Abstract
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer type among women, and morbidity and mortality rates are still very high. Despite new innovative therapeutic approaches for all BC molecular subtypes, the discovery of new molecular biomarkers involved in tumor progression has been fundamental for the implementation of personalized treatment strategies and improvement of patient management. Many experimental studies indicate that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are strongly involved in BC initiation, metastatic progression, and drug resistance. In particular, aberrant expression of HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) lncRNA plays an important role in BC contributing to its progression and represents a predictor of BC metastasis. For its proven prognostic value, HOTAIR could represent a potential therapeutic target in BC. In the present review, we summarize the role of HOTAIR in cancer progression and drug resistance, in particular in BC, and we illustrate the main approaches for silencing it.
1. Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most prevalent cancer type in women and a leading cause of cancer mortality in the world. Breast cancer is a very heterogeneous disease, and its histological classification is mainly based on the expression of hormonal receptors such as estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and ERBB2 receptor (HER2) [1]. With respect to gene expression, BC is classified into five molecular subtypes including luminal ER positive (luminal A and luminal B), HER2 enriched, basal-like (also known as triple-negative breast cancer), and normal breast-like subtype [2]. Currently, the choice of routine treatment strategy is based on various factors including tumor size, morphology, grade, metastases, and ER, PR, and HER2 expression [3]. In the last ten years, new innovative therapeutic approaches have been optimized, in particular for triple-negative breast cancer [4]. However, the identification of other prognostic/predictive markers is fundamental for implementing personalized treatment strategies in BC. In this context, our understanding of the mechanisms that regulate gene expression has focused on a class of non-coding RNA molecules (ncRNAs) which have aberrant activity that has largely been described in BC tumor progression [5].
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent a class of ncRNAs, longer than 200 nucleotides, involved in various aspects of cellular homeostasis, such as proliferation, apoptosis, mobility, gene transcription, and post-transcriptional processing [6,7,8]. They can be classified into different categories based on their genomic position, subcellular localization, and function [8]. Regarding their location in the genome, lncRNAs are classified into sense, antisense, bidirectional, and intergenic and intronic lncRNAs, while according to their subcellular location, lncRNAs are classified as nuclear lncRNAs and cytoplasmic lncRNAs. The identification of their precise cellular sub-localization is fundamental to understanding their cellular activity [9]. Long non-coding RNAs are essential epigenetic regulators of transcription functioning as: (i) molecular signals to regulate transcription in response to various stimuli [10]; (ii) decoys, modulating the transcription by sequestering regulatory factors and reducing their availability [11]; (iii) scaffolds, playing a structural role as platforms for the assembly of multiple-component complexes such as ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes [12]; (iv) enhancer RNAs, influencing the three-dimensional (3D) organization of DNA (chromatin interactions) [13]; (v) short peptides coders which may also interfere with transcription [14].
Long non-coding RNA’s role in cancer has been widely described, highlighting their capability to influence cell cycle regulation, cell proliferation, trans-differentiation, survival, immune response, metastatic progression, and therapeutic response [15]. Moreover, many lncRNAs are transcriptionally regulated by key tumor suppressors or oncogenes [16,17]. In cancer, lncRNAs are mainly involved in chromatin remodeling [18]. They can directly interact with many histone and DNA-modifying enzymes to participate in covalent modifications of histones or DNA. Furthermore, several lncRNAs have recently been found to be capable of modulating the non-covalent, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling process, indicating an extensive role of lncRNAs in chromatin regulation.
Being LncRNAs expressed in a specific manner in a type of cancer and regulating fundamental processes during tumor progression, they could represent not only exceptional diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive markers but also potential therapeutic targets. Many lncRNAs have been associated with BC, and most of them interfere with crucial processes during BC carcinogenesis [19,20].
In this review, we will discuss the role of the lncRNA HOTAIR in BC, highlighting in particular its contribution to tumor progression and drug resistance mechanisms and suggesting its potential use as therapeutic target.
2. LncRNAs in Breast Cancer
Long non-coding RNAs play a main role in BC tumor progression (Table 1). They are able of inducing the metastatic process by modulating cell proliferation, invasion, migration, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), and self-renewal capacity. Clinically, many lncRNAs are involved in therapeutic sensitivity, and they are becoming important circulating biomarkers [5,21,22].

Table 1.
Main lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs) involved in BC (breast cancer) progression.
Among the lncRNAs involved in BC evolution, H19 is one of the most studied. Its aberrant expression is associated with an increased risk of BC, both in human and cell models [23]. Moreover, its detection in plasma of BC patients also suggests its use as a circulating marker [24]. The expression level of H19 is associated with tumor size, lymph nodes status, and poor prognosis, especially in triple-negative BC (TNBC) [25]. Furthermore, the overexpression of H19 is able to induce chemotherapy resistance in BC cells and its silencing sensitizes BC endocrine therapy resistance (ETR) cells to tamoxifen and fulvestran treatment [26,27]. Long non-coding RNA XIST (X inactive specific transcript) is strongly associated with BC evolution, and it is able to suppress BC cell growth, migration, and invasion via the miR-155/CDX1 axis [28]. Aberrant expression of BCAR4 (breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 4) is mainly involved in acquiring BC tamoxifen resistance [29] in an independent manner of estrogen receptor I (ESRI) [30]. In addition, BCAR4 is able to promote metastasis through the interaction with chemokine CCL21 and its receptor CXCR7 in BC cell models [31]. Colon cancer-associated transcript 2 (CCAT2) is overexpressed, in particular, in TNBC cells, in which it is able to promote cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. In addition, aberrant expression of CCAT2 significantly induces stem-like characteristics in TNBC cells [32]. Urothelial carcinoma associated 1 (UCA1) is upregulated in tamoxifen-resistant BC cells [33], and its knockdown reduces cell survival and migration ability and promotes apoptosis of tamoxifen-resistant BC cells [34]. The role of lncRNA MALAT1 (metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1) in BC has been widely discussed. Many studies suggested its role as a metastasis-promoting marker [35], but other in vitro and xenograft studies have highlighted contradictory effects on BC tumor cells [36]. A recent genetic study has showed that MALAT1 is able to bind and inactive TEAD (TEA domain transcription factor 1), a pro-metastatic transcription factor, and consequently suppresses BC metastasis [37]. Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) is another lncRNA involved in breast gland development, and it has been associated with BC evolution. It is able to promote proliferation and progression in BC cells [38]. Nuclear enriched abundant transcript overexpression is associated with tumor size, histological grade, metastasis, and poor survival [39]. Most of the other lncRNAs described in the literature are mainly associated with therapeutic resistance in BC. The upregulation of lncRNA-ATB (long non-coding RNA activated by TGF-Beta) [40], TINCR (Tissue differentiation-inducing non-protein coding RNA) [41], UCA1 [42], AGAP2-ASI (Arf GAP with GTP-binding protein-like domain, Ankyrin repeat, and PH domain 2) [43], and the downregulation of GAS5 (growth arrest-specific 5) [44] are strongly involved in acquiring trastuzumab resistance in BC patients. The upregulation of BCAR4, UCA1, and CCAT2, as previously indicated, together with the aberrant expression of lncRNA-ROR (regulator of reprogramming) [45], lncRNA uc.57 [46], LINP1 (LncRNA in non-homologous end-joining pathway 1) [47], DSCAM-ASI (Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule-antisense RNA 1) [48], ADAMTS9-AS2 (ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin Type 1 motif 9-antisense RNA 2) [49], CyTOR (cytoskeleton regulator RNA) [50], and the downregulation of GAS5 [51] are involved in the promotion resistance mechanisms of tamoxifen and chemotherapy [34].
3. LncRNA HOTAIR and Its Role in Cancer
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is an lncRNA 2158 bp long, consisting of 6 exones, located on chromosome 12q13.13 between HOXC11 and HOXC12 genes [52]. Its promoter contains binding sites for many transcription factors, such as AP1, Sp1, ERE elements, HRE elements, and NF-kB [53]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is a key regulator of chromatin status and a mediator of transcriptional silencing [53]. Early studies showed that HOTAIR is capable to bind the PRC2 (Polycomb repressive complex) at the 5′ end [52]. The formation of the molecular complex is able to maintain cell stemness and suppress cell differentiation by trimethylation of the H3K27 histone complex and subsequent transcriptional repression of differentiation genes [53]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is also able to interact at the 3′ end with the lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (LSD1), another chromatin modifier which is critical for gene silencing [54]. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (LSD1) can form a multiprotein complex via activation of RE1-silencing transcription factor (REST) and CoREST which are critical players in gene silencing [54]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) acts as a molecular scaffold for the conjunction of the two complexes. The HOTAIR-PRC2-LSD1 complex leads epigenetic changes contributing to the targeted gene silencing and represses their transcription via H3K27 trimethylation (PRC2 activity) and H3K4 demethylation (LSD1 activity). For example, the HOTAIR-PRC2-LSD1 complex can be redirected towards the 5′ end of the HOXD locus on chromosome 2 where the genes, implicated in metastatic suppression are silenced by methylation and demethylation of H3K27 and H3K4, respectively [52,55].
