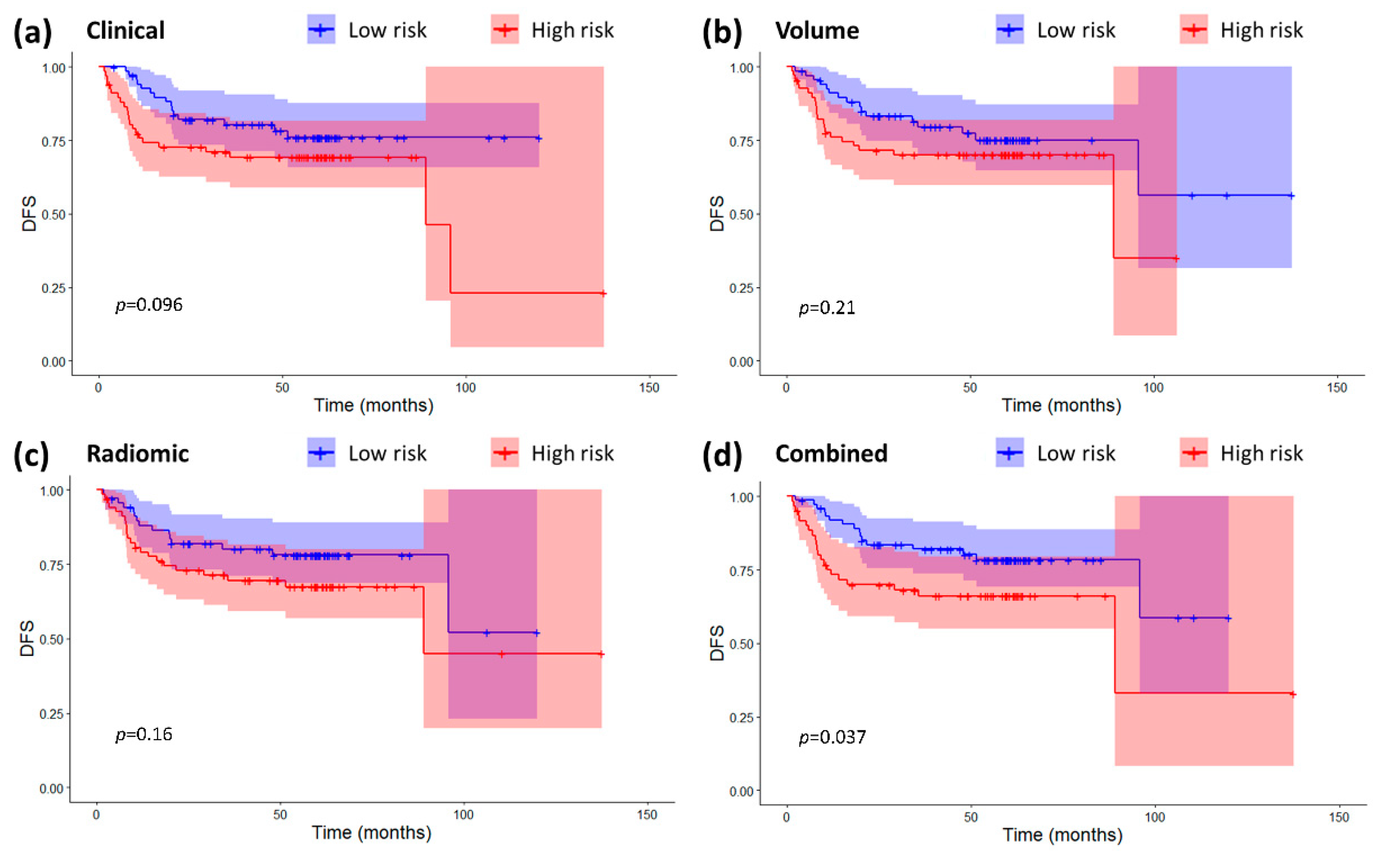
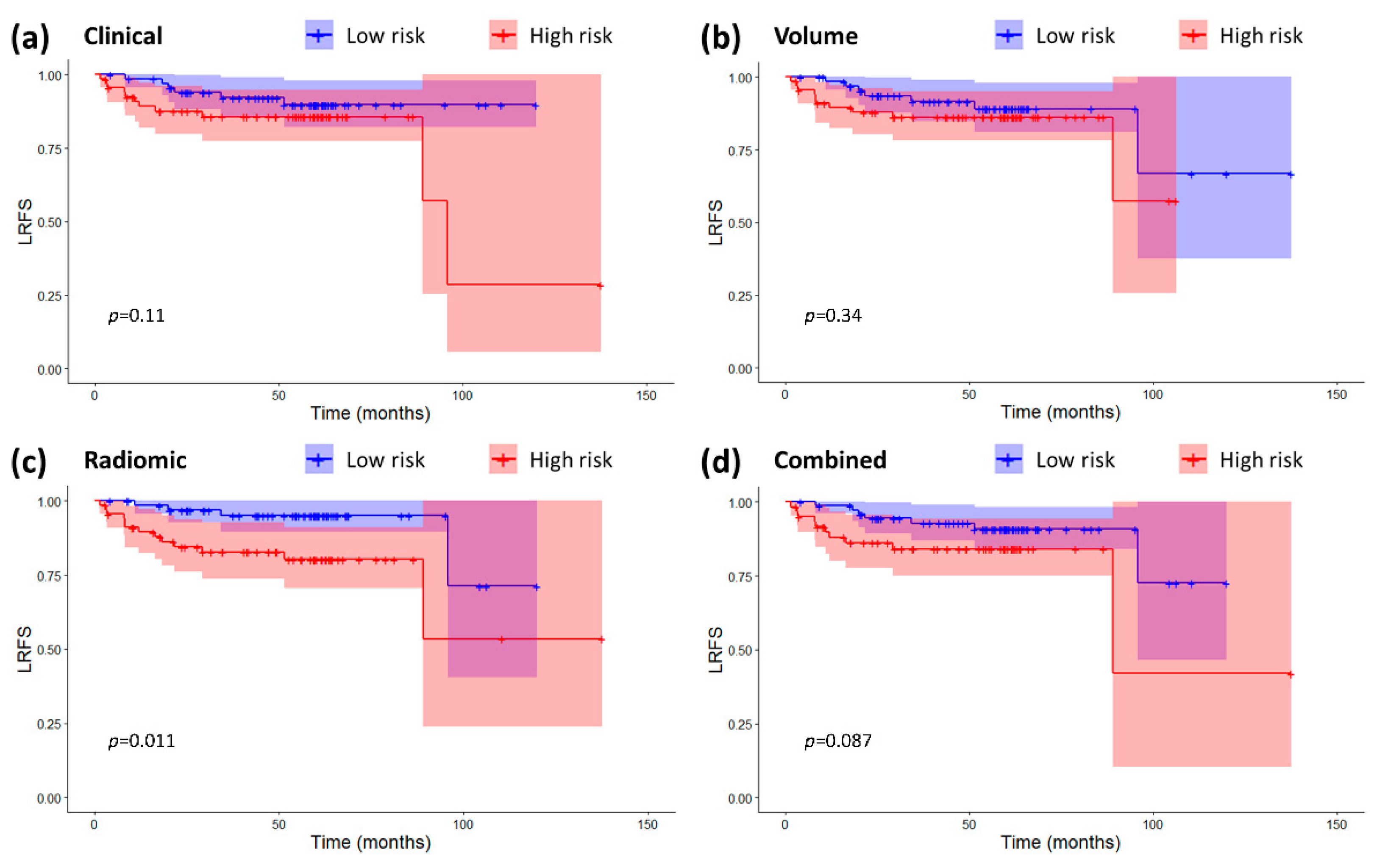
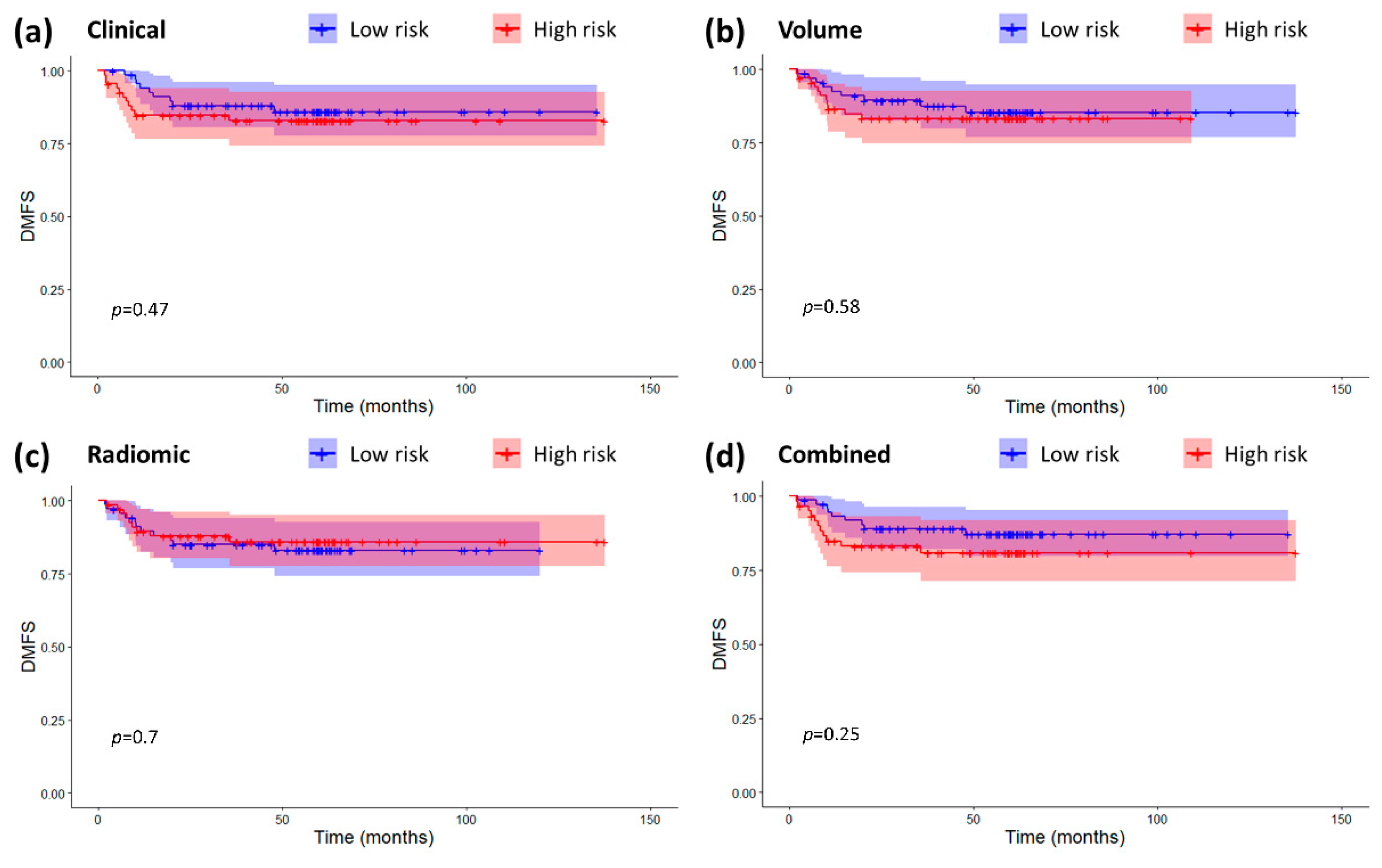
2.3. Models Validation and Comparison
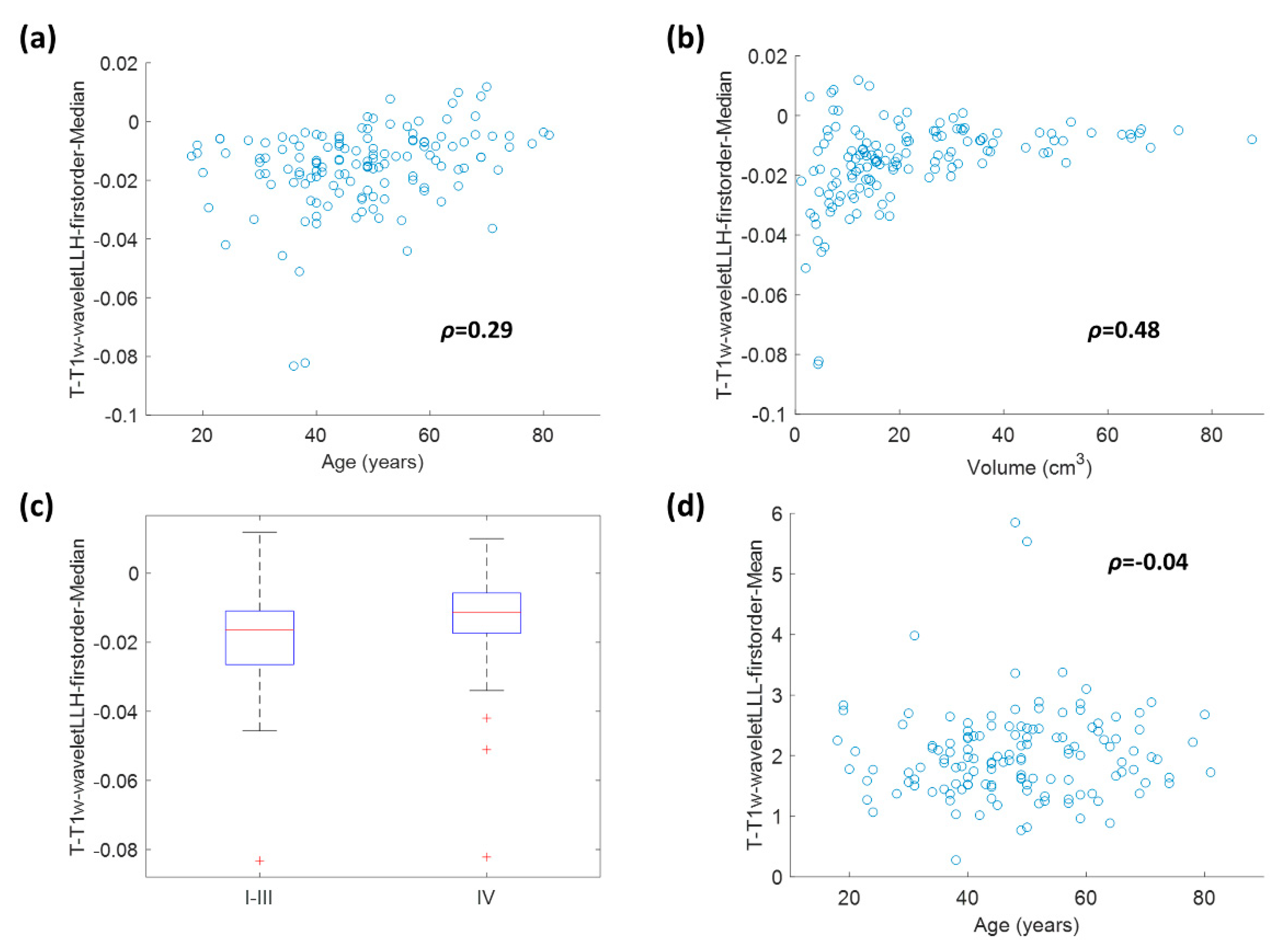
2.4. Correlation between Radiomic Features and Clinical/Volumetric Variables
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients Population
4.2. Treatment
4.3. Follow-up
4.4. MRI Acquisition
4.5. Image Segmentation
4.6. Image Preprocessing
4.7. Radiomic Features Extraction
4.8. Survival Endpoints
4.9. Radiomic Features Postprocessing and Radiomic Model Development
4.10. Volume-Based Model Development
4.11. Clinical Model Development
4.12. Combined Model Development
4.13. Models Validation and Comparison
4.14. Correlation between Radiomic Features and Clinical/Volumetric Variables
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, L.; Chen, W.; Xue, W.-Q.; He, Y.-Q.; Zheng, R.-S.; Zeng, Y.-X.; Jia, W.-H. Global trends in incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, P.; Grisanti, S.; Mohamad, I.; Linares Galiana, I.; Ozyar, E.; Franco, P.; Vecchio, S.; Livi, L.; Cirauqui Cirauqui, B.; El-Sherify, M.; et al. Survival and prognostic factors of nasopharyngeal cancer patients in non-endemic countries: A large multicentric database analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, M.; Orlandi, E.; Bossi, P.; Pignoli, E.; Potepan, P.; Guzzo, M.; Franceschini, M.; Scaramellini, G.; Cantù, G.; Licitra, L.; et al. Further Improvement in Outcomes of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma With Optimized Radiotherapy and Induction Plus Concomitant Chemotherapy: An Update of the Milan Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colevas, A.D.; Yom, S.S.; Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Adkins, D.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; Cmelak, A.J.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Head and Ne.ck cancers, version 1.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, L.; Qi, Z.; Zhou, G.; Guo, R.; Hu, J.; Lin, A.; Ma, J. Pretreatment Nomograms for Local and Regional Recurrence after Radical Radiation Therapy for Primary Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Straub, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D956–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Cavalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.L.; King, A.D. State of the art MRI in head and neck cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Oei, R.W.; Zhai, R.; Kong, F.; Du, C.; Hu, C.