Intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Treatment for T1 High-Grade Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer with Divergent Differentiation or Variant Morphologies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Intravesical BCG Treatment after TURBT
2.3. Patient Selection
2.4. Surveillance after Intravesical BCG and During mBCG
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DD and VMs Detected in ur Cohort
3.2. Comparison of Patient Characteristics and Outcomes among the Groups
3.3. IPTW-Adjusted Comparison of Outcomes between the pUC and UC-VM Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Iida, K.; Nishimura, N.; Miyamoto, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Tomida, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Numakura, K.; Inokuchi, J.; Morizane, S.; et al. Non-maintenance intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin induction therapy with eight doses in patients with high- or highest-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A retrospective non-randomized comparative study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gontero, P.; Mostafid, A.H.; Palou, J.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Rouprêt, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Sylvester, R.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and Carcinoma In Situ)—2019 Update. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, T.; Spiess, P.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chang, S.; Downs, T.M.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Friedlander, T.; et al. Bladder Cancer, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.S.; Bochner, B.H.; Chou, R.; Dreicer, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Lotan, Y.; Meeks, J.J.; Michalski, J.M.; Morgan, T.M.; et al. Treatment of Non-Metastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Azuma, H.; Inoue, K.; Uemura, H.; Eto, M.; Ohyama, C.; Ogawa, O.; Kikuchi, E.; Kitamura, H.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bladder Cancer 2019 update by the Japanese Urological Association: Summary of the revision. Int. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Miyake, M.; Toyoshima, Y.; Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Nishimura, N.; Iida, K.; Nakahama, T.; Hori, S.; Gotoh, D.; et al. Clinical outcomes after intravesical bacillus Calmette–Guérin for the highest-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer newly defined in the Japanese Urological Association Guidelines 2019. Int. J. Urol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, P.A.; Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Bladder Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, S.C.; de Souza, M.F.; Amaral, M.E.P.; Athanazio, D.A. Divergent differentiation and variant morphology in invasive urothelial carcinomas–association with muscle-invasive disease. Surg. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Montgomery, J.S.; Montie, J.E.; Kunju, L.P. Variant (divergent) histologic differentiation in urothelial carcinoma is under-recognized in community practice: Impact of mandatory central pathology review at a large referral hospital. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B. Histological variants of urothelial carcinoma: Diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostic implications. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, S96–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, P.C.; Brown, G.A.; Dinney, C.P. The impact of variant histology on the outcome of bladder cancer treated with curative intent. Urol. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeks, J.J.; Taylor, J.M.; Matsushita, K.; Herr, H.W.; Donat, S.M.; Bochner, B.H.; Dalbagni, G. Pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive micropapillary bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2013, 111, E325–E330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siefker-Radtke, A.O.; Dinney, C.P.; Shen, Y.; Williams, D.L.; Kamat, A.M.; Grossman, H.B.; Millikan, R.E. A phase 2 clinical trial of sequential neoadjuvant chemotherapy with ifosfamide, doxorubicin, and gemcitabine followed by cisplatin, gemcitabine, and ifosfamide in locally advanced urothelial cancer: Final results. Cancer 2013, 119, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayyani, F.; Czerniak, B.A.; Sircar, K.; Munsell, M.F.; Millikan, R.E.; Dinney, C.P.; Siefker-Radtke, A.O. Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma, a chemosensitive cancer with poor prognosis, and peritoneal carcinomatosis. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, M.; Kamat, A.M.; McConkey, D. Does Variant Histology Change Management of Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer? Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.H.; Noon, A.P. Selection of patients and benefit of immediate radical cystectomy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, P.; Zamboni, S.; Mattei, A.; Antonelli, A.; Simeone, C.; Mordasini, L.; DiBona, C.; Moschini, M. Histological variants in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, D.L.; Fernandez, M.I.; Dickstein, R.J.; Parikh, S.; Shah, J.B.; Pisters, L.L.; Guo, C.C.; Henderson, S.; Czerniak, B.A.; Grossman, H.B.; et al. Clinical outcomes of cT1 micropapillary bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1129–1134. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25254936 (accessed on 22 April 2021). [CrossRef]
- Gofrit, O.N.; Yutkin, V.; Shapiro, A.; Pizov, G.; Zorn, K.C.; Hidas, G.; Gielchinsky, I.; Duvdevani, M.; Landau, E.H.; Pode, D.; et al. The Response of Variant Histology Bladder Cancer to Intravesical Immunotherapy Compared to Conventional Cancer. Front Oncol. 2016, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapur, N.K.; Katz, R.; Pode, D.; Shapiro, A.; Yutkin, V.; Pizov, G.; Appelbaum, L.; Zorn, K.C.; Duvdevan, I.M.; Landau, E.H.; et al. Is radical cystectomy mandatory in every patient with variant histology of bladder cancer. Rare Tumors 2011, 3, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellinga, A.; Cormican, M.; Hanahoe, B.; Bennett, K.; Murphy, A.W. Opt-out as an acceptable method of obtaining consent in medical research: A short report. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, D.L.; Blumenstein, B.A.; Crissman, J.D.; Montie, J.E.; Gottesman, J.E.; Lowe, B.A.; Sarosdy, M.F.; Bohl, R.D.; Grossman, H.B.; Beck, T.M.; et al. Maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy for recurrent TA, T1 and carcinoma in situ transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: A randomized Southwest Oncology Group Study. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.M.; Sylvester, R.J.; Böhle, A.; Palou, J.; Lamm, D.L.; Brausi, M.; Soloway, M.; Persad, R.; Buckley, R.; Colombel, M.; et al. Definitions, End Points, and Clinical Trial Designs for Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Recommendations from the International Bladder Cancer Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Stuart, E.A. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 3661–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.M.; Oosterlinck, W.; Witjes, J.A.; Bouffioux, C.; Denis, L.; Newling, D.W.; Kurth, K. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gomez, J.; Madero, R.; Solsona, E.; Unda, M.; Martinez-Piñeiro, L.; Gonzalez, M.; Portillo, J.; Ojea, A.; Pertusa, C.; Rodriguez-Molina, J.; et al. Predicting nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer recurrence and progression in patients treated with Bacillus Calmette–Guerin: The Cueto scoring model. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.P.; Fairey, A.S.; Skinner, E.C.; Boorjian, S.A.; Frank, I.; Schoenberg, M.P.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Hyndman, M.E.; Reese, A.C.; Steinberg, G.D.; et al. Implications of micropapillary urothelial carcinoma variant on prognosis following radical cystectomy: A multi-institutional investigation. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorozuya, W.; Nishiyama, N.; Shindo, T.; Kyoda, Y.; Itoh, N.; Sugita, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Masumori, N. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin may have clinical benefit for glandular or squamous differentiation in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients: Retrospective multicenter study. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 48, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Moon, K.C.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.; Song, W.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Ku, J.H. BCG instillation versus radical cystectomy for high-risk NMIBC with squamous/glandular histologic variants. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantica, G.; Simonato, A.; Du Plessis, D.E.; Maffezzini, M.; De Rose, A.F.; van der Merwe, A.; Terrone, C. The pathologist’s role in the detection of rare variants of bladder cancer and analysis of the impact on incidence and type detection. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2018, 70, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Tiscione, D.; Verze, P.; Pomara, G.; Racioppi, M.; Nesi, G.; Barbareschi, M.; Brausi, M.; Gacci, M.; Luciani, L.G.; et al. Concordance and clinical significance of uncommon variants of bladder urothelial carcinoma in transurethral resection and radical cystectomy specimens. Urology 2014, 84, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

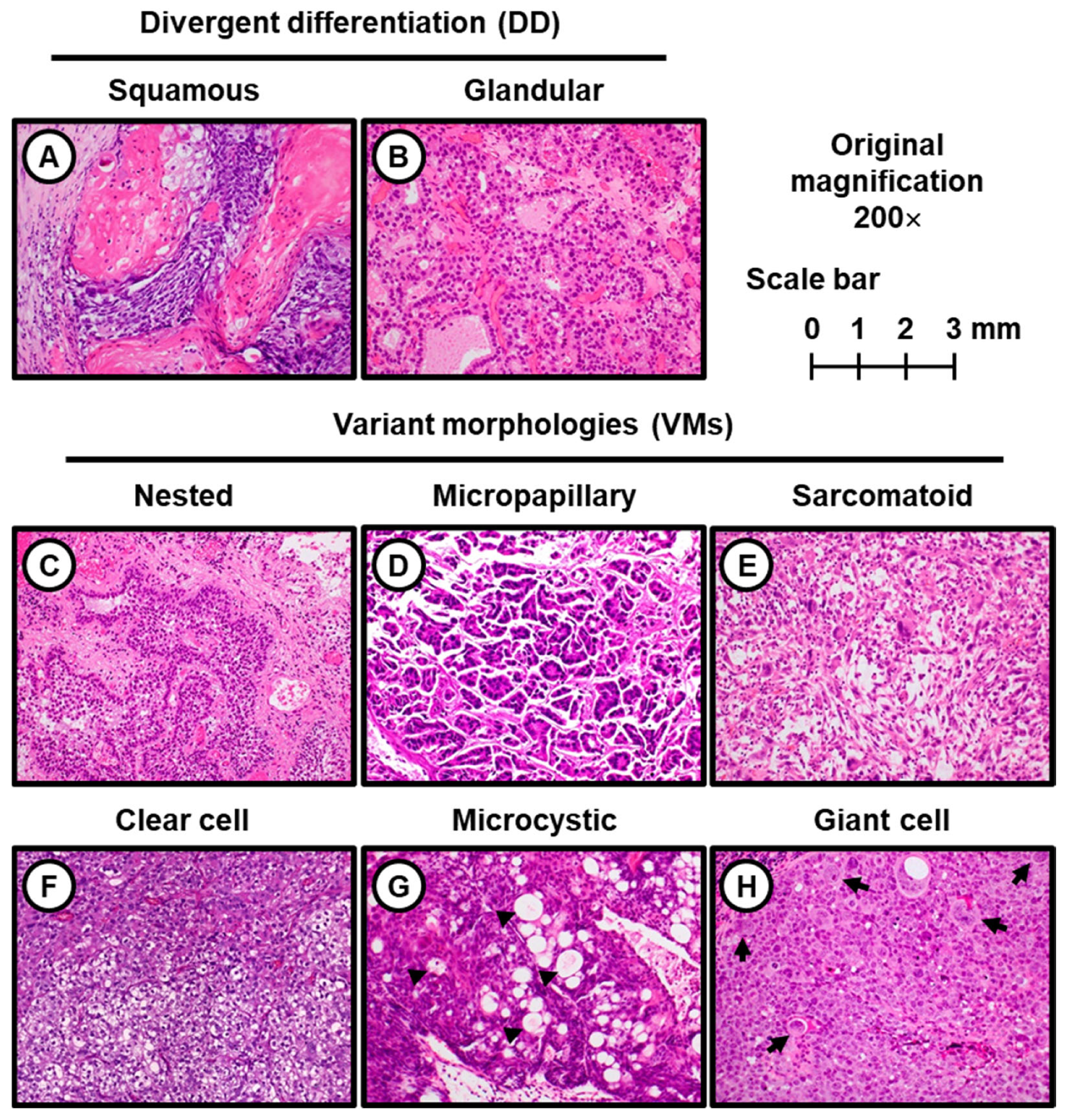

| Histology | UC with DD
(UC-DD Group) | UC with VMs
(UC-VM Group) |
|---|---|---|
| N | 65 (100%) | 30 (100%) |
| Glandular differentiation | 38 (69%) | - |
| Squamous differentiation | 27 (41%) | - |
| Micropapillary variant | - | 13 (43%) |
| Nested variant | - | 9 (30%) |
| Sarcomatoid variant | - | 4 (13%) |
| Clear cell variant | - | 2 (6.7%) |
| Microcystic variant | - | 1 (3.3%) |
| Giant cell variant | - | 1 (3.3%) |
| Valiables | Unweighted Population (n) | IPTW Population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure UC (pUC) | UC with VMs (UC-VM) | p Value | SMD | Pure UC (pUC) | UC with VMs (UC-VM) | SMD | ||
| N | 1395 | 30 | 1425 | 1442 | ||||
| Age, mean ± SD | 70.7 ± 9.5 | 67.4 ± 9.8 | 0.06 # | 0.35 | 70.7 ± 9.4 | 69.8 ± 1.4 | 0.13 | |
| Sex | 1.00 ## | 0.014 | 0.16 | |||||
| Male | 1155 (83%) | 25 (83%) | 83% | 88% | ||||
| Female | 240 (17%) | 5 (17%) | 17% | 12% | ||||
| Multiplicity | 0.13 ## | 0.28 | 0.19 | |||||
| Single | 503 (36%) | 15 (50%) | 36% | 27% | ||||
| Multiple | 892 (64%) | 15 (50%) | 64% | 73% | ||||
| Tumor size | 0.83 ## | 0.021 | 0.047 | |||||
| <3 cm | 1082 (78%) | 23 (77%) | 77% | 79% | ||||
| ≥3 cm | 313 (22%) | 7 (23%) | 23% | 21% | ||||
