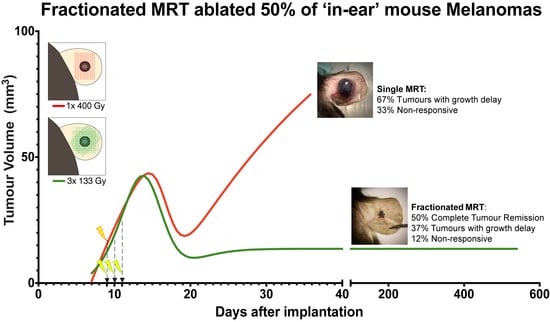
Complete Remission of Mouse Melanoma after Temporally Fractionated Microbeam Radiotherapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
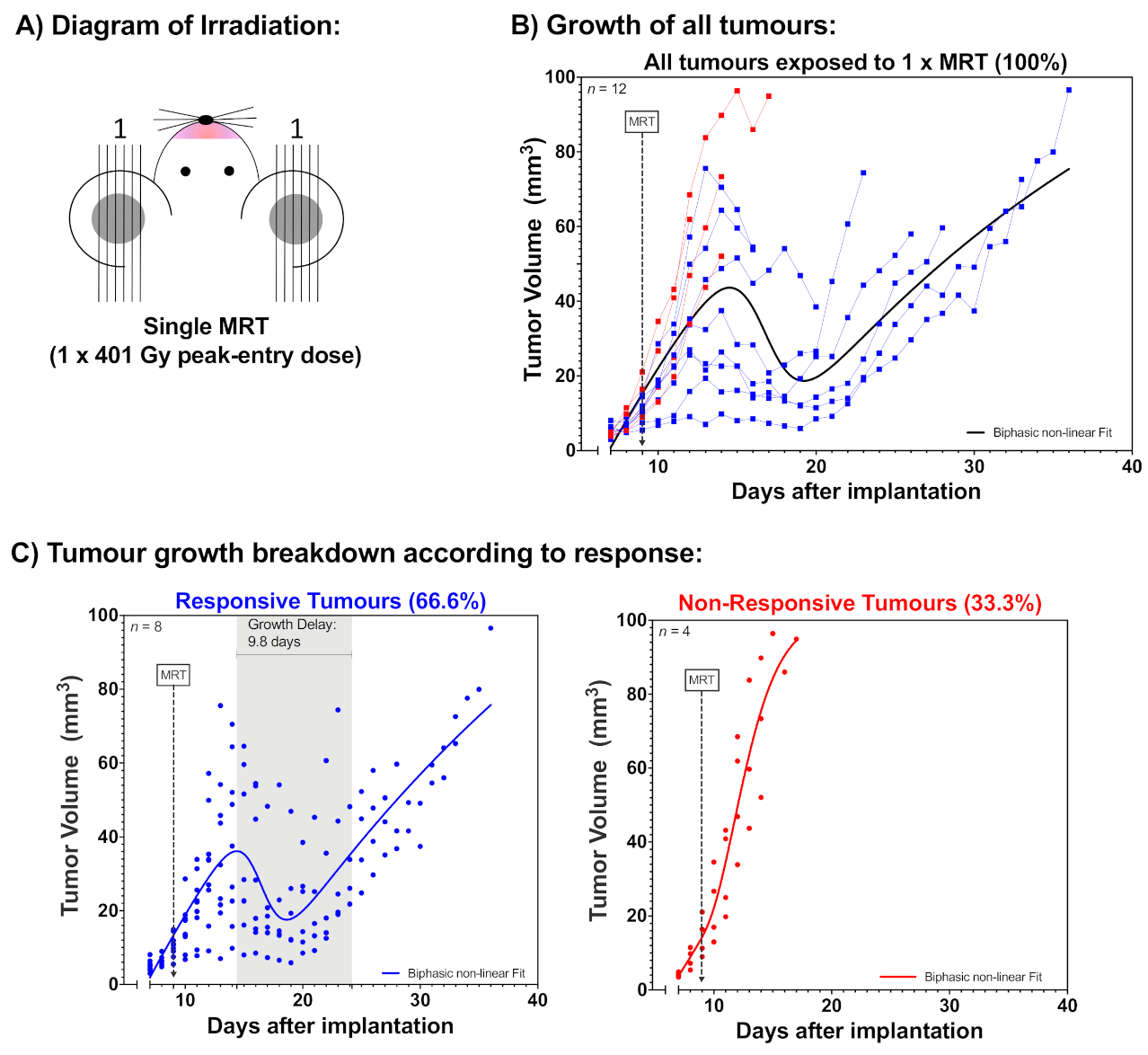
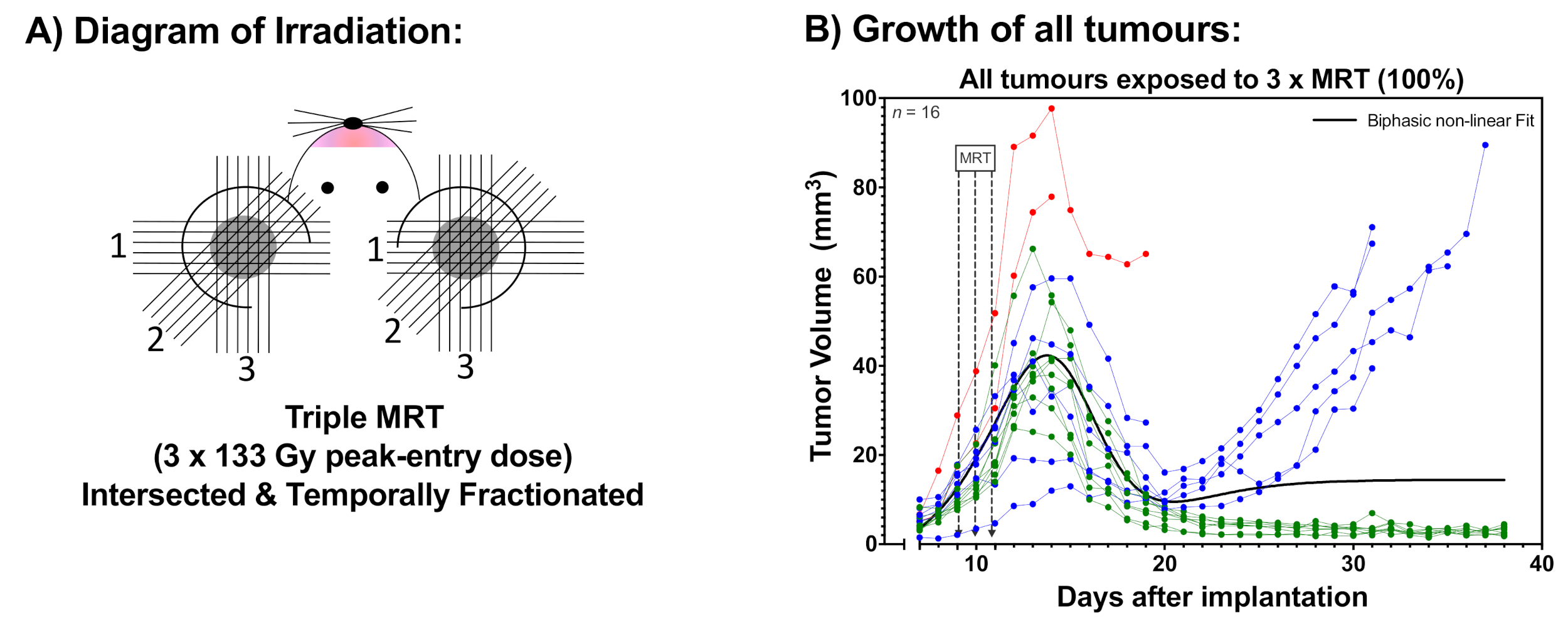
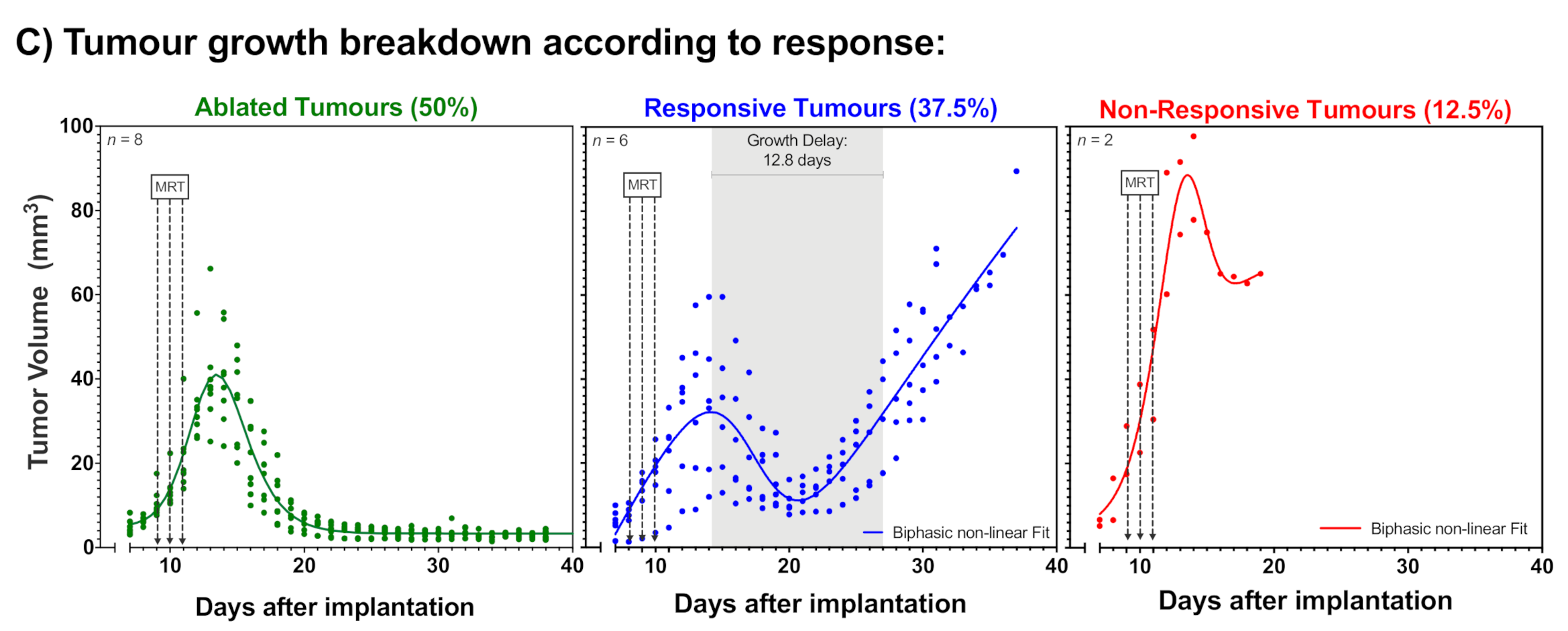
2.1. Tumour Growth
2.2. Animal Survival
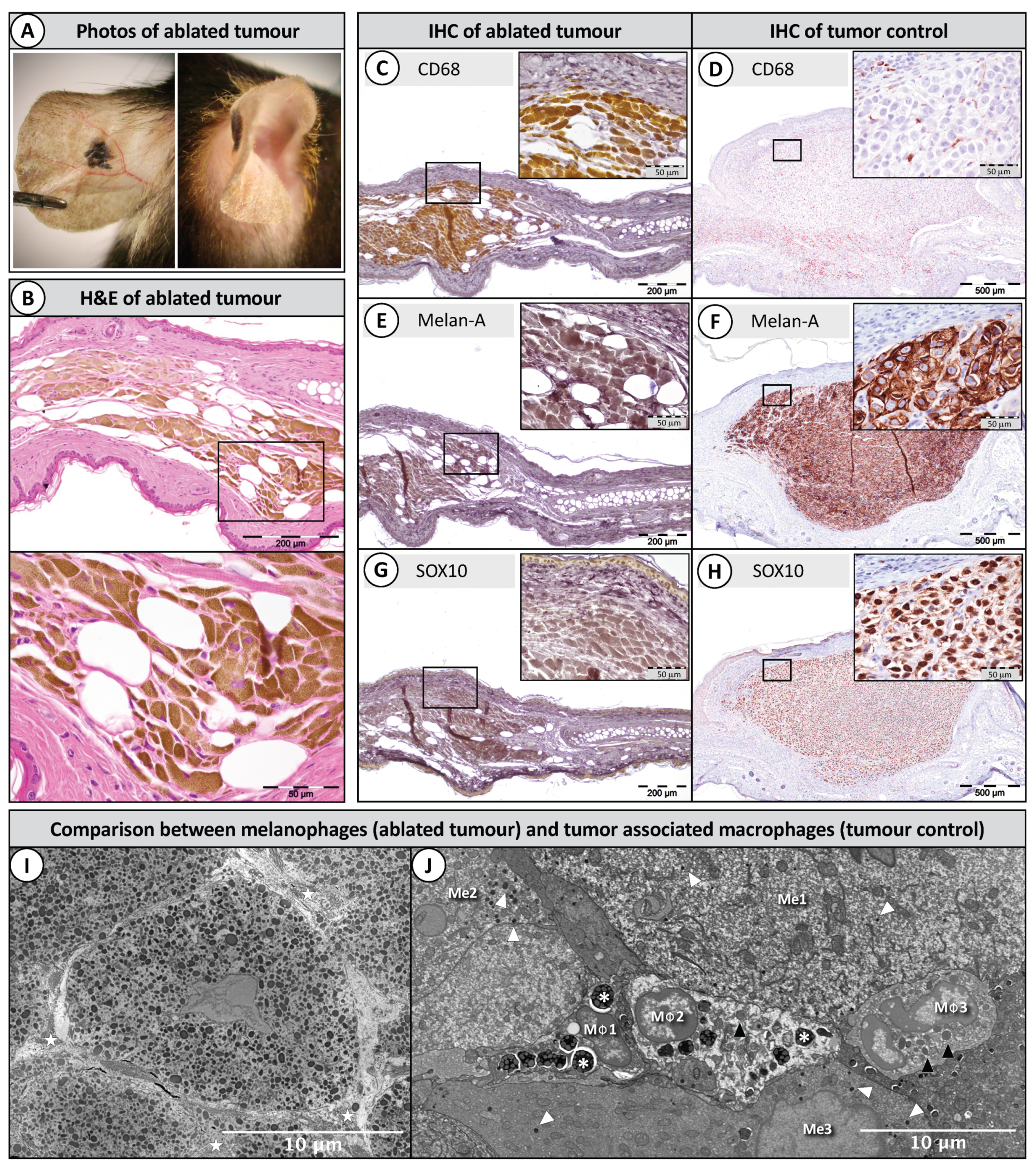
2.3. Histopathology of Ablated Tumours
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal and Tumour Model
4.2. Culture of B16-F10 Cells
4.3. Tumour Implantation
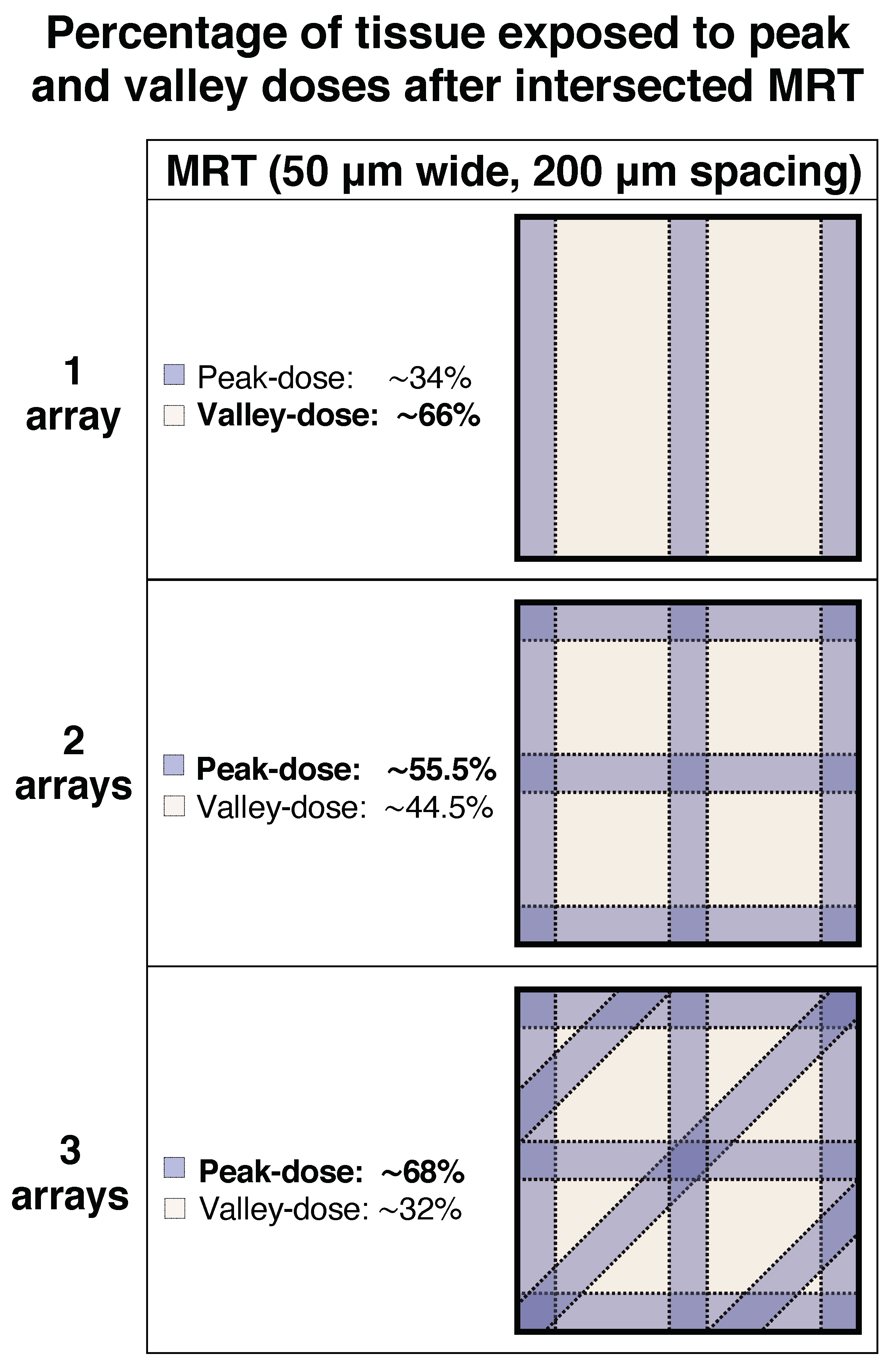
4.4. Irradiation and Dosimetry
4.5. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchet, A.; Potez, M.; Coquery, N.; Rome, C.; Lemasson, B.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Rémy, C.; Laissue, J.; Barbier, E.L.; Djonov, V.; et al. Permeability of Brain Tumor Vessels Induced by Uniform or Spatially Microfractionated Synchrotron Radiation Therapies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilmanian, F.A.; Morris, G.M.; Zhong, N.; Bacarian, T.; Hainfeld, J.F.; Kalef-Ezra, J.; Brewington, L.J.; Tammam, J.; Rosen, E.M. Murine EMT-6 carcinoma: High therapeutic efficacy of microbeam radiation therapy. Radiat. Res. 2003, 159, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potez, M.; Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Bouchet, A.; Trappetti, V.; Donzelli, M.; Krisch, M.; Laissue, J.; Volarevic, V.; Djonov, V. Synchrotron Microbeam Radiation Therapy as a New Approach for the Treatment of Radioresistant Melanoma: Potential Underlying Mechanisms. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Fazzari, J.; Trappetti, V.; Smyth, L.; Janka, H.; Laissue, J.; Djonov, V. Animal Models in Microbeam Radiation Therapy: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Petersson, K.; Jaccard, M.; Boivin, G.; Germond, J.F.; Petit, B.; Doenlen, R.; Favaudon, V.; Bochud, F.; Bailat, C.; et al. Irradiation in a flash: Unique sparing of memory in mice after whole brain irradiation with dose rates above 100 Gy/s. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatkin, D.N.; Spanne, P.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Gebbers, J.O.; Laissue, J.A. Subacute neuropathological effects of microplanar beams of x-rays from a synchrotron wiggler. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8783–8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laissue, J.A.; Blattmann, H.; Di Michiel, M.; Slatkin, D.N.; Lyubimova, N.; Guzman, R.; Zimmermann, W.; Birrer, S.; Bley, T.; Kircher, P.; et al. The weanling piglet cerebellum: A surrogate for tolerance to MRT (microbeam radiation therapy) in pediatric neuro-oncology. In Penetrating Radiation Systems and Applications III, International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology, San Diego, CA, USA, 19 December 2001; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Belingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4508, pp. 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laissue, J.A.; Blattmann, H.; Wagner, H.P.; Grotzer, M.A.; Slatkin, D.N. Prospects for microbeam radiation therapy of brain tumours in children to reduce neurological sequelae. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serduc, R.; van de Looij, Y.; Francony, G.; Verdonck, O.; van der Sanden, B.; Laissue, J.