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ying, H.; Wang, J. MRI-based radiomics signature is a quantitative prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, J.; Xi, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, C.; Kang, X.; Yin, Y.; Qin, W.; Yin, H.; Shi, M. MRI-based radiomics nomogram may predict the response to induction chemotherapy and survival in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ouyang, F.; Gu, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L. Advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Pre-treatment prediction of progression based on multi-parametric MRI radiomics. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72457–72465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, J.; Dong, D.; Gu, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Pei, S.; et al. Radiomics features of multiparametric MRI as novel prognostic factors in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4259–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Huang, M.Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.H.; Gao, T.S.; Deng, B.; Yao, J.J.; Lin, L.; Chen, F.P.; Huang, X.D.; et al. Pretreatment MRI radiomics analysis allows for reliable prediction of local recurrence in non-metastatic T4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfieri, S.; Iacovelli, N.A.; Marceglia, S.; Lasorsa, I.; Resteghini, C.; Taverna, F.; Mazzocchi, A.; Orlandi, E.; Bianchi, R.; Fanti, D.; et al. Circulating pre-treatment Epstein-Barr virus DNA as prognostic factor in locally-advanced nasopharyngeal cancer in a non- endemic area. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47780–47789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Fang, J.; Duan, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, M.; Zhang, F.; Lu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Ding, Y.; et al. Predictive value of pretreatment MRI texture analysis in patients with primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogowicz, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Guckenberger, M.; Riesterer, O. Combined CT radiomics of primary tumor and metastatic lymph nodes improves prediction of loco-regional control in head and neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Van Dijk, L.V.; Huang, B.; Lin, Z.; Ribeiro, C.O.; Brouwer, C.L.; Oosting, S.F.; Halmos, G.B.; Witjes, M.J.H.; Langendijk, J.A.; et al. Improving the prediction of overall survival for head and neck cancer patients using image biomarkers in combination with clinical parameters. