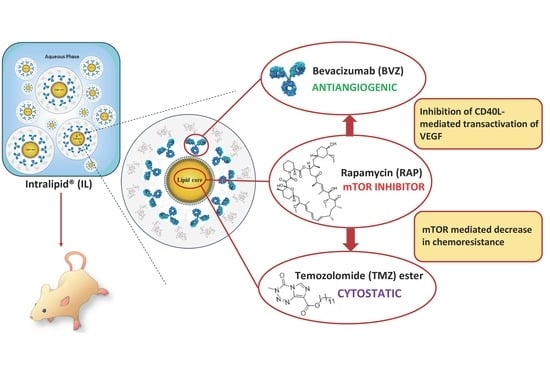
Nanoemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poly-Chemotherapy Aiming at Melanoma Treatment
Abstract
Share and Cite
Dianzani, C.; Monge, C.; Miglio, G.; Serpe, L.; Martina, K.; Cangemi, L.; Ferraris, C.; Mioletti, S.; Osella, S.; Gigliotti, C.L.; et al. Nanoemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poly-Chemotherapy Aiming at Melanoma Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051198
Dianzani C, Monge C, Miglio G, Serpe L, Martina K, Cangemi L, Ferraris C, Mioletti S, Osella S, Gigliotti CL, et al. Nanoemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poly-Chemotherapy Aiming at Melanoma Treatment. Cancers. 2020; 12(5):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051198
Chicago/Turabian StyleDianzani, Chiara, Chiara Monge, Gianluca Miglio, Loredana Serpe, Katia Martina, Luigi Cangemi, Chiara Ferraris, Silvia Mioletti, Sara Osella, Casimiro Luca Gigliotti, and et al. 2020. "Nanoemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poly-Chemotherapy Aiming at Melanoma Treatment" Cancers 12, no. 5: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051198
APA StyleDianzani, C., Monge, C., Miglio, G., Serpe, L., Martina, K., Cangemi, L., Ferraris, C., Mioletti, S., Osella, S., Gigliotti, C. L., Boggio, E., Clemente, N., Dianzani, U., & Battaglia, L. (2020). Nanoemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poly-Chemotherapy Aiming at Melanoma Treatment. Cancers, 12(5), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051198