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) can also alter gene expression both at the post-transcriptional level, either by base pairing with translation factors or ribosomes to control translation or by binding to splicing factors to modulate splicing, and at the post-translational level. For this last function, it is reported that HOTAIR could serve as a ubiquitination protein and subsequent degradation platform [56].
Most lncRNAs possess miRNA recognition elements (MREs), suggesting that the transcription of some miRNAs is regulated by lncRNAs and some lncRNAs are involved in synthesis, maturation, and degradation of miRNAs [57]. Many studies reported the interaction between HOTAIR and microRNAs highlighting that these interactions are able to modulate different cellular processes [58,59].
During embryogenesis, HOTAIR is involved in the development of the lumbosacral region, and its activity is closely linked to the recruitment of PRC2 to its targeted HOX D genes for their repression [52].
Several studies have pointed out the role of HOTAIR as a cell cycle-associated gene. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) promotes the cell cycle passing through the restriction point during the G1 phase by regulating CDK4/6-cyclin D and the Rb-E2F pathway [60].
In the last ten years, the aberrant HOTAIR expression in the majority of solid cancers has been reported, underlining its main role in modulating tumor initiation, growth, angiogenesis, progression, recurrence, drug resistance, and poor prognosis [53,61,62]. In urological cancers, HOTAIR overexpression is able to increase prostate cancer cells growth and invasion by binding androgen receptor (AR) protein and blocking its degradation [63]. In bladder cancer patients, HOTAIR is an independent prognostic factor of tumor recurrence [64]. It is also involved in chemo sensitivity to doxorubicin [65] and can be detected in the urine of bladder cancer patients [66]. In gynecological tumors, HOTAIR is overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer tissues and correlates with International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage, histological grade of the tumor, lymph node metastases, and poor survival [67]. In cervical cancer tissues, HOTAIR is associated with clinical-pathological features, lymph node metastases, and prognosis [68]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is also able to interact with different mRNAs in cervical cancer cells modulating cell growth and proliferation [69]. Moreover, the detection of circulating levels of HOTAIR is strongly associated with advanced tumor disease, lymph nodes metastases, and poor survival in cervical cancer patients [70]. Aberrant HOTAIR expression in endometrial carcinoma correlates with grade, lymph nodes metastases, and poor prognosis [71], and it is associated with cisplatin resistance acquisition [72]. In gastrointestinal tract tumors, HOTAIR upregulation appears as an important marker in colorectal cancer [73] and gastric cancer [74], showing a strong relation with stage, lymph nodes, distant metastases, and worse survival. In gastric cancer, HOTAIR has been detected in patients’ plasma, and its circulating level is able to predict which patient can benefit from fluorouracil and platinum combination therapy [74]. In liver cancer, HOTAIR is overexpressed and strongly correlates with clinical-pathological features, and tumor progression [75]. In addition, HOTAIR silencing increases chemotherapy sensitivity to cisplatin and doxorubicin hepatocellular carcinoma patients [76]. In oral cancers, HOTAIR overexpression has been described in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) and is associated with histopathological grade and stage [77]. Also, in LSCC cells, HOTAIR is involved in the modulation of sensitivity to cisplatin [78]. In lung cancer, aberrant expression of HOTAIR correlates with advanced stage, lymph nodes metastases, and poor prognosis [79]. A higher HOTAIR expression is also strongly associated with cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients [80]. Circulating HOTAIR has been detected in lung cancer plasma, and it appears to be associated with clinical-pathological features of the patients [81].
Many studies have highlighted the role of HOTAIR also in tumor microenvironment (TME) intracellular signaling. In TME, HOTAIR is able to modulate different molecular pathways involved in tumor phenotype modifications during metastatic progression [82].
4. HOTAIR’s Role in Breast Cancer
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) belongs to the first lncRNAs which have aberrant expressions that have been identified to associate with BC progression [61]. It is able to interact with the main molecular pathways involved in BC carcinogenesis. Estradiol can regulate HOTAIR expression in ER+ BC cells for the presence of several EREs elements in its promoter [83]. Estradiol agonists, bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol are able to stimulate HOTAIR expression in in vitro and in vivo BC models [84]. Moreover, both HOTAIR and breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) are able to bind the subunit of EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Subunit) coordinating the PRC-dependent epigenetic regulation of the chromosome [85]. Breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) is able to inhibit the binding of EZH2 to HOTAIR and its transfer on the promoter of PRC2 target gene HOXA9 in human BC cells and fibroblasts [85]. The promoter of the HOTAIR gene can also be bound by IRF1 (interferon regulatory factor-1) able to induce its inhibition in BC cells [86]. It is known that HOTAIR is also associated with an aberrant DNA methylation profile in cancer [87]. In BC, the combination of HOTAIR overexpression and methylation status represents an important predictor of poor prognosis [88,89].
4.1. HOTAIR’s Role in BC Metastatic Progression
Early studies highlighted the aberrant expression of HOTAIR in primary BC tumors with high metastatic potential and poor survival, suggesting HOTAIR as a powerful predictor of BC tumor progression [90]. Further studies have then proved contrasting results about the role of HOTAIR in prediction of metastatic risk in the different molecular subtypes of BC [91]. Some authors suggested that HOTAIR is an independent predictor of metastasis in ER+ patients but not in ER− BC patients [92]. On the contrary, other studies showed that the upregulation of HOTAIR can be considered a marker of metastatic progression only in ER− BC patients [91]. These latest data have also been confirmed by in vitro investigations pointing out aberrant expression of HOTAIR, in particular in basal-like BCs [93]. A recent study analyzed the in situ expression of HOTAIR in a large case series of TNBC patients and showed that high HOTAIR expression in tumor tissues is strongly correlated with lymph node metastasis, and it is directly associated with androgen receptor (AR) expression therefore potentially involved in the regulation of the AR pathway [94].
4.2. HOTAIR’s Role in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Many studies have demonstrated that HOTAIR is also a critical modulator of EMT in BC. The treatment of HCC1954 BC cells with TGF-B1 leads HOTAIR upregulation and modulates the EMT process. This condition is reversed by induced downregulation of HOTAIR with a consequent reduction in the ability to form colonies [95]. Recently, it was shown that Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are able to promote BC metastasis via paracrine TGF-B1. The CAF-conditioned media of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 BC cells strongly increases HOTAIR expression promoting EMT [96]. Autophagy is also strongly involved in the modulation of EMT. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR)-mediated autophagy could be a critical step in BC progression thanks to its ability to induce upregulation of metalloproteinases (MMPs) and B-catenin [83]. The modulation of the EMT process as well as the consequent induction of metastatic processes is also strongly influenced by the activity of a series of microRNAs, especially in BC. The downregulation of miR-7 in BC patients is strongly associated with BC cancer stem cells and correlates with HOTAIR expression. The knockdown of HOTAIR leads to miR7 upregulation and reverts EMT and BC cancer stem cells proliferation [97]. A recent study has highlighted that HOTAIR is able to induce BC evolution by increasing the Bclw gene, belonging to the B-cell lymphoma 2 (bcl-2) family, via sequestering miR-206 at the post-transcriptional level [58]. Moreover, HOTAIR is able to physically interact with the miR34 promoter to silence miR34a in cancer stem cells (CSCs) from BC cells [98]. Recently, Han et al. [59] showed that delphinidin, an anthocyanidin, is able to suppress BC progression by upregulating the miR34a inhibition of HOTAIR and suppressing EMT through the downregulation of MMPs and the beta-catenin signaling pathway.
4.3. HOTAIR’s Role as a Circulating Marker
The great diagnostic and prognostic potential of HOTAIR has also been supported by its detection in the blood of BC patients [99]. The circulating DNA level of HOTAIR from BC patients strongly correlates with the clinical stage, regardless of the molecular subtype [100]. Zhang et al. [101] showed that HOTAIR expression, analyzed in 148 plasma samples from BC patients, significantly correlates with ER and HER2 expression and with lymph node metastasis. In post-operative BC patients, a substantial reduction of its circulating level has been described [101]. More recently, Tang et al. [102] showed that serum exosomal HOTAIR is a potent predictor of poor survival and drug response in BC patients, regardless of the molecular subtype [102].
5. HOTAIR in Breast Cancer Therapeutic Resistance
One of the main problems in breast cancer therapy is the establishment of an intrinsic or acquired resistance to treatment. Resistance to anti-tumor therapies can be linked to a variety of different factors such as genetic mutations, increased drug efflux, tumor heterogeneity, altered crosstalk between tumor cells and environmental factors or epigenetic changes related to the aberrant activity of many ncRNAs [103,104,105,106,107,108,109]. However, the knowledge of the mechanisms of resistance to the routine therapeutic agents in BC remains widely unknown. Long non coding RNA (LncRNAs) seem to be largely involved in drug responses for their ability to modulate the expression pattern of many oncogenes and oncosuppressor genes [110,111,112,113,114]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) aberrant expression has been widely described as a marker of drug resistance in different solid tumors [61,115]. It can be involved in different resistance mechanisms related to the main routine treatments including radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and target therapies.