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Siegbahn, E.A.; Bravin, A. Characterization and quantification of cerebral edema induced by synchrotron x-ray microbeam radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potez, M.; Bouchet, A.; Wagner, J.; Donzelli, M.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Hopewell, J.W.; Laissue, J.; Djonov, V. Effects of Synchrotron X-Ray Micro-beam Irradiation on Normal Mouse Ear Pinnae. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, A.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Prezado, Y.; El Atifi, M.; Rogalev, L.; Le Clec’h, C.; Laissue, J.A.; Pelletier, L.; Duc, G.L. Better Efficacy of Synchrotron Spatially Microfractionated Radiation Therapy Than Uniform Radiation Therapy on Glioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatasso, S.; Laissue, J.A.; Hlushchuk, R.; Graber, W.; Bravin, A.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Corde, S.; Blattmann, H.; Gruber, G.; Djonov, V. Microbeam radiation-induced tissue damage depends on the stage of vascular maturation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattmann, H.; Gebbers, J.O.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Bravin, A.; Le Duc, G.; Burkard, W.; Di Michiel, M.; Djonov, V.; Slatkin, D.N.; Stepanek, J.; et al. Applications of synchrotron X-rays to radiotherapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2005, 548, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serduc, R.; Vérant, P.; Vial, J.-C.; Farion, R.; Rocas, L.; Rémy, C.; Fadlallah, T.; Brauer, E.; Bravin, A.; Laissue, J.; et al. In vivo two-photon microscopy study of short-term effects of microbeam irradiation on normal mouse brain microvasculature. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brönnimann, D.; Bouchet, A.; Schneider, C.; Potez, M.; Serduc, R.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Graber, W.; von Gunten, S.; Laissue, J.A.; Djonov, V. Synchrotron microbeam irradiation induces neutrophil infiltration, thrombocyte attachment and selective vascular damage in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Schültke, E.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Laissue, J.A.; Blattmann, H.; Seymour, C.; Mothersill, C. Investigation of abscopal and bystander effects in immunocompromised mice after exposure to pencilbeam and microbeam synchrotron radiation. Health Phys. 2016, 111, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Laissue, J.; Vukmirovic, D.; Blattmann, H.; Seymour, C.; Schültke, E.; Mothersill, C. Use of synchrotron medical microbeam irradiation to investigate radiation-induced bystander and abscopal effects in vivo. Phys. Med. 2015, 31, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Mothersill, C.; Laissue, J.; Seymour, C.; Schültke, E. γ-H2AX as a marker for dose deposition in the brain of wistar rats after synchrotron microbeam radiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothersill, C.; Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Fazzari, J.; Smith, R.; Schültke, E.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Laissue, J.; Schroll, C.; Seymour, C. Transmission of Signals from Rats Receiving High Doses of Microbeam Radiation to Cage Mates: An Inter-Mammal Bystander Effect. Dose Response 2013, 12, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, H.R. Cell Cycle Redistribution as a Factor in Multifraction Irradiation. Radiology 1975, 114, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallman, R.F. The Phenomenon of Reoxygenation and Its Implications for Fractionated Radiotherapy. Radiology 1972, 105, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denekamp, J. Changes in the rate of repopulation during multifraction irradiation of mouse skin. Br. J. Ratiol. 1973, 46, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serduc, R.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Bouchet, A.; Renaud, L.; Brochard, T.; Bravin, A.; Laissue, J.A.; Le Duc, G. First trial of spatial and temporal fractionations of the delivered dose using synchrotron microbeam radiation therapy. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2009, 16, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyama, A.; Kondoh, T.; Nariyama, N.; Umetani, K.; Fukumoto, M.; Shinohara, K.; Kohmura, E. A narrow microbeam is more effective for tumor growth suppression than a wide microbeam: An in vivo study using implanted human glioma cells. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2011, 18, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.W.; Griffin, R.J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Cho, H.; Seo, J.; Park, I.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Dusenbery, K.E.; et al. Reoxygenation and Repopulation of Tumor Cells after Ablative Hypofractionated Radiotherapy (SBRT and SRS) in Murine Tumors. Radiat. Res. 2019, 192, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, M.Z.; Galloway, A.E.; Kawashima, N.; Dewyngaert, J.K.; Babb, J.S.