Combination of Decitabine and Entinostat Synergistically Inhibits Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells via Activation of FoxO1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
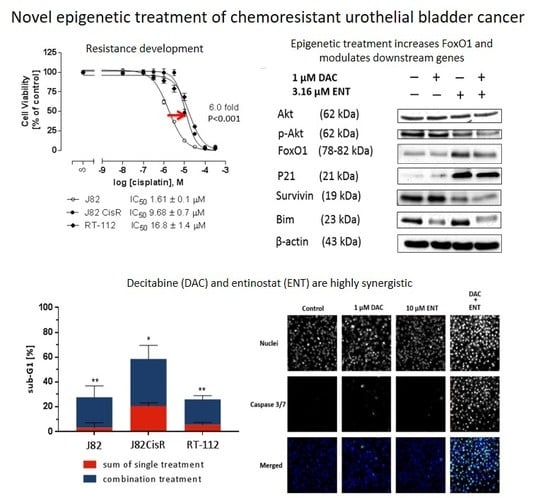
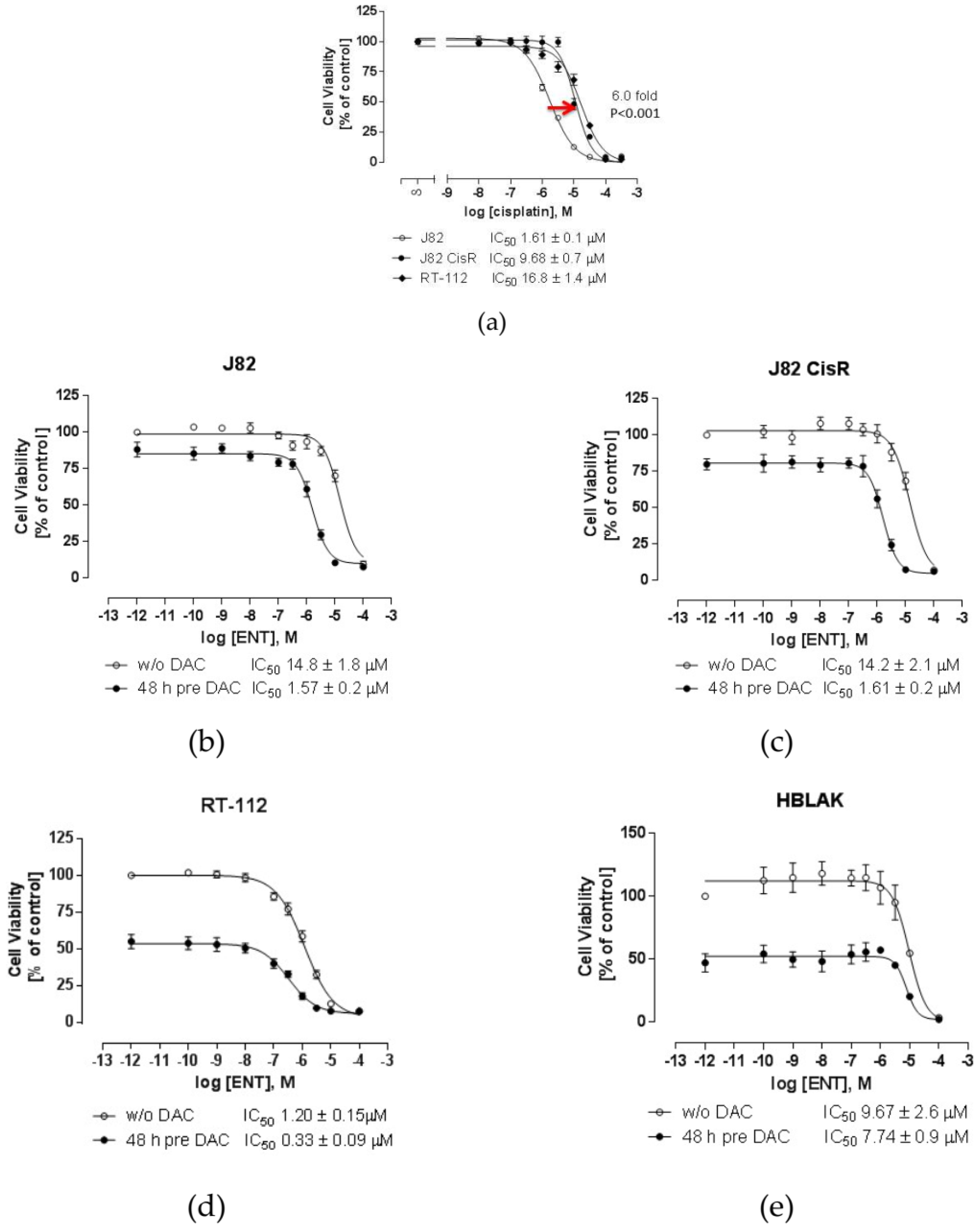
2.1. Combining DNMTi and HDACi Induces Synergistic Cytotoxicity in Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cell Lines
2.2. Combination Treatment of DAC and ENT Induces Apoptosis in Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells Mediated by the Activation of Caspase 3/7
2.3. DAC Combined with ENT Affects the Cell Cycle Distribution in Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells
2.4. DAC and ENT Alter RNA- and Protein-Expression and Protein Phosphorylation of Genes Involved in the Akt/FoxO Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Synergistic Study
4.5. Apoptosis Assay
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Caspase 3/7 Activation
4.8. Total RNA Extraction and RNA-seq Analysis
4.9. Analysis of RNA-Seq Data
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer Stat Facts: Bladder Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Bellmunt, J.; Orsola, A.; Leow, J.J.; Wiegel, T.; De Santis, M.; Horwich, A. Bladder cancer: ESMO Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iii40–iii48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, F.; Sternberg, C.N. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2009, 55, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafi, F.A.; North, S.; Kassouf, W. First- and second-line therapy for metastatic urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Curr Oncol. 2011, 18, e25–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, D.W.; Pouliot, L.M.; Hall, M.D.; Gottesman, M.M. Cisplatin resistance: A cellular self-defense mechanism resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddik, Z.H. Cisplatin: Mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7265–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.A.; Baylin, S.B. The epigenomics of cancer. Cell 2007, 128, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, W.A.; Koutsogiannouli, E.A.; Niegisch, G.; Hoffmann, M.J. Epigenetics of urothelial carcinoma. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1238, 183–215. [Google Scholar]
- Baylin, S.B. DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A.; Issa, J.P.; Baylin, S. Targeting the cancer epigenome for therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.S.; Jones, P.A. Cancer genetics and epigenetics: Two sides of the same coin? Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chueh, A.C.; Tse, J.W.; Togel, L.; Mariadason, J.M. Mechanisms of histone deacetylase inhibitor-regulated gene expression in cancer cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Ruijter, A.J.; van Gennip, A.H.; Caron, H.N.; Kemp, S.; van Kuilenburg, A.B. Histone deacetylases (HDACs): Characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montezuma, D.; Henrique, R.M.; Jeronimo, C. Altered expression of histone deacetylases in cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2015, 20, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niegisch, G.; Knievel, J.; Koch, A.; Hader, C.; Fischer, U.; Albers, P.; Schulz, W.A. Changes in histone deacetylase (HDAC) expression patterns and activity of HDAC inhibitors in urothelial cancers. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination therapy with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) for the treatment of cancer: Achieving the full therapeutic potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.F.; Ou, C.C.; Chien, P.J.; Chang, H.Y.; Ko, J.L.; Wang, B.Y. Chidamide-induced ROS accumulation and miR-129-3p-dependent cell cycle arrest in non-small lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, K.; Hamacher, A.; Hansen, F.K.; Gertzen, C.G.W.; Senger, J.; Marquardt, V.; Marek, L.; Marek, M.; Romier, C.; Remke, M.; et al. Alkoxyurea-Based Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Increase Cisplatin Potency in Chemoresistant Cancer Cell Lines. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5334–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, V.; Hamacher, A.; Gertzen, C.G.W.; Senger, J.; Zwinderman, M.R.H.; Marek, M.; Romier, C.; Dekker, F.J.; Kurz, T.; Jung, M.; et al. Design, Multicomponent Synthesis, and Anticancer Activity of a Focused Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Library with Peptoid-Based Cap Groups. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5493–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandolik, J.J.; Hamacher, A.; Schrenk, C.; Weishaupt, R.; Kassack, M.U. Class I-Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibition is Superior to pan-HDAC Inhibition in Modulating Cisplatin Potency in High Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pflieger, M.; Hamacher, A.; Oz, T.; Horstick-Muche, N.; Boesen, B.; Schrenk, C.; Kassack, M.U.; Kurz, T. Novel alpha,beta-unsaturated hydroxamic acid derivatives overcome cisplatin resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, e115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, N.; Choukrallah, M.A.; Matthias, P. Multiple roles of class I HDACs in proliferation, differentiation, and development. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaletsch, A.; Pinkerneil, M.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Jaguva Vasudevan, A.A.; Wang, C.; Hansen, F.K.; Wiek, C.; Hanenberg, H.; Gertzen, C.; Gohlke, H.; et al. Effects of novel HDAC inhibitors on urothelial carcinoma cells. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malempati, S.; Chang, B.H.; Reid, J.M.; Liu, X.; Minard, C.G.; Keller, C.; Fox, E.; Weigel, B. ADVL1513: Results of a phase 1 trial of entinostat, an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, in pediatric patients with recurrent or refractory solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Window of Opportunity Study of Pembrolizumab Alone and in Combinations in Bladder Cancer 2019. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03978624 (accessed on 9 November 2019).