5.1. Radiotherapy Resistance
In cervical cancers, HOTAIR overexpression is able to induce radio-resistance via inhibiting p21, and its knockdown, by upregulating p21, increases the radio-sensitivity of cervical cancer cells [116]. Moreover, HOTAIR silencing is able to increase radio sensitivity and influence autophagy in prostate cancer cells [117]. Radiotherapy is the leading therapeutic strategy for inoperable and locally advanced breast cancers. Zhou et al. [118] investigated HOTAIR gene expression in five breast cancer tumor cell lines showing that the upregulation of HOTAIR in MDA-MB231 cells accelerates cell proliferation and enhances the resistance to radiotherapy.
To investigate the mechanism controlling HOTAIR induced radio-resistance, the expression of HOXD10, the translation of which is repressed by HOTAIR [52] contributing to the acquisition of metastatic phenotypes, was analyzed. For the same purpose, the expressions of pBAD (Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death) involved in apoptotic pathway, and pAKT, involved in the cell proliferation pathway, were evaluated. The results showed that HOTAIR promotes the proliferation of BC cells during radiation therapy by targeting HOXD10 and the PI3K/AKT-BAD pathway [118].
Lately, it has been described that the expression of HOTAIR increases following ionizing radiation treatment. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) knockdown results in slower proliferation of BC cells, DNA damage accumulation, cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase, and an increase in radiation-induced cell apoptosis. The radiosensitizing effects of HOTAIR silencing are related to the recruitment of miR-218, a ceRNA of HOTAIR, involved in repairing radiation-induced DNA damage and in apoptosis [119] (Figure 1).
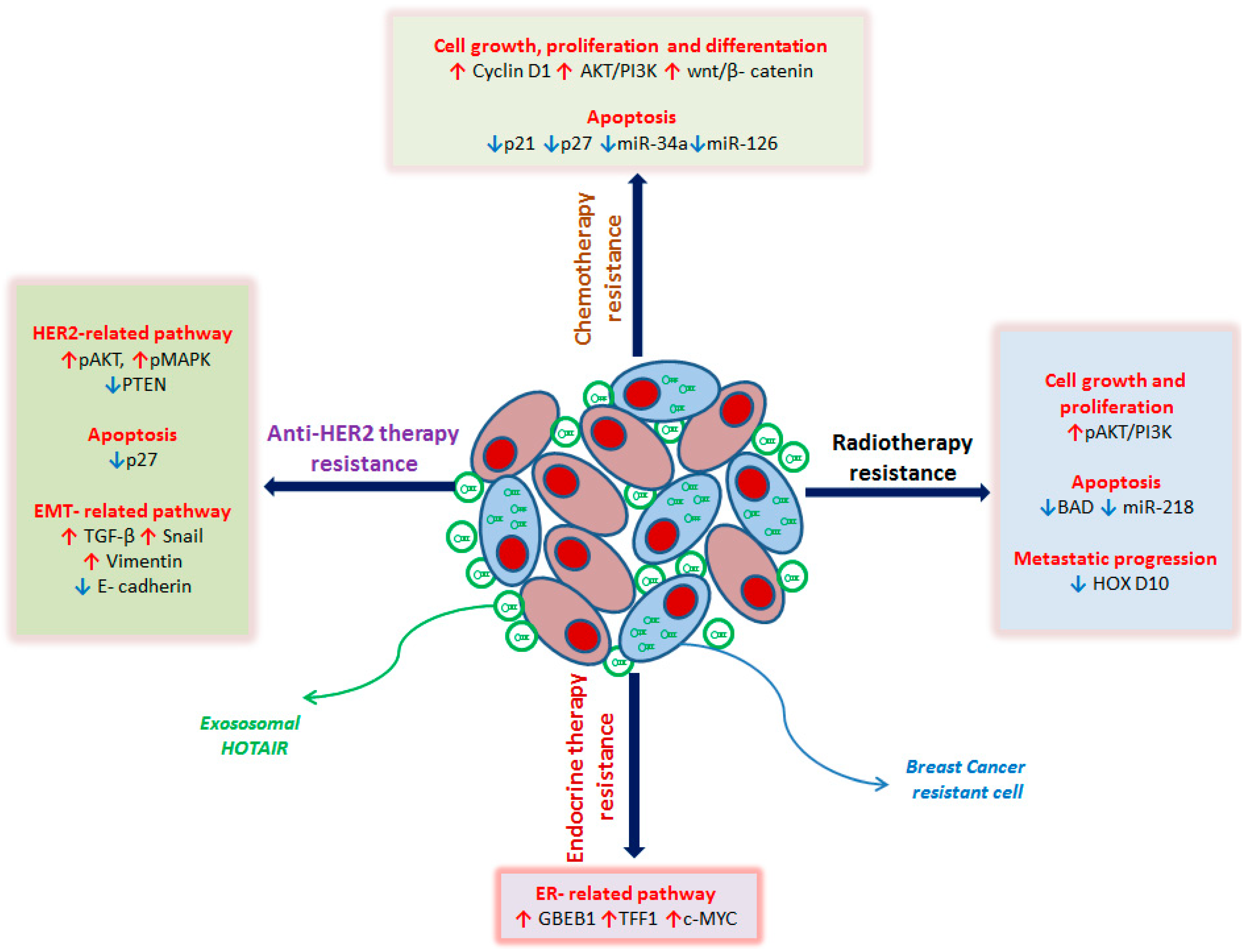
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of HOTAIR role in breast cancer (BC) drug resistance mechanisms with details of the main molecular pathways involved. In anti-HER2 treatment-resistant BC cells, the overexpression of HOTAIR leads to: (i) deregulation of HER2-related genes by upregulating the signal transduction pathway PI3K-Akt and downregulating the tumor suppressor gene PTEN with the consequent increase in proliferation, cell growth, and survival; (ii) inhibition of apoptosis by the downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27; (iii) induction of EMT by TGF-β, Snail and Vimentin upregulation, and decrease in E-cadherin expression. In endocrine therapy resistant BC cells, the overexpression of HOTAIR leads to the repression of ER and the activation of ER-responsive genes, such as GREB1, TFF1, and c-MYC, promoting cell proliferation. In BC radio-resistant cells, the overexpression of HOTAIR leads to: (i) promotion of cell growth and proliferation by upregulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway; (ii) blockage of apoptosis by downregulating the pro-apoptosis gene BAD and miR-218, normally involved in the repair of radiation-induced DNA damage; (iii) induction of metastatic spread by silencing of HOXD10, a metastasis suppressor gene. In chemo-resistant BC cells, the overexpression of HOTAIR leads to: (i) promotion of cell growth, differentiation, and proliferation by upregulating Cyclin D1, the PI3K-Akt pathway, and the wnt/β-catenin pathway; (ii) inhibition of apoptosis by downregulating cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27, miR-34a and miR-216, both involved in promoting programmed cell death. The red arrows indicate the upregulated genes, the blue arrows the downregulated genes. HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinases, Akt: protein kinase B, PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog, TGF-beta: Transforming growth factor beta 1, EMT: epithelial–mesenchymal transition, ER: Estrogen Receptor, GREB1: Growth Regulating Estrogen Receptor Binding 1, TFF1: Transcription Termination Factor 1, c-MYC: myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog, BAD: BCL2 antagonist of cell death, HOXD10: Homeobox D10.
5.2. Endocrine Therapy Resistance
The antagonist of the estrogen receptor Tamoxifen is the most commonly used drug for ER+ BC patients, but the acquired resistance to the treatment represents the most important limitation for its use [120]. Xue et al. showed that 37 lncRNA genes are repressed by estrogen and up regulated in tamoxifen-resistant MCF7 cells. HOTAIR is the main upregulated lncRNA in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and it is able to interact with ER, repressing it, but enhancing its transcriptional activity also in the absence of ligand. HOTAIR overexpression is able to induce ER-target gene expression such as GREB1, TFF1 and c-MYC in the absence of estrogen.
Knockdown of HOTAIR strongly decreases tamoxifen-resistant MCF7 cell growth and inhibits the colony-formation abilities. These data suggest that HOTAIR is involved in tamoxifen-resistant cell growth and that this drug resistance may be reverted by targeting HOTAIR [121] (Figure 1).
Aromatase Inhibitors (AI) act blocking the enzyme aromatase, involved in the biosynthesis of estrogen reducing the growth of hormone-receptor-positive BC cells. AI are mainly used in postmenopausal women in whom it has better therapeutic effects than tamoxifen [122].
Preliminary data performed on a large series of hormone receptor-positive early BC patients treated with AI, directly or after tamoxifen switch, showed that HOTAIR overexpression strongly correlates with clinic-pathological parameters, survival and AI resistance [123].