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Fractionated but not single-dose radiotherapy induces an immune-mediated abscopal effect when combined with anti-CTLA-4 antibody. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5379–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potez, M.; Trappetti, V.; Bouchet, A.; Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Güç, E.; Kilarski, W.W.; Hlushchuk, R.; Laissue, J.; Djonov, V. Characterization of a B16-F10 melanoma model locally implanted into the ear pinnae of C57BL/6 mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinelli, S.; Allison, J.; Amako, K.; Apostolakis, J.; Araujo, H.; Arce, P.; Asai, M.; Axen, D.; Banerjee, B.; Barrand, G.; et al. GEANT4-A simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2003, 506, 250–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, P.; Crosbie, J.C.; Cornelius, I.; Berkvens, P.; Donzelli, M.; Clavel, A.H.; Rosenfeld, A.B.; Petasecca, M.; Lerch, M.L.F.; Bräuer-Krisch, E. Absorbed dose-to-water protocol applied to synchrotron-generated x-rays at very high dose rates. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, N349–N361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Technical Parameters | Single MRT | Cross-Fired Temporally Fractionated MRT |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental Parameters: | ||
| Sessions | 1 | 3 (1 per day) |
| Peak dose in the tumour centre * | 401.23 Gy | 133.41 Gy |
| Valley dose in the tumour centre * | 7.40 Gy | 2.46 Gy |
| Peak to valley dose ratio (PVDR) | 54.24 | 54.24 |
| Number of microbeams | 38 | 38 |
| Microbeam width | 50 µm | 50 µm |