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, S.; Zwanenburg, A.; Pilz, K.; Lohaus, F.; Linge, A.; Zöphel, K.; Kotzerke, J.; Schreiber, A.; Tinhofer, I.; Budach, V.; et al. A comparative study of machine learning methods for time-To-event survival data for radiomics risk modelling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.Z.; Fang, X.L.; Dong, D.; Peng, H.; Fang, M.J.; Huang, C.L.; He, B.X.; Lin, L.; Ma, J.; Tang, L.L.; et al. A deep learning MR-based radiomic nomogram may predict survival for nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with stage T3N1M0. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotolo, F.; Pignon, J.P.; Bourhis, J.; Marguet, S.; Leclercq, J.; Tong Ng, W.; Ma, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Huang, P.Y.; Zhu, G.; et al. Surrogate end points for overall survival in loco-regionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An individual patient data meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.N.; Liang, S.B.; Zong, J.F.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y.P.; Tang, L.L.; Li, W.F.; Liu, X.; et al. Potential surrogate endpoints for overall survival in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An analysis of a phase III randomized trial. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Lu, J.J.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Hu, C.; He, S. Prognostic impact of primary Tumor volume in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated by definitive radiation therapy. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Wang, W.; Fan, Z.; Fu, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Lang, J. Tumor volume is an independent prognostic indicator of local control in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Su, Y.; Zeng, R.F.; Gu, M.F.; Huang, S.M. Prognostic value of tumor volume for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with concurrent chemotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovelli, N.A.; Cicchetti, A.; Cavallo, A.; Alfieri, S.; Locati, L.; Ivaldi, E.; Ingargiola, R.; Romanello, D.A.; Bossi, P.; Cavalieri, S.; et al. Role of IMRT/VMAT-Based