5.3. Anti-HER2 Therapy Resistance
Trastuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binding HER2 receptor suppresses the formation of HER2 dimer interfering with downstream signaling pathways and promotes the inhibition of cell proliferation and apoptosis [122]. Resistance to trastuzumab is one of most clinic issues for HER2+ BC patients [124]. A more recent study has showed that, in trastuzumab-resistant BC cell line, HOTAIR is overexpressed. In these cells, HOTAIR promotes the transition of tumor cells from G1 phase to S phase and inhibits the apoptosis.
To define the molecular mechanisms underlying the trastuzumab resistance mediated by HOTAIR, HER2 receptor signaling pathway related, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MEK/MAPK, have been analyzed in the sensitive and resistant BC cells. In resistant cells, HOTAIR overexpression is associated with the upregulation of p-AKT, p-MAPK and CyclinD1 and with the downregulation of tumor suppressor gene PTEN and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor P27, involved in the block of G1/S-phase transition. This leads to an increase in the cell growth, proliferation, survival and apoptosis.
The knockdown of HOTAIR leads to the downregulation of p-AKT, p-MAPK and CyclinD1, and upregulation of PTEN and P27. This silencing is able to sensitize BC cells to trastuzumab blocking cell division at G0/G1 phases and promoting apoptosis.
Moreover, in the resistant cells, the transcription and translation of TGF-β, Snail and Vimentin are up regulated while E-cadherin is downregulated, promoting EMT. HOTAIR silencing reverts these results [125] (Figure 1).
5.4. Chemotherapy Resistance
Cytotoxic chemotherapy is largely used in routine therapeutic schemes both in advanced and early BC stages [122]. In particular, anthracyclines (mainly epirubicin and doxorubicin) are considered standard adjuvant therapy for patients with high-risk early BC [126]. Along with anthracyclines, which are extremely cardiotoxic, taxanes (mainly docetaxel and paclitaxel) are the most active cytotoxic drugs in BC. [127]. Furthermore, fluorine derivatives (5-fluorouracil and capecitabine), methotrexate, vinorelbine, gemcitabine, and platinum derivatives (mainly cisplatin and carboplatin) represent the therapeutic alternatives for BC patients, alone or in combination with other drugs [128].
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) has been described as being involved in doxorubicin resistance in gastric and bladder cancer [65,129], in taxanes resistance in gastric cancer (GC) and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma [129,130], and in 5-fluoruracil resistance in GC and colorectal cancer [74,131]. Regarding platinum derivatives, HOTAIR is involved in modulating resistance to carboplatin in ovarian cancer [132]. In addition, many studies have shown that HOTAIR plays a key role in cisplatin resistance. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) upregulation can promote the resistance of lung cancer cells to cisplatin by downregulating p21, involved in the block of G1 and G2 cell cycle phases [80,133]. In ovarian cancer cells, HOTAIR induces cisplatin resistance by activating the wnt/β-catenin pathway, involved in key cellular functions including proliferation, differentiation, migration, genetic stability, apoptosis, and stem cell renewal. Pre-treatment with the wnt/β-catenin inhibitor, XAV939, and HOTAIR knockdown increases the sensitivity of cisplatin by inhibiting cisplatin-induced autophagy [134]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) overexpression is related with cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer [135,136] and in oral cancers [137]. In gastric cancers, HOTAIR-induced cisplatin resistance is mainly related with the activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathways via miR-34a and miR-126, both involved in the modulating the apoptotic process [135,136].
Despite the numerous contributions for other solid tumors, in BC, very few studies have been performed to verify the role of HOTAIR in cytotoxic chemotherapy resistance and are mainly aimed at defining the predictive value of its circulating levels. Tang et al. [102] analyzed circulating HOTAIR levels in the serum of 112 breast cancer patients before neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) treated with different cytotoxic drugs to evaluate its predictive value. The study showed that high circulating HOTAIR levels strongly correlate with poor response to NAC [138]. Furthermore, a recent study showed that serum exosomal HOTAIR levels in BC patients 3 months after surgery are significantly reduced compared to levels before surgery, and a high level correlated with poor neoadjuvant chemotherapy [102].
Many natural products derived from dietary sources can be used in BC treatment [139]. Delphinidin is one of the main anthocyanidins and has strong anti-cancer properties, and it is able to suppress tumor transformation in breast cancer cells [140]. Delphinidin is able to downregulate HOTAIR and simultaneously upregulate miR-34a, inducing apoptosis, in BC cells. Moreover, delphinidin treatment significantly decreases β-catenin, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (Gsk3β), c-Myc, cyclin-D1, and matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) expression. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) overexpression, in turn, can block the effect of delphinidin on the miR-34a and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells, suggesting that delphinidin may potentially suppress breast carcinogenesis through the HOTAIR/miR-34a axis [59] (Figure 1).
6. HOTAIR as Therapeutic Targets in Breast Cancer
In recent years, having been strongly validated the clinic-diagnostic capabilities of lncRNAs, many therapeutic strategies have been suggested for targeting lncRNAs [141]. Some lncRNAs have already been validated as potential therapeutic targets, with very encouraging results obtained on cell and animal models. The interference systems used can be of different types even if lncRNAs silencing strategies must necessarily take into account their cytoplasmic or nuclear sub-location [142,143,144]. For nuclear lncRNAs, the best approaches are represented by anti-sense-oligos (ASOs) targeting, while for knockout of cytoplasmic lncRNAs, the best results have been obtained with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). [145]. The ASOs are short (8–50 nt) single-stranded DNAs or RNAs designed considering target RNAs specific sequences. The ASOs are characterized by high stability and sensitivity and act by binding and degrading target RNAs. Ribonuclease (RNAse) H1 recognizes the DNA:RNA heteroduplex and cuts RNA molecules [146,147]. Several studies reported the use of the ASO approach in the silencing of lncRNAs in different tumors [148]. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are short (19–30 nt) double-stranded RNAs able to target RNA molecules via complementary to sequence. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) act through the association with RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) complex leading to argonaute mediated degradation as a result of perfect sequence similarity [149]. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can represent an easy method for both the design and synthesis and have high silencing efficiency against numerous lncRNAs. For this reason, it represents, together with ASOs, the most used method in functional studies to validate lncRNAs’ role in cancer [150]. However, other strategies could be developed to block lncRNA activity: (i) Aptamers are short DNA or RNA oligonucleotides or peptides with a stable three-dimensional structures. Integration of aptamers into cancer cell genomes could produce functional aptamers able to target both nuclear and cytoplasmic lncRNAs [151]. (ii) Ribozymes are RNA molecules involved in intracellular catalytic functions, able to degrade different RNA molecules. They could be artificially synthesized to target lncRNAs [152]. (iii) Small molecules, such as tetracyclines or aminoglycosides that are able to degrade bacterial ribosomes, could be synthetically developed for lncRNAs targeting [153]. (iv) microRNAs’ induction to target lncRNAs could also be a valid strategy, having been largely demonstrated that microRNA-lncRNA interaction could inhibit lncRNAs function. The targeting strategy could be developed by analyzing the putative regulating microRNAs of the lncRNA to be silenced [154].
Regarding HOTAIR silencing, the most used experimental approach is siRNA, able to deplete HOTAIR molecules both at the cytoplasmic and nuclear level [155]. The first knockout studies of HOTAIR have been performed on BC cells [90]. Gupta et al. [90] examined the effects of manipulating HOTAIR levels in several breast cancer cell lines. In particular, its silencing by siRNAs in MCF7, a cell line that expresses endogenous HOTAIR, decreases its capacity to invade Matrigel, a basement-membrane-like extracellular matrix [90]. Knockout HOTAIR studies made it possible to validate the main role of HOTAIR in the modulation of cell proliferation, invasion, migration as well as in the apoptotic processes in BC models [58,83,156] (Figure 2). Bhan et al. [157] used a synthetic small interfering sense (siSENSE) oligonucleotide DNA complementary to HOTAIR transcript. The normal phosphodiester bonds of the HOTAIR-siSENSE DNA molecule were replaced with phosphorothioate linkage to minimize the nuclease digestion and enhance its in vivo stability. The HOTAIR siSENSE is able to silence specifically and effectively HOTAIR transcript levels in a dose-dependent manner. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) silencing leads to apoptosis in MCF7 BC cells though upregulation of Bcl2 and BAD expression. Moreover, HOTAIR knockdown induces upregulation of its target genes HOXD10 and PCDHB5 [157] (Figure 2). These data on MCF7 BC cells have been confirmed by the siRNA downregulation of HOTAIR or EZH2, a member of PRC2. This silencing is able to repress BC cells’ proliferation, invasion, and migration and, at the same time, to promote apoptosis [158]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) siRNA in MCF7 BC cells is also able to increase mRNA levels of the luminal markers such as GATA3, KRT8, and E-cadherin and to reduce the basal marker as VCAN (Figure 2). HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) expression in BC cells can be enhanced through prolonged and progressive exposure to TNF-α, a cytokine produced by the tumor microenvironment. The inhibition of p38 and SRC kinases, two mediators of the cell responses to TNF-α, can decrease HOTAIR expression and restore the expression of E-cadherin and KRT8 in MCF-7 cells [93]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) silencing in BC cells also shows a great impact on the modulation of EMT processes and in the self-renewal capacity of BC CSCs, being the majority of EMT/stemness genes regulated by HOTAIR (Figure 2). HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) silencing leads to a downregulation of TGF-β, Snail, Vimentin, p-AKT, p-APK, and CyclinD1 and an upregulation of E-cadherin, PTEN, and P27, causing the inhibition of EMT in BC cells [159]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) knockdown also leads to a strong reduction in colonosphere and mammosphere formation, suggesting its main role in the maintenance of the CSC phenotype in BC cell lines [95] (Figure 2). Deng et al. [98] further confirmed these observations though HOTAIR silencing with lentivirus LV-HOTAIRKD, highlighting a strong inhibition of proliferation, colony formation, migration, and self-renewal capacity of an enriched of CSCs MCF7 cell lines [98].