| Microbeam spacing (centre-to-centre) | 200 µm | 200 µm |
| Field size | 7.6 wide × 8 high (mm2) | 7.6 wide × 8 high (mm2) |
| Mean dose rate | 11,704 Gy/s | 12,870 Gy/s |
| Average irradiation time per slice | 34.2 ms | 11.4 ms |
| ESRF Parameters: | ||
| Filling pattern | 7/8 + 1 | 7/8 + 1 |
| Current | 171–168 mA | 200–171 mA |
| Dose rate | 68.99 Gy/s/mA | 68.99 Gy/s/mA |
| Mean energy of spectrum | 104 keV | 104 keV |
| Peak energy of spectrum | 88 keV | 88 keV |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandez-Palomo, C.; Trappetti, V.; Potez, M.; Pellicioli, P.; Krisch, M.; Laissue, J.; Djonov, V. Complete Remission of Mouse Melanoma after Temporally Fractionated Microbeam Radiotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092656
Fernandez-Palomo C, Trappetti V, Potez M, Pellicioli P, Krisch M, Laissue J, Djonov V. Complete Remission of Mouse Melanoma after Temporally Fractionated Microbeam Radiotherapy. Cancers. 2020; 12(9):2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092656
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandez-Palomo, Cristian, Verdiana Trappetti, Marine Potez, Paolo Pellicioli, Michael Krisch, Jean Laissue, and Valentin Djonov. 2020. "Complete Remission of Mouse Melanoma after Temporally Fractionated Microbeam Radiotherapy" Cancers 12, no. 9: 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092656
APA StyleFernandez-Palomo, C., Trappetti, V., Potez, M., Pellicioli, P., Krisch, M., Laissue, J., & Djonov, V. (2020). Complete Remission of Mouse Melanoma after Temporally Fractionated Microbeam Radiotherapy. Cancers, 12(9), 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092656