- Gosepath, E.M.; Eckstein, N.; Hamacher, A.; Servan, K.; von Jonquieres, G.; Lage, H.; Gyorffy, B.; Royer, H.D.; Kassack, M.U. Acquired cisplatin resistance in the head-neck cancer cell line Cal27 is associated with decreased DKK1 expression and can partially be reversed by overexpression of DKK1. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.J.; Koutsogiannouli, E.; Skowron, M.A.; Pinkerneil, M.; Niegisch, G.; Brandt, A.; Stepanow, S.; Rieder, H.; Schulz, W.A. The new immortalized uroepithelial cell line HBLAK contains defined genetic aberrations typical of early stage urothelial tumors. Bladder Cancer. 2016, 2, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, T.-C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Laird, P.W. Interplay between the cancer genome and epigenome. Cell 2013, 153, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, C.B.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetic therapy of cancer: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.A.; Rifkind, R.A.; Richon, V.M.; Breslow, R.; Miller, T.; Kelly, W.K. Histone deacetylases and cancer: Causes and therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W.; Klisovic, R.B.; Hackanson, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Devine, H.; Vukosavljevic, T.; Huynh, L.; Lozanski, G.; Kefauver, C.; et al. Phase I study of decitabine alone or in combination with valproic acid in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3884–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juergens, R.A.; Wrangle, J.; Vendetti, F.P.; Murphy, S.C.; Zhao, M.; Coleman, B.; Sebree, R.; Rodgers, K.; Hooker, C.M.; Franco, N.; et al. Combination epigenetic therapy has efficacy in patients with refractory advanced non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, e598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najem, S.A.; Khawaja, G.; Hodroj, M.H.; Rizk, S. Synergistic effect of epigenetic inhibitors decitabine and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid on colorectal cancer in vitro. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Oda, Y.; Eguchi, T.; Aishima, S.; Yao, T.; Hosoi, F.; Basaki, Y.; Ono, M.; Kuwano, M.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Expression profile of class I histone deacetylases in human cancer tissues. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilley, J.; Coffer, P.J.; Ham, J. FOXO transcription factors directly activate bim gene expression and promote apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, N.; Hadden, T.J.; Rishi, A.K. Akt, FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papapetropoulos, A.; Fulton, D.; Mahboubi, K.; Kalb, R.G.; O’Connor, D.S.; Li, F.; Altieri, D.C.; Sessa, W.C. Angiopoietin-1 inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis via the Akt/survivin pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9102–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gohr, K.; Hamacher, A.; Engelke, L.H.; Kassack, M.U. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR overcomes cisplatin resistance in the triple negative breast cancer cell line HCC38. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, e711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, T.-C. The combination index (CI<1) as the definition of synergism and of synergy claims. Synergy 2018, 7, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Engelke, L.; Bickel, D.; Hamacher, A.; Frank, M.; Proksch, P.; Gohlke, H.; Kassack, M.U. The tetrahydroxanthone-dimer phomoxanthone A is a strong inducer of apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant solid cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, e115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, L.H.; Hamacher, A.; Proksch, P.; Kassack, M.U. Ellagic acid and resveratrol prevent the development of cisplatin resistance in the epithelial ovarian cancer cell line A2780. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Cell Lines | DAC | ENT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 [µM] | pIC50 ± SEM | IC50 [µM] | pIC50 ± SEM | |
| J82 | 30.5 | 4.52 ± 0.08 | 14.3 | 4.84 ± 0.06 |
| J82CisR | 28.2 | 4.55 ± 0.18 | 15.6 | 4.81 ± 0.06 |
| RT-112 | 0.22 | 6.65 ± 0.09 | 3.41 | 5.47 ± 0.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Hamacher, A.; Petzsch, P.; Köhrer, K.; Niegisch, G.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Schulz, W.A.; Kassack, M.U. Combination of Decitabine and Entinostat Synergistically Inhibits Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells via Activation of FoxO1. Cancers 2020, 12, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020337
Wang C, Hamacher A, Petzsch P, Köhrer K, Niegisch G, Hoffmann MJ, Schulz WA, Kassack MU. Combination of Decitabine and Entinostat Synergistically Inhibits Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells via Activation of FoxO1. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020337
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chenyin, Alexandra Hamacher, Patrick Petzsch, Karl Köhrer, Günter Niegisch, Michèle J. Hoffmann, Wolfgang A. Schulz, and Matthias U. Kassack. 2020. "Combination of Decitabine and Entinostat Synergistically Inhibits Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells via Activation of FoxO1" Cancers 12, no. 2: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020337
APA StyleWang, C., Hamacher, A., Petzsch, P., Köhrer, K., Niegisch, G., Hoffmann, M. J., Schulz, W. A., & Kassack, M. U. (2020). Combination of Decitabine and Entinostat Synergistically Inhibits Urothelial Bladder Cancer Cells via Activation of FoxO1. Cancers, 12(2), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020337