Dose and Volume Parameters in Predicting 5-Year Local Control and Survival in Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020. In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Dong, A.; Ai, F.; Quan, T.; Cui, C.; Zhou, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Nodal grouping in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Prognostic significance, N classification, and a marker for the identification of candidates for induction chemotherapy. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, E.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, H.J.; Zhang, G.Y.; Jing, B.Z.; Zhou, J.; Cui, C.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; et al. Radiomics on multi-modalities MR sequences can subtype patients with non-metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) into distinct survival subgroups. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5590–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G.M. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): The TRIPOD statement. BMJ 2015, 350, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, D.; Li, H.; Tian, J.; Ouyang, F.; Mo, X.; Zhang, B.; Luo, X.; Lian, Z.; Pei, S.; et al. Development and validation of a magnetic resonance imaging-based model for the prediction of distant metastasis before initial treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, M.; Corino, V.D.A.; Montin, E.; Messina, A.; Calareso, G.; Greco, G.; Sdao, S. Assessment of Stability and Discrimination Capacity of Radiomic Features on Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Images. J. Digit. Imaging 2018, 31, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Leger, S.; Agolli, L.; Pilz, K.; Troost, E.G.C.; Richter, C.; Löck, S. Assessing robustness of radiomic features by image perturbation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Song, C.; Chang, W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J. Delta-radiomics signature predicts treatment outcomes after preoperative chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, iv24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, M.; Corino, V.; Tenconi, C.; Facchinetti, N.; Calareso, G.; Iacovelli, N.; Cavallo, A.; Alfieri, S.; Cavalieri, S.; Fallai, C.; et al. Methodology and technology for the development of a prognostic MRI-based radiomic model for the outcome of head and neck cancer patients. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 632–635. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Hahm, M.H.; Bae, B.K.; Chong, G.O.; Jeong, S.Y.; Na, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.C. Magnetic resonance imaging features of tumor and lymph node to predict clinical outcome in node-positive cervical cancer: A retrospective analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, F.C.H.; Tham, I.W.K.; Earnest, A.; Lee, K.M.; Lu, J.J. Patterns of regional lymph node metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis of clinical evidence. BMC Cancer 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, E.; Tomatis, S.; Potepan, P.; Bossi, P.; Mongioj, V.; Carrara, M.; Palazzi, M.; Franceschini, M.; Bergamini, C.; Locati, L.; et al. Critical analysis of locoregional failures following intensity-modulated radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Futur. Oncol. 2013, 9, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, N.J.; Cook, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijenaar, R.T.; Bogowicz, M.; Jochems, A.; Hoebers, F.J.; Wesseling, F.W.; Huang, S.H.; Chan, B.; Waldron, J.N.; O’Sullivan, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Development and validation of a radiomic signature to predict HPV (p16) status from standard CT imaging: A multicenter study. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, S.; Halle, M.; Kikinis, R. 3D Slicer. In Proceedings of the 2004 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Macro to Nano (IEEE Cat No. 04EX821), Arlington, VA, USA, 18 April 2004; pp. 632–635. [Google Scholar]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts. Hugo, J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Leger, S.; Vallières, M.; Löck, S. Image biomarker standardization initiative. Radiology 2020, 295, 1–178. [Google Scholar]
- Pyradiomics Features Description. Available online: https://pyradiomics.readthedocs.io/en/2.1.0/features.html (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Bologna, M.; Corino, V.; Mainardi, L. Technical Note: Virtual phantom analyses for preprocessing evaluation and detection of a robust feature set for MRI-radiomics of the brain. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.R. Regression models and life tables. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1972, 34, 187–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E.; Kerry, L.L.; Mark, D.B. Tutorial in biostatistics multivariable prognostic models: Issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, M.L.; McIntosh, C.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Milosevic, M.F.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Huang, S.H.; Purdie, T.G.; O’Sullivan, B.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; et al. Vulnerabilities of radiomic signature development: The need for safeguards. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peto, R.; Peto, J. Asymptotically Efficient Rank Invariant Test Procedures. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1972, 135, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete samples. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 73, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PATIENTS CLINICAL DATA (N = 136) | |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (years) 1 | 48 (39–57) |
| Sex | Females: 41 (30%) Males: 95 (70%) |
| T stage (VIII edition) | T2: 77 (57%) T3–T4: 59 (43%) |
| N stage (VIII edition) | N1–N2: 69 (51%) N3: 67 (49%) |
| Overall TNM stage (VIII edition) | I–III: 50 (37%) IV: 86 (63%) |
| EBER positivity | Positive: 136 (100%) |
| EBV-DNA load | Positive: 122 (90%) Negative: 14 (10%) |
| Treatment | RT alone: 2 (1%) Concomitant CHT-RT: 43 (32%) Induction CHT + concomitant CHT-RT: 91 (67%) |
| MRI ACQUISITION PARAMETERS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Image Type | T1-Weighted | T2-Weighted |
| MRI scanner | Siemens Magnetom Avanto 1.5 T: 133 Others 1.5 T: 3 | |
| Pulse sequence | Spin-echo | |
| Echo train length 1 | 3 (3–3) | 13 (13–13) |
| Number of averaging 1 | 2 (2–2) | 2 (2–2) |
| Time of repetition (ms) 1 | 524 (477–588) | 4670 (3230–5300) |
| Time of echo (ms) 1 | 12 (12–12) | 109 (107–109) |
| Slice thickness (mm) 1 | 3 (3–3) | 3 (3–3) |
| Slice spacing (mm) 1 | 3.9 (3.9–3.9) | 3.9 (3.9–3.9) |
| Pixel spacing (mm) 1 | 0.57 (0.57–0.69) | 0.51 (0.49–0.57) |
| Flip angle (°) 1 | 127 (127–127) | 134 (134–134) |
| RF coil | Body | |
| RADIOMIC FEATURES STATISTICS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | T-T1w-WaveletLLH-Firstorder-Median | T-T1w-WaveletLLL-Firstorder-Mean |
| Mean (before/after normalization) | −0.015/0 | 2.006/0 |
| Standard deviation (before/after normalization) | 0.014/1 | 0.737/1 |
| Median (before/after normalization) | −0.013/0.151 | 1.940/−0.090 |