| Bladder CIS | 0.85 ## | 0.044 | 0.132 | |||||
| No | 854 (61%) | 19 (63%) | 61% | 45% | ||||
| Yes | 541 (39%) | 11 (37%) | 39% | 55% | ||||
| Prostate-involving CIS | 1.00 ## | 0.199 | 0.197 | |||||
| No | 1368 (98%) | 30 (100%) | 98% | 100% | ||||
| Yes | 27 (1.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1.9% | 0% | ||||
| LVI | <0.01 ## | 0.64 | 0.030 | |||||
| No | 1275 (91%) | 20 (67%) | 91% | 92% | ||||
| Yes | 120 (9.1%) | 10 (33%) | 9.1% | 8.3% | ||||
| Second TUR | 0.14 ## | 0.32 | 0.026 | |||||
| No | 629 (45%) | 9 (30%) | 45% | 46% | ||||
| Yes | 766 (55%) | 21 (70%) | 55% | 54% | ||||
| Maintenance BCG | 0.81 ## | 0.085 | 0.20 | |||||
| No | 1167 (84%) | 26 (87%) | 84% | 76% | ||||
| Yes | 228 (16%) | 4 (13%) | 16% | 24% | ||||
| Oncological Outcomes | Variables | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder Recurrence-Free Survival | |||||
| Age | ≥70 yo/<70 yo | 1.31 | 1.07–1.60 | <0.01 | |
| Multiplicity | multiple/solitary | 1.46 | 1.18–1.80 | <0.01 | |
| Prostate-involving CIS | yes/no | 2.96 | 1.82–4.79 | <0.01 | |
| LVI | yes/no | 1.45 | 1.06–1.97 | 0.02 | |
| Second TUR | yes/no | 0.73 | 0.60–0.89 | <0.01 | |
| Maintenance BCG | yes/no | 0.49 | 0.36–0.68 | <0.01 | |
| Progression-free survival | |||||
| Age | ≥ 70 yo/<70 yo | 1.25 | 0.93–1.67 | 0.14 | |
| Prostate-involving CIS | yes/no | 3.38 | 1.92–5.93 | <0.01 | |
| LVI | yes/no | 1.56 | 1.02–2.37 | 0.04 | |
| Second TUR | yes/no | 0.75 | 0.56–1.00 | 0.05 | |
| Maintenance BCG | yes/no | 0.59 | 0.37–0.94 | 0.03 | |
| Cancer-specific survival | |||||
| Age | ≥ 70 yo/<70 yo | 1.90 | 1.15–3.13 | 0.01 | |
| Histology type | UC-VM/pUC | 3.38 | 1.92–5.93 | <0.01 | |
| Second TUR | yes/no | 0.58 | 0.34–0.97 | 0.04 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyake, M.; Nishimura, N.; Iida, K.; Fujii, T.; Nishikawa, R.; Teraoka, S.; Takenaka, A.; Kikuchi, H.; Abe, T.; Shinohara, N.; et al. Intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Treatment for T1 High-Grade Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer with Divergent Differentiation or Variant Morphologies. Cancers 2021, 13, 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112615
Miyake M, Nishimura N, Iida K, Fujii T, Nishikawa R, Teraoka S, Takenaka A, Kikuchi H, Abe T, Shinohara N, et al. Intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Treatment for T1 High-Grade Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer with Divergent Differentiation or Variant Morphologies. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112615
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyake, Makito, Nobutaka Nishimura, Kota Iida, Tomomi Fujii, Ryoma Nishikawa, Shogo Teraoka, Atsushi Takenaka, Hiroshi Kikuchi, Takashige Abe, Nobuo Shinohara, and et al. 2021. "Intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Treatment for T1 High-Grade Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer with Divergent Differentiation or Variant Morphologies" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112615
APA StyleMiyake, M., Nishimura, N., Iida, K., Fujii, T., Nishikawa, R., Teraoka, S., Takenaka, A., Kikuchi, H., Abe, T., Shinohara, N., Okajima, E., Shimizu, T., Hori, S., Tsuchiya, N., Owari, T., Murakami, Y., Taoka, R., Kobayashi, T., Kojima, T., ... Fujimoto, K. (2021). Intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Treatment for T1 High-Grade Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer with Divergent Differentiation or Variant Morphologies. Cancers, 13(11), 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112615