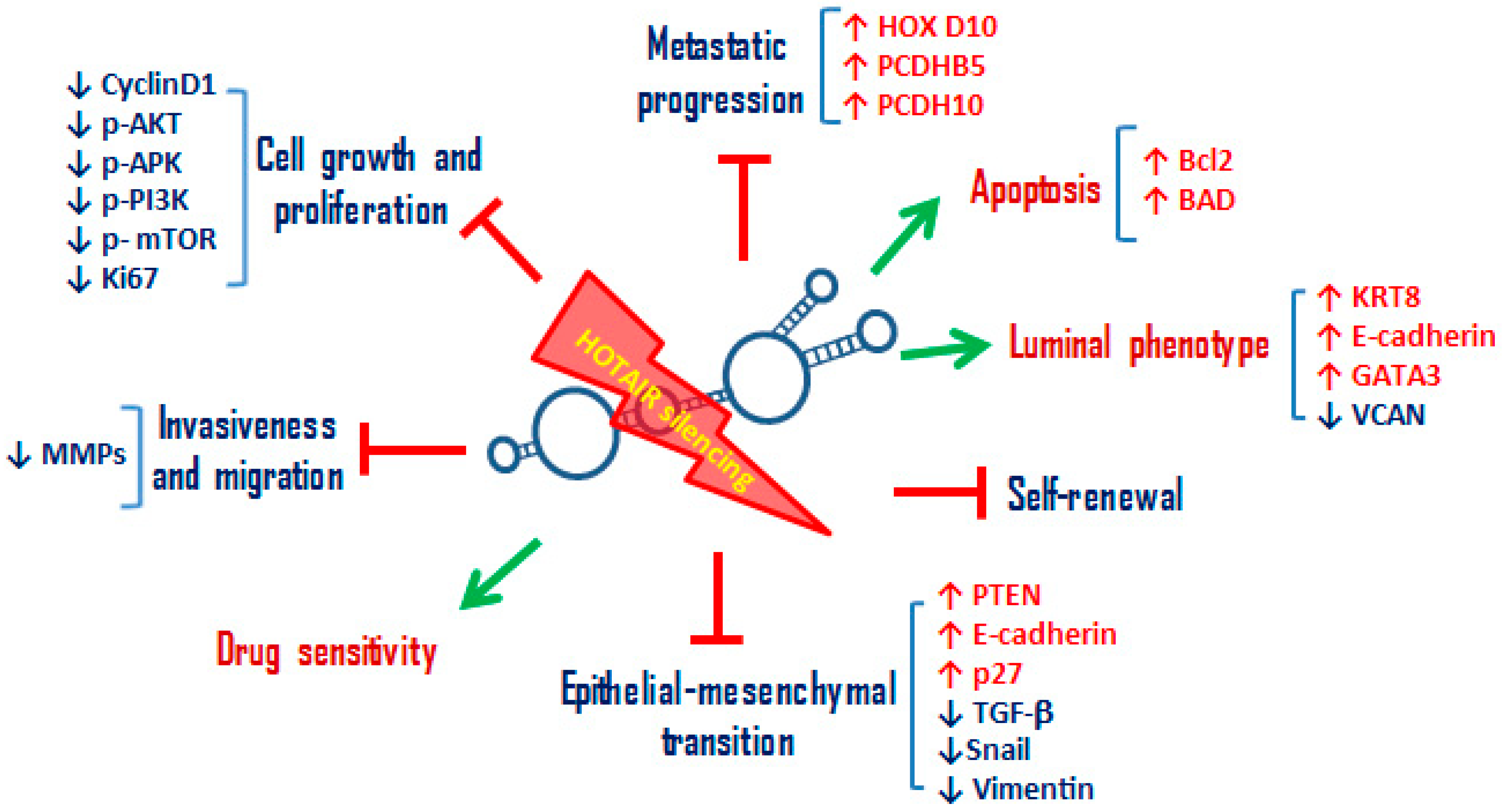
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the main cellular processes inhibited or activated by the silencing of HOTAIR in BC cells. HOTAIR knockdown in BC cells leads to the promotion of: (i) sensitivity to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapies and anti-HER2 therapies; (ii) luminal phenotype acquisition with the upregulation of luminal cytokeratins (KRT8), of cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, and of transcription factor GATA3, responsible of luminal epithelial differentiation in the adult mammary gland. Furthermore, HOTAIR silencing in BC cells leads to the inhibition of: (i) cell growth and proliferation by downregulating the main signaling pathways involved in these cellular processes, such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK/ERK pathway, cyclin D1 and proliferation index Ki67; (ii) invasion and migration by downregulation of metalloproteinases; (iii) EMT by upregulating epithelial markers, such as E-cadherin, downregulating mesenchymal markers, such as Vimentin, and TGF-beta signaling; (iv) self-renewal, reducing colonosphere and mammosphere formation; (v) metastatic progression by upregulating metastasis suppressor genes, such as HOXD10, PCDHB5, and PCDH10. The green arrow indicates the activated processes, the symbol † the inhibited ones. KRT8: Keratin 8, GATA3: GATA Binding Protein 3, mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, ERK: Extracellular regulated kinases, PCDHB5: Protocadherin Beta 5, PCDH10: Protocadherin 10.
Due to the fact of its important role in therapeutic resistance mechanisms, several studies have reported that HOTAIR downregulation is able to make BC cells sensitive to different therapeutic treatments (Figure 2). Hu et al. [119] showed that silencing of HOTAIR in MCF7 BC cells is able to reduce cell survival inducing apoptosis in response to ionizing radiation. Moreover, in HOTAIR knockdown cells ionizing radiation induces more DNA damage and cell cycle arrest than in control cells [119]. In a doxorubicin-resistant BC cell line (DOXR-MCF-7), HOTAIR silencing decreases cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in BC cells reducing doxorubicin resistance and simultaneously determines a reduction of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR phosphorylation inhibiting the molecular pathway [160]. Similarly, in a trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3-TR, knockdown of HOTAIR sensitizes BC cells to trastuzumab [125].
Although the majority of the functional studies on HOTAIR performed its direct inhibition by siRNA methods, the ability to translate these methods in clinical practice is complicated. In fact, most lncRNAs are preferentially expressed in the nucleus and can be integrated into more complex structures that are not easily accessible. Therefore, small molecules designed to specifically interfere with conserved RNA structures and to block RNA protein complexes may be useful. Two very recent studies showed how HOTAIR activity can be efficiently blocked by molecular interference in HOTAIR/EZH2 scaffold interaction [161,162]. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) promotes BC progression in a PRC2-dependent manner [90,163] by recruiting and binding EZH2, the catalytic subunit of PRC2, to silence target genes [164]. Ren et al. [161], analyzing the structure and function of HOTAIR, identified a small molecule, named AC1NOD4Q, able to inhibit HOTAIR/PRC2 complex interaction [161]. The minimal 5′ domain of HOTAIR required for PRC2 binding is 212–300 nt. Using a 3D modeling prediction, it turned out that this domain contains several hairpin loop structures and serves as a target for small molecule intervention. By performing in silico high-throughput screening, Ren et al. [161] highlighted that AC1NOD4Q (ADQ) binds to a specific HOTAIR micro-domain (36G46A) and induces strong molecular inference in the scaffold interaction between PRC2 complex and HOTAIR. Its validation on cell and animal models has provided encouraging results. In ADQ-treated MDA-MB-231 cells, the migration and invasion proprieties of BC cells are strongly reduced by cell adhesion molecules and EMT biomarkers downregulation. An MDA-MB-231 orthotopic tumor transplantation model in nude mice as performed to test ADQ treatment. A significant reduction of tumor growth and lung metastatic nodules was detected in ADQ-treated mice. Moreover, the analysis by situ hybridization and immunofluorescence of the HOTAIR/PRC2 interaction in ADQ-treated mice tissues clearly highlights that ADQ treatment reduces and relocates EZH2 signals from nucleus to cytoplasm with HOTAIR disassociation. This is the first study demonstrating that ADQ is able to efficiently block HOTAIR/EZH2 interaction and recruitment of EZH2 to target genes [161].