| Interquartile range (before/after normalization) | 0.014/1.016 | 0.841/1.141 |
| 10th percentile (before/after normalization) | −0.032/−1.209 | 1.260/−1.012 |
| 90th percentile (before/after normalization) | −0.003/0.918 | 2.743/1.000 |
| COX MODELS COEFFICIENT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature Name | Radiomic Model | Clinical Model | Combined Model | Volume Model |
| T-T1w-waveletLLH-firstorder-Median | 1.11 | - | 0.69 | - |
| T-T1w-waveletLLL- firstorder-Mean | −0.75 | - | −0.45 | - |
| Tumor volume 1 | - | - | - | 9.75 × 10−6 |
| Age 2 | - | 0.07 | 0.05 | - |
| Overall stage (VIII edition) | - | 1.48 | 1.27 | - |
| Threshold for high risk | 0.29 | 4.29 | 3.23 | 0.16 |
| Baseline Cumulative hazard (60 months) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.14 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bologna, M.; Corino, V.; Calareso, G.; Tenconi, C.; Alfieri, S.; Iacovelli, N.A.; Cavallo, A.; Cavalieri, S.; Locati, L.; Bossi, P.; et al. Baseline MRI-Radiomics Can Predict Overall Survival in Non-Endemic EBV-Related Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102958
Bologna M, Corino V, Calareso G, Tenconi C, Alfieri S, Iacovelli NA, Cavallo A, Cavalieri S, Locati L, Bossi P, et al. Baseline MRI-Radiomics Can Predict Overall Survival in Non-Endemic EBV-Related Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancers. 2020; 12(10):2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102958
Chicago/Turabian StyleBologna, Marco, Valentina Corino, Giuseppina Calareso, Chiara Tenconi, Salvatore Alfieri, Nicola Alessandro Iacovelli, Anna Cavallo, Stefano Cavalieri, Laura Locati, Paolo Bossi, and et al. 2020. "Baseline MRI-Radiomics Can Predict Overall Survival in Non-Endemic EBV-Related Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients" Cancers 12, no. 10: 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102958
APA StyleBologna, M., Corino, V., Calareso, G., Tenconi, C., Alfieri, S., Iacovelli, N. A., Cavallo, A., Cavalieri, S., Locati, L., Bossi, P., Romanello, D. A., Ingargiola, R., Rancati, T., Pignoli, E., Sdao, S., Pecorilla, M., Facchinetti, N., Trama, A., Licitra, L., ... Orlandi, E. (2020). Baseline MRI-Radiomics Can Predict Overall Survival in Non-Endemic EBV-Related Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancers, 12(10), 2958. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102958







