Src Family Tyrosine Kinases in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Tumorigenesis
Abstract
:1. Colorectal Cancer
2. Tyrosine Kinases in CRC
3. SFKs in Intestinal Tumours
3.1. SFKs
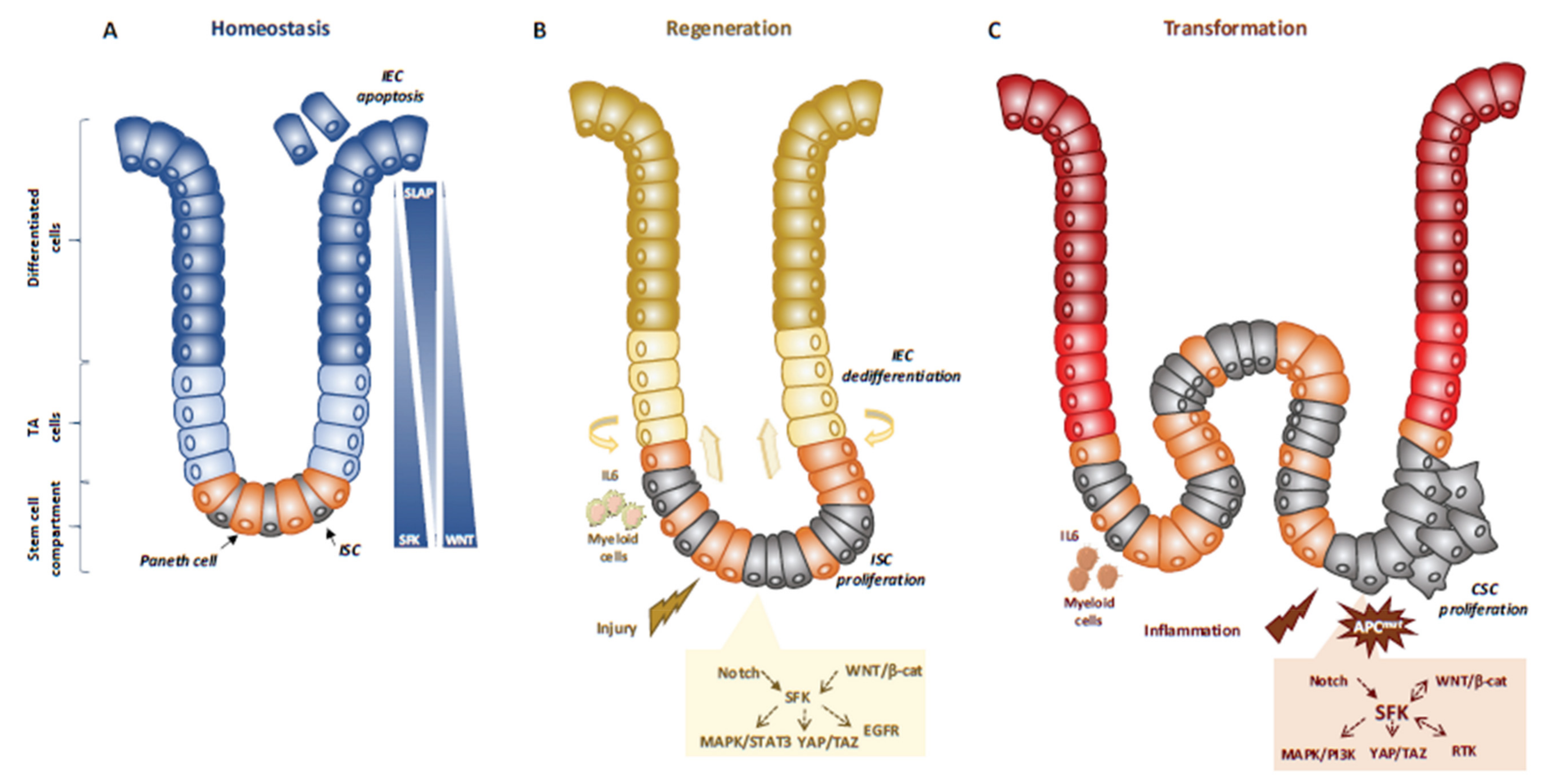
3.2. SFKs in Intestinal Homeostasis and Regeneration
3.3. SFKs in Intestinal Cell Transformation
4. SFKs in Human CRC
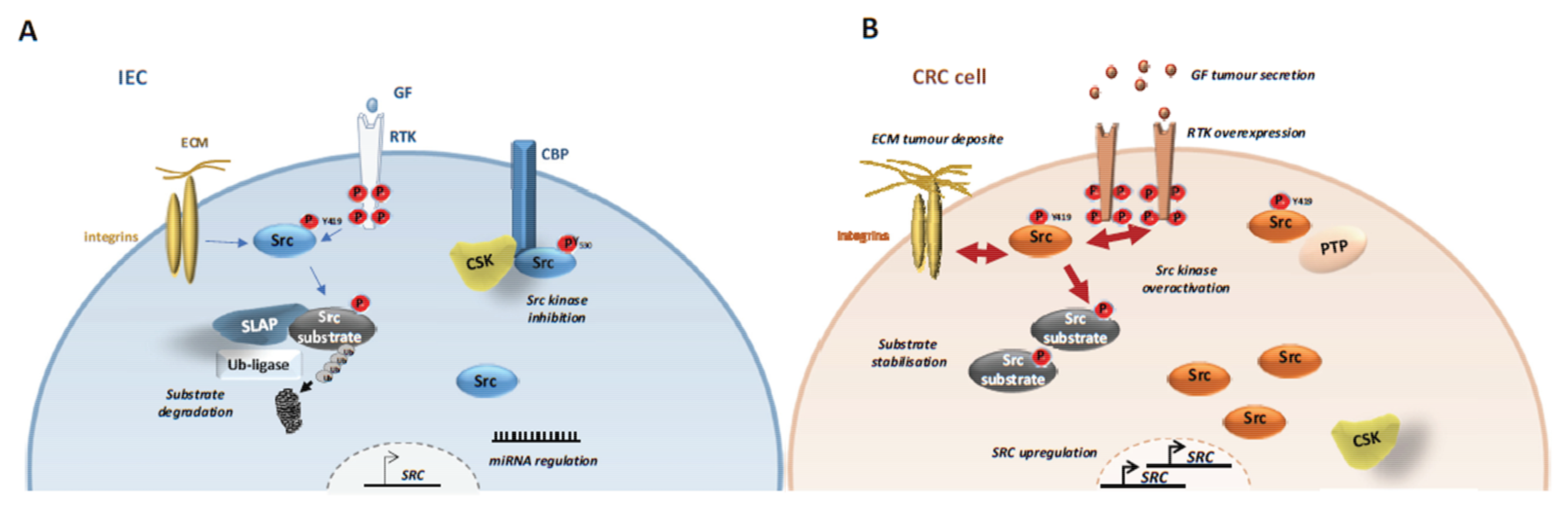
4.1. SFKs Deregulation
4.1.1. SFK Upregulation
4.1.2. CSK Inactivation
4.1.3. SLAP Inactivation
4.1.4. SFK Post-Translational Modifications
4.2. SFKs Signalling in Early CRC
4.2.1. Wnt/Beta-Catenin and YAP Pathways
4.2.2. RTK Pathway
4.2.3. Cell-Cycle Progression
4.3. SFKs Signalling in Advanced CRC
4.3.1. CRC Angiogenesis, Survival and Metabolism
4.3.2. CRC Cell Dissemination and Colonization
4.3.3. Metastasis Development
5. Therapeutic Strategies to Target SFKs Signalling in CRC
5.1. Therapeutic Utility
5.2. Therapeutic Strategies
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, H.; Kloor, M.; Pox, C.P. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2014, 383, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanharanta, S.; Massague, J. Origins of metastatic traits. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guinney, J.; Dienstmann, R.; Wang, X.; de Reynies, A.; Schlicker, A.; Soneson, C.; Marisa, L.; Roepman, P.; Nyamundanda, G.; Angelino, P.; et al. The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Vermeulen, L.; Guinney, J.; Kopetz, S.; Tejpar, S.; Tabernero, J. Consensus molecular subtypes and the evolution of precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaeger, R.; Chatila, W.K.; Lipsyc, M.D.; Hechtman, J.F.; Cercek, A.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Jayakumaran, G.; Middha, S.; Zehir, A.; Donoghue, M.T.A.; et al. Clinical Sequencing Defines the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 125–136.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, K.P.; Loizou, E.; Livshits, G.; Schatoff, E.M.; Baslan, T.; Manchado, E.; Simon, J.; Romesser, P.B.; Leach, B.; Han, T.; et al. Transplantation of engineered organoids enables rapid generation of metastatic mouse models of colorectal cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tauriello, D.V.F.; Palomo-Ponce, S.; Stork, D.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Badia-Ramentol, J.; Iglesias, M.; Sevillano, M.; Ibiza, S.; Canellas, A.; Hernando-Momblona, X.; et al. TGFbeta drives immune evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis. Nature 2018, 554, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Pawson, T. Modular evolution of phosphorylation-based signalling systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2540–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, A.; Kopetz, S.; Lothe, R.A. Biomarker-guided therapy for colorectal cancer: Strength in complexity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellucci, S.; Clementi, L.; Sabetta, S.; Mattei, V.; Botta, L.; Angelucci, A. Src Family Kinases as Therapeutic Targets in Advanced Solid Tumors: What We Have Learned so Far. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeatman, T.J. A renaissance for SRC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.C.; Song, L.; Haura, E.B. Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggon, T.J.; Eck, M.J. Structure and regulation of Src family kinases. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7918–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M. Regulation of the SRC family kinases by Csk. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, G.S. The hunting of the Src. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 2, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbesu, M.; Maffei, M.; Cordeiro, T.N.; Teixeira, J.M.; Perez, Y.; Bernado, P.; Roche, S.; Pons, M. The Unique Domain Forms a Fuzzy Intramolecular Complex in Src Family Kinases. Structure 2017, 25, 630–640.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maffei, M.; Arbesu, M.; Le Roux, A.L.; Amata, I.; Roche, S.; Pons, M. The SH3 Domain Acts as a Scaffold for the N-Terminal Intrinsically Disordered Regions of c-Src. Structure 2015, 23, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spassov, D.S.; Ruiz-Saenz, A.; Piple, A.; Moasser, M.M. A Dimerization Function in the Intrinsically Disordered N-Terminal Region of Src. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 449–463.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Roux, A.L.; Busquets, M.A.; Sagues, F.; Pons, M. Kinetics characterization of c-Src binding to lipid membranes: Switching from labile to persistent binding. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 138, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagar, B.; Hantschel, O.; Young, M.A.; Scheffzek, K.; Veach, D.; Bornmann, W.; Clarkson, B.; Superti-Furga, G.; Kuriyan, J. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Cell 2003, 112, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Fendrich, G.; Manley, P.W.; Jahnke, W.; Fabbro, D.; Liebetanz, J.; Meyer, T. The crystal structure of a c-Src complex in an active conformation suggests possible steps in c-Src activation. Structure 2005, 13, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Roux, A.L.; Mohammad, I.L.; Mateos, B.; Arbesu, M.; Gairi, M.; Khan, F.A.; Teixeira, J.M.C.; Pons, M. A Myristoyl-Binding Site in the SH3 Domain Modulates c-Src Membrane Anchoring. iScience 2019, 12, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowell, C.A.; Soriano, P. Knockouts of Src-family kinases: Stiff bones, wimpy T cells, and bad memories. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1845–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordero, J.B.; Ridgway, R.A.; Valeri, N.; Nixon, C.; Frame, M.C.; Muller, W.J.; Vidal, M.; Sansom, O.J. c-Src drives intestinal regeneration and transformation. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1474–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casali, A.; Batlle, E. Intestinal stem cells in mammals and Drosophila. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohlmaier, A.; Fassnacht, C.; Jin, Y.; Reuter, H.; Begum, J.; Dutta, D.; Edgar, B.A. Src kinase function controls progenitor cell pools during regeneration and tumor onset in the Drosophila intestine. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2371–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, S.; Murata, Y.; Kotani, T.; Hatano, M.; Sun, C.; Konno, T.; Park, J.H.; Kitamura, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ohdan, H.; et al. Role of Src Family Kinases in Regulation of Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Tsuboi, M.; Asfaha, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Niikura, R.; Konishi, M.; Hata, M.; Oya, Y.; Kim, W.; Middelhoff, M.; et al. BHLHA15-Positive Secretory Precursor Cells Can Give Rise to Tumors in Intestine and Colon in Mice. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1066–1081.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroishi, T.; Hansen, C.G.; Guan, K.L. The emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Wu, L.W.; Grivennikov, S.I.; de Jong, P.R.; Lian, I.; Yu, F.X.; Wang, K.; Ho, S.B.; Boland, B.S.; Chang, J.T.; et al. A gp130-Src-YAP module links inflammation to epithelial regeneration. Nature 2015, 519, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenbluh, J.; Nijhawan, D.; Cox, A.G.; Li, X.; Neal, J.T.; Schafer, E.J.; Zack, T.I.; Wang, X.; Tsherniak, A.; Schinzel, A.C.; et al. beta-Catenin-driven cancers require a YAP1 transcriptional complex for survival and tumorigenesis. Cell 2012, 151, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorrentino, G.; Perino, A.; Yildiz, E.; El Alam, G.; Sleiman, M.B.; Gioiello, A.; Pellicciari, R.; Schoonjans, K. Bile Acids Signal via TGR5 to Activate Intestinal Stem Cells and Epithelial Regeneration. Gastroenterology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtz, P.; Bonfini, A.; Liu, X.; Revah, J.; Guillou, A.; Poidevin, M.; Hens, K.; Huang, H.Y.; Deplancke, B.; Tsai, Y.C.; et al. Hippo, TGF-beta, and Src-MAPK pathways regulate transcription of the upd3 cytokine in Drosophila enterocytes upon bacterial infection. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, N.; van Oudenaarden, A.; Clevers, H. Identifying the stem cell of the intestinal crypt: Strategies and pitfalls. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanpain, C.; Fuchs, E. Stem cell plasticity. Plasticity of epithelial stem cells in tissue regeneration. Science 2014, 344, 1242281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yui, S.; Azzolin, L.; Maimets, M.; Pedersen, M.T.; Fordham, R.P.; Hansen, S.L.; Larsen, H.L.; Guiu, J.; Alves, M.R.P.; Rundsten, C.F.; et al. YAP/TAZ-Dependent Reprogramming of Colonic Epithelium Links ECM Remodeling to Tissue Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 35–49.e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Murata, Y.; Imada, S.; Konno, T.; Kotani, T.; Saito, Y.; Yamada, H.; Matozaki, T. Role of Csk in intestinal epithelial barrier function and protection against colitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, F.; Wang, A.; Smyth, D.; Reyes, J.L.; Doering, A.; Schenck, L.P.; Beck, P.; Waterhouse, C.; McKay, D.M. The Src kinase Fyn is protective in acute chemical-induced colitis and promotes recovery from disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, M.E.; Bishop, J.L.; Fan, X.; Beer, J.L.; Kum, W.W.; Krebs, D.L.; Huang, M.; Gill, N.; Priatel, J.J.; Finlay, B.B.; et al. Lyn deficiency leads to increased microbiota-dependent intestinal inflammation and susceptibility to enteric pathogens. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5249–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bishop, J.L.; Roberts, M.E.; Beer, J.L.; Huang, M.; Chehal, M.K.; Fan, X.; Fouser, L.A.; Ma, H.L.; Bacani, J.T.; Harder, K.W. Lyn activity protects mice from DSS colitis and regulates the production of IL-22 from innate lymphoid cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N.; Ridgway, R.A.; van Es, J.H.; van de Wetering, M.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; Danenberg, E.; Clarke, A.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Clevers, H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009, 457, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Wang, K.; Mucida, D.; Stewart, C.A.; Schnabl, B.; Jauch, D.; Taniguchi, K.; Yu, G.Y.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Hung, K.E.; et al. Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature 2012, 491, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Kim, M.K.; Di Caro, G.; Wong, J.; Shalapour, S.; Wan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Wu, L.W.; et al. Interleukin-17 receptor a signaling in transformed enterocytes promotes early colorectal tumorigenesis. Immunity 2014, 41, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, K.; Moroishi, T.; de Jong, P.R.; Krawczyk, M.; Grebbin, B.M.; Luo, H.; Xu, R.H.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Schweiger, C.; Wang, K.; et al. YAP-IL-6ST autoregulatory loop activated on APC loss controls colonic tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poh, A.R.; Love, C.G.; Masson, F.; Preaudet, A.; Tsui, C.; Whitehead, L.; Monard, S.; Khakham, Y.; Burstroem, L.; Lessene, G.; et al. Inhibition of Hematopoietic Cell Kinase Activity Suppresses Myeloid Cell-Mediated Colon Cancer Progression. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 563–575.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Summy, J.M.; Gallick, G.E. Src family kinases in tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirvent, A.; Benistant, C.; Roche, S. Oncogenic signaling by tyrosine kinases of the SRC family in advanced colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 2, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, W. Regulation of Src Family Kinases during Colorectal Cancer Development and Its Clinical Implications. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, C.A.; Meisler, A.I.; Eckhart, W. Activation of the pp60c-src protein kinase is an early event in colonic carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Perez, J.; Lopez-Calderero, I.; Saez, C.; Benavent, M.; Limon, M.L.; Gonzalez-Exposito, R.; Soldevilla, B.; Riesco-Martinez, M.C.; Salamanca, J.; Carnero, A.; et al. Prognostic relevance of Src activation in stage II-III colon cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 67, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseweir, A.K.; Powell, A.; Horstman, S.L.; Inthagard, J.; Park, J.H.; McMillan, D.C.; Horgan, P.G.; Edwards, J. Src family kinases, HCK and FGR, associate with local inflammation and tumour progression in colorectal cancer. Cell. Signal. 2019, 56, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopetz, S.; Morris, V.K.; Parikh, N.; Overman, M.J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Maru, D.; Elvin, P.; Gallick, G. Src activity is modulated by oxaliplatin and correlates with outcomes after hepatectomy for metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irby, R.B.; Mao, W.; Coppola, D.; Kang, J.; Loubeau, J.M.; Trudeau, W.; Karl, R.; Fujita, D.J.; Jove, R.; Yeatman, T.J. Activating SRC mutation in a subset of advanced human colon cancers. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chambers, M.C.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Shaddox, K.F.; Kim, S.; et al. Proteogenomic characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2014, 513, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Ye, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Mustonen, H.; et al. SIRT2-dependent IDH1 deacetylation inhibits colorectal cancer and liver metastases. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptashkin, R.N.; Pagan, C.; Yaeger, R.; Middha, S.; Shia, J.; O’Rourke, K.P.; Berger, M.F.; Wang, L.; Cimera, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Chromosome 20q Amplification Defines a Subtype of Microsatellite Stable, Left-Sided Colon Cancers with Wild-type RAS/RAF and Better Overall Survival. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimada, Y.; Muneoka, Y.; Nagahashi, M.; Ichikawa, H.; Tajima, Y.; Hirose, Y.; Ando, T.; Nakano, M.; Sakata, J.; Kameyama, H.; et al. BRAF V600E and SRC mutations as molecular markers for predicting prognosis and conversion surgery in Stage IV colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; Lovly, C.M. Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer. Mol Cancer 2018, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuzaki, D.; Yamauchi, T.; Mitani, F.; Miyata, M.; Ninomiya, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Akamatsu, H.; Oneyama, C. c-Src promotes tumor progression through downregulation of microRNA-129-1-3p. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokouchi, M.; Kondo, T.; Sanjay, A.; Houghton, A.; Yoshimura, A.; Komiya, S.; Zhang, H.; Baron, R. Src-catalyzed phosphorylation of c-Cbl leads to the interdependent ubiquitination of both proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35185–35193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Bao, W.; Liu, L.; You, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, L.; Fu, W.; Kou, X.; Shen, W.; et al. SNX10 (sorting nexin 10) inhibits colorectal cancer initiation and progression by controlling autophagic degradation of SRC. Autophagy 2020, 16, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oneyama, C.; Hikita, T.; Enya, K.; Dobenecker, M.W.; Saito, K.; Nada, S.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Okada, M. The lipid raft-anchored adaptor protein Cbp controls the oncogenic potential of c-Src. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirvent, A.; Benistant, C.; Pannequin, J.; Veracini, L.; Simon, V.; Bourgaux, J.F.; Hollande, F.; Cruzalegui, F.; Roche, S. Src family tyrosine kinases-driven colon cancer cell invasion is induced by Csk membrane delocalization. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, K.; Oneyama, C.; Kimura, H.; Tajima, S.; Okada, M. Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor C-terminal Src kinase (Csk)-binding protein (Cbp)/PAG1 is mediated by epigenetic histone modifications via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15698–15706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Janas, J.A.; Niki, M.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Van Aelst, L. Dok-1 independently attenuates Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase and Src/c-myc pathways to inhibit platelet-derived growth factor-induced mitogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mashima, R.; Hishida, Y.; Tezuka, T.; Yamanashi, Y. The roles of Dok family adapters in immunoreceptor signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 232, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curson, J.E.B.; Luo, L.; Sweet, M.J.; Stow, J.L. pTRAPs: Transmembrane adaptors in innate immune signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, P.; Damiano, L.; Cabodi, S.; Aramu, S.; Tordella, L.; Praduroux, A.; Piva, R.; Cavallo, F.; Forni, G.; Silengo, L.; et al. p140Cap protein suppresses tumour cell properties, regulating Csk and Src kinase activity. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veracini, L.; Simon, V.; Richard, V.; Schraven, B.; Horejsi, V.; Roche, S.; Benistant, C. The Csk-binding protein PAG regulates PDGF-induced Src mitogenic signaling via GM1. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benistant, C.; Bourgaux, J.F.; Chapuis, H.; Mottet, N.; Roche, S.; Bali, J.P. The COOH-terminal Src kinase Csk is a tumor antigen in human carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, F.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Saito, Y.; Hatakeyama, M. Mammalian Pragmin regulates Src family kinases via the Glu-Pro-Ile-Tyr-Ala (EPIYA) motif that is exploited by bacterial effectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14938–14943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senda, Y.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Hatakeyama, M. C-terminal Src kinase-mediated EPIYA phosphorylation of Pragmin creates a feed-forward C-terminal Src kinase activation loop that promotes cell motility. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S.; Lecointre, C.; Simon, V.; Labesse, G. SHEDding light on the role of Pragmin pseudo-kinases in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lecointre, C.; Simon, V.; Kerneur, C.; Allemand, F.; Fournet, A.; Montarras, I.; Pons, J.L.; Gelin, M.; Brignatz, C.; Urbach, S.; et al. Dimerization of the Pragmin Pseudo-Kinase Regulates Protein Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Structure 2018, 26, 545–554.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roche, S.; Alonso, G.; Kazlauskas, A.; Dixit, V.M.; Courtneidge, S.A.; Pandey, A. Src-like adaptor protein (Slap) is a negative regulator of mitogenesis. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manes, G.; Bello, P.; Roche, S. Slap negatively regulates Src mitogenic function but does not revert Src-induced cell morphology changes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3396–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevizou, R.; Sirvent, A.; Roche, S. Control of Tyrosine Kinase Signalling by Small Adaptors in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sosinowski, T.; Killeen, N.; Weiss, A. The Src-like adaptor protein downregulates the T cell receptor on CD4+CD8+ thymocytes and regulates positive selection. Immunity 2001, 15, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naudin, C.; Sirvent, A.; Leroy, C.; Larive, R.; Simon, V.; Pannequin, J.; Bourgaux, J.F.; Pierre, J.; Robert, B.; Hollande, F.; et al. SLAP displays tumour suppressor functions in colorectal cancer via destabilization of the SRC substrate EPHA2. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakiyama, T.; Fujita, H.; Tsubouchi, H. Autoantibodies against ubiquitination factor E4A (UBE4A) are associated with severity of Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yang, W.; Kontaridis, M.I.; Bivona, T.G.; Wen, G.; Araki, T.; Luo, J.; Thompson, J.A.; Schraven, B.L.; Philips, M.R.; et al. Shp2 regulates SRC family kinase activity and Ras/Erk activation by controlling Csk recruitment. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Scott, A.; Zhang, P.; Hao, Y.; Feng, X.; Somasundaram, S.; Khalil, A.M.; Willis, J.; Wang, Z. Regulation of paxillin-p130-PI3K-AKT signaling axis by Src and PTPRT impacts colon tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48782–48793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Lee, H.W.; Ayrapetov, M.K.; Zhao, T.C.; Hao, Y.; Gao, J.; Yang, C.; Mehta, G.U.; et al. Acetylation within the N- and C-Terminal Domains of Src Regulates Distinct Roles of STAT3-Mediated Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heppner, D.E.; Dustin, C.M.; Liao, C.; Hristova, M.; Veith, C.; Little, A.C.; Ahlers, B.A.; White, S.L.; Deng, B.; Lam, Y.W.; et al. Direct cysteine sulfenylation drives activation of the Src kinase. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancier, F.; Dumont, A.; Sirvent, A.; Paquay de Plater, L.; Edmonds, T.; David, G.; Jan, M.; de Montrion, C.; Coge, F.; Leonce, S.; et al. Specific oncogenic activity of the Src-family tyrosine kinase c-Yes in colon carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, F.; Leroy, C.; Simon, V.; Benistant, C.; Roche, S. YES oncogenic activity is specified by its SH4 domain and regulates RAS/MAPK signaling in colon carcinoma cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1972–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sirvent, A.; Urbach, S.; Roche, S. Contribution of phosphoproteomics in understanding SRC signaling in normal and tumor cells. Proteomics 2015, 15, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.R.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, K.M.; Park, J.I.; Oh, H.T.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. SRC activates TAZ for intestinal tumorigenesis and regeneration. Cancer Lett. 2017, 410, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emaduddin, M.; Bicknell, D.C.; Bodmer, W.F.; Feller, S.M. Cell growth, global phosphotyrosine elevation, and c-Met phosphorylation through Src family kinases in colorectal cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2358–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leroy, C.; Fialin, C.; Sirvent, A.; Simon, V.; Urbach, S.; Poncet, J.; Robert, B.; Jouin, P.; Roche, S. Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals a cluster of tyrosine kinases that mediates SRC invasive activity in advanced colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirvent, A.; Vigy, O.; Orsetti, B.; Urbach, S.; Roche, S. Analysis of SRC oncogenic signaling in colorectal cancer by stable isotope labeling with heavy amino acids in mouse xenografts. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 1937–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gargalionis, A.N.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Adamopoulos, C.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Protein trafficking in colorectal carcinogenesis-targeting and bypassing resistance to currently applied treatments. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imjeti, N.S.; Menck, K.; Egea-Jimenez, A.L.; Lecointre, C.; Lembo, F.; Bouguenina, H.; Badache, A.; Ghossoub, R.; David, G.; Roche, S.; et al. Syntenin mediates SRC function in exosomal cell-to-cell communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12495–12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hikita, T.; Kuwahara, A.; Watanabe, R.; Miyata, M.; Oneyama, C. Src in endosomal membranes promotes exosome secretion and tumor progression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafitte, M.; Lecointre, C.; Roche, S. Roles of exosomes in metastatic colorectal cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, C869–C880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S.; Koegl, M.; Barone, M.V.; Roussel, M.F.; Courtneidge, S.A. DNA synthesis induced by some but not all growth factors requires Src family protein tyrosine kinases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roche, S.; Fumagalli, S.; Courtneidge, S.A. Requirement for Src family protein tyrosine kinases in G2 for fibroblast cell division. Science 1995, 269, 1567–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandoulaki, M.; Petsalaki, E.; Sumpton, D.; Zanivan, S.; Zachos, G. Src activation by Chk1 promotes actin patch formation and prevents chromatin bridge breakage in cytokinesis. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 3071–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N. Meliodosis presenting as encephalitis. Aust. N. Z. J. Med. 1976, 6, 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Soeda, S.; Ikeuchi, M.; Kakae, K.; Yamaguchi, N. Cytokinesis Failure Leading to Chromosome Instability in v-Src-Induced Oncogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horiuchi, M.; Kuga, T.; Saito, Y.; Nagano, M.; Adachi, J.; Tomonaga, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Nakayama, Y. The tyrosine kinase v-Src causes mitotic slippage by phosphorylating an inhibitory tyrosine residue of Cdk1. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15524–15537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anton, K.A.; Kajita, M.; Narumi, R.; Fujita, Y.; Tada, M. Src-transformed cells hijack mitosis to extrude from the epithelium. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godinho, S.A.; Picone, R.; Burute, M.; Dagher, R.; Su, Y.; Leung, C.T.; Polyak, K.; Brugge, J.S.; Thery, M.; Pellman, D. Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification. Nature 2014, 510, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, L.M.; Staley, C.A.; Liu, W.; Fleming, R.Y.; Parikh, N.U.; Bucana, C.D.; Gallick, G.E. Down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in a human colon carcinoma cell line transfected with an antisense expression vector specific for c-src. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simons, M.; Gordon, E.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windham, T.C.; Parikh, N.U.; Siwak, D.R.; Summy, J.M.; McConkey, D.J.; Kraker, A.J.; Gallick, G.E. Src activation regulates anoikis in human colon tumor cell lines. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7797–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cursi, S.; Rufini, A.; Stagni, V.; Condo, I.; Matafora, V.; Bachi, A.; Bonifazi, A.P.; Coppola, L.; Superti-Furga, G.; Testi, R.; et al. Src kinase phosphorylates Caspase-8 on Tyr380: A novel mechanism of apoptosis suppression. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabandhu, K.; Huault, S.; Durivault, J.; Lang, K.; Ta Ngoc, L.; Bole, A.; Doma, E.; Derijard, B.; Gerard, J.P.; Pierres, M.; et al. An Evolution-Guided Analysis Reveals a Multi-Signaling Regulation of Fas by Tyrosine Phosphorylation and its Implication in Human Cancers. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wen, S.; Tang, H.Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, F.; Suleman, M.; Sun, D.; Chen, A.; et al. c-Src Promotes Tumorigenesis and Tumor Progression by Activating PFKFB3. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4235–4249.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Palmieri, M.; Chaudhury, A.; Klisch, T.J.; di Ronza, A.; Neilson, J.R.; Rodney, G.G.; Sardiello, M. Src regulates amino acid-mediated mTORC1 activation by disrupting GATOR1-Rag GTPase interaction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, B.; Roche, S.; Denoyelle, M.; Thiery, J.P. Src and Ras are involved in separate pathways in epithelial cell scattering. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5904–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canel, M.; Serrels, A.; Frame, M.C.; Brunton, V.G. E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gujral, T.S.; Chan, M.; Peshkin, L.; Sorger, P.K.; Kirschner, M.W.; MacBeath, G. A noncanonical Frizzled2 pathway regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell 2014, 159, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, D.A.; Courtneidge, S.A. The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of podosomes and invadopodia: Characteristics, formation and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massague, J.; Obenauf, A.C. Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature 2016, 529, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, E.M.; Whipple, R.A.; Thompson, K.; Boggs, A.E.; Slovic, J.; Cho, E.H.; Matrone, M.A.; Yoneda, T.; Mueller, S.C.; Martin, S.S. c-Src differentially regulates the functions of microtentacles and invadopodia. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6402–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Lim, Y.B.; Finch-Edmondson, M.L.; Seshachalam, V.P.; Qin, L.; Jiang, T.; Low, B.C.; Singh, H.; Lim, C.T.; et al. YAP Regulates Actin Dynamics through ARHGAP29 and Promotes Metastasis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.J.; Lai, H.M.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, G.Y.; Lee, J.L. Direct reprogramming of stem cell properties in colon cancer cells by CD44. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3186–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subramaniam, V.; Vincent, I.R.; Gardner, H.; Chan, E.; Dhamko, H.; Jothy, S. CD44 regulates cell migration in human colon cancer cells via Lyn kinase and AKT phosphorylation. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 83, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, P.Y.; Kuo, P.C. Osteopontin: Regulation in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, S.; Cui, J.; Barnes, L.; Cheresh, D. Endothelial barrier disruption by VEGF-mediated Src activity potentiates tumor cell extravasation and metastasis. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oskarsson, T.; Batlle, E.; Massague, J. Metastatic stem cells: Sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Ding, J.; Ma, Z.; Sun, R.; Seoane, J.A.; Scott Shaffer, J.; Suarez, C.J.; Berghoff, A.S.; Cremolini, C.; Falcone, A.; et al. Quantitative evidence for early metastatic seeding in colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.M.; Prado-Lopez, S.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.M.; Posada, D. Rapid evolution and biogeographic spread in a colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barkan, D.; El Touny, L.H.; Michalowski, A.M.; Smith, J.A.; Chu, I.; Davis, A.S.; Webster, J.D.; Hoover, S.; Simpson, R.M.; Gauldie, J.; et al. Metastatic growth from dormant cells induced by a col-I-enriched fibrotic environment. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5706–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Touny, L.H.; Vieira, A.; Mendoza, A.; Khanna, C.; Hoenerhoff, M.J.; Green, J.E. Combined SFK/MEK inhibition prevents metastatic outgrowth of dormant tumor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Gerald, W.; Hudis, C.A.; Norton, L.; Smid, M.; Foekens, J.A.; Massague, J. Latent bone metastasis in breast cancer tied to Src-dependent survival signals. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, J.S.; Ino, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Src family kinase inhibitor PP2 restores the E-cadherin/catenin cell adhesion system in human cancer cells and reduces cancer metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2430–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Hekim, C.; Ilander, M.; Yan, J.; Michaud, E.; Smykla, R.; Vaha-Koskela, M.; Savola, P.; Tahtinen, S.; Saikko, L.; Hemminki, A.; et al. Dasatinib Changes Immune Cell Profiles Concomitant with Reduced Tumor Growth in Several Murine Solid Tumor Models. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, M.M.; Lee, F.Y.F.; Jones, R.T.; Kimball, A.K.; Saravia, E.; Graziano, R.F.; Coleman, B.; Menard, K.; Yan, J.; Michaud, E.; et al. Targeting DDR2 enhances tumor response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spranger, S.; Bao, R.; Gajewski, T.F. Melanoma-intrinsic beta-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2015, 523, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Lesslie, D.P.; Dallas, N.A.; Park, S.I.; Johnson, M.; Parikh, N.U.; Kim, M.P.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Ellis, L.M.; Chandra, J.; et al. Synergistic activity of the SRC family kinase inhibitor dasatinib and oxaliplatin in colon carcinoma cells is mediated by oxidative stress. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3842–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, E.F.; Iida, M.; Myers, R.A.; Campbell, D.A.; Hintz, K.A.; Armstrong, E.A.; Li, C.; Wheeler, D.L. Dasatinib sensitizes KRAS mutant colorectal tumors to cetuximab. Oncogene 2011, 30, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, G.R.; Winter, P.S.; Lin, K.H.; Nussbaum, D.P.; Cakir, M.; Stein, E.M.; Soderquist, R.S.; Crawford, L.; Leeds, J.C.; Newcomb, R.; et al. A Landscape of Therapeutic Cooperativity in KRAS Mutant Cancers Reveals Principles for Controlling Tumor Evolution. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.M.; Hwang, C.Y.; Choi, J.; Joung, C.Y.; Cho, K.H. Feedback analysis identifies a combination target for overcoming adaptive resistance to targeted cancer therapy. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3803–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Lucena-Cacace, A.; Marin-Gomez, L.M.; Padillo-Ruiz, J.; Robles-Frias, M.J.; Saez, C.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Carnero, A. Dasatinib, a Src inhibitor, sensitizes liver metastatic colorectal carcinoma to oxaliplatin in tumors with high levels of phospho-Src. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33111–33124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bantscheff, M.; Eberhard, D.; Abraham, Y.; Bastuck, S.; Boesche, M.; Hobson, S.; Mathieson, T.; Perrin, J.; Raida, M.; Rau, C.; et al. Quantitative chemical proteomics reveals mechanisms of action of clinical ABL kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, U.; Hantschel, O.; Durnberger, G.; Remsing Rix, L.L.; Planyavsky, M.; Fernbach, N.V.; Kaupe, I.; Bennett, K.L.; Valent, P.; Colinge, J.; et al. Chemical proteomic profiles of the BCR-ABL inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib reveal novel kinase and nonkinase targets. Blood 2007, 110, 4055–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsing Rix, L.L.; Rix, U.; Colinge, J.; Hantschel, O.; Bennett, K.L.; Stranzl, T.; Muller, A.; Baumgartner, C.; Valent, P.; Augustin, M.; et al. Global target profile of the kinase inhibitor bosutinib in primary chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 2009, 23, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fallah-Tafti, A.; Foroumadi, A.; Tiwari, R.; Shirazi, A.N.; Hangauer, D.G.; Bu, Y.; Akbarzadeh, T.; Parang, K.; Shafiee, A. Thiazolyl N-benzyl-substituted acetamide derivatives: Synthesis, Src kinase inhibitory and anticancer activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4853–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.M.; Kopetz, S.; Morris, J.; Parikh, N.; Qiao, W.; Overman, M.J.; Fogelman, D.; Shureiqi, I.; Jacobs, C.; Malik, Z.; et al. Phase II study of saracatinib (AZD0530) in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakoff, S.J.; Wang, D.; Campone, M.; Calles, A.; Leip, E.; Turnbull, K.; Bardy-Bouxin, N.; Duvillie, L.; Calvo, E. Bosutinib plus capecitabine for selected advanced solid tumours: Results of a phase 1 dose-escalation study. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parseghian, C.M.; Parikh, N.U.; Wu, J.Y.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Henderson, L.; Tian, F.; Pastor, B.; Ychou, M.; Raghav, K.; Dasari, A.; et al. Dual Inhibition of EGFR and c-Src by Cetuximab and Dasatinib Combined with FOLFOX Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4146–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eide, C.A.; Zabriskie, M.S.; Savage Stevens, S.L.; Antelope, O.; Vellore, N.A.; Than, H.; Schultz, A.R.; Clair, P.; Bowler, A.D.; Pomicter, A.D.; et al. Combining the Allosteric Inhibitor Asciminib with Ponatinib Suppresses Emergence of and Restores Efficacy against Highly Resistant BCR-ABL1 Mutants. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 431–443.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garivet, G.; Hofer, W.; Konitsiotis, A.; Klein, C.; Kaiser, N.; Mejuch, T.; Fansa, E.; Alsaabi, R.; Wittinghofer, A.; Bastiaens, P.I.H.; et al. Small-Molecule Inhibition of the UNC-Src Interaction Impairs Dynamic Src Localization in Cells. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 842–851.e847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartwright, C.A.; Kamps, M.P.; Meisler, A.I.; Pipas, J.M.; Eckhart, W. pp60c-src activation in human colon carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 2025–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirvent, A.; Mevizou, R.; Naim, D.; Lafitte, M.; Roche, S. Src Family Tyrosine Kinases in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082014
Sirvent A, Mevizou R, Naim D, Lafitte M, Roche S. Src Family Tyrosine Kinases in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Tumorigenesis. Cancers. 2020; 12(8):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirvent, Audrey, Rudy Mevizou, Dana Naim, Marie Lafitte, and Serge Roche. 2020. "Src Family Tyrosine Kinases in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Tumorigenesis" Cancers 12, no. 8: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082014
APA StyleSirvent, A., Mevizou, R., Naim, D., Lafitte, M., & Roche, S. (2020). Src Family Tyrosine Kinases in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Tumorigenesis. Cancers, 12(8), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082014