Similarly, another molecule capable of selectively inhibiting HOTAIR–EZH2 interaction, named AC1Q3QWB, has recently been validated in BC cells and animal models [162]. AC1Q3QWB treatment inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis in vivo and at the same time leads the upregulation of APC2, HOXD10, PCDH10, HOTAIR–PRC2 target genes, downregulation of β-catenin, tumor cell proliferation antigen (Ki-67), and EMT marker such as Vimentin. Moreover, Li et al. [162] have also shown that the combination of a low dose of AC1Q3QWB with 3-deazaneoplanocin A (DZNep), an EZH2 inhibitor that induces the degradation of PRC2 by impairment of SAH (S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine), already largely used in different tumors, exhibits a marked anti-tumor activity, in orthotopic BC models, superior to the agents used alone [162].
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
The use of different silencing systems for HOTAIR has allowed the obtention of encouraging results. Most of the studies on cellular and animal models have been carried out using siRNA methods. Despite their great usefulness and the easy use to understand functional mechanisms which underlie the aberrant activity of HOTAIR in BC cells, these silencing systems have not yet been contemplated for clinical studies. In fact, the transition from preclinical to clinical studies is quite difficult because, while in vitro models are easy to apply but have limited clinical relevance, in vivo models have higher clinical relevance, but they are expensive and challenging to conduct. To date, only few therapeutic miRNAs have successfully moved into clinical trials due to the enormous difficulty in assessing toxic and off-targets effects and in generating a high stability and successful delivery system [165].
More recently, a detailed analysis of the structure and functional mechanisms of ncRNAs (interaction with the target genes) has allowed the development of a computer-aided structure-based drug design method. This approach could efficiently screen the potential compounds in the shortest possible time, allowing optimal selection of new target compounds [161,162]. A series of compounds specifically capable of blocking the activity of some ncRNAs are already used in clinical practice. For example, some small molecules such as kanamycin, an antimycobacterial drug mainly used to treat tuberculosis, is capable of binding pre-miRNAs inhibiting DICER-mediated miRNA processing [166]. The recent identification of small molecules able to block HOTAIR activity by interfering with HOTAIR/EZH2 scaffold interaction are offering new strategies for its inhibition that may be easier to use in human. Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit (EZH2) inhibitor compounds, such as DZNep, have been previously suggested as potential drugs for clinical usage in solid tumors [167]. In BC preclinical models, the combination of DZNep with a small-molecule involved in the block of HOTAIR–EZH2 interaction, greatly enhances the antitumor activity [162].
Although there are still no clinical studies that can prove their usefulness in BC patients, these small molecules, being also easily synthesizable for large-scale manufacturing, are proving to be powerful anticancer agents and could represent the optimal system to block HOTAIR activity.
In conclusion, HOTAIR plays a key role in BC tumor progression, being able to modulate, directly or indirectly, crucial cell processes such as growth, proliferation, invasiveness, EMT, self-renewal, metastatic spread, and drug resistance. For this reason, although no relevant studies on drugging lncRNAs have been reported, the possibility of interfering with HOTAIR activity could represent an important tool for defining innovative therapeutic strategies in BC, mainly oriented for the reversal of drug resistance.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lakhani, S.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Schnitt, S.J.; Tan, P.H.; van de Vijver, M.J. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sørlie, T. Molecular portraits of breast cancer: Tumour subtypes as distinct disease entities. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolston, C. Breast cancer. Nature 2015, 527, S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.G. Targeted Therapies for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-Y.; Liu, G.-F.; Qian, X.; Tang, L.-B.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Xiong, L.-X. Long Non-Coding RNA: Dual Effects on Breast Cancer Metastasis and Clinical Applications. Cancers 2019, 11, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.-X.; Koirala, P.; Mo, Y.-Y. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, M.; Xu, C.; Xiang, P.; Zhong, X. Long Noncoding RNAs: An Overview. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2016, 1402, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.R.; Mondal, T.; Mohammad, F.; Enroth, S.; Redrup, L.; Komorowski, J. Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.-B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.-S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Froberg, J.E.; Lee, J.T. Long noncoding RNAs: Fresh perspectives into the RNA world. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sun, X. Enhancer LncRNAs Influence Chromatin Interactions in Different Ways. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingolia, N.T.; Lareau, L.F.; Weissman, J.S. Ribosome profiling of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals the complexity and dynamics of mammalian proteomes. Cell 2011, 147, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huarte, M.; Guttman, M.; Feldser, D.; Garber, M.; Koziol, M.J.; Kenzelmann-Broz, D.; Khalil, A.M.; Zuk, O.; Amit, I.; Rabani, M.; et al. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 2010, 142, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.X.; Do, B.T.; Webster, D.E.; Khavari, P.A.; Chang, H.Y. Dicer-microRNA-Myc circuit promotes transcription of hundreds of long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Calle, A.; Kawamura, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, H.; Yan, G.; Wu, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Ning, Y.; Lu, Z. Long Non-Coding RNA and Breast Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, R.A.; Gad, M.Z. Long non-coding RNAs: Functional regulatory players in breast cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2019, 4, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Detection and analysis of circulating large intergenic non-coding RNA regulator of reprogramming in plasma for breast cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ma, P.; Liu, S.M.; Zhou, X. Circulating long noncoding RNA GAS5 as a potential biomarker in breast cancer for assessing the surgical effects. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 6847–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lottin, S.; Adriaenssens, E.; Dupressoir, T.; Berteaux, N.; Montpellier, C.; Coll, J.; Dugimont, T.; Curgy, J.J. Overexpression of an ectopic H19 gene enhances the tumorigenic properties of breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Song, X.; Liu, J. Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, H.; Kida, K.; Adachi, S.; Yamada, A.; Sugae, S.; Narui, K.; Miyagi, Y.; Nishi, M.; Ryo, A.; Murata, S.; et al. Lnc RNA H19 is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients and promotes cancer stemness. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Bhat, V.; Su, A.; Jin, H.; Lee-Wing, V.; Liu, Q.; Hu, P.; Murphy, L.C.; Raouf, A. Long non-coding RNA H19 acts as an estrogen receptor modulator that is required for endocrine therapy resistance in ER+ breast cancer cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.N.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Deng, J.L.; Li, Z.X.; Zhu, Y.S. LncRNA H19 is a major mediator of doxorubicin chemoresistance in breast cancer cells through a cullin4A-MDR1 pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91990–92003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Lin, S.; Guan, L.; Yuan, H.; Liu, K.; Liu, C.; Ye, W.; Liao, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, R. Long non-coding RNA XIST inhibited breast cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion via miR-155/CDX1 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, D.; van Agthoven, T.; Bosma, P.T.; Nooter, K.; Dorssers, L.C. Functional screen for genes responsible for tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.; Meijer, D.; Setyono-Han, B.; Dorssers, L.C.; van Agthoven, T. Characterization of BCAR4, a novel oncogene causing endocrine resistance in human breast cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zou, Z.; Suo, N.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, F.; Zhong, G.; Qu, Y.; Ntaka, K.S.; Tian, H. CCL21/CCR7 axis activating chemotaxis accompanied with epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human breast carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2014, 31, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lü, J.; Ding, X.; Luo, A.; He, J.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; et al. Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes oncogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating stemness of cancer cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.G.; Yang, M.F.; Ren, Y.Q.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, L.Q. Exosomes mediated transfer of lncRNA UCA1 results in increased tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4362–4368. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Parra, A.D.; López-Urrutia, E.; Moreno, L.T.O.; López-Camarillo, C.; Menchaca, T.M.; González, G.F.; Montes, L.P.B.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. Long non-coding RNAs as new master regulators of resistance to systemic treatments in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Tu, J.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, Q. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes relapse of breast cancer patients with postoperative fever. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y. The Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressive Functions of the Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1: An Emerging Controversy. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Piao, H.L.; Kim, B.J.; Yao, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Siverly, A.N.; Lawhon, S.E.; Ton, B.N.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, W.B.; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, X.H. lncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer via promoting proliferation and EMT. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, B.; et al. The FOXN3-NEAT1-SIN3A repressor complex promotes progression of hormonally responsive breast cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 3421–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.J.; Wang, L.J.; Yu, B.; Li, Y.H.; Jin, Y.; Bai, X.Z. LncRNA-ATB promotes trastuzumab resistance and invasion-metastasis cascade in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11652–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Hu, J.; Zou, K.; Ye, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Han, M. Activation of LncRNA TINCR by H3K27 acetylation promotes Trastuzumab resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting MicroRNA-125b in breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Bai, W.D.; Ye, X.M.; Yang, A.G.; Jia, L.T. Long non-coding RNA UCA1 desensitizes breast cancer cells to trastuzumab by impeding miR-18a repression of Yes-associated protein B1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Mo, S.; Chen, R.; Zou, K.; Han, J.; Zhang, F.; Hu, J. SP1-induced lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 expression promotes chemoresistance of breast cancer by epigenetic regulation of MyDJ88. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhai, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Wei, Q. Downregulation of LncRNA GAS5 causes trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27778–27786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Liang, F.; Zhang, J.W.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Kang, X.G. Effects of long noncoding RNA-ROR on tamoxifen resistance of breast cancer cells by regulating microRNA-C205. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.X.; Lu, Y.H.; Ji, T.H.; Xu, L.; Ling, L.J. Shikonin reduces tamoxifen resistance through long non-coding RNA uc.57. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88658–88669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q. LncRNA LINP1 confers tamoxifen resistance and negatively regulated by ER signaling in breast cancer. Cell. Signal. 2020, 68, 109536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknafs, Y.S.; Han, S.; Ma, T.; Speers, C.; Zhang, C.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Iyer, M.K.; Pitchiaya, S.; Malik, R.; Hosono, Y.; et al. The lncRNA landscape of breast cancer reveals a role for DSCAM-AS1 in breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.B. Downregulated lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 in breast cancer enhances tamoxifen resistance by activating microRNA-130a-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Piao, H. lncRNA CYTOR promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells via sponging miR-125a-5p. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Shao, C.; Zhou, M.; He, Z. Downregulation of lncRNA GAS5 confers tamoxifen resistance by activating miR-222 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 434, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majello, B.; Gorini, F.; Saccà, C.D.; Amente, S. Expanding the role of the histone lysine-specific demethylase LSD1 in cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Qu, K.; Zhong, F.L.; Artandi, S.E.; Chang, H.Y. Genomic maps of long noncoding RNA occupancy reveal principles of RNA-chromatin interactions. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kim, J.; Yang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Tominaga-Yamanaka, K.; White, E.J.; Orjalo, A.V.; Rinn, J.L.; Kreft, S.G.; et al. Scaffold function of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Vlachos, I.S.; Karagkouni, D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kanellos, I.; Vergoulis, T.; Zagganas, K.; Tsanakas, P.; Floros, E.; Dalamagas, T.; et al. DIANA-LncBase v2: Indexing microRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D231–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Ren, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, D. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Modulates MiR-206-mediated Bcl-w Signaling to Facilitate Cell Proliferation in Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Peng, X.; Cheng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Yu, X. Delphinidin suppresses breast carcinogenesis through the HOTAIR/microRNA-34a axis. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ren, D.; Liu, H.; Kang, C.; Chen, J. HOTAIR, a long noncoding RNA, is a marker of abnormal cell cycle regulation in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2717–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kong, D.; Chen, Q.; Ping, Y.; Pang, D. Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, G.; Collina, F.; Scognamiglio, G.; Aquino, G.; Cerrone, M.; Liguori, G.; Gigantino, V.; Malzone, M.G.; Cantile, M. LncRNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms Association with Cancer Susceptibility in Different Tumor Types. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhao, J.C.; Kim, J.; Fong, K.W.; Yang, Y.A.; Chakravarti, D.; Mo, Y.Y.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR Enhances the Androgen-Receptor-Mediated Transcriptional Program and Drives Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.H.; Lu, S.W.; Huang, Y.Q.; Que, G.B.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, H.B.; Liang, X.L.; Jiang, J.H. Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR predicts recurrence in stage Ta/T1 bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 10249–10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.X. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is a prognostic biomarker and inhibits chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrondo, C.; Flax, J.; Kucherov, V.; Siebert, A.; Osinski, T.; Rosenberg, A.; Fucile, C.; Richheimer, S.; Beckham, C.J. Expression of the Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Correlates with Disease Progression in Bladder Cancer and Is Contained in Bladder Cancer Patient Urinary Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Ye, L.C.; Ding, J.X.; Feng, W.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hua, K.Q. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR predicts poor patient prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liao, L.M.; Liu, A.W.; Wu, J.B.; Cheng, X.L.; Lin, J.X.; Zheng, M. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR predicts a poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 290, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fan, R. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating BCL2 via targeting miR-143-3p. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Dong, R.; Qiu, H. A high level of circulating HOTAIR is associated with progression and poor prognosis of cervical cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bao, W.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Che, Q.; Wang, H.; Wan, X.P. The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma and correlates with poor prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.N.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, H. Autophagy regulated by lncRNA HOTAIR contributes to the cisplatin-induced resistance in endometrial cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.F.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.Q.; Cui, Y.X.; Ma, N.; Lu, C.X.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhou, Y. Clinical significance of HOTAIR expression in colon cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, S.; Duan, B.; Chen, P.; Shi, L.; Gao, H.; Qi, H. HOTAIR is a predictive and prognostic biomarker for patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma receiving fluorouracil and platinum combination chemotherapy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, M.; Kogo, R.; Shibata, K.; Sawada, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Akiyoshi, S.; Sasaki, S.; Iwaya, T.; Sudo, T.; et al. Clinical significance of the expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wu, L.M.; Lai, M.C.; Xie, H.Y.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, S.S. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients following liver transplantation. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Feng, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, M. Long intergenic noncoding RNA HOTAIR is overexpressed and regulates PTEN methylation in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xiao, X.; Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, L. The role of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in the progression and development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma interacting with EZH2. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Endo, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Abe, J.; Tamai, K.; Tanaka, N.; Sato, I.; Takahashi, S.; Kondo, T.; Satoh, K. Large noncoding RNA HOTAIR enhances aggressive biological behavior and is associated with short disease-free survival in human non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Gao, T.H.; Cui, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.J. Elevated HOTAIR expression associated with cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 3314–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, P.; Jing, W.; Zhu, M.; Tu, J. Identification of Circulating Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, G.; Scognamiglio, G.; Aquino, G.; Liguori, G.; Cantile, M. LncRNA HOTAIR in Tumor Microenvironment: What Role? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Blasiak, J. The Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR in Breast Cancer: Does Autophagy Play a Role? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Hussain, I.; Ansari, K.I.; Bobzean, S.A.; Perrotti, L.I.; Mandal, S.S. Bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol exposure induces the expression of breast cancer associated long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in vitro and in vivo. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 141, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Chen, S.; Ding, L.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, J.C.; Wang, L.; Sarver, A.; Koller, A.; Zhi, J.; et al. BRCA1 is a negative modulator of the PRC2 complex. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1584–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F. Osteopontin enhances the expression of HOTAIR in cancer cells via IRF1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bure, I.; Geer, S.; Knopf, J.; Roas, M.; Henze, S.; Ströbel, P.; Agaimy, A.; Wiemann, S.; Hoheisel, J.D.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is upregulated in an aggressive subgroup of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) and mediates the establishment of gene-specific DNA methylation patterns. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018, 57, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, W.; Lu, J. Expression profile analysis of long noncoding RNA in ER-positive subtype breast cancer using microarray technique and bioinformatics. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Q.; Katsaros, D.; Mayne, S.T.; Risch, H.A.; Mu, L.; Canuto, E.M.; Gregori, G.; et al. Association of large noncoding RNA HOTAIR expression and its downstream intergenic CpG island methylation with survival in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmen-Polar, Y.; Vladislav, I.T.; Neelamraju, Y.; Janga, S.C.; Badve, S. Prognostic impact of HOTAIR expression is restricted to ER-negative breast cancers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, K.P.; Thomassen, M.; Tan, Q.; Bak, M.; Cold, S.; Burton, M.; Larsen, M.J.; Kruse, T.A. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 142, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Nguyen, H.T.; Burow, M.E.; Zhuo, Y.; El-Dahr, S.S.; Yao, X.; Cao, S.; Flemington, E.K.; Nephew, K.P.; Fang, F.; et al. Elevated expression of long intergenic non-coding RNA HOTAIR in a basal-like variant of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1656–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collina, F.; Aquino, G.; Brogna, M.; Cipolletta, S.; Buonfanti, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G. LncRNA HOTAIR upregulation is strongly related with lymph nodes metastasis and LAR subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pádua Alves, C.; Fonseca, A.S.; Muys, B.R.; de Barros, E.; Lima Bueno, R.; Bürger, M.C.; de Souza, J.E.; Valente, V.; Zago, M.A.; Silva, W.A., Jr. Brief report: The lincRNA Hotair is required for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of cancer cell lines. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2827–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Jia, H.H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Song, X.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Sun, T.; Dou, Y.; et al. Paracrine and epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: The role of HOTAIR stimulated by TGF-ß1 secretion. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, K.; Shi, F.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, J. MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2858–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, M.; Jiang, R.; An, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Regulates the Proliferation, Self-Renewal Capacity, Tumor Formation and Migration of the Cancer Stem-Like Cell (CSC) Subpopulation Enriched from Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, G.; Marra, L.; Malzone, M.G.; Anniciello, A.; Botti, C.; Franco, R.; Cantile, M. LncRNA HOTAIR as Prognostic Circulating Marker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Patients with Tumor Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; You, X.; Liang, Z.; Cao, H. Circulating DNA of HOTAIR in serum is a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, J. Circulating long non-coding HOX transcript antisense intergenic ribonucleic acid in plasma as a potential biomarker for diagnosis of breast cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, K.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zou, T.; Liu, D. Overexpression of serum exosomal HOTAIR is correlated with poor survival and poor response to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ni, J.; Beretov, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Cancer stem cell in breast cancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 69, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Fan, S. Predicting and Overcoming Chemotherapeutic Resistance in Breast Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1026, 59–104. [Google Scholar]
- Muluhngwi, P.; Klinge, C.M. Roles for miRNAs in endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R279–R300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Bessone, M.I.; Gattas, M.J.; Laporte, T.; Tanaka, M.; Simian, M. The Tumor Microenvironment as a Regulator of Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houthuijzen, J.M.; Jonkers, J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts as key regulators of the breast cancer tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaei, K.; Samadi, N.; Barazvan, B.; Soleimani Rad, J. Tumor microenvironment-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer. Breast 2016, 30, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, H.; Ren, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance in breast cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Lou, W.; Xu, L.; Fan, W. Non-coding RNA in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Xu, F.; Zhai, W.; Dong, S.; Yin, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z. Role of long non-coding RNA in drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Guo, Z.; He, C.; Ding, L.; Tang, J.H.; Hou, Y. Role of long non-coding RNA in tumor drug resistance. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11623–11631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.N.; Wei, C.C.; Wang, Z.X.; Sun, M. Long non-coding RNAs in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidinia, M.; Yousefi, B. Long non-coding RNAs in cancer drug resistance development. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2016, 45, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, W. The molecular mechanism of HOTAIR in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Yuan, W.; Ruofan, D.; Jinjin, Y.; Haifeng, Q. HOTAIR enhanced aggressive biological behaviors and induced radio-resistance via inhibiting p21 in cervical cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 3611–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Xu, K. Inhibition of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances radiosensitivity via regulating autophagy in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Yin, H. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances radioresistance in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ding, D.; Zhang, J.; Cui, J. Knockdown of lncRNA HOTAIR sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation through activating miR-218. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhang, A.; Fong, K.W.; Kim, J.; Song, B.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.C.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantile, M.; Collina, F.; Aquino, G.; Brogna, M.; Cipolletta, S.; Formisano, L.; Bianco, R.; De Laurentiis, M.; Botti, G.; Di Bonito, M. The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a marker of aromatase inhibitor resistance in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer. Unpublished work. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A. Current Updates on Trastuzumab Resistance in HER2 Overexpressing Breast Cancers. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, W.; Huang, T. Downregulation of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR sensitizes breast cancer to trastuzumab. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, A.F.; Cameron, D.A.; Bartlett, J.M. Targeting anthracyclines in early breast cancer: New candidate predictive biomarkers emerge. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5231–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, M.L.; Burke, L.; Ferguson, T.; Ghersi, D.; Nowak, A.K.; Wilcken, N. Taxanes for adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 9, CD004421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Le Du, F.; Xiao, L.; Kogawa, T.; Barcenas, C.H.; Alvarez, R.H.; Valero, V.; Shen, Y.; Ueno, N.T. Effectiveness of an Adjuvant Chemotherapy Regimen for Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, R.; Guan, A.; Yao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jia, H.; Huang, W.; Gao, J. HOTAIR enhanced paclitaxel and doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer cells partly through inhibiting miR-217 expression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7226–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, J.M.; Tao, L.; Cheng, L.; Tian, J. Cisplatin and paclitaxel target significant long noncoding RNAs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, C. lncRNA HOTAIR Contributes to 5FU Resistance through Suppressing miR-218 and Activating NF-κB/TS Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Lee, S.-H.; Jones, A.; Fiegl, H.; Kalwa, M.; Wagner, W.; Chindera, K.; Evans, I.; Dubeau, L.; Orjalo, A.; et al. HOTAIR and its surrogate DNA methylation signature indicate carboplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, M.; Lu, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, W.; De, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R. The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via downregualtion of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77293. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Su, N.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Qiu, H.; He, X. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR leads to chemoresistance by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Dang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by targeting miR-126 to activate the PI3K/AKT/MRP1 genes. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 16345–16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhi, Q.; Wang, J.; Qin, C. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells through inhibiting the PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways by up-regulating miR-34a. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Li, S. RNA interference of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR suppresses autophagy and promotes apoptosis and sensitivity to cisplatin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, S. Circulating HOTAIR expression predicts the clinical response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.; Zhang, J.-J.; Li, H.-B. Dietary Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer. Nutrients 2017, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Luo, E.; Liu, X.; Han, B.; Yu, X.; Peng, X. Delphinidin-3-glucoside suppresses breast carcinogenesis by inactivating the Akt/HOTAIR signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-J.; Jin, M.-Z.; Xia, B.-R.; Jin, W. Long Non-coding RNA DANCR as an Emerging Therapeutic Target in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Chen, Y. Targeting long non-coding RNAs in cancers: Progress and prospects. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1895–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H. Non-coding RNAs: Therapeutic Strategies and Delivery Systems. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slaby, O.; Laga, R.; Sedlacek, O. Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 4219–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowdy, S.F. Overcoming cellular barriers for RNA therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Gollahon, L. Nek2-targeted ASO or siRNA pretreatment enhances anticancer drug sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.M.; Harris, E.N. Antisense Oligonucleotides: Treatment Strategies and Cellular Internalization. RNA Dis. 2016, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaliha, M.; Zong, X.; Malakar, P.; Ray, T.; Singh, D.K.; Freier, S.M.; Jensen, T.; Prasanth, S.G.; Karni, R.; Ray, P.S.; et al. Functional and prognostic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 as a metastasis driver in ER negative lymph node negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40418–40436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Trivedi, P.; Jain, N.K. Advances in siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorgna, G.; Vago, R.; Sarmini, M.; Montorsi, F.; Salonia, A.; Bellone, M. Long non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 110, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darfeuille, F.; Reigadas, S.; Hansen, J.B.; Orum, H.; Di Primo, C.; Toulmé, J.J. Aptamers targeted to an RNA hairpin show improved specificity compared to that of complementary oligonucleotides. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 12076–12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavco, P.A.; Bouhana, K.S.; Gallegos, A.M.; Agrawal, A.; Blanchard, K.S.; Grimm, S.L.; Jensen, K.L.; Andrews, L.E.; Wincott, F.E.; Pitot, P.A.; et al. Antitumor and antimetastatic activity of ribozymes targeting the messenger RNA of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwudi, C.U. rRNA Binding Sites and the Molecular Mechanism of Action of the Tetracyclines. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4433–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Urrutia, E.; Montes, L.P.B.; Cervantes, D.L.D.G.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Campos-Parra, A.D. Crosstalk between Long Non-coding RNAs, Micro-RNAs and mRNAs: Deciphering Molecular Mechanisms of Master Regulators in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A. Cellular localization of long non-coding RNAs affects silencing by RNAi more than by antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Song, X.Q.; Cai, J.P.; Zhang, S. HOTAIR: A cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Hussain, I.; Ansari, K.I.; Kasiri, S.; Bashyal, A.; Mandal, S.S. Antisense transcript long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR is transcriptionally induced by estradiol. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 3707–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, H.C.; Li, L.; Li, C.X.; Di, X.; Qu, X. Downregulation of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR and EZH2 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2018, 33, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, W.; Huang, T. Brief Report: The lincRNA Hotair Is Required for Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance of Cancer Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2827–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Qian, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, C. Knockdown of lncRNA-HOTAIR downregulates the drug-resistance of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp. Ther Med. 2019, 18, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.X.; Han, L.; Mei, M.; Kang, C.S. Targeted design and identification of AC1NOD4Q to block activity of HOTAIR by abrogating the scaffold interaction with EZH2. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, K.; Yi, K.; et al. A Compound AC1Q3QWB Selectively Disrupts HOTAIR-Mediated Recruitment of PRC2 and Enhances Cancer Therapy of DZNep. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4608–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Han, L.; Chen, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, A.; Ye, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes glioblastoma cell cycle progression in an EZH2 dependent manner. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicentini, C.; Galuppini, F.; Corbo, V.; Fassan, M. Current role of non-coding RNAs in the clinical setting. Noncoding RNA Res. 2019, 4, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.F. Drug target miRNAs: Chances and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Lee, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Duan, X.; Chan, E. Preclinical pharmacokinetic studies of 3-deazaneplanocin A, a potent epigenetic anticancer agent, and its human pharmacokinetic prediction using GastroPlus™. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).